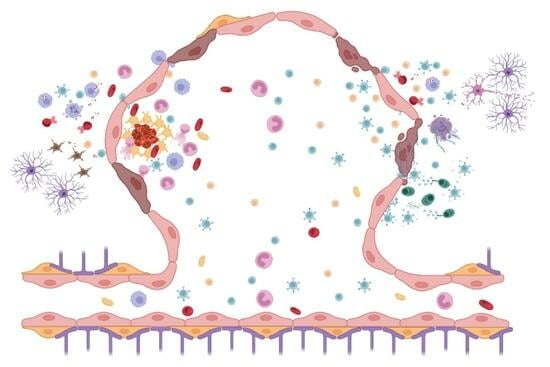
Inflammatory Mechanisms in a Neurovascular Disease: Cerebral Cavernous Malformation
Abstract
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Srinath, A.; Alcazar-Felix, R.J.; Hage, S.; Bindal, A.; Lightle, R.; Shenkar, R.; Shi, C.; Girard, R.; Awad, I.A. Inflammatory Mechanisms in a Neurovascular Disease: Cerebral Cavernous Malformation. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 1336. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13091336
Li Y, Srinath A, Alcazar-Felix RJ, Hage S, Bindal A, Lightle R, Shenkar R, Shi C, Girard R, Awad IA. Inflammatory Mechanisms in a Neurovascular Disease: Cerebral Cavernous Malformation. Brain Sciences. 2023; 13(9):1336. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13091336
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Ying, Abhinav Srinath, Roberto J. Alcazar-Felix, Stephanie Hage, Akash Bindal, Rhonda Lightle, Robert Shenkar, Changbin Shi, Romuald Girard, and Issam A. Awad. 2023. "Inflammatory Mechanisms in a Neurovascular Disease: Cerebral Cavernous Malformation" Brain Sciences 13, no. 9: 1336. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13091336
APA StyleLi, Y., Srinath, A., Alcazar-Felix, R. J., Hage, S., Bindal, A., Lightle, R., Shenkar, R., Shi, C., Girard, R., & Awad, I. A. (2023). Inflammatory Mechanisms in a Neurovascular Disease: Cerebral Cavernous Malformation. Brain Sciences, 13(9), 1336. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13091336