Investigating Whether a Combination of Electro-Encephalography and Gene Expression Profiling Can Predict the Risk of Chronic Pain: A Protocol for an Observational Prospective Cohort Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
Main Objectives
- To identify the key EEG features that can robustly distinguish the different pain states, rest vs evoked experimental pain (by the cold pressor test), and between individuals with different clinical pain statuses.
- To examine potential gene expression changes before and after CP test within individuals with different clinical pain statuses.
- To test for correlations between the EEG activity and blood mRNA profiles.
- To investigate if an individual mRNA sequencing (seq) fingerprinting analysis can be used to predict at-risk patients with a possible persistent LBP trajectory.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.1.1. Inclusion Criteria and Procedure
2.1.2. Exclusion Criteria
2.2. Questionnaires
2.2.1. Demographic
2.2.2. Pain
2.2.3. Symptom Satisfaction and Expectation
2.2.4. Secondary Variables
2.2.5. EEG Measurement
2.2.6. Cold Pressor (CP) Test
2.2.7. mRNA Sequencing
2.3. Statistical Analyses
2.3.1. Descriptive Analyses at Baseline
2.3.2. Power Calculation
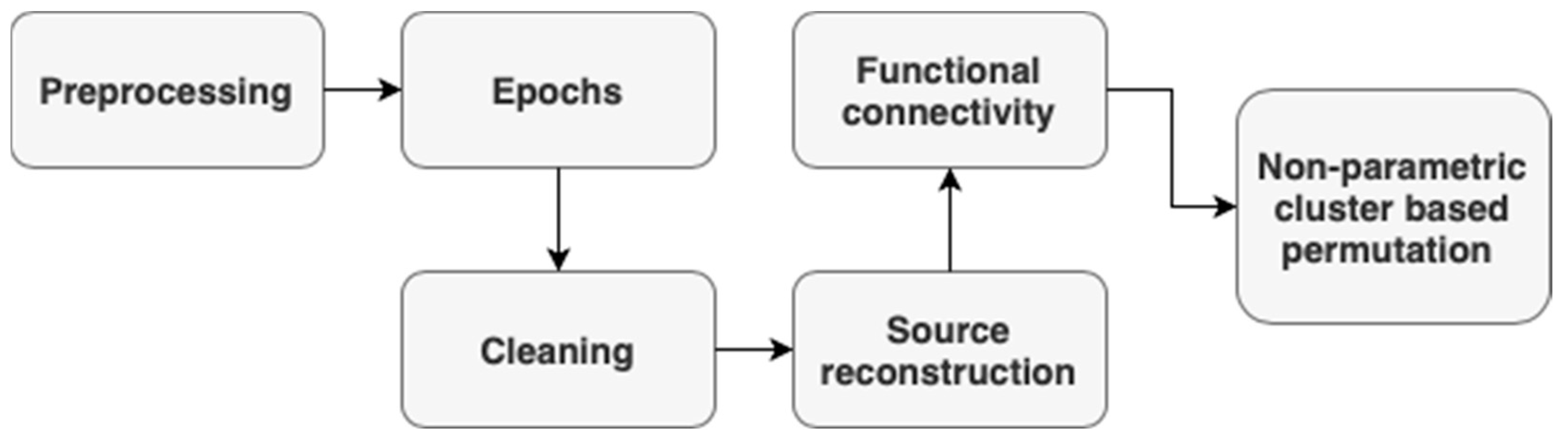
2.3.3. EEG Processing
2.3.4. EEG Source Localization
Forward Modelling
Inverse Modelling
Cluster-Based Permutation Using GraphVar
2.3.5. EEG Frequency and Time–Frequency Analysis
2.3.6. mRNA Sequencing Analyses
3. Expected Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Limitations
4.2. Data Management, Storage, and Security
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferreira, M.L.; de Luca, K.; Haile, L.M.; Steinmetz, J.D.; Culbreth, G.T.; Cross, M.; Kopec, J.A.; Ferreira, P.H.; Blyth, F.M.; Buchbinder, R.; et al. Global, Regional, and National Burden of Low Back Pain, 1990–2020, Its Attributable Risk Factors, and Projections to 2050: A Systematic Analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet Rheumatol. 2023, 5, e316–e329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, A.; March, L.; Zheng, X.; Huang, J.; Wang, X.; Zhao, J.; Blyth, F.M.; Smith, E.; Buchbinder, R.; Hoy, D. Global Low Back Pain Prevalence and Years Lived with Disability from 1990 to 2017: Estimates from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koes, B.W.; van Tulder, M.W.; Thomas, S. Diagnosis and Treatment of Low Back Pain. BMJ 2006, 332, 1430–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, C.; Underwood, M.; Buchbinder, R. Non-Specific Low Back Pain. Lancet 2017, 389, 736–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicol, V.; Verdaguer, C.; Daste, C.; Bisseriex, H.; Lapeyre, É.; Lefèvre-Colau, M.-M.; Rannou, F.; Rören, A.; Facione, J.; Nguyen, C. Chronic Low Back Pain: A Narrative Review of Recent International Guidelines for Diagnosis and Conservative Treatment. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroenke, K.; Outcalt, S.; Krebs, E.; Bair, M.J.; Wu, J.; Chumbler, N.; Yu, Z. Association between Anxiety, Health-Related Quality of Life and Functional Impairment in Primary Care Patients with Chronic Pain. Gen. Hosp. Psychiatry 2013, 35, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turk, D.C.; Fillingim, R.B.; Ohrbach, R.; Patel, K.V. Assessment of Psychosocial and Functional Impact of Chronic Pain. J. Pain. 2016, 17, T21–T49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, R.; Shekelle, P. Will This Patient Develop Persistent Disabling Low Back Pain? JAMA 2010, 303, 1295–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treede, R.