Gamma Transcranial Alternating Current Stimulation Enhances Working Memory Ability in Healthy People: An EEG Microstate Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
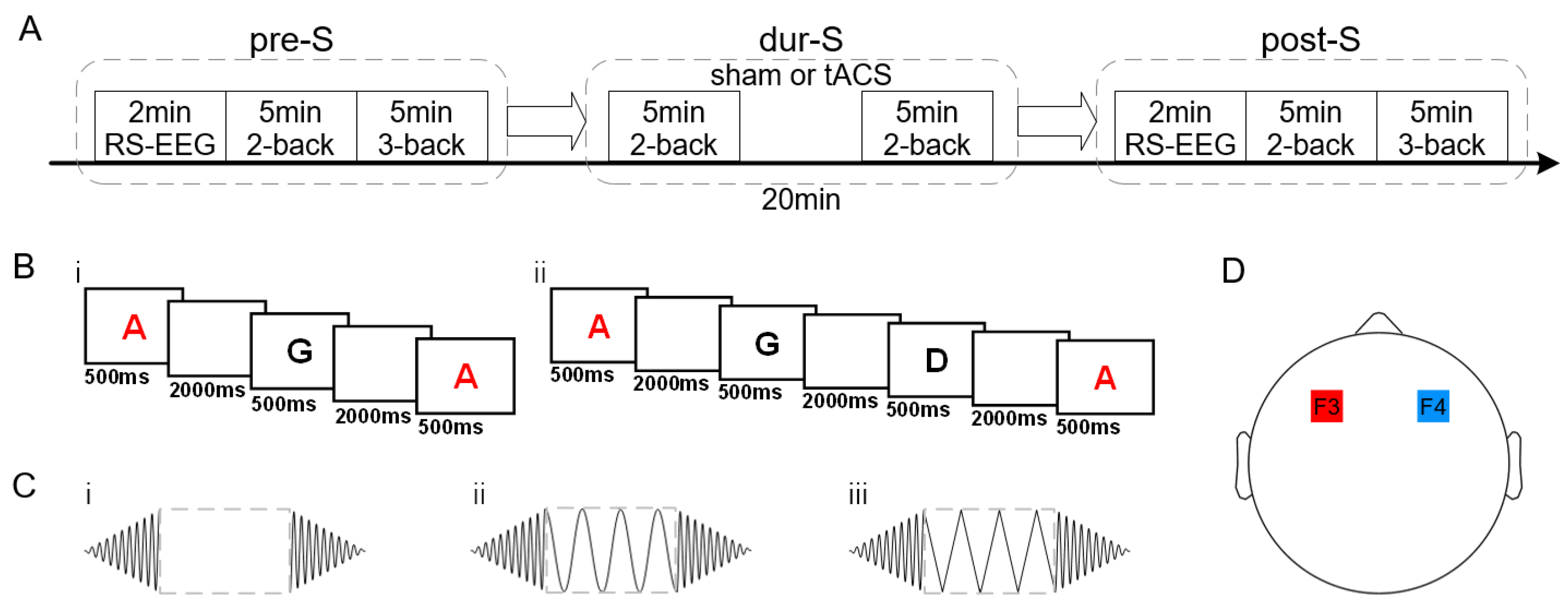
2.2. Experimental Procedures
2.3. EEG Acquisition and Preprocessing
2.4. Microstate Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Details
3.2. WM Performances
3.3. Microstate Topographies
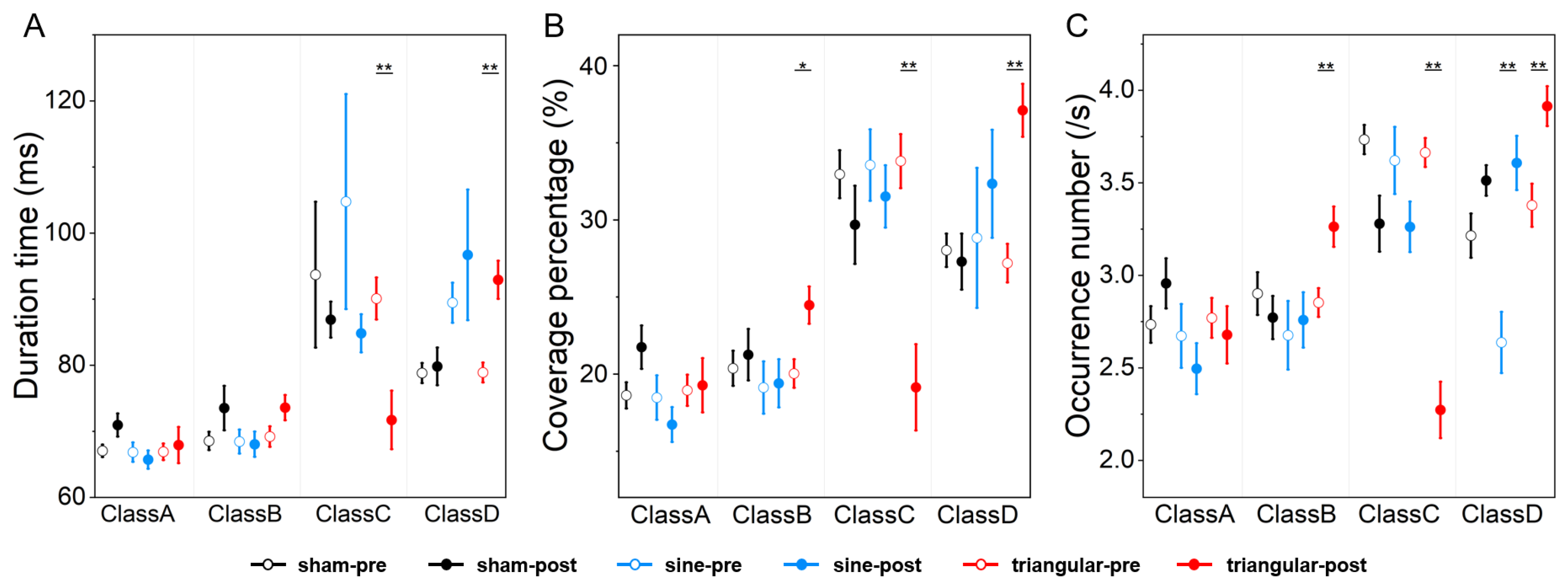
3.4. Microstate Parameters
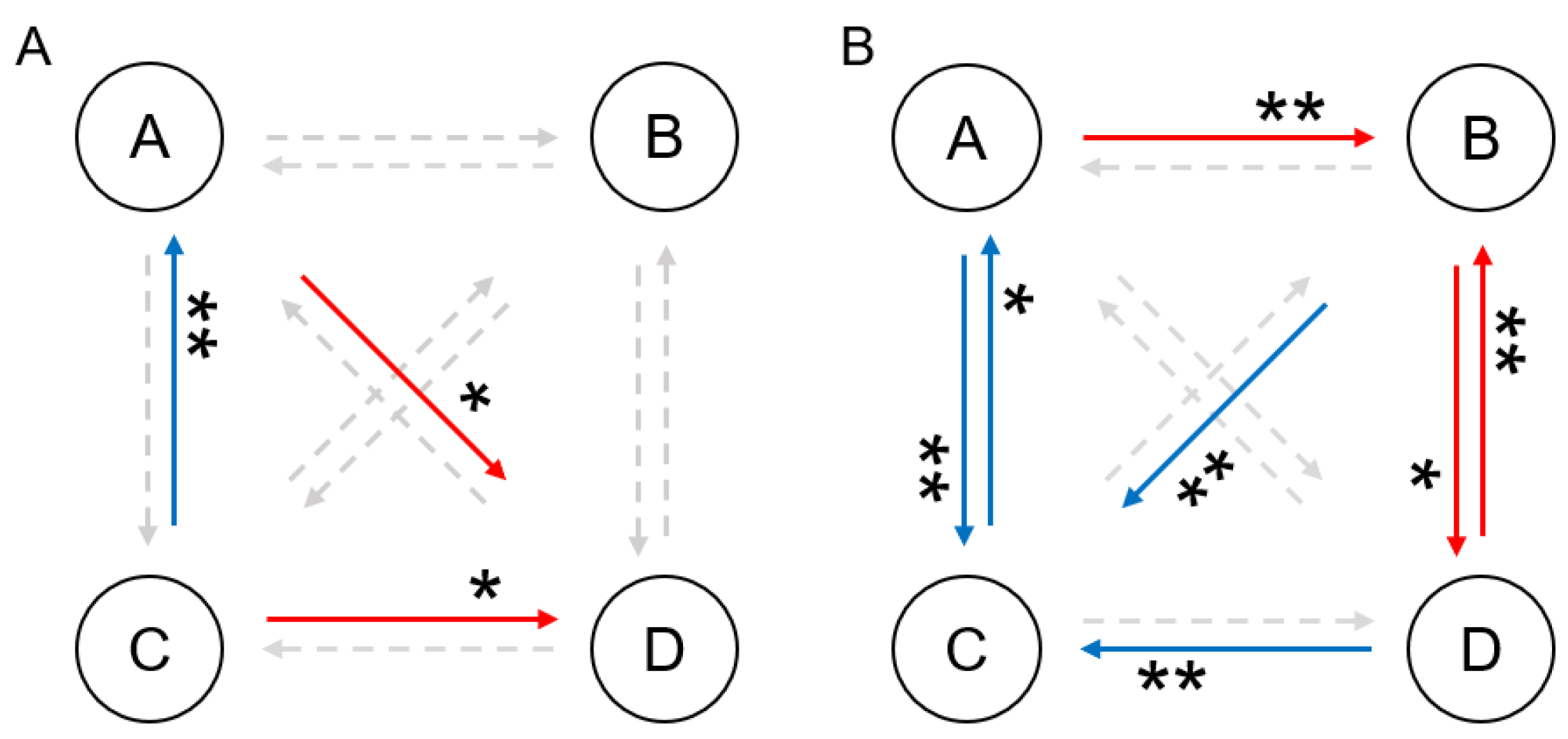
3.5. Correlation Between Microstate and Behavior Parameters
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, Y.X.; Shen, L.J.; Huang, J.; Xu, X.R.; Wang, Y.; Jin, H. Efficacy and Safety of tDCS and tACS in Treatment of Major Depressive Disorder: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Factorial Placebo-Controlled Study Design. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2021, 17, 1459–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Gu, N.N.; Cao, X.Y.; Zhu, Y.K.; Wang, J.J.; Smith, R.C.; Li, C.B. Effects of transcranial electrical stimulation on working memory in patients with schizophrenia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychiatry Res. 2021, 296, 113656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagliano, L.; Atripaldi, D.; De Vita, D.; D’Olimpio, F.; Trojano, L. Non-invasive brain stimulation in generalized anxiety disorder: A systematic review. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2019, 93, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philip, N.S.; Nelson, B.G.; Frohlich, F.; Lim, K.O.; Widge, A.S.; Carpenter, L.L. Low-Intensity Transcranial Current Stimulation in Psychiatry. Am. J. Psychiatry 2017, 174, 628–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, M.L.; Alagapan, S.; Lugo, C.E.; Mellin, J.M.; Lustenberger, C.; Rubinow, D.R.; Frohlich, F. Double-blind, randomized pilot clinical trial targeting alpha oscillations with transcranial alternating current stimulation (tACS) for the treatment of major depressive disorder (MDD). Transl. Psychiatry 2019, 9, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.M.; Sellers, K.K.; Frohlich, F. Transcranial Alternating Current Stimulation Modulates Large-Scale Cortical Network Activity by Network Resonance. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 11262–11275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, L.; Helgadóttir, H.; Mölle, M.; Born, J. Boosting slow oscillations during sleep potentiates memory. Nature 2006, 444, 610–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senkowski, D.; Sobirey, R.; Haslacher, D.; Soekadar, S.R. Boosting working memory: Uncovering the differential effects of tDCS and tACS. Cereb. Cortex Commun. 