Ouabain Counteracts Retinal Ganglion Cell Death Through Modulation of BDNF and IL-1 Signaling Pathways
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Animals
2.3. Primary Retinal Cell Cultures
2.4. Retrograde Labeling, Identification, and Quantification of Retinal Ganglion Cells
2.5. Western Blotting
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
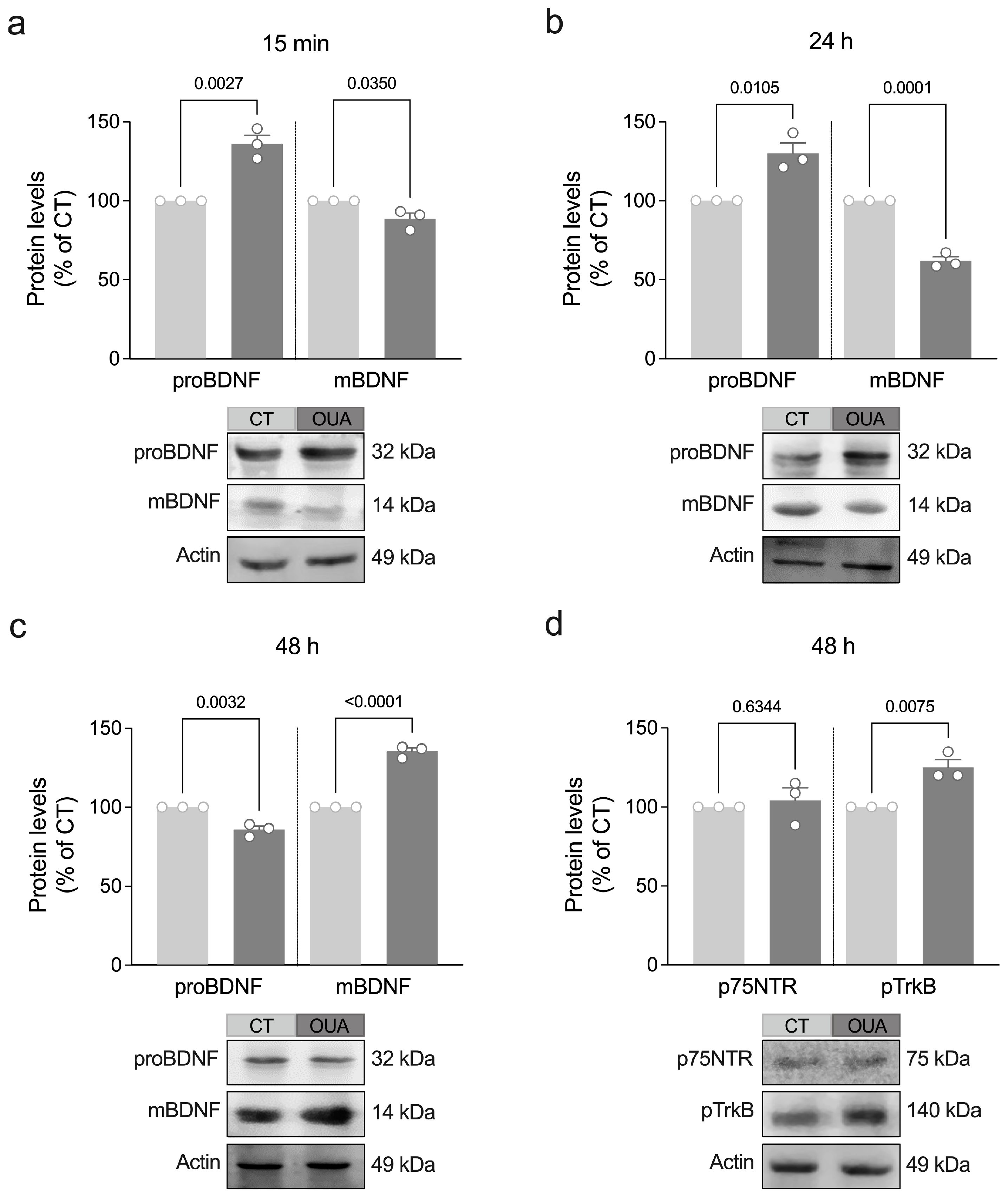
3.1. Ouabain Stimulates Maturation of BDNF and TrkB Phosphorylation
3.2. MMP-9 Mediates Ouabain-Induced Maturation of BDNF
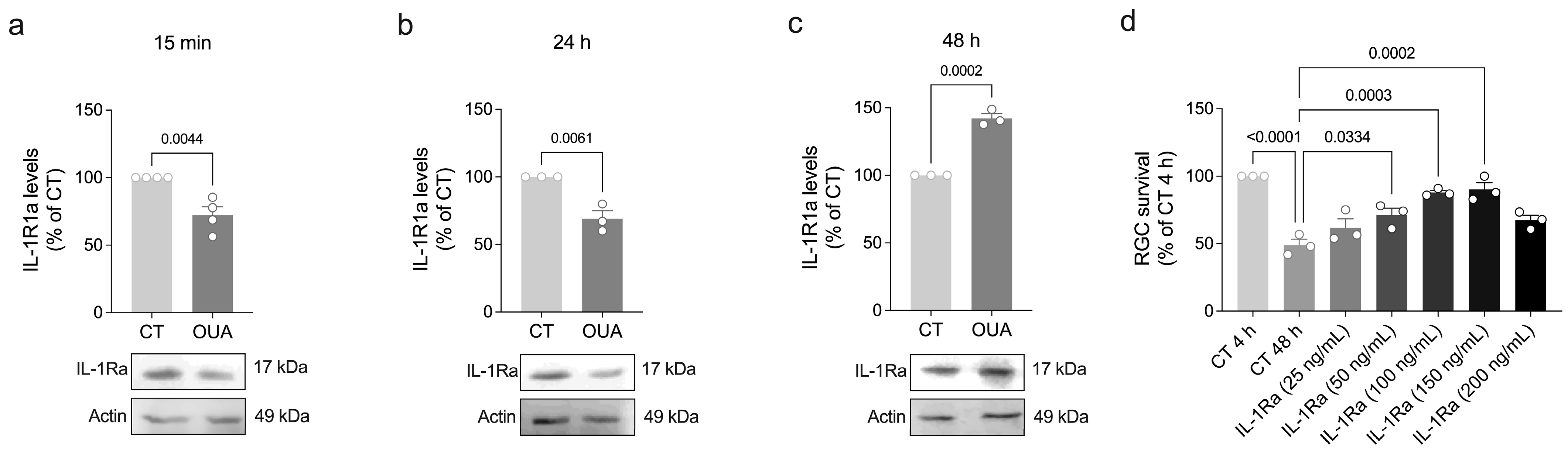
3.3. Ouabain Promotes a Physiological IL-1β Signaling
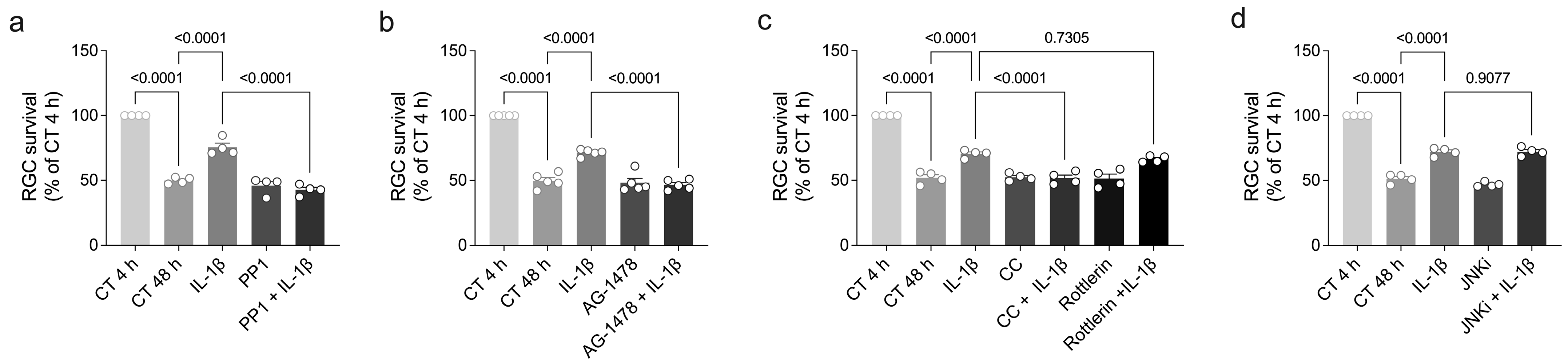
3.4. Ouabain Promotes RGC Survival Through a Signaling Mechanism Shared by IL-1β, TNF-α, and BDNF
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khatib, T.; Martin, K. Protecting retinal ganglion cells. Eye 2017, 31, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tempone, M.H.; Borges-Martins, V.P.; César, F.; Alexandrino-Mattos, D.P.; de Figueiredo, C.S.; Raony, Í.; dos Santos, A.A.; Duarte-Silva, A.T.; Dias, M.S.; Freitas, H.R.; et al. The healthy and diseased retina seen through neuron–glia interactions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Benowitz, L.I. In vitro and in vivo methods for studying retinal ganglion cell survival and optic nerve regeneration. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1695, 187–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vision Loss Expert Group of the Global Burden of Disease Study. Global estimates on the number of people blind or visually impaired by glaucoma: A meta-analysis from 2000 to 2020. Eye 2024, 38, 2036–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Rezende Corrêa, G.; dos Santos, A.A.; Fontes, C.F.; de Araujo, E.G. Ouabain induces an increase of retinal ganglion cell survival in vitro: The involvement of protein kinase C. Brain Res. 2005, 5, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Rezende Corrêa, G.; da Silva Cunha, K.C.; Dos Santos, A.A.; de Araujo, E.G. The trophic effect of ouabain on retinal ganglion cell is mediated by EGF receptor and PKC δ activation. Neurochem. Res. 2010, 35, 1343–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Rezende Corrêa, G.; Soares, V.H.; de Araújo-Martins, L.; Dos Santos, A.A.; Giestal-de-Araujo, E. Ouabain and BDNF crosstalk on ganglion cell survival in mixed retinal cell cultures. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 2015, 35, 651–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambuk, L.; Mohd Lazaldin, M.A.; Ahmad, S.; Iezhitsa, I.; Agarwal, R.; Uskoković, V.; Mohamud, R. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor mediated neuroprotection in glaucoma: A review of current state of the art. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 20, 875662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, L.; Joo, D.; Sun, S.C. NF-κB signaling in inflammation. Sig. Transduct Target Ther. 2017, 2, 17023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramani, M.; Lambrecht, B.; Ahmad, I. Human microglia-derived proinflammatory cytokines facilitate human retinal ganglion cell development and regeneration. Stem Cell Rep. 2024, 19, 1092–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von-Held-Ventura, J.S.; Mázala-de-Oliveira, T.; da Rocha Oliveira, A.C.; Granja, M.G.; Gonçalves-de-Albuquerque, C.F.; Castro-Faria-Neto, H.C.; Giestal-de-Araujo, E. The trophic effect of ouabain on retinal ganglion cells is mediated by IL-1β and TNF-α. BBRC 2016, 478, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mázala-de-Oliveira, T.; de Figueiredo, C.S.; de Rezende Corrêa, G.; da Silva, M.S.; Miranda, R.L.; de Azevedo, M.A.; Cossenza, M.; Dos Santos, A.A.; Giestal-de-Araujo, E. Ouabain-Na+/K+-ATPase signaling regulates retinal neuroinflammation and ROS production preventing neuronal death by an autophagy-dependent mechanism following optic nerve axotomy in vitro. Neurochem. Res. 2022, 47, 723–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colares, T.G.; de Figueiredo, C.S.; de Oliveira Jesus Souza, L.; Dos Santos, A.A.; Giestal-de-Araujo, E. Increased retinal ganglion cell survival by exogenous IL-2 depends on IL-10, dopamine D1 receptors, and classical IL-2/IL-2R signaling pathways. Neurochem. Res. 2021, 46, 1701–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mesulam, M. Tracing Neural Connections with Horseradish Peroxidase, 1st ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Barde, Y.A.; Edgar, D.; Thoenen, H. Purification of a new neurotrophic factor from mammalian brain. EMBO J. 1982, 1, 549–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, M. Neurotrophins and their receptors: A convergence point for many signalling pathways. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2003, 4, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levi-Montalcini, R.; Hamburger, V. Selective growth stimulating effects of mouse sarcoma on the sensory and sympathetic nervous system of the chick embryo. J. Exp. Zool. 1951, 116, 321–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Pang, P.; Woo, N. The yin and yang of neurotrophin action. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2005, 6, 603–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinhard, S.M.; Razak, K.; Ethell, I.M. A delicate balance: Role of MMP-9 in brain development and pathophysiology of neurodevelopmental disorders. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2015, 29, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.J.; Park, M.H.; Choi, S.Y.; Koh, J.Y. Activation of the Trk signaling pathway by extracellular zinc: Role of metalloproteinases. JBC 2005, 280, 11995–12001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinelli, S.; Anderzhanova, E.A.; Bajaj, T.; Wiechmann, S.; Dethloff, F.; Weckmann, K.; Heinz, D.E.; Ebert, T.; Hartmann, J.; Geiger, T.M.; et al. Stress-primed secretory autophagy promotes extracellular BDNF maturation by enhancing MMP9 secretion. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabay, C.; Lamacchia, C.; Palmer, G. IL-1 pathways in inflammation and human diseases. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2010, 6, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peinado-Ramon, P.; Salvador, M.; Villegas-Perez, M.P.; Vidal-Sanz, M. Effects of axotomy and intraocular administration of NT-4, NT-3 and Brain-derived neurotrophic factor on the survival of adult rat retinal ganglion cells: A quantitative In Vivo Study. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1996, 37, 489–500. [Google Scholar]
- Aguayo, A.J.; Clarke, D.B.; Jelsma, T.N.; Kittlérova, P.; Friedman, H.C.; Bray, G.M. Effects of neurotrophins on the survival and regrowth of injured retinal neurons. Ciba Found. Symp. 1996, 196, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klöcker, N.; Cellerino, A.; Bähr, M. Free radical scavenging and inhibition of nitric oxide synthase potentiates the neurotrophic effect of brain-derived neurotrophic factor on axotomized retinal ganglion cells in vivo. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 1038–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Weber, A.J. BDNF enhances retinal ganglion cell survival in cats with optic nerve damage. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2001, 42, 966–974. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mansour-Robaey, S.; Clarke, D.B.; Wang, Y.-C.; Bray, G.M.; Aguayo, A.J. Effects of ocular injury and administration of Brain-derived neurotrophic factor on survival and regrowth of axotomized retinal ganglion cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 1632–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mey, J.; Thanos, S. Intravitreal injections of neurotrophic factors support the survival of axotomized retinal ganglion cells in adult rats in vivo. Brain Res. 1993, 602, 304–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrilla-Reverter, G.; Agudo, M.; Vidal-Sanz, M.; Villegas-Perez, M.P. Effects of different neurotrophic factors