Toxicity of Synthetic Cannabinoids in K2/Spice: A Systematic Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Eligibility
2.2. Information Sources
2.3. Search Strategy
2.4. Study Selection
2.5. Data Items
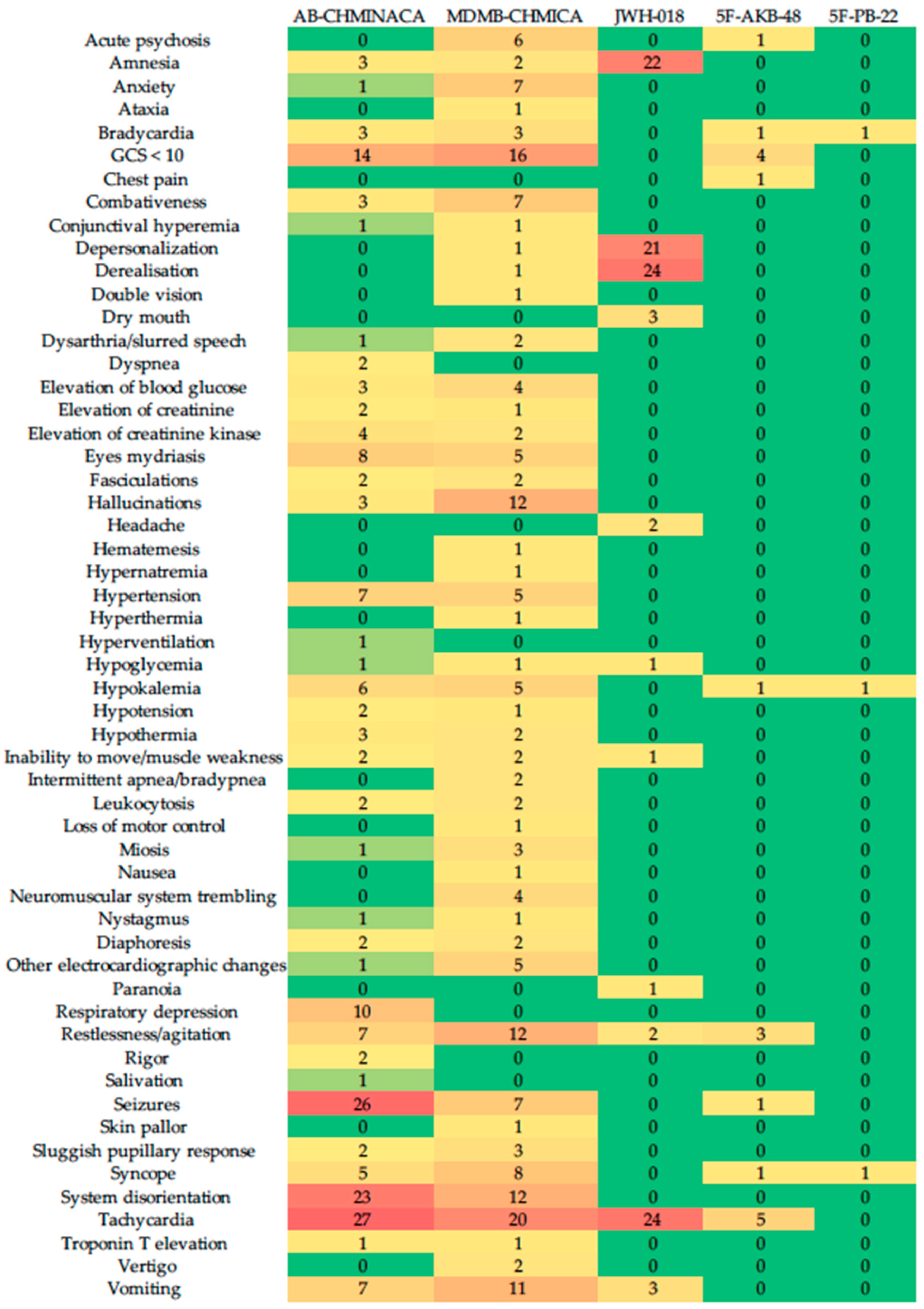
3. Results
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime. World Drug Report 2020 (Sales No. E. 20). Available online: https://wdr.unodc.org/wdr2020/index2020.html (accessed on 20 December 2022).
- Brents, L.K.; Prather, P.L. The K2/Spice Phenomenon: Emergence, identification, legislation and metabolic characterization of synthetic cannabinoids in herbal incense products. Drug Metab. Rev. 2013, 46, 72–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Palamar, J.J.; Acosta, P. Synthetic cannabinoid use in a nationally representative sample of US high school seniors. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2015, 149, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wiley, J.L.; Marusich, J.A.; Huffman, J.W. Moving around the molecule: Relationship between chemical structure and in vivo activity of synthetic cannabinoids. Life Sci. 2013, 97, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fantegrossi, W.E.; Moran, J.H.; Radominska-Pandya, A.; Prather, P.L. Distinct pharmacology and metabolism of K2 synthetic cannabinoids compared to Δ9-THC: Mechanism underlying greater toxicity? Life Sci. 2014, 97, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hudson, S.; Ramsey, J. The emergence and analysis of synthetic cannabinoids. Drug Test. Anal. 2011, 3, 466–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraemer, M.; Boehmer, A.; Madea, B.; Maas, A. Death cases involving certain new psychoactive substances: A review of the literature. Forensic Sci. Int. 2019, 298, 186–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giorgetti, A.; Busardò, F.P.; Tittarelli, R.; Auwärter, V.; Giorgetti, R. Post-Mortem Toxicology: A Systematic Review of Death Cases Involving Synthetic Cannabinoid Receptor Agonists. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drugs Addiction. Perspectives on Drugs: Synthetic Cannabinoids in Europe; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2017. Available online: https://www.emcdda.europa.eu/system/files/publications/2753/POD_Synthetic%20cannabinoids_0.pdf (accessed on 20 December 2022).