2022, 3, tgac018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, S.J.; Taylor, J.R.; Brown, L.J.E.; Pobric, G. The effects of transcranial alternating current stimulation on memory performance in healthy adults: A systematic review. Cortex 2022, 147, 112–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polanía, R.; Nitsche, M.A.; Ruff, C.C. Studying and modifying brain function with non-invasive brain stimulation. Nat. Neurosci. 2018, 21, 174–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baddeley, A.D. Working memory: Theories, models, and controversies. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2012, 63, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baddeley, A.D. Working memory: Looking back and looking forward. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2003, 4, 829–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dienel, S.J.; Lewis, D.A. Alterations in cortical interneurons and cognitive function in schizophrenia. Neurobiol. Dis. 2019, 131, 104208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, F.; Margari, F.; Legrottaglie, A.R.; Palumbi, R.; de Giambattista, C.; Margari, L. A review of executive function deficits in autism spectrum disorder and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2016, 12, 1191–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirova, A.M.; Bays, R.B.; Lagalwar, S. Working Memory and Executive Function Decline across Normal Aging, Mild Cognitive Impairment, and Alzheimer’s Disease. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 748212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozonoff, S.; Strayer, D.L. Further Evidence of Intact Working Memory in Autism. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2001, 31, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanslmayr, S.; Axmacher, N.; Inman, C.S. Modulating Human Memory via Entrainment of Brain Oscillations. Trends Neurosci. 2019, 42, 485–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, C.S.; Rach, S.; Neuling, T.; Strüber, D. Transcranial alternating current stimulation: A review of the underlying mechanisms and modulation of cognitive processes. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vossen, A.Y.; Gross, J.; Thut, G. Alpha Power Increase After Transcranial Alternating Current Stimulation at Alpha Frequency (alpha-tACS) Reflects Plastic Changes Rather Than Entrainment. Brain Stimul. 2015, 8, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.L.; Lee, H.; Kang, N. A meta-analysis showing improved cognitive performance in healthy young adults with transcranial alternating current stimulation. npj Sci. Learn. 2023, 8, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grover, S.; Fayzullina, R.; Bullard, B.M.; Levina, V.; Reinhart, R.M.G. A meta-analysis suggests that tACS improves cognition in healthy, aging, and psychiatric populations. Sci. Transl. Med. 2023, 15, eabo2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilla, Y.; Link, F.; Sauseng, P. Alpha-tACS alters attentional control but not cognitive functions as video games do: A psychophysical investigation based on the theory of visual attention. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2023, 57, 1705–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daughters, S.B.; Yi, J.Y.; Phillips, R.D.; Carelli, R.M.; Fröhlich, F. Alpha-tACS effect on inhibitory control and feasibility of administration in community outpatient substance use treatment. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2020, 213, 108132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolinski, N.; Cooper, N.R.; Sauseng, P.; Romei, V. The speed of parietal theta frequency drives visuospatial working memory capacity. PLoS Biol. 2018, 16, e2005348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Li, Z.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Q. Modulation of Visual Working Memory Performance via Different Theta Frequency Stimulations. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feurra, M.; Galli, G.; Pavone, E.F.; Rossi, A.; Rossi, S. Frequency-specific insight into short-term memory capacity. J. Neurophysiol. 2016, 116, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaple, Z.; Martinez-Saito, M.; Awasthi, B.; Feurra, M.; Shestakova, A.; Klucharev, V. Transcranial Alternating Current Stimulation Modulates Risky Decision Making in a Frequency-Controlled Experiment. eNeuro 2017, 4, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santarnecchi, E.; Polizzotto, N.R.; Godone, M.; Giovannelli, F.; Feurra, M.; Matzen, L.; Rossi, A.; Rossi, S. Frequency-dependent enhancement of fluid intelligence induced by transcranial oscillatory potentials. Curr. Biol. 2013, 23, 1449–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, L.; Khuc, J.; Saccani, M.S.; Zokaei, N.; Cappelletti, M. Gamma oscillations modulate working memory recall precision. Exp. Brain Res. 2021, 239, 2711–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoy, K.E.; Bailey, N.; Arnold, S.; Windsor, K.; John, J.; Daskalakis, Z.J.; Fitzgerald, P.B. The effect of gamma-tACS on working memory performance in healthy controls. Brain Cogn. 2015, 101, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alekseichuk, I.; Turi, Z.; Amador de Lara, G.; Antal, A.; Paulus, W. Spatial Working Memory in Humans Depends on Theta and High Gamma Synchronization in the Prefrontal Cortex. Curr. Biol. 2016, 26, 1513–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, A.; Pascual-Leone, A.; Michel, C.M.; Farzan, F. Microstates in resting-state EEG: Current status and future directions. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2015, 49, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, D.; Ozaki, H.; Pal, I. EEG alpha map series: Brain micro-states by space-oriented adaptive segmentation. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. Pract. 