Seeing a Face in a Crowd of Emotional Voices: Changes in Perception and Cortisol in Response to Emotional Information across the Senses
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Processing Emotion across the Senses
1.2. Exposure to Emotion: Perceptual Changes
1.3. Exposure to Emotion: Cortisol Changes
2. Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Questionnaires
2.3. Behavioral Measures
2.3.1. Apparatus
2.3.2. Stimuli
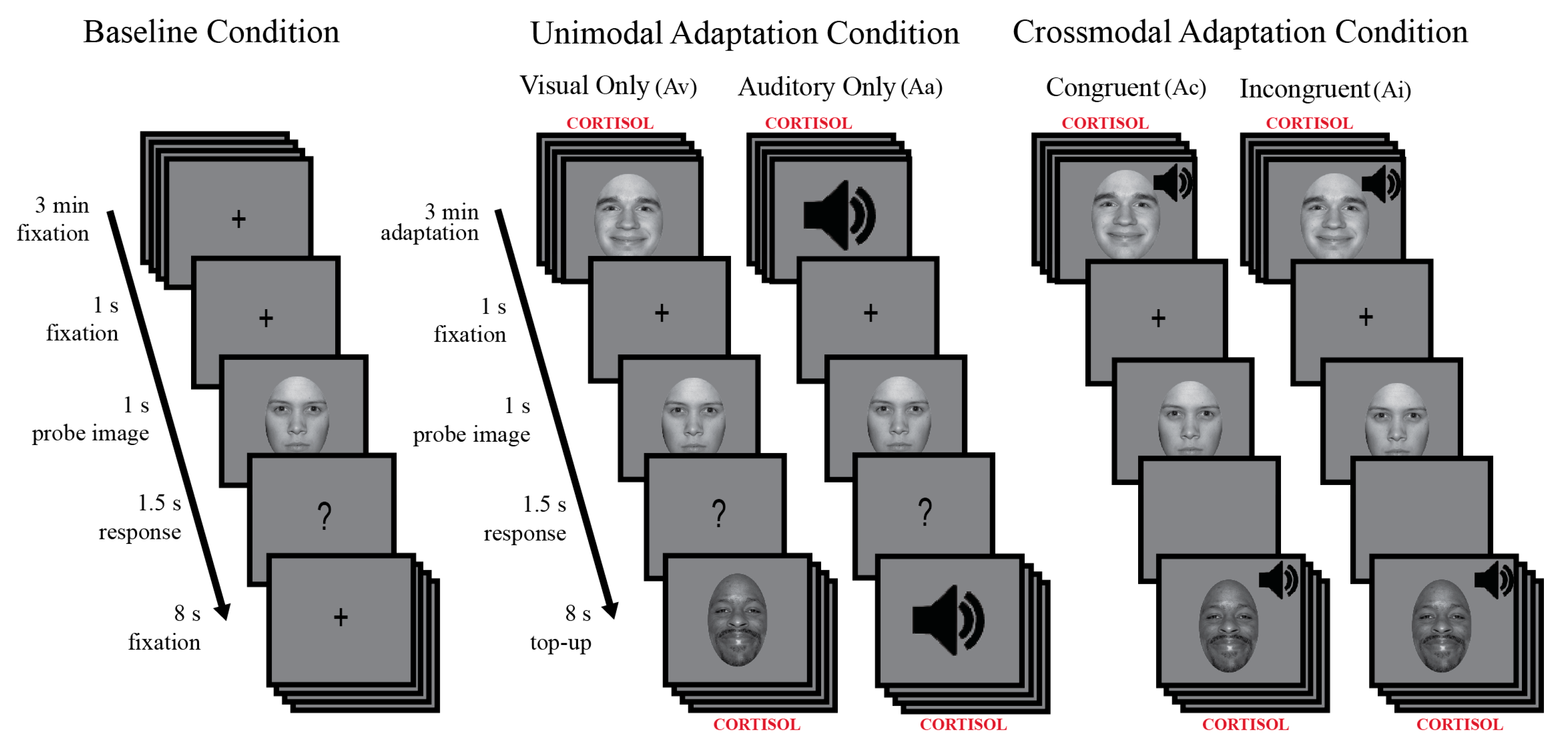
2.3.3. Behavioral Procedure
2.3.4. Data Analysis for Behavioral Measures
2.4. Physiological Measures
2.4.1. Quantifying Salivary Cortisol
2.4.2. Data Analysis for Cortisol Measures
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Behavioral Measures
3.2. Physiological Measures
3.3. Correlations between Behavioral and Physiological Measures
3.4. Underlying Biases in Behavioral and Physiological Measures
4. Discussion
Is Cortisol a Proxy for Stress, Arousal or Attention?