on the survival of retinal ganglion cells after a complete intraorbital nerve crush injury: A quantitative in vivo study. Exp. Eye Res. 2009, 89, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, A.; Namekata, K.; Guo, X.; Harada, C.; Harada, T. Neuroprotection, growth factors, and BDNF-TrkB signalling in retinal degeneration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quigley, H.; Pease, M.E.; Zack, D.J. Retrograde axonal transport of BDNF in retinal ganglion cells is blocked by acute IOP elevation in rats. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2000, 41, 3460–3466. [Google Scholar]
- Oddone, F.; Roberti, G.; Micera, A.; Busanello, A.; Bonini, S.; Quaranta, L. Exploring serum levels of Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and nerve growth factor across glaucoma stages. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0168565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uzel, M.; Gungor, K.; Uzun, S.; Keskin, H.; Uncu, G. The effect of trabeculectomy on serum Brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels in primary open-angle glaucoma. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2018, 256, 1173–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, M.T.R.; Caminos, E. Expression of Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and its functional receptor in neonatal and adult rat retina. Neurosci. Lett. 1995, 183, 96–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y.; Dergham, P.; Nedev, H.; Xu, Y.; Galan, A.; Cooper, E.; Di Polo, A. Chronic and acute models of retinal neurodegeneration TrkA activity are neuroprotective whereas p75NTR activity is neurotoxic through a paracrine mechanism. JBC 2010, 285, 39392–39400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.; Sapieha, P.; Kittlerova, P.; Hauswirth, W.W.; Di Polo, A. TrkB gene transfer protects retinal ganglion cells from axotomy-induced death in vivo. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 3977–3986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orellana, A.M.; Kinoshita, P.F.; Leite, J.A.; Kawamoto, E.M.; Scavone, C. Cardiotonic steroids as modulators of neuroinfammation. Front. Endocrinol. 2016, 7, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forshammar, J.; Jörneberg, P.; Björklund, U.; Westerlund, A.; Lundborg, C.; Biber, B.; Hansson, E. Anti-inflammatory substances can influence some glial cell types but not others. Brain Res. 2013, 1539, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, P.F.; Yshii, L.M.; Vasconcelos, A.R.; Orellana, A.M.; de Sá, L.L.; Davel, A.P.; Rossoni, L.V.; Kawamoto, E.M.; Scavone, C. Signaling function of Na, K-ATPase induced by ouabain against LPS as an inflammation model in hippocampus. J. Neuroinflammation 2014, 11, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wooff, Y.; Man, S.M.; Aggio-Bruce, R.; Natoli, R.; Fernando, N. IL-1 Family members mediate cell death, inflammation and angiogenesis in retinal degenerative diseases. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todd, L.; Palazzo, I.; Suarez, L.; Liu, X.; Volkov, L.; Hoang, T.V.; Campbell, W.A.; Blackshaw, S.; Quan, N.; Fischer, A.J. Reactive microglia and IL1β/IL-1R1-signaling mediate neuroprotection in excitotoxin-damaged mouse retina. J. Neuroinflammation 2019, 16, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomasoni, R.; Morini, R.; Lopez-Atalaya, J.P.; Corradini, I.; Canzi, A.; Rasile, M.; Mantovani, C.; Pozzi, D.; Garlanda, C.; Mantovani, A.; et al. Lack of IL-1R8 in neurons causes hyperactivation of IL-1 receptor pathway and induces MECP2-dependent synaptic defects. eLife 2017, 6, e21735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yazdi, A.S.; Ghoreschi, K. The interleukin-1 family. In Regulation of Cytokine Gene Expression in Immunity and Diseases. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Ma, X., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2016; Volume 941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coughlin, B.A.; Christian, B.; Trombley, B.; Mohr, S. Interleukin-1 receptor-dependent and-independent caspase-1 activity in retinal cells mediated by receptor interacting protein 2. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2024, 12, 1467799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, E.C.; Oliveira, A.C.D.R.; Garcia, C.G.; Cossenza, M.; Gonçalves-de-Albuquerque, C.F.; Castro-Faria-Neto, H.C.; Giestal-de-Araujo, E.; Dos Santos, A.A. PMA treatment fosters rat retinal ganglion cell survival via TNF signaling. Neurosci. Lett. 2021, 763, 136197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, L.E.G.; Miranda, R.L.; Granja, M.G.; Giestal-de-Araujo, E.; Dos Santos, A.A. PKC delta activation increases neonatal rat retinal cells survival in vitro: Involvement of neurotrophins and M1 muscarinic receptors. BBRC 2018, 500, 917–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saba-El-Leil, M.K.; Frémin, C.; Meloche, S. Redundancy in the world of MAP kinases: All for one. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2016, 4, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Name | Company | Dilution |
|---|---|---|
| Primary antibodies | ||
| Rabbit anti-IL-1β | PeproTech (Cranbury, NJ, USA) | 1:1500 |
| Mouse anti-caspase-1 | Santa Cruz Biotechnology (Dallas, TX, USA) | 1:1000 |
| Rabbit anti-IL-1Ra | PeproTech (Cranbury, NJ, USA) | 1:1250 |