1987, 67, 271–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, C.M.; Koenig, T. EEG microstates as a tool for studying the temporal dynamics of whole-brain neuronal networks: A review. Neuroimage 2018, 180, 577–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britz, J.; Van De Ville, D.; Michel, C.M. BOLD correlates of EEG topography reveal rapid resting-state network dynamics. Neuroimage 2010, 52, 1162–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual-Marqui, R.D.; Lehmann, D.; Faber, P.; Milz, P.; Kochi, K.; Yoshimura, M.; Nishida, K.; Isotani, T.; Kinoshita, T. The resting microstate networks (RMN): Cortical distributions, dynamics, and frequency specific information flow. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1411.1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Custo, A.; Van De Ville, D.; Wells, W.M.; Tomescu, M.I.; Brunet, D.; Michel, C.M. Electroencephalographic Resting-State Networks: Source Localization of Microstates. Brain Connect. 2017, 7, 671–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.; Peng, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, S.; Li, J.; Zou, F.; Wang, Y.; Wu, X.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Effect of trait anxiety on cognitive flexibility: Evidence from event-related potentials and resting-state EEG. Biol. Psychol. 2022, 170, 108319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, K.; Kleinert, T.; Leota, J.; Scott, A.; Schimel, J. Resting-state networks of believers and non-believers: An EEG microstate study. Biol. Psychol. 2022, 169, 108283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spring, J.N.; Sallard, E.F.; Trabucchi, P.; Millet, G.P.; Barral, J. Alterations in spontaneous electrical brain activity after an extreme mountain ultramarathon. Biol. Psychol. 2022, 171, 108348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Suo, D.; Yan, T.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Funahashi, S.; Wu, J. EEG Microstate Analysis of Transcranial Alternating Current Stimulation in Healthy People. In Proceedings of the 2022 16th ICME International Conference on Complex Medical Engineering (CME), Zhongshan, China, 4–6 November 2022; pp. 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Cruz, J.R.; Favrod, O.; Roinishvili, M.; Chkonia, E.; Brand, A.; Mohr, C.; Figueiredo, P.; Herzog, M.H. EEG microstates are a candidate endophenotype for schizophrenia. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.; Wang, G.; Liu, T.; Li, G.; Wang, C.; Funahashi, S.; Suo, D.; Pei, G. Effects of Microstate Dynamic Brain Network Disruption in Different Stages of Schizophrenia. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2023, 31, 2688–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sverak, T.; Albrechtova, L.; Lamos, M.; Rektorova, I.; Ustohal, L. Intensive repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation changes EEG microstates in schizophrenia: A pilot study. Schizophr. Res. 2018, 193, 451–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Duc, N.T.; Choi, M.; Lee, B. EEG microstate features according to performance on a mental arithmetic task. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamano, R.; Ogawa, T.; Katagiri, A.; Cai, C.; Asai, T.; Kawanabe, M. Event-related microstate dynamics represents working memory performance. NeuroImage 2022, 263, 119669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, S.C.; Hoy, K.E.; Enticott, P.G.; Daskalakis, Z.J.; Fitzgerald, P.B. Improving working memory: The effect of combining cognitive activity and anodal transcranial direct current stimulation to the left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex. Brain Stimul. 2011, 4, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoy, K.E.; Whitty, D.; Bailey, N.; Fitzgerald, P.B. Preliminary investigation of the effects of gamma-tACS on working memory in schizophrenia. J. Neural Transm. 2016, 123, 1205–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, A.M.; McMillan, K.M.; Laird, A.R.; Bullmore, E.T. N-back working memory paradigm: A meta-analysis of normative functional neuroimaging studies. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2005, 25, 46–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Shi, Z.; Sun, W.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Shi, Y.; Yang, R.; Li, C.; Chen, D.; Wu, J.; et al. Development of a Non-invasive Deep Brain Stimulator With Precise Positioning and Real-Time Monitoring of Bioimpedance. Front. Neuroinform. 2020, 14, 574189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Yuan, K.; Chu, W.C.w.; Tong, R.K.y. The Effects of 10 Hz and 20 Hz tACS in Network Integration and Segregation in Chronic Stroke: A Graph Theoretical fMRI Study. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Jang, K.I.; Roh, D.; Kim, H.; Kim, D.H. A direct comparison of the electrophysiological effects of transcranial direct and alternating current stimulation in healthy subjects. Brain Res. 2020, 1747, 147065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delorme, A.; Makeig, S. EEGLAB: An open source toolbox for analysis of single-trial EEG dynamics including independent component analysis. J. Neurosci. Methods 2004, 134, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pernet, C.; Garrido, M.I.; Gramfort, A.; Maurits, N.; Michel, C.M.; Pang, E.; Salmelin, R.; Schoffelen, J.M.; Valdes-Sosa, P.A.; Puce, A. Issues and recommendations from the OHBM COBIDAS MEEG committee for reproducible EEG and MEG research. Nat. Neurosci. 2020, 23, 1473–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulsen, A.; Pedroni, A.; Langer, N.; Hansen, L. Microstate EEGlab toolbox An introductory guide. bioRxiv 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, R.; Song, M.; Shi, L.; Pei, Y.; Li, H.; Tan, S.; Wang, B. Microstate D as a Biomarker in Schizophrenia: Insights from Brain State Transitions. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.; Wu, Z.; Chen, B.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Q.; Liu, M.; Zhang, S.; Yang, M.; Ning, Y.; Zhong, X. Altered Microstate Dynamics and Spatial Complexity in Late-Life Schizophrenia. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 907802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, D.; Skrandies, W. Reference-free identification of components of checkerboard-evoked multichannel potential fields. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1980, 48, 609–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, A.; Pascual-Leone, A.; Farzan, F. Reliability of resting-state microstate features in electroencephalography. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e114163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, D.; Faber, P.L.; Galderisi, S.; Herrmann, W.M.; Kinoshita, T.; Koukkou, M.; Mucci, A.; Pascual-Marqui, R.D.; Saito, N.; Wackermann, J.; et al. EEG microstate duration and syntax in acute, medication-naïve, first-episode schizophrenia: A multi-center study. Psychiatry Res. Neuroimaging 2005, 138, 141–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakens, D. Calculating and reporting effect sizes to facilitate cumulative science: A practical primer for t-tests and ANOVAs. Front. Psychol. 2013, 4, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tait, L.; Zhang, J. +microstate: A MATLAB toolbox for brain microstate analysis in sensor and cortical EEG/MEG. Neuroimage 2022, 258, 119346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koenig, T.; Prichep, L.S.; Lehmann, D.; Valdés-Sosa, P.A.; Braeker, E.; Kleinlogel, H.; Isenhart, R.; John, E.R. Millisecond by Millisecond, Year by Year: Normative EEG Microstates and Developmental Stages. NeuroImage 2002, 16, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenig, T.; Lehmann, D.; Merlo, M.C.G.; Kochi, K.; Hell, D.; Koukkou, M. A deviant EEG brain microstate in acute, neuroleptic-naive schizophrenics at rest. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 1999, 249, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhart, R.M.G.; Nguyen, J.A. Working memory revived in older adults by synchronizing rhythmic brain circuits. Nat. Neurosci. 2019, 22, 820–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roux, F.; Uhlhaas, P.J. Working memory and neural oscillations: alpha-gamma versus theta-gamma codes for distinct WM information? Trends Cogn. Sci. 2014, 18, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pahor, A.; Jaušovec, N. The Effects of Theta and Gamma tACS on Working Memory and Electrophysiology. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinert, M.L.; Szymanski, C.; Müller, V. Frequency-Unspecific Effects of θ-tACS Related to a Visuospatial Working Memory Task. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowsett, J.; Herrmann, C.S. Transcranial Alternating Current Stimulation with Sawtooth Waves: Simultaneous Stimulation and EEG Recording. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potok, W.; van der Groen, O.; Sivachelvam, S.; Bächinger, M.; Fröhlich, F.; Kish, L.B.; Wenderoth, N. Contrast detection is enhanced by deterministic, high-frequency transcranial alternating current stimulation with triangle and sine waveform. J. Neurophysiol. 