Abstract
(1) Background: Schizophrenia is a chronic and progressive neuropsychiatric illness. Apart from positive and negative symptoms, 98% of the population diagnosed with schizophrenia have impaired cognitive functioning, which significantly influences the quality of life. The correlation between lipids and cognitive functioning has been well established. Our study aimed to investigate correlations between cognitive functions, the severity of schizophrenia symptoms, and lipid profiles. (2) Methods: Fifty-two women diagnosed with schizophrenia participated in this study. Cognitive functioning was measured using the Wisconsin Card Sorting Test (WCST). The Positive and Negative Symptom Scale (PANSS) was used. The serum lipid profile, including low-density lipoproteins (LDLs), high-density lipoproteins (HDLs), and triglycerides was measured. (3) Results: Better cognitive functions were associated with normal HDL levels, while low HDL levels correlated with worse WSCT scores. Only the PANSS negative subscale showed a correlation with HDL levels. Correlations with chronicity of schizophrenia and the patient’s age with poorer cognitive functions, but not with symptom severity, were detected. Early/late age at onset did not influence WSCT scores. (4) Conclusions: Our results suggest high HDL levels might be a protective factor against cognitive impairment. The influences of age and illness duration also play a vital role in cognitive performance.
1. Introduction
Approximately 1% of the population worldwide is afflicted with schizophrenia [1]. In accordance with data from the Global Burden of Disease, the prevalence of schizophrenia has been increasing since 1990 [2]. Schizophrenia is a chronic and progressive neuropsychiatric illness, which constitutes symptoms conventionally divided into two groups: positive and negative; in recent years, the role of a third group of symptoms, cognitive deficits, has increased significantly due to its influence on daily functioning and the quality of life of patients [3,4,5]. A total of 98% of the population diagnosed with schizophrenia have impaired cognitive functioning [6]. Treatment of cognitive dysfunctions may prove to be essential in hindering the progression of the disease leading to disability, of which schizophrenia is a sizable contributor worldwide [5,7,8].
Commonly found neurocognitive deficits in schizophrenia are processing speed, attention, working memory, problem-solving, verbal memory, and learning, as well as visual learning [5,9,10]. Studies show that cognitive dysfunctions are present during the first episode of the illness [11,12,13], as well as during its course [14], some of them suggest that even before the onset of the disease, cognitive symptoms are already in existence [15,16].
The correlation between lipids and cognitive functioning has been well established. Although the blood–brain barrier obstructs the free flow of lipids [17], the changes in serum cholesterol levels still influence brain cholesterol content [18]. Studies conducted on animals showed that learning and memory impairment reversed when adding cholesterol to the diet of animals with cholesterol deficiency and animals with a cholesterol synthesis block [19,20]. Furthermore, they proved a connection between a cholesterol-enriched diet and improved results in memory acquisition and retention, as well as performance [21,22]. The results in the human population are inconsistent. On the one hand, Elias et al. found a strong correlation between low total serum cholesterol and worse scores for cognitive functions such as abstract reasoning, attention, word fluency, and cognitive control [23]. Moreover, introducing treatments aiming at lowering cholesterol levels, both pharmacological [24] and dietary ones [25], worsened some of the cognitive measures. However, other publications suggest a negative correlation between cognitive functions and total serum cholesterol levels [26]. Meanwhile, Okusaga et al. reported no significant links between cholesterol levels and cognition [27].
Cognitive impairment is a primary determinant of functional disability and the indirect costs of schizophrenia. Pharmacological treatment options for cognitive deficits are unsatisfactory due to limited efficacy or tolerability. In the past, the main focus of treatment response was positive symptoms. At the same time, less attention was paid to negative symptoms and cognitive impairment, considering it as the “residual phase” of illness. In recent years, there has been increasing interest in assessing functional improvement in the remission of positive symptoms. Non-pharmacological interventions, such as cognitive remediation, suggest potential benefits. The augmentation of antipsychotic treatment with pharmacological cognitive enhancers has been studied, with a lack of evidence in the long term. Combined treatment approaches appear particularly promising, potentially significantly increasing the percentage of treatment responders [28].
The Aim of the Study
In this paper, we plan to underline the links between cholesterol levels and neurocognitive deficits in schizophrenic patients, using the WCTS as a measurement method. Additionally, we will show associations between negative and positive symptoms during an acute episode and in remission, using PANSS results and cognitive functioning. Furthermore, we will investigate the correlations between cognitive impairment and the severity of positive and negative symptoms of schizophrenia in relation to biomedical variables such as age, age of onset, and illness duration.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
Fifty-two women (mean age 32.96, SD 10.9) diagnosed with schizophrenia were recruited from 2008–2015 at the Department of Psychiatry, Poznan University of Medical Sciences, Poland. All subjects were of Caucasian origin, and they were the native Polish population from the Great Poland region. This study was performed in accordance with the ethical standards established in the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the medical ethics committee of the Poznan University of Medical Sciences (approval no 266/08). All participants gave written informed consent before being included in this study, and their anonymity was preserved. During recruitment, male patients often refused to participate in the study, resulting in a significant disproportion between females and males. Therefore, in the present study, we decided to include only women to improve the study group homogeneity.
2.2. Clinical Assessment
Participants were recruited during the exacerbation of psychotic symptoms, within a week from admission to the hospital ward. The inclusion criteria included the exacerbation of psychotic symptoms at hospital admission (T0), a diagnosis of schizophrenia according to DSM-IV criteria, and being aged between 18–65 years. The exclusion criteria included chronic or acute somatic or neurological diseases, pregnancy or breastfeeding, and increased CRP (C-reactive protein). A consensus diagnosis of schizophrenia was made by two experienced psychiatrists for each patient using the Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV Axis I Disorders (SCID) [29]. Patients were evaluated also for lifetime psychiatric symptomatology with the Operational Criteria for Psychotic Illness (OPCRIT) [30]. The Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS) [31] was used to assess the severity of schizophrenia symptoms at admission (T0) and after eight weeks of treatment (T8). The PANSS is a 30-item semi-structured scale used to determine the severity of schizophrenia symptoms. Each item is rated on a Likert scale from 1 (absent) to 7 (extreme). It consists of three subscales: positive (PANSS P) and negative (PANSS N), each with seven items, and general psychopathology (PANSS G), with sixteen items. The total score on the scale is also evaluated (PANSS total).