-D.; Rief, W.; Barke, A.; Aziz, Q.; Bennett, M.I.; Benoliel, R.; Cohen, M.; Evers, S.; Finnerup, N.B.; First, M.B.; et al. A Classification of Chronic Pain for ICD-11. Pain 2015, 156, 1003–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apkarian, A.V.; Hashmi, J.A.; Baliki, M.N. Pain and the Brain: Specificity and Plasticity of the Brain in Clinical Chronic Pain. Pain 2011, 152, S49–S64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeater, T.D.; Cruz, C.J.; Cruz-Almeida, Y.; Allen, K.D. Autonomic Nervous System Dysregulation and Osteoarthritis Pain: Mechanisms, Measurement, and Future Outlook. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2022, 24, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashmi, J.A.; Baliki, M.N.; Huang, L.; Baria, A.T.; Torbey, S.; Hermann, K.M.; Schnitzer, T.J.; Apkarian, A.V. Shape Shifting Pain: Chronification of Back Pain Shifts Brain Representation from Nociceptive to Emotional Circuits. Brain 2013, 136, 2751–2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiemann, L.; May, E.S.; Postorino, M.; Schulz, E.; Nickel, M.M.; Bingel, U.; Ploner, M. Differential Neurophysiological Correlates of Bottom-up and Top-down Modulations of Pain. Pain 2015, 156, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannibal, K.E.; Bishop, M.D. Chronic Stress, Cortisol Dysfunction, and Pain: A Psychoneuroendocrine Rationale for Stress Management in Pain Rehabilitation. Phys. Ther. 2014, 94, 1816–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jennings, E.M.; Okine, B.N.; Roche, M.; Finn, D.P. Stress-Induced Hyperalgesia. Prog. Neurobiol. 2014, 121, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankord, R.; Herman, J.P. Limbic regulation of hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenocortical function during acute and chronic stress. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2008, 1148, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissman-Fogel, I.; Sprecher, E.; Pud, D. Effects of Catastrophizing on Pain Perception and Pain Modulation. Exp. Brain Res. 2008, 186, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, L.E.; McNeil, D.W.; Vowles, K.E.; Sorrell, J.T.; Turk, C.L.; Ries, B.J.; Hopko, D.R. Effects of Emotion on Pain Reports, Tolerance and Physiology. Pain Res. Manag. 2002, 7, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rainville, P.; Feine, J.S.; Bushnell, M.C.; Duncan, G.H. A Psychophysical Comparison of Sensory and Affective Responses to Four Modalities of Experimental Pain. Somatosens. Mot. Res. 1992, 9, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahman-Averbuch, H.; Nir, R.-R.; Sprecher, E.; Yarnitsky, D. Psychological Factors and Conditioned Pain Modulation: A Meta-Analysis. Clin. J. Pain. 2016, 32, 541–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Raecke, R.; Niemeier, A.; Ihle, K.; Ruether, W.; May, A. Structural Brain Changes in Chronic Pain Reflect Probably Neither Damage Nor Atrophy. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stampanoni Bassi, M.; Iezzi, E.; Gilio, L.; Centonze, D.; Buttari, F. Synaptic Plasticity Shapes Brain Connectivity: Implications for Network Topology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwak, Y.S.; Hulsebosch, C.E.; Leem, J.W. Neuronal-Glial Interactions Maintain Chronic Neuropathic Pain after Spinal Cord Injury. Neural Plast. 2017, 2017, 2480689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohenschurz-Schmidt, D.J.; Calcagnini, G.; Dipasquale, O.; Jackson, J.B.; Medina, S.; O’Daly, O.; O’Muircheartaigh, J.; de Lara Rubio, A.; Williams, S.C.R.; McMahon, S.B.; et al. Linking Pain Sensation to the Autonomic Nervous System: The Role of the Anterior Cingulate and Periaqueductal Gray Resting-State Networks. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, A.; Vogelzangs, N.; Licht, C.M.M.; Geenen, R.; MacFarlane, G.J.; de Geus, E.J.C.; Smit, J.H.; Penninx, B.W.J.H.; Dekker, J. Dysregulation of the Autonomic Nervous System and Its Association with the Presence and Intensity of Chronic Widespread Pain. Arthritis Care Res. 2012, 64, 1209–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenoglio, K.A.; Chen, Y.; Baram, T.Z. Neuroplasticity of the Hypothalamic–Pituitary–Adrenal Axis Early in Life Requires Recurrent Recruitment of Stress-Regulating Brain Regions. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 2434–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mussigmann, T.; Bardel, B.; Lefaucheur, J.-P. Resting-State Electroencephalography (EEG) Biomarkers of Chronic Neuropathic Pain. A Systematic Review. Neuroimage 2022, 258, 119351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gram, M.; Graversen, C.; Olesen, S.S.; Drewes, A.M. Dynamic Spectral Indices of the Electroencephalogram Provide New Insights into Tonic Pain. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2015, 126, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, M.T.; Bartling, J.; Pachur, D.; Woikowsky-Biedau, S.V.; Lautenbacher, S. EEG Responses to Tonic Heat Pain. Exp. Brain Res. 2006, 173, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nir, R.-R.; Sinai, A.; Raz, E.; Sprecher, E.; Yarnitsky, D. Pain Assessment by Continuous EEG: Association between Subjective Perception of Tonic Pain and Peak Frequency of Alpha Oscillations during Stimulation and at Rest. Brain Res. 2010, 1344, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nir, R.-R.; Sinai, A.; Moont, R.; Harari, E.; Yarnitsky, D. Tonic Pain and Continuous EEG: Prediction of Subjective Pain Perception by Alpha-1 Power during Stimulation and at Rest. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2012, 123, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, B.; Figueroa, A.; Robinson-Papp, J. Structural and Functional Connections between the Autonomic Nervous System, Hypothalamic–Pituitary–Adrenal Axis, and the Immune System: A Context and Time Dependent Stress Response Network. Neurol. Sci. 2022, 43, 951–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glotov, A.S.; Zelenkova, I.E.; Vashukova, E.S.; Shuvalova, A.R.; Zolotareva, A.D.; Polev, D.E.; Barbitoff, Y.A.; Glotov, O.S.; Sarana, A.M.; Shcherbak, S.G.; et al. RNA Sequencing of Whole Blood Defines the Signature of High Intensity Exercise at Altitude in Elite Speed Skaters. Genes 2022, 13, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorrells, S.F.; Sapolsky, R.M. An Inflammatory Review of Glucocorticoid Actions in the CNS. Brain Behav. Immun. 2007, 21, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudheimer, K.D.; O’Hara, R.; Spiegel, D.; Powers, B.; Kraemer, H.C.; Neri, E.; Weiner, M.; Hardan, A.; Hallmayer, J.; Dhabhar, F.S. Cortisol, Cytokines, and Hippocampal Volume Interactions in the Elderly. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2014, 6, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitlic, A.; Lord, J.M.; Phillips, A.C. Stress, Ageing and Their Influence on Functional, Cellular and Molecular Aspects of the Immune System. Age 2014, 36, 9631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zefferino, R.; Di Gioia, S.; Conese, M. Molecular Links between Endocrine, Nervous and Immune System during Chronic Stress. Brain Behav. 