- Huffman, J.W.; Zengin, G.; Wu, M.J.; Lu, J.; Hynd, G.; Bushell, K.; Thompson, A.L.; Bushell, S.; Tartal, C.; Hurst, D.P.; et al. Structure-activity relationships for 1-alkyl-3-(1-naphthoyl)indoles at the cannabinoid CB(1) and CB(2) receptors: Steric and electronic effects of naphthoyl substituents. New highly selective CB(2) receptor agonists. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2005, 13, 89–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spaderna, M.; Addy, P.H.; D’souza, D.C. Spicing things up: Synthetic cannabinoids. Psychopharmacology 2013, 228, 525–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermanns-Clausen, M.; Kneisel, S.; Szabo, B.; Auwärter, V. Acute toxicity due to the confirmed consumption of synthetic cannabinoids: Clinical and laboratory findings. Addiction 2013, 108, 534–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tait, R.; Caldicott, D.; Mountain, D.; Hill, S.L.; Lenton, S. A systematic review of adverse events arising from the use of synthetic cannabinoids and their associated treatment. Clin. Toxicol. 2015, 54, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacher, P.; Steffens, S.; Haskó, G.; Schindler, T.H.; Kunos, G. Cardiovascular effects of marijuana and synthetic cannabinoids: The good, the bad, and the ugly. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2017, 15, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, H.; Verrico, C.D.; Kosten, T.R.; Nielsen, D.A. Psychosis and synthetic cannabinoids. Psychiatry Res. 2018, 268, 400–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debruyne, D.; LE Boisselier, R. Emerging drugs of abuse: Current perspectives on synthetic cannabinoids. Subst. Abus. Rehabil. 2015, 6, 113–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Busardò, F.P.; Malaca, S.; Nittari, G.; Sirignano, A.; Ricci, G. Fourth Generation of Synthetic Cannabinoid Receptor Agonists: A Review on the Latest Insights. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2022, 28, 2603–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Boisselier, R.; Alexandre, J.; Lelong-Boulouard, V.; Debruyne, D. Focus on cannabinoids and synthetic cannabinoids. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 101, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, S.; Fantegrossi, W.E. Synthetic Cannabinoids: Pharmacology, Behavioral Effects, and Abuse Potential. Curr. Addict. Rep. 2014, 1, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pintori, N.; Loi, B.; Mereu, M. Synthetic cannabinoids: The hidden side of Spice drugs. Behav. Pharmacol. 2017, 28, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattore, L.; Fratta, W. Beyond THC: The New Generation of Cannabinoid Designer Drugs. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2011, 5, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; the PRISMA Group. Reprint—Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: The PRISMA Statement. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2009, 89, 873–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Psychiatric Association. Substance Use Disorders. In Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th ed.; American Psychiatric Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2013; Volume 55, pp. 220–223. [Google Scholar]
- Tyndall, J.A.; Gerona, R.; De Portu, G.; Trecki, J.; Elie, M.C.; Lucas, J.; Schwartz, M. An outbreak of acute delirium from ex-posure to the synthetic cannabinoid AB-CHMINACA. Clin. Toxicol. 2015, 53, 950–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seywright, A.; Torrance, H.J.; Wylie, F.M.; McKeown, D.A.; Lowe, D.J.; Stevenson, R. Analysis and clinical findings of cases positive for the novel synthetic cannabinoid receptor agonist MDMB-CHMICA. Clin. Toxicol. 2016, 54, 632–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abouchedid, R.; Hudson, S.; Thurtle, N.; Yamamoto, T.; Ho, J.H.; Bailey, G.; Wood, M.; Sadones, N.; Stove, C.P.; Dines, A.; et al. Analytical confirmation of synthetic cannabinoids in a cohort of 179 presentations with acute recreational drug toxicity to an Emergency Department in London, UK in the first half of 2015. Clin. Toxicol. 2017, 55, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermanns-Clausen, M.; Müller, D.; Kithinji, J.; Angerer, V.; Franz, F.; Eyer, F.; Auwärter, V. Acute side effects after con-sumption of the new synthetic cannabinoids AB-CHMINACA and MDMB-CHMICA. Clin. Toxicol. 2018, 56, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamijo, Y.; Takai, M.; Fujita, Y.; Sakamoto, T. A multicenter retrospective survey of poisoning after consumption of products containing novel psychoactive substances from 2013 to 2014 in Japan. Am. J. Drug Alcohol Abus. 2016, 42, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theunissen, E.L.; Hutten, N.R.P.W.; Mason, N.L.; Toennes, S.W.; Kuypers, K.P.C.; de Sousa Fenandes Perna, E.B.; Ramaekers, J.G. Neurocognition and subjective experience following acute doses of the synthetic cannabinoid JWH-018: A phase 1, placebo-controlled, pilot study. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 175, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tebo, C.; Mazer-Amirshahi, M.; DeGeorge, L.; Gelfand, B.; Leak, C.; Tolliver, S.; Sauter, D. Suspected synthetic cannabinoid receptor agonist intoxication: Does analysis of samples reflect the presence of suspected agents? Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2018, 37, 1846–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theunissen, E.L.; Reckweg, J.T.; Hutten, N.R.; Kuypers, K.P.; Toennes, S.W.; Neukamm, M.A.; Ramaekers, J.G. Psychotomimetic symptoms after a moderate dose of a synthetic cannabinoid (JWH-018): Implications for psychosis. Psychopharmacology 2022, 239, 1251–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theunissen, E.L.; Kuypers, K.P.C.; Mason, N.L.; Ramaekers, J.G. A comparison of acute neurocognitive and psychotomimetic effects of a synthetic cannabinoid and natural cannabis at psychotropic dose equivalence. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 891811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manini, A.F.; Krotulski, A.J.; Schimmel, J.; Allen, L.; Hurd, Y.L.; Richardson, L.D.; Logan, B.K. Respiratory failure in confirmed synthetic cannabinoid overdose. Clin. Toxicol. 2022, 60, 524–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaPoint, J.; James, L.P.; Moran, C.L.; Nelson, L.S.; Hoffman, R.S.; Moran, J.H. Severe toxicity following synthetic cannabinoid ingestion. Clin. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 760–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneir, A.B.; Cullen, J.; Ly, B.T. “Spice” girls: Synthetic cannabinoid intoxication. J. Emerg. Med. 2011, 40, 296–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, A.C.; Schwarz, E.; Medina, G.; Obafemi, A.; Feng, S.-Y.; Kane, C.; Kleinschmidt, K. Cardiotoxicity associated with the synthetic cannabinoid, K9, with laboratory confirmation. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2012, 30, 320-e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pant, S.; Dholaria, B.; Kaur, V.; Ramavaram, S.; Ukor, M.; Deshmukh, A.; Teran, G.A. Spicy seizure. Am. J. Med. Sc. 2012, 344, 67–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, M.J.; Rose, D.Z.; Myers, M.A.; Gooch, C.L.; Bozeman, A.C.; Burgin, W.S. Ischemic stroke after use of the synthetic marijuana “spice”. Neurology 2013, 81, 2090–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hopkins, C.Y.; Gilchrist, B.L. A Case of Cannabinoid Hyperemesis Syndrome Caused by Synthetic Cannabinoids. J. Emerg. Med. 2013, 45, 544–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patton, A.L.; Chimalakonda, K.C.; Moran, C.L.; McCain, K.; Radominska-Pandya, A.; James, L.P.; Kokes, C.; Moran, J.H. K2 Toxicity: Fatal Case of Psychiatric Complications Following AM2201 Exposure. J. Forensic Sci. 2013, 58, 1676–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wikström, M.; Thelander, G.; Dahlgren, M.; Kronstrand, R. An Accidental Fatal Intoxication with Methoxetamine. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2012, 37, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chan, W.L.; Wood, D.M.; Hudson, S.; Dargan, P. Acute Psychosis Associated with Recreational Use of Benzofuran 6-(2-Aminopropyl)Benzofuran (6-APB) and Cannabis. J. Med. Toxicol. 2013, 9, 278–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McQuade, D.; Hudson, S.; Dargan, P.; Wood, D.M. First European case of convulsions related to analytically confirmed use of the synthetic cannabinoid receptor agonist AM-2201. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2012, 69, 373–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemos, N.P. Driving Under the Influence of Synthetic Cannabinoid Receptor Agonist XLR-11. J. Forensic Sci. 2014, 59, 1679–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takematsu, M.; Hoffman, R.S.; Nelson, L.S.; Schechter, J.M.; Moran, J.H.; Wiener, S.W. A case of acute cerebral ischemia following inhalation of a synthetic cannabinoid. Clin. Toxicol. 2014, 52, 973–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musshoff, F.; Madea, B.; Kernbach-Wighton, G.; Bicker, W.; Kneisel, S.; Hutter, M.; Auwärter, V. Driving under the influence of synthetic cannabinoids (“Spice”): A case series. Int. J. Legal Med. 2014, 128, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gugelmann, H.; Gerona, R.; Li, C.; Tsutaoka, B.; Olson, K.R.; Lung, D. ‘Crazy Monkey’ poisons man and dog: Human and canine seizures due to PB-22, a novel synthetic cannabinoid. Clin. Toxicol. 2014, 52, 635–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behonick, G.; Shanks, K.G.; Firchau, D.; Mathur, G.; Lynch, C.F.; Nashelsky, M.; Jaskierny, D.J.; Meroueh, C. Four Postmortem Case Reports with Quantitative Detection of the Synthetic Cannabinoid, 5F-PB-22. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2014, 38, 559–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonati, D.; Buscaglia, E.; Papa, P.; Valli, A.; Coccini, T.; Giampreti, A.; Locatelli, C.A. MAM-2201 (analytically confirmed) intoxication after “synthacaine” consumption. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2014, 64, 629–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celofiga, A.; Koprivsek, J.; Klavz, J. Use of Synthetic Cannabinoids in Patients with Psychotic Disorders: Case Series. J. Dual Diagn. 