A computer version 4 of the Wisconsin Card Sorting Test (WCST) was given to the patients in the remission of psychotic symptoms, after 8 weeks of hospitalization. We analyzed all the domains of the WCST, but only a percentage (%) of errors, perseverative responses, perseverative errors, nonperseverative errors, and conceptual level responses are presented in the article [32].
2.3. Lipid Profile
The fasting blood lipid profile, including low-density lipoproteins (LDLs), high-density lipoproteins (HDLs), and triglycerides (TGs), were measured at admission to the psychiatric ward (T0), and after 8 weeks of treatment (T8) using standard laboratory procedures, on a Beckman Coulter AU 680 biochemistry analyzer (Beckman Coulter, Inc., Brea, CA, USA). The Polish lipid norm cut-offs are LDL < 115 mg/dL, HDL > 50 mg/dL, and TG < 150 mg/dL.
2.4. Statistical Analyses
The Kolmogorov–Smirnov and Shapiro–Wilk tests were used to test the normality of the data. Most of the data showed non-normal distribution, thus non-parametric statistical tests were applied in the analyses, including the Mann–Whitney U-test, Wilcoxon test, and Spearman’s correlation. The statistical significance level was set at p < 0.05. Statistical analyses were conducted in Statistica v13 software.
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Characteristic
We enrolled 52 women (mean age, 32.96 (±10.90) years) diagnosed with schizophrenia in this study, with a mean age at onset of 24.85 (±6.50) years and a mean illness duration of 8.12 (±8.69) years. In our group, patients with recent onset (≤5 years) schizophrenia constituted 58% (n = 30), while the chronic (>5 years) schizophrenia group was represented by 42% (n = 22) patients. Pharmacological treatment was as follows: three patients (n = 3) were medicated exclusively with a typical antipsychotic (haloperidol), and two of them with adjuvant benzodiazepines. Fourteen participants (n = 14) were treated with a typical antipsychotic (haloperidol) with adjuvant atypical neuroleptics: olanzapine (n = 7), clozapine (n = 4), ziprasidone (n = 2), risperidone (n = 2), and aripiprazole (n = 1). Other patients were treated with atypical neuroleptics: olanzapine (n = 15), clozapine (n = 9), aripiprazole (n = 6), amisulpride (n = 4), ziprasidone (n = 3), risperidone (n = 3), and quetiapine (n = 1). Additionally, benzodiazepines (n = 16) and antidepressants (n = 12) were administered to the patients. Demographic and clinical characteristics of the participants are presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
Clinical characterization and lipid profile of the study group.
3.2. Changes in Severity of Schizophrenia Symptoms, Lipid Profile, and Weight during Eight Weeks of Treatment
We observed a significant decrease in all subscales of the PANSS after eight weeks of treatment (PANSS P p < 0.001, PANSS N p < 0.001, PANSS G p < 0.001, and PANSS total p < 0.001). The serum levels of LDL (p = 0.02) and TG (p = 0.002) increased during eight weeks of treatment. We did not detect differences in serum HDL (p = 0.074) concentrations during eight weeks of hospitalization. We detected a significant increase in weight (p < 0.001) during eight weeks of treatment; however, weight gain during treatment did not exceed the BMI norms in patients with BMI ≥ 25.
3.3. Comparisons of Wisconsin Card Sorting Test (WCST) Results, Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS), and Lipid Profile with Regard to Disease Onset (Recent (≤5 years) vs. Chronic (>5 Years)
During our research, we divided our patients into two groups: recent onset with the duration of the disease ≤5 years, and chronic, who suffered from schizophrenia for longer than five years. We have compared the result of the WCTS of those two fractions and found significant differences in the following psychometric scores: total correct (p = 0.003), % perseverative errors (p = 0.039), and failure to maintain set (p = 0.044). We did not find significant differences in the PANSS at T0 and T8, as well as lipids LDL, HDL, and TG at T0 and T8 when comparing recent onset vs. chronic patients diagnosed with schizophrenia. The results are presented in Table 2.

Table 2.
Comparisons of Wisconsin Card Sorting Test (WCST) results, Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS), and lipid profile with regard to disease onset (recent (≤5 years) vs. chronic (>5 years)).
3.4. Comparisons of Wisconsin Card Sorting Test (WCST) Results and Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS) with Regard to LDL, HDL, and TG Concentrations (Normal vs. beyond the Norm)
We detected significant differences in WCST results concerning HDL levels: normal levels of HDL corresponded to lower scores of trials administered (p = 0.012), % errors (p = 0.007), % perseverative errors (p = 0.007), and % nonperseverative errors (p = 0.004). Higher scores in % conceptual responses (p = 0.008) and categories completed (p = 0.007) were also noticed in patients with normal HDL levels, while a lower-than-average HDL level was associated with lower scores in these two domains of the WSCT. In our study, patients with higher PANSS negative scores at T8 had low HDL levels (p = 0.035). We found no differences in WCST and PANSS scores concerning LDL and TG concentrations. Results are presented in Table 3.

Table 3.
Analysis of Wisconsin Card Sorting Test results and PANSS T8 scores with regard to high-density lipoprotein (HDL) levels (normal vs. low).
3.5. Comparisons of Wisconsin Card Sorting Test (WCST) Results with Regard to Pharmacological Treatment and Smoking Status
Comparing groups of patients treated with clozapine vs. olanzapine we did not reveal any significant differences in WCST performance: trials administered (Z = 1.19, p = 0.23), total correct (Z = 0.7, p = 48), % errors (Z = 0.81, p = 0.42), % perseverative responses (Z = 0.97, p = 0.33), % perseverative errors (Z = 1.06, p = 0.28), % nonperseverative errors (Z = 0.56, p = 0.58), % conceptual level responses (Z = −0.92, p = 0.36), categories completed (Z = −49, p = 0.62), trials to complete 1st category (Z = 0.32, p = 0.75), failure to maintain set (Z = 0.07, p = 0.95), and learning to learn (Z = −0.32, p = 0.75).
We also did not detect differences in WCST performance with regard to haloperidol, benzodiazepines, nor antidepressants.
Non-smoking patients had a significantly lower % of nonperseverative errors (p = 0.022) as well as a higher % of conceptual level responses (p = 0.049) compared to smoking patients.
The results are presented in Supplementary Table S1.
