Altered Hemispheric Asymmetry of Functional Hierarchy in Schizophrenia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants and Data Acquisition
2.2. Data Preprocessing
2.3. Hemispheric Functional Gradients
2.4. Asymmetry Index
2.5. Between-Group Comparison of Gradient Asymmetries
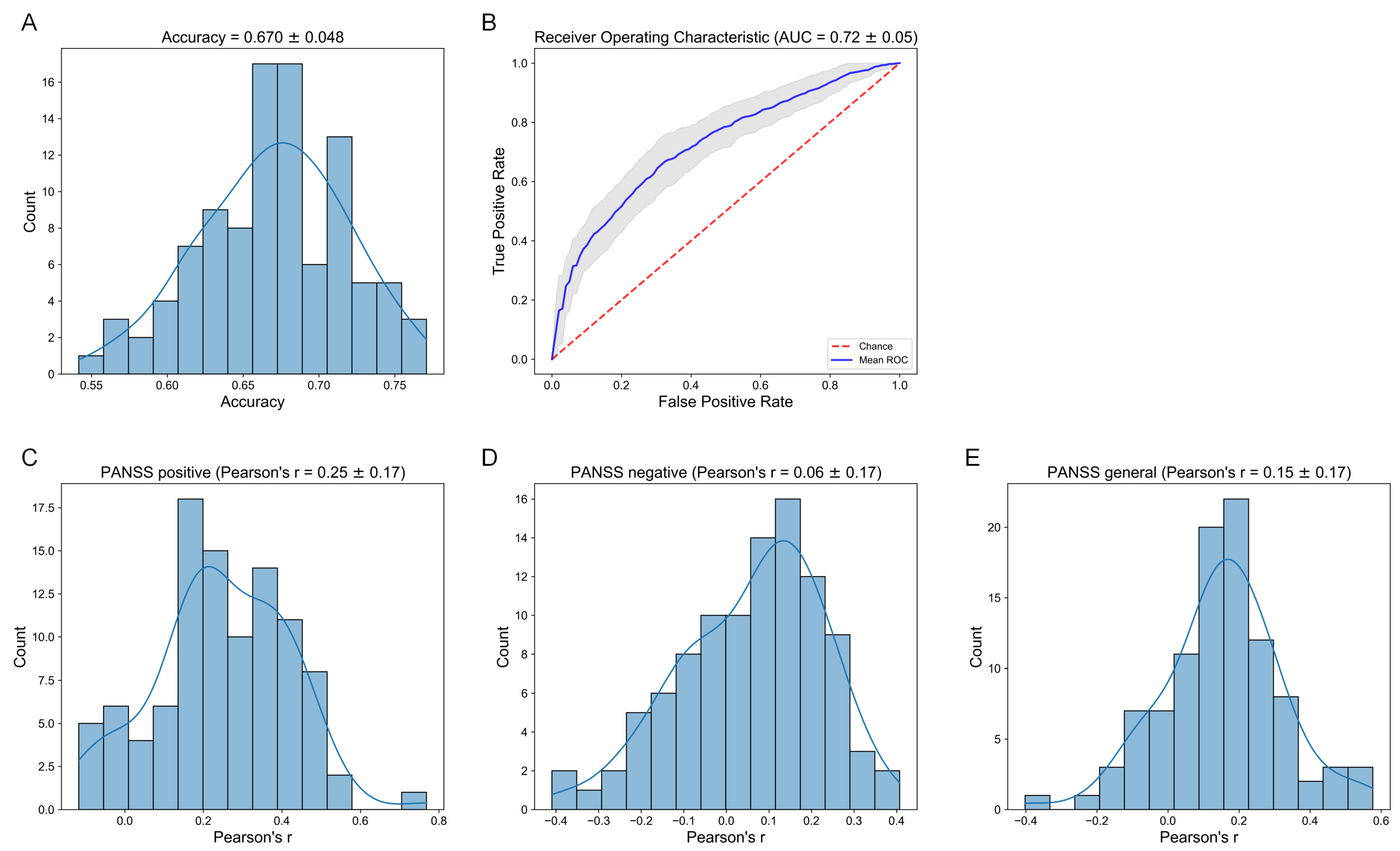
2.6. Prediction
3. Results
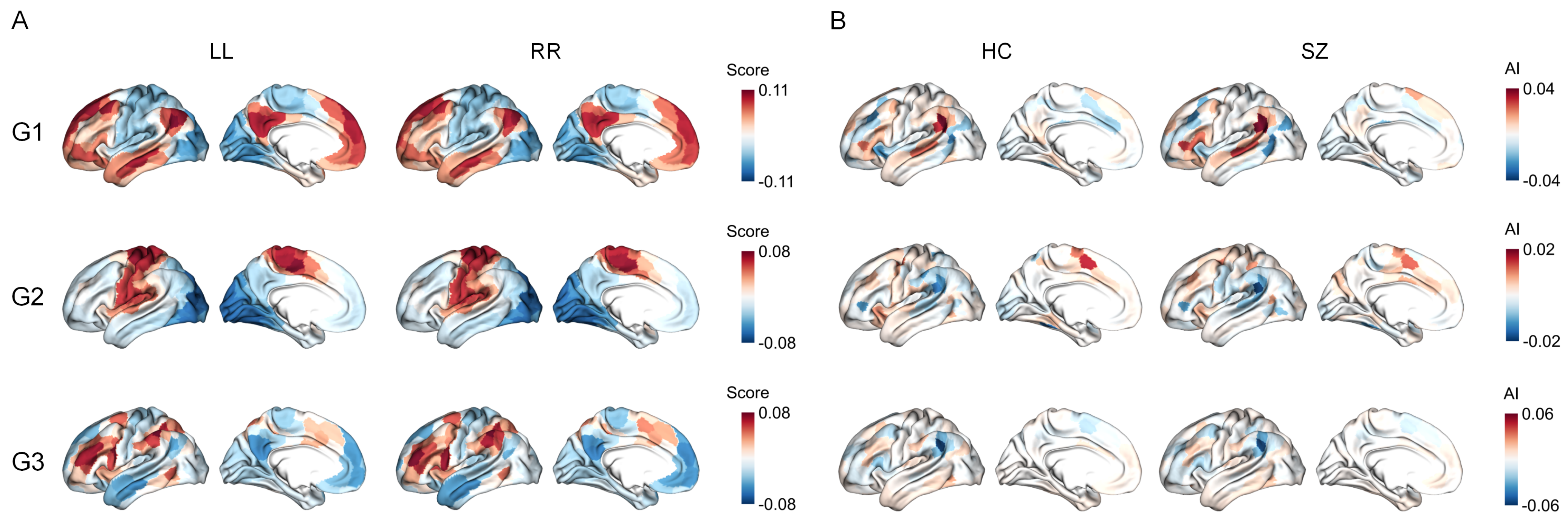
3.1. Functional Gradients and Their Hemispheric Asymmetry
3.2. Network-Level Comparisons
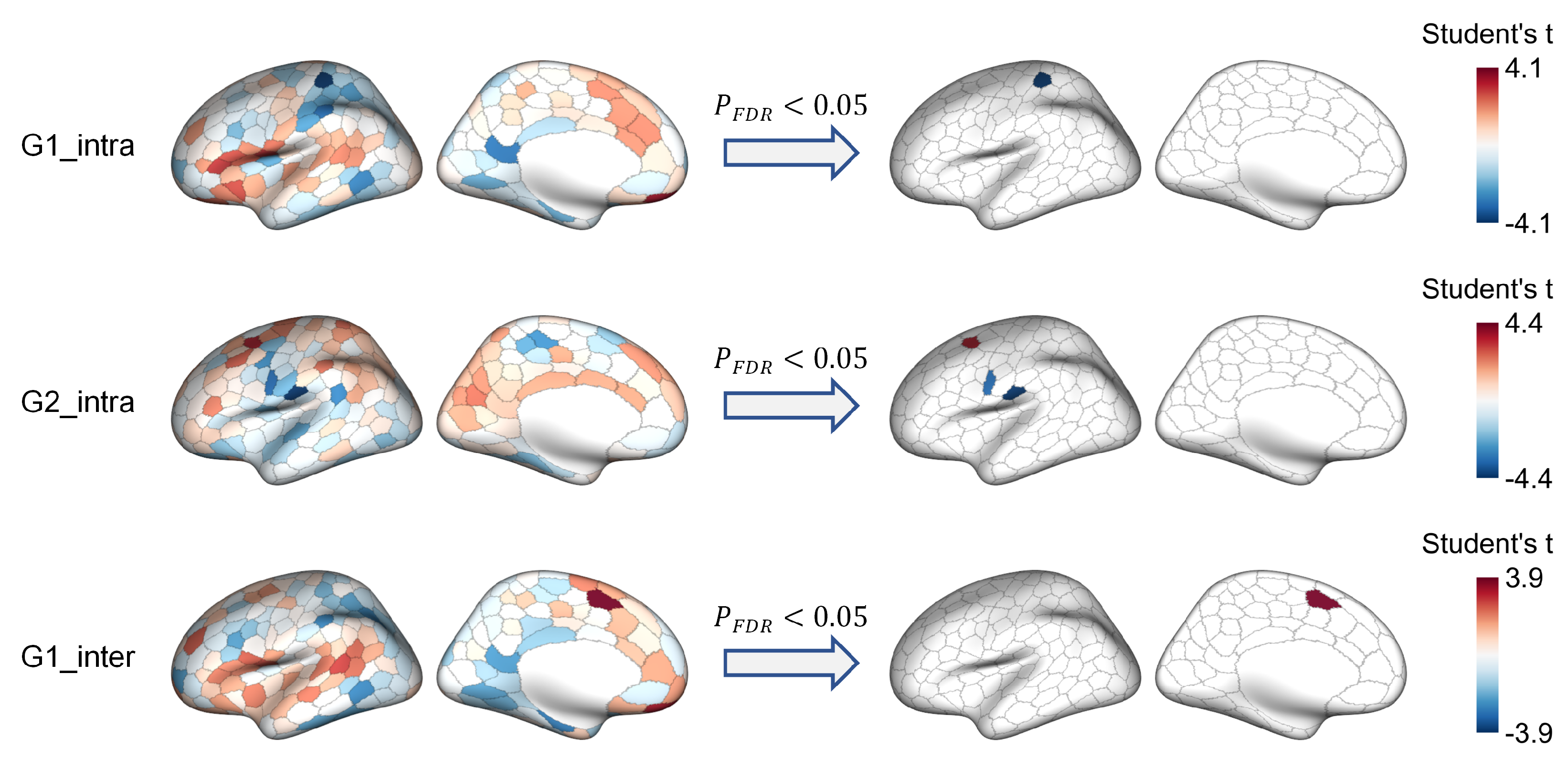
3.3. Region-Level Comparisons
3.4. Relation to Clinical Data
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Insel, T.R. Rethinking schizophrenia. Nature 2010, 468, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultz, S.H.; North, S.W.; Shields, C.G. Schizophrenia: A review. Am. Fam. Physician 2007, 75, 1821–1829. [Google Scholar]
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders: DSM-5; American Psychiatric Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2013; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- Keefe, R.S.; Harvey, P.D. Cognitive impairment in schizophrenia. In Novel Antischizophrenia Treatments; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 11–37. [Google Scholar]
- Canu, E.; Agosta, F.; Filippi, M. A selective review of structural connectivity abnormalities of schizophrenic patients at different stages of the disease. Schizophr. Res. 2015, 161, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynall, M.E.; Bassett, D.S.; Kerwin, R.; McKenna, P.J.; Kitzbichler, M.; Muller, U.; Bullmore, E. Functional connectivity and brain networks in schizophrenia. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 9477–9487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friston, K.J.; Frith, C.D. Schizophrenia: A disconnection syndrome. Clin. Neurosci. 1995, 3, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Friston, K.J. Schizophrenia and the disconnection hypothesis. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 1999, 99, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, D.; Wang, Y.; Chang, X.; Luo, C.; Yao, D. Dysfunction of large-scale brain networks in schizophrenia: A meta-analysis of resting-state functional connectivity. Schizophr. Bull. 2018, 44, 168–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Hu, N.; Zhang, W.; Tao, B.; Dai, J.; Gong, Y.; Tan, Y.; Cai, D.; Lui, S. Dysconnectivity of multiple brain networks in schizophrenia: A meta-analysis of resting-state functional connectivity. Front. Psychiatry 2019, 10, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vercammen, A.; Knegtering, H.; den Boer, J.A.; Liemburg, E.J.; Aleman, A. Auditory hallucinations in schizophrenia are associated with reduced functional connectivity of the temporo-parietal area. Biol. Psychiatry 2010, 67, 912–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Ye, E.; Jin, X.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, L. Association between thalamocortical functional connectivity abnormalities and cognitive deficits in schizophrenia. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, N.; Fukunaga, M.; Yamashita, F.; Koshiyama, D.; Yamamori, H.; Ohi, K.; Yasuda, Y.; Fujimoto, M.; Watanabe, Y.; Yahata, N.; et al. Abnormal asymmetries in subcortical brain volume in schizophrenia. Mol. Psychiatry 2016, 21, 1460–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schijven, D.; Postema, M.C.; Fukunaga, M.; Matsumoto, J.; Miura, K.; de Zwarte, S.M.; Van Haren, N.E.; Cahn, W.; Hulshoff Pol, H.E.; Kahn, R.S.; et al. Large-scale analysis of structural brain asymmetries in schizophrenia via the ENIGMA consortium. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2213880120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribolsi, M.; Daskalakis, Z.J.; Siracusano, A.; Koch, G. Abnormal asymmetry of brain connectivity in schizophrenia. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, S.; Miyata, J.; Mori, Y.; Isobe, M.; Urayama, S.i.; Aso, T.; Fukuyama, H.; Murai, T.; Takahashi, H. Lateralization of intrinsic frontoparietal network connectivity and symptoms in schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res. Neuroimaging 2017, 260, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Yang, L.; Yan, W.; An, W.; Xiang, J.; Li, D. Brain asymmetry: A novel perspective on hemispheric network. Brain Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, 56–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toga, A.W.; Thompson, P.M. Mapping brain asymmetry. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2003, 4, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, S.; Wang, D.; Pan, R.; Holt, D.J.; Liu, H. Abnormalities in hemispheric specialization of caudate nucleus connectivity in schizophrenia. JAMA Psychiatry 2015, 72, 552–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Q.; Van der Haegen, L.; Brysbaert, M. Complementary hemispheric specialization for language production and visuospatial attention. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E322–E330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goel, V.; Tierney, M.; Sheesley, L.; Bartolo, A.; Vartanian, O.; Grafman, J. Hemispheric specialization in human prefrontal cortex for resolving certain and uncertain inferences. Cereb. Cortex 2007, 17, 2245–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Van der Haegen, L.; Tao, L.; Cai, Q. Brain functional organization associated with language lateralization. Cereb. Cortex 2019, 29, 4312–4320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbanski, M.; Bréchemier, M.L.; Garcin, B.; Bendetowicz, D.; Thiebaut de Schotten, M.; Foulon, C.; Rosso, C.; Clarençon, F.; Dupont, S.; Pradat-Diehl, P.; et al. Reasoning by analogy requires the left frontal pole: Lesion-deficit mapping and clinical implications. Brain 2016, 139, 1783–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demaree, H.A.; Everhart, D.E.; Youngstrom, E.A.; Harrison, D.W. Brain lateralization of emotional processing: Historical roots and a future incorporating “dominance”. Behav. Cogn. Neurosci. Rev. 2005, 4, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Beaty, R.E.; Cui, Z.; Sun, J.; He, H.; Zhuang, K.; Ren, Z.; Liu, G.; Qiu, J. Brain hemispheric involvement in visuospatial and verbal divergent thinking. NeuroImage 2019, 202, 