Evaluation of a Dietary Grape Extract on Oxidative Status, Intestinal Morphology, Plasma Acute-Phase Proteins and Inflammation Parameters of Weaning Piglets at Various Points of Time
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
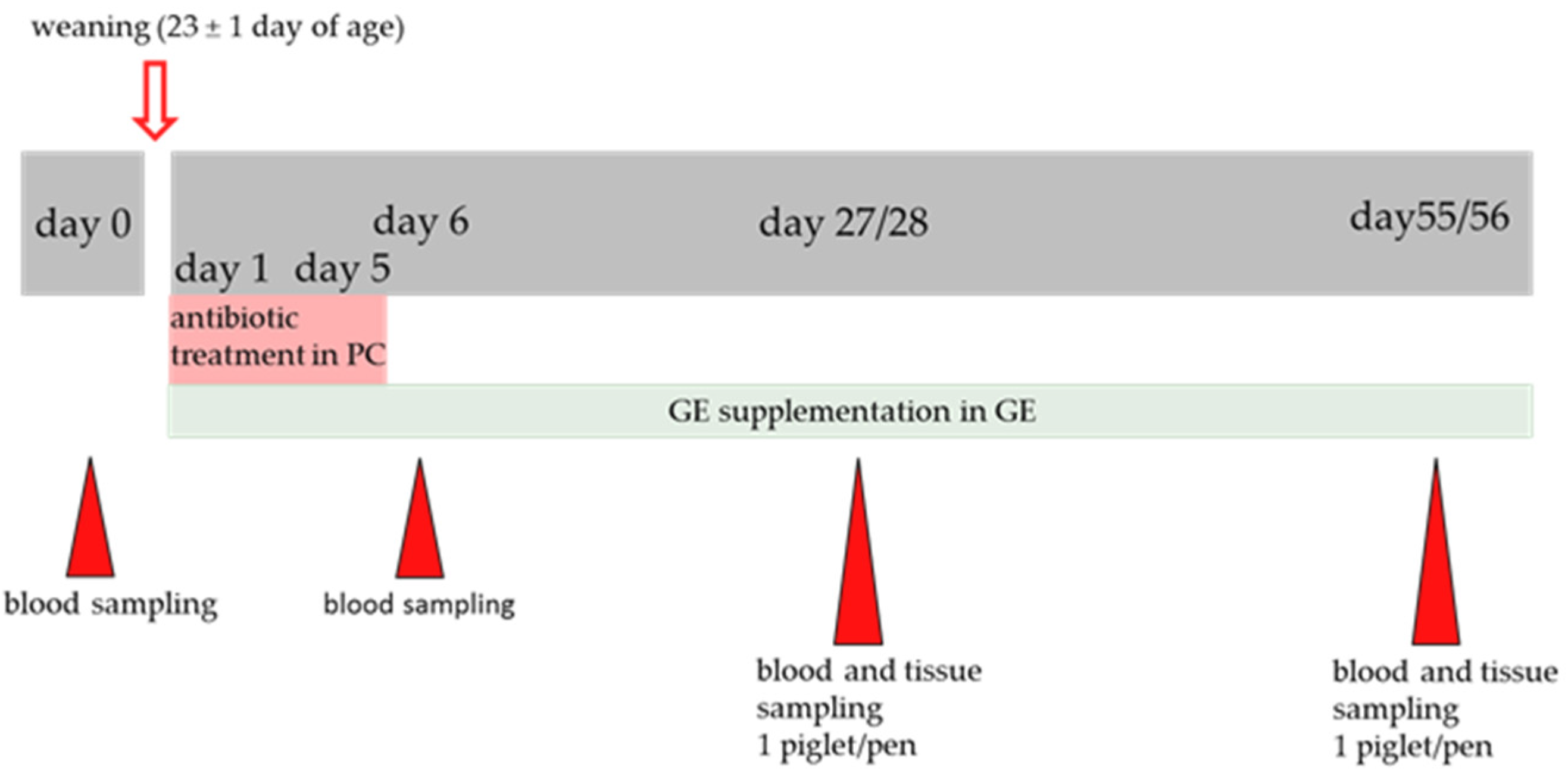
2.1. Piglets, Diets and Housing
2.2. Sample Collection and Storage
2.3. Analyses
2.3.1. Morphology of Ileum, Jejunum and Colon
2.3.2. Antioxidant Measurements of Liver, Jejunum and Ileum Tissue
2.3.3. Blood Parameters
Blood Antioxidant Status
Acute-Phase Proteins as Inflammatory Parameter
2.3.4. Gene Expression Analyses of Liver, Jejunum and Ileum Tissue
2.3.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Intestinal Morphology
3.2. Tissue Antioxidant Status Capacity and Gene Analyses
3.2.1. Antioxidant Enzyme Activity, TBARS, DPPH and ABTS
3.2.2. Gene Expression
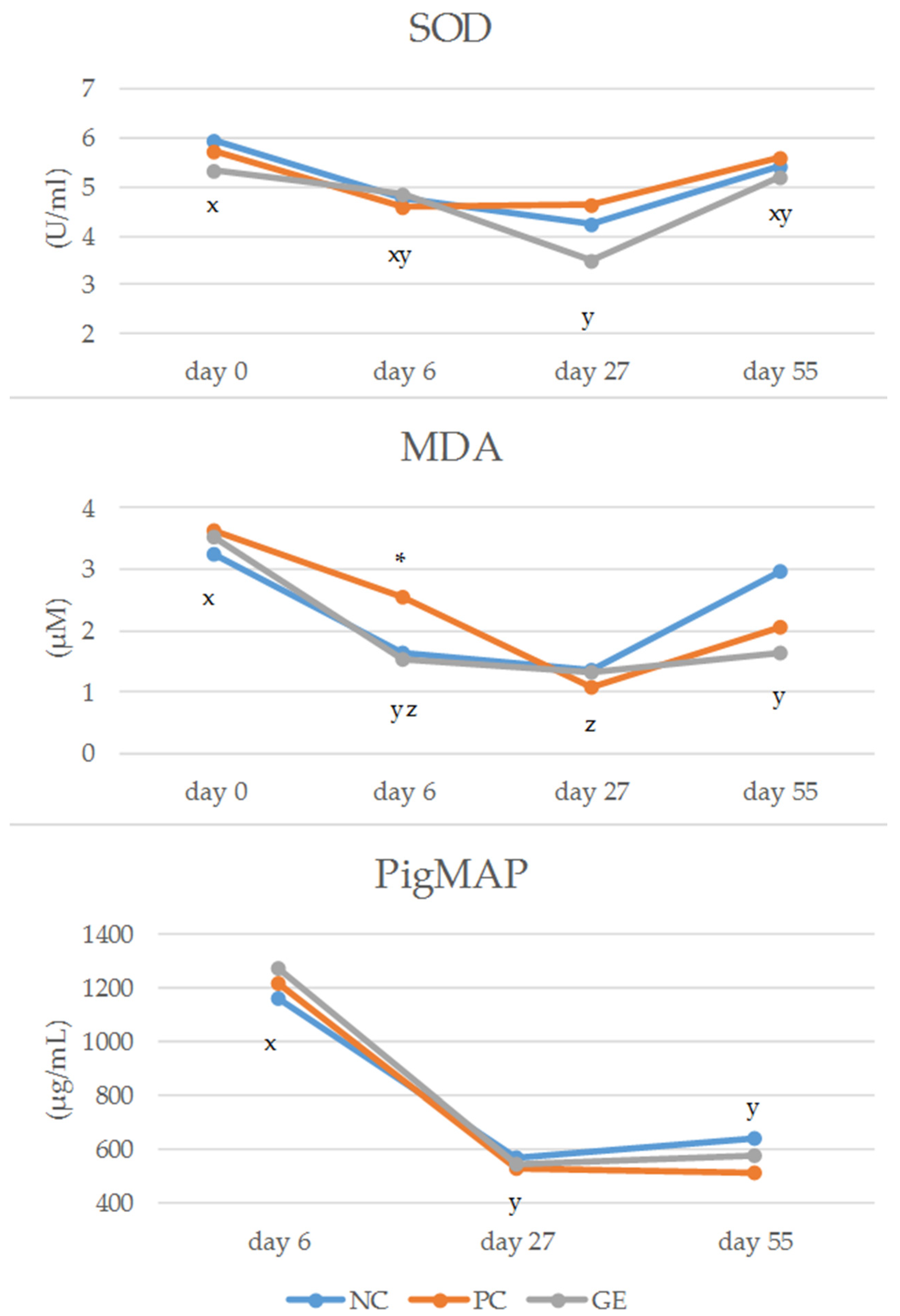
3.3. Plasma Antioxidant Measurements and Acute-Phase Proteins (APPs)
4. Discussion
4.1. Intestinal Morphology
4.2. Tissue and Plasma Antioxidant Capacity
4.2.1. Antioxidant Enzyme Activity of Jejunum, Ileum and Liver Tissue
4.2.2. Antioxidant Capacity of Jejunum, Ileum and Liver Tissue Measured by DPPH, ABTS and TBARS Assays
4.2.3. Plasma Antioxidant Measurements
4.3. Gene Expression Analyses from Jejunum, Ileum and Liver Tissue
4.4. Plasma Acute-Phase Proteins (APPs)
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lallès, J.-P.; Bosi, P.; Smidt, H.; Stokes, C.R. Nutritional management of gut health in pigs around weaning. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2007, 66, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modina, S.C.; Aidos, L.; Rossi, R.; Pocar, P.; Corino, C.; Di Giancamillo, A. Stages of gut development as a useful tool to prevent gut alterations in piglets. Animals 2021, 11, 1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, K.; Sun, Z.; Liu, Z.; Li, Z.; Yin, Y. Development of the gastrointestinal tract in pigs. In Nutritional and Physiological Functions of Amino Acids in Pigs; Blachier, F., Wu, G., Yin, Y., Eds.; Springer: Vienna, Austria, 2013; pp. 3–18. ISBN 978-3-7091-1327-1. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, X.; Tsai, T.; Howe, S.; Zhao, J. Weaning induced gut dysfunction and nutritional interventions in nursery pigs: A partial review. Animals 2021, 11, 1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.H.; Zhao, K.L.; Chen, X.L.; Xu, J.X. Impact of weaning and an antioxidant blend on intestinal barrier function and antioxidant status in pigs. J. Anim. Sci. 2013, 8, 2581–2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birben, E.; Sahiner, U.M.; Sackesen, C.; Erzurum, S.; Kalayci, O. Oxidative stress and antioxidant defense. World Allergy Organ. J. 2012, 5, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- García-Sánchez, A.; Miranda-Díaz, A.G.; Cardona-Muñoz, E.G. The role of oxidative stress in physiopathology and pharmacological treatment with pro- and antioxidant properties in chronic diseases. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 2082145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lallès, J.P.; Bosi, P.; Janczyk, P.; Koopmans, S.J.; Torrallardona, D. Impact of bioactive substances on the gastrointestinal tract and performance of weaned piglets: A review. Animal 2009, 3, 1625–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peterson, L.W.; Artis, D. Intestinal epithelial cells: Regulators of barrier function and immune homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruys, E.; Toussaint, M.J.M.; Niewold, T.A.; Koopmans, S.J. Acute phase reaction and acute phase proteins. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. 2005, 6B, 1045–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mittal, M.; Siddiqui, M.R.; Tran, K.; Reddy, S.P.; Malik, A.B. Reactive oxygen species in inflammation and tissue injury. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014, 20, 1126–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- John, L.J.; Fromm, M.; Schulzke, J.D. Epithelial barriers in intestinal inflammation. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2011, 15, 1255–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aviello, G.; Knaus, U.G. ROS in gastrointestinal inflammation: Rescue or sabotage? Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 174, 1704–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kajino-Sakamoto, R.; Omori, E.; Nighot, P.K.; Blikslager, A.T.; Matsumoto, K.; Ninomiya-Tsuji, J. TGF-beta-activated kinase 1 signaling maintains intestinal integrity by preventing accumulation of reactive oxygen species in the intestinal epithelium. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 4729–4737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- van der Sluis, M.; de Koning, B.A.E.; de Bruijn, A.C.J.M.; Velcich, A.; Meijerink, J.P.P.; van Goudoever, J.B.; Büller, H.A.; Dekker, J.; van Seuningen, I.; Renes, I.B.; et al. Muc2-deficient mice spontaneously develop colitis, indicating that MUC2 is critical for colonic protection. Gastroenterology 2006, 131, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluske, J.R.; Turpin, D.L.; Kim, J.-C. Gastrointestinal tract (gut) health in the young pig. Anim. Nutr. 2018, 4, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artis, D. Epithelial-cell recognition of commensal bacteria and maintenance of immune homeostasis in the gut. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuzzocrea, S.; Riley, D.P.; Caputi, A.P.; Salvemini, D. Antioxidant therapy: A new pharmacological approach in shock, inflammation, and ischemia/reperfusion injury. Pharmacol. Rev. 2001, 53, 135–159. [Google Scholar]
- Barszcz, M.; Skomiał, J. The development of the small intestine of piglets—Chosen aspects. J. Anim. Feed Sci. 2011, 20, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, L.; Duarte, M.E.; Sevarolli Loftus, A.; Kim, S.W. Intestinal health of pigs upon weaning: Challenges and nutritional intervention. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 628258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.; Zhang, L.; Gan, Z.; Xiong, H.; Yu, C.; Du, H.; Wang, Y. High therapeutic efficacy of Cathelicidin-WA against postweaning diarrhea via inhibiting inflammation and enhancing epithelial barrier in the intestine. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhouma, M.; Fairbrother, J.M.; Beaudry, F.; Letellier, A. Post weaning diarrhea in pigs: Risk factors and non-colistin-based control strategies. Acta Vet. Scand. 2017, 59, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- European Food Safety Authority and European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. The european union summary report on antimicrobial resistance in zoonotic and indicator bacteria from humans, animals and food in 2018/2019. EFSA J. 2021, 19, e06490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holota, Y.; Dovbynchuk, T.; Kaji, I.; Vareniuk, I.; Dzyubenko, N.; Chervinska, T.; Zakordonets, L.; Stetska, V.; Ostapchenko, L.; Serhiychuk, T.; et al. The long-term consequences of antibiotic therapy: Role of colonic short-chain fatty acids (SCFA) system and intestinal barrier integrity. