Correlation between DWI-ASPECTS Score, Ischemic Stroke Volume on DWI, Clinical Severity and Short-Term Prognosis: A Single-Center Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Background
1.2. Rationale, Research Question, and Objectives
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Setting
2.2. Patient Enrollment
2.3. Inclusion Criteria
2.4. Exclusion Criteria
2.5. Statistical Analysis
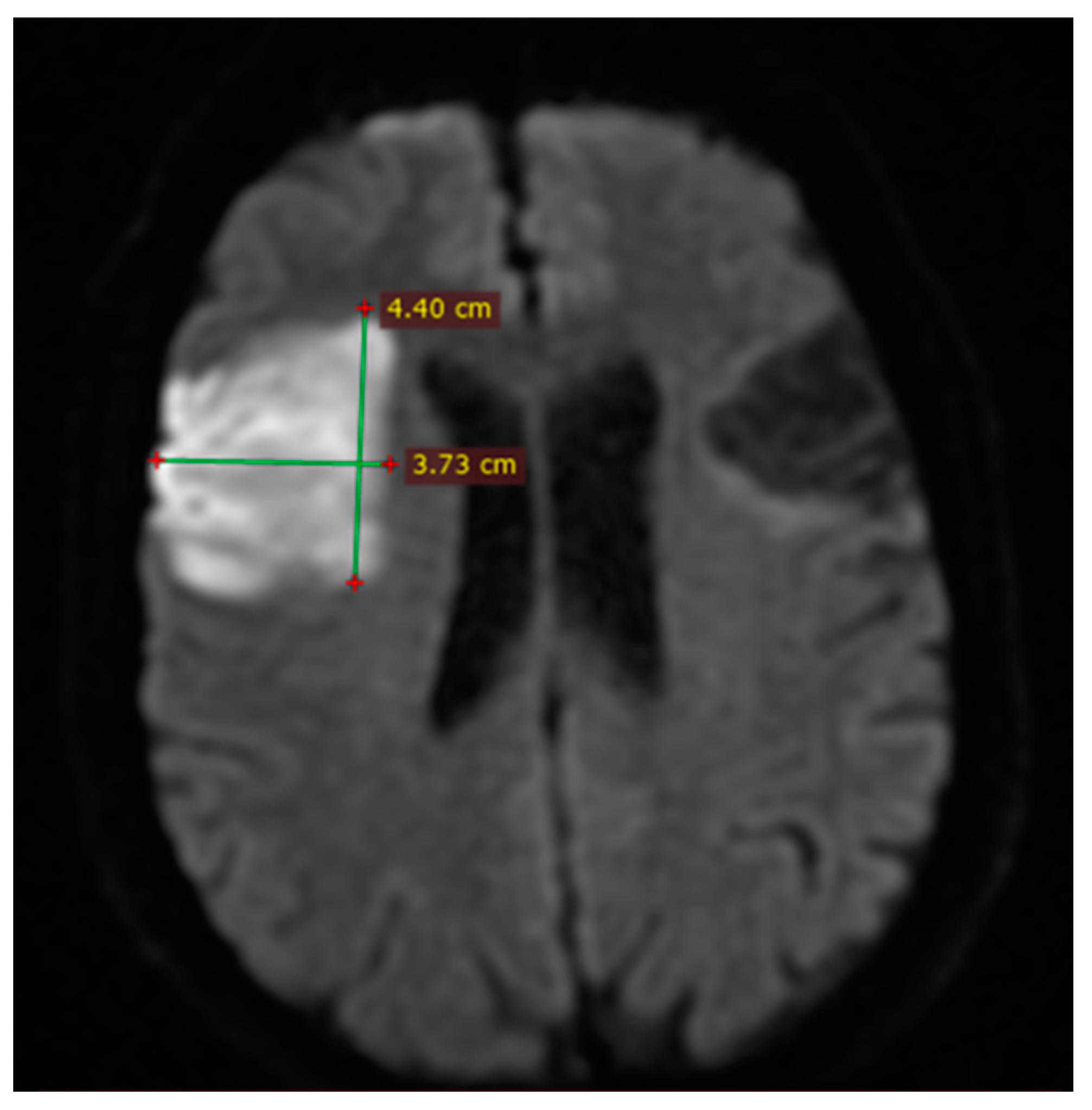
2.6. Imaging and Clinical Assessment
2.7. Inter-Rater Reliability Analysis
2.8. Inter-Rater Reliability
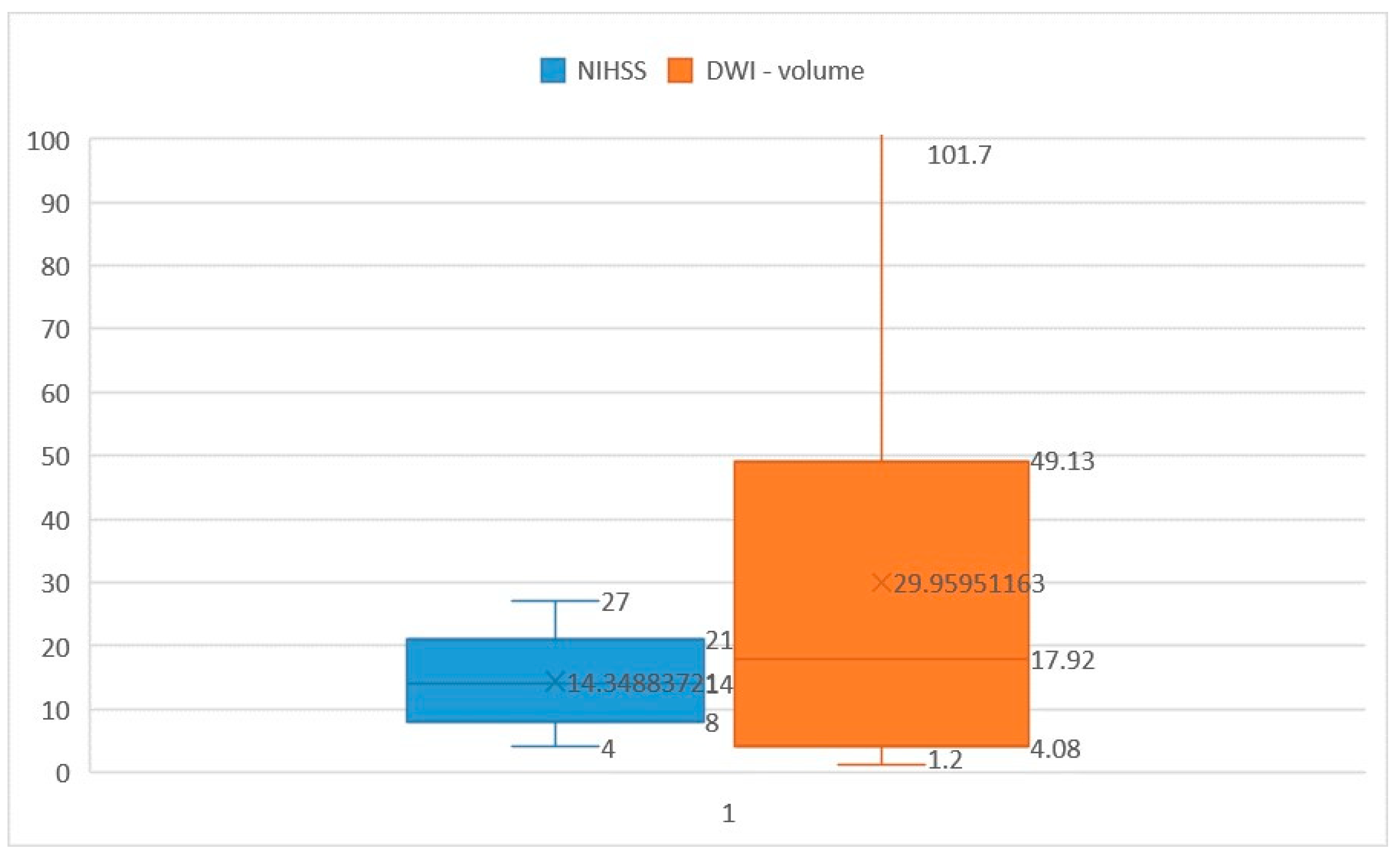
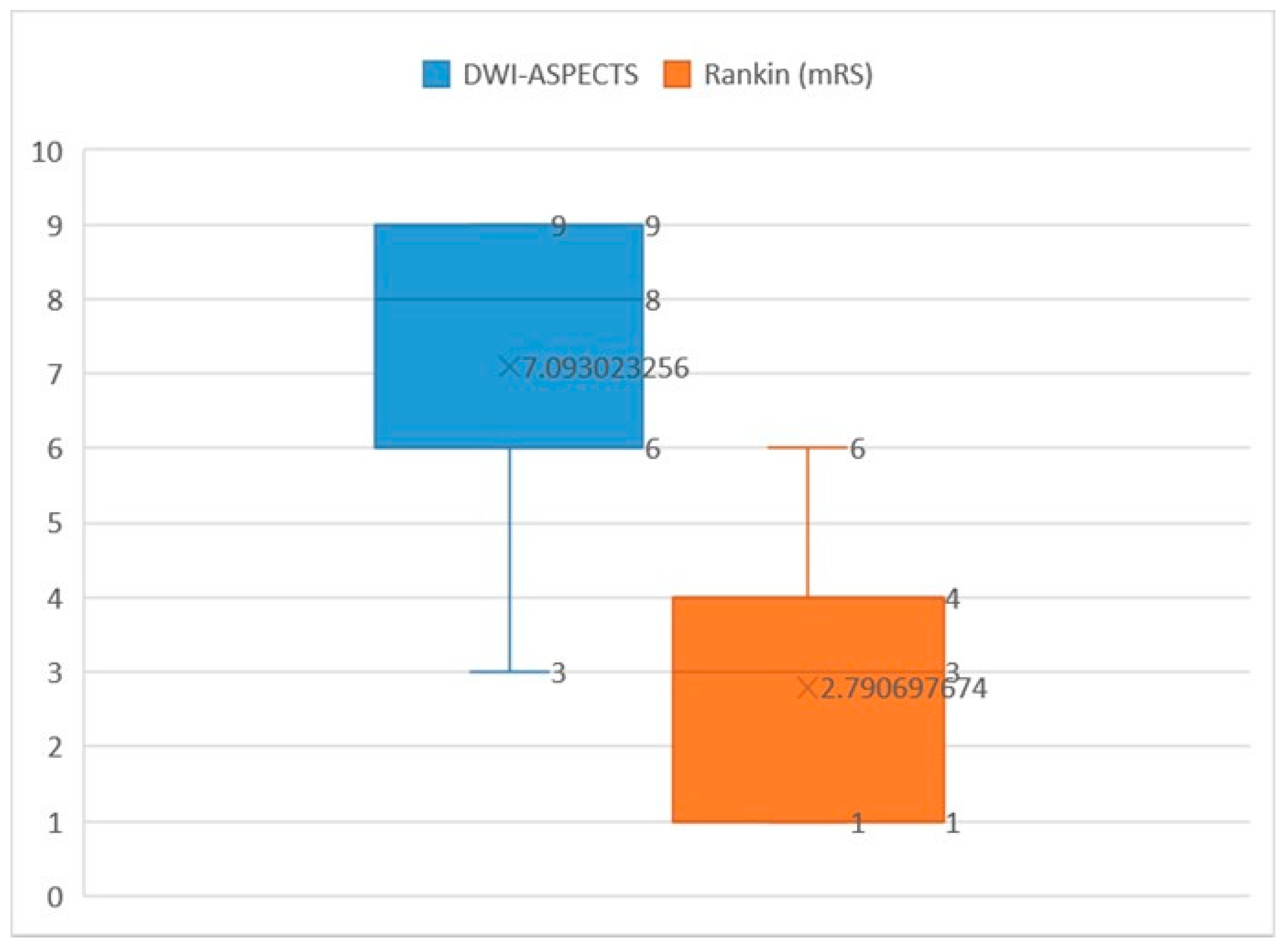
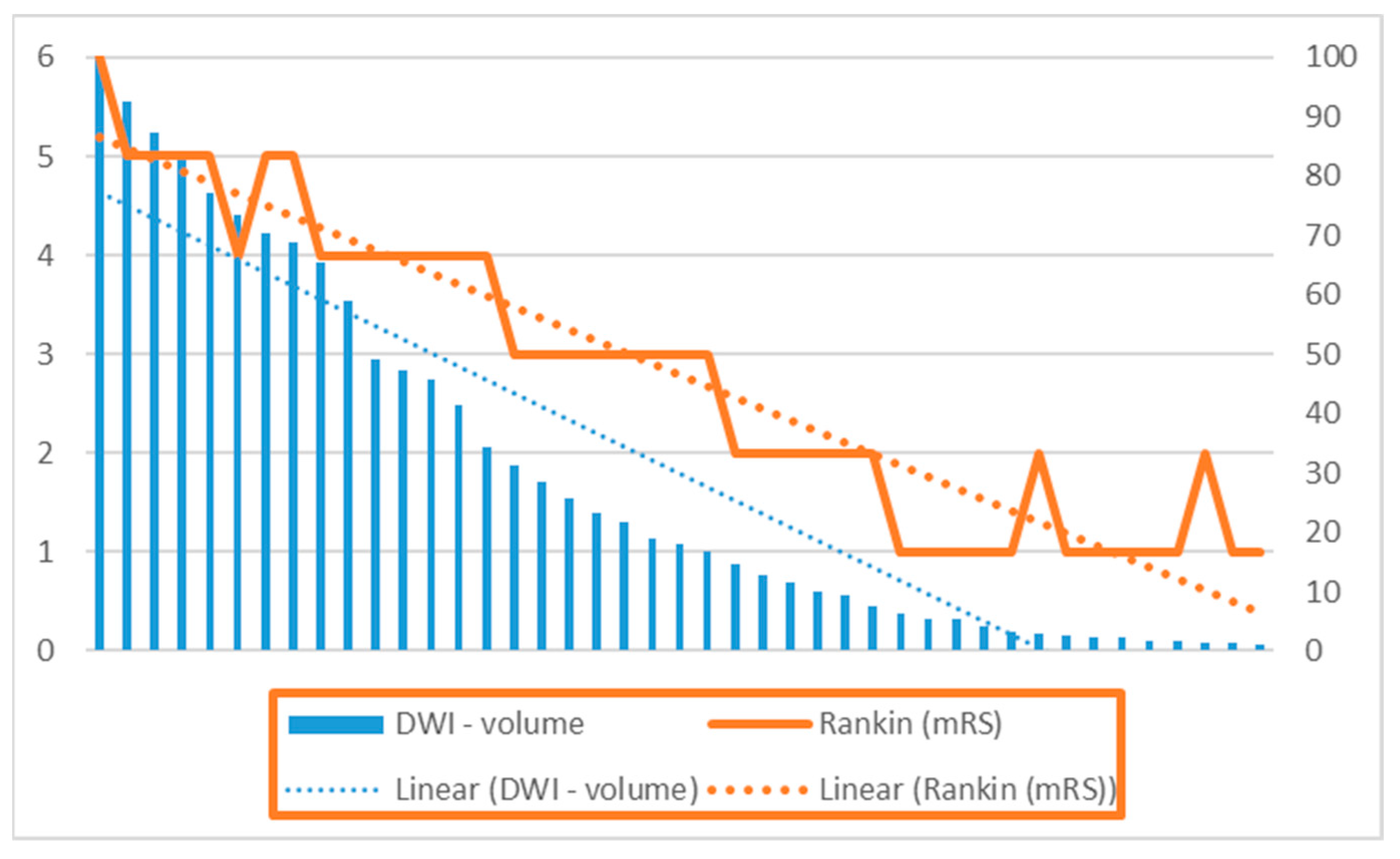
3. Results
3.1. Demographic and Risk Factor Distribution by Gender (Table 1)
3.2. Etiology (Table 2)
3.3. Affected Vascular Territories (Table 2)
3.4. Presenting Symptoms (Table 2)
3.5. Translation of Research Findings into Clinical Practice
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Future Research Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saini, V.; Guada, L.; Yavagal, D.R. Global Epidemiology of Stroke and Access to Acute Ischemic Stroke Interventions. Neurology 2021, 97 (Suppl. S2), S6–S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howard, G.; Goff, D.C. Population shifts and the future of stroke: Forecasts of the future burden of stroke. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2012, 1268, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donkor, E.S. Stroke in the 21st Century: A Snapshot of the Burden, Epidemiology, and Quality of Life. Stroke Res. Treat. 