The Role of The Rostral Ventromedial Medulla in Stress Responses
Abstract
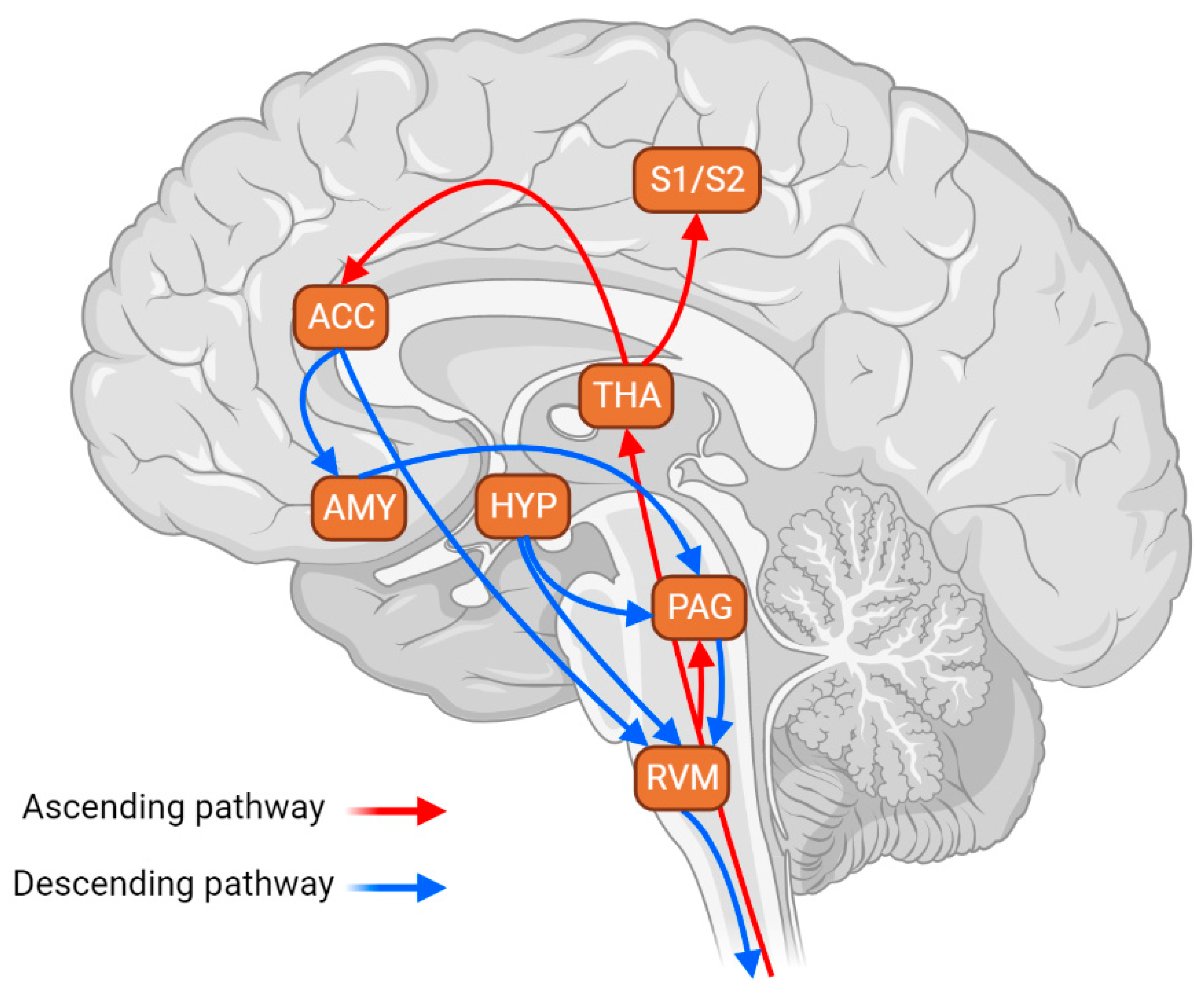
:1. Introduction
2. RVM Mediates Stress Response through the Endocannabinoid and Opioid Systems
3. Involvement of RVM-Targeting Pathways in Stress Response
4. Other Mechanisms Implicating the RVM in Stress Response
5. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fields, H.L.; Bry, J.; Hentall, I.; Zorman, G. The Activity of Neurons in the Rostral Medulla of the Rat during Withdrawal from Noxious Heat. J. Neurosci. 1983, 3, 2545–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fields, H.L.; Heinricher, M.M. Anatomy and Physiology of a Nociceptive Modulatory System. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B. Biol. Sci. 1985, 308, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denk, F.; McMahon, S.B.; Tracey, I. Pain Vulnerability: A Neurobiological Perspective. Nat. Neurosci. 2014, 17, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bushnell, M.C.; Čeko, M.; Low, L.A. Cognitive and Emotional Control of Pain and Its Disruption in Chronic Pain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2013, 14, 502–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auvray, M.; Myin, E.; Spence, C. The Sensory-Discriminative and Affective-Motivational Aspects of Pain. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2010, 34, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ossipov, M.H.; Morimura, K.; Porreca, F. Descending Pain Modulation and Chronification of Pain. Curr. Opin. Support. Palliat. Care 2014, 8, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fields, H. State-Dependent Opioid Control of Pain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2004, 5, 565–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basbaum, A.I.; Bautista, D.M.; Scherrer, G.; Julius, D. Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Pain. Cell 2009, 139, 267–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, M. Descending Facilitation: From Basic Science to the Treatment of Chronic Pain. Mol. Pain 2017, 13, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Felice, M.; Ossipov, M.H. Cortical and Subcortical Modulation of Pain. Pain Manag. 2016, 6, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Felice, M.; Sanoja, R.; Wang, R.; Vera-Portocarrero, L.; Oyarzo, J.; King, T.; Ossipov, M.H.; Vanderah, T.W.; Lai, J.; Dussor, G.O.; et al. Engagement of Descending Inhibition from the Rostral Ventromedial Medulla Protects against Chronic Neuropathic Pain. Pain 2011, 152, 2701–2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiwei, Y.; Wendi, F.; Mengru, C.; Tuo, Y.; Chen, G. The Cellular Mechanism by Which the Rostral Ventromedial Medulla Acts on the Spinal Cord during Chronic Pain. Rev. Neurosci. 2021, 32, 545–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferdousi, M.; Finn, D.P. Stress-Induced Modulation of Pain: Role of the Endogenous Opioid System, 1st ed.; Elsevier B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; Volume 239, ISBN 9780444641670. [Google Scholar]