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0220642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monaghan, P.; Metcalfe, N.B.; Torres, R. Oxidative stress as a mediator of life history trade-offs: Mechanisms, measurements and interpretation. Ecol. Lett. 2009, 12, 75–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, M.; Song, P.; Huang, C.; Rezaei, A.; Farrar, S.; Brown, M.A.; Ma, X. Dietary grape seed proanthocyanidins (GSPs) improve weaned intestinal microbiota and mucosal barrier using a piglet model. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 80313–80326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hao, R.; Li, Q.; Zhao, J.; Li, H.; Wang, W.; Gao, J. Effects of grape seed procyanidins on growth performance, immune function and antioxidant capacity in weaned piglets. Livest. Sci. 2015, 178, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunan, C. Ending Routine Farm Antibiotic Use in Europe. Achieving Responsible Farm Antibiotic Use through Improving Animal Health and Welfare in Pig and Poultry Production. 2022. Available online: https://epha.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/02/report-ending-routine-farm-antibiotic-use-in-europe-final-2022.pdf (accessed on 26 April 2022).
- Filocamo, A.; Bisignano, C.; Mandalari, G.; Navarra, M.; Tomczyk, M. In Vitro antimicrobial activity and effect on biofilm production of a white grape juice (Vitis vinifera) extract. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2015, 2015, 856243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meyer, A.S.; Yi, O.-S.; Pearson, D.A.; Waterhouse, A.L.; Frankel, E.N. Inhibition of human low-density lipoprotein oxidation in relation to composition of phenolic antioxidants in grapes (Vitis vinifera). J. Agric. Food Chem. 1997, 45, 1638–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chedea, V.S.; Palade, L.M.; Pelmus, R.S.; Dragomir, C.; Taranu, I. Red grape pomace rich in polyphenols diet increases the antioxidant status in key organs-kidneys, liver, and spleen of piglets. Animals 2019, 9, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gessner, D.K.; Ringseis, R.; Siebers, M.; Keller, J.; Kloster, J.; Wen, G.; Eder, K. Inhibition of the pro-inflammatory NF-κB pathway by a grape seed and grape marc meal extract in intestinal epithelial cells. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. (Berl.) 2012, 96, 1074–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafka, T.I.; Sinanoglou, V.; Lazos, E.S. On the extraction and antioxidant activity of phenolic compounds from winery wastes. Food Chem. 2007, 104, 1206–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.; Dey, S.; Marbaniang, D.; Pal, P.; Ray, S.; Mazumder, B. Grape seed extract: Having a potential health benefits. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 1205–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, E.Q.; Deng, G.F.; Guo, Y.J.; Li, H.B. Biological activities of polyphenols from grapes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2010, 11, 622–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawabata, K.; Yoshioka, Y.; Terao, J. Role of intestinal microbiota in the bioavailability and physiological functions of dietary polyphenols. Molecules 2019, 24, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Soobrattee, M.A.; Neergheen, V.S.; Luximon-Ramma, A.; Aruoma, O.I.; Bahorun, T. Phenolics as potential antioxidant therapeutic agents: Mechanism and actions. Mutat. Res. 2005, 579, 200–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajković, E.; Schwarz, C.; Tischler, D.; Schedle, K.; Reisinger, N.; Emsenhuber, C.; Ocelova, V.; Roth, N.; Frieten, D.; Dusel, G.; et al. Potential of grape extract in comparison with therapeutic dosage of antibiotics in weaning piglets: Effects on performance, digestibility and microbial metabolites of the ileum and colon. Animals 2021, 11, 2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GfE. Gesellschaft für Ernährungsphysiologie/Ausschuß für Bedarfsnormen. In Empfehlungen zur Energie- und Nährstoffversorgung von Schweinen 2006; Deutsche Landwirtschafts-Gesellschaft Verlag: Frankfurt a.M., Germany, 2006; p. 247. ISBN 978-3-7690-0683-4. [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence, R.A.; Burk, R.F. Species, tissue and subcellular distribution of non Se-dependent glutathione peroxidase activity. J. Nutr. 1978, 108, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marklund, S.; Marklund, G. Involvement of the superoxide anion radical in the autoxidation of pyrogallol and a convenient assay for superoxide dismutase. Eur. J. Biochem. 2005, 47, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beers, R.F.; Sizer, I.W. A spectrophotometric method for measuring the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide by catalase. J. Biol. Chem. 1952, 195, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkawa, H.; Ohishi, N.; Yagi, K. Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal. Biochem. 1979, 95, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand-Williams, W.; Cuvelier, M.E.; Berset, C. Use of a free radical method to evaluate antioxidant activity. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 1995, 28, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Re, R.; Pellegrini, N.; Proteggente, A.; Pannala, A.; Yang, M.; Rice-Evans, C. Antioxidant activity applying an improved ABTS radical cation decolorization assay. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 26, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustin, S.A.; Benes, V.; Garson, J.A.; Hellemans, J.; Huggett, J.; Kubista, M.; Mueller, R.; Nolan, T.; Pfaffl, M.W.; Shipley, G.L.; et al. The MIQE guidelines: Minimum information for publication of quantitative real-time PCR experiments. Clin. Chem. 2009, 55, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reisinger, N.; Emsenhuber, C.; Doupovec, B.; Mayer, E.; Schatzmayr, G.; Nagl, V.; Grenier, B. Endotoxin translocation and gut inflammation are increased in broiler chickens receiving an oral lipopolysaccharide (LPS) bolus during heat stress. Toxins 2020, 12, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endo, H.; Niioka, M.; Sugioka, Y.; Itoh, J.; Kameyama, K.; Okazaki, I.; Ala-Aho, R.; Kähäri, V.-M.; Watanabe, T. Matrix metalloproteinase-13 promotes recovery from experimental liver cirrhosis in rats. Pathobiology 2011, 78, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pluske, J.R.; Hampson, D.J.; Williams, I.H. Factors influencing the structure and function of the small intestine in the weaned pig: A review. Livest. Prod. Sci. 1997, 51, 215–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, J.M.; Opapeju, F.O.; Pluske, J.R.; Kim, J.C.; Hampson, D.J.; Nyachoti, C.M. Gastrointestinal health and function in weaned pigs: A review of feeding strategies to control post-weaning diarrhoea without using in-feed antimicrobial compounds. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. (Berl.) 2013, 97, 207–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosi, P.; Merialdi, G.; Scandurra, S.; Messori, S.; Bardasi, L.; Nisi, I.; Russo, D.; Casini, L.; Trevisi, P. Feed supplemented with 3 different antibiotics improved food intake and decreased the activation of the humoral immune response in healthy weaned pigs but had differing effects on intestinal microbiota. J. Anim. Sci. 2011, 89, 4043–4053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biagi, G.; Cipollini, I.; Paulicks, B.R.; Roth, F.X. Effect of tannins on growth performance and intestinal ecosystem in weaned piglets. Arch. Anim. Nutr. 2010, 64, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.T.; Mun, H.-S.; Islam, M.M.; Ko, S.-Y.; Yang, C.-J. Effects of dietary natural and fermented herb combination on growth performance, carcass traits and meat quality in grower-finisher pigs. Meat Sci. 2016, 122, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.R.; Zhang, H.J.; Mantovani, G.; Alborali, G.L.; Caputo, J.M.; Savoini, G.; Dell`Orto, V.; Bontempo, V. The effect of plant polyphenols on the antioxidant defence system of weaned piglets subjected to an Escherichia coli challenge. J. Anim. Feed Sci. 2014, 23, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, S.M.; Lee, S.I.; Kim, I.H. Effect of phytogenics on growth performance, fecal score, blood profiles, fecal noxious gas emission, digestibility, and intestinal morphology of weanling pigs challenged with Escherichia coli K88. Pol. J. Vet. Sci. 2015, 18, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kafantaris, I.; Stagos, D.; Kotsampasi, B.; Hatzis, A.; Kypriotakis, A.; Gerasopoulos, K.; Makri, S.; Goutzourelas, N.; Mitsagga, C.; Giavasis, I.; et al. Grape pomace improves performance, antioxidant status, fecal microbiota and meat quality of piglets. Animal 2018, 12, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brenes, A.; Viveros, A.; Goñi, I.; Centeno, C.; Saura-Calixto, F.; Arija, I. Effect of grape seed extract on growth performance, protein and polyphenol digestibilities, and antioxidant activity in chickens. Span. J. Agric. Res. 2010, 8, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sehm, J.; Treutter, D.; Lindermayer, H.; Meyer, H.H.D.; Pfaffl, M.W. The influence of apple- or red-grape pomace enriched piglet diet on blood parameters, bacterial colonisation, and marker gene expression in piglet white blood cells. Food Nutr. Sci. 2011, 02, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pácha, J. Development of intestinal transport function in mammals. Physiol. Rev. 2000, 80, 1633–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudry, G.; Péron, V.; Le Huërou-Luron, I.; Lallès, J.P.; Sève, B. Weaning induces both transient and long-lasting modifications of absorptive, secretory, and barrier properties of piglet intestine. J. Nutr. 2004, 134, 2256–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampson, D.J. Alterations in piglet small intestinal structure at weaning. Res. Vet. Sci. 1986, 40, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibi, S.; Kang, Y.; Yang, G.; Zhu, M.-J. Grape seed extract improves small intestinal health through suppressing inflammation and regulating alkaline phosphatase in IL-10-deficient mice. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 20, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grondin, J.A.; Kwon, Y.H.; Far, P.M.; Haq, S.; Khan, W.I. Mucins in intestinal mucosal defense and inflammation: Learning from clinical and experimental studies. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ao, X.; Kim, I.H. Effects of grape seed extract on performance, immunity, antioxidant capacity, and meat quality in Pekin ducks. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 2078–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viveros, A.; Chamorro, S.; Pizarro, M.; Arija, I.; Centeno, C.; Brenes, A. Effects of dietary polyphenol-rich grape products on intestinal microflora and gut morphology in broiler chicks. Poult. Sci. 2011, 90, 566–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marion, J.; Biernat, M.; Thomas, F.; Savary, G.; Le Breton, Y.; Zabielski, R.; Le Huërou-Luron, I.; Le Dividich, J. Small intestine growth and morphometry in piglets weaned at 7 days of age. Effects of level of energy intake. Reprod. Nutr. Dev. 2002, 42, 339–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gimenez, A.C.; Riccardi, R.R.; Malheiros, E.B.; Boleli, I.C. Influence of sex and egg weight on villus and crypt size of the small intestine in broiler embryos and chicks. Ciênc. Anim. Bras. 2008, 9, 608–616. [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz, C.; Schinwald, K.; Wanka, K.; Leitgeb, R.; Gierus, M. Impact of increasing concentrations of a grape extract on morphometric and antioxidative parameters in the proximal small intestine of broilers. In Proceedings of the 14. Tagung Schweine- und Geflügelernährung, Lutherstadt Wittenberg, Germany, 21–23 November 2017; Zeyner, A., Kluth, H., Bulang, M., Bochnia, M., Eds.; Institut für Agrar- und Ernährungswissenschaften, Universität Halle-Wittenberg: Wittenberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 107–109. [Google Scholar]
- Montoro-Huguet, M.A.; Belloc, B.; Domínguez-Cajal, M. Small and large intestine (I): Malabsorption of nutrients. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajati, H.; Hassanabadi, A.; Golian, A.; Nassiri-Moghaddam, H.; Nassiri, M. The effect of grape seed extract and vitamin C feed supplements on carcass characteristics, gut morphology and ileal microflora in broiler chickens exposed to chronic heat stress. Iran J. Appl. Anim. Sci. 2015, 5, 155–165. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.S.; Ho, S.B. Intestinal goblet cells and mucins in health and disease: Recent insights and progress. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2010, 12, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Gao, Y.; Xiong, H.; Yang, Z. The electrochemical redox mechanism and antioxidant activity of polyphenolic compounds based on inlaid multi-walled carbon nanotubes-modified graphite electrode. Open Chem. 2021, 19, 961–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gessner, D.K.; Ringseis, R.; Eder, K. Potential of plant polyphenols to combat oxidative stress and inflammatory processes in farm animals. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. (Berl.) 2017, 101, 605–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabel, A. Free radicals and antioxidants: Role of enzymes and nutrition. J. Nutr. Health 2014, 2, 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taranu, I.; Marin, D.E.; Palade, M.; Pistol, G.C.; Chedea, V.S.; Gras, M.A.; Rotar, C. Assessment of the efficacy of a grape seed waste in counteracting the changes induced by aflatoxin B1 contaminated diet on performance, plasma, liver and intestinal tissues of pigs after weaning. Toxicon 2019, 162, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breinholt, V.; Lauridsen, S.T.; Dragsted, L.O. Differential effects of dietary flavonoids on drug metabolizing and antioxidant enzymes in female rat. Xenobiotica 1999, 29, 1227–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olszowy, M.; Dawidowicz, A.L. Is it possible to use the DPPH and ABTS methods for reliable estimation of antioxidant power of colored compounds? Chem. Pap. 2018, 72, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghani, M.A.; Barril, C.; Bedgood, D.R.; Prenzler, P.D. Measurement of antioxidant activity with the thiobarbituric acid reactive substances assay. Food Chem. 2017, 230, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gessner, D.K.; Fiesel, A.; Most, E.; Dinges, J.; Wen, G.; Ringseis, R.; Eder, K. Supplementation of a grape seed and grape marc meal extract decreases activities of the oxidative stress-responsive transcription factors NF-κB and Nrf2 in the duodenal mucosa of pigs. Acta Vet. Scand. 2013, 55, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pohl, C.S.; Medland, J.E.; Mackey, E.; Edwards, L.L.; Bagley, K.D.; DeWilde, M.P.; Williams, K.J.; Moeser, A.J. Early weaning stress induces chronic functional diarrhea, intestinal barrier defects, and increased mast cell activity in a porcine model of early life adversity. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2017, 29, e13118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalán, V.; Frühbeck, G.; Gómez-Ambrosi, J. Chapter 8—Inflammatory and oxidative stress markers in skeletal muscle of obese subjects. In Obesity; Del Moral, A.M., Aguilera García, C.M., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 163–189. ISBN 978-0-12-812504-5. [Google Scholar]
- Andrade, R.J.; Tulkens, P.M. Hepatic safety of antibiotics used in primary care. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2011, 66, 1431–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scalbert, A.; Morand, C.; Manach, C.; Rémésy, C. Absorption and metabolism of polyphenols in the gut and impact on health. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2002, 56, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stukelj, M.; Toplak, I.; Svete, A.N. Blood antioxidant enzymes (SOD, GPX), biochemical and haematological parameters in pigs naturally infected with porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus. Pol. J. Vet. Sci. 2013, 16, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Ma, N.; Song, P.; He, T.; Levesque, C.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, A.; Ma, X. Grape seed proanthocyanidin affects lipid metabolism via changing gut microflora and enhancing propionate production in weaned pigs. J. Nutr. 2019, 149, 1523–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala, A.; Muñoz, M.F.; Argüelles, S. Lipid peroxidation: Production, metabolism, and signaling mechanisms of malondialdehyde and 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2014, 2014, 360438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trachootham, D.; Lu, W.; Ogasawara, M.A.; Nilsa, R.-D.V.; Huang, P. Redox regulation of cell survival. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2008, 10, 1343–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, C.; Chowdhury, M.A.K.; Huo, Y.; Gong, J. Phytogenic compounds as alternatives to in-feed antibiotics: Potentials and challenges in application. Pathogens 2015, 4, 137–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yin, B.; Lian, R.; Li, Z.; Liu, Y.; Yang, S.; Huang, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Li, Y.; Sun, C.; Lin, S.; et al. Tea polyphenols enhanced the antioxidant capacity and induced Hsps to relieve heat stress injury. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 9615429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Blomberg, A.; Long, E.L.; Sonstegard, T.S.; van Tassell, C.P.; Dobrinsky, J.R.; Zuelke, K.A. Serial analysis of gene expression during elongation of the peri-implantation porcine trophectoderm (conceptus). Physiol. Genom. 2005, 20, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hussain, T.; Wang, J.; Murtaza, G.; Metwally, E.; Yang, H.; Kalhoro, M.S.; Kalhoro, D.H.; Rahu, B.A.; Tan, B.; Sahito, R.G.A.; et al. The role of polyphenols in regulation of heat shock proteins and gut microbiota in weaning stress. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 6676444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Yue, Z.; Liu, Z.; Islam, A.; Rehana, B.; Tang, S.; Bao, E.; Hartung, J. Hsp70 and HSF-1 expression is altered in the tissues of pigs transported for various periods of times. J. Vet. Sci. 2012, 13, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bao, E.; Sultan, K.R.; Nowak, B.; Hartung, J. Expression and distribution of heat shock proteins in the heart of transported pigs. Cell Stress Chaperones 2008, 13, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Negrato, E.; Di Martino, G.; Vascellari, M.; Radaelli, G.; Capello, K.; Pascoli, F.; Bertotto, D.; Bonfanti, L. Expression of heat shock protein 70 in the liver of extensively and intensively kept heavy pigs. Animal 2013, 7, 1362–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fiesel, A.; Gessner, D.K.; Most, E.; Eder, K. Effects of dietary polyphenol-rich plant products from grape or hop on pro-inflammatory gene expression in the intestine, nutrient digestibility and faecal microbiota of weaned pigs. BMC Vet. Res. 2014, 10, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gessner, D.K.; Bonarius, M.; Most, E.; Fiesel, A.; Eder, K. Effects of polyphenol-rich plant products from grape or hop as feed supplements on the expression of inflammatory, antioxidative, cytoprotective and endoplasmic reticulum stress-related genes and the antioxidative status in the liver of piglets. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. (Berl.) 2017, 101, e185–e194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, S.D.; Parikh, H.; Hickey, E.; Bagchi, M.; Bagchi, D. Differential effects of IH636 grape seed proanthocyanidin extract and a DNA repair modulator 4-aminobenzamide on liver microsomal cytochrome 4502E1-dependent aniline hydroxylation. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2001, 218, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckersall, P.D. The time is right for acute phase protein assays. Vet. J. 2004, 168, 3–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christoffersen, B.Ø.; Jensen, S.J.; Ludvigsen, T.P.; Nilsson, S.K.; Grossi, A.B.; Heegaard, P.M.H. Age- and sex-associated effects on acute-phase proteins in Göttingen minipigs. Comp. Med. 2015, 65, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Segalés, J.; Piñeiro, C.; Lampreave, F.; Nofrarías, M.; Mateu, E.; Calsamiglia, M.; Andrés, M.; Morales, J.; Piñeiro, M.; Domingo, M. Haptoglobin and pig-major acute protein are increased in pigs with postweaning multisystemic wasting syndrome (PMWS). Vet. Res. 2004, 35, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sauerwein, H.; Schmitz, S.; Hiss, S. The acute phase protein haptoglobin and its relation to oxidative status in piglets undergoing weaning-induced stress. Redox Rep. 2005, 10, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pomorska-Mól, M.; Kwit, K.; Markowska-Daniel, I. Major acute phase proteins in pig serum from birth to slaughter. Bull. Vet. Inst. Pulawy 2012, 56, 553–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Gene Symbol | Official Full Name | Reference Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| Jejunum and ileum | ||