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Robins, D.L.; Hunyadi, E.; Schultz, R.T. Superior temporal activation in response to dynamic audio-visual emotional cues. Brain Cogn. 2009, 69, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bestelmeyer, P.E.G.; Maurage, P.; Rouger, J.; Latinus, M.; Belin, P. Adaptation to Vocal Expressions Reveals Multistep Perception of Auditory Emotion. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 8098–8105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herz, R.S.; McCall, C.; Cahill, L. Hemispheric Lateralization in the Processing of Odor Pleasantness versus Odor Names. Chem. Sens. 1999, 24, 691–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niedenthal, P.M. Embodying Emotion. Science 2007, 316, 1002–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zald, D.H.; Pardo, J.V. Emotion, olfaction, and the human amygdala: Amygdala activation during aversive olfactory stimulation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 4119–4124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flom, R.; Bahrick, L.E. The Development of Infant Discrimination of Affect in Multimodal and Unimodal Stimulation: The Role of Intersensory Redundancy. Dev. Psychol. 2007, 43, 238–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossmann, T.; Striano, T.; Friederici, A.D. Crossmodal integration of emotional information from face and voice in the infant brain. Dev. Sci. 2006, 9, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, M.; Monesson, A.; Scott, L.S. Building biases in infancy: The influence of race on face and voice emotion matching. Dev. Sci. 2012, 15, 359–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zieber, N.; Kangas, A.; Hock, A.; Bhatt, R.S. The development of intermodal emotion perception from bodies and voices. J. Exp. Child Psychol. 2014, 126, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, K.E.; Brannon, E.M. The multisensory representation of number in infancy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 3486–3489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Little, A.C.; Feinberg, D.R.; DeBruine, L.M.; Jones, B.C. Adaptation to Faces and Voices: Unimodal, Cross-Modal, and Sex-Specific Effects. Psychol. Sci. 2013, 24, 2297–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webster, M.A.; MacLeod, D.I.A. Visual adaptation and face perception. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2011, 366, 1702–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bestelmeyer, P.E.; Rouger, J.; Debruine, L.M.; Belin, P. Auditory adaptation in vocal affect perception. Cognition 2010, 117, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, S.; Young, A.W.; Stolz, J.A.; Besner, D.; Carr, T.H. Adaptation effects in facial expression recognition. Vis. Cogn. 2004, 12, 284–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutherford, M.D.; Chattha, H.M.; Krysko, K.M. The use of aftereffects in the study of relationships among emotion categories. J. Exp. Psychol. Hum. Percept. Perform. 2008, 34, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webster, M.A.; Kaping, D.; Mizokami, Y.; Duhamel, P. Adaptation to natural facial categories. Nature 2004, 428, 557–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pye, A.; Bestelmeyer, P.E. Evidence for a supra-modal representation of emotion from cross-modal adaptation. Cognition 2015, 134, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skuk, V.G.; Schweinberger, S.R. Adaptation Aftereffects in Vocal Emotion Perception Elicited by Expressive Faces and Voices. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Guo, X.; Chen, L.; Liu, Y.; Goldberg, M.E.; Xu, H. Auditory to Visual Cross-Modal Adaptation for Emotion: Psychophysical and Neural Correlates. Cereb. Cortex 2016, 27, 1337–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Gelder, B.; Vroomen, J. The perception of emotions by ear and by eye. Cogn. Emot. 2000, 14, 289–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, V.I.; Habel, U.; Derntl, B.; Schneider, F.; Zilles, K.; Turetsky, B.I.; Eickhoff, S.B. Incongruence effects in crossmodal emotional integration. NeuroImage 2011, 54, 2257–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, C.J.; Barton, J.J. What is adapted in face adaptation? The neural representations of expression in the human visual system. Brain Res. 2007, 1127, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallup, A.C.; Hale, J.J.; Sumpter, D.J.T.; Garnier, S.; Kacelnik, A.; Krebs, J.R.; Couzin, I.D. Visual attention and the acquisition of information in human crowds. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 7245–7250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haberman, J.; Harp, T.; Whitney, D. Averaging facial expression over time. J. Vis. 2009, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haberman, J.; Whitney, D. Rapid extraction of mean emotion and gender from sets of faces. Curr. Biol. 2007, 17, R751–R753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Westermann, R.; Spies, K.; Stahl, G.; Hesse, F.W. Relative effectiveness and validity of mood induction procedures: A meta-analysis. Eur. J. Soc. Psychol. 1996, 26, 557–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, D.A.; Hayes-Skelton, S.A.; Ciaramitaro, V.M. What’s in a Face? How Face Gender and Current Affect Influence Perceived Emotion. Front. Psychol. 2016, 7, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, M.C.; Arlegui-Prieto, M. Variation in normal mood state influences sensitivity to dynamic changes in emotional expression. Emotion 2016, 16, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruessner, J.; Wolf, O.; Hellhammer, D.; Buske-Kirschbaum, A.; Von Auer, K.; Jobst, S.; Kaspers, F.; Kirschbaum, C. Free Cortisol Levels after Awakening: A Reliable Biological Marker for the Assessment of Adrenocortical Activity. Life Sci. 1997, 61, 2539–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalin, N.H.; Larson, C.; Shelton, S.E.; Davidson, R.J. Asymmetric frontal brain activity, cortisol, and behavior associated with fearful temperament in rhesus monkeys. Behav. Neurosci. 1998, 112, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirschbaum, C.; Hellhammer, D. Response variability of salivary cortisol under psychological stimulation. J. Clin. Chem. Clin. Biochem. Z. fur Klin. Chem. und Klin. Biochem. 1989, 27, 237. [Google Scholar]
- Van Honk, J.; Tuiten, A.; Hout, M.V.D.; Koppeschaar, H.; Thijssen, J.; De Haan, E.; Verbaten, R. Baseline salivary cortisol levels and preconscious selective attention for threat. A pilot study. Psychoneuroendocrinology 1998, 23, 741–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Peer, J.M.; Spinhoven, P.; Van Dijk, J.G.; Roelofs, K. Cortisol-induced enhancement of emotional face processing in social phobia depends on symptom severity and motivational context. Boil. Psychol. 2009, 81, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchanan, T.W.; Al’Absi, M.; Lovallo, W.R. Cortisol fluctuates with increases and decreases in negative affect. Psychoneuroendocrinology 1999, 24, 227–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadea, M.; Gomez, C.; González-Bono, E.; Espert, R.; Salvador, A. Increased cortisol and decreased right ear advantage (REA) in dichotic listening following a negative mood induction. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2005, 30, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, D.; Clark, L.A.; Tellegen, A. Development and validation of brief measures of positive and negative affect: The PANAS scales. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 1988, 54, 1063–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brainard, D.H. The Psychophysics Toolbox. Spat. Vis. 1997, 10, 433–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pelli, D.G. The VideoToolbox software for visual psychophysics: Transforming numbers into movies. Spat. Vis. 1997, 10, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleiner, M.; Brainard, D.; Pelli, D.; Ingling, A.; Murray, R.; Broussard, C. What’s new in Psychtoolbox-3? Perception 36 ECVP Abstract Supplement. Percaption 2007, 36, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Tottenham, N.; Tanaka, J.W.; Leon, A.C.; McCarry, T.; Nurse, M.; Hare, T.A.; Marcus, D.J.; Westerlund, A.; Casey, B.; Nelson, C. The NimStim set of facial expressions: Judgments from untrained research participants. Psychiatry Res. 2009, 168, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harris, D.A.; Ciaramitaro, V.M. Interdependent Mechanisms for Processing Gender and Emotion: The Special Status of Angry Male Faces. Front. Psychol. 2016, 7, 836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fründ, I.; Hänel, V.; Wichmann, F. Psignifit. Available online: https://uni-tuebingen.de/en/faculties/faculty-of-science/departments/computer-science/lehrstuehle/neural-information-processing/research/resources/software/psignifit (accessed on 1 September 2017).