- Crofford, L.J. Chronic Pain: Where the Body Meets the Brain. Trans. Am. Clin. Climatol. Assoc. 2015, 126, 167–183. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Heinricher, M.; Tavares, I.; Leith, J.L.; Lumb, B.M. Descending Control of Nociception. Brain Res. Rev. 2010, 60, 214–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, C.W.; Hermes, S.M.; Chavkin, C.I.; Drake, C.T.; Morrison, S.F.; Aicher, S.A. Kappa Opioid Receptor (KOR) and GAD67 Immunoreactivity Are Found in OFF and NEUTRAL Cells in the Rostral Ventromedial Medulla. J. Neurophysiol. 2006, 96, 3465–3473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miki, K.; Zhou, Q.Q.; Guo, W.; Guan, Y.; Terayama, R.; Dubner, R.; Ren, K. Changes in Gene Expression and Neuronal Phenotype in Brain Stem Pain Modulatory Circuitry after Inflammation. J. Neurophysiol. 2002, 87, 750–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandkühler, J. Models and Mechanisms of Hyperalgesia and Allodynia. Physiol. Rev. 2009, 89, 707–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, J.; Keshavan, M. The Neurobiology of Depression: An Integrated View. Asian J. Psychiatry 2017, 27, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, J.; Liu, S.; Wang, Y.; Cui, R.; Zhang, X. The Link between Depression and Chronic Pain: Neural Mechanisms in the Brain. Neural Plast. 2017, 2017, 9724371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maletic, V.; Raison, C.L. Neurobiology of Depression, Fibromyalgia and Neuropathic Pain. Front. Biosci. (Landmark Ed.) 2009, 14, 5291–5338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imbe, H.; Iwai-Liao, Y.; Senba, E. Stress-Induced Hyperalgesia: Animal Models and Putative Mechanisms. Front. Biosci. 2006, 11, 2179–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagliusi, M.O.F.; Bonet, I.J.M.; Dias, E.V.; Vieira, A.S.; Tambeli, C.H.; Parada, C.A.; Sartori, C.R. Social Defeat Stress Induces Hyperalgesia and Increases Truncated BDNF Isoforms in the Nucleus Accumbens Regardless of the Depressive-like Behavior Induction in Mice. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2018, 48, 1635–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagliusi, M.; Bonet, I.J.M.; Brandão, A.F.; Magalhães, S.F.; Tambeli, C.H.; Parada, C.A.; Sartori, C.R. Therapeutic and Preventive Effect of Voluntary Running Wheel Exercise on Social Defeat Stress (SDS)-Induced Depressive-like Behavior and Chronic Pain in Mice. Neuroscience 2020, 428, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennings, E.M.; Okine, B.N.; Roche, M.; Finn, D.P. Stress-Induced Hyperalgesia. Prog. Neurobiol. 2014, 121, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piardi, L.; Pagliusi, M.; Bonet, I.; Brandão, A.; Magalhães, S.; Zanelatto, F.; Tambeli, C.; Parada, C.; Sartori, C. Social Stress as a Trigger for Depressive-like Behavior and Persistent Hyperalgesia in Mice: Study of the Comorbidity between Depression and Chronic Pain. J. Affect. Disord. 2020, 274, 759–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, R.K.; Finn, D.P. Stress-Induced Analgesia. Prog. Neurobiol. 2009, 88, 184–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.-M.; Meng, J.; Li, L.-T.; Guo, T.; Yang, L.-K.; Shi, Q.-X.; Li, X.-B.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Q.; Zhao, J.