| COL4A4 | Collagen, type IV, alpha 4 | XM_013984558 |
| COL7A1 | Collagen, type VII, alpha 1 | XM_005669519 |
| SPP1 | Secreted phosphorprotein 1 | NM_214023 |
| ADAM8 | ADAM metallopeptidase domain 8 | XM_013994286 |
| SOD1 | Superoxide dismutase 1, soluble | NM_001190422 |
| GAPDH | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase | NM_001206359 |
| ACTB | Actin, beta | XM_003124280 |
| LAMB3 | Laminin, beta 3 | XM_013989670 |
| GPX2 | Glutathione peroxidase 2 (gastrointestinal) | NM_001115136 |
| CAT | Catalase | NM_214301 |
| B2M | Beta-2-microglobulin | NM_213978 |
| Liver | ||
| GPX1 | Glutathione perioxidase 1 | NM_214201 |
| CAT | Catalase | NM_214301 |
| SOD1 | Superoxide dismutase 1, soluble | NM_001190422 |
| MMP-13 | Matrix metalloproteinase 13 precursor | XM_003129808 |
| TNFSF14 | Tumour necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 14-like | NM_001260482 |
| HSP70 | Heat shock protein | NM_001123127 |
| CYP8B1 | Cytochrome P-450 8B1 | NM_214426 |
| HSP90AA1 | 90 kDa heat shock protein | NM_213973 |
| CCL4 | Chemokine (C–C motif) ligand 4 | NM_213779 |
| GAPDH | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase | NM_001206359 |
| ACTB | Actin, beta | XM_003124280 |
| Item 4 | Diet 1 | Sex | SEM 2 | p-Value 3 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NC | PC | GE | m | f | Diet | Sex | d | Diet × Sex | Diet × d | Sex × d | |||
| Villus height (µm) | |||||||||||||
| Jejunum | |||||||||||||
| Main effects | 273 | 270 | 311 | 282 | 288 | 9.3 | 0.005 | 0.60 | <0.001 | 0.008 § | 0.63 | 0.88 | |
| IA | day 27/28 | 229 b | 237 b | 278 a | 246 | 250 | 11 | 0.010 | 0.75 | 0.98 | |||
| day 55/56 | 318 | 304 | 344 | 318 | 326 | 15 | 0.17 | 0.67 | 0.002 | ||||
| Ileum | |||||||||||||
| Main effects | 354 | 404 | 405 | 391 | 385 | 14 | 0.012 | 0.698 | 0.002 | 0.055 | 0.020 | 0.78 | |
| IA | day 27/28 | 361 | 366 | 362 | 368 | 358 | 17 | 0.98 | 0.608 | 0.14 | |||
| day 55/56 | 347 b | 443 a | 448 a | 212 | 199 | 21 | 0.002 | 0.943 | 0.321 | ||||
| Villus surface area (mm2) | |||||||||||||
| Jejunum | |||||||||||||
| Main effects | 31.8 | 32.9 | 37.5 | 34.0 | 34.1 | 1.5 | 0.023 | 0.98 | <0.001 | 0.006 § | 0.71 | 0.94 | |
| IA | day 27/28 | 24.4 b | 27.1 ab | 31.7 a | 27.8 | 27.7 | 1.7 | 0.016 | 0.96 | 0.35 | |||
| day 55/56 | 39.2 | 38.7 | 43.5 | 39.9 | 41.1 | 2.6 | 0.35 | 0.77 | 0.023 | ||||
| Ileum | |||||||||||||
| Main effects | 53.4 | 62.6 | 62.9 | 60.6 | 58.6 | 2.3 | 0.006 | 0.46 | <0.001 | 0.13 | 0.003 | 0.81 | |
| IA | day 27/28 | 53.4 | 52.7 | 52.7 | 53.6 | 52.3 | 2.9 | 0.98 | 0.69 | 0.040 * | |||
| day 55/56 | 53.4 b | 72.4 a | 73.1 a | 67.6 | 65.0 | 3.5 | <0.001 | 0.53 | 0.72 | ||||
| Villus goblet cells (n/villus) | |||||||||||||
| Jejunum | |||||||||||||
| Main effects | 14.9 | 14.5 | 15.3 | 14.4 | 15.4 | 0.8 | 0.78 | 0.24 | 0.41 | 0.78 | 0.15 | 0.34 | |
| IA | day 27/28 | 13.9 | 15.4 | 14.3 | 13.6 | 15.5 | 1.1 | 0.63 | 0.15 | 0.79 | |||
| day 55/56 | 15.9 | 13.6 | 16.3 | 15.3 | 15.4 | 1.1 | 0.18 | 0.86 | 0.29 | ||||
| Ileum | |||||||||||||
| Main effects | 12.5 | 14.7 | 14.9 | 13.8 | 14.3 | 0.7 | 0.024 | 0.48 | <0.001 | 0.72 | 0.035 | 0.27 | |
| IA | day 27/28 | 12.1 | 12.2 | 12.3 | 12.4 | 12.1 | 0.9 | 0.99 | 0.79 | 0.40 | |||
| day 55/56 | 12.9 b | 17.1 a | 17.6 a | 15.2 | 16.6 | 0.9 | 0.002 | 0.21 | 0.87 | ||||
| VC ratio | |||||||||||||
| Jejunum | |||||||||||||
| Main effects | 0.59 ab | 0.56 b | 0.64 a | 0.60 | 0.59 | 0.02 | 0.007 | 0.58 | <0.001 | 0.15 | 0.21 | 0.15 | |
| IA | day 27/28 | 0.51 | 0.52 | 0.59 | 0.56 | 0.52 | 0.003 | 0.10 | 0.25 | 1.00 | |||
| day 55/56 | 0.66 | 0.61 | 0.67 | 0.64 | 0.65 | 0.03 | 0.31 | 0.72 | 0.079 | ||||
| Ileum | |||||||||||||
| Main effects | 1.19 | 1.32 | 1.30 | 1.29 | 1.24 | 0.06 | 0.31 | 0.48 | 0.24 | 0.25 | 0.016 | 0.25 | |
| IA | day 27/28 | 1.39 | 1.28 | 1.27 | 1.42 | 1.34 | 0.1 | 0.68 | 0.27 | 0.65 | |||
| day 55/56 | 0.99 b | 1.36 a | 1.33 a | 1.21 | 1.34 | 0.07 | 0.002 | 0.70 | 0.21 | ||||
| Item 4 | Diet 1 | Sex | SEM 2 | p-Value 3 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NC | PC | GE | m | f | Diet | Sex | d | Diet × Sex | Diet × d | Sex × d | |||
| Crypt depth (µm) | |||||||||||||
| Jejunum | |||||||||||||
| Main effects | 478 | 490 | 498 | 480 | 499 | 7.3 | 0.16 | 0.027 | <0.001 | 0.55 | 0.90 | 0.06 | |
| IA | day 27/28 | 461 | 469 | 478 | 451 | 487 | 13 | 0.67 | 0.024 | 0.91 | |||
| day 55/56 | 495 | 512 | 519 | 507 | 510 | 13 | 0.42 | 0.84 | 0.67 | ||||
| Ileum | |||||||||||||
| Main effects | 323 | 321 | 325 | 319 | 327 | 11 | 0.98 | 0.56 | <0.001 | 0.90 | 0.36 | 0.33 | |
| IA | day 27/28 | 283 | 302 | 299 | 285 | 305 | 16 | 0.65 | 0.29 | 0.60 | |||
| day 55/56 | 364 | 340 | 350 | 354 | 349 | 15 | 0.54 | 0.77 | 0.65 | ||||
| Colon | |||||||||||||
| Main effects | 529 (a) | 492 (b) | 506 (ab) | 505 | 513 | 12 | 0.084 | 0.58 | 0.80 | 0.98 | 0.59 | 0.23 | |
| IA | day 27/28 | 527 | 497 | 496 | 494 | 520 | 19 | 0.41 | 0.23 | 0.29 | |||
| day 55/56 | 528 | 487 | 517 | 515 | 506 | 15 | 0.13 | 0.60 | 0.16 | ||||
| Crypt surface area (mm2) | |||||||||||||
| Jejunum | |||||||||||||
| Main effects | 26.4 | 27.5 | 27.0 | 26.1 | 27.8 | 0.7 | 0.55 | 0.033 | 0.51 | 0.20 | 0.83 | 0.41 | |
| IA | day 27/28 | 26.3 | 26.9 | 26.8 | 25.4 | 27.9 | 1.1 | 0.93 | 0.058 | 0.58 | |||
| day 55/56 | 26.5 | 28.0 | 27.2 | 26.7 | 27.8 | 1.1 | 0.61 | 0.40 | 0.47 | ||||
| Ileum | |||||||||||||
| Main effects | 18.8 | 19.2 | 19.1 | 19.0 | 16.4 | 0.8 | 0.96 | 0.92 | <0.001 | 0.65 | 0.74 | 0.36 | |
| IA | day 27/28 | 15.7 | 16.7 | 16.8 | 15.9 | 16.9 | 1.0 | 0.69 | 0.40 | 0.61 | |||
| day 55/56 | 22.0 | 21.7 | 21.3 | 22.1 | 21.3 | 1.3 | 0.94 | 0.62 | 0.62 | ||||
| Colon | |||||||||||||
| Main effects | 37.2 a | 32.7 b | 34.5 ab | 35.5 | 34.2 | 1.3 | 0.047 | 0.35 | 0.97 | 0.51 | 0.83 | 0.52 | |
| IA | day 27/28 | 37.0 | 33.3 | 34.4 | 35.1 | 34.8 | 1.7 | 0.31 | 0.94 | 0.83 | |||
| day 55/56 | 37.4 | 32.1 | 35.0 | 36.2 | 33.7 | 1.8 | 0.15 | 0.29 | 0.11 | ||||
| Crypt goblet cells (n/crypt) | |||||||||||||
