Reward History and Statistical Learning Independently Impact Attention Search: An ERP Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Instrumentation and Stimulation
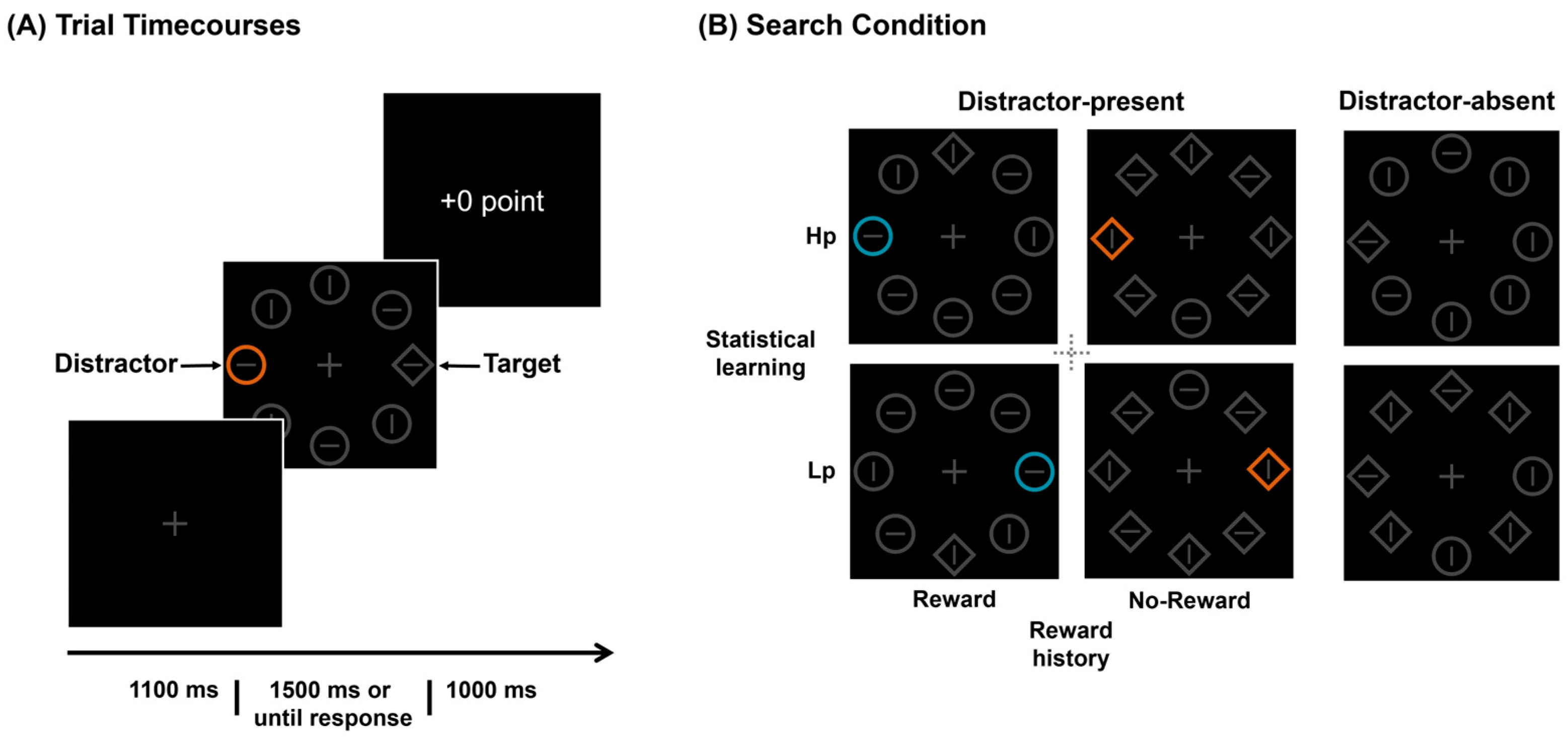
2.3. Design and Process
3. Data Analysis
4. Results
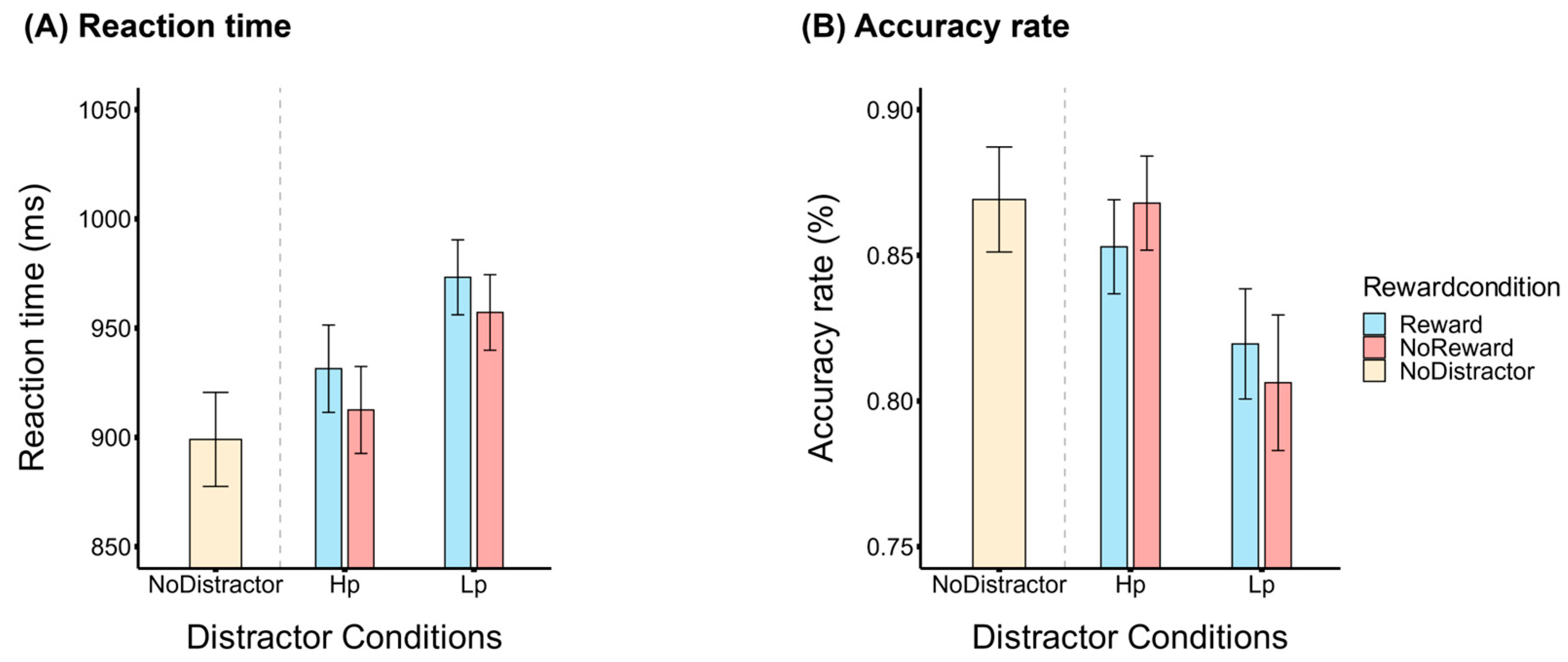
4.1. Behavioral Results
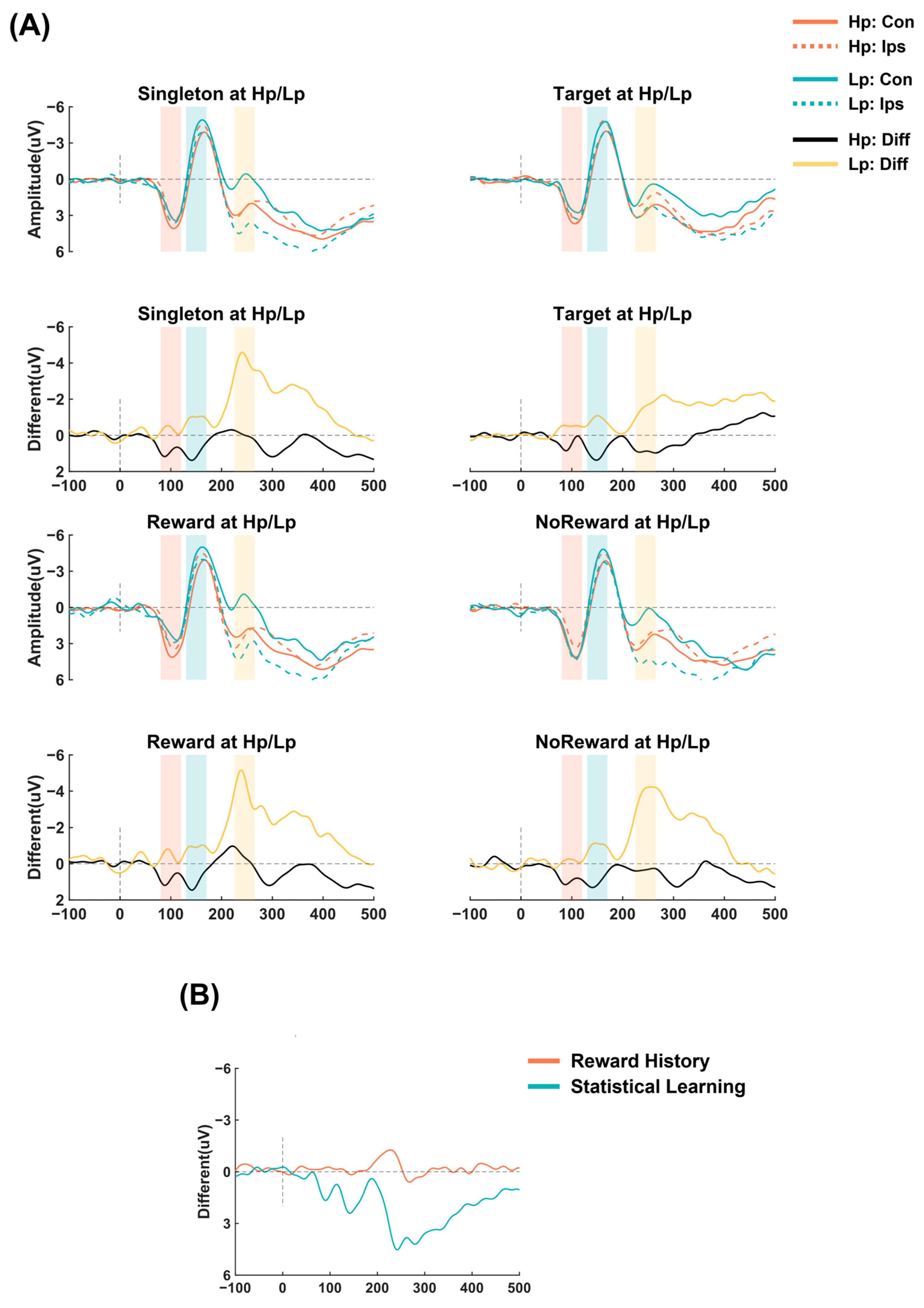
4.2. EEG Results
4.2.1. Statistical Learning-Related Early Pd, Pd, and N2pc
4.2.2. Reward History and Its Relationship with Statistical Learning
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Corbetta, M.; Shulman, G.L. Control of Goal-Directed and Stimulus-Driven Attention in the Brain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2002, 3, 201–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theeuwes, J. Goal-Driven, Stimulus-Driven, and History-Driven Selection. Curr. Opin. Psychol. 2019, 29, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awh, E.; Belopolsky, A.V.; Theeuwes, J. Top-down versus Bottom-up Attentional Control: A Failed Theoretical Dichotomy. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2012, 16, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, B.A.; Laurent, P.A.; Yantis, S. Value-Driven Attentional Capture. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 10367–10371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, B.A.; Laurent, P.A.; Yantis, S. Learned Value Magnifies Salience-Based Attentional Capture. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e27926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, B.A.; Laurent, P.A.; Yantis, S. Generalization of Value-Based Attentional Priority. Vis. Cogn. 2012, 20, 647–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Theeuwes, J. Statistical Regularities Modulate Attentional Capture Independent of Search Strategy. Atten. Percept. Psychophys. 2018, 80, 1763–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Theeuwes, J. Statistical Regularities Modulate Attentional Capture. J. Exp. Psychol. Human. Percept. Perform. 2018, 44, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Theeuwes, J. How to Inhibit a Distractor Location? Statistical Learning versus Active, Top-Down Suppression|SpringerLink. 2018. Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.3758/s13414-018-1493-z (accessed on 26 August 2024).