-N. Effect of ZBD-2 on Chronic Pain, Depressive-like Behaviors, and Recovery of Motor Function Following Spinal Cord Injury in Mice. Behav. Brain Res. 2017, 322, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nestler, E.J.; Waxman, S.G. Resilience to Stress and Resilience to Pain: Lessons from Molecular Neurobiology and Genetics. Trends Mol. Med. 2020, 26, 924–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vialou, V.; Robison, A.J.; Laplant, Q.C.; Covington, H.E.; Dietz, D.M.; Ohnishi, Y.N.; Mouzon, E.; Rush, A.J.; Watts, E.L.; Wallace, D.L.; et al. ΔfosB in Brain Reward Circuits Mediates Resilience to Stress and Antidepressant Responses. Nat. Neurosci. 2010, 13, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laine, M.A.; Sokolowska, E.; Dudek, M.; Callan, S.A.; Hyytiä, P.; Hovatta, I. Brain Activation Induced by Chronic Psychosocial Stress in Mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hathway, G.J.; Vega-Avelaira, D.; Fitzgerald, M. A Critical Period in the Supraspinal Control of Pain: Opioid-Dependent Changes in Brainstem Rostroventral Medulla Function in Preadolescence. Pain 2012, 153, 775–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fields, H.L.; Vanegas, H.; Hentall, I.D.; Zorman, G. Evidence That Disinhibition of Brain Stem Neurones Contributes to Morphine Analgesia. Nature 1983, 306, 684–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanegas, H.; Vazquez, E.; Tortorici, V. NSAIDS, Opioids, Cannabinoids and the Control of Pain by the Central Nervous System. Pharmaceuticals 2010, 3, 1335–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, I.D.; Manning, B.H.; Martin, W.J.; Fields, H.L. An Analgesia Circuit Activated by Cannabinoids. Nature 1998, 395, 381–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagley, E.E.; Ingram, S.L. Endogenous Opioid Peptides in the Descending Pain Modulatory Circuit. Neuropharmacology 2020, 173, 108131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinricher, M.M.; Morgan, M.M.; Tortorici, V.; Fields, H.L. Disinhibition of Off-Cells and Antinociception Produced by an Opioid Action within the Rostral Ventromedial Medulla. Neuroscience 1994, 63, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, J.M.; Lowe, D.; Fields, H.L. The Contribution of the Rostral Ventromedial Medulla to the Antinociceptive Effects of Systemic Morphine in Restrained and Unrestrained Rats. Neuroscience 1998, 87, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corcoran, L.; Roche, M.; Finn, D.P. The Role of the Brain’s Endocannabinoid System in Pain and Its Modulation by Stress, 1st ed.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; Volume 125, ISBN 9780128012789. [Google Scholar]
- Palazzo, E.; Luongo, L.; de Novellis, V.; Rossi, F.; Maione, S. The Role of Cannabinoid Receptors in the Descending Modulation of Pain. Pharmaceuticals 2010, 3, 2661–2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suplita, R.L.; Farthing, J.N.; Gutierrez, T.; Hohmann, A.G. Inhibition of Fatty-Acid Amide Hydrolase Enhances Cannabinoid Stress-Induced Analgesia: Sites of Action in the Dorsolateral Periaqueductal Gray and Rostral Ventromedial Medulla. Neuropharmacology 2005, 49, 1201–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rea, K.; Olango, W.M.; Okine, B.N.; Madasu, M.K.; McGuire, I.C.; Coyle, K.; Harhen, B.; Roche, M.; Finn, D.P. Impaired