Early Taurine Administration Decreases the Levels of Receptor-Interacting Serine/Threonine Protein Kinase 1 in the Duchenne Mouse Model mdx
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
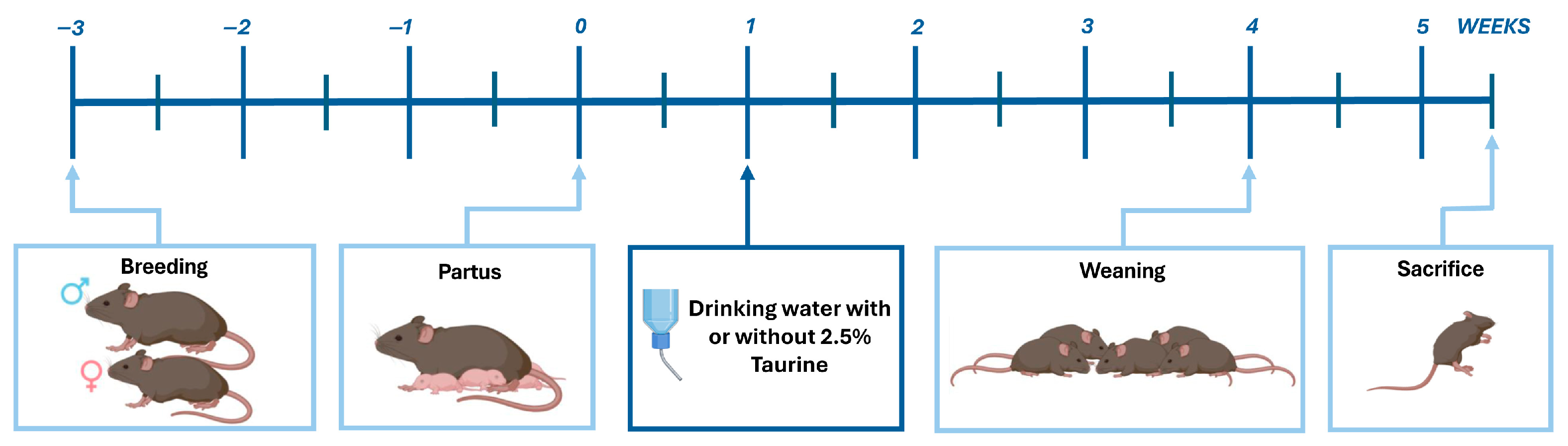
2.1. Mice
2.2. Antibodies
2.3. Proteome Arrays
2.4. Western Blotting of Muscle Total Protein Fractions
2.5. Western Blotting of Muscle Mitochondrial Protein Fractions
2.6. Immunofluorescence
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
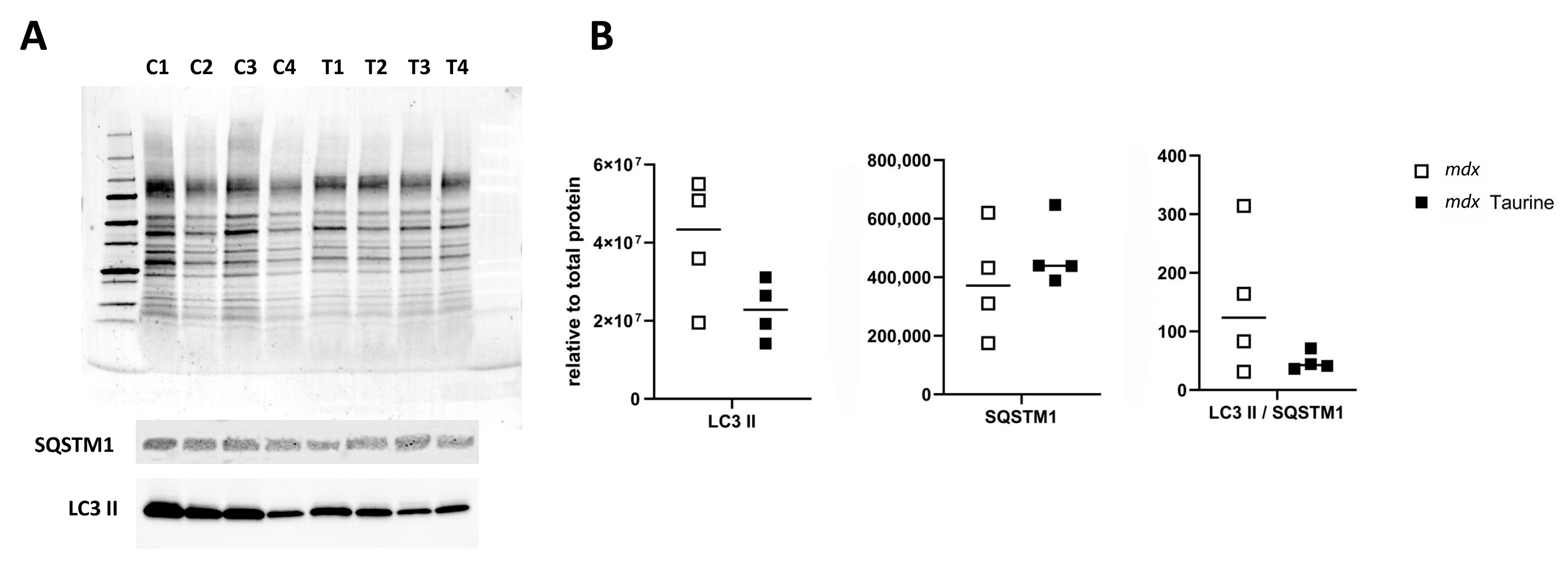
3.1. Protein Expression Levels
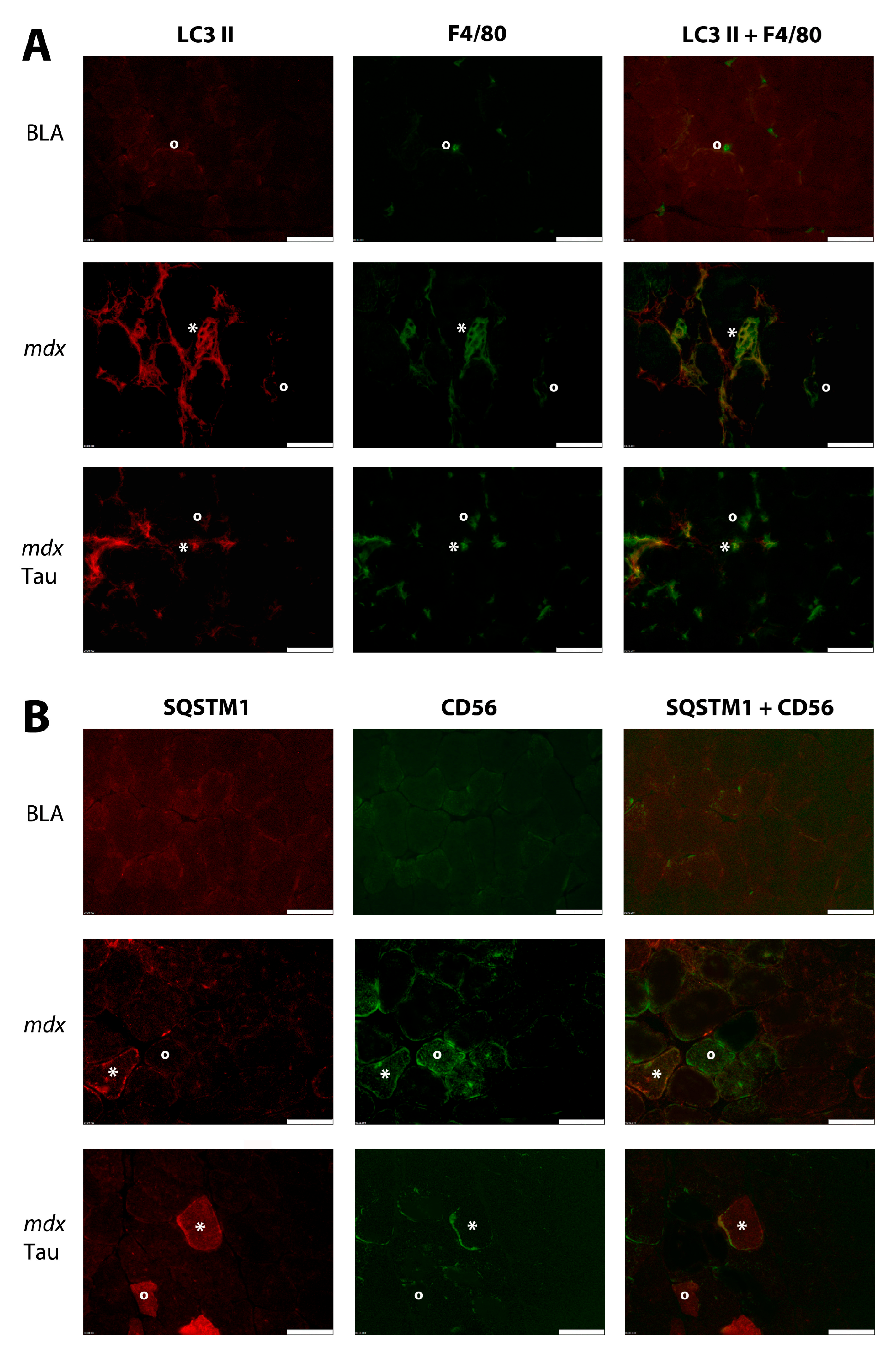
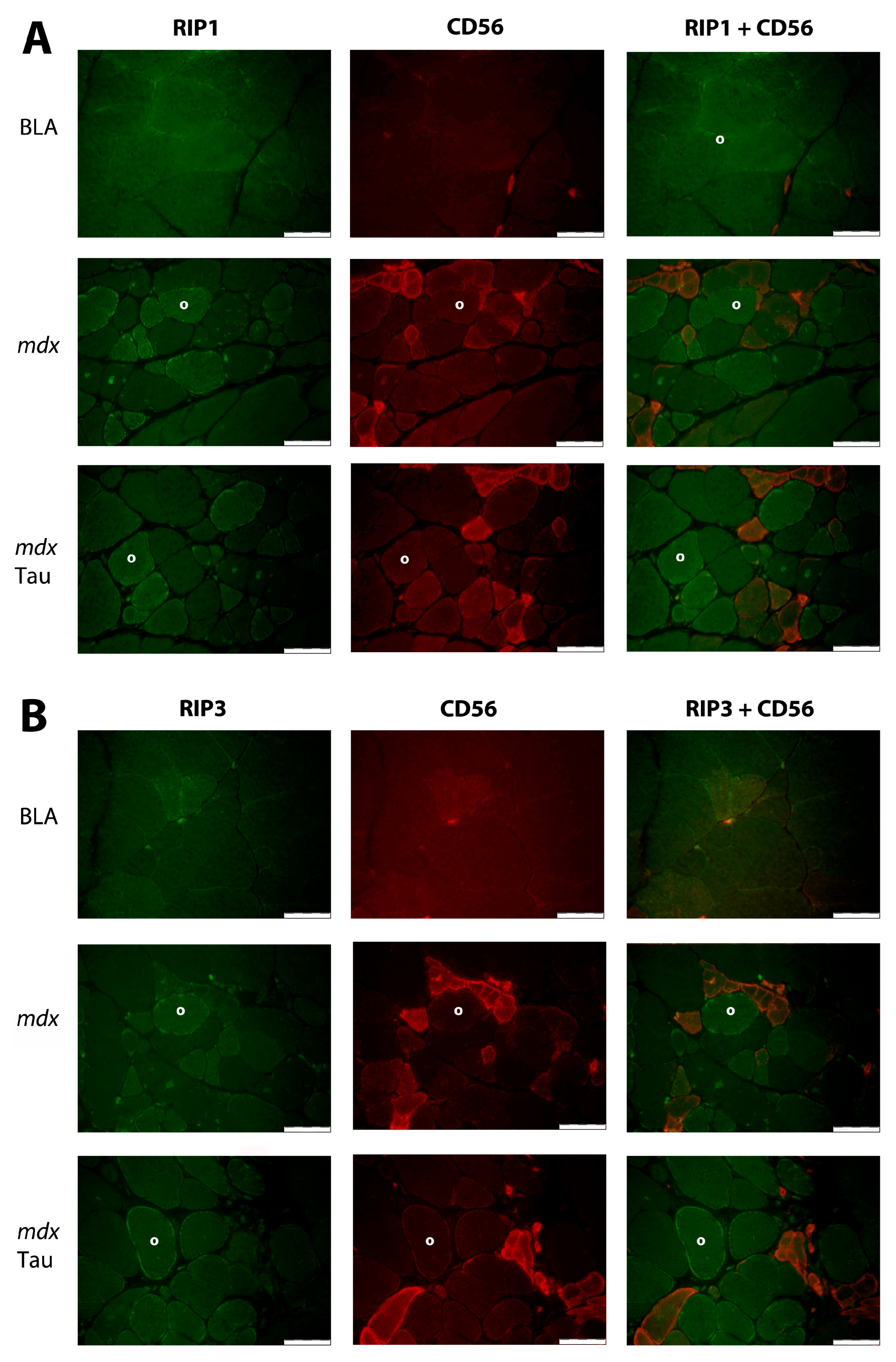
3.2. Protein Distribution in Muscle
4. Discussion
4.1. Influence of Taurine on Muscle Cell Necroptosis
4.2. Influence of Taurine on Muscle Cell Apoptosis
4.3. Influence of Taurine on Autophagy
4.4. Consequences for DMD Therapy
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DMD | Duchenne muscular dystrophy |
| RIP1 | Receptor-interacting Serine/Threonine protein kinase 1 |
| AAV | Adeno-associated virus |
| ASO | Antisense oligonucleotide |
| DAMPs | Damage-Associate Molecular Patterns |
| TLRs | Toll-like receptors |
| RIPs | Receptor-interacting Serine/Threonine protein kinases |
| TNFα | Tumor Necrosis Factorα |
| TIB | Tibialis anterior |
| TNFR1 | TNFα Receptor 1 |
| NFκB | Nuclear factor κB complex |
| MLKL | Mixed Lineage Kinase domain-Like protein |
| LC3 II | Microtubule-associated protein 1 Light Chain 3 |
| SQSTM1 | Sequestosome 1 |
| mdx | C57BL/10ScSn-Dmdmdx/J |
| BLA | Untreated age-matched healthy controls |
| WB | Western blotting |
| IF | Immunofluorescence |
| EDL | Extensor digitorum longus |
| GAS | Gastrocnemius |
| GAPDH | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase |
| TBS | Tris-Buffered Saline |
| TBST | TBS with 0.1% Tween 20 |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| Kip1 | Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1B p27 |
| SMAC | Second Mitochondria-derived Activator of Caspases |
| Diablo | Direct IAP-Binding protein with Low PI |
| HSP | Heat Shock Protein |
| TLR | Toll-like receptor |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| AMPK | AMP-activated Protein Kinase |
| GDF-15 | Growth differentiation factor-15 |
| Tug1 | Taurine-upregulated gene 1 |
| iNOS | Inducible nitric oxide synthase |
| PINK1 | PTEN-induced kinase 1 |
References
- Duan, D.; Goemans, N.; Takeda, S.; Mercuri, E.; Aartsma-Rus, A. Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 7, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Palma, C.; Perrotta, C.; Pellegrino, P.; Clementi, E.; Cervia, D. Skeletal Muscle Homeostasis in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: Modulating Autophagy as a Promising Therapeutic Strategy. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2014, 6, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deconinck, N.; Dan, B. Pathophysiology of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: Current Hypotheses. Pediatr. Neurol. 