Immunohistochemical Detection of Tentonin-3/TMEM150C in Human Dorsal Root Ganglion, Cutaneous End-Organ Complexes, and Muscle Spindles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material
2.2. Immunohistochemistry
2.3. Quantitative Image Analysis
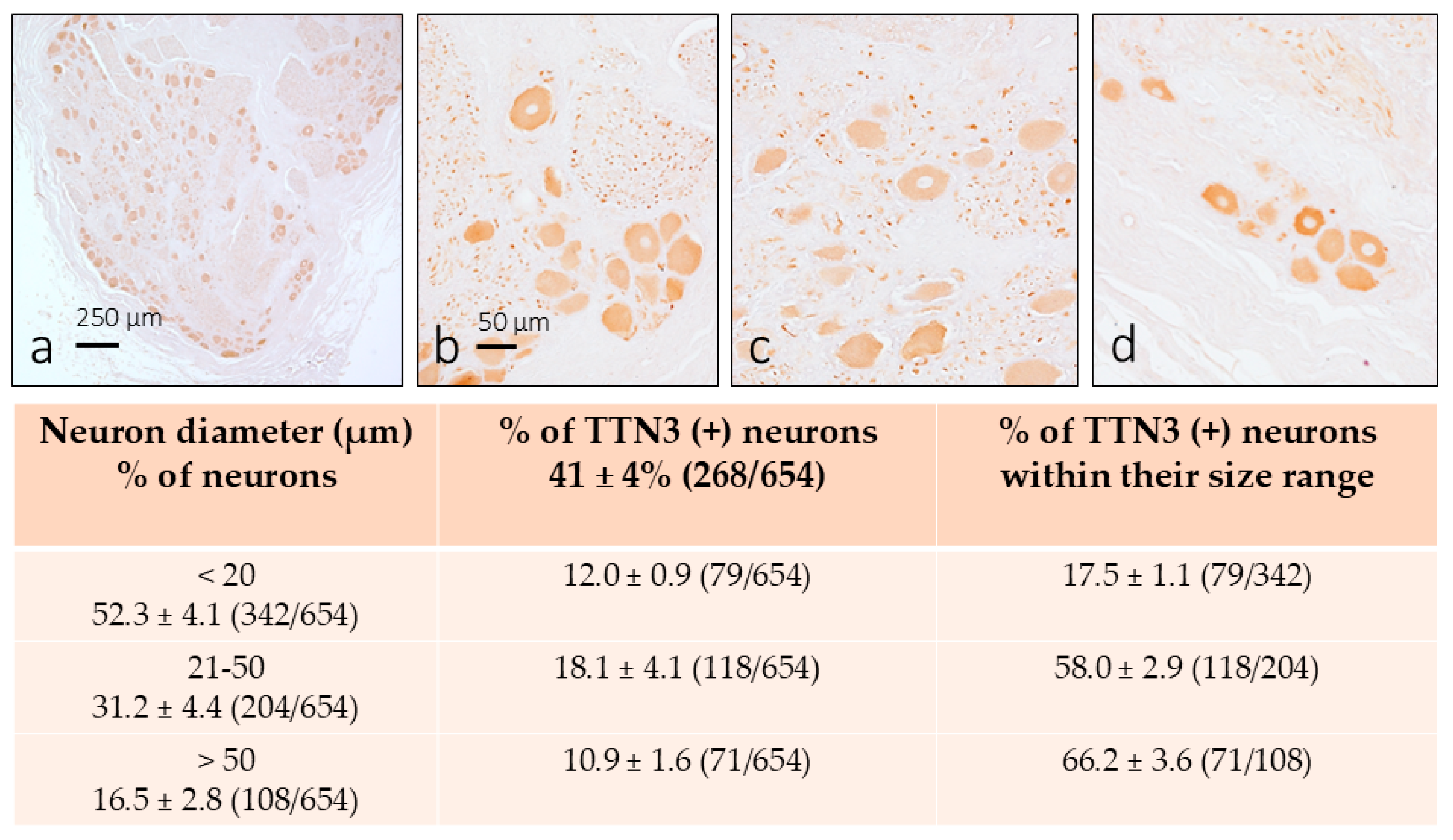
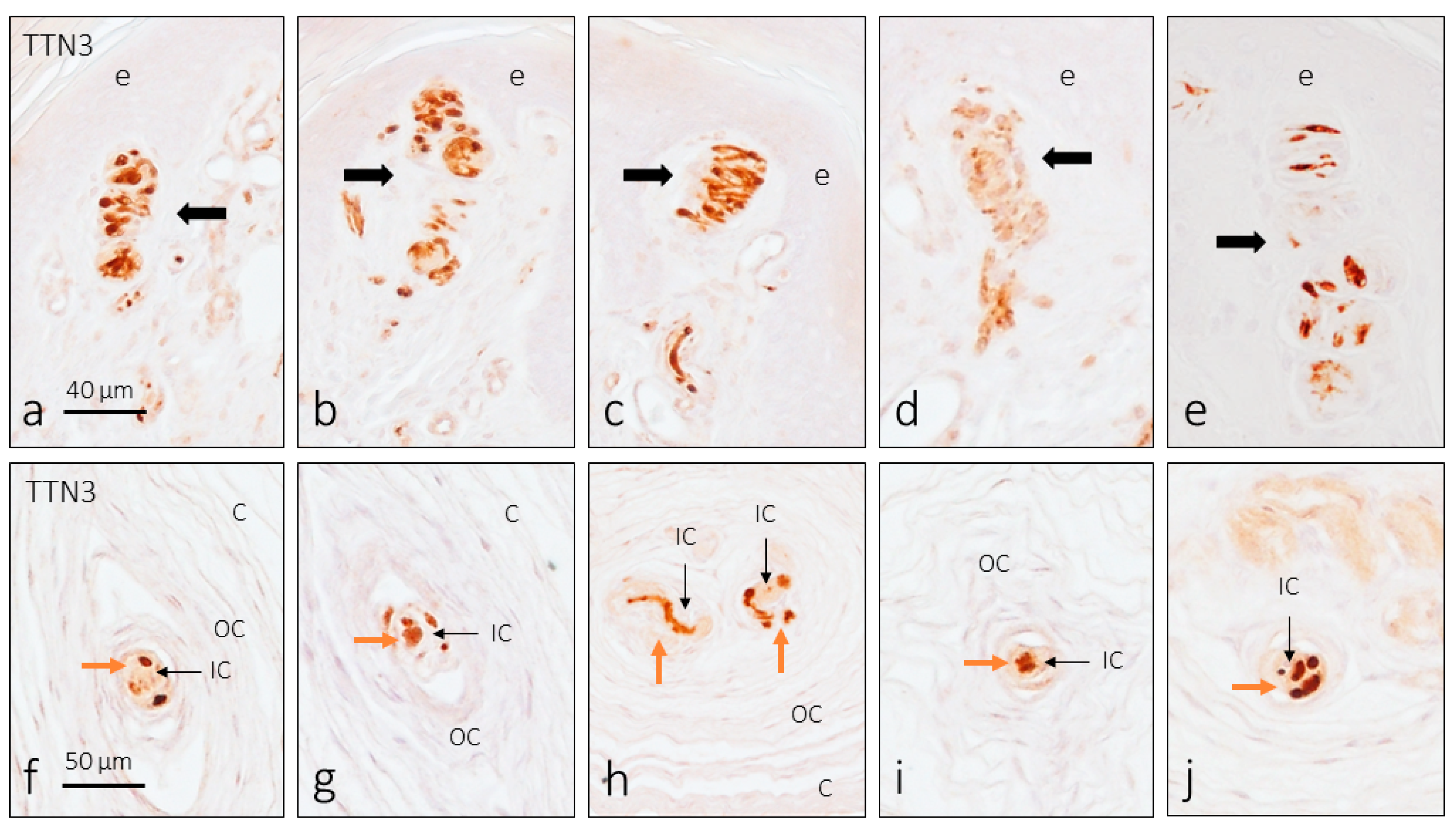
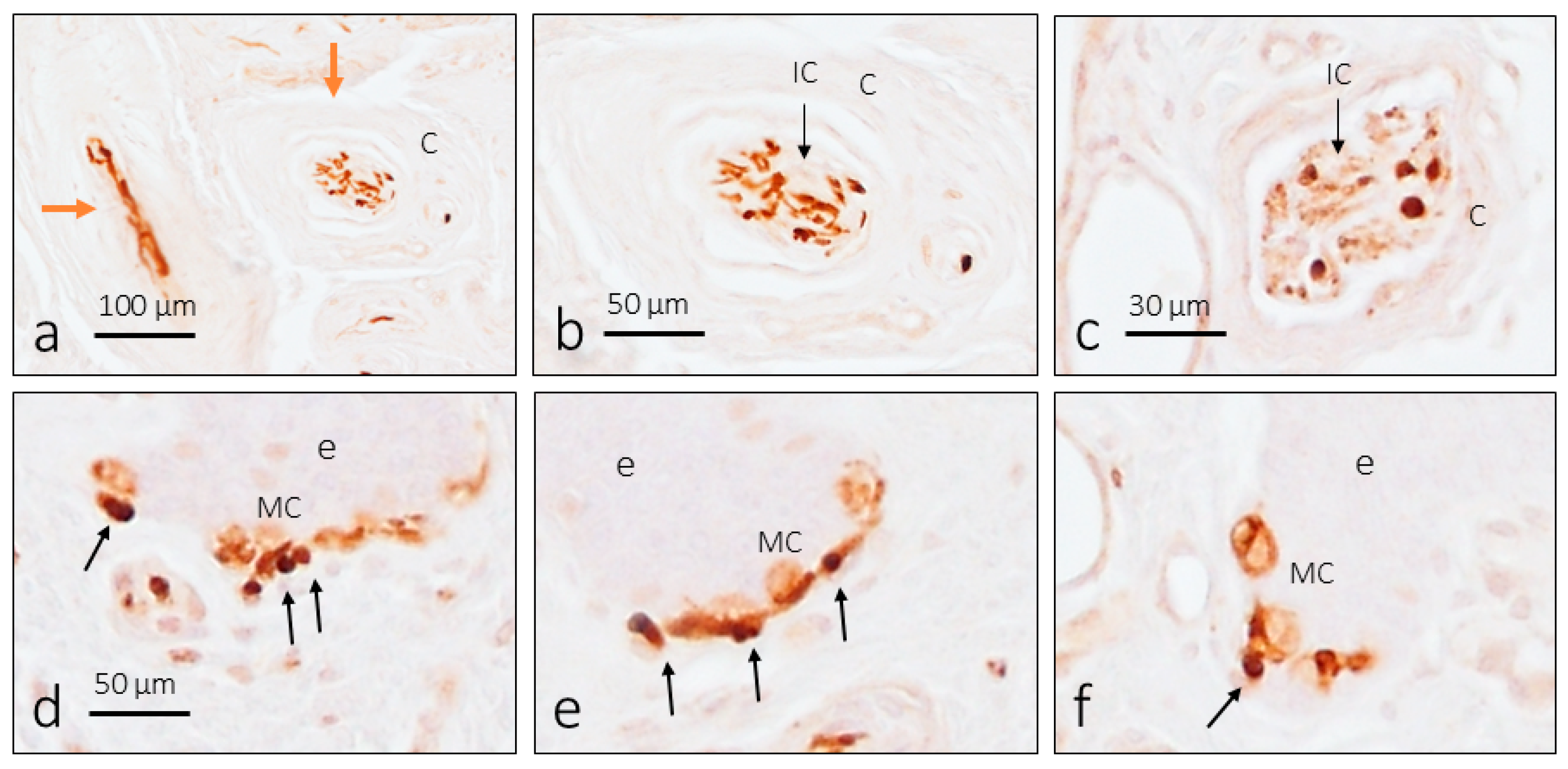
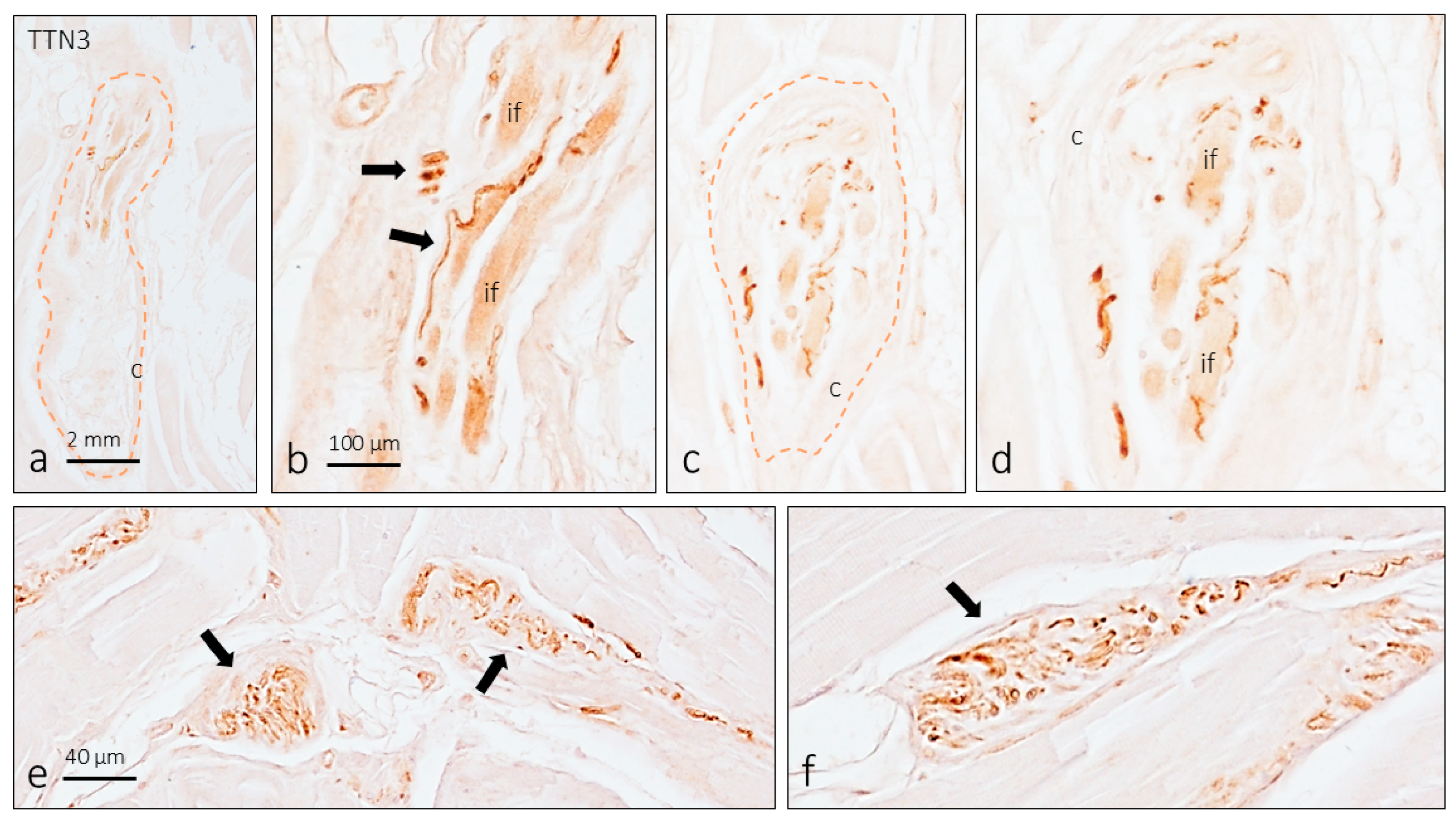
3. Results
3.1. TTN3 Immunoreactivity in Human DRG
3.2. TTN3 Immunoreactivity in Human Digital CEOCs
3.3. TTN3 Immunoreactivity in Human Digital Merkel Cell–Axon Complexes
3.4. TTN3 Immunoreactivity in Muscle Spindles
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TTN3 | Tentonin-3/TMEM150C. |
| CEOCs | Cutaneous end-organ complexes. |
| DRG | Dorsal root ganglia. |
| LTMRs | Low-threshold mechanoreceptors. |
References
- Zimmerman, A.; Bai, L.; Ginty, D.D. The gentle touch receptors of mammalian skin. Science 2014, 346, 950–9544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cobo, R.; García-Piqueras, J.; Cobo, J.; Vega, J.A. The human cutaneous sensory corpuscles: An update. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handler, A.; Ginty, D.D. The mechanosensory neurons of touch and their mechanisms of activation. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2021, 22, 521–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín-Alguacil, N.; de Gaspar, I.; Schober, J.M.; Pfaff, D.W.; Vega, J.A. Somatosensation. In Neuroscience in the 21st Century; Pfaff, D.W., Volkow, N.D., Rubenstein, J.L., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 1143–1182. [Google Scholar]
