Voxel-Based Lesion Analysis of Ideomotor Apraxia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Behavioral Data
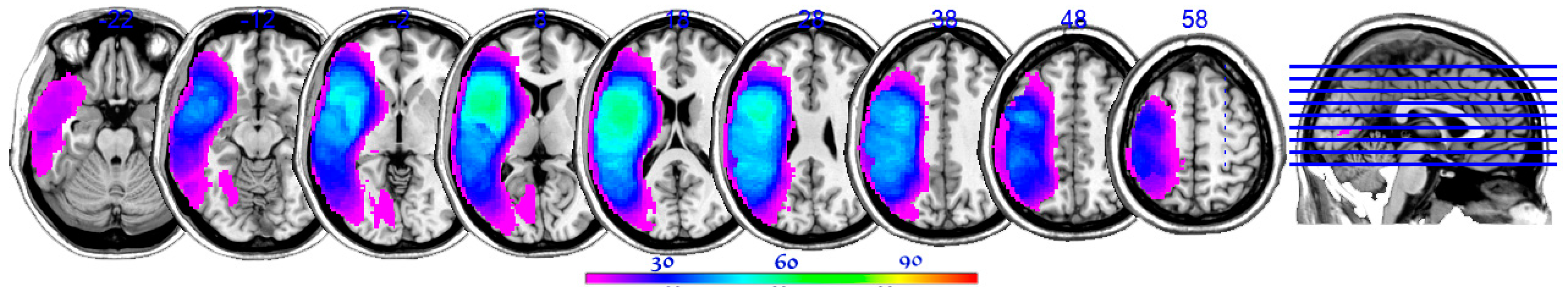
2.3. Lesion Reconstructions and Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Behavioral Results
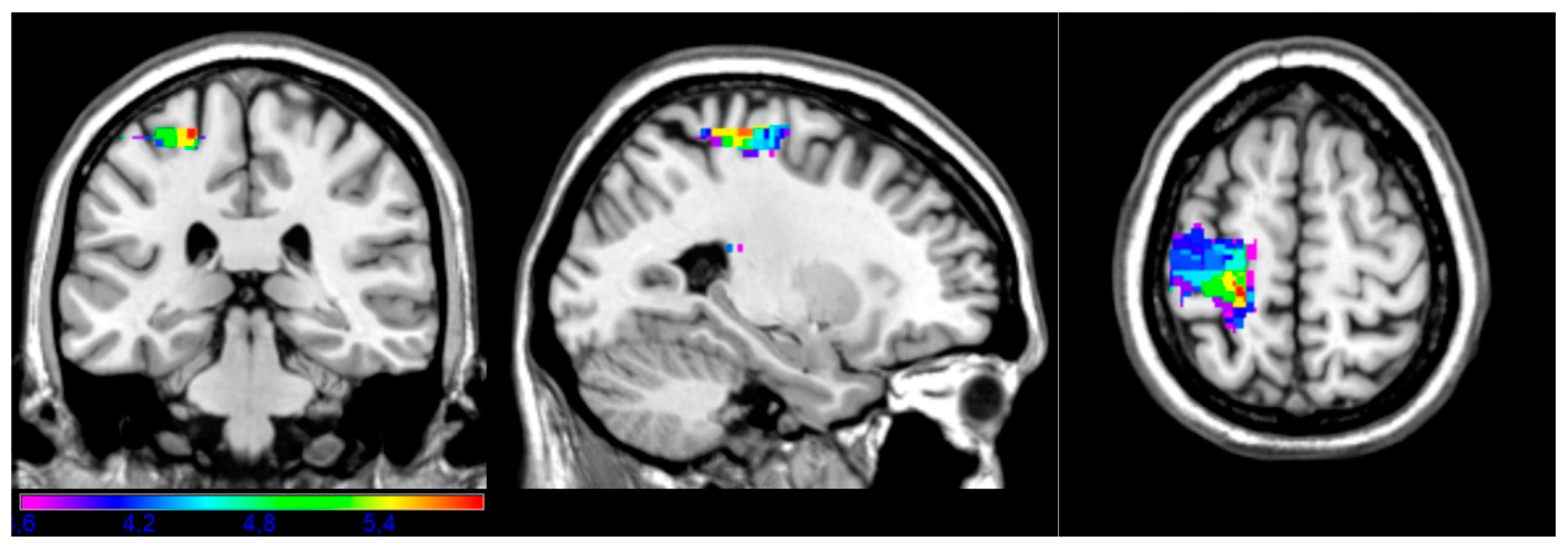
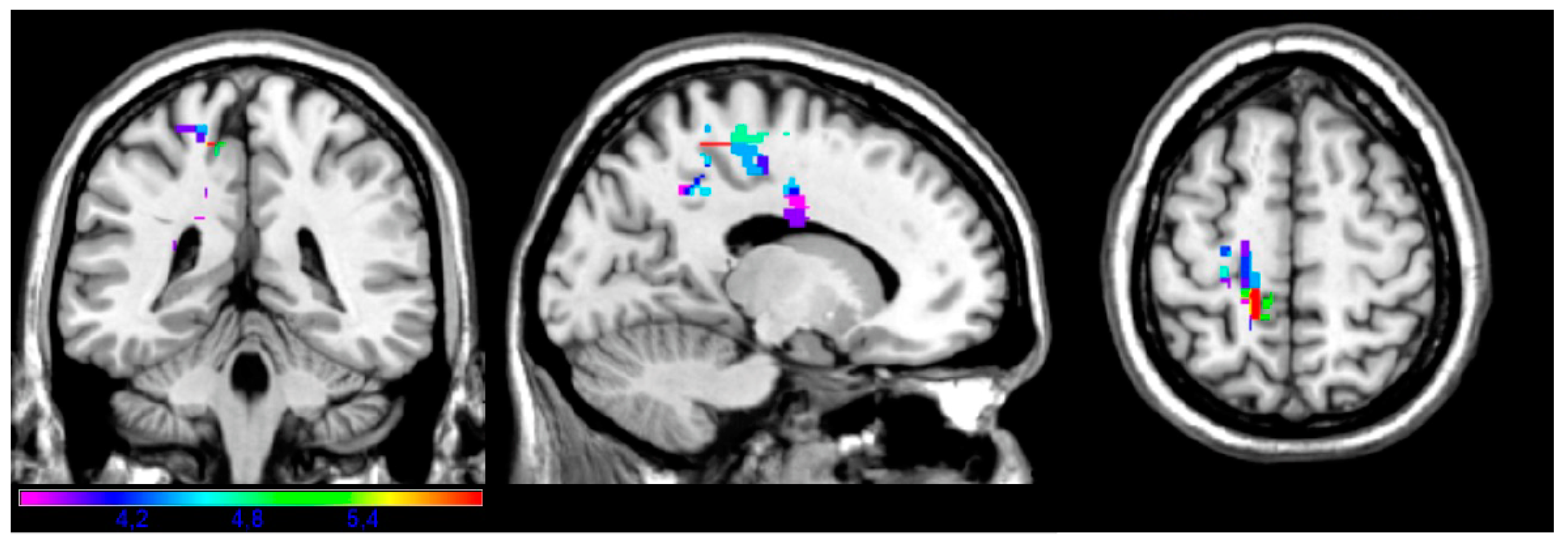
3.2. LSM Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Capitani, E.; Sala, S.D.; Spinnler, H.; Basso, A.; Laiacona, M. Recovery from ideomotor apraxia: A study on acute stroke patients. Brain 1987, 110, 747–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, M.P.; Baker, E.; Naeser, M.A.; Kaplan, E.; Palumbo, C. Neuropsychological and neuroanatomical dimensions of ideomotor apraxia. Brain 1992, 115, 87–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mozaz, M.J. Ideational and Ideomotor Apraxia: A Qualitative Analysis. Behav. Neurol. 1992, 5, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cubelli, R. Definition: Apraxia. Cortex 2017, 93, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumard, J.; Gall, D.L. The Challenge of Apraxia: Toward an Operational Definition? Cortex 2021, 141, 66–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koski, L.; Iacoboni, M.; Mazziotta, J.C.; Williams, L. Deconstructing Apraxia: Understanding Disorders of Intentional Movement after Stroke. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2002, 15, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Liepmann, H. Drei Aufsätze Aus Dem Apraxiegebiet; Karger: Basel, Switzerland, 1908. [Google Scholar]
- Liepmann, H. Apraxie. Ergebn. Ges. Med. 1920, 1, 516–543. [Google Scholar]
- Liepmann, H. The Left Hemisphere and Action. Translations from Liepmann’s Essays on Apraxia. Res. Bull. 1980, 506, 17–50. [Google Scholar]
- Bates, E.; Wilson, S.M.; Saygin, A.P.; Dick, F.; Sereno, M.I.; Knight, R.T.; Dronkers, N.F. Voxel-Based Lesion-Symptom Mapping. Nat. Neurosci. 2003, 6, 448–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, M.V.; Herron, T.J.; Dronkers, N.F.; Baldo, J.V. An Empirical Comparison of Univariate versus Multivariate Methods for the Analysis of Brain–Behavior Mapping. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2021, 42, 1070–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldenberg, G.; Hermsdörfer, J.; Spatt, J. Ideomotor Apraxia and Cerebral Dominance for Motor Control. Cogn. Brain Res. 1996, 3, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haaland, K.Y.; Harrington, D.L.; Knight, R.T. Neural Representations of Skilled Movement. Brain 2000, 123, 2306–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canzano, L.; Scandola, M.; Gobbetto, V.; Moretto, G.; D’Imperio, D.; Moro, V. The Representation of Objects in Apraxia: From Action Execution to Error Awareness. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buxbaum, L.J.; Kalénine, S. Action Knowledge, Visuomotor Activation, and Embodiment in the Two Action Systems. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2010, 1191, 201–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binkofski, F.; Buxbaum, L.J. Two Action Systems in the Human Brain. Brain Lang. 2013, 127, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeren, M.; Kümmerer, D.; Bormann, T.; Beume, L.; Ludwig, V.M.; Vry, M.S.; Mader, I.; Rijntjes, M.; Kaller, C.P.; Weiller, C. Neural Bases of Imitation and Pantomime in Acute Stroke Patients: Distinct Streams for Praxis. Brain 2014, 137, 2796–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manuel, A.L.; Radman, N.; Mesot, D.; Chouiter, L.; Clarke, S.; Annoni, J.M.; Spierer, L. Inter- and Intrahemispheric Dissociations in Ideomotor Apraxia: A Large-Scale Lesion-Symptom Mapping Study in Subacute Brain-Damaged Patients. Cereb. Cortex N. Y. N 1991 2013, 23, 2781–2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, C.C.; Achilles, E.I.S.; Fink, G.R.; Weiss, P.H. Distinct Cognitive Components and Their Neural Substrates Underlying Praxis and Language Deficits Following Left Hemisphere Stroke. Cortex 2022, 146, 200–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rounis, E.; Halai, A.; Pizzamiglio, G.; Lambon Ralph, M.A. Characterising Factors Underlying Praxis Deficits in Chronic Left Hemisphere Stroke Patients. Cortex 2021, 142, 154–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyler, L.K.; Marslen-Wilson, W.; Stamatakis, E.A. Dissociating Neuro-Cognitive Component Processes: Voxel-Based Correlational Methodology. Neuropsychologia 2005, 43, 771–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basso, A.; Burgio, F.; Paulin, M.; Prandoni, P. Long-Term Follow-up of Ideomotor Apraxia. Neuropsychol. Rehabil. 