2023, 130, 458–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertrand, O.; Tallon-Baudry, C. Oscillatory gamma activity in humans: A possible role for object representation. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2000, 38, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witkowski, M.; Garcia-Cossio, E.; Chander, B.S.; Braun, C.; Birbaumer, N.; Robinson, S.E.; Soekadar, S.R. Mapping entrained brain oscillations during transcranial alternating current stimulation (tACS). NeuroImage 2016, 140, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, D.; Strik, W.; Henggeler, B.; Koenig, T.; Koukkou, M. Brain electric microstates and momentary conscious mind states as building blocks of spontaneous thinking: I. Visual imagery and abstract thoughts. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 1998, 29, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seitzman, B.A.; Abell, M.; Bartley, S.C.; Erickson, M.A.; Bolbecker, A.R.; Hetrick, W.P. Cognitive manipulation of brain electric microstates. NeuroImage 2017, 146, 533–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz Hernandez, L.; Rieger, K.; Baenninger, A.; Brandeis, D.; Koenig, T. Towards Using Microstate-Neurofeedback for the Treatment of Psychotic Symptoms in Schizophrenia. A Feasibility Study in Healthy Participants. Brain Topogr. 2016, 29, 308–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spreng, R.N.; Stevens, W.D.; Chamberlain, J.P.; Gilmore, A.W.; Schacter, D.L. Default network activity, coupled with the frontoparietal control network, supports goal-directed cognition. NeuroImage 2010, 53, 303–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roux, F.; Wibral, M.; Mohr, H.M.; Singer, W.; Uhlhaas, P.J. Gamma-Band Activity in Human Prefrontal Cortex Codes for the Number of Relevant Items Maintained in Working Memory. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 12411–12420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Lee, C.; Lee, S.; Im, C.H. 80 Hz but not 40 Hz, transcranial alternating current stimulation of 80 Hz over right intraparietal sulcus increases visuospatial working memory capacity. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 13762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochab, J.K.; Wątorek, M.; Ceglarek, A.; Fafrowicz, M.; Lewandowska, K.; Marek, T.; Sikora-Wachowicz, B.; Oświęcimka, P. Task-dependent fractal patterns of information processing in working memory. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 17866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pileckyte, I.; Soto-Faraco, S. Sensory stimulation enhances visual working memory capacity. Commun. Psychol. 2024, 2, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Sham | Sine | Triangular | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 38) | (n = 28) | (n = 38) | |||
