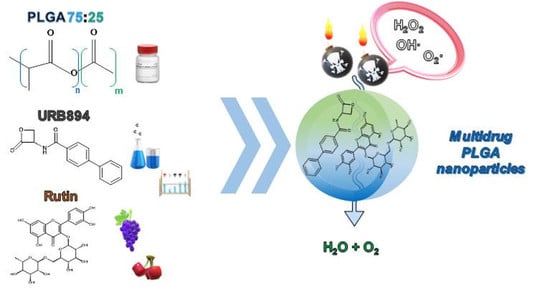
Characterization and Preliminary In Vitro Antioxidant Activity of a New Multidrug Formulation Based on the Co-Encapsulation of Rutin and the α-Acylamino-β-Lactone NAAA Inhibitor URB894 within PLGA Nanoparticles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis and Characterization of URB894
2.3. Preparation of PLGA Nanoparticles
2.4. Physicochemical Characterization
2.5. Evaluation of the Drug Entrapment Efficiency (EE), Loading Capacity (LC) and Release Profiles
2.6. Cell Viability and Treatments
2.7. DPPH Antioxidant Activity
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physicochemical Characterization of PLGA-Based Multidrug Carriers
3.2. Evaluation of the Entrapment Efficiency, Loading Capacity and Release Profiles
3.3. Protection of Human Cells from Hydrogen Peroxide-Induced Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant Activity
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hu, S.-H.; Chen, S.-Y.; Gao, X. Multifunctional nanocapsules for simultaneous encapsulation of hydrophilic and hydrophobic compounds and on-demand release. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 2558–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Han, X.; Fu, Y.; Dai, H.; Wang, H.; Ma, L.; Zhang, Y. Compartmentalized chitooligosaccharide/ferritin particles for controlled co-encapsulation of curcumin and rutin. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 290, 119484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, X.; Zhao, D.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, J.; Yuan, G.; Zhuo, R.; Li, F. A co-delivery system based on a reduction-sensitive polymeric prodrug capable of loading hydrophilic and hydrophobic drugs for combination chemotherapy. Polym. Chem. 2016, 7, 5966–5977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Yan, L.; Chang, M.Y.Z.; Carter, K.A.; Zhang, R.; Slyker, L.; Lovell, J.F.; Wu, Y.; Cheng, C. A multifunctional biodegradable brush polymer-drug conjugate for paclitaxel/gemcitabine co-delivery and tumor imaging. Nanoscale Adv. 2019, 1, 2761–2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Liu, R.; Ji, W.; Li, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhang, X. Delivery systems for theranostics in neurodegenerative diseases. Nano Res. 2018, 11, 5535–5555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maqsoudlou, A.; Assadpour, E.; Mohebodini, H.; Jafari, S.M. Improving the efficiency of natural antioxidant compounds via different nanocarriers. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 278, 102122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poprac, P.; Jomova, K.; Simunkova, M.; Kollar, V.; Rhodes, C.J.; Valko, M. Targeting free radicals in oxidative stress-related human diseases. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 38, 592–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisoschi, A.M.; Pop, A. The role of antioxidants in the chemistry of oxidative stress: A review. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 97, 55–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimse, S.B.; Pal, D. Free radicals, natural antioxidants, and their reaction mechanisms. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 27986–28006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mir, M.; Ahmed, N.; ur Rehman, A. Recent applications of PLGA based nanostructures in drug delivery. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 159, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Operti, M.C.; Bernhardt, A.; Grimm, S.; Engel, A.; Figdor, C.G.; Tagit, O. PLGA-based nanomedicines manufacturing: Technologies overview and challenges in industrial scale-up. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 605, 120807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gullón, B.; Lú-Chau, T.A.; Moreira, M.T.; Lema, J.M.; Eibes, G. Rutin: A review on extraction, identification and purification methods, biological activities and approaches to enhance its bioavailability. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 67, 220–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negahdari, R.; Bohlouli, S.; Sharifi, S.; Maleki Dizaj, S.; Rahbar Saadat, Y.; Khezri, K.; Jafari, S.; Ahmadian, E.; Gorbani Jahandizi, N.; Raeesi, S. Therapeutic benefits of rutin and its nanoformulations. Phytother. Res. 2021, 35, 1719–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishak, R.A.H.; Mostafa, N.M.; Kamel, A.O. Stealth lipid polymer hybrid nanoparticles loaded with rutin for effective brain delivery–comparative study with the gold standard (Tween 80): Optimization, characterization and biodistribution. Drug Deliv. 2017, 24, 1874–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kızılbey, K. Optimization of rutin-loaded PLGA nanoparticles synthesized by single-emulsion solvent evaporation method. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Júlio, A.; Caparica, R.; Costa Lima, S.A.; Fernandes, A.S.; Rosado, C.; Prazeres, D.M.F.; Reis, S.; Santos de Almeida, T.; Fonte, P. Ionic liquid-polymer nanoparticle hybrid systems as new tools to deliver poorly soluble drugs. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vu, H.T.H.; Streck, S.; Hook, S.M.; McDowell, A. Utilization of microfluidics for the preparation of polymeric nanoparticles for the antioxidant rutin: A comparison with bulk production. Pharm. Nanotechnol. 2019, 7, 469–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, P.; Rahman, M.; Bhatt, P.C.; Beg, S.; Paul, B.; Hafeez, A.; Al-Abbasi, F.A.; Nadeem, M.S.; Baothman, O.; Anwar, F. Implication of nano-antioxidant therapy for treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma using PLGA nanoparticles of rutin. Nanomedicine 2018, 13, 849–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagliardi, A.; Molinaro, R.; Fresta, M.; Duranti, A.; Cosco, D. α-Acylamino-β-lactone N-acylethanolamine-hydrolyzing acid amidase inhibitors encapsulated in PLGA nanoparticles: Improvement of the physical stability and protection of human cells from hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo Verme, J.; Fu, J.; Astarita, G.; La Rana, G.; Russo, R.; Calignano, A.; Piomelli, D. The nuclear receptor peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α mediates the anti-inflammatory actions of palmitoylethanolamide. Mol. Pharmacol. 2005, 67, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solorzano, C.; Zhu, C.; Battista, N.; Astarita, G.; Lodola, A.; Rivara, S.; Mor, M.; Russo, R.; Maccarrone, M.; Antonietti, F. Selective N-acylethanolamine-hydrolyzing acid amidase inhibition reveals a key role for endogenous palmitoylethanolamide in inflammation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 20966–20971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sasso, O.; Moreno-Sanz, G.; Martucci, C.; Realini, N.; Dionisi, M.; Mengatto, L.; Duranti, A.; Tarozzo, G.; Tarzia, G.; Mor, M. Antinociceptive effects of the N-acylethanolamine acid amidase inhibitor ARN077 in rodent pain models. Pain 2013, 154, 350–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Solorzano, C.; Antonietti, F.; Duranti, A.; Tontini, A.; Rivara, S.; Lodola, A.; Vacondio, F.; Tarzia, G.; Piomelli, D.; Mor, M. Synthesis and structure−activity relationships of N-(2-oxo-3-oxetanyl)amides as N-acylethanolamine-hydrolyzing acid amidase inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 5770–5781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gagliardi, A.; Paolino, D.; Costa, N.; Fresta, M.; Cosco, D. Zein-vs PLGA-based nanoparticles containing rutin: A comparative investigation. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 118, 111538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimenez-Rota, C.; Palazzo, I.; Scognamiglio, M.R.; Mainar, A.; Reverchon, E.; Della Porta, G. β-Carotene, α-tocoferol and rosmarinic acid encapsulated within PLA/PLGA microcarriers by supercritical emulsion extraction: Encapsulation efficiency, drugs shelf-life and antioxidant activity. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2019, 146, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano, A.; Ettcheto, M.; Chang, J.-H.; Barroso, E.; Espina, M.; Kühne, B.A.; Barenys, M.; Auladell, C.; Folch, J.; Souto, E.B. Dual-drug loaded nanoparticles of Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG)/Ascorbic acid enhance therapeutic efficacy of EGCG in a APPswe/PS1dE9 Alzheimer’s disease mice model. J. Control. Release 2019, 301, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggisano, V.; Celano, M.; Malivindi, R.; Barone, I.; Cosco, D.; Mio, C.; Mignogna, C.; Panza, S.; Damante, G.; Fresta, M. Nanoparticles loaded with the BET inhibitor JQ1 block the growth of triple negative breast cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Cancers 2019, 12, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Voci, S.; Gagliardi, A.; Salvatici, M.C.; Fresta, M.; Cosco, D. Development of polyoxyethylene (2) oleyl ether-gliadin nanoparticles: Characterization and in vitro cytotoxicity. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 162, 105849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuliano, E.; Paolino, D.; Cristiano, M.C.; Fresta, M.; Cosco, D. Rutin-Loaded Poloxamer 407-Based Hydrogels for In Situ Administration: Stability Profiles and Rheological Properties. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosco, D.; Failla, P.; Costa, N.; Pullano, S.; Fiorillo, A.; Mollace, V.; Fresta, M.; Paolino, D. Rutin-loaded chitosan microspheres: Characterization and evaluation of the anti-inflammatory activity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 152, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardi, M.; Brocchini, S.; Somavarapu, S.; Procopio, A. Hydroxytyrosol oleate: A promising neuroprotective nanocarrier delivery system of oleuropein and derivatives. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 631, 122498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lombardo, G.E.; Maggisano, V.; Celano, M.; Cosco, D.; Mignogna, C.; Baldan, F.; Lepore, S.M.; Allegri, L.; Moretti, S.; Durante, C. Anti-hTERT siRNA-loaded nanoparticles block the growth of anaplastic thyroid cancer xenograft. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2018, 17, 1187–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cosco, D.; Mare, R.; Paolino, D.; Salvatici, M.C.; Cilurzo, F.; Fresta, M. Sclareol-loaded hyaluronan-coated PLGA nanoparticles: Physico-chemical properties and in vitro anticancer features. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 132, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deepika, M.S.; Thangam, R.; Sheena, T.S.; Vimala, R.T.V.; Sivasubramanian, S.; Jeganathan, K.; Thirumurugan, R. Dual drug loaded PLGA nanospheres for synergistic efficacy in breast cancer therapy. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 103, 109716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zerrillo, L.; Gigliobianco, M.R.; D’Atri, D.; Garcia, J.P.; Baldazzi, F.; Ridwan, Y.; Fuentes, G.; Chan, A.; Creemers, L.B.; Censi, R. PLGA nanoparticles grafted with hyaluronic acid to improve site-specificity and drug dose delivery in osteoarthritis nanotherapy. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota, A.H.; Duarte, N.; Serra, A.T.; Ferreira, A.; Bronze, M.R.; Custódio, L.; Gaspar, M.M.; Simões, S.; Rijo, P.; Ascensão, L.; et al. Further Evidence of Possible Therapeutic Uses of Sambucus nigra L. Extracts by the Assessment of the In Vitro and In Vivo Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Its PLGA and PCL-Based Nanoformulations. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djiokeng Paka, G.; Doggui, S.; Zaghmi, A.; Safar, R.; Dao, L.; Reisch, A.; Klymchenko, A.; Roullin, V.G.; Joubert, O.; Ramassamy, C. Neuronal uptake and neuroprotective properties of curcumin-loaded nanoparticles on SK-N-SH cell line: Role of poly (lactide-co-glycolide) polymeric matrix composition. Mol. Pharm. 2016, 13, 391–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platel, A.; Carpentier, R.; Becart, E.; Mordacq, G.; Betbeder, D.; Nesslany, F. Influence of the surface charge of PLGA nanoparticles on their in vitro genotoxicity, cytotoxicity, ROS production and endocytosis. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2016, 36, 434–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, A.; Esendagli, G.; Yerlikaya, F.; Caban-Toktas, S.; Yoyen-Ermis, D.; Horzum, U.; Aktas, Y.; Khan, M.; Couvreur, P.; Capan, Y. A small variation in average particle size of PLGA nanoparticles prepared by nanoprecipitation leads to considerable change in nanoparticles’ characteristics and efficacy of intracellular delivery. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2017, 45, 1657–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Q.; Karthivashan, G.; Nakhaei-Nejad, M.; Anand, B.G.; Giuliani, F.; Kar, S. Native PLGA nanoparticles regulate APP metabolism and protect neurons against β-amyloid toxicity: Potential significance in Alzheimer’s disease pathology. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 219, 1180–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duranti, A.; Tontini, A.; Antonietti, F.; Vacondio, F.; Fioni, A.; Silva, C.; Lodola, A.; Rivara, S.; Solorzano, C.; Piomelli, D. N-(2-Oxo-3-oxetanyl)carbamic acid esters as N-acylethanolamine acid amidase inhibitors: Synthesis and structure–activity and structure–property relationships. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 4824–4836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Checa, J.; Aran, J.M. Reactive oxygen species: Drivers of physiological and pathological processes. J. Inflamm. Res. 2020, 13, 1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Huang, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, L.; Li, Y.; Gong, Z.; Ai, K. Harnessing reactive oxygen/nitrogen species and inflammation: Nanodrugs for liver injury. Mater. Today Bio 2022, 13, 100215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, H.; Ku, S.-K.; Baek, Y.-D.; Bae, J.-S. Anti-inflammatory effects of rutin on HMGB1-induced inflammatory responses in vitro and in vivo. Inflamm. Res. 2014, 63, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mascaraque, C.; Aranda, C.; Ocón, B.; Monte, M.J.; Suárez, M.D.; Zarzuelo, A.; Marín, J.J.G.; Martínez-Augustin, O.; de Medina, F.S. Rutin has intestinal antiinflammatory effects in the CD4+ CD62L+ T cell transfer model of colitis. Pharmacol. Res. 2014, 90, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, S.; Dai, C.; Lang, F.; Hu, L.; Tang, Q.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Hao, Z. Rutin attenuates vancomycin-induced nephrotoxicity by ameliorating oxidative stress, apoptosis, and inflammation in rats. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, e01545-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| URB894 (mg/mL) | Rutin (mg/mL) | Mean Sizes (nm) | Polydispersity Index | Zeta Potential (mV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | - | 110 ± 2 | 0.06 ± 0.01 | −32 ± 1 |
| 0.2 | - | 134 ± 2 * | 0.19 ± 0.02 * | −34 ± 1 |
| 0.4 | - | 170 ± 1 ** | 0.25 ± 0.03 ** | −32 ± 2 |
| 0.6 | - | 196 ± 3 ** | 0.32 ± 0.05 ** | −33 ± 2 |
| - | 0.2 | 115 ± 6 | 0.14 ± 0.01 ** | −32 ± 1 |
| - | 0.4 | 132 ± 6 * | 0.18 ± 0.08 | −28 ± 2 |
| - | 0.6 | 141 ± 5 * | 0.24 ± 0.04 | −31 ± 2 |
| - | 0.8 | 314 ± 4 ** | 0.36 ± 0.01 | −29 ±3 |
| 0.4 | 0.2 | 119 ± 2 | 0.19 ± 0.03 | −31 ± 2 |
| 0.4 | 0.4 | 142 ± 1 | 0.18 ± 0.05 | −27 ± 1 |
| 0.4 | 0.6 | 150 ± 2 * | 0.19± 0.07 * | −29 ± 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gagliardi, A.; Voci, S.; Ambrosio, N.; Fresta, M.; Duranti, A.; Cosco, D. Characterization and Preliminary In Vitro Antioxidant Activity of a New Multidrug Formulation Based on the Co-Encapsulation of Rutin and the α-Acylamino-β-Lactone NAAA Inhibitor URB894 within PLGA Nanoparticles. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 305. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12020305
Gagliardi A, Voci S, Ambrosio N, Fresta M, Duranti A, Cosco D. Characterization and Preliminary In Vitro Antioxidant Activity of a New Multidrug Formulation Based on the Co-Encapsulation of Rutin and the α-Acylamino-β-Lactone NAAA Inhibitor URB894 within PLGA Nanoparticles. Antioxidants. 2023; 12(2):305. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12020305
Chicago/Turabian StyleGagliardi, Agnese, Silvia Voci, Nicola Ambrosio, Massimo Fresta, Andrea Duranti, and Donato Cosco. 2023. "Characterization and Preliminary In Vitro Antioxidant Activity of a New Multidrug Formulation Based on the Co-Encapsulation of Rutin and the α-Acylamino-β-Lactone NAAA Inhibitor URB894 within PLGA Nanoparticles" Antioxidants 12, no. 2: 305. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12020305
APA StyleGagliardi, A., Voci, S., Ambrosio, N., Fresta, M., Duranti, A., & Cosco, D. (2023). Characterization and Preliminary In Vitro Antioxidant Activity of a New Multidrug Formulation Based on the Co-Encapsulation of Rutin and the α-Acylamino-β-Lactone NAAA Inhibitor URB894 within PLGA Nanoparticles. Antioxidants, 12(2), 305. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12020305