Emotion Recognition Based on a EEG–fNIRS Hybrid Brain Network in the Source Space
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- A novel EEG–fNIRS fusion method for constructing coupled brain networks in an emotion-evoked experimental paradigm is proposed.
- (2)
- Emotion recognition based on hybrid brain networks, achieved by integrating causal brain networks and coupled brain networks in the source space, is explored for the first time in this paper.
- (3)
- Evaluations on our self-built dataset (ENTER) and public datasets (SEED-IV, DEAP) show the superior performance of the proposed method.
2. Data Acquisition and Preprocessing
2.1. Data Acquisition
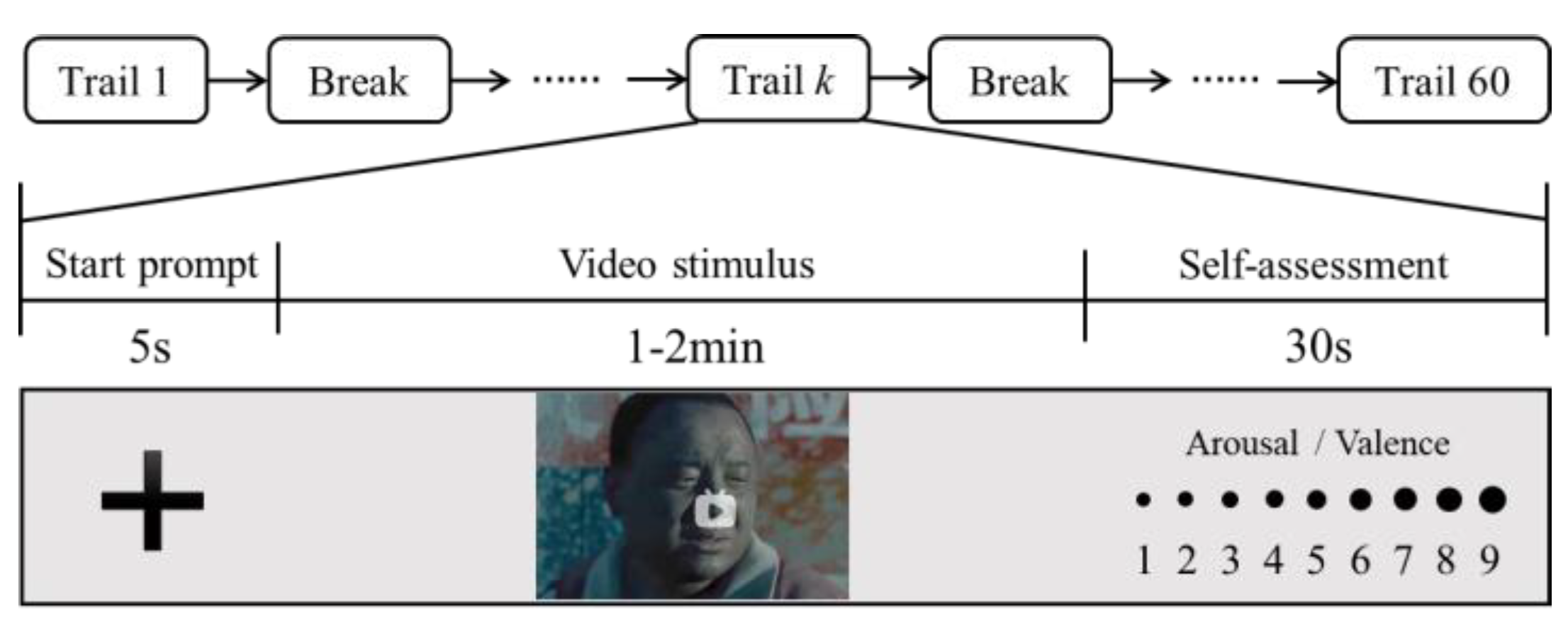
- Emotion-inducing materials: 60 videos (1–2 min long) were carefully selected to induce four types of emotions, including sadness, happiness, calm, and fear (there are 15 videos pertaining to each emotion).