2000, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, A.; Nicholas, M. Language Rehabilitation in Chronic Aphasia and Time Postonset: A Review of Single-Subject Data. Stroke 2006, 37, 3043–3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zumbansen, A.; Kneifel, H.; Lazzouni, L.; Ophey, A.; Black, S.E.; Chen, J.L.; Edwards, D.; Funck, T.; Hartmann, A.E.; Heiss, W.D.; et al. Differential Effects of Speech and Language Therapy and rTMS in Chronic Versus Subacute Post-Stroke Aphasia: Results of the NORTHSTAR-CA Trial. Neurorehabil. Neural Repair 2022, 36, 306–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemmetyinen, S.; Hokkanen, L.; Klippi, A. Long-Term Recovery from Apraxia and Its Relation to Severe Apraxic-Aphasic Disorder in Left Hemisphere Stroke–a Systematic Review. Aphasiology 2020, 34, 735–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kertesz, A. Western Aphasia Battery—Revised (WAB-R); APA PsychTests: Washington, DC, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Kertesz, A. The Western Aphasia Battery: A Systematic Review of Research and Clinical Applications. Aphasiology 2022, 36, 21–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raade, A.S.; Gonzalez Rothi, L.J.; Heilman, K.M. The Relationship between Buccofacial and Limb Apraxia. Brain Cogn. 1991, 16, 130–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scandola, M.; Canzano, L.; Avesani, R.; Leder, M.; Bertagnoli, S.; Gobbetto, V.; Aglioti, S.M.; Moro, V. Anosognosia for Limb and Bucco-facial Apraxia as Inferred from the Recognition of Gestural Errors. J. Neuropsychol. 2021, 15, 20–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Square-Storer, P.A.; Hogg, S.C.; Roy, E.A. The Dissociation of Aphasia from Apraxia of Speech, Ideomotor Limb, and Buccofacial Apraxia. In Advances in Psychology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1990; Volume 70, pp. 451–476. ISBN 978-0-444-88477-0. [Google Scholar]
- Rorden, C.; Brett, M. Stereotaxic Display of Brain Lesions. Behav. Neurol. 2000, 12, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, R.T.; Scabini, D.; Woods, D.L.; Clayworth, C. The Effects of Lesions of Superior Temporal Gyrus and Inferior Parietal Lobe on Temporal and Vertex Components of the Human AEP. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1988, 70, 499–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedrich, F.J.; Egly, R.; Rafal, R.D.; Beck, D. Spatial Attention Deficits in Humans: A Comparison of Superior Parietal and Temporal-Parietal Junction Lesions. Neuropsychology 1998, 12, 193–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, D.L.; Neelin, P.; Peters, T.M.; Evans, A.C. Automatic 3D Intersubject Registration of MR Volumetric Data in Standardized Talairach Space. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 1994, 18, 192–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldo, J.V.; Ivanova, M.V.; Herron, T.J.; Wilson, S.M.; Dronkers, N.F. Voxel-Based Lesion Symptom Mapping. Neuromethods 2022, 180, 95–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimberg, D.Y.; Coslett, H.B.; Schwartz, M.F. Power in Voxel-Based Lesion-Symptom Mapping. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2007, 19, 1067–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neal, C.M.; Ahsan, S.A.; Dadario, N.B.; Fonseka, R.D.; Young, I.M.; Parker, A.; Maxwell, B.D.; Yeung, J.T.; Briggs, R.G.; Teo, C.; et al. A Connectivity Model of the Anatomic Substrates Underlying Ideomotor Apraxia: A Meta-Analysis of Functional Neuroimaging Studies. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2021, 207, 106765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcea, F.E.; Greene, C.; Grafton, S.T.; Buxbaum, L.J. Structural Disconnection of the Tool Use Network after Left Hemisphere Stroke Predicts Limb Apraxia Severity. Cereb. Cortex Commun. 2020, 1, tgaa035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dressing, A.; Kaller, C.P.; Martin, M.; Nitschke, K.; Kuemmerer, D.; Beume, L.A.; Schmidt, C.S.M.; Musso, M.; Urbach, H.; Rijntjes, M.; et al. Anatomical Correlates of Recovery in Apraxia: A Longitudinal Lesion-Mapping Study in Stroke Patients. Cortex 2021, 142, 104–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleineberg, N.N.; Schmidt, C.C.; Richter, M.K.; Bolte, K.; Schloss, N.; Fink, G.R.; Weiss, P.H. Gesture Meaning Modulates the Neural Correlates of Effector-Specific Imitation Deficits in Left Hemisphere Stroke. NeuroImage Clin. 2023, 37, 103331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessari, A.; Canessa, N.; Ukmar, M.; Rumiati, R.I. Neuropsychological Evidence for a Strategic Control of Multiple Routes in Imitation. Brain 2006, 130, 1111–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzamiglio, G.; Zhang, Z.; Kolasinski, J.; Riddoch, J.M.; Passingham, R.E.; Mantini, D.; Rounis, E. A Role for the Action Observation Network in Apraxia After Stroke. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenzopf, H.; Wiesen, D.; Basilakos, A.; Yourganov, G.; Bonilha, L.; Rorden, C.; Fridriksson, J.; Karnath, H.O.; Sperber, C. Mapping the Human Praxis Network: An Investigation of White Matter Disconnection in Limb Apraxia of Gesture Production. Brain Commun. 2022, 4, fcac004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busby, N.; Hillis, A.E.; Bunker, L.; Rorden, C.; Newman-Norlund, R.; Bonilha, L.; Meier, E.; Goldberg, E.; Hickok, G.; Yourganov, G.; et al. Comparing the Brain–Behaviour Relationship in Acute and Chronic Stroke Aphasia. Brain Commun. 