Pathophysiology and Treatment of Lipid Abnormalities in Cerebrotendinous Xanthomatosis: An Integrative Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Cholesterol Metabolism
3.2. Cholesterol Metabolism in CTX
3.3. Metabolic Abnormalities and Laboratory Diagnosis of CTX
3.3.1. Serum Profile in CTX
3.3.2. CSF Profile in CTX
3.3.3. Bile, Urine and Tissue Abnormalities in CTX
3.3.4. Laboratorial Differentials for CTX
3.3.5. CTX Laboratory Findings and Other Diseases
3.4. CTX Treatment and Its Effect on Metabolism
3.5. Diet Effects in CTX
3.6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Höflinger, P.; Hauser, S.; Yutuc, E.; Hengel, H.; Griffiths, L.; Radelfahr, F.; Howell, O.W.; Wang, Y.; Connor, S.L.; Duell, P.B.; et al. Metabolic profiling in serum, cerebrospinal fluid, and brain of patients with cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis. J. Lipid Res. 2021, 62, 100078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyama, S.; Sekijima, Y.; Ogura, M.; Hori, M.; Matsuki, K.; Miida, T.; Harada-Shiba, M. Cerebrotendinous Xanthomatosis: Molecular Pathogenesis, Clinical Spectrum, Diagnosis, and Disease-Modifying Treatments. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2021, 28, 905–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nóbrega, P.R.; Bernardes, A.M.; Ribeiro, R.M.; Vasconcelos, S.C.; Araújo, D.A.B.S.; Gama, V.C.d.V. Cerebrotendinous Xanthomatosis: A practice review of pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 1049850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salen, G.; Steiner, R.D. Epidemiology, diagnosis, and treatment of cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis (CTX). J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2017, 40, 771–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, S.; Chen, G.; Cao, X.; Zhang, Y. Cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis: A comprehensive review of pathogenesis, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, and management. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2014, 9, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.Y.; Setchell, K.D.R.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, W.; Wolfe, B.; Lu, Y.; Lackner, K.; Knisely, A.S.; Wang, N.L.; Hao, C.Z.; et al. Severe Neonatal Cholestasis in Cerebrotendinous Xanthomatosis: Genetics, Immunostaining, Mass Spectrometry. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2017, 65, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verrips, A.; Dotti, M.T.; Mignarri, A.; Stelten, B.M.L.; Verma, S.; Federico, A. The safety and effectiveness of chenodeoxycholic acid treatment in patients with cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis: Two retrospective cohort studies. Neurol. Sci. 2020, 41, 943–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, D.W. The enzymes, regulation, and genetics of bile acid synthesis. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2003, 72, 137–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton, P.T.; Verrips, A.; Sistermans, E.; Mann, A.; Mieli-Vergani, G.; Wevers, R. Mutations in the sterol 27-hydroxylase gene (CYP27A) cause hepatitis of infancy as well as cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2002, 25, 501–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atallah, I.; San Millán, D.; Benoît, W.; Campos-Xavier, B.; Superti-Furga, A.; Tran, C. Spinal Cerebrotendinous Xanthomatosis: A case report and literature review. Mol. Genet. Metab. Rep. 2021, 26, 100719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mignarri, A.; Gallus, G.N.; Dotti, M.T.; Federico, A. A suspicion index for early diagnosis and treatment of cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2014, 37, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berginer, V.M.; Abeliovich, D. Genetics of cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis (CTX): An autosomal recessive trait with high gene frequency in Sephardim of Moroccan origin. Am. J. Med. Genet. 1981, 10, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stelten, B.M.L.; Dotti, M.T.; Verrips, A.; Elibol, B.; Falik-Zaccai, T.C.; Hanman, K.; Mignarri, A.; Sithole, B.; Steiner, R.D.; Verma, S.; et al. Expert opinion on diagnosing, treating and managing patients with cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis (CTX): A modified Delphi study. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2021, 16, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amador, M.D.M.; Masingue, M.; Debs, R.; Lamari, F.; Perlbarg, V.; Roze, E. Treatment with chenodeoxycholic acid in Cerebrotendinous Xanthomatosis: Clinical, neurophysiological, and quantitative brain structural outcomes. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2018, 41, 799–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duell, P.B.; Salen, G.; Eichler, F.S.; DeBarber, A.E.; Connor, S.L.; Casaday, L. Diagnosis, treatment, and clinical outcomes in 43 cases with Cerebrotendinous Xanthomatosis. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2018, 12, 1169–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salen, G.; Shefer, S.; Berginer, V. Biochemical abnormalities in cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis. Dev. Neurosci. 1991, 13, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, J.Y. Bile acid metabolism and signaling. Compr. Physiol. 2013, 3, 1191–1212. [Google Scholar]