2007, 36, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsov, A.V.; Winkler, K.; Wiedemann, F.; von Bossanyi, P.; Dietzmann, K.; Kunz, W.S. Impaired Mitochondrial Oxidative Phosphorylation in Skeletal Muscle of the Dystrophin-Deficient Mdx Mouse. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 1998, 183, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, M.C.; Ramos, S.V.; Turnbull, P.C.; Rebalka, I.A.; Cao, A.; Monaco, C.M.F.; Varah, N.E.; Edgett, B.A.; Huber, J.S.; Tadi, P.; et al. Early Myopathy in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Is Associated with Elevated Mitochondrial H2O2 Emission during Impaired Oxidative Phosphorylation. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2019, 10, 643–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishna, L.; Prashant, A.; Kumar, Y.H.; Paneyala, S.; Patil, S.J.; Ramachandra, S.C.; Vishwanath, P. Molecular and Biochemical Therapeutic Strategies for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Neurol. Int. 2024, 16, 731–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bengtsson, N.E.; Tasfaout, H.; Chamberlain, J.S. The Road toward AAV-Mediated Gene Therapy of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Mol. Ther. 2025, 33, 2035–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aartsma-Rus, A.; Takeda, S. A Historical Perspective on the Development of Antisense Oligonucleotide Treatments for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy and Spinal Muscular Atrophy. J. Neuromuscul. Dis. 2025, 22143602251317422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Ayuso, D.; Pierdomenico, J.D.; Martínez-Vacas, A.; Vidal-Sanz, M.; Picaud, S.; Villegas-Pérez, M.P. Taurine: A Promising Nutraceutic in the Prevention of Retinal Degeneration. Neural Regen. Res. 2023, 19, 606–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Gollapalli, K.; Mangiola, S.; Schranner, D.; Yusuf, M.A.; Chamoli, M.; Shi, S.L.; Lopes Bastos, B.; Nair, T.; Riermeier, A.; et al. Taurine Deficiency as a Driver of Aging. Science 2023, 380, eabn9257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirupathi, A.; Pinho, R.A.; Baker, J.S.; István, B.; Gu, Y. Taurine Reverses Oxidative Damages and Restores the Muscle Function in Overuse of Exercised Muscle. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 582449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, J.A.; VanDusseldorp, T.A.; Doyle, J.A.; Otis, J.S. Taurine in Sports and Exercise. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2021, 18, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrill, J.R.; Pinniger, G.J.; Graves, J.A.; Grounds, M.D.; Arthur, P.G. Increasing Taurine Intake and Taurine Synthesis Improves Skeletal Muscle Function in the Mdx Mouse Model for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. J. Physiol. 