2021, 11, e01960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEwen, B.S. The Ever-Changing Brain: Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms for the Effects of Stressful Experiences. Dev. Neurobiol. 2012, 72, 878–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galon, J.; Franchimont, D.; Hiroi, N.; Frey, G.; Boettner, A.; Ehrhart-Bornstein, M.; O’shea, J.J.; Chrousos, G.P.; Bornstein, S.R. Gene Profiling Reveals Unknown Enhancing and Suppressive Actions of Glucocorticoids on Immune Cells. FASEB J. 2002, 16, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapitzke, D.; Vetter, I.; Cabot, P.J. Endogenous Opioid Analgesia in Peripheral Tissues and the Clinical Implications for Pain Control. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2005, 1, 279–297. [Google Scholar]
- El-Brolosy, M.A.; Stainier, D.Y.R. Genetic Compensation: A Phenomenon in Search of Mechanisms. PLoS Genet. 2017, 13, e1006780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bortsov, A.V.; Parisien, M.; Khoury, S.; Martinsen, A.E.; Lie, M.U.; Heuch, I.; Hveem, K.; Zwart, J.-A.; Winsvold, B.S.; Diatchenko, L. Brain-Specific Genes Contribute to Chronic but Not to Acute Back Pain. Pain Rep. 2022, 7, e1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiarotto, A.; Maxwell, L.J.; Ostelo, R.W.; Boers, M.; Tugwell, P.; Terwee, C.B. Measurement Properties of Visual Analogue Scale, Numeric Rating Scale, and Pain Severity Subscale of the Brief Pain Inventory in Patients with Low Back Pain: A Systematic Review. J. Pain. 2019, 20, 245–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nim, C.G.; Vach, W.; Downie, A.; Kongsted, A. Do Visual Pain Trajectories Reflect the Actual Course of Low Back Pain? A Longitudinal Cohort Study. J. Pain. 2023, 24, 1506–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tubach, F.; Wells, G.A.; Ravaud, P.; Dougados, M. Minimal Clinically Important Difference, Low Disease Activity State, and Patient Acceptable Symptom State: Methodological Issues. J. Rheumatol. 2005, 32, 2025–2029. [Google Scholar]
- Grotle, M.; Brox, J.I.; Vøllestad, N.K. Reliability, Validity and Responsiveness of the Fear-Avoidance Beliefs Questionnaire: Methodological Aspects of the Norwegian Version. J. Rehabil. Med. 2006, 38, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williamson, E. Fear Avoidance Beliefs Questionnaire (FABQ). Aust. J. Physiother. 2006, 52, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikemoto, T.; Hayashi, K.; Shiro, Y.; Arai, Y.-C.; Marcuzzi, A.; Costa, D.; Wrigley, P. A Systematic Review of Cross-Cultural Validation of the Pain Catastrophizing Scale. Eur. J. Pain. 2020, 24, 1228–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiarotto, A.; Ostelo, R.W.; Boers, M.; Terwee, C.B. A Systematic Review Highlights the Need to Investigate the Content Validity of Patient-Reported Outcome Measures for Physical Functioning in Patients with Low Back Pain. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2018, 95, 73–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallesen, S.; Bjorvatn, B.; Nordhus, I.H.; Sivertsen, B.; Hjørnevik, M.; Morin, C.M. A New Scale for Measuring Insomnia: The Bergen Insomnia Scale. Percept. Mot. Skills 2008, 107, 691–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compton, P.A.; Wu, S.M.; Schieffer, B.; Pham, Q.; Naliboff, B.D. Introduction of a Self-Report Version of the Prescription Drug Use Questionnaire and Relationship to Medication Agreement Non-Compliance. J. Pain. Symptom Manag. 