Taurine Chloramine-Mediated Nrf2 Activation and HO-1 Induction Confer Protective Effects in Astrocytes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. C6 Cell Culture and Tau-Cl Treatment
2.2. Nuclear and Cytoplasmic Extract Preparation
2.3. Immunoblotting
2.4. Immunocytochemistry
2.5. Modification of the Thiol Groups of Keap1 by Tau-Cl
2.6. Reaction of the Thiol Groups of Keap1 with Tau-Cl
2.7. Cell Viability Assay
2.8. siRNA Transfection
2.9. Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Quantification
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
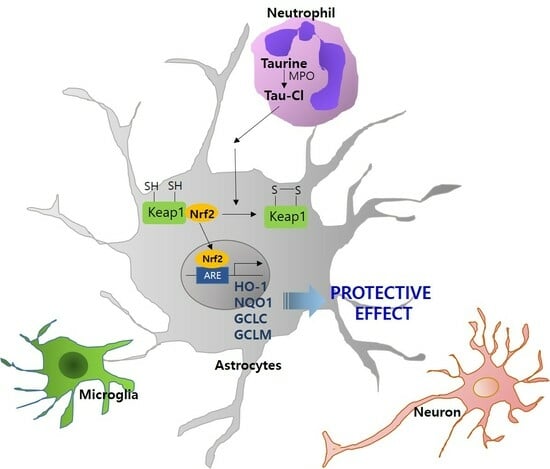
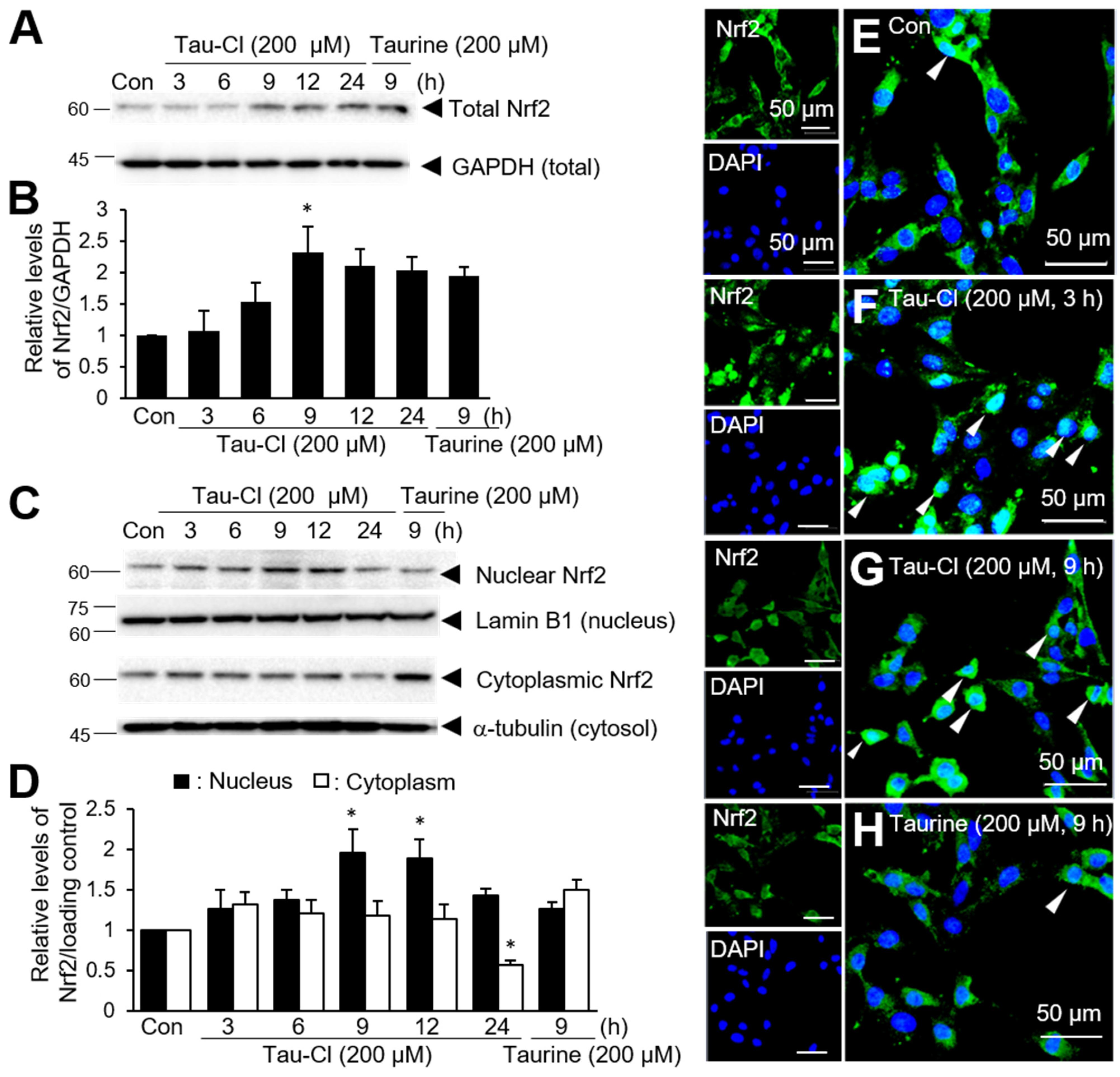
3.1. Tau-Cl Enhances the Expression and Nuclear Translocation of Nrf2 in C6 Cells
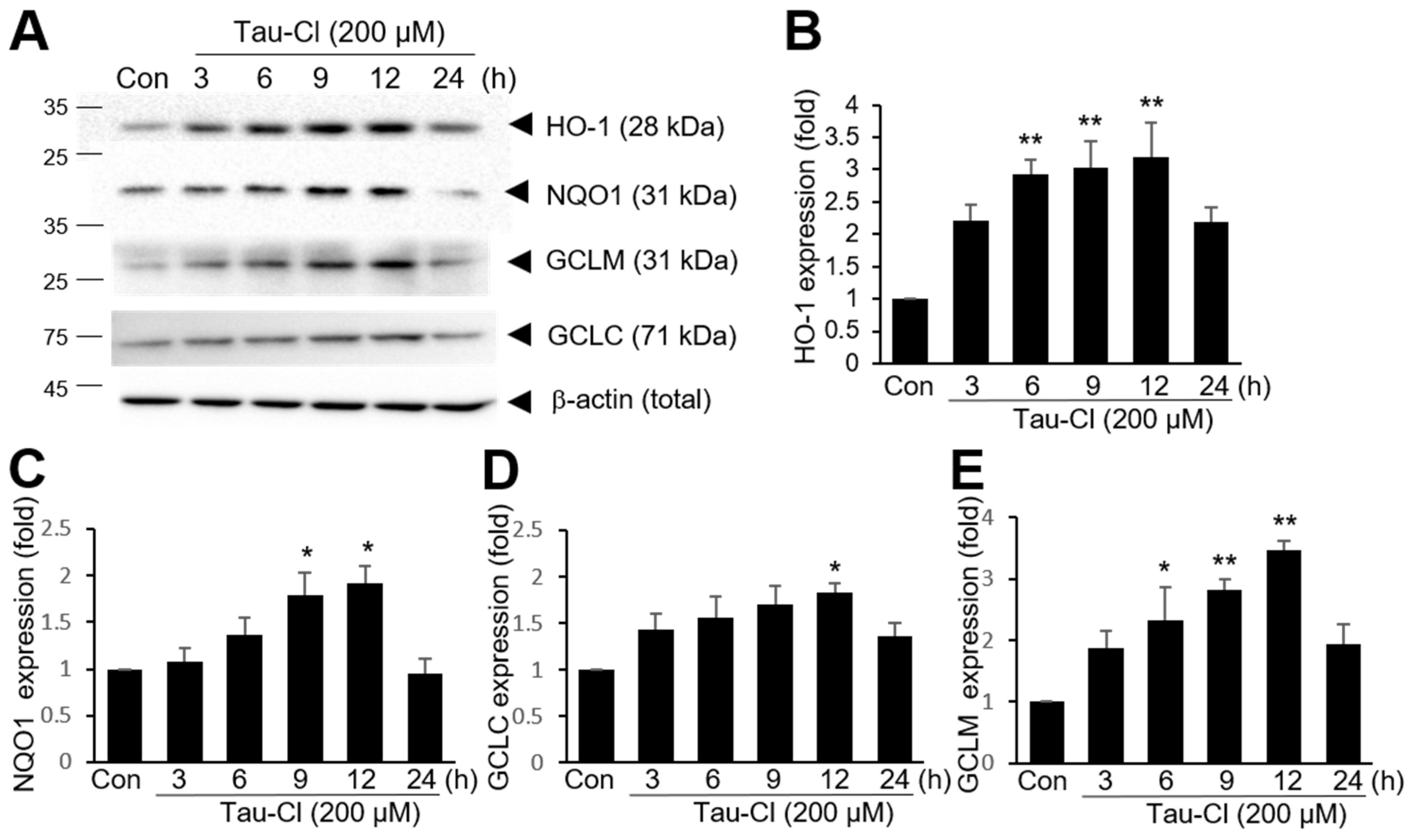
3.2. Tau-Cl Induces the Upregulation of Various Antioxidant Enzymes Downstream of Nrf2
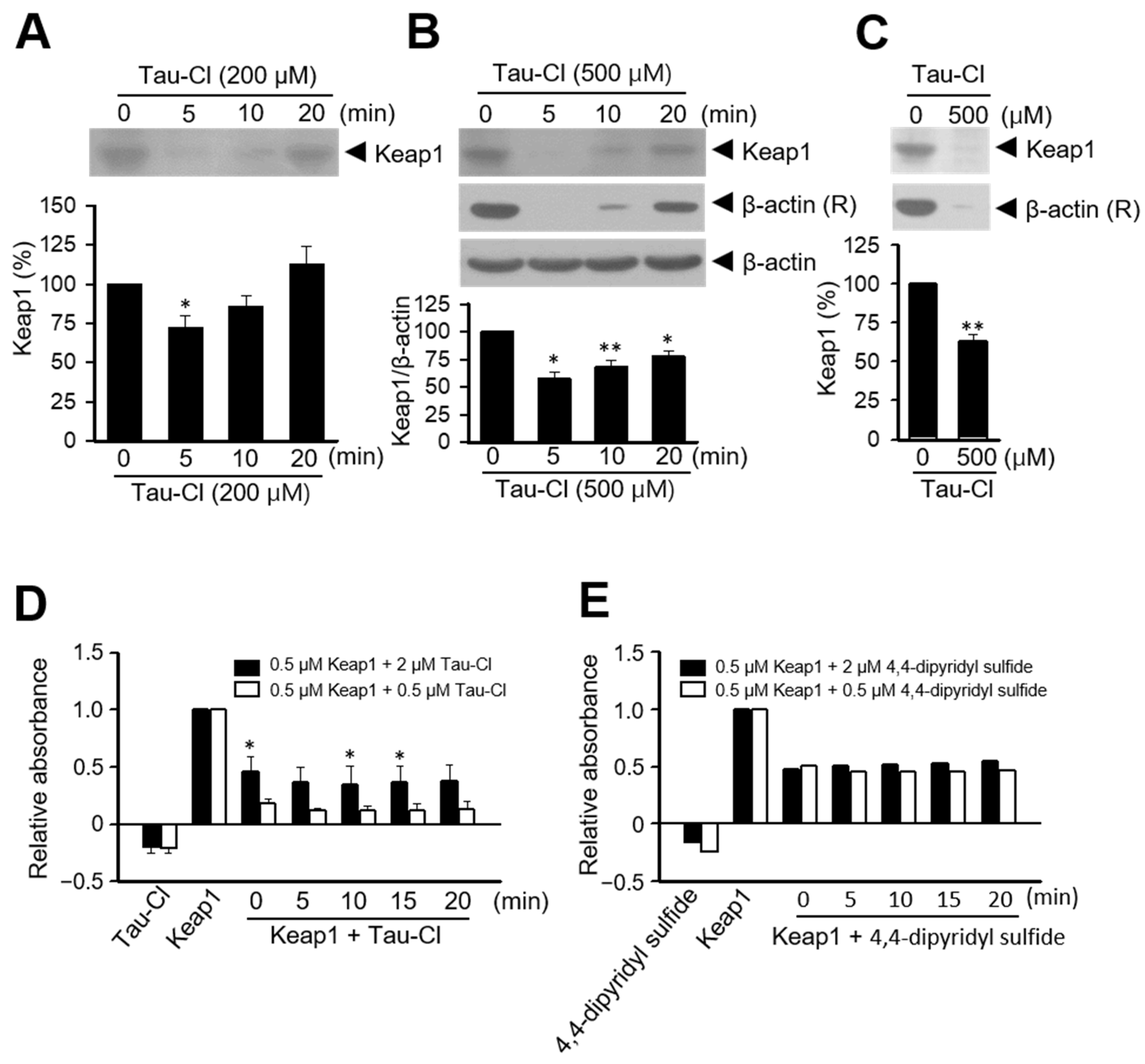