2023, 5, fcad014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusch, M.; Gillessen, S.; Saliger, J.; Karbe, H.; Binder, E.; Fink, G.R.; Vossel, S.; Weiss, P.H. Reduced Awareness for Apraxic Deficits in Left Hemisphere Stroke. Neuropsychology 2018, 32, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Mean | SD | Min | Max | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 60.14 | 11.79 | 31 | 86 |
| Years of education | 15.10 | 2.31 | 12 | 20 |
| Lesion volume (cc) | 114.80 | 94.35 | 0.12 | 450.79 |
| Months post-onset | 45.30 | 50.29 | 12 | 271 |
| Overall praxis score | 52.63 | 10.57 | 17 | 60 |
| AQ 1 | 71.67 | 28.25 | 9.1 | 100 |
| CQ 2 | 74.60 | 24.09 | 17.33 | 99.95 |
| Subtest | Mean | SD | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upper limb | 13.63 | 2.26 | 5 | 15 |
| Instrumental | 13.29 | 2.83 | 3 | 15 |
| Facial | 13.10 | 2.97 | 2 | 15 |
| Complex | 12.68 | 3.39 | 0 | 15 |
| Subtest | Volume | Px | Py | Pz | Min T | Max T |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Complex | 614 | −24 | −30 | 62 | 3.60 | 5.89 |
| Instrumental | 356 | −14 | −44 | 58 | 3.61 | 5.99 |
| Facial | 88 | −50 | −34 | −20 | 3.67 | 5.58 |
| Upper limb | 68 | −72 | −16 | 2 | 3.57 | 5.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oliveira Santos, G.; Arévalo, A.L.; Herron, T.J.; Curran, B.C.; Lepski, G.; Dronkers, N.F.; Baldo, J.V. Voxel-Based Lesion Analysis of Ideomotor Apraxia. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 853. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14090853
Oliveira Santos G, Arévalo AL, Herron TJ, Curran BC, Lepski G, Dronkers NF, Baldo JV. Voxel-Based Lesion Analysis of Ideomotor Apraxia. Brain Sciences. 2024; 14(9):853. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14090853
Chicago/Turabian StyleOliveira Santos, Giovanna, Analía L. Arévalo, Timothy J. Herron, Brian C. Curran, Guilherme Lepski, Nina F. Dronkers, and Juliana V. Baldo. 2024. "Voxel-Based Lesion Analysis of Ideomotor Apraxia" Brain Sciences 14, no. 9: 853. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14090853
APA StyleOliveira Santos, G., Arévalo, A. L., Herron, T. J., Curran, B. C., Lepski, G., Dronkers, N. F., & Baldo, J. V. (2024). Voxel-Based Lesion Analysis of Ideomotor Apraxia. Brain Sciences, 14(9), 853. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14090853