2016, 594, 3095–3110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrill, J.R.; Webb, S.M.; Arthur, P.G.; Hackett, M.J. Investigation of the Effect of Taurine Supplementation on Muscle Taurine Content in the Mdx Mouse Model of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Using Chemically Specific Synchrotron Imaging. Analyst 2020, 145, 7242–7251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrill, J.R.; Pinniger, G.J.; Nair, K.V.; Grounds, M.D.; Arthur, P.G. Beneficial Effects of High Dose Taurine Treatment in Juvenile Dystrophic Mdx Mice Are Offset by Growth Restriction. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0187317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merckx, C.; De Paepe, B. The Role of Taurine in Skeletal Muscle Functioning and Its Potential as a Supportive Treatment for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Metabolites 2022, 12, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tidball, J.G.; Albrecht, D.E.; Lokensgard, B.E.; Spencer, M.J. Apoptosis Precedes Necrosis of Dystrophin-deficient Muscle. J. Cell Sci. 1995, 108, 2197–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, W.; Zhang, Q.; Yan, Z.; Chen, R.; Zeh Iii, H.J.; Kang, R.; Lotze, M.T.; Tang, D. Strange Attractors: DAMPs and Autophagy Link Tumor Cell Death and Immunity. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenberg, A.S.; Puig, M.; Nagaraju, K.; Hoffman, E.P.; Villalta, S.A.; Rao, V.A.; Wakefield, L.M.; Woodcock, J. Immune-Mediated Pathology in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 299rv4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bencze, M. Mechanisms of Myofibre Death in Muscular Dystrophies: The Emergence of the Regulated Forms of Necrosis in Myology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 24, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, J.E.; Prola, A.; Mariot, V.; Pini, V.; Meng, J.; Hourde, C.; Dumonceaux, J.; Conti, F.; Relaix, F.; Authier, F.-J.; et al. Necroptosis Mediates Myofibre Death in Dystrophin-Deficient Mice. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphries, F.; Yang, S.; Wang, B.; Moynagh, P.N. RIP Kinases: Key Decision Makers in Cell Death and Innate Immunity. Cell Death Differ. 2015, 22, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Festjens, N.; Vanden Berghe, T.; Cornelis, S.; Vandenabeele, P. RIP1, a Kinase on the Crossroads of a Cell’s Decision to Live or Die. Cell Death Differ. 2007, 14, 400–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merckx, C.; Zschüntzsch, J.; Meyer, S.; Raedt, R.; Verschuere, H.; Schmidt, J.; De Paepe, B.; De Bleecker, J.L. Exploring the Therapeutic Potential of Ectoine in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: Comparison with Taurine, a Supplement with Known Beneficial Effects in the Mdx Mouse. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Jiang, N.; Su, W.; Zhuo, Y. Necroptosis: A Novel Pathway in Neuroinflammation. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 701564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merckx, C.; Cosemans, G.; Zschüntzsch, J.; Raedt, R.; Schmidt, J.; De Paepe, B.; De Bleecker, J.L. Description of Osmolyte Pathways in Maturing Mdx Mice Reveals Altered Levels of Taurine and Sodium/Myo-Inositol Co-Transporters. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiMario, J.X.; Uzman, A.; Strohman, R.C. Fiber Regeneration Is Not Persistent in Dystrophic (MDX) Mouse Skeletal Muscle. Dev. Biol. 1991, 148, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimauro, I.; Pearson, T.; Caporossi, D.; Jackson, M.J. A Simple Protocol for the Subcellular Fractionation of Skeletal Muscle Cells and Tissue. BMC Res. Notes 2012, 5, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bencze, M.; Periou, B.; Punzón, I.; Barthélémy, I.; Taglietti, V.; Hou, C.; Zaidan, L.; Kefi, K.; Blot, S.; Agbulut, O.; et al. Receptor Interacting Protein Kinase-3 Mediates Both Myopathy and Cardiomyopathy in Preclinical Animal Models of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2023, 14, 2520–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, H.; Wang, Z.; Yang, S.; Zheng, X.; Bao, Y.; Lin, W.; Huang, C.; Qiu, L. Taurine Inhibits Necroptosis Helps to Alleviate Inflammatory and Injury Induced by Klebsiella Infection. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2022, 250, 110444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, X.; Ren, P.; Bai, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, L.; Hu, J.; Li, X.; Ding, K. Modulatory Effects of Regulated Cell Death: An Innovative Preventive Approach for the Control of Mastitis. Cells 2024, 13, 1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodayar, M.J.; Kalantari, H.; Khorsandi, L.; Ahangar, N.; Samimi, A.; Alidadi, H. Taurine Attenuates Valproic Acid-Induced Hepatotoxicity via Modulation of RIPK1/RIPK3/MLKL-Mediated Necroptosis Signaling in Mice. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2021, 48, 4153–4162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delanghe, T.; Huyghe, J.; Lee, S.; Priem, D.; Coillie, S.V.; Gilbert, B.; Choi, S.M.; Vandenabeele, P.; Degterev, A.; Cuny, G.D.; et al. Antioxidant and Food Additive BHA Prevents TNF Cytotoxicity by Acting as a Direct RIPK1 Inhibitor. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegner, K.W.; Saleh, D.; Degterev, A. Complex Pathologic Roles of RIPK1 and RIPK3: Moving Beyond Necroptosis. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 38, 202–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreenivasan, K.; Ianni, A.; Künne, C.; Strilic, B.; Günther, S.; Perdiguero, E.; Krüger, M.; Spuler, S.; Offermanns, S.; Gómez-Del Arco, P.; et al. Attenuated Epigenetic Suppression of Muscle Stem Cell Necroptosis Is Required for Efficient Regeneration of Dystrophic Muscles. Cell Rep. 2020, 31, 107652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.-Y.; Kang, J.-H.; Lee, S.-B.; Kang, T.-B.; Lee, K.