2018, 2018, 3238165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagaraja, N. Diffusion weighted imaging in acute ischemic stroke: A review of its interpretation pitfalls and advanced diffusion imaging application. J. Neurol. Sci. 2021, 425, 117435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogueira, R.G.; Jadhav, A.P.; Haussen, D.C.; Bonafe, A.; Budzik, R.F.; Bhuva, P.; Yavagal, D.R.; Ribo, M.; Cognard, C.; Hanel, R.A.; et al. DAWN Trial Investigators. Thrombectomy 6 to 24 Hours after Stroke with a Mismatch between Deficit and Infarct. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bammer, R. Basic principles of diffusion-weighted imaging. Eur. J. Radiol. 2003, 45, 169–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farooque, U.; Lohano, A.K.; Kumar, A.; Karimi, S.; Yasmin, F.; Bollampally, V.C.; Ranpariya, M.R. Validity of National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale for Severity of Stroke to Predict Mortality Among Patients Presenting with Symptoms of Stroke. Cureus 2020, 5112, e10255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Berthier, E.; Decavel, P.; Vuillier, F.; Verlut, C.; Moulin, T.; de Bustos Medeiros, E. Reliability of NIHSS by telemedicine in non-neurologists. Int. J. Stroke 2013, 8, E11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaraja, N.; Forder, J.R.; Warach, S.; Merino, J.G. Reversible diffusion-weighted imaging lesions in acute ischemic stroke: A systematic review. Neurology 2020, 94, 571–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edlow, B.L.; Hurwitz, S.; Edlow, J.A. Diagnosis of DWI-negative acute ischemic stroke: A meta-analysis. Neurology 2017, 89, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Baird, A.E.; Lövblad, K.O.; Schlaug, G.; Edelman, R.R.; Warach, S. Multiple acute stroke syndrome: Marker of embolic disease? Neurology 2000, 54, 674–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomalla, G.; Cheng, B.; Ebinger, M.; Hao, Q.; Tourdias, T.; Wu, O.; Kim, J.S.; Breuer, L.; Singer, O.C.; Warach, S.; et al. DWI-FLAIR mismatch for the identification of patients with acute ischaemic stroke within 4·5 h of symptom onset (PRE-FLAIR): A multicentre observational study. Lancet Neurol. 