3.3. Tau-Cl Induces the Disulfide Bond Formation of Keap1
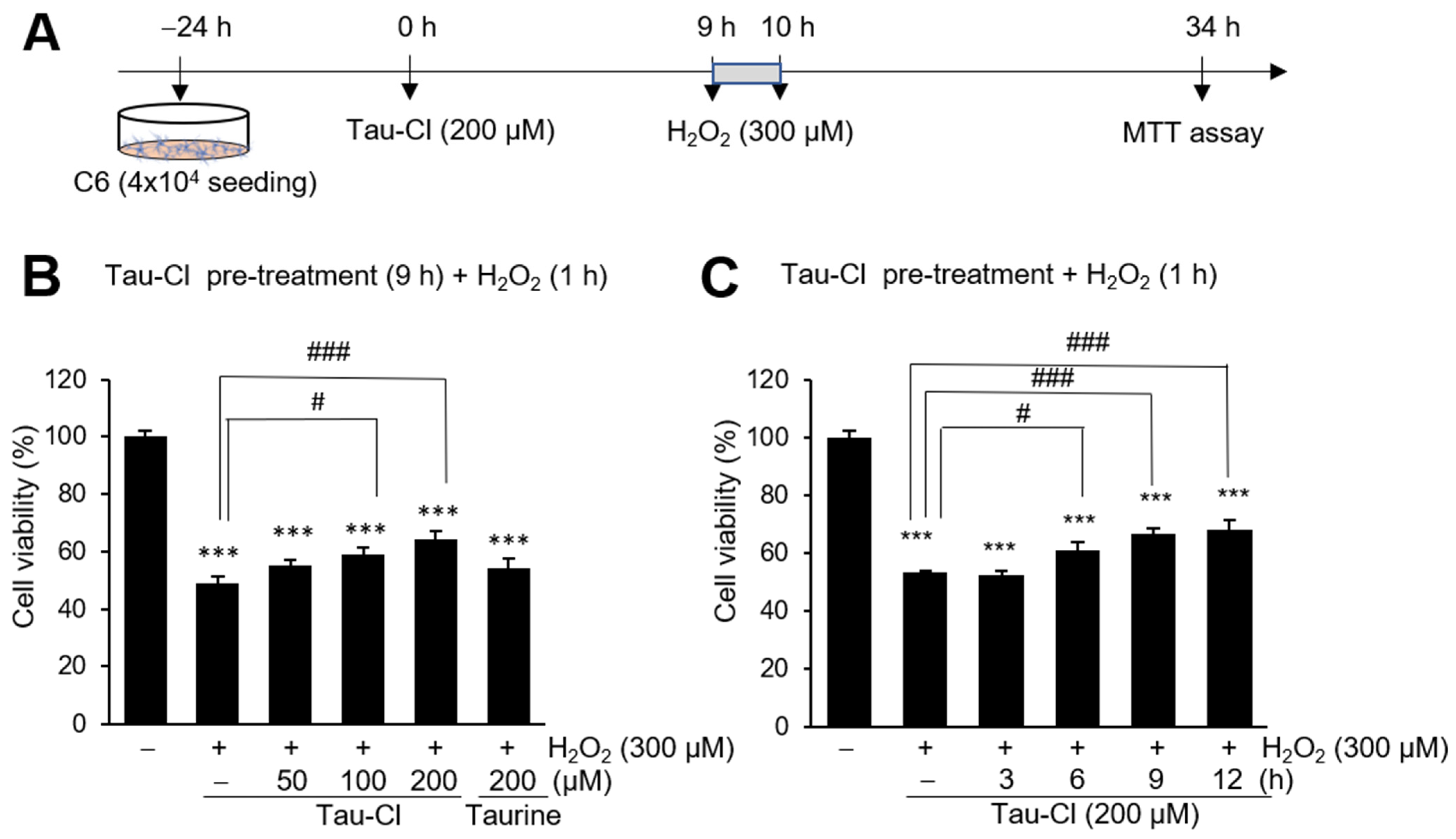
3.4. Tau-Cl Suppresses H2O2-Induced Cell Death in C6 Cells
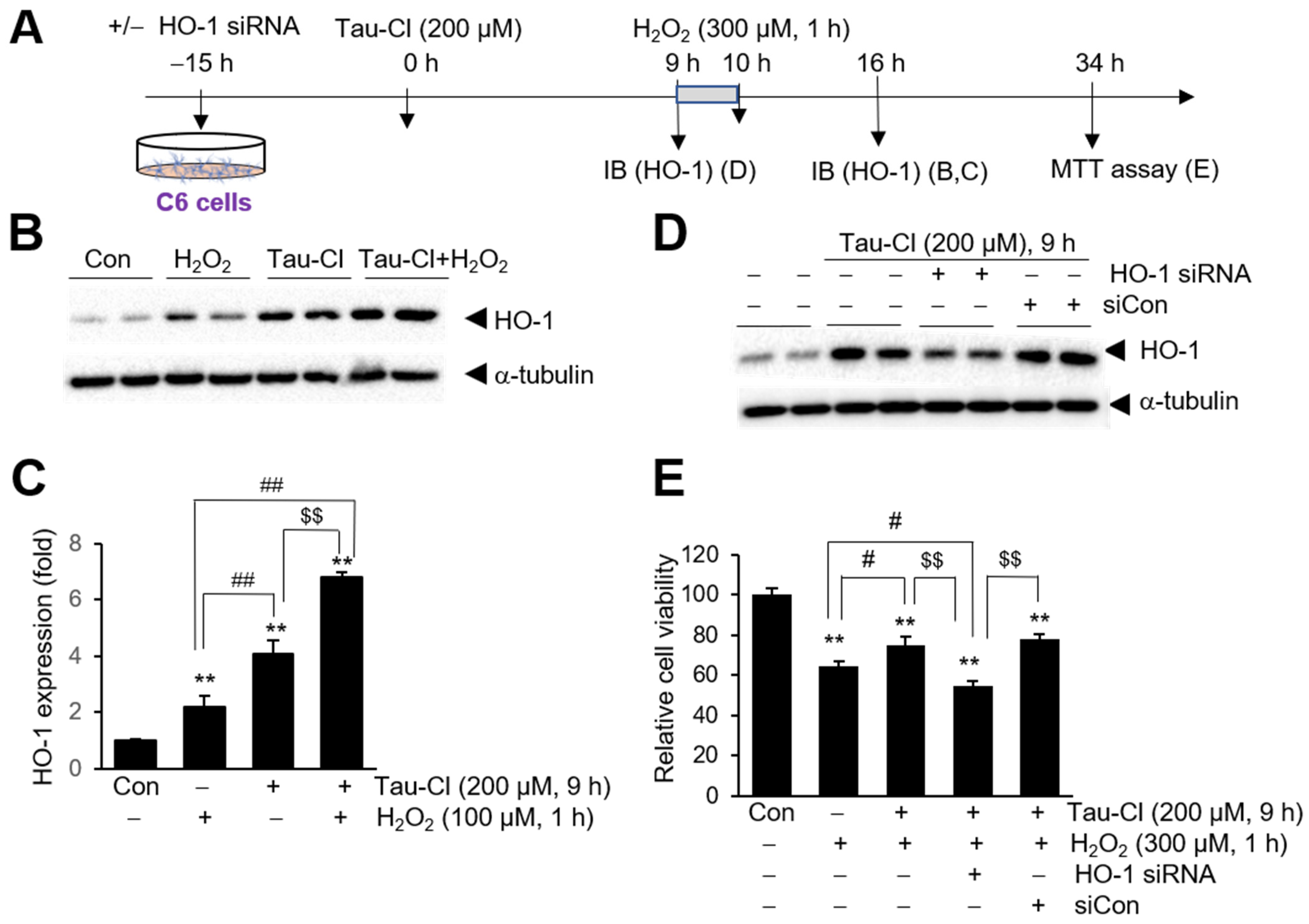
3.5. Tau-Cl-Mediated HO-1 Induction Is Responsible for the Protective Effects in C6 Cells
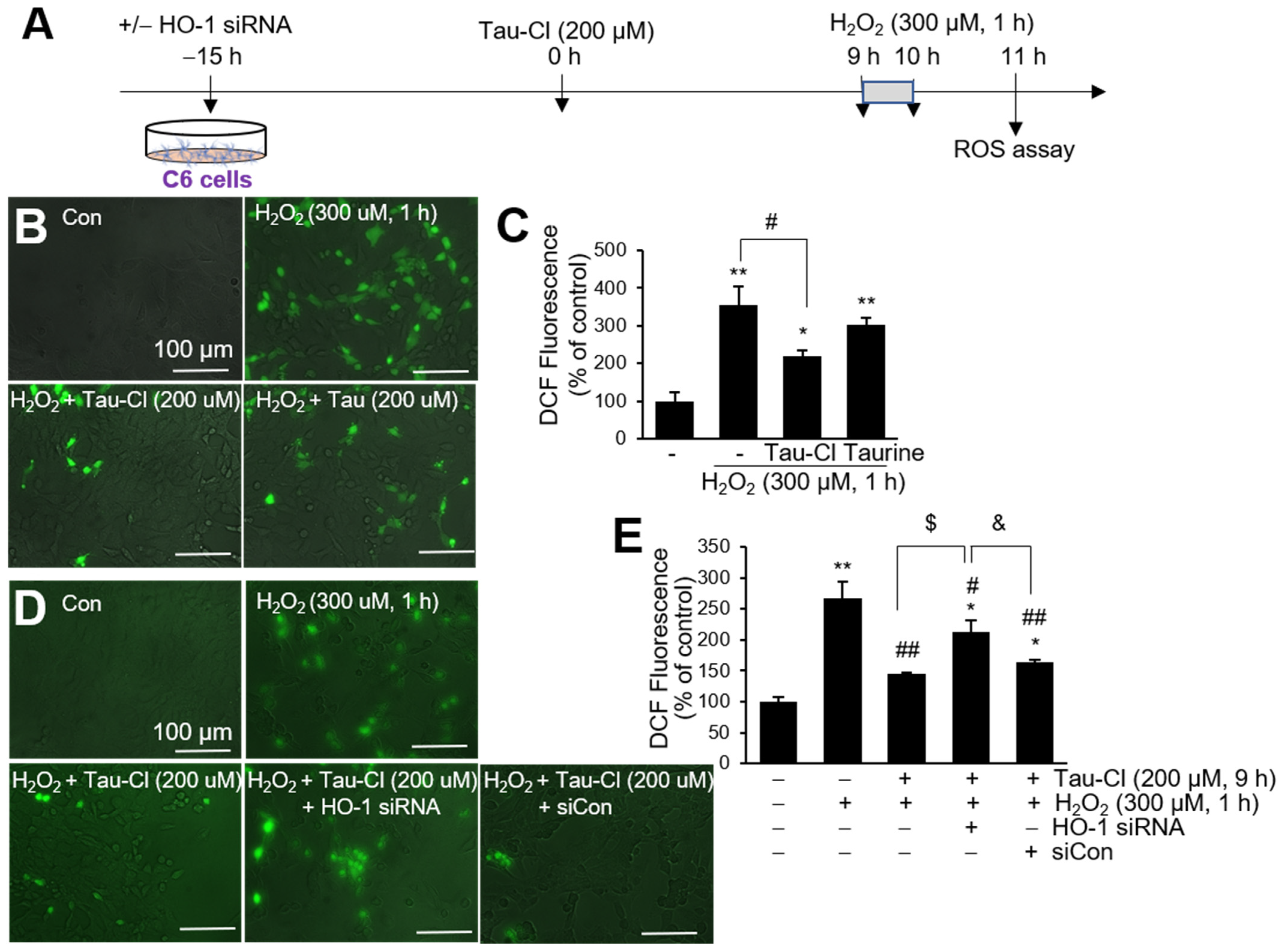
3.6. Tau-Cl Inhibits ROS Production in H2O2-Treated C6 Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huxtable, R.J. Physiological actions of taurine. Physiol. Rev. 1992, 72, 101–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, K.; Hirai, Y.; Yoshida, H.; Nakajima, T.; Usui, T. Free amino acid content of lymphocytes and granulocytes compared. Clin. Chem. 1982, 28, 1758–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, T.R.; Fellman, J.H.; Eicher, A.L.; Pratt, K.L. Antioxidant role and subcellular location of hypotaurine and taurine in human neutrophils. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1991, 1073, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojcik, O.P.; Koenig, K.L.; Zeleniuch-Jacquotte, A.; Costa, M.; Chen, Y. Temporal reproducibility of taurine measurements in frozen serum of healthy postmenopausal women. Br. J. Nutr. 2010, 104, 629–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuller-Levis, G.B.; Park, E. Taurine: New implications for an old amino acid. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2003, 226, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.; Cha, Y.N. Taurine chloramine produced from taurine under inflammation provides anti-inflammatory and cytoprotective effects. Amino Acids 2014, 46, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcinkiewicz, J.; Kontny, E. Taurine and inflammatory diseases. Amino Acids 2014, 46, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, S.J.; Klein, R.; Slivka, A.; Wei, M. Chlorination of taurine by human neutrophils. Evidence for hypochlorous acid generation. J. Clin. Investig. 1982, 70, 598–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, J.; Schousboe, A. Taurine interaction with neurotransmitter receptors in the CNS: An update. Neurochem. Res. 2005, 30, 1615–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oja, S.S.; Saransaari, P. Significance of taurine in the brain. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 975 Pt 1, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.H.; Jiang, Z.L.; Fan, X.J.; Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Ke, K.F. Neuroprotective effect of taurine against focal cerebral ischemia in rats possibly mediated by activation of both GABAA and glycine receptors. Neuropharmacology 2007, 52, 1199–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Zhao, Y.; Gu, Y.; Xu, C. Anti-inflammatory