- Burnett, J.R.; Moses, E.A.; Croft, K.D.; Brown, A.J.; Grainger, K.; Vasikaran, S.D.; Leitersdorf, E.; Watts, G.F. Clinical and biochemical features, molecular diagnosis and long-term management of a case of cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis. Clin. Chim. Acta 2001, 306, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shore, V.; Salen, G.; Cheng, F.W.; Forte, T.; Shefer, S.; Tint, G.S.; Lindgren, F.T. Abnormal high density lipoproteins in cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis. J. Clin. Investig. 1981, 68, 1295–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mast, N.; Anderson, K.W.; Lin, J.B.; Li, Y.; Turko, I.V.; Tatsuoka, C. Cytochrome P450 27A1 deficiency and regional differences in brain sterol metabolism cause preferential cholestanol accumulation in the cerebellum. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 4913–4924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razi, S.M.; Gupta, A.K.; Gupta, D.C.; Gutch, M.; Gupta, K.K.; Usman, S.I. Cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis (a rare lipid storage disorder): A case report. J. Med. Case Rep. 2016, 10, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, P.J.H.; Rideout, T. Lipids, sterols, and their metabolites. In Modern Nutrition in Health and Disease, 11th ed.; Ross, A.C., Caballero, B., Cousins, J.R., Tucker, K.L., Ziegler, T.R., Eds.; Lippincott Williams and Wilkins: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2012; pp. 65–87. [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein, J.L.; Brown, M.S. Regulation of the mevalonate pathway. Nature 1990, 343, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, S.; Stevenson, J.; Kristiana, I.; Brown, A.J. Cholesterol-dependent degradation of squalene monooxygenase, a control point in cholesterol synthesis beyond HMG-CoA reductase. Cell Metab. 2011, 13, 260–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnesjo, B.; Nilsson, A.; Barrowman, J.; Borgstrom, B. Intestinal digestion and absorption of cholesterol and lecithin in the human. Intubation studies with a fat-soluble reference substance. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 1969, 4, 653–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borgstrom, B. Studies on intestinal cholesterol absorption in the human. J. Clin. Investig. 1960, 39, 809–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woollett, L.A.; Wang, Y.; Buckley, D.D.; Yao, L.; Chin, S.; Granholm, N.; Jones, P.J.; Setchell, K.D.; Tso, P.; Heubi, J.E. Micellar solubilization of cholesterol is essential for absorption in humans. Gut 2006, 55, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.Q. Regulation of intestinal cholesterol absorption. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2007, 69, 221–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, H.R., Jr.; Altmann, S.W. Niemann-Pick C1 Like 1 (NPC1L1) an intestinal sterol transporter. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1791, 679–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berge, K.E.; Tian, H.; Graf, G.A.; Yu, L.; Grishin, N.V.; Schultz, J.; Kwiterovich, P.; Shan, B.; Barnes, R.; Hobbs, H.H. Accumulation of dietary cholesterol in sitosterolemia caused by mutations in adjacent ABC transporters. Science 2000, 290, 1771–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, D.A.; Jamil, H. Progress towards understanding the role of microsomal triglyceride transfer protein in apolipoprotein-B lipoprotein assembly. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2000, 1486, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Ciaula, A.; Wang, D.Q.; Bonfrate, L.; Portincasa, P. Current views on genetics and epigenetics of cholesterol gallstone disease. Cholesterol 2013, 2013, 298421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salen, G.; Grundy, S.M. The metabolism of cholestanol, cholesterol, and bile acids in cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis. J. Clin. Investig. 1973, 52, 2822–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petar Brlek, P.; Bulić, L.; Weinberger, D.G.; Bošnjak, J.; Pavlović, T.; Tomić, S.; Dupan, Z.K.; Borić, I.; Primorac, D. Successful Treatment of a Rare Cholesterol Homeostasis Disorder Due to CYP27A1 Gene Mutation with Chenodeoxycholic Acid Therapy. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, D.; Yang, X.; Ma, G.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhao, H.; Liang, Y.; et al. CYP27A1 inhibits bladder cancer cells proliferation by regulating cholesterol homeostasis. Cell Cycle 2019, 18, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menkes, J.H.; Schimschock, J.R.; Swanson, P.D. Cerebrotendinous Xanthomatosis: The Storage of Cholestanol Within the Nervous System. Arch. Neurol. 1968, 19, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, K.; Kubota, S.; Seyama, Y. Cholestanol induces apoptosis of cerebellar neuronal cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1999, 256, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Bogaert, L.; Philippart, M.; De Barsy, T. Nouvelles recherches sur la xanthomatose cérébro-tendineuse [New research on cerebro-tendinal xanthomatosis]. Rev. Neurol. 1969, 121, 98–100. [Google Scholar]
- Federico, A.; Gallus, G.N. Cerebrotendinous Xanthomatosis. Adam, M.P., Mirzaa, G.M., Pagon, R.A., et al., Eds.; In GeneReviews®; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 1993–2023. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1409/ (accessed on 12 June 2023).
