Machine Learning-Based Classification of Anterior Circulation Cerebral Infarction Using Computational Fluid Dynamics and CT Perfusion Metrics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Subjects
2.2. Classification of Stroke Mechanisms in Patients Based on CISS
2.3. Acquisition of CTP Data
2.4. CTA-Based Cerebral Hemodynamic Modeling and Quantitative Analysis
2.5. Machine Learning and Modeling
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. CT Perfusion, Anatomy, and Computational Fluid Dynamics Index Analysis
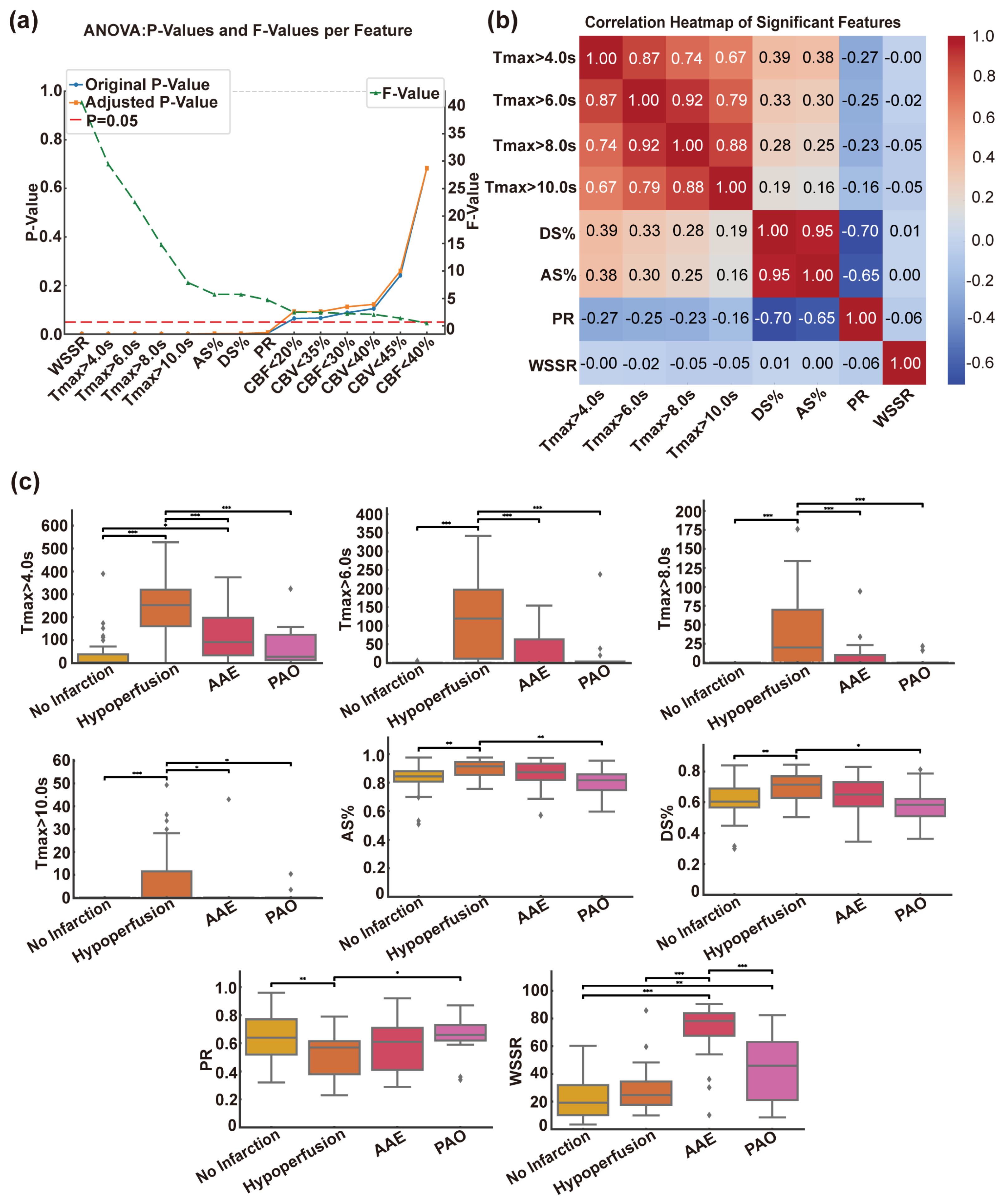
3.2.1. Selection of Features for CISS Categorization
3.2.2. Correlation Heatmap Analysis of Various Indicators
3.2.3. Differences in Indicators in the CISS Classification
3.3. Threshold Values for Critical Indicators in CISS Typing
3.4. Machine Learning Model Construction and Comparison
3.4.1. Quantitative Assessment of Model Performance
3.4.2. Comparison of Machine Learning Models Based on Cross-Validation Results
3.4.3. Comparative Analysis of Model Performance Using ROC Curves
3.4.4. Precision–Recall Analysis and Model Performance Comparison
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ICAS | Intracranial atherosclerotic stenosis |
| TIA | Transient ischemic attack |
| MCA | Middle cerebral artery |
| CISS | The Chinese Ischemic Stroke Subclassification |
| TOAST | Trial of Organ 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment |
| CFD | Computational fluid dynamics |
| WSSR | Wall shear stress ratio |
| PR | Pressure ratio |
| CTP | Computed tomography perfusion |
| CTA | Computed tomography angiography |
| DSA | Digital subtraction angiography |
| mRS | Modified Rankin Scale |
| NIHSS | National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale |
| DWI | Diffusion-Weighted Imaging |
| AAE | Artery-to-artery embolism |
| PAO | Parent artery occlusion |
| CBF | Cerebral blood flow |
| CBV | Cerebral blood volume |
| DT | Decision Tree |
| RF | Random Forest |
| NB | Naive Bayes |
| KNN | K-Nearest Neighbors |
| LAA | Large-artery atherosclerosis |
References
- Ding, Q.; Liu, S.; Yao, Y.; Liu, H.; Cai, T.; Han, L. Global, Regional, and National Burden of Ischemic Stroke, 1990–2019. Neurology 2022, 98, e279–e290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saini, V.; Guada, L.; Yavagal, D.R. Global Epidemiology of Stroke and Access to Acute Ischemic Stroke Interventions. Neurology 2021, 97 (Suppl. S2), S6–S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, J.; Turan, T.N.; Hoh, B.L.; Chimowitz, M.I. Intracranial atherosclerotic stenosis: Risk factors, diagnosis, and treatment. Lancet Neurol. 