3.6. Spearman’s Correlation of Wisconsin Card Sorting Test (WCST) Results with Clinical Variables and Lipid Profile
3.6.1. Correlations between Scores on Wisconsin Card Sorting Test (WCST) and Lipid Serum Levels
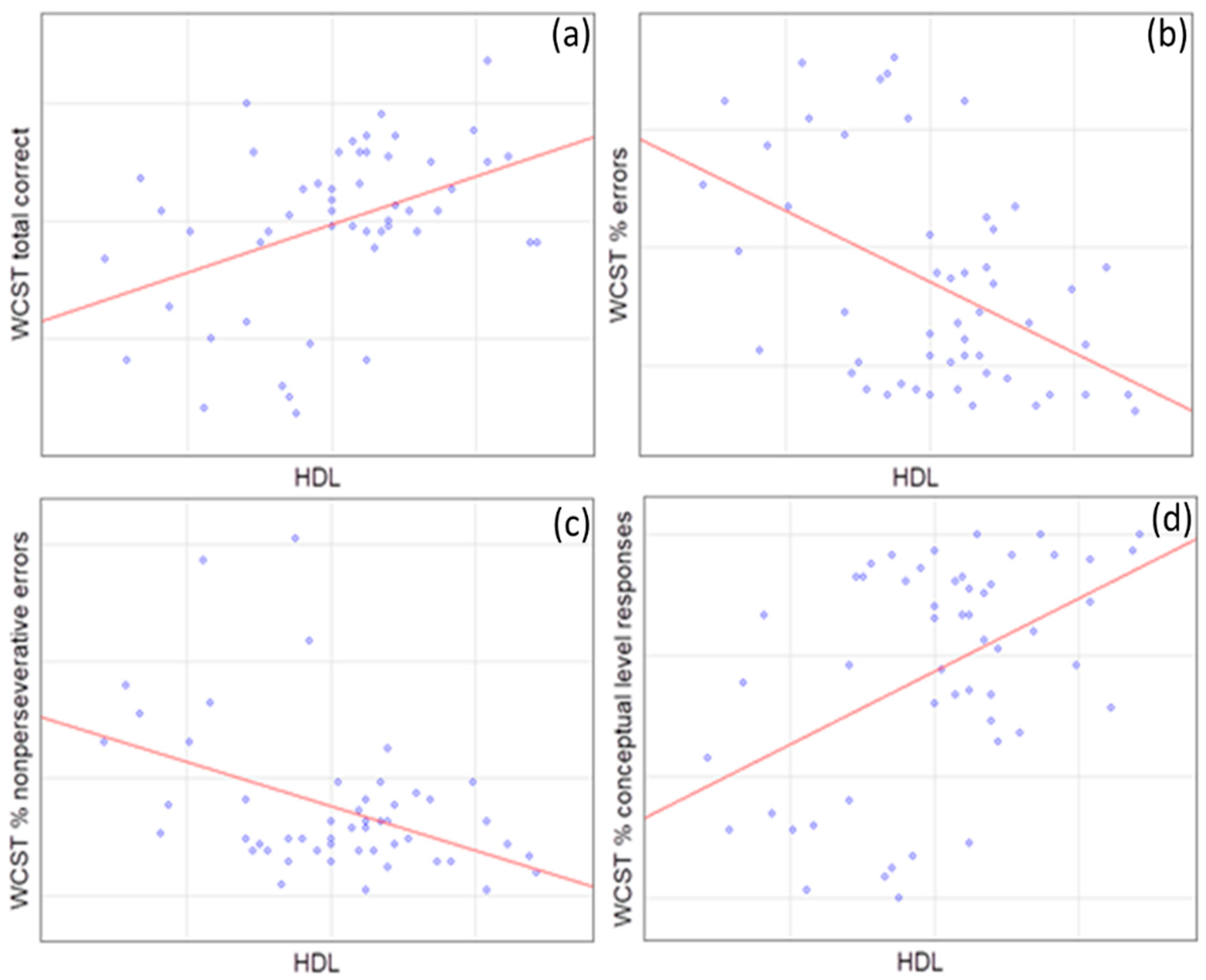
In accordance with our findings, HDL levels corresponded positively to the WCST total correct score (p = 0.005), as well as the % of conceptual level responses (p = 0.003) and WCST categories completed (p = 0.015), contrary to the % of errors (p = 0.002), the % of nonperseverative errors (p = 0.017), and WCST trials to complete the 1st category (p = 0.016) to which it corresponds negatively (Figure 1).
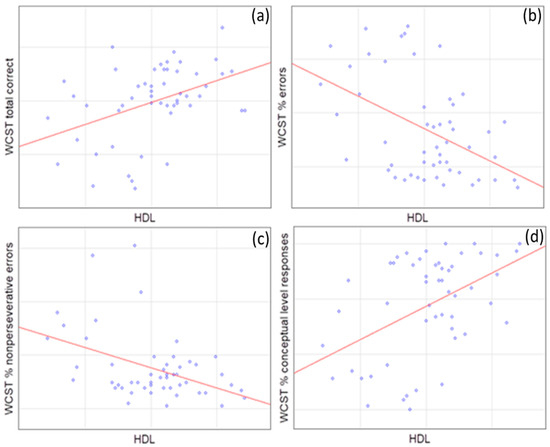
Figure 1.
Spearman’s correlations of WCST domains with high-density lipoprotein (HDL) levels. (a) WCST total correct (R = 0.38, p = 0.005); (b) WCST % errors (R = −0.40, p = 0.002); (c) WCST % nonpersererative errors (R = −0.33, p = 0.017); and (d) WCST % conceptual level responses (R = 0.41, p = 0.003).
LDL levels and WCST learning-to-learn score (p = 0.038) were significantly positively correlated. There was no other association between LDL levels and the WCTS, which was statistically significant. Triglycerides (TGs) showed a weak positive correlation with the % of nonperseverative errors (p = 0.047). Our research shows no other influence of TG serum levels on cognitive scoring.
3.6.2. Correlations between Scores of Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS) and Lipid Serum Levels
The only notable correspondence detected was between negative symptoms PANSS N at T8 and HDL levels (p = 0.03). We did not identify any significant links between the severity of positive symptoms, the score of the general psychopathology subscale, or the total score on the PANSS test with lipid serum levels.
