The Role of the Thalamus in Nociception: Important but Forgotten
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Pain Transmission Pathway
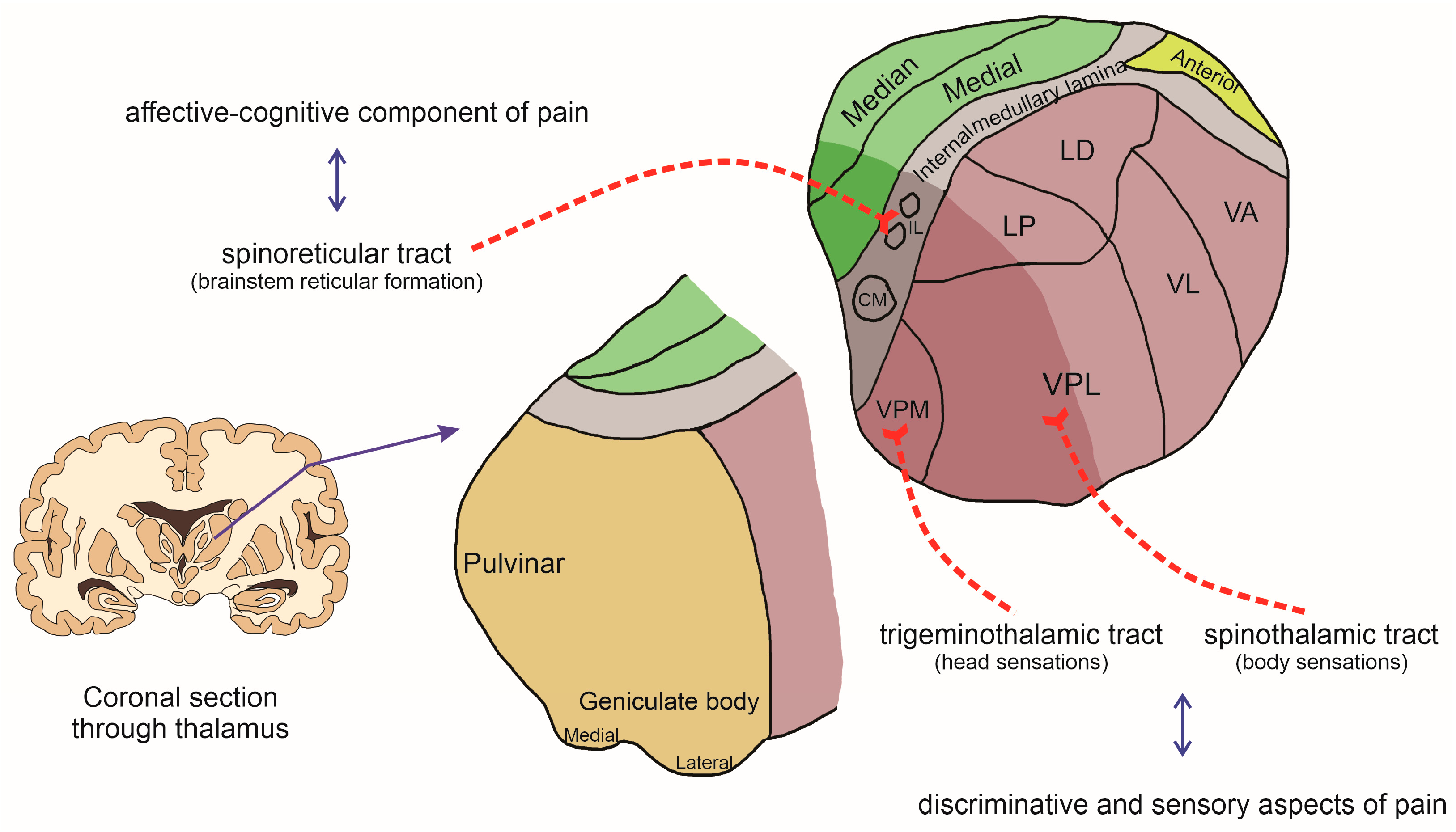
3. The Thalamus and Nociception
4. Chronic Pain and Central Pain Sensitization: Likely Involvement of the Thalamus
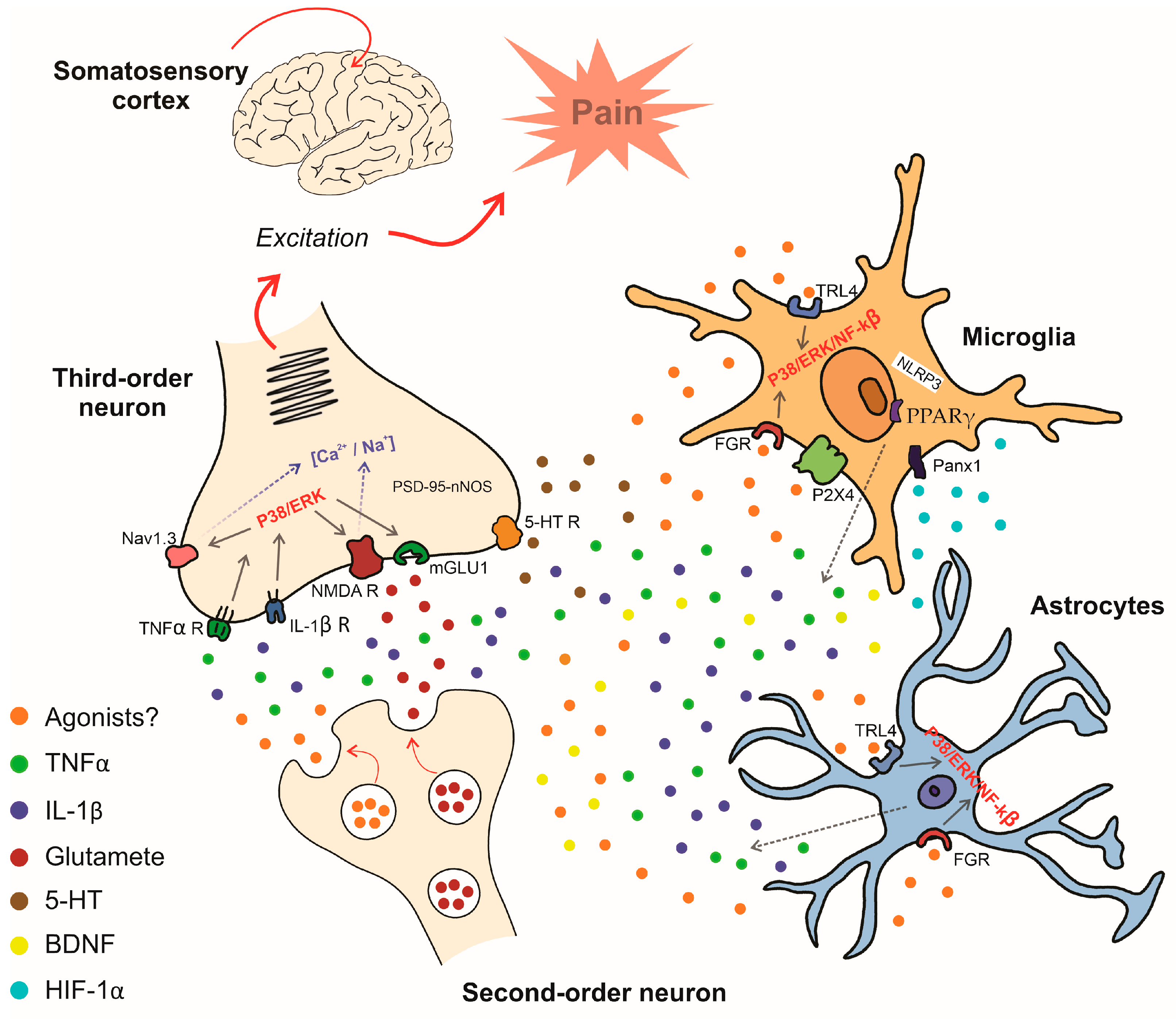
5. Mechanisms Involved in Central Pain Sensitization via Glial Cells
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Santiago, V. Painful Truth: The Need to Re-Center Chronic Pain on the Functional Role of Pain. J. Pain Res. 2022, 15, 497–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raja, S.N.; Carr, D.B.; Cohen, M.; Finnerup, N.B.; Flor, H.; Gibson, S.; Keefe, F.J.; Mogil, J.S.; Ringkamp, M.; Sluka, K.A.; et al. The Revised International Association for the Study of Pain Definition of Pain: Concepts, Challenges, and Compromises. Pain 2020, 161, 1976–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afridi, B.; Khan, H.; Akkol, E.K.; Aschner, M. Pain Perception and Management: Where Do We Stand? Curr. Mol. Pharmacol. 2021, 14, 678–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavalli, E.; Mammana, S.; Nicoletti, F.; Bramanti, P.; Mazzon, E. The Neuropathic Pain: An Overview of the Current Treatment and Future Therapeutic Approaches. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2019, 33, 2058738419838383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Hecke, O.; Austin, S.K.; Khan, R.A.; Smith, B.H.; Torrance, N. Neuropathic Pain in the General Population: A Systematic Review of Epidemiological Studies. Pain 2014, 155, 654–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truini, A.; Cruccu, G. How Diagnostic Tests Help to Disentangle the Mechanisms Underlying Neuropathic Pain Symptoms in Painful Neuropathies. Pain 2016, 157, S53–S59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truini, A. A Review of Neuropathic Pain: From Diagnostic Tests to Mechanisms. Pain Ther. 2017, 6, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijs, J.; De Baets, L.; Hodges, P. Phenotyping Nociceptive, Neuropathic, and Nociplastic Pain: Who, How, & Why? Braz. J. Phys. Ther. 2023, 27, 100537. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nikolenko, V.N.; Shelomentseva, E.M.; Tsvetkova, M.M.; Abdeeva, E.I.; Giller, D.B.; Babayeva, J.V.; Achkasov, E.E.; Gavryushova, L.V.; Sinelnikov, M.Y. Nociceptors: Their Role in Body’s Defenses, Tissue Specific Variations and Anatomical Update. J. Pain Res. 2022, 15, 867–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, D.I.; Todd, A.J. Central Nervous System Targets: Inhibitory Interneurons in the Spinal Cord. Neurother. J. Am. Soc. Exp. Neurother. 2020, 17, 874–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendroud, S.; Fitzgerald, L.A.; Murray, I.V.; Hanna, A. Physiology, Nociceptive Pathways; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Ab Aziz, C.B.; Ahmad, A.H. The Role of the Thalamus in Modulating Pain. Malays. J. Med. Sci. 2006, 13, 11–18. [Google Scholar]