- Abraira, V.E.; Ginty, D.D. The sensory neurons of touch. Neuron 2013, 79, 618–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bewick, G.S.; Banks, R.W. Mechanotransduction in the muscle spindle. Pflugers Arch. 2015, 467, 175–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, W.R.; Webster, H.F.; Yoon, K.S. Human muscle spindles: Fine structure of the primary sensory ending. J. Neurocytol. 1975, 4, 675–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranade, S.S.; Syeda, R.; Patapoutian, A. Mechanically Activated Ion Channels. Neuron 2015, 87, 1162–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, P.; Jan, L.Y.; Jan, Y.N. Mechanosensitive Ion Channels: Structural Features Relevant to Mechanotransduction Mechanisms. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2020, 43, 207–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, J.D.; Dufresne, E.R.; Schwartz, M.A. Mechanotransduction and extracellular matrix homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 802–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohashi, K.; Fujiwara, S.; Mizuno, K. Roles of the cytoskeleton, cell adhesion and rho signalling in mechanosensing and mechanotransduction. J. Biochem. 2017, 161, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delmas, P.; Hao, J.; Rodat-Despoix, L. Molecular mechanisms of mechanotransduction in mammalian sensory neurons. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2011, 12, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delmas, P.; Parpaite, T.; Coste, B. PIEZO channels and newcomers in the mammalian mechanosensitive ion channel family. Neuron 2022, 110, 2713–2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, B. Mechanisms of mechanotransduction and physiological roles of PIEZO channels. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2024, 25, 886–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, G.S.; Lee, B.; Oh, U. Evidence for Mechanosensitive Channel Activity of Tentonin 3/TMEM150C. Neuron 2017, 94, 271–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, G.S.; Lee, B.; Wee, J.; Chun, H.; Kim, H.; Jung, J.; Cha, J.Y.; Riew, T.R.; Kim, G.H.; Kim, I.B.; et al. Tentonin 3/TMEM150c Confers Distinct Mechanosensitive Currents in Dorsal-Root Ganglion Neurons with Proprioceptive Function. Neuron 2016, 91, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pak, S.; Ryu, H.; Lim, S.; Nguyen, T.L.; Yang, S.; Kang, S.; Yu, Y.G.; Woo, J.; Kim, C.; Fenollar-Ferrer, C.; et al. Tentonin 3 is a pore-forming subunit of a slow inactivation mechanosensitive channel. Cell Rep. 2024, 43, 114334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.J.; Nguyen, T.L.; Hong, G.S.; Pak, S.; Kim, H.; Kim, H.; Kim, D.Y.; Kim, S.Y.; Shen, Y.; Ryu, P.D.; et al. Tentonin 3/TMEM150C senses blood pressure changes in the aortic arch. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 3671–3683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, J.G.; Berkowitz, D.E. Tentonin 3 as a baroreceptor mechanosensor: Not a stretch. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 3412–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, E.O.; Schneider, E.R.; Matson, J.D.; Gracheva, E.O.; Bagriantsev, S.N. TMEM150C/Tentonin3 Is a regulator of mechano-gated ion channels. Cell Rep. 2018, 23, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parpaite, T.; Brosse, L.; Séjourné, N.; Laur, A.; Mechioukhi, Y.; Delmas, P.; Coste, B. Patch-seq of mouse DRG neurons reveals candidate genes for specific mechanosensory functions. Cell Rep. 2021, 37, 109914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojeda-Alonso, J.; Bégay, V.; Garcia-Contreras, J.A.; Campos-Pérez, A.F.; Purfürst, B.; Lewin, G.R. Lack of evidence for participation of TMEM150C in sensory mechanotransduction. J. Gen. Physiol. 2022, 154, e202213098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Rutlin, M.; Abraira, V.E.; Cassidy, C.; Kus, L.; Gong, S.; Jankowski, M.P.; Luo, W.; Heintz, N.; Koerber, H.R.; et al. The functional organization of cutaneous low-threshold mechanosensory neurons. Cell 2011, 147, 1615–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, M.; Dourado, M.; Maksymetz, J.; Jacobson, A.; Laufer, B.I.; Baca, M.; Foreman, O.; Hackos, D.H.; Riol-Blanco, L.; Kaminker, J.S. Cross-species transcriptomic atlas of dorsal root ganglia reveals species-specific programs for sensory function. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haberberger, R.V.; Barry, C.; Dominguez, N.; Matusica, D. Human Dorsal Root Ganglia. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, S.N.; Perry, M.J.; Prabhakar, E.; McCarthy, P.W. Primary sensory neurons: Neurofilament, neuropeptides, and conduction velocity. Brain Res. Bull. 1993, 30, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usoskin, D.; Furlan, A.; Islam, S.; Abdo, H.; Lönnerberg, P.; Lou, D.; Hjerling-Leffler, J.; Haeggström, J.; Kharchenko, O.; Kharchenko, P.V.; et al. Unbiased classification of sensory neuron types by large-scale single-cell RNA sequencing. Nat. Neurosci. 2015, 18, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, W.; Dong, P.; Fleming, M.; Luo, W. The specification and wiring of mammalian cutaneous low-threshold mechanoreceptors. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Dev. Biol. 2016, 5, 389–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubin, A.E.; Murthy, S.; Lewis, A.H.; Brosse, L.; Cahalan, S.M.; Grandl, J.; Coste, B.; Patapoutian, A. Endogenous Piezo1 Can Confound Mechanically Activated Channel Identification and Characterization. Neuron 2017, 94, 266–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naves, F.J.; Huerta, J.J.; Garcia-Suarez, O.; Urdangaray, N.; Esteban, I.; Del Valle, M.E.; Vega, J.A. Distribution of immunoreactivity for cytoskeletal (microtubule, microtubule-associated, and neurofilament) proteins in adult human dorsal root ganglia. Anat. Rec. 1996, 244, 246–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, J.A.; Humara, J.M.; Naves, F.J.; Esteban, I.; Del Valle, M.E. Immunoreactivity for phosphorylated 200-kDa neurofilament subunit is heterogeneously expressed in human sympathetic and primary sensory neurons. Anat. Embryol. 