3.6.3. Correlations between Scores on Wisconsin Card Sorting Test (WCST) and Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS)
Our results show no significant correlation between the severity of schizophrenia symptoms at the beginning of the study (T0) measured with the PANSS scale, PANSS total, PANSS P, PANSS N, and PANSS G, and cognitive functioning after eight weeks of treatment. The apparent associations were detected while comparing PANSS scores obtained at the eight weeks of treatment. We found correlations of WCST results with the severity of negative symptoms (PANSS N) at T8. The higher the score on PANSS N (T8), the more errors the patients made. A significant positive correlation was found with WCST trials administered (p = 0.006), the % of total errors (p = 0.004), the % of perseverative errors (p = 0.043), and the % of nonperseverative errors (p = 0.014). A PANSS N score (T8) was negatively associated with the WCST % of conceptual level responses (p = 0.005) and categories completed (p = 0.024).
We found the general psychopathology subscale of PANSS G at T8 to be positively correlated with the total % of errors made on the WCST (p = 0.027), in contrast to the WCST % of conceptual level responses, which was negatively correlated with a PANSS G score (T8) (p = 0.384). Positive symptoms (PANSS P at T8) significantly influence WCST failure to maintain set (p = 0.013) and the % of nonperseverative errors (p = 0.039). A high total score on the PANSS correlated to the severity of cognitive impairment, which was apparent in its positive association between the WCST % of nonperseverative errors (p = 0.047).
3.6.4. Correlations between Scores on Wisconsin Card Sorting Test (WCST), PANSS (T8), and Lipid Profile with Age, Age of Onset, and Illness Duration
We found the patient’s age to be a significant variable in scores of cognitive functioning tests. Our research exhibited a positive correlation between age and the % of errors (p = 0.036). This is in contrast to the negative connotation between age and a WCTS total correct score (p = 0.0004) and conceptual level response (p = 0.0009), in addition to categories completed (p = 0.037).
The most significant results were noted while comparing the impact of illness duration on cognitive functioning. The scores on the WCST most impaired by the continuing span of the disease were trials administered (p = 0.033), the % of error (p = 0.002), the % of perseverative responses (p = 0.014), the % of perseverative errors (p = 0.008), as well as the % of nonperseverative errors (p = 0.042). Moreover, negatively correlated with illness duration, WCST psychometric scores were the total correct (p = 0.007), the % of conceptual level responses (p = 0.003), in addition to categories completed (p = 0.003).
We did not detect any notable correlations between the age of onset of schizophrenia and cognitive impairment in the tested sample.
We did not detect any correlations between PANSS scores, low-density lipoprotein (LDL), high-density lipoprotein (HDL), and triglyceride (TG) levels either at T0 or at T8, with age, age at onset, or illness duration.
4. Discussion
Our study’s main focus was to determine the correlation between lipid serum levels and cognitive functioning in schizophrenic patients. The available literature presents inconsistent findings in this area of research.
HDL serum levels have been researched in association with cognitive functioning for many years. For example, experiments on animal models of Alzheimer’s disease have proven HDL to be a protective factor of cognition [33,34]. Exploration was also conducted on a healthy population of subjects when it comes to the impact of HDL on cognitive functioning. According to many published researchers, high-density cholesterol serum levels may be treated as a protective factor against cognitive decline [35,36,37,38]. In Azheimer’s disease, HDL levels are lowered, which corresponds to a decrease in MMSE results [39,40]. Whereas, according to the findings of Mehdi et al. (2024), depressive symptoms influenced the protective character of HDL on memory function, thus leading to a worsening of cognitive functions in patients with diagnosed depression [41]. In their paper, Jia et al. (2020) present a positive correlation between HDL levels and cognitive functioning [42]. Furthermore, low serum levels of HDL in bipolar patients corresponded to cognitive deficits [43].
According to our results, higher HDL levels correspond to better cognitive functioning in patients with schizophrenia. Similar findings were reported by Lindenmayer et al. (2012) [44], in contrast to the paper by Liu et al. (2022) in which for the group of patients under 45 years of age, high levels of HDL corresponded to poorer cognition [45].
Other papers produce results of a strong positive correlation between total cholesterol serum levels and cognitive functioning [45,46,47]. The outcome of our research does not support that premise, similar to our conclusions published before [48,49].
Triglyceride serum levels significantly contributed to cognitive functioning in previously published papers [47,48] as a protective factor. Our results cannot support that hypothesis because a significant positive correlation between TG levels was only detected in relation to WCST nonperseverative errors, which did not remain significant after considering laboratory norms of TG serum levels.
The important role of lipids in the pathology underlying schizophrenia and the cognitive impairment that goes with it may be explained by more than one hypothesis. Cholesterol levels can influence the activity of neurotransmitters in the brain. According to Dufour et al. (2006), low cholesterol levels impair glutaminergic synaptic functioning in the hippocampus [21], which is a part of the brain of great importance in short-term memory processing [50]. Decreased cholesterol may also reduce serotonin activity in the brain, influencing the number of serotonin transporters and receptors [51]. Another notifiable theory is the correlation between increased total cholesterol serum levels and increased brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in the population of schizophrenic patients [52], which was found to play a role in cognitive impairment [53,54]. Some researchers propose serum cholesterol levels as a representative marker for polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), which take part in synthesizing neurotransmitters and are involved in neuron membrane formation, thus explaining the correlation between cognitive functioning and cholesterol [55].
The progressive character of cognitive decline of schizophrenia patients has been widely reported throughout time [48,56,57,58]. Our study supports this premise. Illness duration was significantly positively correlated with the number of WCST trials administered, including total amount of error, percentage of error, number and percentage of perseverative response, number and percentage of perseverative errors, and percentage of nonperseverative errors. At the same time, it negatively correlated with the WCST total correct score, and the number and percentage of conceptual level responses, in addition to categories completed. Banno et al. (2012) found a similar association using WCST as a measuring tool for cognitive functioning [58]. We divided our group into two sub-groups depending on the duration of illness: recent onset, with the duration of the disease less than five years, and chronic, who suffered from schizophrenia for longer than five years. We compared the result of the WCTS of those two fractions and found significant associations in the following psychometric scores: total correct, number and percentage of errors, number and percentage of perseverative responses, number and percentage of perseverative errors, and conceptional level responses. However, not all the studies are in agreement with the progressive character of cognitive dysfunction in schizophrenia. Stratta et al. (2004) divided the group of schizophrenic patients into “good” and “poor” performers on the WCST and observed them throughout the years. The results of the sub-group of “poor performers” did not indicate the deteriorating character of schizophrenia. Meanwhile, “good performers” improved their WCST scores in the intermediate length-of-illness group (6–10 years of illness) and then declined in the third one (>10 years) [59].