-H. Down-Regulation of pro-Necroptotic Molecules Blunts Necroptosis during Myogenesis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 557, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, R.; Ferry, A.L.; Dupont-Versteegden, E.E. Cell Death-Resistance of Differentiated Myotubes Is Associated with Enhanced Anti-Apoptotic Mechanisms Compared to Myoblasts. Apoptosis 2011, 16, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, W.J.; Sridharan, H.; Huang, C.; Mandal, P.; Upton, J.W.; Gough, P.J.; Sehon, C.A.; Marquis, R.W.; Bertin, J.; Mocarski, E.S. Toll-like Receptor 3-Mediated Necrosis via TRIF, RIP3, and MLKL. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 31268–31279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Paepe, B. Progressive Skeletal Muscle Atrophy in Muscular Dystrophies: A Role for Toll-Like Receptor-Signaling in Disease Pathogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spencer, M.J.; Walsh, C.M.; Dorshkind, K.A.; Rodriguez, E.M.; Tidball, J.G. Myonuclear Apoptosis in Dystrophic Mdx Muscle Occurs by Perforin-Mediated Cytotoxicity. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 99, 2745–2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, C.Y.; Lim, R.W. Involvement of P27(Kip1) and Cyclin D3 in the Regulation of Cdk2 Activity during Skeletal Muscle Differentiation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2000, 1497, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.I.; Huang, Y.Y.; Deshmukh, M. Skeletal Muscle Differentiation Evokes Endogenous XIAP to Restrict the Apoptotic Pathway. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, T.V.A.; McMahon, J.M.; Howley, B.A.; Stanley, A.; Ritter, T.; Mohr, A.; Zwacka, R.; Fearnhead, H.O. A Non-Apoptotic Role for Caspase-9 in Muscle Differentiation. J. Cell Sci. 2008, 121, 3786–3793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, B.; Xiao, W.; Shi, Y.; Liu, M.; Xiao, X. Role of Smac/DIABLO in Hydrogen Peroxide-Induced Apoptosis in C2C12 Myogenic Cells. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2005, 39, 658–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J.P.; Billin, A.N.; Campbell, M.E.; Russell, A.J.; Huffman, K.M.; Kraus, W.E. The AMPK/p27Kip1 Axis Regulates Autophagy/Apoptosis Decisions in Aged Skeletal Muscle Stem Cells. Stem Cell Rep. 2018, 11, 425–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, S.Y.; Mikhail, A.I.; Mattina, S.R.; Manta, A.; Diffey, I.J.; Ljubicic, V. Acute, next-Generation AMPK Activation Initiates a Disease-Resistant Gene Expression Program in Dystrophic Skeletal Muscle. FASEB J. 2023, 37, e22863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fennel, Z.J.; Amorim, F.T.; Deyhle, M.R.; Hafen, P.S.; Mermier, C.M. The Heat Shock Connection: Skeletal Muscle Hypertrophy and Atrophy. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2022, 323, R133–R148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosemans, G.; Merckx, C.; De Bleecker, J.L.; De Paepe, B. Inducible Heat Shock Protein 70 Levels in Patients and the Mdx Mouse Affirm Regulation during Skeletal Muscle Regeneration in Muscular Dystrophy. Front. Biosci. 