2014, 10, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, M.D.; Trecki, J.; Edison, L.A.; Steck, A.R.; Arnold, J.K.; Gerona, R.R. A Common Source Outbreak of Severe Delirium Associated with Exposure to the Novel Synthetic Cannabinoid ADB-PINACA. J. Emerg. Med. 2015, 48, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shanks, K.G.; Winston, D.; Heidingsfelder, J.; Behonick, G. Case reports of synthetic cannabinoid XLR-11 associated fatalities. Forensic Sci. Int. 2015, 252, e6–e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, C.; Stockhausen, S.; Kernbach-Wighton, G.; Madea, B. Death due to diabetic ketoacidosis: Induction by the consumption of synthetic cannabinoids? Forensic Sci. Int. 2015, 257, e6–e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, B.L.; Couper, F.J. Concentrations of AB-CHMINACA and AB-PINACA and Driving Behavior in Suspected Impaired Driving Cases. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2015, 39, 642–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thornton, S.L.; Akpunonu, P.; Glauner, K.; Hoehn, K.S.; Gerona, R. Unintentional pediatric exposure to a synthetic canna-binoid (AB-PINACA) resulting in coma and intubation. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2015, 66, 343–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buser, G.L.; Gerona, R.R.; Horowitz, B.Z.; Vian, K.P.; Troxell, M.L.; Hendrickson, R.G.; Leman, R.F. Acute kidney injury asso-ciated with smoking synthetic cannabinoid. Clin. Toxicol. 2014, 52, 664–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamowicz, P.; Gieroń, J. Acute intoxication of four individuals following use of the synthetic cannabinoid MAB-CHMINACA. Clin. Toxicol. 2016, 54, 650–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klavž, J.; Gorenjak, M.; Marinšek, M. Suicide attempt with a mix of synthetic cannabinoids and synthetic cathinones: Case report of non-fatal intoxication with AB-CHMINACA, AB-FUBINACA, alpha-PHP, alpha-PVP and 4-CMC. Forensic Sci. Int. 2016, 265, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanks, K.G.; Clark, W.; Behonick, G. Death Associated with the Use of the Synthetic Cannabinoid ADB-FUBINACA. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2016, 40, 236–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barceló, B.; Pichini, S.; López-Corominas, V.; Gomila, I.; Yates, C.; Busardò, F.P.; Pellegrini, M. Acute intoxication caused by synthetic cannabinoids 5F-ADB and MMB-2201: A case series. Forensic Sci. Int. 2017, 273, e10–e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamowicz, P. Fatal intoxication with synthetic cannabinoid MDMB-CHMICA. Forensic Sci. Int. 2016, 261, e5–e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abouchedid, R.; Ho, J.H.; Hudson, S.; Dines, A.; Archer, J.R.H.; Wood, D.M.; Dargan, P.I. Acute Toxicity Associated with Use of 5F-Derivations of Synthetic Cannabinoid Receptor Agonists with Analytical Confirmation. J. Med. Toxicol. 2016, 12, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Westin, A.A.; Frost, J.; Brede, W.R.; Gundersen, P.O.M.; Einvik, S.; Aarset, H.; Slørdal, L. Sudden Cardiac Death Following Use of the Synthetic Cannabinoid MDMB-CHMICA. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2015, 40, 86–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rojek, S.; Kłys, M.; Maciów-Głąb, M.; Kula, K. A new challenge in forensic toxicology exemplified by a case of murder under the influence of a synthetic cannabinoid—AM-2201. Leg. Med. 2017, 27, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angerer, V.; Jacobi, S.; Franz, F.; Auwärter, V.; Pietsch, J. Three fatalities associated with the synthetic cannabinoids 5F-ADB, 5F-PB-22, and AB-CHMINACA. Forensic Sci. Int. 2017, 281, e9–e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bäckberg, M.; Tworek, L.; Beck, O.; Helander, A. Analytically Confirmed Intoxications Involving MDMB-CHMICA from the STRIDA Project. J. Med. Toxicol. 2016, 13, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meyyappan, C.; Ford, L.; Vale, A. Poisoning due to MDMB-CHMICA, a synthetic cannabinoid receptor agonist. Clin. Toxicol. 2017, 55, 151–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, R.P.K.; Tang, M.H.Y.; Leung, S.C.; Chong, Y.K.; Tsui, M.S.H.; Mak, T.W.L. Supraventricular tachycardia and acute confusion following ingestion of e-cigarette fluid containing AB-FUBINACA and ADB-FUBINACA: A case report with quantitative analysis of serum drug concentrations. Clin. Toxicol. 2017, 55, 662–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppola, M.; Mondola, R. JWH-122 Consumption Adverse Effects: A Case of Hallucinogen Persisting Perception Disorder Five-Year Follow-Up. J. Psychoact. Drugs 2017, 49, 262–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moeller, S.; Lücke, C.; Struffert, T.; Schwarze, B.; Gerner, S.T.; Schwab, S.; Köhrmann, M.; Machold, K.; Philipsen, A.; Müller, H.H. Ischemic stroke associated with the use of a synthetic cannabinoid (spice). Asian J. Psychiatry 2016, 25, 127–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langford, A.M.; Bolton, J.R. Synthetic cannabinoids: Variety is definitely not the spice of life. J. Forensic Leg. Med. 2018, 59, 36–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nacca, N.; Schult, R.; Loflin, R.; Weltler, A.; Gorodetsky, R.; Kacinko, S.; Moran, J.; Krotulski, A.; Wiegand, T. Coma, Seizures, Atrioventricular Block, and Hypoglycemia in an ADB-FUBINACA Body-Packer. J. Emerg. Med. 2018, 55, 788–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, H.; Kikura-Hanajiri, R.; Kawamura, M.; Nagashima, E.; Yoshida, K.-I. AB-CHMINACA-induced sudden death from non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema. Clin. Toxicol. 