- Theeuwes, J.; Bogaerts, L.; van Moorselaar, D. What to Expect Where and When: How Statistical Learning Drives Visual Selection. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2022, 26, 860–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Failing, M.; Wang, B.; Theeuwes, J. Spatial Suppression Due to Statistical Regularities Is Driven by Distractor Suppression Not by Target Activation. Atten. Percept. Psychophys. 2019, 81, 1405–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrante, O.; Patacca, A.; Di Caro, V.; Della Libera, C.; Santandrea, E.; Chelazzi, L. Altering Spatial Priority Maps via Statistical Learning of Target Selection and Distractor Filtering. Cortex 2018, 102, 67–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Vilotijević, A.; Theeuwes, J.; Donk, M. Proactive Distractor Suppression Elicited by Statistical Regularities in Visual Search. Psychon. Bull. Rev. 2021, 28, 918–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Theeuwes, J. Learning to Suppress a Distractor Is Not Affected by Working Memory Load. Psychon. Bull. Rev. 2020, 27, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, B.-Y.; Jiang, Y.V. Spatial Working Memory Interferes with Explicit, but Not Probabilistic Cuing of Spatial Attention. J. Exp. Psychol. Learn. Mem. Cogn. 2015, 41, 787–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.V. Habitual versus Goal-Driven Attention. Cortex 2018, 102, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turk-Browne, N.B.; Jungé, J.A.; Scholl, B.J. The Automaticity of Visual Statistical Learning. J. Exp. Psychol. General 2005, 134, 552–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, B.A. A Value-Driven Mechanism of Attentional Selection. J. Vision. 2013, 13, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, B.A.; Kim, H.; Kim, A.J.; Liao, M.-R.; Mrkonja, L.; Clement, A.; Grégoire, L. The Past, Present, and Future of Selection History. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2021, 130, 326–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, B.A.; Liao, M.-R.; Grégoire, L. Pavlovian Learning in the Selection History-Dependent Control of Overt Spatial Attention. J. Exp. Psychol. Human. Percept. Perform. 2022, 48, 783–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Failing, M.; Theeuwes, J. Selection History: How Reward Modulates Selectivity of Visual Attention. Psychon. Bull. Rev. 2018, 25, 514–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britton, M.K.; Anderson, B.A. Specificity and Persistence of Statistical Learning in Distractor Suppression. J. Exp. Psychol. Human. Percept. Perform. 2020, 46, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Anderson, B.A. Combined Influence of Valence and Statistical Learning on the Control of Attention: Evidence for Independent Sources of Bias. Cognition 2021, 208, 104554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chelazzi, L.; Eštočinová, J.; Calletti, R.; Gerfo, E.L.; Sani, I.; Libera, C.D.; Santandrea, E. Altering Spatial Priority Maps via Reward-Based Learning. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 8594–8604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, M.M.; Phelps, E.A. Memory Deficits for Implicit Contextual Information in Amnesic Subjects with Hippocampal Damage. Nat. Neurosci. 1999, 2, 844–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, N.J.; Eichenbaum, H. Memory, Amnesia, and the Hippocampal System; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1993; p. xii, 330. ISBN 978-0-262-03203-2. [Google Scholar]
- Turk-Browne, N.B.; Scholl, B.J.; Chun, M.M.; Johnson, M.K. Neural Evidence of Statistical Learning: Efficient Detection of Visual Regularities Without Awareness. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2009, 21, 1934–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, B.A. Neurobiology of Value-Driven Attention. Curr. Opin. Psychol. 2019, 29, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burra, N.; Kerzel, D. The Distractor Positivity (Pd) Signals Lowering of Attentional Priority: Evidence from Event-Related Potentials and Individual Differences. Psychophysiology 2014, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosman, J.D.; Lowe, K.A.; Zinke, W.; Woodman, G.F.; Schall, J.D. Prefrontal Control of Visual Distraction. Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, 1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldmann-Wüstefeld, T.; Vogel, E.K. Neural Evidence for the Contribution of Active Suppression During Working Memory Filtering. Cereb. Cortex 2019, 29, 529–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspar, J.M.; McDonald, J.J. Suppression of Salient Objects Prevents Distraction in Visual Search. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 5658–5666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspelin, N.; Luck, S.J. The Role of Inhibition in Avoiding Distraction by Salient Stimuli. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2018, 22, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaspelin, N.; Luck, S.J. Combined Electrophysiological and Behavioral Evidence for the Suppression of Salient Distractors. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2018, 30, 1265–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liesefeld, H.R.; Liesefeld, A.M.; Pollmann, S.; Müller, H.J. Biasing Allocations of Attention via Selective Weighting of Saliency Signals: Behavioral and Neuroimaging Evidence for the Dimension-Weighting Account. Curr. Top. Behav. Neurosci. 2019, 41, 87–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawaki, R.; Luck, S.J. Active Suppression after Involuntary Capture of Attention. Psychon. Bull. Rev. 2013, 20, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Moorselaar, D.; Slagter, H.A. Learning What Is Irrelevant or Relevant: Expectations Facilitate Distractor Inhibition and Target Facilitation through Distinct Neural Mechanisms. J. Neurosci. 2019, 39, 6953–6967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Van Driel, J.; Ort, E.; Theeuwes, J. Anticipatory Distractor Suppression Elicited by Statistical Regularities in Visual Search. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2019, 31, 1535–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachman, M.D.; Wang, L.; Gamble, M.L.; Woldorff, M.G. Physical Salience and Value-Driven Salience Operate through Different Neural Mechanisms to Enhance Attentional Selection. J. Neurosci. 2020, 40, 5455–5464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hickey, C.; Chelazzi, L.; Theeuwes, J. Reward Changes Salience in Human Vision via the Anterior Cingulate. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 11096–11103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, S.; Zeng, Q.; Ding, C.; Li, H. Neural Correlates of Reward-Driven Attentional Capture in Visual Search. Brain Res. 2013, 1532, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Anderson, B.A. Dissociable Components of Experience-Driven Attention. Curr. Biol. 2019, 29, 841–845.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Pelley, M.E.; Ung, R.; Mine, C.; Most, S.B.; Watson, P.; Pearson, D.; Theeuwes, J. Reward Learning and Statistical Learning Independently Influence Attentional Priority of Salient Distractors in Visual Search. Atten. Percept. Psychophys. 2022, 84, 1446–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, P.; Pearson, D.; Theeuwes, J.; Most, S.B.; Le Pelley, M.E. Delayed Disengagement of Attention from Distractors Signalling Reward. Cognition 2020, 195, 104125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Failing, M.; Feldmann-Wüstefeld, T.; Wang, B.; Olivers, C.; Theeuwes, J. Statistical Regularities Induce Spatial as Well as Feature-Specific Suppression. J. Exp. Psychol. Hum. Percept. Perform. 2019, 45, 1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Failing, M.; Theeuwes, J. More Capture, More Suppression: Distractor Suppression Due to Statistical Regularities Is Determined by the Magnitude of Attentional Capture. Psychon. Bull. Rev. 2020, 27, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearson, D.; Osborn, R.; Whitford, T.J.; Failing, M.; Theeuwes, J.; Le Pelley, M.E. Value-Modulated Oculomotor Capture by Task-Irrelevant Stimuli Is a Consequence of Early Competition on the Saccade Map. Atten. Percept. Psychophys. 2016, 78, 2226–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, P.; Pearson, D.; Most, S.B.; Theeuwes, J.; Wiers, R.W.; Le Pelley, M.E. Attentional Capture by Pavlovian Reward-Signalling Distractors in Visual Search Persists When Rewards Are Removed. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0226284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Electroencephalographic Society Guidelines in Electroencephalography, Evoked Potentials, and Polysomnography. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1994, 11, 1–147.