2022, 14, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, S.S.; Swiderski, K.; Ryall, J.G.; Lynch, G.S. Therapeutic Potential of Heat Shock Protein Induction for Muscular Dystrophy and Other Muscle Wasting Conditions. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2018, 373, 20160528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, S.L.; Cookson, B.T. Apoptosis, Pyroptosis, and Necrosis: Mechanistic Description of Dead and Dying Eukaryotic Cells. Infect. Immun. 2005, 73, 1907–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fefelova, N.; Mareedu, S.; Pamarthi, S.H.; Babu, G.J.; Gwathmey, J.K.; Xie, L.-H. Abstract P1156: Potential Role Of Ferroptosis In Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy-Associated Cardiomyopathy. Circ. Res. 2023, 133, AP1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubuisson, N.; Davis-López de Carrizosa, M.A.; Versele, R.; Selvais, C.M.; Noel, L.; Van den Bergh, P.Y.D.; Brichard, S.M.; Abou-Samra, M. Inhibiting the Inflammasome with MCC950 Counteracts Muscle Pyroptosis and Improves Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1049076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willemart, C.; Seurinck, R.; Stroobants, T.; Van Coillie, S.; De Loor, J.; Choi, S.M.; Roelandt, R.; Rajapurkar, M.; Ligthart, S.; Jorens, P.G.; et al. Potential of Biomarker-Based Enrichment Strategies to Identify Critically Ill Patients for Emerging Cell Death Interventions. Cell Death Differ. 2025, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Paepe, B. Growth Differentiation Factor-15 as an Emerging Biomarker for Identifying Myositis. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2022, 18, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Qi, Z.; Huang, C.; Lin, D. Taurine Alleviates Ferroptosis-Induced Metabolic Impairments in C2C12 Myoblasts by Stabilizing the Labile Iron Pool and Improving Redox Homeostasis. J. Proteome Res. 2024, 23, 3444–3459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Qi, Z.; Yang, L.; Huang, C.; Wang, L.; Lin, D. Taurine Attenuates Disuse Muscle Atrophy Through Modulation of the xCT-GSH-GPX4 and AMPK-ACC-ACSL4 Pathways. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, T.; Pei, P.; Yao, X.; Jiang, L.; Wei, S.; Wang, Z.; Bai, J.; Yang, G.; Gao, N.; Yang, L.; et al. Taurine Attenuates Arsenic-Induced Pyroptosis and Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis by Inhibiting the Autophagic-Inflammasomal Pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, J.; Liu, K.; Liu, S.; Yue, D.; Zhang, P.; Mao, X.; He, W.; Huang, K.; Chen, X. Taurine Alleviates Ochratoxin A-Induced Pyroptosis in PK-15 Cells by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2023, 37, e23249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Palma, C.; Morisi, F.; Cheli, S.; Pambianco, S.; Cappello, V.; Vezzoli, M.; Rovere-Querini, P.; Moggio, M.; Ripolone, M.; Francolini, M.; et al. Autophagy as a New Therapeutic Target in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Cell Death Dis. 2012, 3, e418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez Armengol, E.; Merckx, C.; De Sutter, H.; De Bleecker, J.L.; De Paepe, B. Changes to the Autophagy-Related Muscle Proteome Following Short-Term Treatment with Ectoine in the Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Mouse Model Mdx. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaffer, S.; Kim, H.W. Effects and Mechanisms of Taurine as a Therapeutic Agent. Biomol. Ther. 2018, 26, 225–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbiera, A.; Sorrentino, S.; Lepore, E.; Carfì, A.; Sica, G.; Dobrowolny, G.; Scicchitano, B.M. Taurine Attenuates Catabolic Processes Related to the Onset of Sarcopenia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, A.L.; Alexander, M.S. The Interplay of Mitophagy and Inflammation in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Life 2021, 11, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mucha, O.; Kaziród, K.; Podkalicka, P.; Rusin, K.; Dulak, J.; Łoboda, A. Dysregulated Autophagy and Mitophagy in a Mouse Model of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Remain Unchanged Following Heme Oxygenase-1 Knockout. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 23, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Li, T.; Zhang, B.; Wang, P. Taurine Rescues Intervertebral Disc Degeneration by Activating Mitophagy through the PINK1/Parkin Pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2024, 739, 150587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jong, C.J.; Sandal, P.; Schaffer, S.W. The role of taurine in mitochondria health: More than just an antioxidant. Molecules 2021, 26, 4913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, T.L.; Matsuda, T.; Cepko, C.L. The Noncoding RNA Taurine Upregulated Gene 1 Is Required for Differentiation of the Murine Retina. Curr. Biol. 2005, 15, 501–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trewin, A.J.; Silver, J.; Dillon, H.T.; Della Gatta, P.A.; Parker, L.; Hiam, D.S.; Lee, Y.P.; Richardson, M.; Wadley, G.D.; Lamon, S. Long Non-Coding RNA Tug1 Modulates Mitochondrial and Myogenic Responses to Exercise in Skeletal Muscle. BMC Biol. 2022, 20, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripodi, L.; Villa, C.; Molinaro, D.; Torrente, Y.; Farini, A. The Immune System in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Pathogenesis. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrof, B.J.; Podolsky, T.; Bhattarai, S.; Tan, J.; Ding, J. Trained Immunity as a Potential Target for Therapeutic Immunomodulation in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1183066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Paepe, B.; De Bleecker, J.L. Cytokines and Chemokines as Regulators of Skeletal Muscle Inflammation: Presenting the Case of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Mediat. Inflamm. 2013, 2013, 540370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Carvalho, S.C.; Apolinário, L.M.; Matheus, S.M.M.; Santo Neto, H.; Marques, M.J. EPA Protects against Muscle Damage in the Mdx Mouse Model of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy by Promoting a Shift from the M1 to M2 Macrophage Phenotype. J. Neuroimmunol. 