116065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallortigara, G.; Rogers, L. Survival with an asymmetrical brain: Advantages and disadvantages of cerebral lateralization. Behav. Brain Sci. 2005, 28, 575–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartwigsen, G.; Bengio, Y.; Bzdok, D. How does hemispheric specialization contribute to human-defining cognition? Neuron 2021, 109, 2075–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royer, C.; Delcroix, N.; Leroux, E.; Alary, M.; Razafimandimby, A.; Brazo, P.; Delamillieure, P.; Dollfus, S. Functional and structural brain asymmetries in patients with schizophrenia and bipolar disorders. Schizophr. Res. 2015, 161, 210–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleich-Cohen, M.; Hendler, T.; Kotler, M.; Strous, R.D. Reduced language lateralization in first-episode schizophrenia: An fMRI index of functional asymmetry. Psychiatry Res. Neuroimaging 2009, 171, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, I.; Ramsey, N.; Kahn, R. Language lateralization in schizophrenia, an fMRI study. Schizophr. Res. 2001, 52, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Peng, C.K.; Huang, C.C.; Lin, C.P.; Tsai, S.J.; Yang, A.C. Functional brain lateralization in schizophrenia based on the variability of resting-state fMRI signal. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2018, 86, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, M.; Zou, R.; Shen, H.; Huang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, Z.; Xue, Z.; Hu, D. Bilateral functional asymmetry disparity in positive and negative schizophrenia revealed by resting-state fMRI. Psychiatry Res. Neuroimaging 2010, 182, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, J.T.; Holmes, A.J.; Masters, G.A.; Yeo, B.T.; Krienen, F.; Buckner, R.L.; Öngür, D. Disruption of cortical association networks in schizophrenia and psychotic bipolar disorder. JAMA Psychiatry 2014, 71, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotarska-Jagiela, A.; van de Ven, V.; Oertel-Knöchel, V.; Uhlhaas, P.J.; Vogeley, K.; Linden, D.E. Resting-state functional network correlates of psychotic symptoms in schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2010, 117, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesulam, M.M. From sensation to cognition. Brain 1998, 121, 1013–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, M.; Liu, J.; Mechelli, A.; Sun, X.; Ma, Q.; Wang, X.; Wei, D.; Chen, Y.; Liu, B.; Huang, C.C.; et al. Connectome gradient dysfunction in major depression and its association with gene expression profiles and treatment outcomes. Mol. Psychiatry 2022, 27, 1384–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margulies, D.S.; Ghosh, S.S.; Goulas, A.; Falkiewicz, M.; Huntenburg, J.M.; Langs, G.; Bezgin, G.; Eickhoff, S.B.; Castellanos, F.X.; Petrides, M.; et al. Situating the default-mode network along a principal gradient of macroscale cortical organization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 12574–12579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huntenburg, J.M.; Bazin, P.L.; Margulies, D.S. Large-scale gradients in human cortical organization. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2018, 22, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayrak, Ş.; Khalil, A.A.; Villringer, K.; Fiebach, J.B.; Villringer, A.; Margulies, D.S.; Ovadia-Caro, S. The impact of ischemic stroke on connectivity gradients. NeuroImage Clin. 2019, 24, 101947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.M.; Margulies, D.S.; Zuo, X.N.; Holmes, A.J. Shifting gradients of macroscale cortical organization mark the transition from childhood to adolescence. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2024448118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bethlehem, R.A.; Paquola, C.; Seidlitz, J.; Ronan, L.; Bernhardt, B.; Tsvetanov, K.A.; Cam-CAN Consortium. Dispersion of functional gradients across the adult lifespan. NeuroImage 2020, 222, 117299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, N.; Paquola, C.; Pomares, F.B.; Perrault, A.A.; Jegou, A.; Nguyen, A.; Aydin, U.; Bernhardt, B.C.; Grova, C.; Dang-Vu, T.T. Cortical gradients of functional connectivity are robust to state-dependent changes following sleep deprivation. NeuroImage 2021, 226, 117547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samara, A.; Eilbott, J.; Margulies, D.S.; Xu, T.; Vanderwal, T. Cortical gradients during naturalistic processing are hierarchical and modality-specific. NeuroImage 2023, 271, 120023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.J.; Vos de Wael, R.; Bethlehem, R.A.; Lariviere, S.; Paquola, C.; Valk, S.L.; Milham, M.P.; Di Martino, A.; Margulies, D.S.; Smallwood, J.; et al. Atypical functional connectome hierarchy in autism. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, D.; Yao, D.; Wang, Y.; Hong, S.J.; Genon, S.; Xin, F.; Jung, K.; He, H.; Chang, X.; Duan, M.; et al. Compressed sensorimotor-to-transmodal hierarchical organization in schizophrenia. Psychol. Med. 2023, 53, 771–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, D.; Luo, C.; Guell, X.; Wang, Y.; He, H.; Duan, M.; Eickhoff, S.B.; Yao, D. Compression of cerebellar functional gradients in schizophrenia. Schizophr. Bull. 2020, 46, 1282–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.S.; Xu, Y.; Bayrak, Ş.; Shine, J.M.; Wan, B.; Li, H.; Li, L.; Yang, S.; Meng, Y.; Valk, S.L.; et al. Macroscale thalamic functional organization disturbances and underlying core cytoarchitecture in early-onset schizophrenia. Schizophr. Bull. 2023, 49, 1375–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, B.; Bayrak, Ş.; Xu, T.; Schaare, H.L.; Bethlehem, R.A.; Bernhardt, B.C.; Valk, S.L. Heritability and cross-species comparisons of human cortical functional organization asymmetry. eLife 2022, 11, e77215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Zhao, C.; Jin, X.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, L.; Chen, Y.; Gong, G. Sex-related human brain asymmetry in hemispheric functional gradients. NeuroImage 2021, 229, 117761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, B.; Hong, S.J.; Bethlehem, R.A.; Floris, D.L.; Bernhardt, B.C.; Valk, S.L. Diverging asymmetry of intrinsic functional organization in autism. Mol. Psychiatry 2023, 28, 4331–4341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhen, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, L.; Zheng, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Zheng, H.; Tang, S. Altered asymmetry of functional connectome gradients in major depressive disorder. Front. Neurosci. 