The age factor on the WCTS result was significant—it was evident that the older patients are, the poorer their cognitive skills. Similar reports have been published before [48,53].
However, the age of onset of schizophrenia was not shown as a risk factor for cognitive deterioration in our study, supporting results presented by Banno et al. (2012) [58]. Our findings differ from those of Bellino et al. (2004) [60].
Our sample consisted only of women. However, the role of gender in the cognitive functioning of patients with schizophrenia remains unclear. Female patients with schizophrenia were found to score worse than males in reasoning, working memory, and problem-solving, according to Pérez-Garza et al. (2016) [61] and Peng et al. (2021) [62]. Their results contrast with the data presented by Zhang et al. (2017) [14].
The negative symptoms themselves are associated with cognitive dysfunction. During our research, we also compared the scores of the PANSS and WCST. Our findings are in accordance with Mellilo et al. (2023), who, in their published systematic review, revealed a significant connection between the severity of negative symptoms and cognitive functioning [63].
Even though for many years, the positive symptoms of schizophrenia were the main aim of the pharmacological industry, as far as the cognitive functions are concerned, many of the studies prove no significant correlation between them [64,65,66,67]. Our results support their conclusions. However, such a premise is not validated by the paper by Ruiz-Castanera et al. (2023), which states that positive symptoms influence cognitive and emotional functions [68].
Correlation between negative symptoms and serum lipid levels was also evident in some previous studies. We found two different significant associations between a PANSS N score and lipid levels. The total cholesterol level was negatively correlated with the severity of negative symptoms at the beginning of the experiment, and a lower HDL level was indicative of more prominent negative symptoms at the 8th week of testing. Kim et al. (2019) found a similar correlation between HDL and PANSS negative subscale results [69]. Our result is partially in alliance with Goldsmith et al. (2021) results, which detected a significant connection between a PANSS negative subscale score and total cholesterol levels as well as LDLs [70].
In our study, we did not reveal any differences in WCST scores concerning antipsychotic treatment, possibly due to a naturalistic approach, treating patients with different antipsychotics, often not in monotherapy, and with adjuvant other pharmacological agents, such as benzodiazepines and antidepressants patient groups. A short (8 weeks) clinical observation could also influence the obtained results. The effect of antipsychotics on cognitive functioning in schizophrenia is not well understood. Antipsychotics may partially improve cognitive functioning, and this improvement may vary depending on the class of the antipsychotic agent, and the specific cognitive domain. There is a large amount of research on the effect of first- and second-generation antipsychotics on cognitive functions in schizophrenia. However, results from the Clinical Antipsychotic Trials of Intervention Effectiveness (CATIE) study indicated that antipsychotics are very similar in their action across chemical classes, and the effect size for improvement in cognition was small, with questionable clinical significance [71].
Limitations
There are several limitations in the generalizability of our results. Firstly, the size of our sample was relatively small, and the sample itself was homogenous in terms of gender (only women were recruited for this study). Secondly, there was a lack of an age-matched control group. Furthermore, the patients were treated with various antipsychotic agents, which might have influenced the results. In addition, we only used the WCTS as a measurement for cognitive functioning; in the future, the use of standardized batteries of tests (e.g., MATRICS) might enable more accurate cross-study comparisons.
5. Conclusions
In summary, our research found a significant correlation between cognitive functioning, lipid serum levels, and biomedical variables in schizophrenic patients. Our results suggest a high HDL level might be considered a protective factor against cognitive impairment. In contrast to other studies, we found no correlation between total cholesterol serum levels and cognitive impairment. The influences of age and illness duration also played a vital role in cognitive performance. While taking into consideration our findings, the severity of negative symptoms seemed to strongly influence the cognitive performance of schizophrenic patients, whereas positive symptoms were not proven to be a significant factor in cognitive test results. We are aware that these results should be interpreted with caution due to the limitations of our study. However, our results seem promising for further studies conducted with larger samples, which should further explore the potential influence of serum cholesterol levels, especially HDL levels, and biomedical factors on the cognitive functioning of patients suffering from schizophrenia.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/brainsci14070699/s1, Table S1: WCST performance with regard to pharmacological treatment.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.S. (Maria Skibinska); methodology, M.S. (Maria Skibinska), P.K. and A.R.-R.; software, M.S. (Maria Skibinska); validation, M.S. (Maria Skibinska) and M.S. (Maria Staniek); formal analysis, M.S. (Maria Skibinska); investigation, M.S. (Maria Staniek), P.K., P.Z. and A.R.-R.; resources, M.S. (Maria Skibinska), P.Z. and K.W.-P.; data curation, M.S. (Maria Skibinska); writing—original draft preparation, M.S. (Maria Staniek); writing—review and editing, M.S. (Maria Skibinska); visualization, M.S. (Maria Skibinska) and K.W.-P.; supervision, M.S. (Maria Skibinska); project administration, M.S. (Maria Skibinska); funding acquisition, M.S. (Maria Skibinska). All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Polish Ministry of Sciences and Education, grant number NN402243635 and statute sources: 502-20-22196440.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Ethics Committee of Poznan University of Medical Sciences, Poland (no 266/08, date of approval 3 April 2008).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Materials, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our gratitude to Karolina Bilska, Maciej Rozanski, and Dorota Zaremba for their technical assistance.