2017, 56, 143–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamagishi, I.; Minakata, K.; Nozawa, H.; Hasegawa, K.; Suzuki, M.; Kitamoto, T.; Suzuki, O.; Watanabe, K. A case of intoxication with a mixture of synthetic cannabinoids EAM-2201, AB-PINACA and AB-FUBINACA, and a synthetic cathinone α-PVP. Leg. Med. 2018, 35, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandehoff, N.; Adams, A.; McDaniel, K.; Banister, S.D.; Gerona, R.; Monte, A.A. Synthetic cannabinoid “Black Mamba” infidelity in patients presenting for emergency stabilization in Colorado: A P SCAN Cohort. Clin. Toxicol. 2017, 56, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Paul, A.B.M.; Simms, L.; Amini, S.; Paul, A.E. Teens and spice: A review of adolescent fatalities associated with synthetic cannabinoid use. J. Forensic Sci. 2018, 63, 1321–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usui, K.; Fujita, Y.; Kamijo, Y.; Kokaji, T.; Funayama, M. Identification of 5-Fluoro ADB in Human Whole Blood in Four Death Cases. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2017, 42, e21–e25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaunitz, F.; Lehmann, S.; Thomas, A.; Thevis, M.; Rothschild, M.A.; Mercer-Chalmers-Bender, K. Post-mortem distribution of the synthetic cannabinoid MDMB-CHMICA and its metabolites in a case of combined drug intoxication. Int. J. Leg. Med. 2018, 132, 1645–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanov, I.D.; Stoykova, S.; Ivanova, E.; Vlahova, A.; Burdzhiev, N.; Pantcheva, I.; Atanasov, V.N. A case of 5F-ADB/FUB-AMB abuse: Drug-induced or drug-related death? Forensic Sci. Int. 2019, 297, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Fawaz, S.; Al Deeb, M.; Huffman, J.L.; Al Kholaif, N.A.; Garlich, F.; Chuang, R. A Case of Status Epilepticus and Transient Stress Cardiomyopathy Associated with Smoking the Synthetic Psychoactive Cannabinoid, UR-144. Am. J. Case Rep. 2019, 20, 1902–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraemer, M.; Fels, H.; Dame, T.; Musshoff, F.; Halter, S.; Mogler, L.; Maas, A. Mono-/polyintoxication with 5F-ADB: A case series. Forensic Sci. Int. 2019, 301, e29–e37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, S.; Wu, J.; Lee, B. Fatalities related to new psychoactive substances in Singapore—A case series. Forensic Sci. Int. 2019, 304, 109892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovács, K.; Kereszty, É.; Berkecz, R.; Tiszlavicz, L.; Sija, É.; Körmöczi, T.; Jenei, N.; Révész-Schmehl, H.; Institóris, L. Fatal intoxication of a regular drug user following N-ethyl-hexedrone and ADB-FUBINACA consumption. J. Forensic Leg. Med. 2019, 65, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hvozdovich, J.; Chronister, C.W.; Logan, B.K.; Goldberger, B. Case Report: Synthetic Cannabinoid Deaths in State of Florida Prisoners. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2020, 44, 298–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salle, S.; Sevestre, C.; Richeval, C.; Hakim, F.; Allorge, D.; Gaulier, J.-M. Involuntary 5F-ADB-related intoxication following e-cigarette use. Int. J. Leg. Med. 2021, 135, 1467–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, G.; Tóth, D.; Heckmann, V.; Kuzma, M.; Mayer, M. Lethal case of myocardial ischemia following overdose of the synthetic cannabinoid ADB-FUBINACA. Leg. Med. 2022, 54, 102004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaunitz, F.; Andresen-Streichert, H. Analytical findings in a non-fatal intoxication with the synthetic cannabinoid 5F-ADB (5F-MDMB-PINACA): A case report. Int. J. Leg. Med. 2021, 136, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castaneto, M.S.; Gorelick, D.A.; Desrosiers, N.A.; Hartman, R.L.; Pirard, S.; Huestis, M.A. Synthetic Cannabinoids: Epidemi-ology, Pharmacodynamics, and Clinical Implications. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2014, 144, 12–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Every-Palmer, S. Synthetic cannabinoid JWH-018 and psychosis: An explorative study. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2011, 117, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colizzi, M.; McGuire, P.; Pertwee, R.G.; Bhattacharyya, S. Effect of cannabis on glutamate signalling in the brain: A systematic review of human and animal evidence. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2016, 64, 359–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cannaert, A.; Sparkes, E.; Pike, E.; Luo, J.L.; Fang, A.; Kevin, R.C.; Ellison, R.; Gerona, R.; Banister, S.D.; Stove, C.P. Synthesis and in Vitro Cannabinoid Receptor 1 Activity of Recently Detected Synthetic Cannabinoids 4F-MDMB-Bica, 5F-MPP-PICA, MMB-4en-Pica, Cumyl-CBMICA, ADB-BINACA, App-BINACA, 4F-MDMB-Binaca, MDMB-4en-Pinaca, A-CHMINACA, 5F-AB-P7AICA, 5F-MDMB-p7aica, and 5F-AP7AICA. ACS Chem. Neurosc. 2020, 11, 4434–4446. [Google Scholar]
- Krotulski, A.J.; Cannaert, A.; Stove, C.; Logan, B.K. The next generation of synthetic cannabinoids: Detection, activity, and potential toxicity of pent-4en and but-3en analogues including MDMB-4en-PINACA. Drug Test. Anal. 2020, 13, 427–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction. Risk Assessment of New Psychoactive Substances: Operating Guidelines; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2009. Available online: https://www.emcdda.europa.eu/attachements.cfm/att_100979_EN_RiskGuidelines2010.pdf (accessed on 20 December 2022).