- Mignarri, A.; Magni, A.; Del Puppo, M.; Gallus, G.N.; Björkhem, I.; Federico, A.; Dotti, M.T. Evaluation of cholesterol metabolism in cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2016, 39, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuriyama, M.; Fujiyama, J.; Yoshidome, H.; Takenaga, S.; Matsumuro, K.; Kasama, T.; Fukuda, K.; Kuramoto, T.; Hoshita, T.; Seyama, Y.; et al. Cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis: Clinical and biochemical evaluation of eight patients and review of the literature. J. Neurol. Sci. 1991, 102, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patni, N.; Wilson, D.P. Cerebrotendinous Xanthomatosis. In Endotext [Internet]; Feingold, K.R., Anawalt, B., Blackman, M.R., Boyce, A., Chrousos, G., Corpas, E., de Herder, W.W., Dhatariya, K., Dungan, K., Hofland, J., et al., Eds.; MDText.com, Inc.: South Dartmouth, MA, USA, 2000. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK395578/ (accessed on 12 June 2023).
- Björkhem, I.; Hansson, M. Cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis: An inborn error in bile acid synthesis with defined mutations but still a challenge. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 396, 46–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sain-van der Velden, M.G.; Verrips, A.; Prinsen, B.H.; de Barse, M.; Berger, R.; Visser, G. Elevated cholesterol precursors other than cholestanol can also be a hallmark for CTX. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2008, 31 (Suppl. S2), S387–S393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelzo, M.; Di Taranto, M.D.; Sica, C.; Boscia, A.; Papagni, F.; Fortunato, G.; Corso, G.; Russo, A.D. Age-related changes of cholestanol and lathosterol plasma concentrations: An explorative study. Lipids Health Dis. 2019, 18, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilo de la Fuente, B.; Ruiz, I.; Lopez de Munain, A.; Jimenez-Escrig, A. Cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis: Neuropathological findings. J. Neurol. 2008, 255, 839–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilo-de-la-Fuente, B.; Jimenez-Escrig, A.; Lorenzo, J.R.; Pardo, J.; Arias, M.; Ares-Luque, A.; Duarte, J.; Muñiz-Pérez, S.; Sobrido, M.J. Cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis in Spain: Clinical, prognostic, and genetic survey. Eur. J. Neurol. 2011, 18, 1203–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimazu, K.; Kuwabara, M.; Yoshii, M.; Kihira, K.; Takeuchi, H.; Nakano, I.; Ozawa, S.; Onuki, M.; Hatta, Y.; Hoshita, T. Bile alcohol profiles in bile, urine, and feces of a patient with cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis. J. Biochem. 1986, 99, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekijima, Y.; Koyama, S.; Yoshinaga, T.; Koinuma, M.; Inaba, Y. Nationwide survey on cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis in Japan. J. Hum Genet. 2018, 63, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guenzelm, A.J.; DeBarber, A.; Raymond, K.; Dhamija, R. Familial variability of cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis lacking typical biochemical findings. JIMD Rep. 2021, 59, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, X.; Daiker, J.; Sadilek, M.; DeBarber, A.E.; Chiang, J.; Duan, J.; Bootsma, A.H.; Huidekoper, H.H.; Vaz, F.M.; Gelb, M.H. Toward newborn screening of cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis: Results of a biomarker research study using 32,000 newborn dried blood spots. Genet. Med. 2020, 22, 1606–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitt, J.J. High-throughput urine screening for Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome and cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis using negative electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. Clin. Chim. Acta. 2007, 380, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panzenboeck, U.; Andersson, U.; Hansson, M.; Sattler, W.; Meaney, S.; Björkhem, I. On the mechanism of cerebral accumulation of cholestanol in patients with cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis. J. Lipid Res. 2007, 48, 1167–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeBarber, A.E.; Connor, W.E.; Pappu, A.S.; Merkens, L.S.; Steiner, R.D. ESI-MS/MS quantification of 7α-hydroxy-4-cholesten-3-one facilitates rapid, convenient diagnostic testing for cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis. Clin. Chim. Acta. 2010, 411, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beppu, T.; Seyama, Y.; Kasama, T.; Serizawa, S.; Yamakawa, T. Serum bile acid profiles in cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis. Clin. Chim. Acta. 1982, 118, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salen, G.; Batta, A.K.; Tint, G.S.; Shefer, S. Comparative effects of lovastatin and chenodeoxycholic acid on plasma cholestanol levels and abnormal bile acid metabolism in cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis. Metabolism. 1994, 43, 1018–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Bahr, S.; Björkhem, I.; Van’t Hooft, F.; Alvelius, G.; Nemeth, A.; Sjövall, J.; Fischler, B. Mutation in the sterol 27-hydroxylase gene associated with fatal cholestasis in infancy. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2005, 40, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierre, G.; Setchell, K.; Blyth, J.; Preece, M.A.; Chakrapani, A.; McKiernan, P. Prospective treatment of cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis with cholic acid therapy. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2008, 31, S241–S245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundaram, S.S.; Bove, K.E.; Lovell, M.A.; Sokol, R.J. Mechanisms of disease: Inborn errors of bile acid synthesis. Nat. Clin. Pract. Gastroenterol. Hepatol 2008, 5, 456–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berginer, V.M.; Shany, S.; Alkalay, D.; Berginer, J.; Dekel, S.; Salen, G.; Tint, G.S.; Gazit, D. Osteoporosis and increased bone fractures in cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis. Metabolism 1993, 42, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, G.; Mignarri, A.; Ruvio, M.; Valenti, R.; Franci, B.; Del Puppo, M.; Federico, A.; Nuti, R.; Dotti, M.T. Long-term bone density evaluation in cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis: Evidence of improvement after chenodeoxycholic acid treatment. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2013, 92, 282–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zübarioğlu, T.; Bilen, İ.P.; Kıykım, E.; Doğan, B.B.; Enver, E.Ö.; Cansever, M.Ş.; Zeybek, A.Ç.A. Evaluation of the effect of chenodeoxycholic acid treatment on skeletal system findings in patients with cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis. Turk. Pediatri. Ars. 2019, 54, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federico, A.; Dotti, M.T.; Loré, F.; Nuti, R. Cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis: Pathophysiological study on bone metabolism. J. Neurol. Sci. 1993, 115, 67–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koopman, B.J.; Wolthers, B.G.; van der Molen, J.C.; van der Slik, W.; Waterreus, R.J.; van Spreeken, A. Cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis: A review of biochemical findings of the patient population in The Netherlands. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 1988, 11, 56–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salen, G. Cholestanol deposition in cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis: A possible mechanism. Ann. Intern. Med. 1971, 75, 843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouwes Bavinck, J.N.; Vermeer, B.J.; Gevers Leuven, J.A.; Koopman, B.J.; Wolthers, B.G. Capillary gas chromatography of urine samples in diagnosing cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis. Arch. Dermatol. 1986, 122, 1269–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claesen, J.L.A.; Koomen, E.; Schene, I.F.; Jans, J.J.M.; Mast, N.; Pikuleva, I.A.; van der Ham, M.; de Sain-van der Velden, M.G.M.; Fuchs, S.A. Misdiagnosis of CTX due to propofol: The interference of total intravenous propofol anaesthesia with bile acid profiling. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2020, 43, 843–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Taranto, M.D.; Gelzo, M.; Giacobbe, C.; Gentile, M.; Marotta, G.; Savastano, S.; Dello Russo, A.; Fortunato, G.; Corso, G. Cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis, a metabolic disease with different neurological signs: Two case reports. Metab. Brain Dis. 2016, 31, 1185–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björkhem, I. Cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2013, 24, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, D.; Gan-Schreier, H.; Langhans, C.D.; Rohrer, T.; Engelmann, G.; Heverin, M.; Russell, D.W.; Clayton, P.T.; Hoffmann, G.F.; Okun, J.G. Differential diagnosis in patients with suspected bile acid synthesis defects. World J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 1067–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolthers, B.G.; Volmer, M.; van der Molen, J.; Koopman, B.J.; de Jager, A.E.; Waterreus, R.J. Diagnosis of cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis (CTX) and effect of chenodeoxycholic acid therapy by analysis of urine using capillary gas chromatography. Clin. Chim. Acta. 1983, 131, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setoguchi, T.; Salen, G.; Tint, G.S.; Mosbach, E.H. A biochemical abnormality in cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis. Impairment of bile acid biosynthesis associated with incomplete degradation of the cholesterol side chain. J. Clin. Investig. 1974, 53, 1393–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lütjohann, D.; Stellaard, F.; Björkhem, I. Levels of 7alpha-hydroxycholesterol and/or 7alpha-hydroxy-4-cholest-3-one are the optimal biochemical markers for the evaluation of treatment of cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis. J. Neurol. 2020, 267, 572–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadasian, M.H.; Salen, G.; Frohlich, J.J.; Scudamore, C.H. Cerebrotendinous Xanthomatosis: A Rare Disease with Diverse Manifestations. Arch. Neurol. 2002, 59, 527–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izar, M.C.d.O.; Giraldez, V.Z.R.; Bertolami, A.; Filho, R.D.d.S.; Lottenberg, A.M.; Assad, M.H.V.; Saraiva, J.F.K.; Chacra, A.P.M.; Martinez, T.L.R.; Bahia, L.R.; et al. Atualização da Diretriz Brasileira de Hipercolesterolemia Familiar. Arquivos Brasileiros de Cardiologia 2021, 117, 782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaefer, E.J.; Tint, G.S.; Duell, P.B.; Steiner, R.D. Cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis, sitosterolemia, Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome and the seminal contributions of Gerald Salen, MD (1935–2020). J. Clin. Lipidol. 2021, 15, 540–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pajares, S.; Arias, A.; García-Villoria, J.; MacÍas-Vidal, J.; Ros, E.; de Las Heras, J.; Girós, M.; Coll, M.J.; Ribes, A. Cholestane-3β,5α,6β-triol: High levels in Niemann-Pick type C, cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis, and lysosomal acid lipase deficiency. J. Lipid Res. 2015, 56, 1926–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonney, H.; de Silva, R.; Giunti, P.; Greenfeld, J.; Hunt, B.; Ataxia, U.K. Management of the Ataxias towards Best Clinical Practice. 2016. Available online: https://www.ataxia.org.uk/wp-content/uploads/2020/11/Ataxia_UK_Medical_Guidelines_Third_Edition._v3m_Dec_2016_-_updated_Sep_2019.pdf (accessed on 30 June 2021).