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Saha, S.; Chant, D.; Welham, J.; McGrath, J. A Systematic Review of the Prevalence of Schizophrenia. PLoS Med. 2005, 2, e141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solmi, M.; Seitidis, G.; Mavridis, D.; Correll, C.U.; Dragioti, E.; Guimond, S.; Tuominen, L.; Dargél, A.; Carvalho, A.F.; Fornaro, M.; et al. Incidence, Prevalence, and Global Burden of Schizophrenia—Data, with Critical Appraisal, from the Global Burden of Disease (GBD) 2019. Mol. Psychiatry 2023, 28, 5319–5327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, M.F.; Kern, R.S.; Braff, D.L.; Mintz, J. Neurocognitive Deficits and Functional Outcome in Schizophrenia: Are We Measuring the “Right Stuff”? Schizophr. Bull. 2000, 26, 119–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fett, A.-K.J.; Viechtbauer, W.; Dominguez, M.-G.; Penn, D.L.; van Os, J.; Krabbendam, L. The Relationship between Neurocognition and Social Cognition with Functional Outcomes in Schizophrenia: A Meta-Analysis. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2011, 35, 573–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuechterlein, K.H.; Ventura, J.; Subotnik, K.L.; Bartzokis, G. The Early Longitudinal Course of Cognitive Deficits in Schizophrenia. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2014, 75, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, A.; Kar, S.K.; Shukla, R. Cognitive Deficits in Schizophrenia: Understanding the Biological Correlates and Remediation Strategies. Clin. Psychopharmacol. Neurosci. 2018, 16, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasrallah, H.A. Linkage of Cognitive Impairments With Metabolic Disorders in Schizophrenia. Am. J. Psychiatry 2010, 167, 1155–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorostiaga, A.; Balluerka, N.; Guilera, G.; Aliri, J.; Barrios, M. Functioning in Patients with Schizophrenia: A Systematic Review of the Literature Using the International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health (ICF) as a Reference. Qual. Life Res. 2017, 26, 531–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, P.D.; Strassing, M. Predicting the Severity of Everyday Functional Disability in People with Schizophrenia: Cognitive Deficits, Functional Capacity, Symptoms, and Health Status. World Psychiatry 2012, 11, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, A.; Poursharifi, H.; Dolatshahi, B.; Rezaee, O.; Hassanabadi, H.R.; Naeem, F. The Cognitive Model of Negative Symptoms in Schizophrenia: A Hierarchical Component Model With PLS-SEM. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 707291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesholam-Gately, R.I.; Giuliano, A.J.; Goff, K.P.; Faraone, S.V.; Seidman, L.J. Neurocognition in First-Episode Schizophrenia: A Meta-Analytic Review. Neuropsychology 2009, 23, 315–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.F.; Wang, Y.P.; Zhang, P.F.; Yuan, X.X.; Zhu, Q.Y.; Li, X.; Pang, L.J.; Li, H.; Song, X.Q. Correlation of serum level of homocysteine and insulin resistance with cognitive dysfunction in first-episode schizophrenics. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 2018, 98, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiu, M.-H.; Wang, D.; Chen, S.; Du, X.-D.; Chen, D.-C.; Chen, N.; Wang, Y.-C.; Yin, G.; Zhang, Y.; Tan, Y.-L.; et al. Interleukin-3, Symptoms and Cognitive Deficits in First-Episode Drug-Naïve and Chronic Medicated Schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res. 2018, 263, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Han, M.; Tan, S.; De Yang, F.; Tan, Y.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, X.; Huang, X.-F. Gender Differences Measured by the MATRICS Consensus Cognitive Battery in Chronic Schizophrenia Patients. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, P.; Murray, R.; Jones, P.; Rodgers, B.; Marmot, M. Child Developmental Risk Factors for Adult Schizophrenia in the British 1946 Birth Cohort. Lancet 1994, 344, 1398–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloemen, O.J.N.; de Koning, M.B.; Schmitz, N.; Nieman, D.H.; Becker, H.E.; de Haan, L.; Dingemans, P.; Linszen, D.H.; van Amelsvoort, T.A.M.J. White-Matter Markers for Psychosis in a Prospective Ultra-High-Risk Cohort. Psychol. Med. 2010, 40, 1297–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Björkhem, I.; Meaney, S. Brain Cholesterol: Long Secret Life behind a Barrier. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2004, 24, 806–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoknecht, P.A.; Ebner, S.; Pond, W.G.; Zhang, S.; McWhinney, V.; Wong, W.W.; Klein, P.D.; Dudley, M.; Goddard-Finegold, J.; Mersmann, H.J. Dietary Cholesterol Supplementation Improves Growth and Behavioral Response of Pigs Selected for Genetically High and Low Serum Cholesterol. J. Nutr. 1994, 124, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, Y.; Nishimura, J.-I.; Kimura, F. Impairment of Maze Learning in Rats Following Long-Term Glucocorticoid Treatments. Neurosci. Lett. 1996, 203, 199–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, W.T.; Xu, G.; Batta, A.; Tint, G.S.; Salen, G.; Dyer, C.A.; Kendler, A.; Servatius, R.J. Developmental Sensitivity of Associative Learning to Cholesterol Synthesis Inhibitors. Behav. Brain Res. 2002, 129, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufour, F.; Liu, Q.-Y.; Gusev, P.; Alkon, D.; Atzori, M. Cholesterol-Enriched Diet Affects Spatial Learning and Synaptic Function in Hippocampal Synapses. Brain Res. 2006, 1103, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreurs, B.G.; Smith-Bell, C.A.; Darwish, D.S.; Wang, D.; Burhans, L.B.; Gonzales-Joekes, J.; Deci, S.; Stankovic, G.; Sparks, D.L. Cholesterol Enhances Classical Conditioning of the Rabbit Heart Rate Response. Behav. Brain Res. 2007, 181, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Elias, P.K.; Elias, M.F.; D’Agostino, R.B.; Sullivan, L.M.; Wolf, P.A. Serum Cholesterol and Cognitive Performance in the Framingham Heart Study. Psychosom. Med. 2005, 67, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muldoon, M.F.; Barger, S.D.; Ryan, C.M.; Flory, J.D.; Lehoczky, J.P.; Matthews, K.A.; Manuck, S.B. Effects of Lovastatin on Cognitive Function and Psychological Well-Being. Am. J. Med. 2000, 108, 538–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wardle, J.; Rogers, P.; Judd, P.; Taylor, M.A.; Rapoport, L.; Green, M.; Nicholson Perry, K. Randomized Trial of the Effects of Cholesterol-Lowering Dietary Treatment on Psychological Function. Am. J. Med. 2000, 108, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anstey, K.J.; Lipnicki, D.M.; Low, L.-F. Cholesterol as a Risk Factor for Dementia and Cognitive Decline: A Systematic Review of Prospective Studies With Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2008, 16, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okusaga, O.; Stewart, M.C.W.; Butcher, I.; Deary, I.; Fowkes, F.G.R.; Price, J.F. Smoking, Hypercholesterolaemia and Hypertension as Risk Factors for Cognitive Impairment in Older Adults. Age Ageing 2013, 42, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, P.D.; Bosia, M.; Cavallaro, R.; Howes, O.D.; Kahn, R.S.; Leucht, S.; Müller, D.R.; Penadés, R.; Vita, A. Cognitive Dysfunction in Schizophrenia: An Expert Group Paper on the Current State of the Art. Schizophr. Res. Cogn. 2022, 29, 100249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- First, M.B.; Gibbon, M. The Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV Axis I Disorders (SCID-I) and the Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV Axis II Disorders (SCID-II). In Comprehensive Handbook of Psychological Assessment, Vol. 2: Personality Assessment; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004; pp. 134–143. ISBN 978-0-471-41612-8. [Google Scholar]