2024, 18, 1385920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazzaniga, M.S. Cerebral specialization and interhemispheric communication: Does the corpus callosum enable the human condition? Brain 2000, 123, 1293–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aine, C.; Bockholt, H.J.; Bustillo, J.R.; Cañive, J.M.; Caprihan, A.; Gasparovic, C.; Hanlon, F.M.; Houck, J.M.; Jung, R.E.; Lauriello, J.; et al. Multimodal neuroimaging in schizophrenia: Description and dissemination. Neuroinformatics 2017, 15, 343–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustillo, J.R.; Jones, T.; Chen, H.; Lemke, N.; Abbott, C.; Qualls, C.; Stromberg, S.; Canive, J.; Gasparovic, C. Glutamatergic and neuronal dysfunction in gray and white matter: A spectroscopic imaging study in a large schizophrenia sample. Schizophr. Bull. 2017, 43, 611–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poldrack, R.A.; Congdon, E.; Triplett, W.; Gorgolewski, K.; Karlsgodt, K.; Mumford, J.; Sabb, F.; Freimer, N.; London, E.; Cannon, T.; et al. A phenome-wide examination of neural and cognitive function. Sci. Data 2016, 3, 160110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, S.C.; Yamashita, A.; Yahata, N.; Itahashi, T.; Lisi, G.; Yamada, T.; Ichikawa, N.; Takamura, M.; Yoshihara, Y.; Kunimatsu, A.; et al. A multi-site, multi-disorder resting-state magnetic resonance image database. Sci. Data 2021, 8, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keane, B.P.; Krekelberg, B.; Mill, R.D.; Silverstein, S.M.; Thompson, J.L.; Serody, M.R.; Barch, D.M.; Cole, M.W. Dorsal attention network activity during perceptual organization is distinct in schizophrenia and predictive of cognitive disorganization. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2023, 57, 458–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keane, B.P.; Barch, D.M.; Mill, R.D.; Silverstein, S.M.; Krekelberg, B.; Cole, M.W. Brain network mechanisms of visual shape completion. NeuroImage 2021, 236, 118069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markiewicz, C.J.; Gorgolewski, K.J.; Feingold, F.; Blair, R.; Halchenko, Y.O.; Miller, E.; Hardcastle, N.; Wexler, J.; Esteban, O.; Goncavles, M.; et al. The OpenNeuro resource for sharing of neuroscience data. eLife 2021, 10, e71774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteban, O.; Markiewicz, C.J.; Blair, R.W.; Moodie, C.A.; Isik, A.I.; Erramuzpe, A.; Kent, J.D.; Goncalves, M.; DuPre, E.; Snyder, M.; et al. fMRIPrep: A robust preprocessing pipeline for functional MRI. Nat. Methods 2019, 16, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, A.; Pedregosa, F.; Eickenberg, M.; Gervais, P.; Mueller, A.; Kossaifi, J.; Gramfort, A.; Thirion, B.; Varoquaux, G. Machine learning for neuroimaging with scikit-learn. Front. Neuroinform. 