- Subjects: 50 college students, 25 male and 25 female, were recruited for emotion data collection. Prior to the experiment, all subjects were informed of the experimental purpose, procedures, and important notes, and all subjects provided written informed consent.
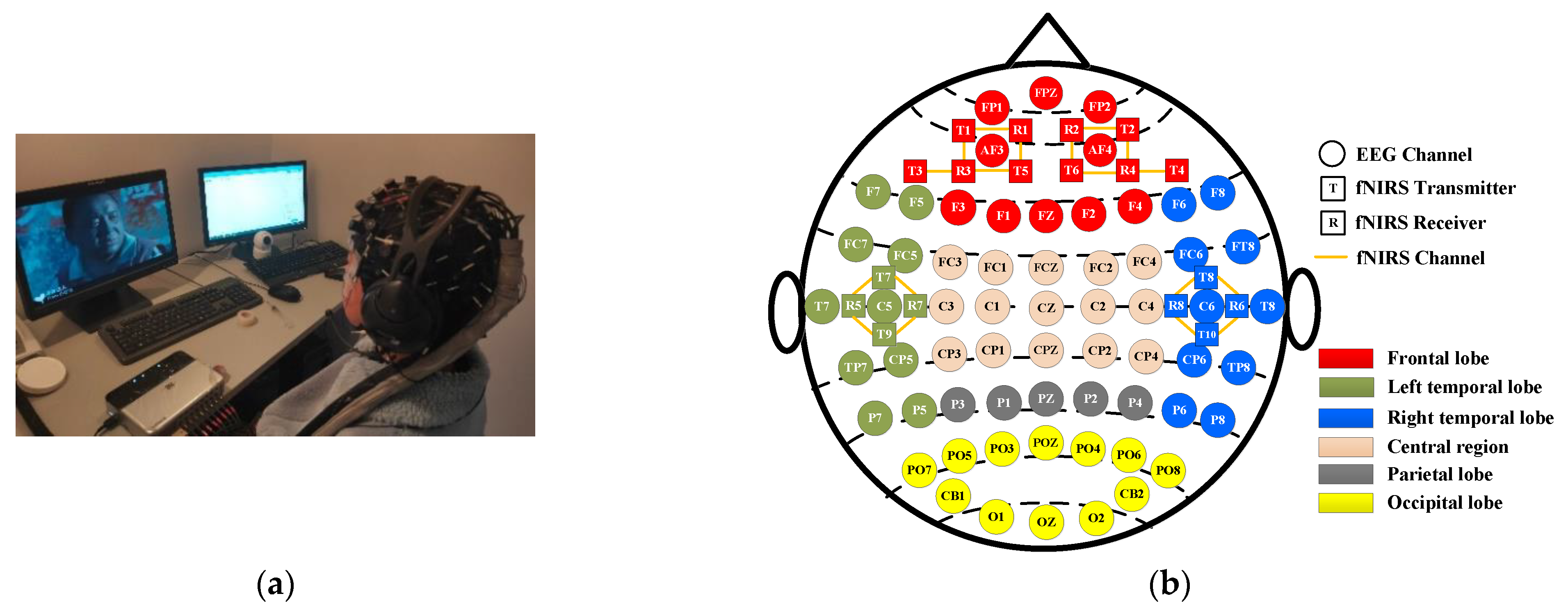
- Signal acquisition equipment: EEG signals were acquired at 1000 Hz using the ESI NeuroScan system (Compumedics Ltd., Victoria, Australia), which comprises 62 channels placed across the entire brain region. Concurrently, a portable near-infrared brain functional imaging system, NirSmart, was used to collect fNIRS signals at 11 Hz, with 18 channels created by adjacent transmitter–receiver pairs, which are distributed only in the frontal and temporal lobes. The experimental scenario is shown in Figure 1a, and a schematic illustration of the positions of the EEG electrodes and fNIRS optodes is shown in Figure 1b.