- Wichmann, F.A.; Hill, N.J. The psychometric function: I. Fitting, sampling, and goodness of fit. Percept. Psychophys. 2001, 63, 1293–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mumenthaler, C.; Roesch, E.B.; Sander, D.; Kerzel, D.; Scherer, K.R. Psychophysics of emotion: The QUEST for Emotional Attention. J. Vis. 2010, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Kirschbaum, C.; Hellhammer, D.H. Encyclopedia of Stress; Fink, G., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2000; Volume 3, pp. 379–383. [Google Scholar]
- Kudielka, B.M.; Hellhammer, D.; Wüst, S. Why do we respond so differently? Reviewing determinants of human salivary cortisol responses to challenge. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2009, 34, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovallo, W.R.; Farag, N.H.; Vincent, A.S.; Thomas, T.L.; Wilson, M.F. Cortisol responses to mental stress, exercise, and meals following caffeine intake in men and women. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2006, 83, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smyth, J.; Ockenfels, M.C.; Porter, L.; Kirschbaum, C.; Hellhammer, D.H.; Stone, A.A. Stressors and mood measured on a momentary basis are associated with salivary cortisol secretion. Psychoneuroendocrinology 1998, 23, 353–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steptoe, A.; Wardle, J.; Marmot, M. Positive affect and health-related neuroendocrine, cardiovascular, and inflammatory processes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 6508–6512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schaeffer, M.A.; Baum, A. Adrenal Cortical Response to Stress at Three Mile Island. Psychosom. Med. 1984, 46, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eck, M.; Berkhof, H.; Nicolson, N.; Sulon, J. The Effects of Perceived Stress, Traits, Mood States, and Stressful Daily Events on Salivary Cortisol. Psychosom. Med. 1996, 58, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, L.; Iversen, S.; Goodwin, G. The influence of positive and negative mood states on risk taking, verbal fluency, and salivary cortisol. J. Affect. Disord. 2001, 63, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagan, J. An overly permissive extension. Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 2016, 11, 442–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McEwen, B.S.; McEwen, C.A. Response to Jerome Kagan’s Essay on Stress. Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 2016, 11, 451–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhodes, G.; Jeffery, L.; Evangelista, E.; Ewing, L.; Peters, M.; Taylor, L. Enhanced attention amplifies face adaptation. Vis. Res. 2011, 51, 1811–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jessen, S.; Kotz, S.A. On the role of crossmodal prediction in audiovisual emotion perception. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2013, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klasen, M.; Kreifelts, B.; Chen, Y.-H.; Seubert, J.; Mathiak, K. Neural processing of emotion in multimodal settings. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2014, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Pan, Z.; Wang, P.; Yang, X.; Liu, P.; You, X.; Yuan, J. The integration of facial and vocal cues during emotional change perception: EEG markers. Soc. Cogn. Affect. Neurosci. 2016, 11, 1152–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delle-Vigne, D.; Kornreich, C.; Verbanck, P.; Campanella, S. Subclinical alexithymia modulates early audio-visual perceptive and attentional event-related potentials. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2014, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokinous, J.; Kotz, S.A.; Tavano, A.; Schröger, E. The role of emotion in dynamic audiovisual integration of faces and voices. Soc. Cogn. Affect. Neurosci. 2015, 10, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oswald, L.M.; Zandi, P.; Nestadt, G.; Potash, J.B.; Kalaydjian, A.E.; Wand, G.S. Relationship between Cortisol Responses to Stress and Personality. Neuropsychopharmacology 2006, 31, 1583–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peschard, V.; Philippot, P. Overestimation of threat from neutral faces and voices in social anxiety. J. Behav. Ther. Exp. Psychiatry 2017, 57, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, D.J.; Quinn, P.C.; Slater, A.M.; Lee, K.; Ge, L.; Pascalis, O. The Other-Race Effect Develops During Infancy: Evidence of Perceptual Narrowing. Psychol. Sci. 2007, 18, 1084–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meissner, C.A.; Brigham, J.C. Thirty years of investigating the own-race bias in memory for faces: A meta-analytic review. Psychol. Public Policy Law 2001, 7, 3–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Demographics | Congruent | Incongruent | Visual | Auditory | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean Age (SD) | 20.5 (2.2) | 22.5 (4.7) | 25.5 (9.5) | 22.1 (2.8) | |
| White | |||||
| Male | N | 0 (0%) | 1 (50%) | 2 (33.3%) | 0 (0%) |
| Female | N | 7 (36.8%) | 7 (36.8%) | 6 (50%) | 8 (50%) |
| Hispanic | |||||
| Male | N | 1 (25%) | 0 (0%) | 2 (33.3%) | 1 (33.3%) |
| Female | N | 4 (21.1%) | 7 (38.9%) | 2 (16.7%) | 0 (0%) |
| African/African American | |||||
| Male | N | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (16.7%) | 0 (0%) |
| Female | N | 1 (5.3%) | 0 (0%) | 3 (25%) | 4 (25%) |
| Asian | |||||
| Male | N | 0 (0%) | 1 (50%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (33.3%) |
| Female | N | ||||
| Multiracial | |||||
| Male | N | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) |
| Female | N | 1 (5.3%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (6.3%) |
| Unspecified | |||||
| Male | N | 3 (75%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (16.7%) | 1 (33.3%) |
| Female | N | 3 (15.8%) | 2 (11.1%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Izen, S.C.; Lapp, H.E.; Harris, D.A.; Hunter, R.G.; Ciaramitaro, V.M. Seeing a Face in a Crowd of Emotional Voices: Changes in Perception and Cortisol in Response to Emotional Information across the Senses. Brain Sci. 2019, 9, 176. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci9080176
Izen SC, Lapp HE, Harris DA, Hunter RG, Ciaramitaro VM. Seeing a Face in a Crowd of Emotional Voices: Changes in Perception and Cortisol in Response to Emotional Information across the Senses. Brain Sciences. 2019; 9(8):176. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci9080176
Chicago/Turabian StyleIzen, Sarah C., Hannah E. Lapp, Daniel A. Harris, Richard G. Hunter, and Vivian M. Ciaramitaro. 2019. "Seeing a Face in a Crowd of Emotional Voices: Changes in Perception and Cortisol in Response to Emotional Information across the Senses" Brain Sciences 9, no. 8: 176. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci9080176
APA StyleIzen, S. C., Lapp, H. E., Harris, D. A., Hunter, R. G., & Ciaramitaro, V. M. (2019). Seeing a Face in a Crowd of Emotional Voices: Changes in Perception and Cortisol in Response to Emotional Information across the Senses. Brain Sciences, 9(8), 176. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci9080176





