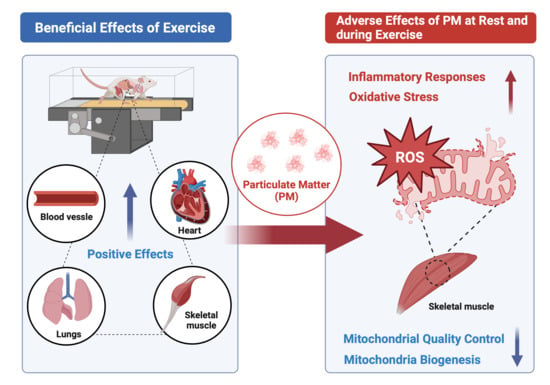
Effects of Particulate Matter Inhalation during Exercise on Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial Function in Mouse Skeletal Muscle
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Animals
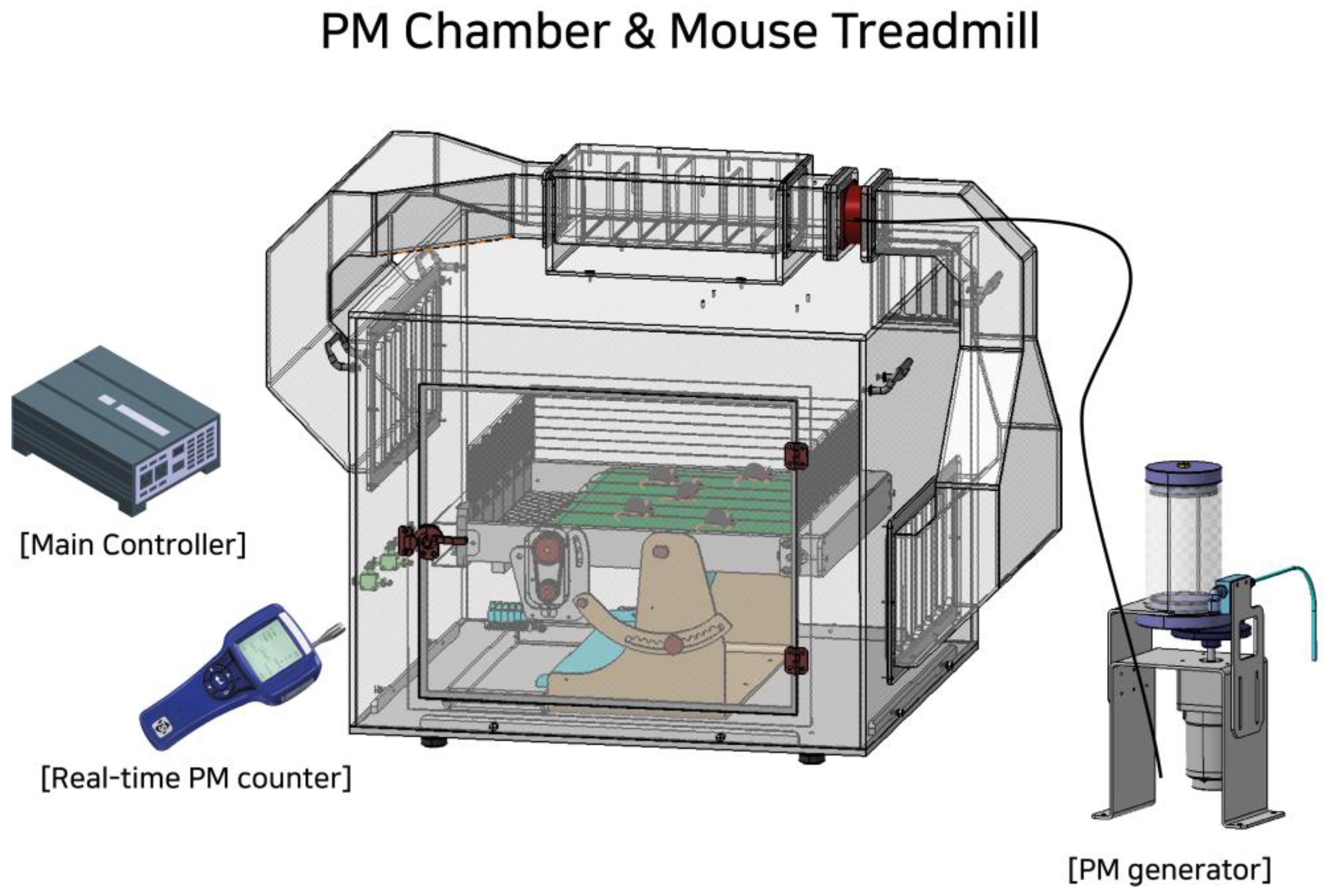
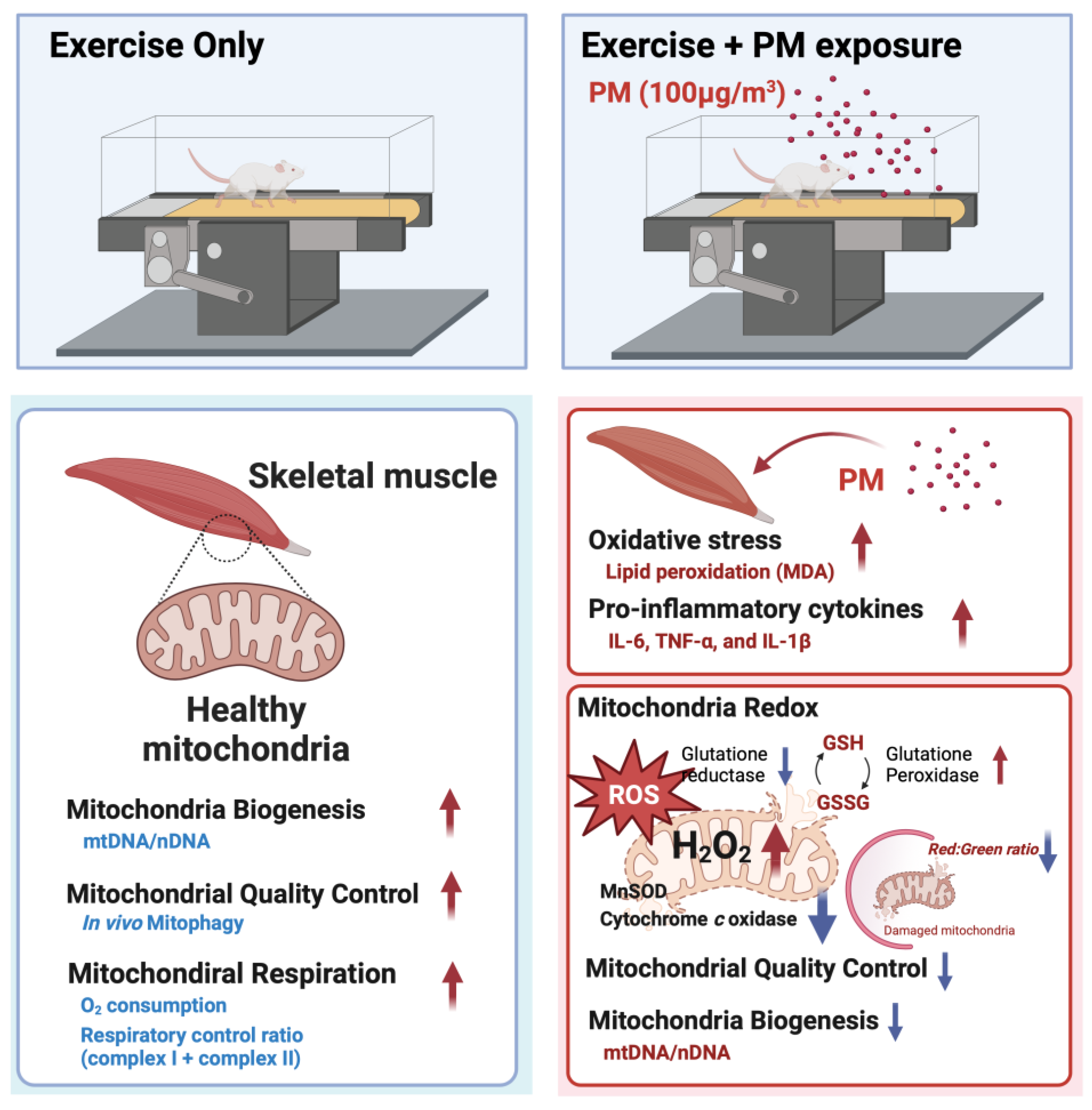
2.2. PM Chamber and Treadmill Exercise
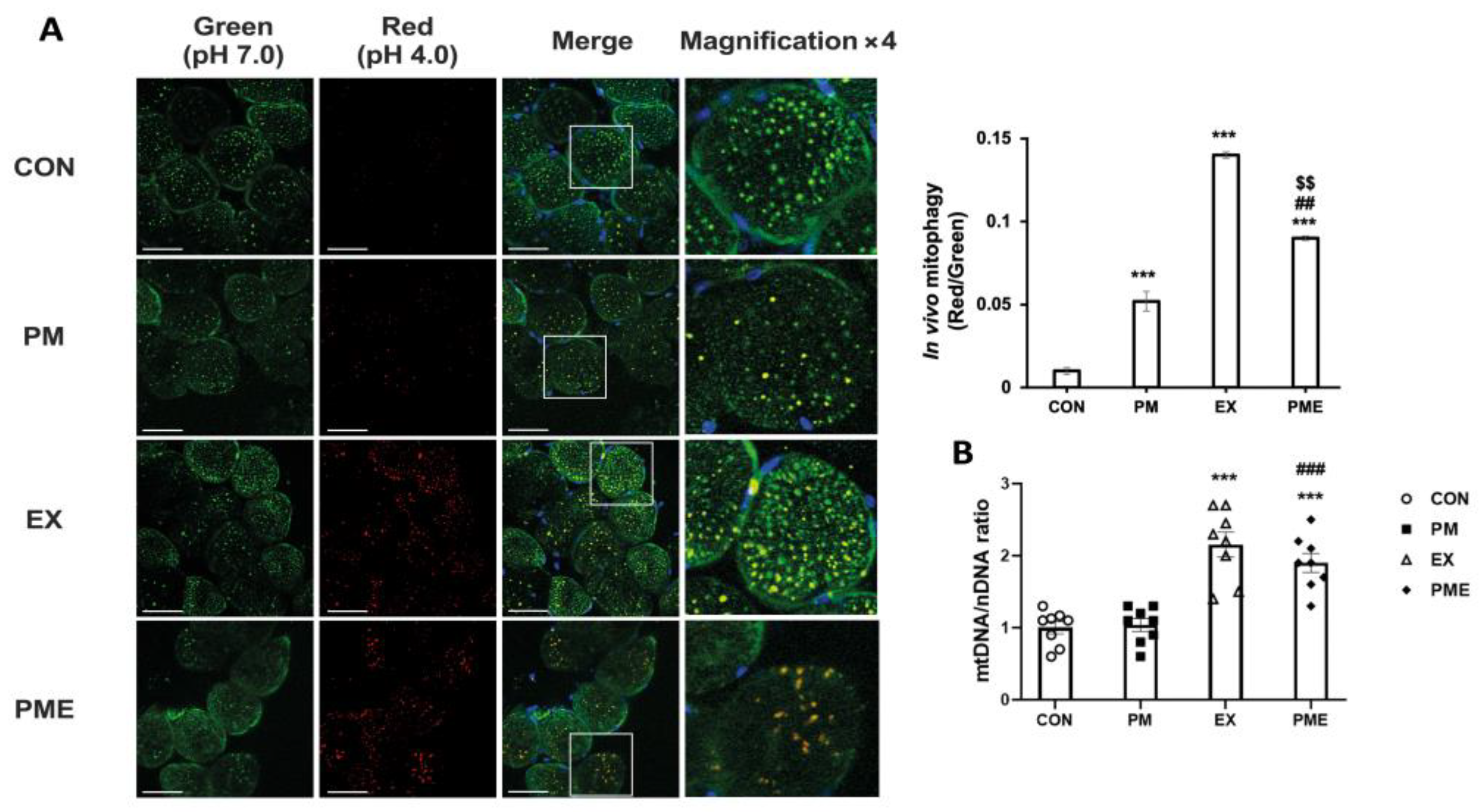
2.3. In Vivo Mitophagy Analysis
2.4. Quantification of Mitochondrial DNA
2.5. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
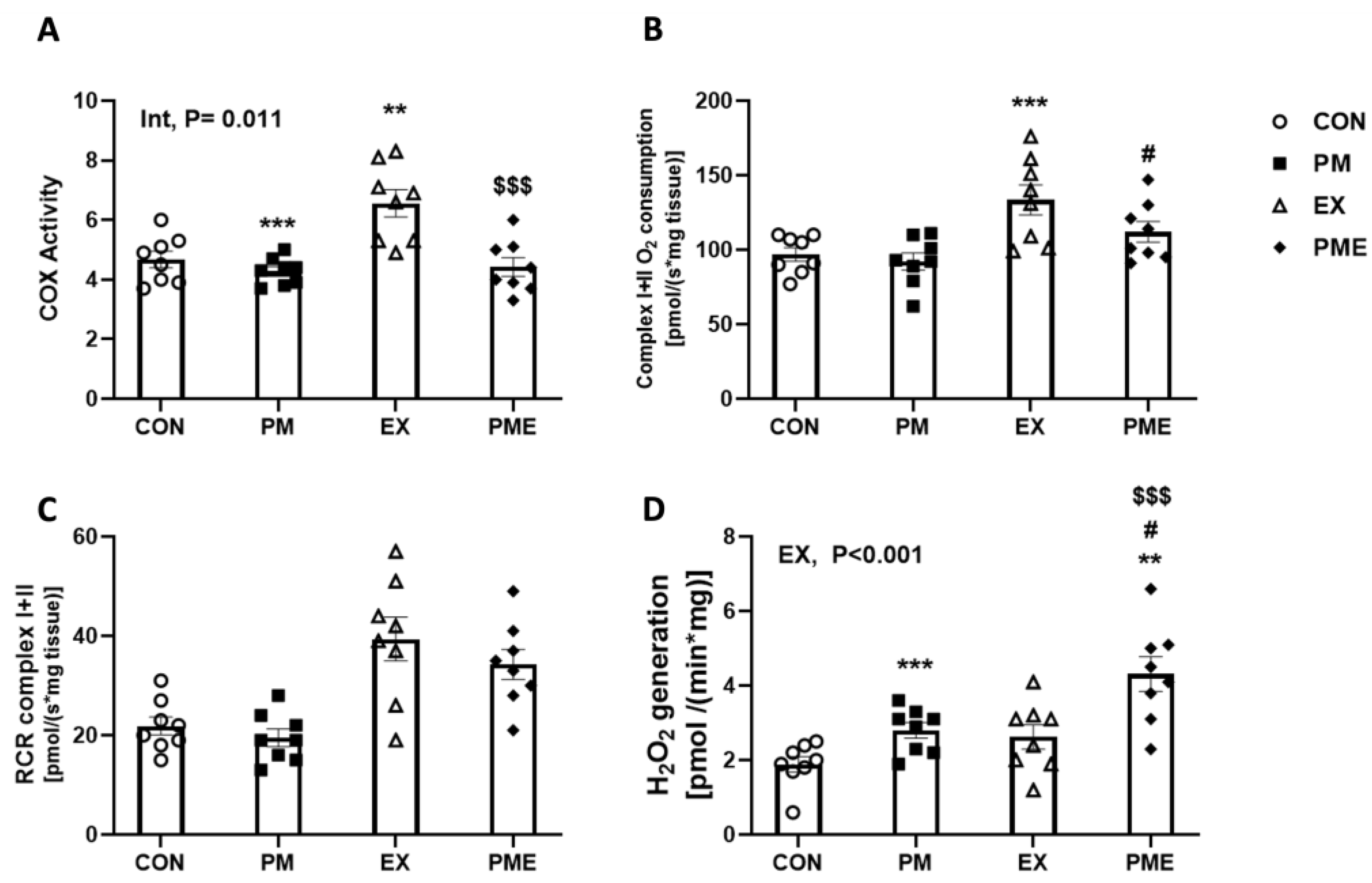
2.6. Permeabilization of Muscle Fibers and Measurement of Respiration and H2O2 Generation
2.7. Cyclooxygenase (COX) Activity Assay
2.8. Malondialdehyde (MDA) Measurements
2.9. Glutathione/Oxidized Glutathione Assay
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shah, A.S.; Langrish, J.P.; Nair, H.; McAllister, D.A.; Hunter, A.L.; Donaldson, K.; Newby, D.E.; Mills, N.L. Global association of air pollution and heart failure: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 2013, 382, 1039–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Harrison, R.M.; Feng, Y.; Shi, Z.; Liang, Y.; Li, Y.; Xue, Q.; Xu, J. Size-resolved source apportionment of particulate matter from a megacity in northern China based on one-year measurement of inorganic and organic components. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 289, 117932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agency, U.E.P. National ambient air quality standards for particulate matter. Fed. Regist. 1997, 62, 138. [Google Scholar]
- Dockery, D.W.; Pope, C.A., 3rd. Acute respiratory effects of particulate air pollution. Annu. Rev. Public Health 1994, 15, 107–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prahalad, A.K.; Inmon, J.; Dailey, L.A.; Madden, M.C.; Ghio, A.J.; Gallagher, J.E. Air pollution particles mediated oxidative DNA base damage in a cell free system and in human airway epithelial cells in relation to particulate metal content and bioreactivity. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2001, 14, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Liu, J.; Zeng, H. Interactions of particulate matter and pulmonary surfactant: Implications for human health. Adv. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2020, 284, 102244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajagopalan, S.; Brook, R.D. Air pollution and type 2 diabetes: Mechanistic insights. Diabetes 2012, 61, 3037–3045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, C.A.; Bhatnagar, A.; McCracken, J.P.; Abplanalp, W.; Conklin, D.J.; O’Toole, T. Exposure to Fine Particulate Air Pollution Is Associated with Endothelial Injury and Systemic Inflammation. Circ. Res. 2016, 119, 1204–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haberzettl, P.; Bhatnagar, A.; Conklin, D.J. Particulate Matter and Oxidative Stress—Pulmonary and Cardiovascular Targets and Consequences. In Systems Biology of Free Radicals and Antioxidants; Laher, I., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 1557–1586. [Google Scholar]
- Schraufnagel, D.E.; Balmes, J.R.; Cowl, C.T.; De Matteis, S.; Jung, S.H.; Mortimer, K.; Perez-Padilla, R.; Rice, M.B.; Riojas-Rodriguez, H.; Sood, A.; et al. Air Pollution and Noncommunicable Diseases: A Review by the Forum of International Respiratory Societies’ Environmental Committee, Part 2: Air Pollution and Organ Systems. Chest 2019, 155, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Mahendran, R.; Yu, P.; Xu, R.; Yu, W.; Godellawattage, S.; Li, S.; Guo, Y. Health Effects of Long-Term Exposure to Ambient PM(2.5) in Asia-Pacific: A Systematic Review of Cohort Studies. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2022, 9, 130–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- To, T.; Zhu, J.; Villeneuve, P.J.; Simatovic, J.; Feldman, L.; Gao, C.; Williams, D.; Chen, H.; Weichenthal, S.; Wall, C.; et al. Chronic disease prevalence in women and air pollution—A 30-year longitudinal cohort study. Environ. Int. 2015, 80, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Huang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Wang, X. The pathophysiological and molecular mechanisms of atmospheric PM2.5 affecting cardiovascular health: A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 249, 114444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iizuka, K.; Machida, T.; Hirafuji, M. Skeletal muscle is an endocrine organ. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2014, 125, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.C. The role of in vitro gene expression profiling in particulate matter health research. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health B Crit. Rev. 2013, 16, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyth, T.; Georas, S.N. Effects of ozone and particulate matter on airway epithelial barrier structure and function: A review of in vitro and in vivo studies. Inhal. Toxicol. 2021, 33, 177–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valderrama, A.; Ortiz-Hernández, P.; Agraz-Cibrián, J.M.; Tabares-Guevara, J.H.; Gómez, D.M.; Zambrano-Zaragoza, J.F.; Taborda, N.A.; Hernandez, J.C. Particulate matter (PM(10)) induces in vitro activation of human neutrophils, and lung histopathological alterations in a mouse model. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 7581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garber, C.E.; Blissmer, B.; Deschenes, M.R.; Franklin, B.A.; Lamonte, M.J.; Lee, I.M.; Nieman, D.C.; Swain, D.P. American College of Sports Medicine position stand. Quantity and quality of exercise for developing and maintaining cardiorespiratory, musculoskeletal, and neuromotor fitness in apparently healthy adults: Guidance for prescribing exercise. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2011, 43, 1334–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, F.; Li, J.; Liu, Z.; Chuang, C.C.; Yang, W.; Zuo, L. Redox Mechanism of Reactive Oxygen Species in Exercise. Front. Physiol. 2016, 7, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.; Tominaga, T.; Ruhee, R.T.; Ma, S. Characterization and Modulation of Systemic Inflammatory Response to Exhaustive Exercise in Relation to Oxidative Stress. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Xu, Q.; Newland, B.; Foley, R.; Lara-Sáez, I.; Curtin, J.F.; Wang, W. Reactive oxygen species (ROS): Utilizing injectable antioxidative hydrogels and ROS-producing therapies to manage the double-edged sword. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 6326–6346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schippinger, G.; Wonisch, W.; Abuja, P.M.; Fankhauser, F.; Winklhofer-Roob, B.M.; Halwachs, G. Lipid peroxidation and antioxidant status in professional American football players during competition. Eur. J. Clin. Invest. 2002, 32, 686–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincent, H.K.; Powers, S.K.; Demirel, H.A.; Coombes, J.S.; Naito, H. Exercise training protects against contraction-induced lipid peroxidation in the diaphragm. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. Occup. Physiol. 1999, 79, 268–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincent, H.K.; Powers, S.K.; Stewart, D.J.; Demirel, H.A.; Shanely, R.A.; Naito, H. Short-term exercise training improves diaphragm antioxidant capacity and endurance. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2000, 81, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothschild, J.A.; Bishop, D.J. Effects of dietary supplements on adaptations to endurance training. Sports Med. 2020, 50, 25–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battaglia, A.M.; Chirillo, R.; Aversa, I.; Sacco, A.; Costanzo, F.; Biamonte, F. Ferroptosis and Cancer: Mitochondria Meet the “Iron Maiden” Cell Death. Cells 2020, 9, 1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Y.; Zhu, G.; Zhu, M.; Song, J.; Cai, H.; Song, Y.; Wang, J.; Jin, M. Edaravone Attenuated Particulate Matter-Induced Lung Inflammation by Inhibiting ROS-NF-κB Signaling Pathway. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2022, 2022, 6908884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marmett, B.; Pires Dorneles, G.; Böek Carvalho, R.; Peres, A.; Roosevelt Torres Romão, P.; Barcos Nunes, R.; Ramos Rhoden, C. Air pollution concentration and period of the day modulates inhalation of PM(2.5) during moderate- and high-intensity interval exercise. Environ. Res. 2021, 194, 110528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Jia, Z.; Ping, Y.; Liu, Z.; Yan, X.; Xing, G.; Yan, W. Testosterone alleviates mitochondrial ROS accumulation and mitochondria-mediated apoptosis in the gastric mucosa of orchiectomized rats. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2018, 649, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tostes, R.C.; Carneiro, F.S.; Carvalho, M.H.; Reckelhoff, J.F. Reactive oxygen species: Players in the cardiovascular effects of testosterone. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2016, 310, R1–R14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katayama, H.; Kogure, T.; Mizushima, N.; Yoshimori, T.; Miyawaki, A. A sensitive and quantitative technique for detecting autophagic events based on lysosomal delivery. Chem. Biol. 2011, 18, 1042–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, N.; Yun, J.; Liu, J.; Malide, D.; Liu, C.; Rovira, I.I.; Holmström, K.M.; Fergusson, M.M.; Yoo, Y.H.; Combs, C.A.; et al. Measuring In Vivo Mitophagy. Mol. Cell 2015, 60, 685–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czyżowska, A.; Brown, J.; Xu, H.; Sataranatarajan, K.; Kinter, M.; Tyrell, V.J.; O’Donnell, V.B.; Van Remmen, H. Elevated phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase (GPX4) expression modulates oxylipin formation and inhibits age-related skeletal muscle atrophy and weakness. Redox Biol. 2023, 64, 102761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, C.C.; Hsieh, W.Y.; Tsai, C.H.; Chen, C.Y.; Chang, H.F.; Lin, C.S. In Vitro and In Vivo Experimental Studies of PM(2.5) on Disease Progression. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dey, S.K.; Sugur, K.; Venkatareddy, V.G.; Rajeev, P.; Gupta, T.; Thimmulappa, R.K. Lipid peroxidation index of particulate matter: Novel metric for quantifying intrinsic oxidative potential and predicting toxic responses. Redox Biol. 2021, 48, 102189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberdörster, G.; Sharp, Z.; Atudorei, V.; Elder, A.; Gelein, R.; Lunts, A.; Kreyling, W.; Cox, C. Extrapulmonary translocation of ultrafine carbon particles following whole-body inhalation exposure of rats. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health. Part A 2002, 65, 1531–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, L.N.; Aung, H.; Lamé, M.; Wegesser, T.; Wilson, D. Fine particulate matter from urban ambient and wildfire sources from California’s San Joaquin Valley initiate differential inflammatory, oxidative stress, and xenobiotic responses in human bronchial epithelial cells. Toxicol. Vitr. 2011, 25, 1895–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phaniendra, A.; Jestadi, D.B.; Periyasamy, L. Free radicals: Properties, sources, targets, and their implication in various diseases. Indian. J. Clin. Biochem. 