2.2. Data Preprocessing
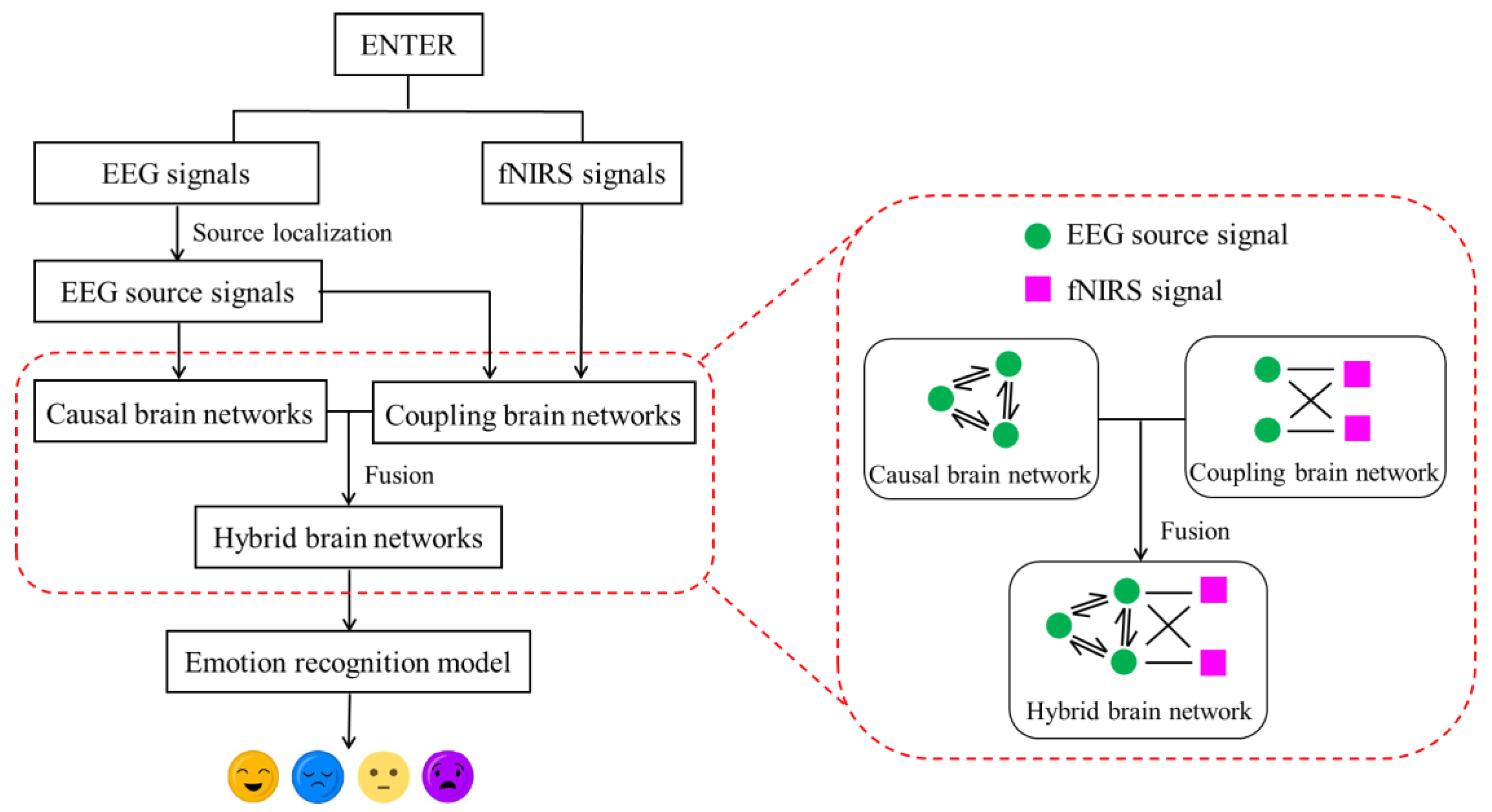
3. Proposed Method
3.1. Causal Brain Networks Construction in the Source Space
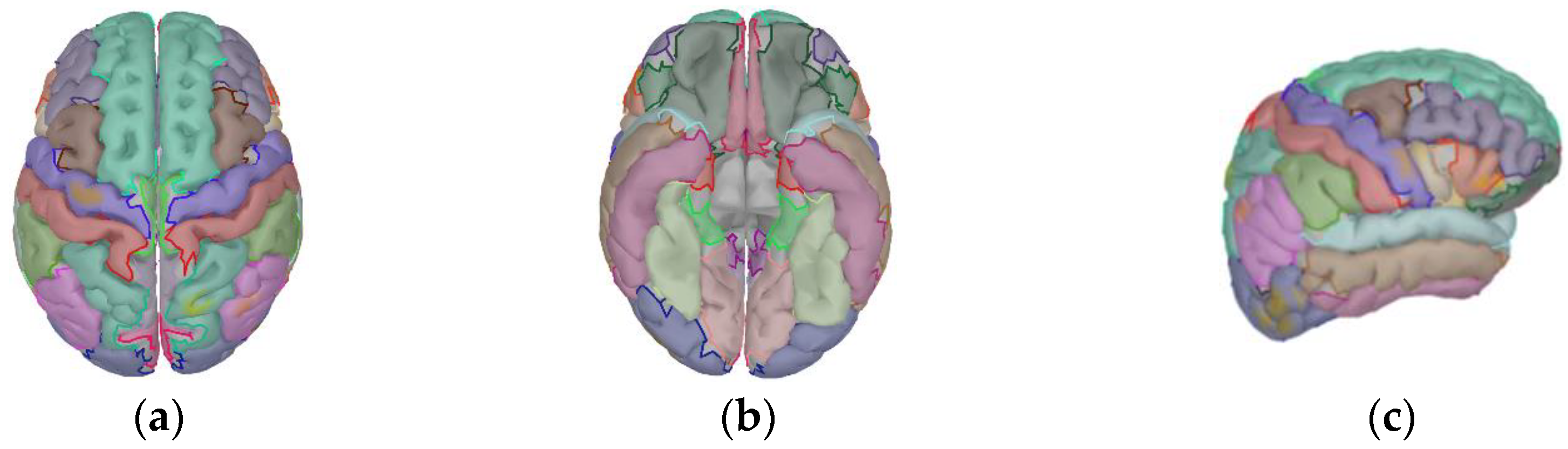
3.1.1. Source Localization
3.1.2. Causal Brain Networks Construction
| Algorithm 1: Calculation of a causal matrix in the source space. |
1: for , do 2: for , do 3: Calculate the residual in autoregressive model by Equation (4). 4: Calculate the residual in vector regression model by Equation (5). 5: Calculate the Granger causality between the and EEG source sign by Equation (6). 6: end for 7: end for |
3.2. Coupled Brain Networks Construction in the Source Space
| Algorithm 2: Calculation of a coupling matrix in the source space. |
1: for , do 2: Calculate the time-frequency power spectrum for by Equation (8). 3: Calculate the normalized time-varying power for by Equation (9). 4: Calculate the predicted fNIRS signal by Equation (10). 5: end for 6: Create matrix by utilizing all . 7: Segment and into samples; each sample contains and . 8: for , do 9: Fit within general linear model by Equation (13). 10: Calculate the coupling matrix in the source space by Equation (14). 11: end for |
3.3. Hybrid Brain Networks Construction in the Source Space
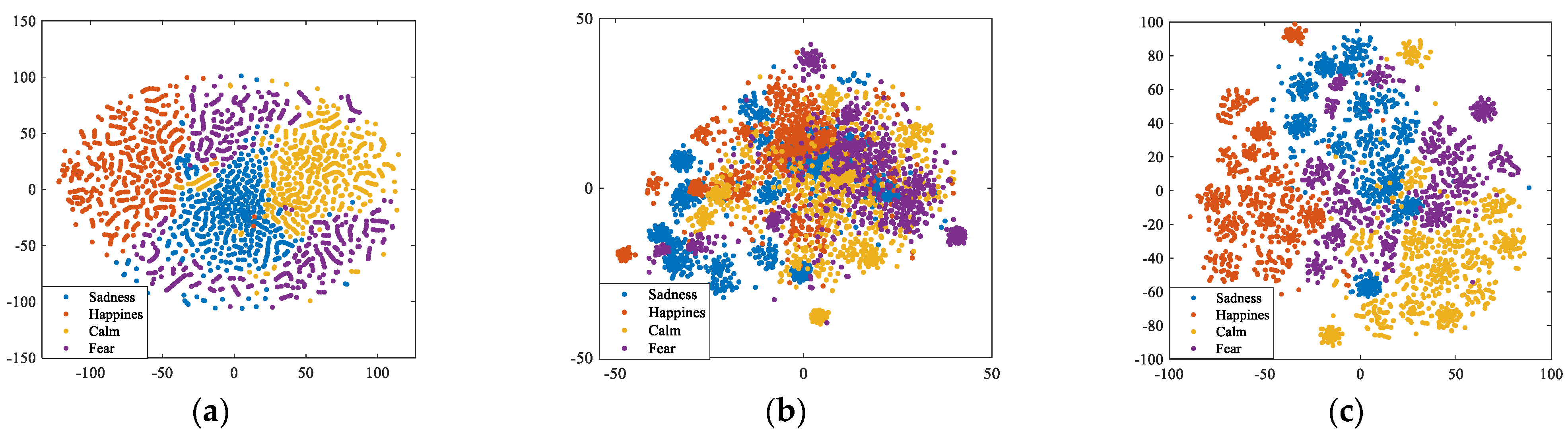
4. Experimental Results and Analysis
4.1. Performance Evaluation
4.2. Performance Comparison
4.2.1. Recognition Performance in Different Datasets
4.2.2. Comparison with Existing Methods
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hortensius, R.; Hekele, F.; Cross, E.S. The perception of emotion in artificial agents. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Dev. Syst. 2018, 10, 852–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepa, L.; Spalazzi, L.; Capecci, M.; Ceravolo, M.G. Automatic emotion recognition in clinical scenario: A systematic review of methods. IEEE Trans. Affect Comput. 2021, 14, 1675–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Saadawi; Hussein, F.T.; Das, B.; Das, R. A systematic review of trimodal affective computing approaches: Text, audio, and visual integration in emotion recognition and sentiment analysis. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 255, 124852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarcao, S.M.; Fonseca, M.J. Emotions Recognition Using EEG Signals: A Survey. IEEE Trans. Affect Comput. 