2022, 21, 355–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komotar, R.J.; Wilson, D.A.; Mocco, J.; Jones, J.E.; Connolly, E.S.; Lavine, S.D.; Meyers, P.M. Natural history of intracranial atherosclerosis: A critical review. Neurosurgery 2006, 58, 595–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Meng, R.; Liu, G.; Cao, C.; Chen, F.; Jin, K.; Ji, X.; Cao, G. Intracranial atherosclerotic disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2019, 124, 118–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, H.P., Jr.; Bendixen, B.H.; Kappelle, L.J.; Biller, J.; Love, B.B.; Gordon, D.L.; Marsh, E.E., 3rd. Classification of subtype of acute ischemic stroke. Definitions for use in a multicenter clinical trial. TOAST. Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment. Stroke 1993, 24, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomyo, M.; Tsuchiya, K.; Yokoyama, K. Vessel Wall Imaging of Intracranial Arteries: Fundamentals and Clinical Applications. Magn. Reson. Med. Sci. 2023, 22, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.H.; Gao, S.; Wang, Y.J.; Xu, A.D.; Li, Y.S.; Wang, D. Classifying Ischemic Stroke, from TOAST to CISS. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2012, 18, 452–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Wang, Y.J.; Xu, A.D.; Li, Y.S.; Wang, D.Z. Chinese ischemic stroke subclassification. Front. Neurol. 2011, 2, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Chan, K.L.; Lan, L.; Abrigo, J.; Liu, J.; Fang, H.; Xu, Y.; Soo, Y.; Leng, X.; Leung, T.W. Stroke Mechanisms in Symptomatic Intracranial Atherosclerotic Disease: Classification and Clinical Implications. Stroke 2019, 50, 2692–2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, S.; Liu, H.; Tian, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z.; Leung, T.W.; Leng, X. Clinical implications of haemodynamics in symptomatic intracranial atherosclerotic stenosis by computational fluid dynamics modelling: A systematic review. Stroke Vasc. Neurol. 2024, 10, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Fang, H.; Ip, B.Y.M.; Chan, K.L.; Li, S.; Tian, X.; Zheng, L.; Liu, Y.; Lan, L.; Liu, H.; et al. Cerebral Hemodynamics Underlying Artery-to-Artery Embolism in Symptomatic Intracranial Atherosclerotic Disease. Transl. Stroke Res. 2024, 15, 572–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Tian, X.; Ip, B.; Feng, X.; Ip, H.L.; Abrigo, J.; Lan, L.; Liu, H.; Zheng, L.; Liu, Y.; et al. Cerebral hemodynamics and stroke risks in symptomatic intracranial atherosclerotic stenosis with internal versus cortical borderzone infarcts: A computational fluid dynamics study. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2024, 44, 516–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suo, S.; Zhao, Z.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, B.; Xu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Tu, S. Cerebral hemodynamics in symptomatic anterior circulation intracranial stenosis measured by angiography-based quantitative flow ratio: Association with CT perfusion. Eur. Radiol. 2023, 33, 5687–5697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Yu, J.; Hou, Z.; Chiu, T.-C.; Liu, X.; Pan, Y.; Yan, L.; Fu, W.; Jia, B.; Lui, W.; et al. Tmax > 4 s volume predicts stroke recurrence in symptomatic intracranial atherosclerotic stenosis with optimal medical treatment. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2024, 022418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Li, Z.-A.; Zhai, X.-Y.; Han, L.; Zhang, P.; Cheng, S.-J.; Yue, J.-Y.; Cui, H.-K. An interpretable machine learning model for stroke recurrence in patients with symptomatic intracranial atherosclerotic arterial stenosis. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1323270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, J.; Tan, G.; Lin, Y.; Guan, J.; Dai, Z.; Wang, F.; Zhuang, C.; Wilman, A.H.; Huang, H.; Cao, Z.; et al. Automated detection of intracranial artery stenosis and occlusion in magnetic resonance angiography: A preliminary study based on deep learning. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2022, 94, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- On behalf of the Atlas Writing Group; Developed in collaboration with the national societies of the European Society of Cardiology member countries; Timmis, A.; Townsend, N.; Gale, C.P.; Torbica, A.; Lettino, M.; E Petersen, S.; A Mossialos, E.; Maggioni, A.P.; et al. European Society of Cardiology: Cardiovascular Disease Statistics 2019 (Executive Summary). Eur. Heart J. Qual. Care Clin. Outcomes 2020, 6, 7–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Wan, S.; Wang, J.; Hu, Y.; Ma, N.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, X.; Shen, F.; et al. Hemodynamic assessment for intracranial atherosclerosis from angiographic images: A clinical validation study. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2024, 16, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, X.; Lan, L.; Ip, H.L.; Abrigo, J.; Scalzo, F.; Liu, H.; Feng, X.; Chan, K.L.; Fan, F.S.Y.; Ma, S.H.; et al. Hemodynamics and stroke risk in intracranial atherosclerotic disease. Ann. Neurol. 2019, 85, 752–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, L.; Liu, H.; Ip, V.; Soo, Y.; Abrigo, J.; Fan, F.; Ma, S.H.; Ma, K.; Ip, B.; Liu, J.; et al. Regional High Wall Shear Stress Associated With Stenosis Regression in Symptomatic Intracranial Atherosclerotic Disease. Stroke 2020, 51, 3064–3073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Li, Z.; Dai, Y.; Guo, E.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Y. Ischaemic stroke etiological classification system: The agreement analysis of CISS, SPARKLE and TOAST. Stroke Vasc. Neurol. 2019, 4, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.; Song, J.; Yu, Y.; Hou, Z.; Fu, W.; Cui, R.; Wan, M.; Xu, X.; Lv, M.; Wang, Y.; et al. Predictors of hyperperfusion syndrome after stent implantation in symptomatic intracranial atherosclerotic stenosis. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2023, 13, 1048–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Hou, Z.; Fu, W.; Yu, Y.; Cui, R.; Miao, Z.; Lou, X.; Ma, N. Association of periprocedural perfusion non-improvement with recurrent stroke after endovascular treatment for Intracranial Atherosclerotic Stenosis. Ther. Adv. Neurol. Disord. 