1994, 190, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Suazo, I.; García-Mesa, Y.; Martín-Cruces, J.; Cuendias, P.; Cobo, T.; García-Suárez, O.; Vega, J.A. Immunohistochemical Detection of Tentonin-3/TMEM150C in Human Dorsal Root Ganglion, Cutaneous End-Organ Complexes, and Muscle Spindles. Brain Sci. 2025, 15, 337. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15040337
Suazo I, García-Mesa Y, Martín-Cruces J, Cuendias P, Cobo T, García-Suárez O, Vega JA. Immunohistochemical Detection of Tentonin-3/TMEM150C in Human Dorsal Root Ganglion, Cutaneous End-Organ Complexes, and Muscle Spindles. Brain Sciences. 2025; 15(4):337. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15040337
Chicago/Turabian StyleSuazo, Iván, Yolanda García-Mesa, José Martín-Cruces, Patricia Cuendias, Teresa Cobo, Olivia García-Suárez, and José A. Vega. 2025. "Immunohistochemical Detection of Tentonin-3/TMEM150C in Human Dorsal Root Ganglion, Cutaneous End-Organ Complexes, and Muscle Spindles" Brain Sciences 15, no. 4: 337. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15040337
APA StyleSuazo, I., García-Mesa, Y., Martín-Cruces, J., Cuendias, P., Cobo, T., García-Suárez, O., & Vega, J. A. (2025). Immunohistochemical Detection of Tentonin-3/TMEM150C in Human Dorsal Root Ganglion, Cutaneous End-Organ Complexes, and Muscle Spindles. Brain Sciences, 15(4), 337. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15040337