2011, 10, 978–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, M.B. Artificial Intelligence for Automated DWI/FLAIR Mismatch Assessment on Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Stroke: A Systematic Review. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barber, P.A.; Demchuk, A.M.; Zhang, J.; Buchan, A.M. Validity and reliability of a quantitative computed tomography score in predicting outcome of hyperacute stroke before thrombolytic therapy. ASPECTS Study Group. Alberta Stroke Programme Early CT Score. Lancet 2000, 355, 1670–1674, Published correction appears in Lancet 2000, 355, 2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagel, S.; Sinha, D.; Day, D.; Reith, W.; Chapot, R.; Papanagiotou, P.; Warburton, E.A.; Guyler, P.; Tysoe, S.; Fassbender, K.; et al. e-ASPECTS software is non-inferior to neuroradiologists in applying the ASPECT score to computed tomography scans of acute ischemic stroke patients. Int. J. Stroke 2017, 12, 615–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puetz, V.; Sylaja, P.N.; Coutts, S.B.; Hill, M.D.; Dzialowski, I.; Mueller, P.; Becker, U.; Urban, G.; O’Reilly, C.; Barber, P.A.; et al. Extent of hypoattenuation on CT angiography source images predicts functional outcome in patients with basilar artery occlusion. Stroke 2008, 39, 2485–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, J.; Kimura, K.; Shibazaki, K.; Sakamoto, Y. DWI-ASPECTS as a predictor of dramatic recovery after intravenous recombinant tissue plasminogen activator administration in patients with middle cerebral artery occlusion. Stroke 2013, 44, 534–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, K.; Liebeskind, D.S.; Nishi, Y.; Kutsuna, A.; Katano, T.; Sakamoto, Y.; Saito, T.; Aoki, J. A