- Fantegrossi, W.E.; Wilson, C.D.; Berquist, M.D. Pro-psychotic effects of synthetic cannabinoids: Interactions with central do-pamine, serotonin, and glutamate systems. Drug Metab. Rev. 2018, 50, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papanti, D.; Schifano, F.; Botteon, G.; Bertossi, F.; Mannix, J.; Vidoni, D.; Bonavigo, T. “Spiceophrenia”: A systematic overview of “spice”-related psychopathological issues and a case report. Hum. Psychopharmacol. Clin. Exp. 2013, 28, 379–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Every-Palmer, S. Warning: Legal synthetic cannabinoid-receptor agonists such as jwh-018 may precipitate psychosis in vulnerable individuals. Addiction 2010, 105, 1859–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalix, P. Cathinone, an alkaloid from khat leaves with an amphetamine-like releasing effect. Psychopharmacology 1981, 74, 269–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaami, S.; Giorgetti, R.; Pichini, S.; Pantano, F.; Marinelli, E.; Busardò, F.P. Synthetic cathinones related fatalities: An update. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Montanari, E.M.; Madeo, G.M.; Pichini, S.; Busardò, F.P.M.; Carlier, J. Acute Intoxications and Fatalities Associated with Benzimidazole Opioid (Nitazene Analog) Use: A Systematic Review. Ther. Drug Monit. 2022, 44, 494–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehmann, S.; Kieliba, T.; Thevis, M.; Rothschild, M.A.; Mercer-Chalmers-Bender, K. Fatalities associated with NPS stimulants in the Greater Cologne area. Int. J. Leg. Med. 2022, 134, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Júnior, E.F.; Leite, B.H.M.; Gomes, E.B.; Vieira, T.M.; Sepulveda, P.; Caldas, E.D. Fatal cases involving new psychoactive substances and trends in analytical techniques. Front. Toxicol. 2022, 4, 1033733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trecki, J.; Gerona, R.R.; Schwartz, M.D. Synthetic Cannabinoid–Related Illnesses and Deaths. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, J.R. Synthetic cannabinoids: Treating toxicity. Emerg. Med. News 2015, 37, 12–14. [Google Scholar]

| Author, Year, Country | Synthetic Cannabinoid | N (Sample); Age (Mean); Gender (M:F); Setting (O: Outpatient; I: Inpatient; ED: Emergency Department) | Adverse Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tyndall et al., 2015, EUA [24] | AB-CHMINACA | 35; 36; 31:4; ED | Acute delirium and seizures, required ventilator support |
| Seywright et al., 2016, EUA [25] | MDMB-CHMICA | 11; 26; 82% males; ED | Hypothermia, hypoglycemia, syncope, recurrent vomiting, altered mental state, serotonin toxicity |
| Abouchedid et al., 2017, UK [26] | 5F-AKB-48, MDMB-CHMICA, AB-CHMINACA, Cumyl 5F-PINACA, BB-22 | 18; 31; 79.9% males; ED | Seizures, agitation |
| Hermanns-Clausen et al., 2017, Germany [27] | AB-CHMINACA | 44; 19; 25:4; I | Depression, disorientation, seizures, combativeness, extreme agitation |
| Kamijo et al., 2018, Japan [28] | AB-CHMINACA | 5; 30; NR; O | Tachypnea, tachycardia, hypertension, disturbance of consciousness, agitation, irritability, anxiety, fear, confusion, seizures, psychosis (hallucination, delusion), abnormal behavior |
| Theunissen et al., 2018, Netherlands [29] | JWH-018 | 7; 23; 2:4; I | Well tolerated, no serious side effects reported. |
| Tebo et al., 2019, EUA [30] | AB-FUBINACA, ADB-FUBINACA, AB-CHMINACA, ADB-CHMINACA, 5-flouro-PB-22 | 132; >18; NR; ED | Nausea, vomiting, anxiety, paranoia, palpitations, seizures, psychosis |
| Theunissen et al., 2022, Netherlands [31,32] | JWH-018 | 24; 22; 10:14; I | Internal and external perception, dissociative effects (amnesia, derealization, depersonalization), induced feelings of confusion, impaired psychomotor, divided attention, impulse control |
| Manini et al., 2022, EUA [33] | 5F-MDMB-PICA, ADB-FUBINACA, AB-CHMINACA, AB-FUBINACA, AB-PINACA, MDMB-4en-PINACA, 4F-MDMB-BINACA | 29; >18; NR; ED | Acute respiratory failure |
| Author, Year, Country | Synthetic Cannabinoid | N (Sample); Age (Mean); Gender (M:F); Setting (O: Outpatient; I: Inpatient; ED: Emergency Department) | Adverse Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lapoint et al., 2011, USA [34] | JWH-018 | 1; 48; 1:0; ED | Seizures, supraventricular tachycardia |