- Yen, C.-T.; Lu, P.-L. Thalamus and Pain. Acta Anaesthesiol. Taiwanica Off. J. Taiwan Soc. Anesthesiol. 2013, 51, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, S.; Faull, R.L.M.; Curtis, M.A. The Tracts, Cytoarchitecture, and Neurochemistry of the Spinal Cord. Anat. Rec. 2023, 306, 777–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falconi-Sobrinho, L.L.; dos Anjos-Garcia, T.; Elias-Filho, D.H.; Coimbra, N.C. Unravelling Cortico-Hypothalamic Pathways Regulating Unconditioned Fear-Induced Antinociception and Defensive Behaviours. Neuropharmacology 2017, 113, 367–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, S.A.; Herr, M.J. Physiology, Nociception; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, D.S.; Zhang, Y.; Halassa, M.M.; Feng, G. Thalamic Subnetworks as Units of Function. Nat. Neurosci. 2022, 25, 140–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, A.S.; Sherman, S.M.; Sommer, M.A.; Mair, R.G.; Vertes, R.P.; Chudasama, Y. Advances in Understanding Mechanisms of Thalamic Relays in Cognition and Behavior. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 15340–15346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgescu, I.A.; Popa, D.; Zagrean, L. The Anatomical and Functional Heterogeneity of the Mediodorsal Thalamus. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guilbaud, G.; Kayser, V.; Benoist, J.M.; Gautron, M. Modifications in the Responsiveness of Rat Ventrobasal Thalamic Neurons at Different Stages of Carrageenin-Produced Inflammation. Brain Res. 1986, 385, 86–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guilbaud, G.; Neil, A.; Benoist, J.M.; Kayser, V.; Gautron, M. Thresholds and Encoding of Neuronal Responses to Mechanical Stimuli in the Ventro-Basal Thalamus during Carrageenin-Induced Hyperalgesic Inflammation in the Rat. Exp. Brain Res. 1987, 68, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilbaud, G.; Benoist, J.M.; Neil, A.; Kayser, V.; Gautron, M. Neuronal Response Thresholds to and Encoding of Thermal Stimuli during Carrageenin-Hyperalgesic-Inflammation in the Ventro-Basal Thalamus of the Rat. Exp. Brain Res. 1987, 66, 421–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilbaud, G.; Benoist, J.M.; Jazat, F.; Gautron, M. Neuronal Responsiveness in the Ventrobasal Thalamic Complex of Rats with an Experimental Peripheral Mononeuropathy. J. Neurophysiol. 1990, 64, 1537–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, R.D.; Webster, K.E. Thalamic Afferents from the Spinal Cord and Trigeminal Nuclei. An Experimental Anatomical Study in the Rat. J. Comp. Neurol. 