2014, 8, 71792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friston, K.J.; Williams, S.; Howard, R.; Frackowiak, R.S.; Turner, R. Movement-related effects in fMRI time-series. Magn. Reson. Med. 1996, 35, 346–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satterthwaite, T.D.; Elliott, M.A.; Gerraty, R.T.; Ruparel, K.; Loughead, J.; Calkins, M.E.; Eickhoff, S.B.; Hakonarson, H.; Gur, R.C.; Gur, R.E.; et al. An improved framework for confound regression and filtering for control of motion artifact in the preprocessing of resting-state functional connectivity data. NeuroImage 2013, 64, 240–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindquist, M.A.; Geuter, S.; Wager, T.D.; Caffo, B.S. Modular preprocessing pipelines can reintroduce artifacts into fMRI data. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2019, 40, 2358–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Power, J.D.; Barnes, K.A.; Snyder, A.Z.; Schlaggar, B.L.; Petersen, S.E. Spurious but systematic correlations in functional connectivity MRI networks arise from subject motion. NeuroImage 2012, 59, 2142–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Kong, R.; Xue, A.; Yang, Q.; Orban, C.; An, L.; Holmes, A.J.; Qian, X.; Chen, J.; Zuo, X.N.; et al. Homotopic local-global parcellation of the human cerebral cortex from resting-state functional connectivity. NeuroImage 2023, 273, 120010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vos de Wael, R.; Benkarim, O.; Paquola, C.; Lariviere, S.; Royer, J.; Tavakol, S.; Xu, T.; Hong, S.J.; Langs, G.; Valk, S.; et al. BrainSpace: A toolbox for the analysis of macroscale gradients in neuroimaging and connectomics datasets. Commun. Biol. 2020, 3, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Essen, D.C.; Smith, S.M.; Barch, D.M.; Behrens, T.E.; Yacoub, E.; Ugurbil, K.; Wu-Minn HCP Consortium. The WU-Minn human connectome project: An overview. Neuroimage 2013, 80, 62–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Mashour, G.A.; Hudetz, A.G. Functional geometry of the cortex encodes dimensions of consciousness. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langs, G.; Golland, P.; Ghosh, S.S. Predicting activation across individuals with resting-state functional connectivity based multi-atlas label fusion. In Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2015, Proceedings of the 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Proceedings, Part II 18; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 313–320. [Google Scholar]
- Fortin, J.P.; Cullen, N.; Sheline, Y.I.; Taylor, W.D.; Aselcioglu, I.; Cook, P.A.; Adams, P.; Cooper, C.; Fava, M.; McGrath, P.J.; et al. Harmonization of cortical thickness measurements across scanners and sites. NeuroImage 2018, 167, 104–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, B.T.; Krienen, F.M.; Sepulcre, J.; Sabuncu, M.R.; Lashkari, D.; Hollinshead, M.; Roffman, J.L.; Smoller, J.W.; Zöllei, L.; Polimeni, J.R.; et al. The organization of the human cerebral cortex estimated by intrinsic functional connectivity. J. Neurophysiol. 2011, 106, 1125–1165. [Google Scholar]
- Gale, D.J.; Vos de Wael, R.; Benkarim, O.; Bernhardt, B. Surfplot: Publication-Ready Brain Surface Figures. 2021. Available online: https://zenodo.org/records/5567926 (accessed on 14 May 2024).