| Schneir et al., 2011, USA [35] | JWH-018, JWH-073 | 2; 21; 0:2; ED | Anxiety, palpitation, tachycardia |
| Young et al., 2012, USA [36] | JWH-018, JWH-073 | 1; 17; 1:0; ED | Chest pain, tachycardia, bradycardia |
| Pant et al., 2012, USA [37] | JWH-018 | 1; 48; 1:0; ED | Seizures, GCS < 10 |
| Freeman et al., 2013, USA [38] | JWH-018 | 2; 22; 1:1; ED | Ischemic stroke |
| Hopkins et al., 2013, USA [39] | JWH-018, JWH-073, JWH-122, AM-2201, AM-694 | 1; 30; 1:0; ED | Cannabinoid hyperemesis syndrome |
| Patton et al., 2013, USA [40] | AM-2201 | 1; 23; 1:0; O | Death |
| Wikström et al., 2013, Sweden [41] | AM-694, AM-2201, JWH-018 | 1; 26; 1:0; O | Pulmonary edema, death |
| Chan et al., 2013, UK [42] | 6-APB | 1; 21; 1:0; ED | Acute psychosis, agitation, paranoid behavior |
| McQuade et al., 2013, UK [43] | AM-2201 | 1; 20; 1:0; ED | Seizures |
| Lemos et al., 2014, USA [44] | XLR-11 | 1; 22; 1:0; ED | Low body temperature, rigid muscle tone, normal pulse, lack of horizontal and vertical gaze nystagmus, nonconvergence of the eyes, dilated pupil size |
| Takematsu et al., 2014, USA [45] | XLR-11 | 1; 33; 1:0; ED | Acute cerebral infarction, hemiparesis, dysarthria, aphasia |
| Musshoff et al., 2014, Germany [46] | AM-2201, JWH-018, JWH-019, JWH-122, JWH-210, JWH-307, MAM-2201, JWH-122, UR-144 | 8; 18; 6:2; O | Retarded sequence of movements, lazy, cumbersome, confusion, disorientation, slurred and babbling speech, inappropriate freezing, reduced breathing, enlarged pupils |
| Gugelmann et al., 2014, USA [47] | PB-22, UR-144 | 1; 22; 1:0; ED | Seizures |
| Behonick et al., 2014, USA [48] | 5F-PB-22 | 4; 20; 4:0; O | Pulmonary edema, death |
| Lonati et al., 2014, Italy [49] | AM-2201 | 1; 20; 1:0; ED | Excitatory behavior, xerostomia, chest pain, severe dyspnea, tachycardia |
| Celofiga et al., 2014, Slovenia [50] | AM-2201 | 4; 28; 4:0; I | Psychosis, anxiety |
| Shanks et al., 2015, USA [51] | XLR-11 | 2; 30; 0:2; ED | Anxiety, agitation, hallucinations, hypertension, irritability, seizures, tachycardia |
| Schwartz et al., 2015 [52] | AB-PINACA | 7; 25; 4:3; O | Anxiety, delirium, psychosis, aggressive behaviors, seizures |
| Hess et al., 2015, Germany [53] | AB-CHMINACA, AB-FUBINACA, AM-2201, 5F-AMB, 5F-APINACA, EAM-2201, JWH-018, JWH-122, MAM-2201 | 1; 25; 1:0; O | Tachycardia, sedation, psychosis, anxiety and panic attacks, agitation, convulsions, nausea and emesis |
| Peterson et al., 2015 [54] | AB-CHMINACA, AB-PINACA | 58; 28; 55:3; O | Bloodshot eyes (80%), watery eyes (55%), droopy eyelids (68%), horizontal gaze nystagmus (HGN) observed in 50 and 60%, tachycardia |
| Thornton et al., 2015, USA [55] | AB-PINACA | 1; 10; 0:1; ED | GCS < 10 |
| Buser et al., 2016, USA [56] | XLR-11 | 9; 18; 9:0; I | Nausea and flank or abdominal pain, included two sets of siblings |
| Adamowicz et al., 2016, Poland [57] | AB-CHMINACA | 4; 17; 2:2; ED | Vomiting, seizures, limb twisting, muscle tremors, aggression, agitation, slurred speech, blood pressure spikes, wheezing, respiratory failure, losses of consciousness |
| Klavž et al., 2016, Slovenia [58] | AB-CHMINACA, AB-FUBINACA | 1; 38; 1:0; ED | Dilated pupils, sinus tachycardia, dehydration |
| Shanks et al., 2016, USA [59] | ADB-FUBINACA | 1; 41; 0:1; O | Coronary arterial thrombosis, pulmonary edema, vascular congestion |
| Barceló et al., 2016, Spain [60] | 5F-ADB, MMB-2201 | 5; 17; 1:4; ED | Psychomotor agitation, confusion, anxiety and psychosis, tachycardia, temporary amnesia, loss of consciousness |
| Adamowicz, 2016, Poland [61] | MDMB-CHMICA | 1; 25; 1:0; ED | Loss of consciousness, asystole |
| Abouchedid et al., 2016, UK [62] | 5F-AKB-48, 5F-PB-22 | 1; 19; 0:1; ED | Seizures, agitation, tachycardia |
| Westin et al., 2016, Norway [63] | MDMB-CHMICA | 1; 22; 1:0; ED | Arrythmia |
| Rojek et al., 2017, Poland [64] | AM-2201 | 1; 18; 1:0; O | Hetero-aggressive behaviour |
| Angerer et al., 2017, Germany [65] | 5F-PB-22, AB-CHMINACA, 5F-ADB | 3; 31; 3:0; O | Death |