Endocannabinoid Signalling in the Rostral Ventromedial Medulla Underpins Genotype-Dependent Hyper-Responsivity to Noxious Stimuli. Pain 2014, 155, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohmann, A.G.; Suplita, R.L.; Bolton, N.M.; Neely, M.H.; Fegley, D.; Mangieri, R.; Krey, J.F.; Walker, J.M.; Holmes, P.V.; Crystal, J.D.; et al. An Endocannabinoid Mechanism for Stress-Induced Analgesia. Nature 2005, 435, 1108–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drew, G.M.; Mitchell, V.A.; Vaughan, C.W. Glutamate Spillover Modulates GABAergic Synaptic Transmission in the Rat Midbrain Periaqueductal Grey via Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors and Endocannabinoid Signaling. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 808–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suplita, R.L.; Gutierrez, T.; Fegley, D.; Piomelli, D.; Hohmann, A.G. Endocannabinoids at the Spinal Level Regulate, but Do Not Mediate, Nonopioid Stress-Induced Analgesia. Neuropharmacology 2006, 50, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urits, I.; Gress, K.; Charipova, K.; Habib, K.; Lee, D.; Lee, C.; Jung, J.W.; Kassem, H.; Cornett, E.; Paladini, A.; et al. Use of Cannabidiol (CBD) for the Treatment of Chronic Pain. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Anaesthesiol. 2020, 34, 463–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, W.J.; Tsou, K.; Walker, J.M. Cannabinoid Receptor-Mediated Inhibition of the Rat Tail-Flick Reflex after Microinjection into the Rostral Ventromedial Medulla. Neurosci. Lett. 1998, 242, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foo, H.; Helmstetter, F.J. Expression of Antinociception in Response to a Signal for Shock Is Blocked after Selective Downregulation of μ-Opioid Receptors in the Rostral Ventromedial Medulla. Mol. Brain Res. 2000, 76, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foo, H.; Helmstetter, F.J. Hypoalgesia Elicited by a Conditioned Stimulus Is Blocked by a μ, but Not a δ or a κ, Opioid Antagonist Injected into the Rostral Ventromedial Medulla. Pain 1999, 83, 427–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foo, H.; Helmstetter, F.J. Activation of Kappa Opioid Receptors in the Rostral Ventromedial Medulla Blocks Stress-Induced Antinociception. Neuroreport 2000, 11, 3349–3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, I.D.; Johansen, J.P.; Harasawa, I.; Fields, H.L. Kappa Opioids Inhibit Physiologically Identified Medullary Pain Modulating Neurons and Reduce Morphine Antinociception. J. Neurophysiol. 2005, 93, 1138–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaughlin, J.P.; Li, S.; Valdez, J.; Chavkin, T.A.; Chavkin, C. Social Defeat Stress-Induced Behavioral Responses Are Mediated by the Endogenous Kappa Opioid System. Neuropsychopharmacology 2006, 31, 1241–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsu, Y.; Aubrey, K.R. Kappa Opioids Inhibit the GABA/Glycine Terminals of Rostral Ventromedial Medulla Projections in the Superficial Dorsal Horn of the Spinal Cord. J. Physiol. 