2022, 15, 17562864221143178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, X.; Yang, J.; Li, X.; Zhan, T.; Liu, D.; Yan, H.; Wei, Y.; Liu, X.; Chen, J.; Gong, G.; et al. Prediction of futile recanalisation after endovascular treatment in acute ischaemic stroke: Development and validation of a hybrid machine learning model. Stroke Vasc. Neurol. 2024, 9, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Chen, G.; Mao, L.; Li, X.; Zhou, C.; Xia, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Hu, B.; Lu, G.; et al. Machine Learning-Based Prediction of Small Intracranial Aneurysm Rupture Status Using CTA-Derived Hemodynamics: A Multicenter Study. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2021, 42, 648–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turc, G.; Bhogal, P.; Fischer, U.; Khatri, P.; Lobotesis, K.; Mazighi, M.; Schellinger, P.D.; Toni, D.; de Vries, J.; White, P.; et al. European Stroke Organisation (ESO)—European Society for Minimally Invasive Neurological Therapy (ESMINT) Guidelines on Mechanical Thrombectomy in Acute Ischaemic StrokeEndorsed by Stroke Alliance for Europe (SAFE). Eur. Stroke J. 2019, 4, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafaat, O.; Bernstock, J.D.; Shafaat, A.; Yedavalli, V.S.; Elsayed, G.; Gupta, S.; Sotoudeh, E.; Sair, H.I.; Yousem, D.M.; Sotoudeh, H. Leveraging artificial intelligence in ischemic stroke imaging. J. Neuroradiol. 2022, 49, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Classification | No Infarction | Hypoperfusion | AAE | PAO | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 45) | (n = 39) | (n = 21) | (n = 13) | ||
| Age | 64.0 (49.0–69.0) | 62.0 (50.0–69.0) | 63.0 (47.0–68.0) | 63.0 (57.0–66.0) | 0.915 |
| Male | 25 (55.6) | 31 (79.5) | 14 (66.7) | 9 (69.2) | 0.144 |
| SBP | 138.0 (130.0–154.0) | 135.0 (129.0–155.5) | 135.0 (127.0–151.0) | 140.0 (130.0–148.0) | 0.876 |
| DBP | 79.0 (71.0–85.0) | 82.0 (73.0–88.0) | 80.0 (71.0–86.0) | 83.0 (72.0–87.0) | 0.888 |
| mRs | 2 (0.0–2.0) | 2 (1.5–3.0) | 3 (1.0–4.0) | 1 (1.0–2.0) | <0.001 |
| NIHSS | 1 (0.0–1.0) | 3 (1.0–4.0) | 3 (0.0–3.0) | 3 (0.0–3.0) | 0.001 |
| Relevant past medical history | |||||
| Smoking | 8 (17.8) | 13 (33.3) | 6 (28.6) | 2 (15.4) | 0.326 |
| Hyperlipidemia | 21 (46.7) | 23 (59.0) | 12 (57.1) | 7 (53.8) | 0.707 |
| Hypertension | 33 (73.3) | 32 (82.1) | 13 (61.9) | 9 (69.2) | 0.392 |
| Diabetes | 16 (35.6) | 14 (35.9) | 5 (23.8) | 7 (53.8) | 0.375 |
| Ischemic heart disease | 4 (8.9) | 5 (12.8) | 1 (4.8) | 0 (0.0) | 0.477 |
| Ischemic stroke/TIA | 21 (46.7) | 24 (61.5) | 12 (57.1) | 7 (53.8) | 0.592 |
| Laboratory test results | |||||
| Blood glucose | 5.28 (4.9–5.77) | 5.29 (4.68–6.59) | 5.24 (4.82–5.58) | 5.64 (5.12–6.5) | 0.128 |
| Triglyceride | 1.22 (0.91–1.86) | 1.60 (0.98–1.9) | 1.44 (1.3–1.67) | 1.19 (1.02–1.4) | 0.571 |
| HbA1c | 6.10 (5.7–6.4) | 6.30 (5.75–7.0) | 5.80 (5.7–6.2) | 6.30 (5.6–8.1) | 0.587 |