differential detailed diffusion-weighted imaging-ASPECTS for cerebral infarct volume measurement and outcome prediction. Int. J. Stroke 2023, 18, 1202–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, X.; Su, X.; Shi, J.; Liu, Q.; Zhou, C.; Dong, Z.; Xing, W.; Lu, H.; Pan, C.; Li, X.; et al. Comparison of automated and manual DWI-ASPECTS in acute ischemic stroke: Total and region-specific assessment. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 4130–4137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, J.T.; Hareendran, A.; Grant, M.; Baird, T.; Schulz, U.G.; Muir, K.W.; Bone, I. Improving the assessment of outcomes in stroke: Use of a structured interview to assign grades on the modified Rankin Scale. Stroke 2002, 33, 2243–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sananmuang, T.; Dejsiripongsa, T.; Keandoungchun, J.; Apirakkan, M. Reliability of ABC/2 Method in Measuring of Infarct Volume in Magnetic Resonance Diffusion-Weighted Image. Asian J. Neurosurg. 2019, 14, 801–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, J.R.; Gharai, L.R.; Schaefer, P.W.; Vangel, M.; Rosenthal, E.S.; Lev, M.H. ABC/2 for rapid clinical estimate of infarct, perfusion, and mismatch volumes. Neurology 2009, 72, 2104–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tei, H.; Uchiyama, S.; Usui, T. Clinical-diffusion mismatch defined by NIHSS and ASPECTS in non-lacunar anterior circulation infarction. J. Neurol. 2007, 254, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Margerie-Mellon, C.; Turc, G.; Tisserand, M.; Naggara, O.; Calvet, D.; Legrand, L.; Meder, J.F.; Mas, J.L.; Baron, J.C.; Oppenheim, C. Can DWI-ASPECTS substitute for lesion volume in acute stroke? Stroke 2013, 44, 3565–3567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furlanis, G.; Ajčević, M.; Stragapede, L.; Lugnan, C.; Ridolfi, M.; Caruso, P.; Naccarato, M.; Ukmar, M. Ischemic Volume and Neurological Deficit: Correlation of Computed Tomography Perfusion with the National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale Score in Acute Ischemic Stroke. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2018, 27, 2200–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Löuvbld, K.O.; Baird, A.E.; Schlaug, G.; Benfield, A.; Siewert, B.; Voetsch, B.; Connor, A.; Burzynski, C. Ischemic lesion volumes in acute stroke by diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging correlate with clinical outcome. Ann. Neurol. 1997, 42, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, D.C.; Yenari, M.A.; Albers, G.W.; O’Brien, M.; Marks, M.P.; Moseley, M.E. Correlation of perfusion- and diffusion-weighted MRI with NIHSS score in acute (<6.5 hour) ischemic stroke. Neurology 1998, 50, 864–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baird, A.E.; Lövblad, K.O.; Dashe, J.F.; Connor, A.; Burzynski, C.; Schlaug, G.; Straroselskaya, I. Clinical correlations of diffusion and perfusion lesion volumes in acute ischemic stroke. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2000, 10, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, A.J.; Barak, E.R.; Copen, W.A.; Kamalian, S.; Gharai, L.R.; Pervez, M.A.; Schwamm, L.H. Combining acute diffusion-weighted imaging and mean transmit time lesion volumes with National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale Score improves the prediction of acute stroke outcome. Stroke 2010, 41, 1728–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thijs, V.N.; Lansberg, M.G.; Beaulieu, C.; Marks, M.P.; Moseley, M.E.; Albers, G.W. Is early ischemic lesion volume on diffusion-weighted imaging an independent predictor of stroke outcome? A multivariable analysis. Stroke 2000, 31, 