- McGuffin, P.; Farmer, A.; Harvey, I. A Polydiagnostic Application of Operational Criteria in Studies of Psychotic Illness: Development and Reliability of the OPCRIT System. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1991, 48, 764–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kay, S.R.; Opler, L.A.; Lindenmayer, J.-P. The Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS): Rationale and Standardisation. Br. J. Psychiatry 1989, 155, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heaton, R.K. Wisconsin Card Sorting Test (WCST); Revised and Expanded; Psychological Assessment Resources: Odessa, FL, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Button, E.B.; Robert, J.; Caffrey, T.M.; Fan, J.; Zhao, W.; Wellington, C.L. HDL from an Alzheimer’s Disease Perspective. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2019, 30, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, T.L.; Cao, D.; Lu, H.; Mans, R.A.; Su, Y.R.; Jungbauer, L.; Linton, M.F.; Fazio, S.; LaDu, M.J.; Li, L. Overexpression of Human Apolipoprotein A-I Preserves Cognitive Function and Attenuates Neuroinflammation and Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer Disease. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 36958–36968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, N.M.; An, Y.; Beason-Held, L.; Doshi, J.; Erus, G.; Ferrucci, L.; Davatzikos, C.; Resnick, S.M. Predictors of Neurodegeneration Differ. between Cognitively Normal and Subsequently Impaired Older Adults. Neurobiol. Aging 2019, 75, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chanti-Ketterl, M.; Andel, R.; Lerch, O.; Laczo, J.; Hort, J. Cholesterol and Cognitive Performance among Community Volunteers from the Czech Republic. Int. Psychogeriatr. 2015, 27, 2087–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crichton, G.E.; Elias, M.F.; Davey, A.; Sullivan, K.J.; Robbins, M.A. Higher HDL Cholesterol Is Associated with Better Cognitive Function: The Maine-Syracuse Study. J. Int. Neuropsychol. Soc. 2014, 20, 961–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh-Manoux, A.; Gimeno, D.; Kivimaki, M.; Brunner, E.; Marmot, M.G. Low HDL Cholesterol Is a Risk Factor for Deficit and Decline in Memory in Midlife: The Whitehall II Study. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2008, 28, 1556–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merched, A.; Xia, Y.; Visvikis, S.; Serot, J.M.; Siest, G. Decreased High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol and Serum Apolipoprotein AI Concentrations Are Highly Correlated with the Severity of Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2000, 21, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, Y.-H.; Tsai, K.-J.; Lee, C.-W.; Shiesh, S.-C.; Chen, W.-T.; Pai, M.-C.; Kuo, Y.-M. Apolipoprotein C-III Is an Amyloid-β-Binding Protein and an Early Marker for Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2014, 41, 855–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdi, S.M.A.; Costa, A.P.; Svob, C.; Pan, L.; Dartora, W.J.; Talati, A.; Gameroff, M.J.; Wickramaratne, P.J.; Weissman, M.M.; McIntire, L.B.J. Depression and Cognition Are Associated with Lipid Dysregulation in Both a Multigenerational Study of Depression and the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Transl. Psychiatry 2024, 14, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Q.; Yang, H.; Zhuang, N.; Yin, X.; Zhu, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Yin, X.; Wang, Y.; Cheung, E.F.C.; Chan, R.C.K.; et al. The Role of Lipoprotein Profile in Depression and Cognitive Performance: A Network Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, L.; Yin, X.L.; Chen, J.; Yin, X.Y.; Zhu, H.L.; Li, J.; Yin, G.Z.; Xu, X.W.; Yang, X.N.; Qian, Z.K.; et al. Association between Decreased HDL Levels and Cognitive Deficits in Patients with Bipolar Disorder: A Pilot Study. Int. J. Bipolar Disord. 2019, 7, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindenmayer, J.P.; Khan, A.; Kaushik, S.; Thanju, A.; Praveen, R.; Hoffman, L.; Cherath, L.; Valdez, G.; Wance, D. Relationship between Metabolic Syndrome and Cognition in Patients with Schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2012, 142, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, X.; He, Y.; Gu, S.; Mo, D.; Wang, S.; Yuan, Z.; Huang, Y.; Zhong, Q.; et al. Association between Lipid Metabolism and Cognitive Function in Patients with Schizophrenia. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 1013698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krakowski, M.; Czobor, P. Cholesterol and Cognition in Schizophrenia: A Double-Blind Study of Patients Randomized to Clozapine, Olanzapine and Haloperidol. Schizophr. Res. 2011, 130, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Ye, X.; Wang, X.; Lin, Y.; Zhu, C.; Pan, J.; Yin, X.; Ye, M.; Lv, W.; Tang, W.; et al. Serum Total Cholesterol Levels Associated with Immediate Memory Performance in Patients with Chronic Schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2023, 255, 256–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.; Fan, K.-L.; Zhao, S.-Z.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; Li, Y.; Shao, S.-M.; Wang, Z.; Ke, J.