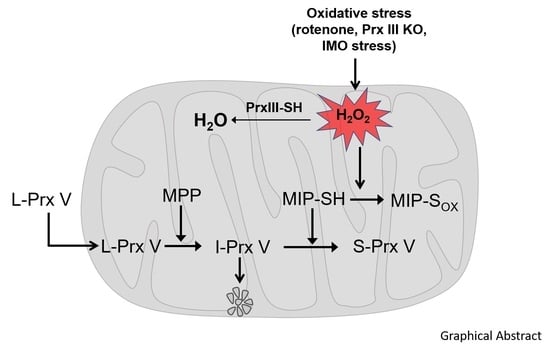
Maturation of Mitochondrially Targeted Prx V Involves a Second Cleavage by Mitochondrial Intermediate Peptidase That Is Sensitive to Inhibition by H2O2
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Antibodies
2.2. Subcellular Fractionation
2.3. Immunoblotting
2.4. Purification of Prx V Containing I-Prx V
2.5. RNA Isolation
2.6. Mass Spectral Sequencing of I-Prx V Peptide
2.7. Cell Culture and Transfection
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Determination of the N-Terminal Sequence of I-Prx V Extracted from the Minor Prx V Band
3.2. I-Prx V is Produced during Processing of L-Prx V to S-Prx V
3.3. Effect of Mitochondrial ROS on the Abundance of I-Prx V and S-Prx V
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Prxs | peroxiredoxins |
| L-Prx V | long form Prx V |
| S-Prx V | short form Prx V |
| I-Prx V | intermediate Prx V containing octa peptide to be cleaved by MIP |
| Srx | sulfiredoxin |
| MTS | mitochondrial targeting sequence |
| MPP | mitochondrial processing peptidase |
| MIP | mitochondrial intermediate peptidase |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| COX IV | cytochrome c oxidase subunit 4 |
| GAPDH | glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase |
| VDAC | voltage-dependent anion channels |
| ACTH | adrenocorticotropic hormone |
| Oct1 | octapeptidyl aminopeptidase |
References
- Rhee, S.G.; Woo, H.A. Multiple functions of peroxiredoxins: Peroxidases, sensors and regulators of the intracellular messenger H2O2, and protein chaperones. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2011, 15, 781–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chae, H.Z.; Chung, S.J.; Rhee, S.G. Thioredoxin-dependent peroxide reductase from yeast. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 27670–27678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhee, S.G.; Chae, H.Z.; Kim, K. Peroxiredoxins: A historical overview and speculative preview of novel mechanisms and emerging concepts in cell signaling. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2005, 38, 1543–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, Z.A.; Schroder, E.; Robin Harris, J.; Poole, L.B. Structure, mechanism and regulation of peroxiredoxins. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2003, 28, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, H.A.; Kang, S.W.; Kim, H.K.; Yang, K.S.; Chae, H.Z.; Rhee, S.G. Reversible oxidation of the active site cysteine of peroxiredoxins to cysteine sulfinic acid. Immunoblot detection with antibodies specific for the hyperoxidized cysteine-containing sequence. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 47361–47364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biteau, B.; Labarre, J.; Toledano, M.B. ATP-dependent reduction of cysteine-sulphinic acid by S. cerevisiae sulphiredoxin. Nature 2003, 425, 980–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, T.S.; Jeong, W.; Woo, H.A.; Lee, S.M.; Park, S.; Rhee, S.G. Characterization of mammalian sulfiredoxin and its reactivation of hyperoxidized peroxiredoxin through reduction of cysteine sulfinic acid in the active site to cysteine. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 50994–51001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Knoops, B.; Clippe, A.; Bogard, C.; Arsalane, K.; Wattiez, R.; Hermans, C.; Duconseille, E.; Falmagne, P.; Bernard, A. Cloning and characterization of AOEB166, a novel mammalian antioxidant enzyme of the peroxiredoxin family. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 30451–30458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yamashita, H.; Avraham, S.; Jiang, S.; London, R.; Van Veldhoven, P.P.; Subramani, S.; Rogers, R.A.; Avraham, H. Characterization of human and murine PMP20 peroxisomal proteins that exhibit antioxidant activity in vitro. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 29897–29904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Knoops, B.; Goemaere, J.; Van der Eecken, V.; Declercq, J.P. Peroxiredoxin 5: Structure, mechanism, and function of the mammalian atypical 2-Cys peroxiredoxin. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2011, 15, 817–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, M.S.; Kang, S.W.; Kim, K.; Baines, I.C.; Lee, T.H.; Rhee, S.G. Identification of a new type of mammalian peroxiredoxin that forms an intramolecular disulfide as a reaction intermediate. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 20346–20354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nguyen-Nhu, N.T.; Berck, J.; Clippe, A.; Duconseille, E.; Cherif, H.; Boone, C.; Van der Eecken, V.; Bernard, A.; Banmeyer, I.; Knoops, B. Human peroxiredoxin 5 gene organization, initial characterization of its promoter and identification of alternative forms of mRNA. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1769, 472–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gakh, O.; Cavadini, P.; Isaya, G. Mitochondrial processing peptidases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2002, 1592, 63–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mossmann, D.; Meisinger, C.; Vogtle, F.N. Processing of mitochondrial presequences. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1819, 1098–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isaya, G.; Kalousek, F.; Fenton, W.A.; Rosenberg, L.E. Cleavage of precursors by the mitochondrial processing peptidase requires a compatible mature protein or an intermediate octapeptide. J. Cell Biol. 1991, 113, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branda, S.S.; Isaya, G. Prediction and identification of new natural substrates of the yeast mitochondrial intermediate peptidase. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 27366–27373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hendrick, J.P.; Hodges, P.E.; Rosenberg, L.E. Survey of amino-terminal proteolytic cleavage sites in mitochondrial precursor proteins: Leader peptides cleaved by two matrix proteases share a three-amino acid motif. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 4056–4060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vogtle, F.N.; Prinz, C.; Kellermann, J.; Lottspeich, F.; Pfanner, N.; Meisinger, C. Mitochondrial protein turnover: Role of the precursor intermediate peptidase Oct1 in protein stabilization. Mol. Biol. Cell 2011, 22, 2135–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, F.; Palma, F.R.; Barros, M.H.; Tsuchida, E.T.; Turano, H.G.; Alegria, T.G.P.; Demasi, M.; Netto, L.E.S. Proteolytic cleavage by the inner membrane peptidase (IMP) complex or Oct1 peptidase controls the localization of the yeast peroxiredoxin Prx1 to distinct mitochondrial compartments. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 17011–17024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nett, J.H.; Trumpower, B.L. Intermediate length Rieske iron-sulfur protein is present and functionally active in the cytochrome bc1 complex of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 9253–9257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Varshavsky, A. The N-end rule pathway and regulation by proteolysis. Protein. Sci. 2011, 20, 1298–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sriram, S.M.; Kim, B.Y.; Kwon, Y.T. The N-end rule pathway: Emerging functions and molecular principles of substrate recognition. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2011, 12, 735–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vögtle, F.-N.; Wortelkamp, S.; Zahedi, R.P.; Becker, D.; Leidhold, C.; Gevaert, K.; Kellermann, J.; Voos, W.; Sickmann, A.; Pfanner, N.; et al. Global analysis of the mitochondrial N-proteome identifies a processing peptidase critical for protein stability. Cell 2009, 139, 428–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Lee, E.G.; Yi, H.J.; Kim, N.H.; Rhee, S.G.; Woo, H.A. Ablation of Peroxiredoxin V Exacerbates Ischemia/Reperfusion-Induced Kidney Injury in Mice. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kil, I.S.; Lee, S.K.; Ryu, K.W.; Woo, H.A.; Hu, M.C.; Bae, S.H.; Rhee, S.G. Feedback control of adrenal steroidogenesis via H2O2-dependent, reversible inactivation of peroxiredoxin III in mitochondria. Mol. Cell 2012, 46, 584–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.; Na, S.; Sim, J.W.; Park, H.; Jeong, J.; Kim, H.; Seo, Y.; Seo, J.; Lee, K.J.; Paek, E. MODi: A powerful and convenient web server for identifying multiple post-translational peptide modifications from tandem mass spectra. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, W258–W263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isaya, G.; Kalousek, F.; Rosenberg, L.E. Amino-terminal octapeptides function as recognition signals for the mitochondrial intermediate peptidase. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 7904–7910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalousek, F.; Isaya, G.; Rosenberg, L.E. Rat liver mitochondrial intermediate peptidase (MIP): Purification and initial characterization. EMBO J. 1992, 11, 2803–2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierotti, A.; Dong, K.W.; Glucksman, M.J.; Orlowski, M.; Roberts, J.L. Molecular cloning and primary structure of rat testes metalloendopeptidase EC 3.4.24.15. Biochemistry 1990, 29, 10323–10329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winterbourn, C.C. The biological chemistry of hydrogen peroxide. Methods Enzymol. 2013, 528, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rhee, S.G.; Woo, H.A.; Kang, D. The Role of Peroxiredoxins in the Transduction of H2O2 Signals. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2018, 28, 537–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hervouet, E.; Pecina, P.; Demont, J.; Vojtiskova, A.; Simonnet, H.; Houstek, J.; Godinot, C. Inhibition of cytochrome c oxidase subunit 4 precursor processing by the hypoxia mimic cobalt chloride. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 344, 1086–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Park, J.; Han, S.J.; Park, I.; Huu, T.N.; Kim, J.S.; Woo, H.A.; Lee, S.R. The critical role of redox regulation of PTEN and peroxiredoxin III in alcoholic fatty liver. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 162, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanukoglu, I. Antioxidant protective mechanisms against reactive oxygen species (ROS) generated by mitochondrial P450 systems in steroidogenic cells. Drug Metab. Rev. 2006, 38, 171–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosol, T.J.; Yarrington, J.T.; Latendresse, J.; Capen, C.C. Adrenal gland: Structure, function, and mechanisms of toxicity. Toxicol. Pathol. 2001, 29, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, A.G.; Winterbourn, C.C.; Hampton, M.B. Mitochondrial peroxiredoxin involvement in antioxidant defence and redox signalling. Biochem. J. 2009, 425, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xiao, H.; Jedrychowski, M.P.; Schweppe, D.K.; Huttlin, E.L.; Yu, Q.; Heppner, D.E.; Li, J.; Long, J.; Mills, E.L.; Szpyt, J.; et al. A Quantitative Tissue-Specific Landscape of Protein Redox Regulation during Aging. Cell 2020, 180, 968–983.e24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eldomery, M.K.; Akdemir, Z.C.; Vögtle, F.-N.; Charng, W.-L.; Mulica, P.; Rosenfeld, J.A.; Gambin, T.; Gu, S.; Burrage, L.C.; Al Shamsi, A.; et al. MIPEP recessive variants cause a syndrome of left ventricular non-compaction, hypotonia, and infantile death. Genome Med. 2016, 8, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]






| Target Gene | Forward Primer (5′-3′) | Reverse Primer (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| GAPDH | AGAACATCATCCCTGCATCC | GGTCCTCAGTGTAGCCCAAG |
| LPrx V | AGAAGCAGGTTGGGAGTGTG | CTTTCTTGCCCTTGAACAGC |
| SPrx V | GGCATTTACACCTGGCTGTT | CGACGATTCCCAAAGAGAGA |
| MIP | TTTCAGCGAGCAGACAAACC | TCCCAGTGACGTGTTGGTAA |
| Target Gene | Sense | Anti-Sense |
|---|---|---|
| Scrambled | AUGAACGUGAAUUGCUCAATT | UUGAGCAAUUCACGUUCAUTT |
| LPrx V | GCUAUAUACUCGUCGGUGGTT | CCACCGACGAGUAUAUAGCTT |
| SPrx V | GGAAGGAGACAGACUUAUUTT | AAUAAGUCUGUCUCCUUCCTT |
| MIP | GCCGGGAUCCGGGCCCGAATT | UUCGGGCCCGGAUCCCGGCTT |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sim, J.; Park, J.; Woo, H.A.; Rhee, S.G. Maturation of Mitochondrially Targeted Prx V Involves a Second Cleavage by Mitochondrial Intermediate Peptidase That Is Sensitive to Inhibition by H2O2. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 346. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10030346
Sim J, Park J, Woo HA, Rhee SG. Maturation of Mitochondrially Targeted Prx V Involves a Second Cleavage by Mitochondrial Intermediate Peptidase That Is Sensitive to Inhibition by H2O2. Antioxidants. 2021; 10(3):346. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10030346
Chicago/Turabian StyleSim, Juhyun, Jiyoung Park, Hyun Ae Woo, and Sue Goo Rhee. 2021. "Maturation of Mitochondrially Targeted Prx V Involves a Second Cleavage by Mitochondrial Intermediate Peptidase That Is Sensitive to Inhibition by H2O2" Antioxidants 10, no. 3: 346. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10030346
APA StyleSim, J., Park, J., Woo, H. A., & Rhee, S. G. (2021). Maturation of Mitochondrially Targeted Prx V Involves a Second Cleavage by Mitochondrial Intermediate Peptidase That Is Sensitive to Inhibition by H2O2. Antioxidants, 10(3), 346. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10030346