2022, 600, 4187–4205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, E.; Smith, K.M.; Cramer, N.; Holland, R.A.; Bleimeister, I.H.; Flores-Felix, K.; Silberberg, H.; Keller, A.; Le Pichon, C.E.; Ross, S.E. Medullary Kappa-Opioid Receptor Neurons Inhibit Pain and Itch through a Descending Circuit. Brain 2022, 145, 2586–2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, J.; Bilsky, E.J.; Meng, I.D. Selective Ablation of Mu-Opioid Receptor Expressing Neurons in the Rostral Ventromedial Medulla Attenuates Stress-Induced Mechanical Hypersensitivity. Life Sci. 2011, 89, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinricher, M.M.; Haws, C.M.; Fields, H.L. Evidence for GABA-Mediated Control of Putative Nociceptive Modulating Neurons in the Rostral Ventromedial Medulla: Iontophoresis of Bicuculline Eliminates the off-Cell Pause. Somatosens. Mot. Res. 1991, 8, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinricher, M.M.; Neubert, M.J. Neural Basis for the Hyperalgesic Action of Cholecystokinin in the Rostral Ventromedial Medulla. J. Neurophysiol. 2004, 92, 1982–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedrich, A.E.; Gebhart, G.F. Modulation of Visceral Hyperalgesia by Morphine and Cholecystokinin from the Rat Rostroventral Medial Medulla. Pain 2003, 104, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maire, J.J.; Close, L.N.; Heinricher, M.M.; Selden, N.R. Distinct Pathways for Norepinephrine- and Opioid-Triggered Antinociception from the Amygdala. Eur. J. Pain 2016, 20, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helmstetter, F.J.; Tershner, S.A.; Poore, L.H.; Bellgowan, P.S.F. Antinociception Following Opioid Stimulation of the Basolateral Amygdala Is Expressed through the Periaqueductal Gray and Rostral Ventromedial Medulla. Brain Res. 1998, 779, 104–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGaraughty, S.; Heinricher, M.M. Microinjection of Morphine into Various Amygdaloid Nuclei Differentially Affects Nociceptive Responsiveness and RVM Neuronal Activity. Pain 2002, 96, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamotte, G.; Shouman, K.; Benarroch, E.E. Stress and Central Autonomic Network. Auton. Neurosci. 2021, 235, 102870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, B.; Mark Dolgas, C.; Kasckow, J.; Cullinan, W.E.; Herman, J.P. Central Stress-Integrative Circuits: Forebrain Glutamatergic and GABAergic Projections to the Dorsomedial Hypothalamus, Medial Preoptic Area, and Bed Nucleus of the Stria Terminalis. Brain Struct. Funct. 2014, 219, 1287–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martenson, M.E.; Cetas, J.S.; Heinricher, M.M. A Possible Neural Basis for Stress-Induced Hyperalgesia. Pain 2009, 142, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, K.M.; Roeder, Z.; DesRochers, K.; Buhler, A.V.; Heinricher, M.M.; Cleary, D.R. The Dorsomedial Hypothalamus Mediates Stress-Induced Hyperalgesia and Is the Source of the Pronociceptive Peptide Cholecystokinin in the Rostral Ventromedial Medulla. Neuroscience 2013, 238, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, M.; Bo, J.; Lei, Y.; Hu, F.; Xia, Z.; Liu, Y.; Lu, C.; Sun, Y.; Hou, B.; Ni, K.; et al. Anxiety-Induced Hyperalgesia in Female Rats Is Mediated by Cholecystokinin 2 Receptor in Rostral Ventromedial Medulla and Spinal 5-Hydroxytryptamine 2B Receptor. J. Pain Res. 2019, 12, 