2017, 10, 374–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Martínez, B.; Martinez-Rodrigo, A.; Alcaraz, R.; Fernández-Caballero, A. A review on nonlinear methods using electroencephalographic recordings for emotion recognition. IEEE Trans. Affect Comput. 2019, 12, 801–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.; Babawale, O.; Kim, T.; Jo, H.J.; Liu, H.; Kim, J.G. Exploring brain functional connectivity in rest and sleep states: A fNIRS study. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrantonakis, P.C.; Hadjileontiadis, L.J. Emotion recognition from EEG using higher order crossings. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2009, 14, 186–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, Z.; Sourina, O.; Wang, L.; Scherer, R.; Müller-Putz, G.R. Domain adaptation techniques for EEG-based emotion recognition: A comparative study on two public datasets. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Dev. Syst. 2018, 11, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.L.; Zhu, J.Y.; Lu, B.L. Identifying stable patterns over time for emotion recognition from EEG. IEEE Trans. Affect Comput. 2017, 10, 417–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.L.; Lu, B.L. Investigating critical frequency bands and channels for EEG-based emotion recognition with deep neural networks. IEEE Trans. Auton. Ment. Dev. 2015, 7, 162–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, P.; Zhang, Y.; Li, N.; Si, Y.; Li, F.; Xu, P. Effective emotion recognition by learning discriminative graph topologies in EEG brain networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn Syst. 2023, 35, 10258–10272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Liu, H.; Si, Y.; Li, C.; Li, F.; Zhu, X.; Xu, P. EEG based emotion recognition by combining functional connectivity network and local activations. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 66, 2869–2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Guo, J.; Chen, C.P.; Wu, X.; Zhang, T. Fine-Grained Interpretability for EEG Emotion Recognition: Concat-Aided Grad-CAM and Systematic Brain Functional Network. IEEE Trans. Affect Comput. 2023, 15, 671–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.M.; Zhou, R.; He, Y.; Guo, X.M. Functional integration and separation of brain network based on phase locking value during emotion processing. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Dev. Syst. 2020, 15, 444–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Li, Z.; Wan, F.; Xu, L.; Bezerianos, A.; Wang, H. Fusing frequency-domain features and brain connectivity features for cross-subject emotion recognition. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 71, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Zhao, Y.; Shan, X.; Wei, H.L.; Guo, Y.; Chen, L.; Sarrigiannis, P.G. Brain functional and effective connectivity based on electroencephalography recordings: A review. Hum. Brain. Mapp. 2022, 43, 860–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugh, Z.H.; Choo, S.; Leshin, J.C.; Lindquist, K.A.; Nam, C.S. Emotion depends on context, culture and their interaction: Evidence from effective connectivity. Soc. Cogn. Affect Neurosci. 2022, 17, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, W.; Qiu, M.; Li, M.; Jin, X.; Zhu, L. Causal graph convolutional neural network for emotion recognition. IIEEE Trans. Cogn. Dev. Syst. 2022, 15, 1686–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Huang, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, C.; Li, P. A novel robust Student’s t-based Granger causality for EEG based brain network analysis. Biomed Signal Proces. 2023, 80, 104321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Chen, G.; Huang, L.; Sun, Y. EEG emotion recognition based on cross-frequency granger causality feature extraction and fusion in the left and right hemispheres. Front Neurosci. 2022, 16, 974673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Broek, S.P.; Reinders, F.; Donderwinkel, M.; Peters, M.J. Volume conduction effects in EEG and MEG. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1998, 106, 522–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Zhang, X.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, J. Emotion feature analysis and recognition based on reconstructed EEG sources. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 11907–11916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, H.; Fleureau, J.; Guillotel, P.; Wendling, F.; Merlet, I.; Albera, L. Emotion recognition based on high-resolution EEG recordings and reconstructed brain sources. IEEE Trans. Affect Comput. 