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V.; et al. Scikit-learn: Machine learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Holmes, A.; Levi, P.T.; Chen, Y.C.; Chopra, S.; Aquino, K.M.; Pang, J.C.; Fornito, A. Disruptions of hierarchical cortical organization in early psychosis and schizophrenia. Biol. Psychiatry Cogn. Neurosci. Neuroimaging 2023, 8, 1240–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, G.; Luo, J.; Li, J.; Feng, K.; Liu, P.; Xu, Y. Functional gradient dysfunction in drug-naïve first-episode schizophrenia and its correlation with specific transcriptional patterns and treatment predictions. Psychol. Med. 2024, 54, 4106–4118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlhaas, P.J.; Mishara, A.L. Perceptual anomalies in schizophrenia: Integrating phenomenology and cognitive neuroscience. Schizophr. Bull. 2007, 33, 142–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, S.K.; Dunlop, K.; Downar, J. Cortico-striatal-thalamic loop circuits of the salience network: A central pathway in psychiatric disease and treatment. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Chen, C.; Rong, B.; Wan, Q.; Chen, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, G.; Wang, H. Resting-state functional connectivity of salience network in schizophrenia and depression. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 11204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banker, L.; Tadi, P. Neuroanatomy, precentral gyrus. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- DiGuiseppi, J.; Tadi, P. Neuroanatomy, postcentral gyrus. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, M.; Wang, R.; Liu, M.; Du, X.; Xue, K.; Ji, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, L.; Qin, W.; et al. Disrupted local functional connectivity in schizophrenia: An updated and extended meta-analysis. Schizophrenia 2022, 8, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Voon, V.; Xue, K.; Xie, C.; Kang, J.; Lin, C.P.; Wang, J.; Cheng, J.; Feng, J. Common abnormal connectivity in first-episode and chronic schizophrenia in pre-and post-central regions: Implications for neuromodulation targeting. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2022, 117, 110556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.X.; Lee, R.R.; Gaa, K.M.; Song, T.; Harrington, D.L.; Loh, C.; Theilmann, R.J.; Edgar, J.C.; Miller, G.A.; Canive, J.M.; et al. Somatosensory system deficits in schizophrenia revealed by MEG during a median-nerve oddball task. Brain Topogr. 2010, 23, 82–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walther, S.; Strik, W. Motor symptoms and schizophrenia. Neuropsychobiology 2012, 66, 77–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shackman, A.J.; McMenamin, B.W.; Maxwell, J.S.; Greischar, L.L.; Davidson, R.J. Right dorsolateral prefrontal cortical activity and behavioral inhibition. Psychol. Sci. 2009, 20, 1500–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbey, A.K.; Koenigs, M.; Grafman, J. Dorsolateral prefrontal contributions to human working memory. Cortex 2013, 49, 1195–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callicott, J.H.; Bertolino, A.; Mattay, V.S.; Langheim, F.J.; Duyn, J.; Coppola, R.; Goldberg, T.E.; Weinberger, D.R. Physiological dysfunction of the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in schizophrenia revisited. Cereb. Cortex 2000, 10, 1078–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunney, W.E.; Bunney, B.G. Evidence for a compromised dorsolateral prefrontal cortical parallel circuit in schizophrenia. Brain Res. Rev. 2000, 31, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talati, A.; Hirsch, J. Functional specialization within the medial frontal gyrus for perceptual go/no-go decisions based on “what”, “when”, and “where” related information: An fMRI study. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2005, 17, 981–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frascarelli, M.; Tognin, S.; Mirigliani, A.; Parente, F.; Buzzanca, A.; Torti, M.C.; Tinelli, E.; Caramia, F.; Di Fabio, F.; Biondi, M.; et al. Medial frontal gyrus alterations in schizophrenia: Relationship with duration of illness and executive dysfunction. Psychiatry Res. Neuroimaging 2015, 231, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orellana, G.; Slachevsky, A. Executive functioning in schizophrenia. Front. Psychiatry 2013, 4, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Chen, Y.; Collinson, S.L.; Bezerianos, A.; Sim, K. Reduced hemispheric asymmetry of brain anatomical networks is linked to schizophrenia: A connectome study. Cereb. Cortex 2017, 27, 602–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.; Collin, G.; Mandl, R.C.; Cahn, W.; Kahn, R.S. Interhemispheric connectivity and hemispheric specialization in schizophrenia patients and their unaffected siblings. NeuroImage Clin. 2019, 21, 101656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Jiang, Y.; Biswal, B.B. Aberrant interhemispheric structural and functional connectivity within whole brain in schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2024, 264, 336–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, Z.; Pepe, A.; Schijven, D.; Carrión-Castillo, A.; Roe, J.M.; Westerhausen, R.; Joliot, M.; Fisher, S.E.; Crivello, F.; Francks, C. Handedness and its genetic influences are associated with structural asymmetries of the cerebral cortex in 31,864 individuals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2113095118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- First, M.B. Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV Axis I Disorders. Biometrics Research Department. 1997. Available online: https://cir.nii.ac.jp/crid/1573387451015011328#citations_container (accessed on 14 May 2024).
- Kay, S.R.; Fiszbein, A.; Opler, L.A. The positive and negative syndrome scale (PANSS) for schizophrenia. Schizophr. Bull. 1987, 13, 261–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders: DSM-IV; American Psychiatric Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1994; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Esteban, O.; Markiewicz, C.J.; Goncalves, M.; Provins, C.; Kent, J.D.; DuPre, E.; Salo, T.; Ciric, R.; Pinsard, B.; Blair, R.W.; et al. fMRIPrep: A Robust Preprocessing Pipeline for Functional MRI 2018. Available online: https://zenodo.org/records/13992697 (accessed on 14 May 2024).