- Salen, G.; Berginer, V.; Shore, V.; Horak, I.; Horak, E.; Tint, G.S.; Shefer, S. Increased concentrations of cholestanol and apolipoprotein B in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis. Effect of chenodeoxycholic acid. N. Engl. J. Med. 1987, 316, 1233–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samenuk, P.; Koffman, B.M. Chenodeoxycholic treatment of cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis. Neurology 2001, 56, 695–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mignarri, A.; Rossi, S.; Ballerini, M.; Gallus, G.N.; Del Puppo, M.; Galluzzi, P.; Federico, A.; Dotti, M.T. Clinical relevance and neurophysiological correlates of spasticity in cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis. J. Neurol. 2011, 258, 783–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginanneschi, F.; Mignarri, A.; Mondelli, M.; Gallus, G.N.; Del Puppo, M.; Giorgi, S.; Federico, A.; Rossi, A.; Dotti, M.T. Polyneuropathy in cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis and response to treatment with chenodeoxycholic acid. J. Neurol. 2013, 260, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stelten, B.M.L.; Nijeholt, G.J.L.A.; Hendriks, E.; Kluijtmans, L.A.J.; Wevers, R.A.; Verrips, A. Long-term MRI findings in patients with Cerebrotendinous Xanthomatosis treated with chenodeoxycholic acid. Neurology 2022, 99, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verrips, A.; Wevers, R.A.; Van Engelen, B.G.; Keyser, A.; Wolthers, B.G.; Barkhof, F.; Stalenhoef, A.; De Graaf, R.; Janssen-Zijlstra, F.; Van Spreeken, A.; et al. Effect of simvastatin in addition to chenodeoxycholic acid in patients with cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis. Metabolism 1999, 48, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bel, S.; Garcia-Patos, V.; Rodriguez, L.; Selvan, A.; Diaz, P.; Wolthers, B.G.; Castells, A. Cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2001, 45, 292–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stelten, B.M.L.; Huidekoper, H.H.; van de Warrenburg, B.P.C.; Brilstra, E.H.; Hollak, C.E.M.; Haak, H.R.; Kluijtmans, L.A.J.; Wevers, R.A.; Verrips, A. Long-term treatment effect in cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis depends on age at treatment start. Neurology 2019, 92, e83–e95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Heijst, A.F.; Verrips, A.; Wevers, R.A.; Cruysberg, J.R.; Renier, W.O.; Tolboom, J.J. Treatment and follow-up of children with cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis. Eur. J. Pediatr. 1998, 157, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salen, G.; Tint, G.S.; Eliav, B.; Deering, N.; Mosbach, E.H. Increased formation of ursodeoxycholic acid in patients treated with chenodeoxycholic acid. J. Clin. Investig. 1974, 53, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuriyama, M.; Tokimura, Y.; Fujiyama, J.; Utatsu, Y.; Osame, M. Treatment of cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis: Effects of chenodeoxycholic acid, pravastatin, and combined use. J. Neurol. Sci. 1994, 125, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Björkhem, I.; Skrede, S.; Buchmann, M.S.; East, C.; Grundy, S. Accumulation of 7α-hydroxy-4-cholesten-3-one and cholesta-4, 6-dien-3-one in patients with cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis: Effect of treatment with chenodeoxycholic acid. Hepatology 1987, 7, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Björkhem, K.; Muri-Boberg, E.; Leitersdorf. Inborn errors in bile acid biosynthesis and storage of sterols other than cholesterol. In The Metabolic Bases of Inherited Diseases; Scriver, C.R., Beaudet, A.L., Sly, W.S., Valle, D., Eds.; McGraw Hill Publishing Co.: New York, NY, USA, 2001; pp. 2961–2988. [Google Scholar]
- Salen, G.; Shefer, S.; Berginer, V.M. Familial diseases with storage of sterols other than cholesterol: Cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis and sitosterolemia with xanthomatosis. In The Metabolic Basis of Inherited Disease, 5th ed.; Stanbury, J.B., Wyngaarden, J., Fredrickson, D.S., Eds.; McGraw-Hill Book: New York, NY, USA, 1983; pp. 713–730. [Google Scholar]
- Oftebro, H.; Bjorkhem, I.; Skrede, S.; Schreiner, A.; Pederson, J.I. Cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis: A defect in mitochondrial 26-hydroxylation required for normal biosynthesis of cholic acid. J. Clin. Investig. 