1967, 130, 313–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindia, J.A.; Köhler, M.G.; Martin, W.J.; Abbadie, C. Relationship between Sodium Channel NaV1.3 Expression and Neuropathic Pain Behavior in Rats. Pain 2005, 117, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hains, B.C.; Saab, C.Y.; Klein, J.P.; Craner, M.J.; Waxman, S.G. Altered Sodium Channel Expression in Second-Order Spinal Sensory Neurons Contributes to Pain after Peripheral Nerve Injury. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 4832–4839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hains, B.C.; Saab, C.Y.; Waxman, S.G. Changes in Electrophysiological Properties and Sodium Channel Nav1.3 Expression in Thalamic Neurons after Spinal Cord Injury. Brain 2005, 128, 2359–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Waxman, S.G.; Hains, B.C. Sodium Channel Expression in the Ventral Posterolateral Nucleus of the Thalamus after Peripheral Nerve Injury. Mol. Pain 2006, 2, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salt, T.E.; Eaton, S.A. Function of Non-NMDA Receptors and NMDA Receptors in Synaptic Responses to Natural Somatosensory Stimulation in the Ventrobasal Thalamus. Exp. Brain Res. 1989, 77, 646–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dougherty, P.M.; Li, Y.J.; Lenz, F.A.; Rowland, L.; Mittman, S. Evidence That Excitatory Amino Acids Mediate Afferent Input to the Primate Somatosensory Thalamus. Brain Res. 1996, 728, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolhekar, R.; Murphy, S.; Gebhart, G.F. Thalamic NMDA Receptors Modulate Inflammation-Produced Hyperalgesia in the Rat. Pain 1997, 71, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordi, F.; Quartaroli, M. Modulation of Nociceptive Transmission by NMDA/Glycine Site Receptor in the Ventroposterolateral Nucleus of the Thalamus. Pain 2000, 84, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abarca, C.; Silva, E.; Sepúlveda, M.J.; Oliva, P.; Contreras, E. Neurochemical Changes after Morphine, Dizocilpine or Riluzole in the Ventral Posterolateral Thalamic Nuclei of Rats with Hyperalgesia. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2000, 403, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salt, T.E.; Jones, H.E.; Andolina, I.M.; Copeland, C.S.; Clements, J.T.C.; Knoflach, F.; Sillito, A.M. Potentiation of Sensory Responses in Ventrobasal Thalamus in Vivo via Selective Modulation of MGlu1 Receptors with a Positive Allosteric Modulator. Neuropharmacology 2012, 62, 1695–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salt, T.E.; Jones, H.E.; Copeland, C.S.; Sillito, A.M. Function of MGlu1 Receptors in the Modulation of Nociceptive Processing in the Thalamus. Neuropharmacology 2014, 79, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, S.; Shi, W.; Liu, W.; Chen, Q.-Y.; Zhuo, M. Multiple Modulatory Roles of Serotonin in Chronic Pain and Injury-Related Anxiety. Front. Synaptic Neurosci. 