2015, 30, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, S.K.; Nelson, W.B.; Hudson, M.B. Exercise-induced oxidative stress in humans: Cause and consequences. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2011, 51, 942–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, S.K.; Goldstein, E.; Schrager, M.; Ji, L.L. Exercise Training and Skeletal Muscle Antioxidant Enzymes: An Update. Antioxidants 2022, 12, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.-A.; Lee, J.-H.; Song, W.; Jun, T.-W. Exercise training improves the antioxidant enzyme activity with no changes of telomere length. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2008, 129, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghozikali, M.G.; Ansarin, K.; Naddafi, K.; Nabizadeh, R.; Yaghmaeian, K.; Jaafari, J.; Dehghanzadeh, R.; Atafar, Z.; Faraji, M.; Mohammadi, A.; et al. Status of TNF-α and IL-6 as pro-inflammatory cytokines in exhaled breath condensate of late adolescents with asthma and healthy in the dust storm and non-dust storm conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 155536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, D.H.; Amyai, N.; Marques-Vidal, P.; Wang, J.L.; Riediker, M.; Mooser, V.; Paccaud, F.; Waeber, G.; Vollenweider, P.; Bochud, M. Effects of particulate matter on inflammatory markers in the general adult population. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2012, 9, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, A.; Oldham, M.; Becaria, A.; Bondy, S.C.; Meacher, D.; Sioutas, C.; Misra, C.; Mendez, L.B.; Kleinman, M. Particulate matter in polluted air may increase biomarkers of inflammation in mouse brain. Neurotoxicology 2005, 26, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Huang, J.; Wang, L.; Chen, C.; Yang, D.; Jin, M.; Bai, C.; Song, Y. Urban particulate matter triggers lung inflammation via the ROS-MAPK-NF-κB signaling pathway. J. Thorac. Dis. 2017, 9, 4398–4412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.-S.; Lai, C.-S.; Chang-Chien, G.-P.; Tseng, Y.-L.; Cheng, F.