2008, 36, 383–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleppang, A.L.; Hagquist, C. The Psychometric Properties of the Hopkins Symptom Checklist-10: A Rasch Analysis Based on Adolescent Data from Norway. Fam. Pract. 2016, 33, 740–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-P.; Gorenstein, C. Psychometric Properties of the Beck Depression Inventory-II: A Comprehensive Review. Braz. J. Psychiatry 2013, 35, 416–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, G.S.; Reitsma, J.B.; Altman, D.G.; Moons, K.G. Transparent Reporting of a Multivariable Prediction Model for Individual Prognosis or Diagnosis (TRIPOD): The TRIPOD Statement. BMC Med. 2015, 13, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosmer, D.W.; Lemeshow, S.; Sturdivant, R.X. Applied Logistic Regression, 1st ed.; Wiley Series in Probability and Statistics; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; ISBN 978-0-470-58247-3. [Google Scholar]
- Delorme, A.; Makeig, S. EEGLAB: An Open Source Toolbox for Analysis of Single-Trial EEG Dynamics Including Independent Component Analysis. J. Neurosci. Methods 2004, 134, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Calderon, J.; Luck, S.J. ERPLAB: An Open-Source Toolbox for the Analysis of Event-Related Potentials. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigdely-Shamlo, N.; Mullen, T.; Kothe, C.; Su, K.-M.; Robbins, K.A. The PREP Pipeline: Standardized Preprocessing for Large-Scale EEG Analysis. Front. Neuroinform. 2015, 9, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Effects of Filter’s Class, Cutoff Frequencies, and Independent Component Analysis on the Amplitude of Somatosensory Evoked Potentials Recorded from Healthy Volunteers—PMC. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6603557/ (accessed on 14 April 2024).
- Pion-Tonachini, L.; Kreutz-Delgado, K.; Makeig, S. ICLabel: An Automated Electroencephalographic Independent Component Classifier, Dataset, and Website. Neuroimage 2019, 198, 181–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadel, F.; Baillet, S.; Mosher, J.C.; Pantazis, D.; Leahy, R.M. Brainstorm: A User-Friendly Application for MEG/EEG Analysis. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2011, 2011, 879716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hämäläinen, M.S.; Ilmoniemi, R.J. Interpreting Magnetic Fields of the Brain: Minimum Norm Estimates. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 1994, 32, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadleir, R.J.; Argibay, A. Modeling Skull Electrical Properties. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2007, 35, 1699–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunovsky, M.; Krajca, V.; Diblikova, F.; Bartos, A.; Zavesicka, L.; Matousek, M. Standardized Low-Resolution Brain Electromagnetic Tomography (sLORETA) in the Prediction of Response to Cholinesterase Inhibitors in Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease. Ann. Gen. Psychiatry 2008, 7, S277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newson, J.J.; Thiagarajan, T.C. EEG Frequency Bands in Psychiatric Disorders: A Review of Resting State Studies. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Chang, M.C. Chronic Pain: Structural and Functional Changes in Brain Structures and Associated Negative Affective States. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waller, L.; Brovkin, A.; Dorfschmidt, L.; Bzdok, D.; Walter, H.; Kruschwitz, J.D. GraphVar 2.0: A User-Friendly Toolbox for Machine Learning on Functional Connectivity Measures. J. Neurosci. Methods 2018, 308, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, M.; Wang, J.; He, Y. BrainNet Viewer: A Network Visualization Tool for Human Brain Connectomics. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goutte, C.; Toft, P.; Rostrup, E.; Nielsen, F.Å.; Hansen, L.K. On Clustering fMRI Time Series. NeuroImage 1999, 9, 298–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navid, M.S.; Kammermeier, S.; Niazi, I.K.; Sharma, V.D.; Vuong, S.M.; Bötzel, K.; Greenlee, J.D.W.; Singh, A. Cognitive Task-Related Oscillations in Human Internal Globus Pallidus and Subthalamic Nucleus. Behav. Brain Res. 2022, 424, 113787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobin, A.; Davis, C.A.; Schlesinger, F.; Drenkow, J.; Zaleski, C.; Jha, S.; Batut, P.; Chaisson, M.; Gingeras, T.R. STAR: Ultrafast Universal RNA-Seq Aligner. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N.; Marth, G.; Abecasis, G.; Durbin, R. The Sequence Alignment/Map Format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Smyth, G.K.; Shi, W. featureCounts: An Efficient General Purpose Program for Assigning Sequence Reads to Genomic Features. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated Estimation of Fold Change and Dispersion for RNA-Seq Data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, G.; Wang, L.-G.; Han, Y.; He, Q.-Y. clusterProfiler: An R Package for Comparing Biological Themes Among Gene Clusters. Omics J. Integr. Biol. 2012, 16, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langfelder, P.; Horvath, S. WGCNA: An R Package for Weighted Correlation Network Analysis. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, M.; Wendling, F. Electroencephalography Source Connectivity: Aiming for High Resolution of Brain Networks in Time and Space. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2018, 35, 81–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, D.V.; Makhnovskii, P.A.; Kurochkina, N.S.; Lysenko, E.A.; Vepkhvadze, T.F.; Vinogradova, O.L. Intensity-Dependent Gene Expression after Aerobic Exercise in Endurance-Trained Skeletal Muscle. Biol. Sport. 2018, 35, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franken, C.; Remy, S.; Lambrechts, N.; Hollanders, K.; Den Hond, E.; Schoeters, G. Peripheral Blood Collection: The First Step towards Gene Expression Profiling. Biomarkers 2016, 21, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Demographics | Baseline | 2 Weeks | 3 Months | 6 Months |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | X | |||
| Age | X | |||
| Marital status | X | |||
| Ethnicity | X | |||
| Education | X | |||
| Employment | X | |||
| Dominant hand | X | |||
| Currently experiencing low back pain a | X | X | X | X |
| Current severity of low back pain (11-point numeric rating scale) | X a | X a | X a | X a |
| Severity of low back pain average last week (11-point numeric rating scale) | X a | X a | X a | X a |
| Duration of current low back pain | X a | X a | X a | X a |
| Low back pain trajectory last 12 months | X a | X a | X a | X a |
| Symptom satisfaction (PASS 5-point Likert scale) | X a | X a | X a | X a |
| Onset of low back pain | X a | X a | X a | X a |
| Perceived cause of low back pain | X a | X a | X a | X a |
| Receiving treatment for low back pain | X a | X a | X a | X a |
| Fear Avoidance Belief Questionnaire—physical activity | X a | X a | X a | X a |
| Pain Catastrophizing Scale | X a | X a | X a | X a |
| Roland–Morris Disability Questionnaire | X a | X a | X a | X a |
| Expectation of recovery within 3 months | X a | X a | X a | X a |