1980, 65, 1418–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batta, A.K.; Shefer, S.; Batta, M.; Salen, G. Effect of chenodeoxycholic acid on biliary and urinary bile acids and bile alcohols in cercbrotendinous xanthomatosis: Monitoring by high performance liquid chromatography. J. Lipid Res. 1985, 26, 690–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batta, A.K.; Salen, G.; Shefer, S.; Tint, G.S.; Batta, M. Increased plasma bile alcohol glucuronides in patients with cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis: Effect of chenodeoxycholic acid. J. Lipid Res. 1987, 28, 1006–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batta, A.K.; Salen, G.; Tint, G.S. Hydrophilic 7β-hydroxy bile acids, lovastatin, and cholestyramine are ineffective in the treatment of Cerebrotendinous Xanthomatosis. Metabolism 2004, 53, 556–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tint, G.S.; Ginsberg, H.; Salen, G.; Le, N.; Shefer, S. Chenodeoxycholic acid normalizes elevated lipoprotein secretion and catabolism in cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis. J. Lipid Res. 1989, 30, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaabjerg, M.; Marjanovic, D. Cerebrotendinøs xantomatose er en sjælden neurologisk sygdom med en specifik behandling [Cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis is a rare disorder, which requires a specific treatment]. Ugeskr Laeger 2013, 175, 285–286. (In Danish) [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Salen, G.; Meriwether, T.W.; Nicolau, G. Chenodeoxycholic acid inhibits increased cholesterol and cholestanol synthesis in patients with cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis. Biochem. Med. 1975, 14, 57–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinoshita, M.; Kawamura, M.; Fujita, M.; Hirota, D.; Suda, T.; Taki, M.; Kusano, J.; Takao, K.; Takenaka, H.; Kubota, S.; et al. Enhanced susceptibility of LDL to oxidative modification in a CTX patient:—role of chenodeoxycholic acid in xanthoma formation. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2004, 11, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjorkhem, I.; Skrede, S. Familial disease with storage of sterols other than cholesterol: Cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis and phytosterolemia. In The Metabolic Basis of Inherited Disease, 6th ed.; Scriver, C.R., Beaudet, A.L., Sly, W.S., Valle, D., Eds.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1989; pp. 1283–1302. [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein, J.L.; Ho, Y.K.; Basu, S.K.; Brown, M.S. Binding site of macrophages that mediate uptake and degradation of acetylated low density lipoprotein, producing massive cholesterol deposition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1979, 76, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparrow, C.P.; Parthasarathy, S.; Steinberg, D. A macrophage receptor that recognizes oxidized LDL but not acetylated LDL. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 2599–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witztum, J.L.; Steinberg, D. Role of oxidized low density-lipoprotein in atherogenesis. J. Clin. Investig. 1991, 88, 1785–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koopman, B.J.; Wolthers, B.G.; van der Molen, J.C.; Waterreus, R.J. Bile acid therapies applied to patients suffering from cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis. Clin. Chim. Acta 1985, 152, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, E.; Axelson, M.; Abrahamsson, A.; Eggertsen, G.; Thörne, A.; Nowak, G.; Ericzon, B.-G.; Björkhem, I.; Einarsson, C. Feedback regulation of bile acid synthesis in primary human hepatocytes: Evidence that CDCA is the strongest inhibitor. Hepatology 2003, 38, 930–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berginer, V.M.; Berginer, J.; Korczyn, A.D.; Tadmor, R. Magnetic resonance imaging in cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis: A prospective clinical and neuroradiological study. J. Neurol. Sci. 1994, 122, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandia, D.; Besson, G.; Lamari, F.; Castelnovo, G.; Curot, J.; Duval, F.; Giral, P.; Lecerf, J.M.; Roland, D.; Pierdet, H.; et al. Cholic acid as a treatment for cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis in adults. J. Neurol. 2019, 266, 2043–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makishima, M.; Okamoto, A.Y.; Repa, J.J.; Tu, H.; Learned, R.M.; Luk, A.; Hull, M.V.; Lustig, K.D.; Mangelsdorf, D.J.; Shan, B. Identification of a nuclear receptor for bile acids. Science 1999, 284, 1362–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parks, D.J.; Blanchard, S.G.; Bledsoe, R.K.; Chandra, G.; Consler, T.G.; Kliewer, S.A.; Stimmel, J.B.; Willson, T.M.; Zavacki, A.M.; Moore, D.D.; et al. Bile acids: Natural ligands for an orphan nuclear receptor. Science 1999, 284, 1365–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.B.; Chen, J.; Hollister, K.; Sowers, L.C.; Forman, B.M. Endogenous bile acids are ligands for the nuclear receptor FXR/BAR. Mol. Cell 1999, 3, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Einarsson, C.; Hillebrant, C.G.; Axelson, M. Effects of treatment with deoxycholic acid and chenodeoxycholic acid on the hepatic synthesis of cholesterol and bile acids in healthy subjects. Hepatology 2001, 33, 1189–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huidekoper, H.H.; Vaz, F.M.; Verrips, A.; Bosch, A.M. Hepatotoxicity due to chenodeoxycholic acid supplementation in an infant with cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis: Implications for treatment. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2016, 175, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medscape. Available online: https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1418820-overview (accessed on 30 June 2021).