2597–2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, K.; Iguchi, Y.; Shibazaki, K.; Terasawa, Y.; Inoue, T.; Uemura, J. Large ischemic lesions on diffusion-weighted imaging done before intravenous tissue plasminogen activator thrombolysis predicts a poor outcome in patients with acute stroke. Stroke 2008, 39, 2388–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singer, O.C.; Kurre, W.; Humpich, M.C.; Lorenz, M.W.; Kastrup, A.; Liebeskind, D.S.; Thomalla, G.; Fiehler, J. Risk assessment of symptomatic intracerebral hemorrhage after thrombolysis using DWI-ASPECTS. Stroke 2009, 40, 2743–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.Y.; Na, D.G.; Kim, S.S.; Lee, K.H.; Ryoo, J.W.; Kim, H.K. Prediction of hemorrhagic transformation in acute ischemic stroke: Role of diffusion-weighted imaging and early parenchymal enhancement. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2005, 26, 1050–1055. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]



| Characteristic | Men (n = 19) | Women (n = 24) | Total (n = 43) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Median age in years | 67 (IQR 53–74) | 56 (IQR 48–63) | 61.5 (IQR 50–69) |
| Smoking history | 11 (25.58%) | 5 (11.62%) | 16 (37.2%) |
| Alcohol consumption | 6 (13.95%) | 2 (4.65%) | 8 (18.6%) |
| Hypertension | 17 (39.53%) | 13 (30.23%) | 30 (69.76%) |
| Atrial fibrillation | 8 (18.6%) | 6 (13.95%) | 14 (32.55%) |
| Hypercholesterolemia | 6 (13.95%) | 9 (20.93%) | 15 (34.88%) |
| Hypertrigliceridemia | 3 (6.97%) | 7 (16.27%) | 10 (23/25%) |
| Mixed dyslipidemia | 4 (9.3%) | 5 (11.62%) | 9 (20.93%) |
| Diabetes mellitus | 6 (13.95%) | 10 (23.25%) | 16 (37.2%) |
| Etiology | |
| ICA stenosis in cervical region (>50%) | 7 (16.27%) |
| ICA occlusion in cervical region | 4 (9.3%) |
| Large vessel occlusion of MCA | 5 (11.62%) |
| Atrial fibrillation | 14 (32.55%) |