| Mouse anti-IL-1R1 | Santa Cruz Biotechnology (Dallas, TX, USA) | 1:1000 |
| Rabbit anti-mBDNF | PeproTech (Cranbury, NJ, USA) | 1:1200 |
| Mouse anti-proBDNF | Santa Cruz Biotechnology (Dallas, TX, USA) | 1:1000 |
| Mouse anti-p75NTR | Santa Cruz Biotechnology (Dallas, TX, USA) | 1:1000 |
| Rabbit anti-pTrkB | Santa Cruz Biotechnology (Dallas, TX, USA) | 1:700 |
| Rabbit anti-NGF | PeproTech (Cranbury, NJ, USA) | 1:750 |
| Rabbit anti-actin | Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA) | 1:500 |
| Secondary antibodies | ||
| Goat anti-rabbit IgG-HRP | GE Healthcare Life Sciences (Chicago, IL, USA) | 1:15,000 |
| Goat anti-mouse IgG-HRP | Santa Cruz Biotechnology (Dallas, TX, USA) | 1:15,000 |
| Src | EGFR | PKC (PKC-δ) | JNK | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ouabain | Yes | Yes | Yes (PKC-δ-dependent) | Yes | [5,6] |
| IL-1β | Yes | Yes | Yes (PKC-δ-independent) | No | Figure 5 |
| TNF-α | No | Yes | Yes (N/A) | N/A | Figure S3 |
| BDNF | Yes | No | Yes (PKC-δ-dependent) | Yes | [7] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oliveira, A.C.d.R.; Figueiredo, C.S.; Raony, Í.; Von-Held-Ventura, J.S.; Granja, M.G.; Mázala-de-Oliveira, T.; Pedrosa-Soares, V.H.; dos Santos, A.A.; Giestal-de-Araujo, E. Ouabain Counteracts Retinal Ganglion Cell Death Through Modulation of BDNF and IL-1 Signaling Pathways. Brain Sci. 2025, 15, 123. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15020123
Oliveira ACdR, Figueiredo CS, Raony Í, Von-Held-Ventura JS, Granja MG, Mázala-de-Oliveira T, Pedrosa-Soares VH, dos Santos AA, Giestal-de-Araujo E. Ouabain Counteracts Retinal Ganglion Cell Death Through Modulation of BDNF and IL-1 Signaling Pathways. Brain Sciences. 2025; 15(2):123. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15020123
Chicago/Turabian StyleOliveira, Amanda Candida da Rocha, Camila Saggioro Figueiredo, Ícaro Raony, Juliana Salles Von-Held-Ventura, Marcelo Gomes Granja, Thalita Mázala-de-Oliveira, Vinícius Henrique Pedrosa-Soares, Aline Araujo dos Santos, and Elizabeth Giestal-de-Araujo. 2025. "Ouabain Counteracts Retinal Ganglion Cell Death Through Modulation of BDNF and IL-1 Signaling Pathways" Brain Sciences 15, no. 2: 123. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15020123
APA StyleOliveira, A. C. d. R., Figueiredo, C. S., Raony, Í., Von-Held-Ventura, J. S., Granja, M. G., Mázala-de-Oliveira, T., Pedrosa-Soares, V. H., dos Santos, A. A., & Giestal-de-Araujo, E. (2025). Ouabain Counteracts Retinal Ganglion Cell Death Through Modulation of BDNF and IL-1 Signaling Pathways. Brain Sciences, 15(2), 123. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15020123