- Bartholdi, D.; Zumsteg, D.; Verrips, A.; Wevers, R.A.; Sistermans, E.; Hess, K.; Jung, H.H. Spinal phenotype of Cerebrotendinous Xanthomatosis—A pitfall in the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis. J. Neurol. 2004, 251, 105–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, B.; Mitchell, W.D.; Marenah, C.B.; Cortese, C.; Reynolds, E.H.; Shakir, R. Cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis: Biochemical response to inhibition of cholesterol synthesis. Br. Med. J. 1983, 287, 21–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, T.; Matsuzawa, Y.; Takemura, K.; Kubo, M.; Miki, H.; Tarui, S. Combined treatment with chenodeoxycholic acid and pravastatin improves plasma cholestanol levels associated with marked regression of tendon xanthomas in cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis. Metabolism 1991, 40, 741–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, M.M.; Gawkrodger, D.J.; Seymour, C.A.; Weismann, K. Metabolic and nutritional disorders. In Rook/Wilkinson/Ebling: Textbook of Dermatology, 6th ed.; Champion, R.H., Burton, J.L., Burns, T., Breathnach, S., Eds.; Blackwell Science: London, UK, 1998; pp. 2577–2677. [Google Scholar]
- Peynet, J.; Laurent, A.; De Liege, P.; Lecoz, P.; Gambert, P.; Legrand, A.; Mikol, J.; Warnet, A. Cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis: Treatments with simvastatin, lovastatin, and chenodeoxycholic acid in 3 siblings. Neurology 1991, 41, 434–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koopman, B.J.; Wolthers, B.G.; van der Moten, J.C.; Nagel, G.T.; Waterreus, R.J.; Oosterhuis, H.J.G.H. Capillary gas chromatographic determinations of urinary bile acids and bile alcohols in CTX-patients proving the ineffectivity of ursodeoxycholic acid treatment. Clin. Chim. Acta 1984, 142, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koopman, B.J.; Wolthers, B.G.; van der Molen, J.C.; Nagel, G.T.; Kruizinga, W. Abnormal urinary bile acids in a patient suffering from cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis during oral administration of ursodeoxycholic acid. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1987, 917, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dotti, M.T.; Lütjohann, D.; von Bergmann, K.; Federico, A. Normalisation of serum cholestanol concentration in a patient with Cerebrotendinous Xanthomatosis by combined treatment with chenodeoxycholic acid, simvastatin and LDL apheresis. Neurol. Sci. 2004, 25, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, S.; Kuwabara, S.; Sakakibara, R.; Oki, T.; Arai, H.; Oda, S.; Hattori, T. Combined treatment with LDL-apheresis, chenodeoxycholic acid and HMG-CoA. J. Neurol. Sci. 2003, 216, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byun, D.S.; Kasama, T.; Shimizu, T.; Yorifuji, H.; Seyama, Y. Effect of cholestanol feeding on sterol concentrations in the serum, liver, and cerebellum of mice. J. Biochem. 1988, 103, 375–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shefer, S.; Hauser, S.; Salen, G.; Zaki, F.G.; Bullock, J.; Salgado, E.; Shevitz, J. Comparative effects of cholestanol and cholesterol on hepatic sterol and bile acid metabolism in the rat. J. Clin. Investig. 1984, 74, 1773–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousuke, S. Cholestanol metabolism, molecular pathology, and nutritional implications. J. Med. Food 2003, 6, 217–224. [Google Scholar]