- Gorgolewski, K.; Burns, C.D.; Madison, C.; Clark, D.; Halchenko, Y.O.; Waskom, M.L.; Ghosh, S.S. Nipype: A flexible, lightweight and extensible neuroimaging data processing framework in python. Front. Neuroinformatics 2011, 5, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorgolewski, K.J.; Esteban, O.; Ellis, D.G.; Notter, M.P.; Ziegler, E.; Johnson, H.; Hamalainen, C.; Yvernault, B.; Burns, C.; Manhães-Savio, A.; et al. Nipype: A Flexible, Lightweight and Extensible Neuroimaging Data Processing Framework in Python. 0.13.1 2018. Available online: https://zenodo.org/records/6834519 (accessed on 14 May 2024).
- Tustison, N.J.; Avants, B.B.; Cook, P.A.; Zheng, Y.; Egan, A.; Yushkevich, P.A.; Gee, J.C. N4ITK: Improved N3 bias correction. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2010, 29, 1310–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avants, B.B.; Epstein, C.L.; Grossman, M.; Gee, J.C. Symmetric diffeomorphic image registration with cross-correlation: Evaluating automated labeling of elderly and neurodegenerative brain. Med. Image Anal. 2008, 12, 26–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Brady, M.; Smith, S. Segmentation of brain MR images through a hidden Markov random field model and the expectation-maximization algorithm. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2001, 20, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dale, A.M.; Fischl, B.; Sereno, M.I. Cortical surface-based analysis: I. Segmentation and surface reconstruction. Neuroimage 1999, 9, 179–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, A.; Ghosh, S.S.; Bao, F.S.; Giard, J.; Häme, Y.; Stavsky, E.; Lee, N.; Rossa, B.; Reuter, M.; Chaibub Neto, E.; et al. Mindboggling morphometry of human brains. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2017, 13, e1005350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, A.C.; Janke, A.L.; Collins, D.L.; Baillet, S. Brain templates and atlases. Neuroimage 2012, 62, 911–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonov, V.S.; Evans, A.C.; McKinstry, R.C.; Almli, C.R.; Collins, D. Unbiased nonlinear average age-appropriate brain templates from birth to adulthood. NeuroImage 2009, 47, S102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greve, D.N.; Fischl, B. Accurate and robust brain image alignment using boundary-based registration. Neuroimage 2009, 48, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkinson, M.; Bannister, P.; Brady, M.; Smith, S. Improved optimization for the robust and accurate linear registration and motion correction of brain images. Neuroimage 2002, 17, 825–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, R.W.; Hyde, J.S. Software tools for analysis and visualization of fMRI data. Nmr Biomed. Int. J. Devoted Dev. Appl. Magn. Reson. Vivo 1997, 10, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glasser, M.F.; Sotiropoulos, S.N.; Wilson, J.A.; Coalson, T.S.; Fischl, B.; Andersson, J.L.; Xu, J.; Jbabdi, S.; Webster, M.; Polimeni, J.R.; et al. The minimal preprocessing pipelines for the Human Connectome Project. Neuroimage 2013, 80, 105–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Power, J.D.; Mitra, A.; Laumann, T.O.; Snyder, A.Z.; Schlaggar, B.L.; Petersen, S.E. Methods to detect, characterize, and remove motion artifact in resting state fMRI. Neuroimage 2014, 84, 320–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behzadi, Y.; Restom, K.; Liau, J.; Liu, T.T. A component based noise correction method (CompCor) for BOLD and perfusion based fMRI. Neuroimage 2007, 37, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanczos, C. Evaluation of noisy data. J. Soc. Ind. Appl. Math. Ser. Numer. Anal. 1964, 1, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, D.; Imai, K.; King, G.; Stuart, E.A. MatchIt: Nonparametric preprocessing for parametric causal inference. J. Stat. Softw. 2011, 42, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhen, Y.; Zheng, H.; Zheng, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Yang, Y.; Tang, S. Altered Hemispheric Asymmetry of Functional Hierarchy in Schizophrenia. Brain Sci. 2025, 15, 313. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15030313
Zhen Y, Zheng H, Zheng Y, Zheng Z, Yang Y, Tang S. Altered Hemispheric Asymmetry of Functional Hierarchy in Schizophrenia. Brain Sciences. 2025; 15(3):313. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15030313
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhen, Yi, Hongwei Zheng, Yi Zheng, Zhiming Zheng, Yaqian Yang, and Shaoting Tang. 2025. "Altered Hemispheric Asymmetry of Functional Hierarchy in Schizophrenia" Brain Sciences 15, no. 3: 313. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15030313
APA StyleZhen, Y., Zheng, H., Zheng, Y., Zheng, Z., Yang, Y., & Tang, S. (2025). Altered Hemispheric Asymmetry of Functional Hierarchy in Schizophrenia. Brain Sciences, 15(3), 313. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15030313