| Affected territories | |
| MCA | 28 (65.11%) |
| ACA | 12 (27.9%) |
| Border zone of ICA (MCA/ACA) | 3 (0.69%) |
| Presenting symptoms | |
| Contralateral motor weakness | 37 (86%) |
| Contralateral hemianopsia | 8 (18.6%) |
| Global aphasia | 5 (11.62%) |
| Broca’s aphasia | 4 (9.3%) |
| Wernike’s aphasia | 3 (6.97%) |
| Hemineglect and disturbed spatial perception | 3 (6.97%) |
| Eye and head deviation | 11 (23.27%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dogariu, O.A.; Gheorman, V.; Dogariu, I.; Berceanu, M.C.; Albu, C.V.; Gheonea, I.A. Correlation between DWI-ASPECTS Score, Ischemic Stroke Volume on DWI, Clinical Severity and Short-Term Prognosis: A Single-Center Study. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 577. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14060577
Dogariu OA, Gheorman V, Dogariu I, Berceanu MC, Albu CV, Gheonea IA. Correlation between DWI-ASPECTS Score, Ischemic Stroke Volume on DWI, Clinical Severity and Short-Term Prognosis: A Single-Center Study. Brain Sciences. 2024; 14(6):577. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14060577
Chicago/Turabian StyleDogariu, Oana Andreea, Veronica Gheorman, Ioan Dogariu, Mihaela Corina Berceanu, Carmen Valeria Albu, and Ioana Andreea Gheonea. 2024. "Correlation between DWI-ASPECTS Score, Ischemic Stroke Volume on DWI, Clinical Severity and Short-Term Prognosis: A Single-Center Study" Brain Sciences 14, no. 6: 577. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14060577
APA StyleDogariu, O. A., Gheorman, V., Dogariu, I., Berceanu, M. C., Albu, C. V., & Gheonea, I. A. (2024). Correlation between DWI-ASPECTS Score, Ischemic Stroke Volume on DWI, Clinical Severity and Short-Term Prognosis: A Single-Center Study. Brain Sciences, 14(6), 577. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14060577