2013, 264, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inomata, M.; Xu, S.; Chandra, P.; Meydani, S.N.; Takemura, G.; Philips, J.A.; Leong, J.M. Macrophage LC3-Associated Phagocytosis Is an Immune Defense against Streptococcus Pneumoniae That Diminishes with Host Aging. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 33561–33569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Lu, C.; Wu, B.; Lan, C.; Mo, L.; Chen, C.; Wang, X.; Zhang, N.; Lan, L.; Wang, Q.; et al. Taurine Antagonizes Macrophages M1 Polarization by Mitophagy-Glycolysis Switch Blockage via Dragging SAM-PP2Ac Transmethylation. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 648913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viola, A.; Munari, F.; Sánchez-Rodríguez, R.; Scolaro, T.; Castegna, A. The Metabolic Signature of Macrophage Responses. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mifflin, L.; Ofengeim, D.; Yuan, J. Receptor-Interacting Protein Kinase 1 (RIPK1) as a Therapeutic Target. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2020, 19, 553–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamberi, T.; Fiaschi, T.; Valocchia, E.; Modesti, A.; Mantuano, P.; Rolland, J.-F.; Sanarica, F.; De Luca, A.; Magherini, F. Proteome Analysis in Dystrophic Mdx Mouse Muscle Reveals a Drastic Alteration of Key Metabolic and Contractile Proteins after Chronic Exercise and the Potential Modulation by Anti-Oxidant Compounds. J. Proteom. 2018, 170, 43–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dias, M.; Dhuyvetter, H.; Byttebier, E.; Merckx, C.; De Bleecker, J.L.; De Paepe, B. Early Taurine Administration Decreases the Levels of Receptor-Interacting Serine/Threonine Protein Kinase 1 in the Duchenne Mouse Model mdx. Brain Sci. 2025, 15, 1175. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15111175
Dias M, Dhuyvetter H, Byttebier E, Merckx C, De Bleecker JL, De Paepe B. Early Taurine Administration Decreases the Levels of Receptor-Interacting Serine/Threonine Protein Kinase 1 in the Duchenne Mouse Model mdx. Brain Sciences. 2025; 15(11):1175. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15111175
Chicago/Turabian StyleDias, Marthe, Hanne Dhuyvetter, Ella Byttebier, Caroline Merckx, Jan L. De Bleecker, and Boel De Paepe. 2025. "Early Taurine Administration Decreases the Levels of Receptor-Interacting Serine/Threonine Protein Kinase 1 in the Duchenne Mouse Model mdx" Brain Sciences 15, no. 11: 1175. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15111175
APA StyleDias, M., Dhuyvetter, H., Byttebier, E., Merckx, C., De Bleecker, J. L., & De Paepe, B. (2025). Early Taurine Administration Decreases the Levels of Receptor-Interacting Serine/Threonine Protein Kinase 1 in the Duchenne Mouse Model mdx. Brain Sciences, 15(11), 1175. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15111175