-J. Kidney damage induced by repeated fine particulate matter exposure: Effects of different components. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 847, 157528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peake, J.M.; Della Gatta, P.; Suzuki, K.; Nieman, D.C. Cytokine expression and secretion by skeletal muscle cells: Regulatory mechanisms and exercise effects. Exerc. Immunol. Rev. 2015, 21, 8–25. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, B.; Dabur, R. Role of Pro-inflammatory Cytokines in Regulation of Skeletal Muscle Metabolism: A Systematic Review. Curr. Med. Chem. 2020, 27, 2161–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Bai, S.; Ding, S.; Zhao, L.; Xu, S.; Wang, X. PM2.5 Exposure Induces Lung Injury and Fibrosis by Regulating Ferroptosis via TGF-β Signaling. Dis. Markers 2022, 2022, 7098463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Shen, X.; Liu, J.; Wu, C.; Gao, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, F.; Ding, W.; Lu, Z. The effect of exposure time and concentration of airborne PM2.5 on lung injury in mice: A transcriptome analysis. Redox Biol. 2019, 26, 101264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damluji, A.A.; Alfaraidhy, M.; AlHajri, N.; Rohant, N.N.; Kumar, M.; Al Malouf, C.; Bahrainy, S.; Ji Kwak, M.; Batchelor, W.B.; Forman, D.E.; et al. Sarcopenia and Cardiovascular Diseases. Circulation 2023, 147, 1534–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Southern, W.M.; Ryan, T.E.; Kepple, K.; Murrow, J.R.; Nilsson, K.R.; McCully, K.K. Reduced skeletal muscle oxidative capacity and impaired training adaptations in heart failure. Physiol. Rep. 2015, 3, e12353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanello, V.; Sandri, M. Mitochondria Quality Control and Muscle Mass Maintenance. Front. Physiol. 2016, 6, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantas, W.S.; Zunica, E.R.M.; Heintz, E.C.; Vandanmagsar, B.; Floyd, Z.E.; Yu, Y.; Fujioka, H.; Hoppel, C.L.; Belmont, K.P.; Axelrod, C.L.; et al. Mitochondrial uncoupling attenuates sarcopenic obesity by enhancing skeletal muscle mitophagy and quality control. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2022, 13, 1821–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sligar, J.; DeBruin, D.A.; Saner, N.J.; Philp, A.M.; Philp, A. The importance of mitochondrial quality control for maintaining skeletal muscle function across health span. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2022, 322, C461–C467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.N.; Tian, H.; Chen, P.; Wang, D.; Ren, J.; Zhang, Y. Physical Exercise and Selective Autophagy: Benefit and Risk on Cardiovascular Health. Cells 2019, 8, 1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.C.W.; Erlich, A.T.; Hood, D.A. Role of Parkin and endurance training on mitochondrial turnover in skeletal muscle. Skelet. Muscle 2018, 8, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Drake, J.C.; Yan, Z. Exercise-Induced Mitophagy in Skeletal Muscle and Heart. Exerc. Sport. Sci. Rev. 2019, 47, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, J.; Jang, J.; So, B.; Lee, K.; Yeom, D.; Zhang, Z.; Shin, W.S.; Kang, C. Effects of Particulate Matter Inhalation during Exercise on Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial Function in Mouse Skeletal Muscle. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox13010113
Park J, Jang J, So B, Lee K, Yeom D, Zhang Z, Shin WS, Kang C. Effects of Particulate Matter Inhalation during Exercise on Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial Function in Mouse Skeletal Muscle. Antioxidants. 2024; 13(1):113. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox13010113
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Jinhan, Junho Jang, Byunghun So, Kanggyu Lee, Dongjin Yeom, Ziyi Zhang, Woo Shik Shin, and Chounghun Kang. 2024. "Effects of Particulate Matter Inhalation during Exercise on Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial Function in Mouse Skeletal Muscle" Antioxidants 13, no. 1: 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox13010113
APA StylePark, J., Jang, J., So, B., Lee, K., Yeom, D., Zhang, Z., Shin, W. S., & Kang, C. (2024). Effects of Particulate Matter Inhalation during Exercise on Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial Function in Mouse Skeletal Muscle. Antioxidants, 13(1), 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox13010113