| HDL | 1.03 (0.24) | 0.95 (0.28) | 0.97 (0.19) | 0.95 (0.26) | 0.494 |
| LDL-C | 1.88 (1.47–2.39) | 1.84 (1.40–2.46) | 1.79 (1.64–2.42) | 1.69 (1.45–2.24) | 0.831 |
| Classification | No Infarction | Hypoperfusion | AAE | PAO | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 45) | (n = 39) | (n = 21) | (n = 13) | ||
| CT Perfusion Indices (mL) | |||||
| Tmax > 4.0 s | 2.9 (0.0–35.9) | 252.6 (160.5–320.4) | 92 (34.0–197.3) | 27.8 (13.0–123.9) | <0.001 |
| Tmax > 6.0 s | 0.0 (0.0–0.0) | 119.0 (10.6–197.0) | 0.0 (0.0–63.0) | 0.0 (0.0–3.1) | <0.001 |
| Tmax > 8.0 s | 0.0 (0.0–0.0) | 20.0 (0.0–69.9) | 0.0 (0.0–10.0) | 0.0 (0.0–0.0) | <0.001 |
| Tmax > 10.0 s | 0.0 (0.0–0.0) | 0.0 (0.0–11.45) | 0.0 (0.0–0.0) | 0.0 (0.0–0.0) | <0.001 |
| CBF < 40% | 0.0 (0.0–5.4) | 0.0 (0.0–19.9) | 9.0 (0.0–47.4) | 9.4 (0.0–37.7) | 0.683 |
| CBF < 30% | 0.0 (0.0–0.0) | 0.0 (0.0–0.0) | 0.0 (0.0–0.004) | 0.0 (0.0–0.0) | 0.089 |
| CBF < 20% | 0.0 (0.0–0.0) | 0.0 (0.0–0.0) | 0.0 (0.0–0.0) | 0.0 (0.0–0.0) | 0.065 |
| CBV < 45% | 4.0 (0.0–27.6) | 28.6 (0.0–48.3) | 9.0 (0.0–35.7) | 17.3 (0.1–31.7) | 0.242 |
| CBV < 40% | 0.0 (0.0–2.5) | 4.0 (0.0–8.8) | 0.4 (0.0–9.0) | 3.3 (0.0–10.3) | 0.105 |
| CBV < 35% | 0.0 (0.0–0.0) | 0.0 (0.0–0.0) | 0.0 (0.0–1.6) | 0.0 (0.0–2.6) | 0.067 |
| Anatomical Indicators | |||||
| DS% | 0.60 (0.11) | 0.70 (0.10) | 0.64 (0.12) | 0.58 (0.13) | 0.001 |
| AS% | 0.84 (0.81–0.88) | 0.91 (0.85–0.95) | 0.87 (0.82–0.93) | 0.82 (0.75–0.86) | 0.001 |
| Computational Fluid Dynamics Indicators | |||||
| PR | 0.63 (0.16) | 0.52 (0.14) | 0.59 (0.18) | 0.66 (0.17) | 0.004 |
| WSSR | 19.2 (10.2–32.0) | 24.7 (17.7–34.5) | 78.3 (67.6–83.9) | 45.9 (21.2–63.1) | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yin, X.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, F.; Wang, H.; Fang, Q. Machine Learning-Based Classification of Anterior Circulation Cerebral Infarction Using Computational Fluid Dynamics and CT Perfusion Metrics. Brain Sci. 2025, 15, 399. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15040399
Yin X, Zhao Y, Huang F, Wang H, Fang Q. Machine Learning-Based Classification of Anterior Circulation Cerebral Infarction Using Computational Fluid Dynamics and CT Perfusion Metrics. Brain Sciences. 2025; 15(4):399. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15040399
Chicago/Turabian StyleYin, Xulong, Yusheng Zhao, Fuping Huang, Hui Wang, and Qi Fang. 2025. "Machine Learning-Based Classification of Anterior Circulation Cerebral Infarction Using Computational Fluid Dynamics and CT Perfusion Metrics" Brain Sciences 15, no. 4: 399. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15040399
APA StyleYin, X., Zhao, Y., Huang, F., Wang, H., & Fang, Q. (2025). Machine Learning-Based Classification of Anterior Circulation Cerebral Infarction Using Computational Fluid Dynamics and CT Perfusion Metrics. Brain Sciences, 15(4), 399. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15040399