2009–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivat, C.; Becker, C.; Blugeot, A.; Zeau, B.; Mauborgne, A.; Pohl, M.; Benoliel, J.J. Chronic Stress Induces Transient Spinal Neuroinflammation, Triggering Sensory Hypersensitivity and Long-Lasting Anxiety-Induced Hyperalgesia. Pain 2010, 150, 358–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imbe, H.; Murakami, S.; Okamoto, K.; Iwai-Liao, Y.; Senba, E. The Effects of Acute and Chronic Restraint Stress on Activation of ERK in the Rostral Ventromedial Medulla and Locus Coeruleus. Pain 2004, 112, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, J.S.; de Souza, G.R.; Kalil-Cutti, B.; Giusti-Paiva, A.; Vilela, F.C. Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Increases Pain Sensitivity by Reducing Descending Noradrenergic and Serotoninergic Modulation. Behav. Brain Res. 2021, 411, 113367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, E.; Spinella, M.; Pavlovic, Z.W.; Bodnar, R.J. Alterations in Swim Stress-Induced Analgesia and Hypothermia Following Serotonergic or NMDA Antagonists in the Rostral Ventromedial Medulla of Rats. Physiol. Behav. 1998, 64, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- François, A.; Low, S.A.; Sypek, E.I.; Christensen, A.J.; Sotoudeh, C.; Beier, K.T.; Ramakrishnan, C.; Ritola, K.D.; Sharif-Naeini, R.; Deisseroth, K.; et al. A Brainstem-Spinal Cord Inhibitory Circuit for Mechanical Pain Modulation by GABA and Enkephalins. Neuron 2017, 93, 822–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, E.K.Y.; Bian, Z.X.; Xu, H.X.; Sung, J.J.Y. Neonatal Maternal Separation Increases Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor and Tyrosine Kinase Receptor B Expression in the Descending Pain Modulatory System. NeuroSignals 2009, 17, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chebbi, R.; Boyer, N.; Monconduit, L.; Artola, A.; Luccarini, P.; Dallel, R. The Nucleus Raphe Magnus OFF-Cells Are Involved in Diffuse Noxious Inhibitory Controls. Exp. Neurol. 2014, 256, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarnitsky, D. Role of Endogenous Pain Modulation in Chronic Pain Mechanisms and Treatment. Pain 2015, 156, S24–S31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.L.; Heinricher, M.M. Descending Control Mechanisms and Chronic Pain. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2019, 21, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pagliusi, M., Jr.; Gomes, F.V. The Role of The Rostral Ventromedial Medulla in Stress Responses. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 776. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13050776
Pagliusi M Jr., Gomes FV. The Role of The Rostral Ventromedial Medulla in Stress Responses. Brain Sciences. 2023; 13(5):776. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13050776
Chicago/Turabian StylePagliusi, Marco, Jr., and Felipe V. Gomes. 2023. "The Role of The Rostral Ventromedial Medulla in Stress Responses" Brain Sciences 13, no. 5: 776. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13050776
APA StylePagliusi, M., Jr., & Gomes, F. V. (2023). The Role of The Rostral Ventromedial Medulla in Stress Responses. Brain Sciences, 13(5), 776. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13050776