2023, 15, 1122381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goettl, V.M.; Huang, Y.; Hackshaw, K.V.; Stephens, R.L.J. Reduced Basal Release of Serotonin from the Ventrobasal Thalamus of the Rat in a Model of Neuropathic Pain. Pain 2002, 99, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, D.Q.; Tang, J.S.; Yuan, B.; Jia, H. Inhibitory Effects of 5-Hydroxytryptamine Microinjection into Thalamic Nucleus Submedius on Rat Tail Flick Reflex Are Mediated by 5-HT2 Receptors. Neurosci. Lett. 1999, 260, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, D.-Q.; Zhu, J.-X.; Tang, J.-S.; Jia, H. 5-Hydroxytryptamine 1A (5-HT1A) but Not 5-HT3 Receptor Is Involved in Mediating the Nucleus Submedius 5-HT-Evoked Antinociception in the Rat. Brain Res. 2005, 1046, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.Q.; Tang, J.S.; Yuan, B. Inhibitory Effects of Electrical Stimulation of Thalamic Nucleus Submedius on the Nociceptive Responses of Spinal Dorsal Horn Neurons in the Rat. Brain Res. 1996, 737, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurna, I. Dose-Dependent Inhibition by Naloxone of Nociceptive Activity Evoked in the Rat Thalamus. Pain 1988, 35, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woolf, C.J. Central Sensitization: Uncovering the Relation between Pain and Plasticity. Anesthesiology 2007, 106, 864–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathews, K.; Kronen, P.W.; Lascelles, D.; Nolan, A.; Robertson, S.; Steagall, P.V.; Wright, B.; Yamashita, K. Guidelines for Recognition, Assessment and Treatment of Pain: WSAVA Global Pain Council Members and Co-Authors of This Document. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2014, 55, E10–E68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nijs, J.; Malfliet, A.; Nishigami, T. Nociplastic Pain and Central Sensitization in Patients with Chronic Pain Conditions: A Terminology Update for Clinicians. Braz. J. Phys. Ther. 2023, 27, 100518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, R.-R.; Nackley, A.; Huh, Y.; Terrando, N.; Maixner, W. Neuroinflammation and Central Sensitization in Chronic and Widespread Pain. Anesthesiology 2018, 129, 343–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.; Wang, J.; Ren, X.; Zang, W. Spinal Sample Showing P-JNK and P38 Associated with the Pain Signaling Transduction of Glial Cell in Neuropathic Pain. Spinal Cord 2015, 53, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vergne-Salle, P.; Bertin, P. Chronic Pain and Neuroinflammation. Jt. Bone Spine 2021, 88, 105222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.-X.; Wang, H.-F.; Chen, J.-Z.; Li, H.-Y.; Hu, J.-C.; Yu, A.-A.; Wen, J.-J.; Chen, S.-J.; Lai, W.