- Delorme, A.; Makeig, S. EEGLAB: An Open Source Toolbox for Analysis of Single-Trial EEG Dynamics Including Independent Component Analysis. J. Neurosci. Methods 2004, 134, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, N.; Zhang, B.; Allenmark, F.; Nasemann, J.; Tsai, S.; Müller, H.J.; Shi, Z. Long-term (Statistically Learnt) and Short-term (Inter-trial) Distractor-location Effects Arise at Different Pre- and Post-selective Processing Stages. Psychophysiology 2023, e14351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eimer, M. The N2pc Component as an Indicator of Attentional Selectivity. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1996, 99, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickey, C.; McDonald, J.J.; Theeuwes, J. Electrophysiological Evidence of the Capture of Visual Attention. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2006, 18, 604–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickey, C.; Di Lollo, V.; McDonald, J.J. Electrophysiological Indices of Target and Distractor Processing in Visual Search. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2009, 21, 760–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajsic, J.; Perera, H.; Pratt, J. Learned Value and Object Perception: Accelerated Perception or Biased Decisions? Atten. Percept. Psychophys. 2017, 79, 603–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Moorselaar, D.; Daneshtalab, N.; Slagter, H.A. Neural Mechanisms Underlying Distractor Inhibition on the Basis of Feature and/or Spatial Expectations. Cortex 2021, 137, 232–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.; Anderson, B. Systemic Effects of Selection History on Learned Ignoring. Psychon. Bull. Rev. 2022, 29, 1347–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berridge, K.C. The Debate over Dopamine’s Role in Reward: The Case for Incentive Salience. Psychopharmacology 2007, 191, 391–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berridge, K.C.; Robinson, T.E. What Is the Role of Dopamine in Reward: Hedonic Impact, Reward Learning, or Incentive Salience? Brain Res. Brain Res. Rev. 1998, 28, 309–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlow, H.B.; Reeves, B.C. The Versatility and Absolute Efficiency of Detecting Mirror Symmetry in Random Dot Displays. Vision. Res. 1979, 19, 783–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannouli, V. VISUAL SYMMETRY PERCEPTION. Encephalos 2013, 50, 31–42. [Google Scholar]
- Locher, P.; Nodine, C. The Perceptual Value of Symmetry. Comput. Math. Appl. 1989, 17, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rollenhagen, J.E.; Olson, C.R. Mirror-Image Confusion in Single Neurons of the Macaque Inferotemporal Cortex. Science 2000, 287, 1506–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Button, K.S.; Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Mokrysz, C.; Nosek, B.A.; Flint, J.; Robinson, E.S.J.; Munafò, M.R. Power Failure: Why Small Sample Size Undermines the Reliability of Neuroscience. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2013, 14, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade, C. Internal, External, and Ecological Validity in Research Design, Conduct, and Evaluation. Indian. J. Psychol. Med. 2018, 40, 498–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bressler, S.L.; Ding, M. Event-Related Potentials; Akay, M., Ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Logothetis, N.K. What We Can Do and What We Cannot Do with fMRI. Nature 2008, 453, 869–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, G.; Wu, R.; Wang, H.; Chen, J.; Li, S.; Wang, Q.; Sun, H.-J. Reward History and Statistical Learning Independently Impact Attention Search: An ERP Study. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 874. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14090874
Zhao G, Wu R, Wang H, Chen J, Li S, Wang Q, Sun H-J. Reward History and Statistical Learning Independently Impact Attention Search: An ERP Study. Brain Sciences. 2024; 14(9):874. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14090874
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Guang, Rongtao Wu, Huijun Wang, Jiahuan Chen, Shiyi Li, Qiang Wang, and Hong-Jin Sun. 2024. "Reward History and Statistical Learning Independently Impact Attention Search: An ERP Study" Brain Sciences 14, no. 9: 874. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14090874
APA StyleZhao, G., Wu, R., Wang, H., Chen, J., Li, S., Wang, Q., & Sun, H.-J. (2024). Reward History and Statistical Learning Independently Impact Attention Search: An ERP Study. Brain Sciences, 14(9), 874. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14090874