| Low back pain trajectories next 12 months | X a | X a | X a | X a |
| Current pain elsewhere | X | X | X | X |
| Bergen Insomnia Scale | X | X | X | X |
| Use of pain medication for low back pain b | X | X | X | X |
| Type of medication | X b | X b | X b | X b |
| Name of medication | X b | X b | X b | X b |
| Administration method for medication | X b | X b | X b | X b |
| Medication use frequency | X b | X b | X b | X b |
| Medication dosage | X b | X b | X b | X b |
| Medication use duration | X b | X b | X b | X b |
| Prescription Drug Use Questionnaire | X b | X b | X b | X b |
| Hopkins Symptom Check List—10 | X | X | X | X |
| Beck’s Depression Inventory | X | X | X | X |
| FP1 | CP6 | FC4 |
| FPz | P7 | C5 |
| FP2 | P3 | C1 |
| F7 | PZ | C2 |
| F3 | P4 | C6 |
| FZ | P8 | CP3 |
| F4 | POZ | CPZ |
| F8 | O1 | CP4 |
| FC5 | OZ | P5 |
| FC1 | O2 | P1 |
| FC2 | AF7 | P2 |
| FC6 | AF3 | P6 |
| T7 | AF4 | PO5 |
| C3 | AF8 | PO3 |
| CZ | F5 | PO4 |
| C4 | F1 | PO6 |
| T8 | F2 | FT7 |
| CP5 | F6 | FT8 |
| CP1 | FC3 | TP7 |
| CP2 | FCZ | TP8 |
| PO7 | PO8 | M1 |
| M2 |
| bankssts (left) | parsorbitalis (left) |
| caudalanteriorcingulate (left) | parsorbitalis (right) |
| caudalanteriorcingulate (right) | posteriorcingulate (left) |
| frontalpole (left) | posteriorcingulate (right) |
| frontalpole (right) | precuneus (left) |
| inferiorparietal (left) | precuneus (right) |
| inferiorparietal (right) | rostralanteriorcingulate (left) |
| insula (left) | rostralanteriorcingulate (right) |
| insula (right) | rostralmiddlefrontal (left) |
| isthmuscingulate (left) | rostralmiddlefrontal (right) |
| isthmuscingulate (right) | superiorparietal (left) |
| lateralorbitofrontal (left) | superiorparietal (right) |
| lateralorbitofrontal (right) | supramarginal (left) |
| medialorbitofrontal (left) | supramarginal (right) |
| medialorbitofrontal (right) | |
| parahippocampal (left) | |
| parahippocampal (right) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sannes, A.-C.; Ghani, U.; Niazi, I.K.; Moberget, T.; Jonassen, R.; Haavik, H.; Gjerstad, J. Investigating Whether a Combination of Electro-Encephalography and Gene Expression Profiling Can Predict the Risk of Chronic Pain: A Protocol for an Observational Prospective Cohort Study. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 641. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14070641
Sannes A-C, Ghani U, Niazi IK, Moberget T, Jonassen R, Haavik H, Gjerstad J. Investigating Whether a Combination of Electro-Encephalography and Gene Expression Profiling Can Predict the Risk of Chronic Pain: A Protocol for an Observational Prospective Cohort Study. Brain Sciences. 2024; 14(7):641. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14070641
Chicago/Turabian StyleSannes, Ann-Christin, Usman Ghani, Imran Khan Niazi, Torgeir Moberget, Rune Jonassen, Heidi Haavik, and Johannes Gjerstad. 2024. "Investigating Whether a Combination of Electro-Encephalography and Gene Expression Profiling Can Predict the Risk of Chronic Pain: A Protocol for an Observational Prospective Cohort Study" Brain Sciences 14, no. 7: 641. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14070641
APA StyleSannes, A.-C., Ghani, U., Niazi, I. K., Moberget, T., Jonassen, R., Haavik, H., & Gjerstad, J. (2024). Investigating Whether a Combination of Electro-Encephalography and Gene Expression Profiling Can Predict the Risk of Chronic Pain: A Protocol for an Observational Prospective Cohort Study. Brain Sciences, 14(7), 641. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14070641