-D.; Wang, S.; et al. Potential Neuroimmune Interaction in Chronic Pain: A Review on Immune Cells in Peripheral and Central Sensitization. Front. Pain Res. 2022, 3, 946846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawson, L.J.; Perry, V.H.; Dri, P.; Gordon, S. Heterogeneity in the Distribution and Morphology of Microglia in the Normal Adult Mouse Brain. Neuroscience 1990, 39, 151–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savchenko, V.L.; Nikonenko, I.R.; Skibo, G.G.; McKanna, J.A. Distribution of Microglia and Astrocytes in Different Regions of the Normal Adult Rat Brain. Neurophysiology 1997, 29, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jäkel, S.; Dimou, L. Glial Cells and Their Function in the Adult Brain: A Journey through the History of Their Ablation. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillen, A.E.J.; Burbach, J.P.H.; Hol, E.M. Cell Adhesion and Matricellular Support by Astrocytes of the Tripartite Synapse. Prog. Neurobiol. 2018, 165–167, 66–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grace, P.M.; Hutchinson, M.R.; Maier, S.F.; Watkins, L.R. Pathological Pain and the Neuroimmune Interface. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gazerani, P. Satellite Glial Cells in Pain Research: A Targeted Viewpoint of Potential and Future Directions. Front. Pain Res. 2021, 2, 646068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieto, F.R.; Clark, A.K.; Grist, J.; Chapman, V.; Malcangio, M. Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide-Expressing Sensory Neurons and Spinal Microglial Reactivity Contribute to Pain States in Collagen-Induced Arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 67, 1668–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, A.K.; Malcangio, M. Fractalkine/CX3CR1 Signaling during Neuropathic Pain. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.-J.; Ji, R.-R. Targeting Astrocyte Signaling for Chronic Pain. Neurother. J. Am. Soc. Exp. Neurother. 2010, 7, 482–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, A.K.; Old, E.A.; Malcangio, M. Neuropathic Pain and Cytokines: Current Perspectives. J. Pain Res. 2013, 6, 803–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biber, K.; Boddeke, E. Neuronal CC Chemokines: The Distinct Roles of CCL21 and CCL2 in Neuropathic Pain. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Yang, Z.; Wang, K.; Chen, Z.; Shen, H. Suppression of Microglial Ccl2 Reduces Neuropathic Pain Associated with Chronic Spinal Compression. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1191188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Ma, S.-B.; Gao, Y.-J.; Xing, J.-L.; Xian, H.; Li, Z.-Z.; Shen, S.-N.; Wu, S.-X.; Luo, C.; Xie, R.