-Q. Correlations between Age, Biomedical Variables, and Cognition in Patients with Schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. Cogn. 2020, 22, 100182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagi, K.; Nosaka, T.; Dickinson, D.; Lindenmayer, J.P.; Lee, J.; Friedman, J.; Boyer, L.; Han, M.; Abdul-Rashid, N.A.; Correll, C.U. Association Between Cardiovascular Risk Factors and Cognitive Impairment in People With Schizophrenia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JAMA Psychiatry 2021, 78, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busquets-Garcia, A.; Gomis-González, M.; Salgado-Mendialdúa, V.; Galera-López, L.; Puighermanal, E.; Martín-García, E.; Maldonado, R.; Ozaita, A. Hippocampal Protein Kinase C Signaling Mediates the Short-Term Memory Impairment Induced by Delta9-Tetrahydrocannabinol. Neuropsychopharmacology 2018, 43, 1021–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelberg, H. Low Serum Cholesterol and Suicide. Lancet 1992, 339, 727–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skibinska, M.; Kapelski, P.; Rajewska-Rager, A.; Szczepankiewicz, A.; Narozna, B.; Duda, J.; Budzinski, B.; Twarowska-Hauser, J.; Dmitrzak-Weglarz, M.; Pawlak, J. Elevated Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) Serum Levels in an Acute Episode of Schizophrenia in Polish Women: Correlation with Clinical and Metabolic Parameters. Psychiatry Res. 2019, 271, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atake, K.; Nakamura, T.; Ueda, N.; Hori, H.; Katsuki, A.; Yoshimura, R. The Impact of Aging, Psychotic Symptoms, Medication, and Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor on Cognitive Impairment in Japanese Chronic Schizophrenia Patients. Front. Psychiatry 2018, 9, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heitz, U.; Papmeyer, M.; Studerus, E.; Egloff, L.; Ittig, S.; Andreou, C.; Vogel, T.; Borgwardt, S.; Graf, M.; Eckert, A.; et al. Plasma and Serum Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) Levels and Their Association with Neurocognition in at-Risk Mental State, First Episode Psychosis and Chronic Schizophrenia Patients. World J. Biol. Psychiatry 2019, 20, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hibbeln, J.R.; Umhau, J.C.; George, D.T.; Shoaf, S.E.; Linnoila, M.; Salem, N. Plasma Total Cholesterol Concentrations Do Not Predict Cerebrospinal Fluid Neurotransmitter Metabolites: Implications for the Biophysical Role of Highly Unsaturated Fatty Acids. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2000, 71, 331S–338S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilder, R.M.; Lipschutz-Broch, L.; Reiter, G.; Geisler, S.H.; Mayerhoff, D.I.; Lieberman, J.A. Intellectual Deficits in First-Episode Schizophrenia: Evidence for Progressive Deterioration. Schizophr. Bull. 1992, 18, 437–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biagianti, B.; Fisher, M.; Howard, L.; Rowlands, A.; Vinogradov, S.; Woolley, J. Feasibility and Preliminary Efficacy of Remotely Delivering Cognitive Training to People with Schizophrenia Using Tablets. Schizophr. Res. Cogn. 2017, 10, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banno, M.; Koide, T.; Aleksic, B.; Okada, T.; Kikuchi, T.; Kohmura, K.; Adachi, Y.; Kawano, N.; Iidaka, T.; Ozaki, N. Wisconsin Card Sorting Test Scores and Clinical and Sociodemographic Correlates in Schizophrenia: Multiple Logistic Regression Analysis. BMJ Open 2012, 2, e001340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stratta, P.; Arduini, L.; Daneluzzo, E.; Rinaldi, O.; di Genova, A.; Rossi, A. Relationship of Good and Poor Wisconsin Card Sorting Test Performance to Illness Duration in Schizophrenia: A Cross-Sectional Analysis. Psychiatry Res. 2004, 121, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellino, S.; Rocca, P.; Patria, L.; Marchiaro, L.; Rasetti, R.; Di Lorenzo, R.; Paradiso, E.; Bogetto, F. Relationships of Age at Onset with Clinical Features and Cognitive Functions in a Sample of Schizophrenia Patients. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2004, 65, 908–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Garza, R.; Victoria-Figueroa, G.; Ulloa-Flores, R.E. Sex Differences in Severity, Social Functioning, Adherence to Treatment, and Cognition of Adolescents with Schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. Treat. 2016, 2016, e1928747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.-J.; Hei, G.-R.; Li, R.-R.; Yang, Y.; Liu, C.-C.; Xiao, J.-M.; Long, Y.-J.; Shao, P.; Huang, J.; Zhao, J.-P.; et al. The Association Between Metabolic Disturbance and Cognitive Impairments in Early-Stage Schizophrenia. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2021, 14, 599720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melillo, A.; Caporusso, E.; Giordano, G.M.; Giuliani, L.; Pezzella, P.; Perrottelli, A.; Bucci, P.; Mucci, A.; Galderisi, S. Correlations between Negative Symptoms and Cognitive Deficits in Individuals at First Psychotic Episode or at High Risk of Psychosis: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 7095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heydebrand, G.; Weiser, M.; Rabinowitz, J.; Hoff, A.L.; DeLisi, L.E.; Csernansky, J.G. Correlates of Cognitive Deficits in First Episode Schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2004, 68, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, M.D.; Lysaker, P.H.; Milstein, R.M.; Beam-Goulet, J.L. Concurrent Validity of the Cognitive Component of Schizophrenia: Relationship of PANSS Scores to Neuropsychological Assessments. Psychiatry Res. 1994, 54, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharawala, S.; Hastedt, C.; Podhorna, J.; Shukla, H.; Kappelhoff, B.; Harvey, P.D. The Relationship between Cognition and Functioning in Schizophrenia: A Semi-Systematic Review. Schizophr. Res. Cogn. 2021, 27, 100217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaefer, J.; Giangrande, E.; Weinberger, D.R.; Dickinson, D. The Global Cognitive Impairment in Schizophrenia: Consistent over Decades and around the World. Schizophr. Res. 2013, 150, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Castañeda, P.; Santiago Molina, E.; Aguirre Loaiza, H.; Daza González, M.T. Positive Symptoms of Schizophrenia and Their Relationship with Cognitive and Emotional Executive Functions. Cogn. Res. Princ. Implic. 2022, 7, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.D.; Barr, A.M.; Fredrikson, D.H.; Honer, W.G.; Procyshyn, R.M. Association between Serum Lipids and Antipsychotic Response in Schizophrenia. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2019, 17, 852–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldsmith, D.R.; Massa, N.; Miller, B.J.; Miller, A.H.; Duncan, E. The Interaction of Lipids and Inflammatory Markers Predict Negative Symptom Severity in Patients with Schizophrenia. npj Schizophr. 2021, 7, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKenzie, N.E.; Kowalchuk, C.; Agarwal, S.M.; Costa-Dookhan, K.A.; Caravaggio, F.; Gerretsen, P.; Chintoh, A.; Remington, G.J.; Taylor, V.H.; Müeller, D.J.; et al. Antipsychotics, Metabolic Adverse Effects, and Cognitive Function in Schizophrenia. Front. Psychiatry 2018, 9, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).