| Bäckberg et al., 2017, Sweden [66] | MDMB-CHMICA | 9; 34; 8;1; I | Seizures, deep unconsciousness |
| Meyyappan et al., 2017, UK [67] | MDMB-CHMICA | 3; 29; 3:0; ED | Hypercapnia, reduced level of consciousness, seizures, bradycardia |
| Lam et al., 2017, China [68] | AB-FUBINACA, ADB-FUBINACA | 1; 24; 1:0; ED | Somnolence, confusion, agitation, palpitation and vomiting, supraventricular tachycardia |
| Coppola et al., 2017, Italy [69] | JWH-122 | 1; 18; 1:0; ED | Hallucinogen persisting perception disorder |
| Moeller et al., 2017, Germany [70] | ADB-FUBINACA | 1; 25; 1:0; ED | Ischemic stroke |
| Langford et al., 2018, UK [71] | 5F-PB-22, 5F-AKB-48 | 1; 35; 1:0; O | Congestion of the lungs, death |
| Nacca et al., 2018, USA [72] | ADB-FUBINACA | 1; 38; 1:0; I | Encephalopathy, seizure activity, second-degree atrioventricular block type I, respiratory failure, hypotension, hypothermia, hypoglycemia |
| Maeda et al., 2018, Japan [73] | AB-CHMINACA | 1; 29; 1:0; O | Hypoxic encephalopathy and systemic hypoxemia, pulmonary edema, seizures |
| Yamagishi et al., 2018, Japan [74] | EAM-2201, AB-PINACA | 1; 1:0; O | Death |
| Brandehoff et al., 2018, USA [75] | ADB-FUBINACA | 8; 28; 4:4; O | Agitation, delirium, chest pain |
| Paul et al., 2018, Canada [76] | AB-CHMINACA, UR-144, XLR-11, JWH-022. | 2; 15; 2:0; O | Paranoid, dilated cardiomyopathy, cardiomegaly, bilateral pulmonary edema, bilateral pleural effusion, ascites, death |
| Usui et al., 2018, Japan [77] | MDMB-PINACA | 4; 35; 4:0; O | Death |
| Gaunitz et al., 2018, Germany [78] | MDMB-CHMICA | 1; 27; 1:0; ED | Death |
| Ivanov et al., 2019, Bulgaria [79] | 5F-ADB, FUB-AMB | 1; 18; 1:0; ED | Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) |
| Al Fawaz et al., 2019, Canada [80] | UR-144 | 1; 19; 0:1; ED | Seizure, cardiomyopathy, respiratory fatigue |
| Kraemer et al., 2019, USA [81] | 5F-ADB | 5; 33; 3:2; O | Confusion, psychosis, collapse, loss of consciousness, unsafe driving style, changing moods |
| Chan et al., 2019, Singapore [82] | ADB-FUBINACA | 4; 30; 4:0; ED | Death |
| Kovács et al., 2019, Hungary [83] | ADB-FUBINACA | 1; 23; 1:0; ED | Hypertrophic and dilated heart, severe atherosclerosis of the valves, coronaries and the arteries, edema of the internal organs, death |
| Hvozdovich et al., 2020, USA [84] | 5F-ADB, FUB-AMB, 5F-AMB, MDMB-FUBINACA, AB-CHMINACA | 57; 45; 57:0; O | Death |
| Salle et al., 2021, France [85] | 5F-ADB | 1; 16; 1:0; ED | Seizure |
| Simon et al., 2022, Hungary [86] | ADB-FUBINACA | 1; 41; 1:0; ED | Myocardial ischemia |
| Gaunitz et al., 2022, Germany [87] | 5F-ADB | 1; 31; 1:0; ED | Panic attack |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de Oliveira, M.C.; Vides, M.C.; Lassi, D.L.S.; Torales, J.; Ventriglio, A.; Bombana, H.S.; Leyton, V.; Périco, C.d.A.-M.; Negrão, A.B.; Malbergier, A.; et al. Toxicity of Synthetic Cannabinoids in K2/Spice: A Systematic Review. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 990. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13070990
de Oliveira MC, Vides MC, Lassi DLS, Torales J, Ventriglio A, Bombana HS, Leyton V, Périco CdA-M, Negrão AB, Malbergier A, et al. Toxicity of Synthetic Cannabinoids in K2/Spice: A Systematic Review. Brain Sciences. 2023; 13(7):990. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13070990
Chicago/Turabian Stylede Oliveira, Mariana Campello, Mariana Capelo Vides, Dângela Layne Silva Lassi, Julio Torales, Antonio Ventriglio, Henrique Silva Bombana, Vilma Leyton, Cintia de Azevedo-Marques Périco, André Brooking Negrão, André Malbergier, and et al. 2023. "Toxicity of Synthetic Cannabinoids in K2/Spice: A Systematic Review" Brain Sciences 13, no. 7: 990. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13070990
APA Stylede Oliveira, M. C., Vides, M. C., Lassi, D. L. S., Torales, J., Ventriglio, A., Bombana, H. S., Leyton, V., Périco, C. d. A.-M., Negrão, A. B., Malbergier, A., & Castaldelli-Maia, J. M. (2023). Toxicity of Synthetic Cannabinoids in K2/Spice: A Systematic Review. Brain Sciences, 13(7), 990. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13070990