-G. Spinal CCL2 Promotes Pain Sensitization by Rapid Enhancement of NMDA-Induced Currents through the ERK-GluN2B Pathway in Mouse Lamina II Neurons. Neurosci. Bull. 2020, 36, 1344–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tozaki-Saitoh, H.; Takeda, H.; Inoue, K. The Role of Microglial Purinergic Receptors in Pain Signaling. Molecules 2022, 27, 1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, K.; Woller, S.A.; Miller, Y.I.; Yaksh, T.L.; Wallace, M.; Beaton, G.; Chakravarthy, K. Targeting Toll-like Receptor-4 (TLR4)-an Emerging Therapeutic Target for Persistent Pain States. Pain 2018, 159, 1908–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, M.; Cui, S.; Liang, W.; Jia, Z.; Guo, F.; Ou, W.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, S. The Core of Maintaining Neuropathic Pain: Crosstalk between Glial Cells and Neurons (Neural Cell Crosstalk at Spinal Cord). Brain Behav. 2023, 13, e2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodds, K.N.; Beckett, E.A.H.; Evans, S.F.; Grace, P.M.; Watkins, L.R.; Hutchinson, M.R. Glial Contributions to Visceral Pain: Implications for Disease Etiology and the Female Predominance of Persistent Pain. Transl. Psychiatry 2016, 6, e888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banati, R.B.; Goerres, G.W.; Myers, R.; Gunn, R.N.; Turkheimer, F.E.; Kreutzberg, G.W.; Brooks, D.J.; Jones, T.; Duncan, J.S. [11C](R)-PK11195 Positron Emission Tomography Imaging of Activated Microglia in Vivo in Rasmussen’s Encephalitis. Neurology 1999, 53, 2199–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Converse, A.K.; Larsen, E.C.; Engle, J.W.; Barnhart, T.E.; Nickles, R.J.; Duncan, I.D. 11C-(R)-PK11195 PET Imaging of Microglial Activation and Response to Minocycline in Zymosan-Treated Rats. J. Nucl. Med. 2011, 52, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parri, H.R.; Gould, T.M.; Crunelli, V. Sensory and Cortical Activation of Distinct Glial Cell Subtypes in the Somatosensory Thalamus of Young Rats. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2010, 32, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, A.M.W.; Mehrabani, S.; Liu, S.; Taylor, A.J.; Cahill, C.M. Topography of Microglial Activation in Sensory- and Affect-Related Brain Regions in Chronic Pain. J. Neurosci. Res. 2017, 95, 1330–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giardini, A.C.; Dos Santos, F.M.; da Silva, J.T.; de Oliveira, M.E.; Martins, D.O.; Chacur, M. Neural Mobilization Treatment Decreases Glial Cells and Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Expression in the Central Nervous System in Rats with Neuropathic Pain Induced by CCI in Rats. Pain Res. Manag. 2017, 2017, 7429761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coull, J.A.M.; Beggs, S.; Boudreau, D.; Boivin, D.; Tsuda, M.; Inoue, K.; Gravel, C.; Salter, M.W.; De Koninck, Y. BDNF from Microglia Causes the Shift in Neuronal Anion Gradient Underlying Neuropathic Pain. Nature 2005, 438, 1017–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trang, T.; Beggs, S.; Salter, M.W. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor from Microglia: A Molecular Substrate for Neuropathic Pain. Neuron Glia Biol. 2011, 7, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cesare Mannelli, L.; Pacini, A.; Bonaccini, L.; Zanardelli, M.; Mello, T.; Ghelardini, C. Morphologic Features and Glial Activation in Rat Oxaliplatin-Dependent Neuropathic Pain. J. Pain 2013, 14, 1585–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaszczyk, L.; Maître, M.; Lesté-Lasserre, T.; Clark, S.; Cota, D.; Oliet, S.H.R.; Fénelon, V.S. Sequential Alteration of Microglia and Astrocytes in the Rat Thalamus Following Spinal Nerve Ligation. J. Neuroinflamm. 2018, 15, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeBlanc, B.W.; Zerah, M.L.; Kadasi, L.M.; Chai, N.; Saab, C.Y. Minocycline Injection in the Ventral Posterolateral Thalamus Reverses Microglial Reactivity and Thermal Hyperalgesia Secondary to Sciatic Neuropathy. Neurosci. Lett. 2011, 498, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elisei, L. Avaliação Da Participação Dos Receptores Potencial Transiente Vanilóide Do Tipo 1 e Toll like 4 e Células Gliais Talâmicas Durante a Dor Neuropática Em Camundongos. Doctoral Thesis, Federal University of Alfenas, Alfenas, Brazil, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, G.; Du, S.; Huang, T.; Cao, M.; Feng, X.; Wu, S.; Albik, S.; Bekker, A.; Tao, Y.-X. FTO (Fat-Mass and Obesity-Associated Protein) Participates in Hemorrhage-Induced Thalamic Pain by Stabilizing Toll-Like Receptor 4 Expression in Thalamic Neurons. Stroke 2021, 52, 2393–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Fu, G.; Gao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, W.; Wu, S.; Jia, S.; Xia, S.; Bachmann, T.; Bekker, A.; et al. Fgr Contributes to Hemorrhage-Induced Thalamic Pain by Activating NF-ΚB/ERK1/2 Pathways. JCI Insight 2020, 5, e139987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.; Li, Y.; Hu, W.; Yu, D.; Gao, J.; Yang, F.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zong, L. Dexmedetomidine Attenuates Haemorrhage-Induced Thalamic Pain by Inhibiting the TLR4/NF-ΚB/ERK1/2 Pathway in Mice. Inflammopharmacology 2021, 29, 1751–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Z.-M.; Jing, J.-J.; Xue, Z.-J.; Chen, W.-J.; Tang, Y.-B.; Chen, D.-J.; Qi, X.-Y.; Huang, L.; Zou, Y.-Q.; Wu, X.-Z.; et al. Stellate Ganglion Block Ameliorated Central Post-Stroke Pain with Comorbid Anxiety and Depression through Inhibiting HIF-1α/NLRP3 Signaling Following Thalamic Hemorrhagic Stroke. J. Neuroinflamm. 2023, 20, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.-F.; Xu, C.-Y.; Zhang, L.; Gan, L.; Chen, C.; Yan, M.-Y.; Guo, X.-N.; Fang, Q.; Xu, G.-Y.; Zhang, Y.