| Jejunum | |||||||||||||
| Main effects | 34.6 | 35.8 | 34.7 | 32.8 | 37.2 | 1.0 | 0.65 | <0.001 | 0.71 | 0.83 | 0.57 | 0.54 | |
| IA | day 27/28 | 35.1 | 35.7 | 33.6 | 32.1 | 37.5 | 1.8 | 0.70 | 0.017 | 0.75 | |||
| day 55/56 | 34.1 | 35.8 | 35.7 | 33.4 | 37.1 | 1.6 | 0.73 | 0.077 | 0.99 | ||||
| Ileum | |||||||||||||
| Main effects | 26.9 | 26.8 | 27.4 | 27.1 | 26.9 | 1.5 | 0.95 | 0.91 | <0.001 | 0.58 | 0.23 | 1.00 | |
| IA | day 27/28 | 20.2 | 22.0 | 24.3 | 22.3 | 22.1 | 1.8 | 0.30 | 0.93 | 0.53 | |||
| day 55/56 | 33.7 | 31.5 | 30.5 | 32.0 | 31.8 | 2.3 | 0.62 | 0.95 | 0.81 | ||||
| Colon | |||||||||||||
| Main effects | 52.8 | 50.1 | 51.7 | 52.6 | 50.5 | 1.5 | 0.45 | 0.22 | 0.059 | 0.14 | 0.092 | 0.90 | |
| IA | day 27/28 | 53.4 | 46.4 | 49.8 | 50.9 | 48.8 | 2.3 | 0.11 | 0.44 | 0.15 | |||
| day 55/56 | 52.0 | 53.9 | 53.7 | 54.2 | 52.2 | 1.9 | 0.73 | 0.40 | 0.59 | ||||
| Item 4 | Diet 1 | Sex | SEM 2 | p-Value 3 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NC | PC | GE | m | f | Diet | Sex | d | Diet × Sex | Diet × d | Sex × d | |||
| GPx (U/g protein) | |||||||||||||
| Jejunum | |||||||||||||
| Main effects | 169 | 179 | 175 | 176 | 173 | 8.6 | 0.75 | 0.81 | 0.033 | 0.27 | 0.50 | 0.36 | |
| IA | day 27/28 | 153 | 165 | 172 | 158 | 169 | 10 | 0.43 | 0.34 | 0.34 | |||
| day 55/56 | 186 | 193 | 177 | 182 | 189 | 14 | 0.74 | 0.67 | 0.40 | ||||
| Ileum | |||||||||||||
| Main effects | 334 | 315 | 310 | 318 | 322 | 12 | 0.33 | 0.76 | 0.016 | 0.50 | 0.85 | 0.64 | |
| IA | day 27/28 | 312 | 298 | 298 | 304 | 302 | 20 | 0.83 | 0.92 | 0.98 | |||
| day 55/56 | 356 | 332 | 323 | 332 | 342 | 14 | 0.23 | 0.51 | 0.083 | ||||
| Liver | |||||||||||||
| Main effects | 1119 | 1091 | 1078 | 1097 | 1095 | 40 | 0.76 | 0.95 | <0.001 | 0.12 | 0.41 | 0.33 | |
| IA | day 27/28 | 987 | 1015 | 1018 | 985 | 1028 | 42 | 0.85 | 0.39 | 0.28 | |||
| day 55/56 | 1251 | 1167 | 1139 | 1209 | 1161 | 67 | 0.48 | 0.54 | 0.12 | ||||
| CAT (U/mg protein) | |||||||||||||
| Jejunum | |||||||||||||
| Main effects | 71.6 | 71.5 | 72.5 | 71.1 | 72.6 | 2.5 | 0.95 | 0.61 | 0.19 | 0.89 | 0.99 | 0.72 | |
| IA | day 27/28 | 73.4 | 73.4 | 74.5 | 72.5 | 75.0 | 3.3 | 0.96 | 0.51 | 0.99 | |||
| day 55/56 | 69.8 | 69.6 | 70.6 | 69.8 | 70.2 | 3.8 | 0.98 | 0.92 | 0.77 | ||||
| Ileum | |||||||||||||
| Main effects | 26.4 | 30.0 | 29.4 | 28.9 | 28.3 | 1.7 | 0.27 | 0.77 | <0.001 | 0.65 | 0.06 | 0.68 | |
| IA | day 27/28 | 31.6 (b) | 40.3 (a) | 39.2 (ab) | 37.7 | 36.4 | 2.8 | 0.072 | 0.68 | 0.36 | |||
| day 55/56 | 21.3 | 19.6 | 19.7 | 20.1 | 20.3 | 1.7 | 0.74 | 0.90 | 0.82 | ||||
| Liver | |||||||||||||
| Main effects | 8.5 | 9.5 | 8.6 | 9.0 | 8.9 | 0.6 | 0.47 | 0.88 | <0.001 | 0.42 | 0.48 | 0.55 | |
| IA | day 27/28 | 7.0 | 8.8 | 6.8 | 7.3 | 7.7 | 1.0 | 0.31 | 0.77 | 0.61 | |||
| day 55/56 | 10.1 | 10.3 | 10.5 | 10.6 | 10 | 0.8 | 0.96 | 0.55 | 0.68 | ||||
| Item 4 | Diet 1 | Sex | SEM 2 | p-Value 3 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NC | PC | GE | m | f | Diet | Sex | d | Diet × Sex | Diet × d | Sex × d | |||
| Total SOD (U/mg protein) | |||||||||||||
| Jejunum | |||||||||||||
| Main effects | 37.9 | 31.4 | 34.7 | 35.9 | 33.4 | 2.5 | 0.19 | 0.38 | 0.62 | 0.95 | 0.38 | 0.46 | |
| IA | day 27/28 | 35.8 | 33.5 | 36.9 | 35.6 | 35.2 | 3.3 | 0.76 | 0.92 | 0.80 | |||
| day 55/56 | 40.0 | 29.4 | 32.5 | 36.3 | 31.6 | 3.6 | 0.12 | 0.28 | 0.97 | ||||
| Ileum | |||||||||||||
| Main effects | 17.6 | 18.0 | 16.8 | 17.1 | 17.9 | 1.0 | 0.68 | 0.46 | 0.21 | 0.84 | 0.36 | 0.88 | |
| IA | day 27/28 | 17.8 | 16.2 | 16.3 | 16.4 | 17.1 | 0.9 | 0.40 | 0.53 | 0.82 | |||
| day 55/56 | 17.5 | 19.7 | 17.3 | 17.7 | 18.7 | 1.7 | 0.53 | 0.61 | 0.61 | ||||
| Liver | |||||||||||||
| Main effects | 236 | 249 | 226 | 242 | 232 | 7.6 | 0.11 | 0.25 | <0.001 | 0.89 | 0.68 | 0.74 | |
| IA | day 27/28 | 255 | 276 | 246 | 266 | 252 | 13 | 0.25 | 0.35 | 0.75 | |||
| day 55/56 | 217 | 223 | 207 | 219 | 212 | 8.5 | 0.39 | 0.51 | 0.96 | ||||
| Mn-SOD (U/mg protein) | |||||||||||||
| Jejunum | |||||||||||||
| Main effects | 13.2 | 13.6 | 13.3 | 13.3 | 13.4 | 0.5 | 0.81 | 0.85 | 0.95 | 0.83 | 0.67 | 0.97 | |
| IA | day 27/28 | 12.9 | 14.0 | 13.1 | 13.3 | 13.4 | 0.7 | 0.52 | 0.86 | 0.46 | |||
| day 55/56 | 13.4 | 13.3 | 13.4 | 13.3 | 13.4 | 0.8 | 0.98 | 0.92 | 0.95 | ||||
| Ileum | |||||||||||||
| Main effects | 9.70 | 9.37 | 9.02 | 9.62 | 9.21 | 0.4 | 0.50 | 0.45 | 0.95 | 0.15 | 0.37 | 0.75 | |
| IA | day 27/28 | 9.93 | 9.59 | 8.54 | 9.45 | 9.25 | 0.5 | 0.17 | 0.74 | 0.28 | |||
| day 55/56 | 9.49 | 9.15 | 9.50 | 9.64 | 9.13 | 0.6 | 0.90 | 0.48 | 0.10 | ||||
| Liver | |||||||||||||
| Main effects | 35.8 | 39.1 | 35.8 | 37.3 | 36.4 | 1.8 | 0.35 | 0.65 | <0.001 | 0.50 | 0.80 | 0.70 | |
| IA | day 27/28 | 40.3 | 45.3 | 41.3 | 42.3 | 42.2 | 3.2 | 0.51 | 0.97 | 0.22 | |||
| day 55/56 | 31.3 | 32.8 | 30.2 | 32.3 | 30.6 | 1.7 | 0.58 | 0.38 | 0.52 | ||||
| Cu/Zn-SOD (U/mg protein) | |||||||||||||
| Jejunum | |||||||||||||
| Main effects | 24.7 | 17.8 | 21.5 | 22.7 | 20 | 2.3 | 0.11 | 0.32 | 0.58 | 0.97 | 0.36 | 0.42 | |
| IA | day 27/28 | 22.9 | 19.5 | 23.8 | 22.3 | 21.8 | 3.2 | 0.61 | 0.89 | 0.88 | |||
| day 55/56 | 26.6 (a) | 16.1 (b) | 19.1 (ab) | 23 | 18.2 | 3.2 | 0.077 | 0.21 | 0.96 | ||||
| Ileum | |||||||||||||
| Main effects | 7.93 | 8.61 | 8.61 | 8.11 | 8.72 | 0.4 | 0.72 | 0.43 | 0.019 | 0.57 | 0.15 | 0.77 | |
| IA | day 27/28 | 7.86 | 6.63 | 7.78 | 7.02 | 7.74 | 0.9 | 0.53 | 0.39 | 0.87 | |||
| day 55/56 | 8.00 | 10.6 | 9.40 | 9.14 | 9.54 | 1.1 | 0.25 | 0.76 | 0.48 | ||||
| Liver | |||||||||||||
| Main effects | 200 | 210 | 191 | 205 | 196 | 7.1 | 0.15 | 0.26 | <0.001 | 0.72 | 0.80 | 0.58 | |
| IA | day 27/28 | 214 | 231 | 205 | 223 | 210 | 12 | 0.32 | 0.33 | 0.45 | |||
| day 55/56 | 185 | 190 | 176 | 186 | 182 | 7.6 | 0.43 | 0.59 | 0.85 | ||||
| Item 4 | Diet 1 | Sex | SEM 2 | p-Value 3 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NC | PC | GE | m | f | Diet | Sex | d | Diet × Sex | Diet × d | Sex × d | |||
| TBARS (μmol/kg) 5 | |||||||||||||
| Jejunum | |||||||||||||
| Main effects | 21.8 | 23.8 | 21.0 | 21.9 | 22.5 | 1.2 | 0.24 | 0.66 | 0.001 | 0.97 | 0.27 | 0.96 | |
| IA | day 27/28 | 23.4 | 27.9 | 22.9 | 24.4 | 25.1 | 2.0 | 0.16 | 0.77 | 0.54 | |||
| day 55/56 | 20.3 | 19.7 | 19.1 | 19.4 | 20.0 | 1.4 | 0.84 | 0.73 | 0.43 | ||||
| Ileum | |||||||||||||
| Main effects | 14.6 | 15.7 | 16.1 | 15.5 | 15.4 | 0.9 | 0.45 | 0.94 | 0.15 | 0.94 | 0.28 | 0.02 | |
| IA | day 27/28 | 13.8 | 16.0 | 14.4 | 13.6 | 15.9 | 1.5 | 0.56 | 0.18 | 0.65 | |||
| day 55/56 | 15.4 | 15.4 | 17.7 | 17.5 | 14.9 | 0.9 | 0.10 | 0.016 | 0.41 | ||||
| Liver | |||||||||||||
| Main effects | 70.2 | 70.2 | 72.9 | 68.4 | 73.8 | 2.9 | 0.75 | 0.11 | 0.58 | 0.82 | 0.43 | 0.82 | |
| IA | day 27/28 | 72.3 | 67.4 | 70.8 | 67.9 | 72.5 | 3.2 | 0.55 | 0.23 | 0.28 | |||
| day 55/56 | 68.1 | 73.0 | 74.9 | 68.9 | 75.1 | 4.7 | 0.58 | 0.27 | 0.67 | ||||
| DPPH (µmol/g) 6 | |||||||||||||
| Jejunum | |||||||||||||