| Age (years, mean ± SD) | 23.9 ± 3.3 | 22.8 ± 2.4 | 23.5 ± 3.2 | 0.921 | 0.401 1 |
| Gender (F/M) | 23/15 | 17/11 | 24/14 | 0.067 | 0.967 2 |
| Parameter | Microstate | Sham | Sine | Triangular | Sham vs. Sine | Sham vs. Triangular | Sine vs. Triangular |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SEM | p | ||||||
| Duration (ms) | Class A | 70.95 ± 1.75 | 65.72 ± 1.39 | 67.92 ± 2.74 | 0.829 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Class B | 73.52 ± 3.36 | 68.04 ± 1.91 | 73.59 ± 1.91 | 0.431 | 0.738 | 0.034(↑) | |
| Class C | 86.90 ± 2.72 | 84.84 ± 2.88 | 71.72 ± 4.43 | 1.000 | <0.001(↓) | <0.001(↓) | |
| Class D | 79.82 ± 2.86 | 96.70 ± 9.89 | 92.92 ± 2.87 | 0.402 | <0.010(↑) | 0.676 | |
| Coverage (%) | Class A | 21.75 ± 1.40 | 16.73 ± 1.13 | 19.27 ± 1.76 | 0.047(↓) | 0.352 | 0.997 |
| Class B | 21.26 ± 1.66 | 19.40 ± 1.55 | 24.47 ± 1.21 | 1.000 | 0.037(↑) | 0.010(↑) | |
| Class C | 29.69 ± 2.53 | 31.52 ± 2.02 | 19.14 ± 2.80 | 0.572 | 0.002(↓) | <0.001(↓) | |
| Class D | 27.30 ± 1.82 | 32.35 ± 3.50 | 37.11 ± 1.72 | 1.000 | 0.002(↑) | 0.019(↑) | |
| Occurrence (/s) | Class A | 2.96 ± 0.14 | 2.50 ± 0.14 | 2.68 ± 0.15 | 0.049(↓) | 0.453 | 0.842 |
| Class B | 2.77 ± 0.12 | 2.76 ± 0.15 | 3.26 ± 0.11 | 1.000 | 0.002(↑) | 0.005(↑) | |
| Class C | 3.28 ± 0.15 | 3.26 ± 0.14 | 2.27 ± 0.15 | 1.000 | <0.001(↓) | 0.001(↓) | |
| Class D | 3.51 ± 0.08 | 3.61 ± 0.15 | 3.91 ± 0.11 | 0.365 | <0.001(↑) | 0.123 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, B.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Pei, G.; Liu, T.; Wang, L.; Funahashi, S.; Wu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J. Gamma Transcranial Alternating Current Stimulation Enhances Working Memory Ability in Healthy People: An EEG Microstate Study. Brain Sci. 2025, 15, 381. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15040381
Gao B, Zhang J, Zhang J, Pei G, Liu T, Wang L, Funahashi S, Wu J, Zhang Z, Zhang J. Gamma Transcranial Alternating Current Stimulation Enhances Working Memory Ability in Healthy People: An EEG Microstate Study. Brain Sciences. 2025; 15(4):381. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15040381
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Binbin, Jinyan Zhang, Jianxu Zhang, Guangying Pei, Tiantian Liu, Li Wang, Shintaro Funahashi, Jinglong Wu, Zhilin Zhang, and Jian Zhang. 2025. "Gamma Transcranial Alternating Current Stimulation Enhances Working Memory Ability in Healthy People: An EEG Microstate Study" Brain Sciences 15, no. 4: 381. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15040381
APA StyleGao, B., Zhang, J., Zhang, J., Pei, G., Liu, T., Wang, L., Funahashi, S., Wu, J., Zhang, Z., & Zhang, J. (2025). Gamma Transcranial Alternating Current Stimulation Enhances Working Memory Ability in Healthy People: An EEG Microstate Study. Brain Sciences, 15(4), 381. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15040381