2017, 11, 244–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, Y.; Song, W.J.; Kim, S.E. FGANet: fNIRS-guided attention network for hybrid EEG-fNIRS brain-computer interfaces. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2022, 30, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shargie, F.; Tang, T.B.; Kiguchi, M. Assessment of mental stress effects on prefrontal cortical activities using canonical correlation analysis: An fNIRS-EEG study. Biomed. Opt. Express 2017, 8, 2583–2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Zheng, X.; Li, T.; Li, Y.; Cui, L. Multimodal emotion classification method and analysis of brain functional connectivity networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2022, 30, 2022–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Shore, J.; Wang, M.; Yuan, F.; Buss, A.; Zhao, X. A systematic review on hybrid EEG/fNIRS in brain-computer interface. Biomed. Signal Process Control 2021, 68, 102595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yu, K.; Wang, F.; Zhou, Z.; Bi, Y.; Zhuang, S.; Zhang, D. Temporal convolutional network-enhanced real-time implicit emotion recognition with an innovative wearable fNIRS-EEG dual-modal system. Electronics 2024, 13, 1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Zhang, X.; Chen, G.; Zhang, J. EEG and fNIRS emotion recognition based on modal attention graph convolutional feature fusion. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. 2023, 57, 1987–1997. [Google Scholar]
- Nia, A.F.; Tang, V.; Malyshau, V.; Barde, A.; Talou, G.M.; Billinghurst, M. FEAD: Introduction to the fNIRS-EEG affective database-video stimuli. IEEE Trans. Affect Comput. 2024, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X. EEG–fNIRS-Based emotion recognition using graph convolution and capsule attention network. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, B.; Liu, Z. Multimodal functional neuroimaging: Integrating functional MRI and EEG/MEG. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2008, 1, 23–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Zhao, C.; Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y. Enhancing fNIRS analysis using EEG rhythmic signatures: An EEG-informed fNIRS analysis study. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 6, 2789–2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Jia, B.; Houston, M.; Zhang, Y. Hybrid EEG-fNIRS Brain computer interface based on common spatial pattern by using EEG-informed general linear model. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2023, 72, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, C.; Duan, L.; Gong, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhu, C. NIRS-KIT: A MATLAB toolbox for both resting-state and task fNIRS data analysis. Neurophotonics 2021, 8, 010802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michel, C.M.; Murray, M.M.; Lantz, G.; Gonzalez, S.; Spinelli, L.; De Peralta, R.G. EEG source imaging. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2004, 115, 2195–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, M.A.; Yoshioka, T.; Kajihara, S.; Toyama, K.; Goda, N.; Doya, K.; Kawato, M. Hierarchical Bayesian estimation for MEG inverse problem. NeuroImage 2004, 23, 806–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potvin, O.; Dieumegarde, L.; Duchesne, S.; Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Freesurfer cortical normative data for adults using Desikan-Killiany-Tourville and ex vivo protocols. Neuroimage 2017, 156, 43–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granger, C.W. Investigating causal relations by econometric models and cross-spectral methods. Econometrica 1969, 37, 424–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neath, A.A.; Cavanaugh, J.E. The Bayesian information criterion: Background, derivation, and applications. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Stat. 2012, 4, 199–203. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, W.L.; Liu, W.; Lu, Y.; Lu, B.L.; Cichocki, A. EmotionMeter: A multimodal framework for recognizing human emotions. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2019, 49, 1110–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koelstra, S.; Muhl, C.; Soleymani, M.; Lee, J.S.; Yazdani, A.; Ebrahimi, T.; Patras, I. Deap: A database for emotion analysis; using physiological signals. IEEE Trans. Affect Comput. 2011, 3, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhang, X.; Chen, G.; Huang, L. EEG emotion recognition based on GC features and brain region frequency band Transformer model. Comput. Eng. 2024, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