| Main effects | 25.2 | 25.9 | 26.5 | 25.2 | 26.5 | 1.0 | 0.63 | 0.26 | <0.001 | 0.33 | 0.94 | 0.99 | |
| IA | day 27/28 | 22.4 | 23.4 | 24.2 | 22.7 | 24.0 | 1.5 | 0.69 | 0.46 | 0.35 | |||
| day 55/56 | 27.8 | 28.3 | 28.9 | 27.7 | 29.2 | 1.3 | 0.89 | 0.39 | 0.85 | ||||
| Ileum | |||||||||||||
| Main effects | 28.8 | 27.6 | 30.4 | 29.7 | 28.2 | 1.7 | 0.49 | 0.42 | 0.90 | 0.12 | 0.99 | 0.15 | |
| IA | day 27/28 | 28.9 | 27.8 | 30.6 | 28.5 | 29.7 | 2.4 | 0.72 | 0.66 | 0.61 | |||
| day 55/56 | 28.7 | 27.5 | 30.3 | 31.0 | 26.7 | 2.3 | 0.68 | 0.10 | 0.011 | ||||
| Liver | |||||||||||||
| Main effects | 75.3 | 76.0 | 75.4 | 74.1 | 77.0 | 2.4 | 0.98 | 0.29 | 0.001 | 0.16 | 0.58 | 0.93 | |
| IA | day 27/28 | 70.4 | 73.3 | 69.2 | 69.3 | 72.5 | 3.5 | 0.70 | 0.44 | 0.70 | |||
| day 55/56 | 80.2 | 78.7 | 81.6 | 78.8 | 81.5 | 3.3 | 0.82 | 0.48 | 0.14 | ||||
| ABTS (μmol/g) 6 | |||||||||||||
| Jejunum | |||||||||||||
| Main effects | 33.3 | 34.6 | 34.7 | 34.0 | 34.4 | 0.6 | 0.21 | 0.65 | <0.001 | 0.34 | 0.93 | 0.76 | |
| IA | day 27/28 | 31.3 | 32.3 | 32.8 | 32.1 | 32.2 | 1.1 | 0.60 | 0.93 | 0.36 | |||
| day 55/56 | 35.4 | 36.8 | 36.7 | 36.0 | 36.6 | 0.6 | 0.15 | 0.42 | <0.001 | ||||
| Ileum | |||||||||||||
| Main effects | 31.4 | 31.2 | 31.8 | 31.7 | 31.1 | 0.5 | 0.70 | 0.31 | 0.35 | 0.32 | 0.78 | 0.02 | |
| IA | day 27/28 | 31.1 | 31.2 | 31.3 | 30.8 | 31.5 | 0.8 | 0.98 | 0.44 | 0.81 | |||
| day 55/56 | 31.7 | 31.2 | 32.3 | 32.7 | 30.7 | 0.6 | 0.43 | 0.007 | 0.21 | ||||
| Liver | |||||||||||||
| Main effects | 71.0 | 73.6 | 73.5 | 72.8 | 72.6 | 1.1 | 0.19 | 0.89 | 0.002 | 0.52 | 0.67 | 0.72 | |
| IA | day 27/28 | 68.4 | 72.3 | 71.0 | 70.4 | 70.7 | 1.7 | 0.25 | 0.89 | 0.38 | |||
| day 55/56 | 73.6 | 75.0 | 76.0 | 75.2 | 74.5 | 1.6 | 0.57 | 0.72 | 0.80 | ||||
| Item 4 | Diet 1 | Sex | SEM 2 | p-Value 3 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NC | PC | GE | m | f | Diet | Sex | d | Diet × Sex | Diet × d | Sex × d | |||
| GPX2 (jejunum and ileum)-GPX1 (liver) | |||||||||||||
| Jejunum | |||||||||||||
| Main effects | 1.00 | 1.26 | 1.16 | 1.00 | 0.93 | 0.2 | 0.45 | 0.89 | <0.001 | 0.15 | 0.71 | 0.69 | |
| IA | day 27/28 | 1.00 | 1.46 | 1.29 | 1.00 | 1.04 | 0.3 | 0.38 | 0.86 | 0.58 | |||
| day 55/56 | 1.00 | 1.09 | 1.04 | 1.00 | 0.87 | 0.3 | 0.95 | 0.69 | 0.037 * | ||||
| Ileum | |||||||||||||
| Main effects | 1.00 | 1.01 | 1.06 | 1.00 | 1.01 | 0.1 | 0.87 | 0.97 | 0.71 | 0.85 | 0.30 | 0.13 | |
| IA | day 27/28 | 1.00 | 1.21 | 1.24 | 1.00 | 0.81 | 0.2 | 0.43 | 0.30 | 0.83 | |||
| day 55/56 | 1.00 | 1.08 | 0.88 | 1.00 | 1.15 | 0.2 | 0.61 | 0.27 | 0.38 | ||||
| Liver | |||||||||||||
| Main effects | 1.00 | 1.12 | 1.15 | 1.00 | 1.05 | 0.1 | 0.26 | 0.48 | <0.001 | 0.12 | 0.56 | 0.98 | |
| IA | day 27/28 | 1.00 | 1.02 | 1.12 | 1.00 | 1.05 | 0.1 | 0.60 | 0.64 | 0.55 | |||
| day 55/56 | 1.00 | 1.20 | 1.14 | 1.00 | 1.05 | 0.1 | 0.23 | 0.59 | 0.18 | ||||
| SOD1 | |||||||||||||
| Jejunum | |||||||||||||
| Main effects | 1.00 | 1.06 | 1.04 | 1.00 | 1.02 | 0.1 | 0.58 | 0.65 | 0.022 | 0.74 | 0.64 | 0.77 | |
| IA | day 27/28 | 1.00 | 1.12 | 1.08 | 1.00 | 1.01 | 0.1 | 0.32 | 0.91 | 0.73 | |||
| day 55/56 | 1.00 | 1.01 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.04 | 0.1 | 0.99 | 0.63 | 0.93 | ||||
| Ileum | |||||||||||||
| Main effects | 1.00 | 0.93 | 0.89 | 1.00 | 0.97 | 0.1 | 0.34 | 0.43 | 0.66 | 0.33 | 0.076 | 0.95 | |
| IA | day 27/28 | 1.00 | 0.80 | 0.90 | 1.00 | 0.95 | 0.1 | 0.17 | 0.56 | 0.68 | |||
| day 55/56 | 1.00 | 1.08 | 0.88 | 1.00 | 0.93 | 0.1 | 0.16 | 0.59 | 0.33 | ||||
| Liver | |||||||||||||
| Main effects | 1.00 | 1.12 | 1.11 | 1.00 | 1.11 | 0.1 | 0.53 | 0.21 | <0.001 | 0.40 | 0.53 | 0.59 | |
| IA | day 27/28 | 1.00 | 1.02 | 1.13 | 1.00 | 1.06 | 0.1 | 0.62 | 0.61 | 0.84 | |||
| day 55/56 | 1.00 | 1.19 | 1.08 | 1.00 | 1.16 | 0.1 | 0.46 | 0.21 | 0.41 | ||||
| CAT | |||||||||||||
| Jejunum | |||||||||||||
| Main effects | 1.00 | 0.88 | 0.93 | 1.00 | 1.10 | 0.1 | 0.28 | 0.12 | 0.24 | 0.38 | 0.52 | 0.90 | |
| IA | day 27/28 | 1.00 | 0.83 | 0.96 | 1.00 | 1.10 | 0.1 | 0.26 | 0.33 | 0.37 | |||
| day 55/56 | 1.00 | 0.93 | 0.90 | 1.00 | 1.10 | 0.1 | 0.63 | 0.22 | 0.44 | ||||
| Ileum | |||||||||||||
| Main effects | 1.00 | 0.97 | 0.98 | 1.00 | 0.95 | 0.1 | 0.83 | 0.16 | 0.039 | 0.17 | 0.54 | 0.25 | |
| IA | day 27/28 | 1.00 | 0.97 | 1.03 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 0.1 | 0.55 | 0.82 | 0.16 | |||
| day 55/56 | 1.00 | 0.84 | 0.92 | 1.00 | 0.88 | 0.1 | 0.73 | 0.13 | 0.059 | ||||
| Liver | |||||||||||||
| Main effects | 1.00 | 1.07 | 1.14 | 1.00 | 1.16 | 0.1 | 0.44 | 0.058 | <0.001 | 0.51 | 0.88 | 0.41 | |
| IA | day 27/28 | 1.00 | 1.02 | 1.14 | 1.00 | 1.07 | 0.1 | 0.58 | 0.45 | 0.88 | |||
| day 55/56 | 1.00 | 1.09 | 1.12 | 1.00 | 1.24 | 0.1 | 0.67 | 0.056 | 0.34 | ||||
| Item 4 | Diet 1 | Sex | SEM 2 | p-Value 3 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NC | PC | GE | m | f | Diet | Sex | d | Diet × Sex | Diet × d | Sex × d | |||
| ADAM8 | |||||||||||||
| Jejunum | |||||||||||||
| Main effects | 1.00 | 1.17 | 1.14 | 1.00 | 1.10 | 0.1 | 0.19 | 0.29 | 0.93 | 0.85 | 0.68 | 0.06 | |
| IA | day 27/28 | 1.00 | 1.11 | 1.05 | 1.00 | 1.23 | 0.1 | 0.75 | 0.051 | 0.94 | |||
| day 55/56 | 1.00 | 1.24 | 1.23 | 1.00 | 0.93 | 0.1 | 0.17 | 0.56 | 0.85 | ||||
| Ileum | |||||||||||||
| Main effects | 1.00 | 0.92 | 0.84 | 1.00 | 0.98 | 0.1 | 0.27 | 0.80 | 0.62 | 0.18 | 0.040 | 0.24 | |
| IA | day 27/28 | 1.00 | 0.73 | 0.86 | 1.00 | 0.90 | 0.2 | 0.20 | 0.38 | 0.73 | |||
| day 55/56 | 1.00 ab | 1.15 a | 0.83 b | 1.00 | 1.09 | 0.1 | 0.036 | 0.42 | 0.11 | ||||
| COL4A4 | |||||||||||||
| Jejunum | |||||||||||||
| Main effects | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.85 | 1.00 | 0.93 | 0.2 | 0.66 | 0.86 | <.0001 | 0.83 | 0.078 | 0.62 | |
| IA | day 27/28 | 1.00 | 0.94 | 0.55 | 1.00 | 1.06 | 0.4 | 0.20 | 0.86 | 0.97 | |||
| day 55/56 | 1.00 | 1.07 | 1.32 | 1.00 | 0.93 | 0.2 | 0.36 | 0.49 | 0.66 | ||||
| Ileum | |||||||||||||
| Main effects | 1.00 | 1.33 | 0.96 | 1.00 | 1.15 | 0.2 | 0.68 | 0.36 | 0.001 | 0.35 | 0.055 | 0.14 | |
| IA | day 27/28 | 1.00 | 0.77 | 0.62 | 1.00 | 1.49 | 0.3 | 0.28 | 0.12 | 0.18 | |||
| day 55/56 | 1.00 | 1.66 | 1.48 | 1.00 | 0.87 | 0.3 | 0.13 | 0.67 | 0.88 | ||||
| COL7A1 | |||||||||||||
| Jejunum | |||||||||||||
| Main effects | 1.00 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 1.00 | 1.15 | 0.1 | 0.89 | 0.28 | 0.85 | 0.39 | 0.57 | 0.88 | |
| IA | day 27/28 | 1.00 | 1.06 | 1.04 | 1.00 | 1.07 | 0.2 | 0.93 | 0.54 | 0.45 | |||
| day 55/56 | 1.00 | 0.87 | 0.89 | 1.00 | 1.10 | 0.1 | 0.51 | 0.36 | 0.52 | ||||
| Ileum | |||||||||||||
| Main effects | 1.00 | 1.09 | 1.10 | 1.00 | 1.05 | 0.1 | 0.43 | 0.38 | 0.54 | 0.53 | 0.93 | 0.15 | |
| IA | day 27/28 | 1.00 | 1.06 | 1.07 | 1.00 | 1.12 | 0.1 | 0.81 | 0.10 | 0.22 | |||
| day 55/56 | 1.00 | 1.12 | 1.12 | 1.00 | 0.97 | 0.1 | 0.51 | 0.69 | 0.96 | ||||
| LAMB3 | |||||||||||||
| Jejunum | |||||||||||||