- Valdivielso, P.; Calandra, S.; Duran, J.C.; Garuti, R.; Herrera, E.; Gonzalez, P. Coronary heart disease in a patient with cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis. J. Intern Med. 2004, 255, 680–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malco, R.; Nestor, W.; Marcelo, M. Cardiac involvement in movement disorders. Mov. Disord. Clin. Pract. 2021, 8, 651–668. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Li, W.; Zheng, R.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, D.; Zhao, C.; Yan, C.; Zhao, Y. Cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis with peripheral neuropathy: A clinical and neurophysiological study in Chinese population. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
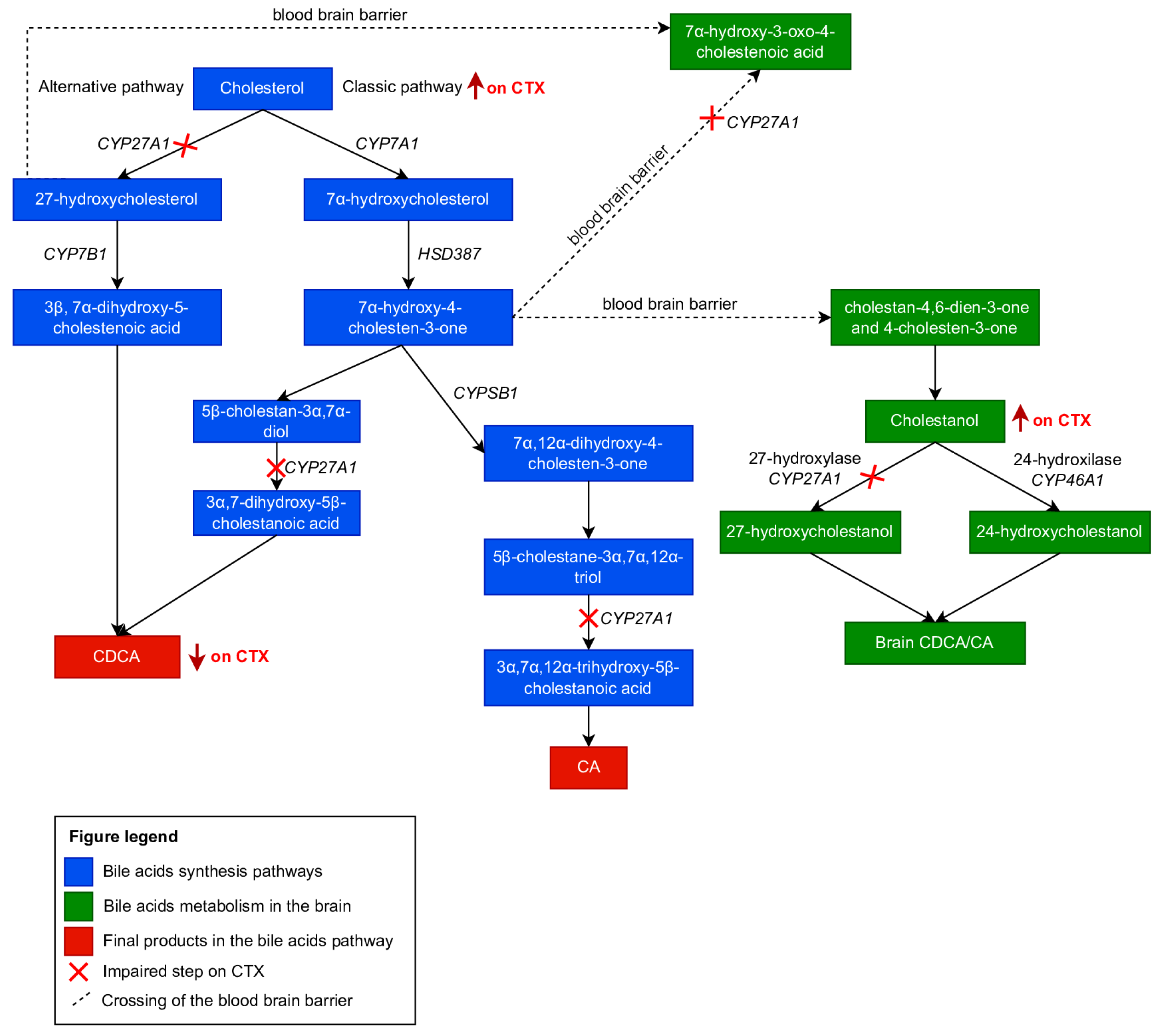

| Biochemical Markers | Serum Changes in CTX | Values Found in CTX (Mean ± Standard Deviation) |
|---|---|---|
| Cholestanol | Very high | 3.42 ± 1.28 mg/dL † |
| Cholesterol | Normal or low | 187 ± 67 mg/dL † |
| 27-hydroxycholesterol | Very low or undetectable | 1 ± 1.2 μg/dL † |
| 7a-hydroxycholesterol | High | 368 ± 221 μg/dL † |
| 25-hydroxyvitamin D | Normal or low | - |
| CDCA | Very low or undetectable | 0.698 ± 0.315 μg/mL ◊ |
| CA | Normal or high | 0.213 ± 0.161 μg/mL ◊ |
| CA/CDCA | High | 1:10 □ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ribeiro, R.M.; Vasconcelos, S.C.; Lima, P.L.G.d.S.B.; Coelho, E.F.; Oliveira, A.M.N.; Gomes, E.d.A.B.M.; Mota, L.d.A.; Radtke, L.S.; Carvalho, M.d.S.; Araújo, D.A.B.S.; et al. Pathophysiology and Treatment of Lipid Abnormalities in Cerebrotendinous Xanthomatosis: An Integrative Review. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 979. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13070979
Ribeiro RM, Vasconcelos SC, Lima PLGdSB, Coelho EF, Oliveira AMN, Gomes EdABM, Mota LdA, Radtke LS, Carvalho MdS, Araújo DABS, et al. Pathophysiology and Treatment of Lipid Abnormalities in Cerebrotendinous Xanthomatosis: An Integrative Review. Brain Sciences. 2023; 13(7):979. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13070979
Chicago/Turabian StyleRibeiro, Rodrigo Mariano, Sophia Costa Vasconcelos, Pedro Lucas Grangeiro de Sá Barreto Lima, Emanuel Ferreira Coelho, Anna Melissa Noronha Oliveira, Emanuel de Assis Bertulino Martins Gomes, Luciano de Albuquerque Mota, Lucas Soares Radtke, Matheus dos Santos Carvalho, David Augusto Batista Sá Araújo, and et al. 2023. "Pathophysiology and Treatment of Lipid Abnormalities in Cerebrotendinous Xanthomatosis: An Integrative Review" Brain Sciences 13, no. 7: 979. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13070979
APA StyleRibeiro, R. M., Vasconcelos, S. C., Lima, P. L. G. d. S. B., Coelho, E. F., Oliveira, A. M. N., Gomes, E. d. A. B. M., Mota, L. d. A., Radtke, L. S., Carvalho, M. d. S., Araújo, D. A. B. S., Pinheiro, M. S. N., Gama, V. C. d. V., Júnior, R. M. M., Braga Neto, P., & Nóbrega, P. R. (2023). Pathophysiology and Treatment of Lipid Abnormalities in Cerebrotendinous Xanthomatosis: An Integrative Review. Brain Sciences, 13(7), 979. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13070979