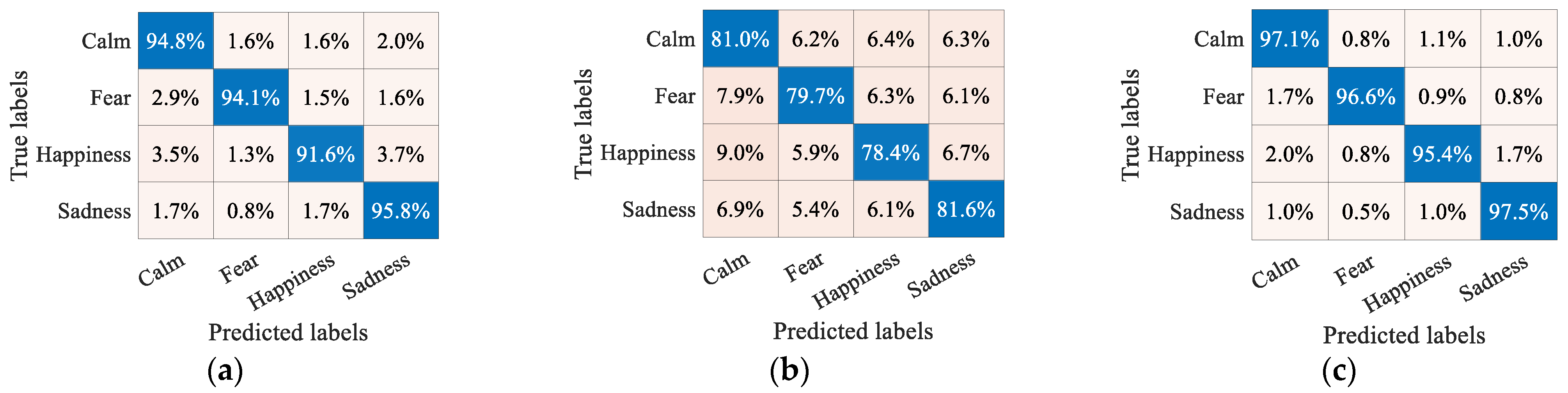

| Method | Feature | Classifier | Calm | Fear | Happiness | Sadness | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Causal brain network | EG | SVM | 86.9 | 84.6 | 85.1 | 87.1 | 86.0 ± 6.54 |
| KNN | 75.9 | 71.4 | 73.1 | 67.2 | 71.9 ± 8.78 | ||
| SG | SVM | 94.8 | 94.1 | 91.6 | 95.8 | 94.1 ± 3.32 | |
| KNN | 84.2 | 79.8 | 77.0 | 88.7 | 82.5 ± 6.30 | ||
| Coupled brain network | EC | SVM | 73.1 | 74.3 | 76.4 | 77.8 | 75.4 ± 7.04 |
| KNN | 70.5 | 74.0 | 74.1 | 75.5 | 73.5 ± 8.51 | ||
| SC | SVM | 81.0 | 79.7 | 78.4 | 81.6 | 80.2 ± 5.12 | |
| KNN | 82.8 | 83.6 | 82.9 | 86.2 | 83.9 ± 4.73 | ||
| Hybrid brain network | EG_EC | SVM | 91.5 | 90.1 | 90.8 | 92.6 | 91.3 ± 4.79 |
| KNN | 81.1 | 80.5 | 82.0 | 81.4 | 81.3 ± 7.10 | ||
| SG_SC (ours) | SVM | 97.1 | 96.6 | 95.4 | 97.5 | 96.6 ± 2.08 | |
| KNN | 91.7 | 90.6 | 89.3 | 95.0 | 91.7 ± 3.02 |
| Dataset | Signal Type | No. Subjects | No. Trails | No. Channels | Emotion Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ENTER | EEG/fNIRS | 50 | 60 | 62/18 | happiness, sadness, fear, calm |
| SEED-IV | EEG | 15 | 24 | 62 | happiness, sadness, fear, neutral |
| DEAP | EEG | 32 | 40 | 32 | HAHV, HALV, LAHV, LALV |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hou, M.; Zhang, X.; Chen, G.; Huang, L.; Sun, Y. Emotion Recognition Based on a EEG–fNIRS Hybrid Brain Network in the Source Space. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 1166. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14121166
Hou M, Zhang X, Chen G, Huang L, Sun Y. Emotion Recognition Based on a EEG–fNIRS Hybrid Brain Network in the Source Space. Brain Sciences. 2024; 14(12):1166. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14121166
Chicago/Turabian StyleHou, Mingxing, Xueying Zhang, Guijun Chen, Lixia Huang, and Ying Sun. 2024. "Emotion Recognition Based on a EEG–fNIRS Hybrid Brain Network in the Source Space" Brain Sciences 14, no. 12: 1166. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14121166
APA StyleHou, M., Zhang, X., Chen, G., Huang, L., & Sun, Y. (2024). Emotion Recognition Based on a EEG–fNIRS Hybrid Brain Network in the Source Space. Brain Sciences, 14(12), 1166. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14121166