| Main effects | 1.00 | 1.14 | 0.96 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.1 | 0.25 | 0.99 | 0.10 | 0.23 | 0.38 | 0.21 | |
| IA | day 27/28 | 1.00 | 1.33 | 1.03 | 1.00 | 0.87 | 0.2 | 0.22 | 0.45 | 0.27 | |||
| day 55/56 | 1.00 | 0.98 | 0.90 | 1.00 | 1.15 | 0.1 | 0.64 | 0.28 | 0.70 | ||||
| Ileum | |||||||||||||
| Main effects | 1.00 | 1.14 | 1.01 | 1.00 | 0.96 | 0.1 | 0.12 | 0.38 | 0.093 | 0.057 | 0.34 | 0.05 | |
| IA | day 27/28 | 1.00 | 1.07 | 1.05 | 1.00 | 0.81 | 0.1 | 0.79 | 0.048 | 0.018 | |||
| day 55/56 | 1.00 (ab) | 1.21 (a) | 0.98 (b) | 1.00 | 1.07 | 0.1 | 0.061 | 0.42 | 0.82 | ||||
| SPP1 | |||||||||||||
| Jejunum | |||||||||||||
| Main effects | 1.00 | 1.18 | 0.98 | 1.00 | 1.07 | 0.2 | 0.67 | 0.81 | 0.020 | 0.85 | 0.19 | 0.12 | |
| IA | day 27/28 | 1.00 | 1.03 | 0.65 | 1.00 | 0.81 | 0.3 | 0.15 | 0.25 | 0.49 | |||
| day 55/56 | 1.00 | 1.35 | 1.48 | 1.00 | 1.39 | 0.4 | 0.55 | 0.28 | 0.71 | ||||
| Ileum | |||||||||||||
| Main effects | 1.00 | 0.95 | 1.05 | 1.00 | 0.93 | 0.2 | 0.84 | 0.86 | 0.49 | 0.90 | 0.72 | 0.18 | |
| IA | day 27/28 | 1.00 | 1.05 | 1.21 | 1.00 | 0.80 | 0.3 | 0.82 | 0.38 | 0.70 | |||
| day 55/56 | 1.00 | 0.85 | 0.91 | 1.00 | 1.14 | 0.2 | 0.70 | 0.28 | 0.10 | ||||
| Item 4 | Diet 1 | Sex | SEM 2 | p-Value 3 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NC | PC | GE | m | f | Diet | Sex | d | Diet × Sex | Diet × d | Sex × d | |||
| HSP70 | |||||||||||||
| Main effects | 1.00 | 1.16 | 1.43 | 1.00 | 1.32 | 0.2 | 0.13 | 0.041 | 0.10 | 0.62 | 0.93 | 0.77 | |
| IA | day 27/28 | 1.00 | 1.24 | 1.41 | 1.00 | 1.23 | 0.3 | 0.38 | 0.27 | 0.38 | |||
| day 55/56 | 1.00 | 1.07 | 1.33 | 1.00 | 1.34 | 0.2 | 0.32 | 0.063 | 0.79 | ||||
| HSP90AA1 | |||||||||||||
| Main effects | 1.00 | 0.98 | 0.95 | 1.00 | 1.18 | 0.1 | 0.94 | 0.092 | 0.76 | 0.31 | 0.17 | 0.93 | |
| IA | day 27/28 | 1.00 | 0.95 | 1.15 | 1.00 | 1.17 | 0.2 | 0.53 | 0.29 | 0.19 | |||
| day 55/56 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.81 | 1.00 | 1.19 | 0.2 | 0.29 | 0.19 | 0.97 | ||||
| CYP8B1 | |||||||||||||
| Main effects | 1.00 | 0.52 | 1.37 | 1.00 | 1.15 | 0.3 | 0.014 | 0.47 | 0.85 | 0.004 § | 0.051 | 0.73 | |
| IA | day 27/28 | 1.00 a | 0.24 b | 1.01 a | 1.00 | 1.32 | 0.4 | <0.001 | 0.35 | 0.20 | |||
| day 55/56 | 1.00 | 1.10 | 1.65 | 1.00 | 1.07 | 0.5 | 0.61 | 0.81 | 0.013 * | ||||
| MMP-13 | |||||||||||||
| Main effects | 1.00 | 0.96 | 1.11 | 1.00 | 1.08 | 0.2 | 0.53 | 0.48 | 0.27 | 0.54 | 0.27 | 0.98 | |
| IA | day 27/28 | 1.00 | 0.96 | 1.40 | 1.00 | 1.07 | 0.2 | 0.21 | 0.66 | 0.86 | |||
| day 55/56 | 1.00 | 0.96 | 0.91 | 1.00 | 1.09 | 0.2 | 0.90 | 0.58 | 0.14 | ||||
| TNFRSF14 | |||||||||||||
| Main effects | 1.00 | 0.81 | 1.01 | 1.00 | 0.93 | 0.2 | 0.28 | 0.54 | 0.071 | 0.88 | 0.43 | 0.38 | |
| IA | day 27/28 | 1.00 | 0.65 | 0.97 | 1.00 | 0.81 | 0.2 | 0.17 | 0.32 | 0.36 | |||
| day 55/56 | 1.00 | 0.98 | 1.04 | 1.00 | 1.01 | 0.2 | 0.95 | 0.85 | 0.67 | ||||
| CCL4 | |||||||||||||
| Main effects | 1.00 | 0.94 | 1.14 | 1.00 | 0.98 | 0.1 | 0.16 | 0.80 | <0.001 | 0.35 | 0.26 | 0.53 | |
| IA | day 27/28 | 1.00 | 0.81 | 1.15 | 1.00 | 0.93 | 0.2 | 0.12 | 0.59 | 0.082 | |||
| day 55/56 | 1.00 | 1.06 | 1.10 | 1.00 | 1.05 | 0.1 | 0.73 | 0.75 | 0.66 | ||||
| Item 4 | Diet 1 | Sex | SEM 2 | p-Value 3 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NC | PC | GE | m | f | Diet | Sex | d | Diet × Sex | Diet × d | Sex × d | |||
| Antioxidant measurements | |||||||||||||
| SOD (U/ml) | |||||||||||||
| Main effects | 5.09 | 5.12 | 4.71 | 5.14 | 4.81 | 0.32 | 0.63 | 0.38 | 0.014 | 0.86 | 0.89 | 0.65 | |
| IA | day 0 | 5.96 | 5.74 | 5.35 | 6.13 | 5.24 | 0.58 | 0.78 | 0.22 | 0.98 | |||
| day 6 | 4.75 | 4.58 | 4.85 | 4.90 | 4.55 | 0.41 | 0.89 | 0.45 | 0.79 | ||||
| day 27/28 | 4.23 | 4.65 | 3.50 | 4.00 | 4.26 | 0.52 | 0.26 | 0.63 | 0.56 | ||||
| day 55/56 | 5.41 | 5.58 | 5.20 | 5.58 | 5.23 | 0.73 | 0.93 | 0.66 | 0.89 | ||||
| MDA (µM) | |||||||||||||
| Main effects | 2.31 | 2.25 | 2.04 | 2.13 | 2.26 | 0.26 | 0.77 | 0.68 | <0.001 | 0.89 | 0.11 | 0.83 | |
| IA | day 0 | 3.24 | 3.64 | 3.52 | 3.31 | 3.60 | 0.37 | 0.74 | 0.47 | 0.18 | |||
| day 6 | 1.62 (ab) | 2.56 (a) | 1.52 (b) | 1.78 | 2.02 | 0.31 | 0.041* | 0.50 | 0.46 | ||||
| day 27/28 | 1.37 | 1.08 | 1.32 | 0.98 | 1.54 | 0.30 | 0.79 | 0.13 | 0.52 | ||||
| day 55/56 | 2.96 | 2.04 | 1.65 | 2.46 | 1.98 | 0.52 | 0.19 | 0.43 | 0.34 | ||||
| Acute-phase proteins | |||||||||||||
| Haptoglobin (µg/mL) | |||||||||||||
| Main effects | 769 | 676 | 720 | 634 | 809 | 93 | 0.78 | 0.11 | 0.070 | 0.10 | 0.86 | 0.07 | |
| IA | day 6 | 957 | 808 | 805 | 802 | 911 | 126 | 0.62 | 0.46 | 0.78 | |||
| day 27/28 | 661 | 619 | 646 | 695 | 589 | 161 | 0.98 | 0.58 | 0.074 | ||||
| day 55/56 | 690 | 598 | 695 | 402 | 920 | 136 | 0.83 | 0.002 | 0.52 | ||||
| pigMAP (µg/mL) | |||||||||||||
| Main effects | 794 | 757 | 797 | 790 | 774 | 48 | 0.81 | 0.77 | <0.001 | 0.27 | 0.63 | 0.74 | |
| IA | day 6 | 1167 | 1221 | 1272 | 1253 | 1187 | 82 | 0.67 | 0.49 | 0.27 | |||
| day 27/28 | 572 | 531 | 549 | 552 | 549 | 39 | 0.76 | 0.95 | 0.39 | ||||
| day 55/56 | 645 | 518 | 577 | 571 | 589 | 46 | 0.14 | 0.74 | 0.080 | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rajković, E.; Schwarz, C.; Kapsamer, S.B.; Schedle, K.; Reisinger, N.; Emsenhuber, C.; Ocelova, V.; Roth, N.; Frieten, D.; Dusel, G.; et al. Evaluation of a Dietary Grape Extract on Oxidative Status, Intestinal Morphology, Plasma Acute-Phase Proteins and Inflammation Parameters of Weaning Piglets at Various Points of Time. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1428. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11081428
Rajković E, Schwarz C, Kapsamer SB, Schedle K, Reisinger N, Emsenhuber C, Ocelova V, Roth N, Frieten D, Dusel G, et al. Evaluation of a Dietary Grape Extract on Oxidative Status, Intestinal Morphology, Plasma Acute-Phase Proteins and Inflammation Parameters of Weaning Piglets at Various Points of Time. Antioxidants. 2022; 11(8):1428. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11081428
Chicago/Turabian StyleRajković, Emina, Christiane Schwarz, Stefan Bruno Kapsamer, Karl Schedle, Nicole Reisinger, Caroline Emsenhuber, Vladimira Ocelova, Nataliya Roth, Dörte Frieten, Georg Dusel, and et al. 2022. "Evaluation of a Dietary Grape Extract on Oxidative Status, Intestinal Morphology, Plasma Acute-Phase Proteins and Inflammation Parameters of Weaning Piglets at Various Points of Time" Antioxidants 11, no. 8: 1428. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11081428
APA StyleRajković, E., Schwarz, C., Kapsamer, S. B., Schedle, K., Reisinger, N., Emsenhuber, C., Ocelova, V., Roth, N., Frieten, D., Dusel, G., & Gierus, M. (2022). Evaluation of a Dietary Grape Extract on Oxidative Status, Intestinal Morphology, Plasma Acute-Phase Proteins and Inflammation Parameters of Weaning Piglets at Various Points of Time. Antioxidants, 11(8), 1428. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11081428