-B.; et al. A New Central Post-Stroke Pain Rat Model: Autologous Blood Injected Thalamic Hemorrhage Involved Increased Expression of P2 × 4 Receptor. Neurosci. Lett. 2018, 687, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.; Chen, X.; Li, Y.; Ge, Y.; Gao, J. MiR-223 Ameliorates Thalamus Hemorrhage-Induced Central Poststroke Pain via Targeting NLRP3 in a Mouse Model. Exp. Ther. Med. 2022, 23, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Wu, S.; Pan, Z.; Xiao, J.; Li, F.; Cao, J.; Zang, W.; Tao, Y.-X. Disrupting Interaction of PSD-95 with NNOS Attenuates Hemorrhage-Induced Thalamic Pain. Neuropharmacology 2018, 141, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; He, L.; Yuan, C.; Ai, Y.; Yang, J.-J. Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Gamma Agonist Pioglitazone Alleviates Hemorrhage-Induced Thalamic Pain and Neuroinflammation. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 124, 110991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bu, F.; Li, Y.; Lan, S.; Yang, T.; He, B.; Dong, P.; Shen, F.; Cai, H.; Lu, Y.; Fei, Y.; et al. Blocking Pannexin-1 Channels Alleviates Thalamic Hemorrhage-Induced Pain and Inflammatory Depolarization of Microglia in Mice. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2023, 14, 2548–2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torrado-Carvajal, A.; Toschi, N.; Albrecht, D.S.; Chang, K.; Akeju, O.; Kim, M.; Edwards, R.R.; Zhang, Y.; Hooker, J.M.; Duggento, A.; et al. Thalamic Neuroinflammation as a Reproducible and Discriminating Signature for Chronic Low Back Pain. Pain 2021, 162, 1241–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loggia, M.L.; Chonde, D.B.; Akeju, O.; Arabasz, G.; Catana, C.; Edwards, R.R.; Hill, E.; Hsu, S.; Izquierdo-Garcia, D.; Ji, R.-R.; et al. Evidence for Brain Glial Activation in Chronic Pain Patients. Brain 2015, 138, 604–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Piero, V.; Jones, A.K.P.; Iannotti, F.; Powell, M.; Perani, D.; Lenzi, G.L.; Frackowiak, R.S.J. Chronic Pain: A PET Study of the Central Effects of Percutaneous High Cervical Cordotomy. Pain 1991, 46, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Galdino, G.; Veras, F.P.; dos Anjos-Garcia, T. The Role of the Thalamus in Nociception: Important but Forgotten. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 741. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14080741
Galdino G, Veras FP, dos Anjos-Garcia T. The Role of the Thalamus in Nociception: Important but Forgotten. Brain Sciences. 2024; 14(8):741. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14080741
Chicago/Turabian StyleGaldino, Giovane, Flavio Protasio Veras, and Tayllon dos Anjos-Garcia. 2024. "The Role of the Thalamus in Nociception: Important but Forgotten" Brain Sciences 14, no. 8: 741. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14080741
APA StyleGaldino, G., Veras, F. P., & dos Anjos-Garcia, T. (2024). The Role of the Thalamus in Nociception: Important but Forgotten. Brain Sciences, 14(8), 741. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14080741