mechanism of taurine against ischemic stroke is related to down-regulation of PARP and NF-kappaB. Amino Acids 2012, 42, 1735–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Zhao, Y.M.; Gu, Y.; Xu, C. Therapeutic window of taurine against experimental stroke in rats. Transl. Res. 2012, 160, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzie, J.; Prentice, H.; Wu, J.Y. Neuroprotective mechanisms of taurine against ischemic stroke. Brain Sci. 2013, 3, 877–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Fan, W.; Ma, Z.; Wen, X.; Wang, W.; Wu, Q.; Huang, H. Taurine improves functional and histological outcomes and reduces inflammation in traumatic brain injury. Neuroscience 2014, 266, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakaria, M.; Azam, S.; Haque, M.E.; Jo, S.H.; Uddin, M.S.; Kim, I.S.; Choi, D.K. Taurine and its analogs in neurological disorders: Focus on therapeutic potential and molecular mechanisms. Redox Biol. 2019, 24, 101223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taranukhin, A.G.; Taranukhina, E.Y.; Saransaari, P.; Djatchkova, I.M.; Pelto-Huikko, M.; Oja, S.S. Taurine reduces caspase-8 and caspase-9 expression induced by ischemia in the mouse hypothalamic nuclei. Amino Acids 2008, 34, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Yang, X.; Zhang, B. Neuroprotection of taurine against bilirubin-induced elevation of apoptosis and intracellular free calcium ion in vivo. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2011, 21, 383–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.Y.; Wu, H.; Jin, Y.; Wei, J.; Sha, D.; Prentice, H.; Lee, H.H.; Lin, C.H.; Lee, Y.H.; Yang, L.L. Mechanism of neuroprotective function of taurine. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2009, 643, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seol, S.I.; Kim, H.J.; Choi, E.B.; Kang, I.S.; Lee, H.K.; Lee, J.K.; Kim, C. Taurine protects against postischemic brain Injury via the antioxidant activity of taurine chloramine. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sofroniew, M.V.; Vinters, H.V. Astrocytes: Biology and pathology. Acta Neuropathol. 2010, 119, 7–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofroniew, M.V. Molecular dissection of reactive astrogliosis and glial scar formation. Trends Neurosci. 2009, 32, 638–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dringen, R.; Gebhardt, R.; Hamprecht, B. Glycogen in astrocytes: Possible function as lactate supply for neighboring cells. Brain Res. 1993, 623, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellerin, L.; Bouzier-Sore, A.K.; Aubert, A.; Serres, S.; Merle, M.; Costalat, R.; Magistretti, P.J. Activity-dependent regulation of energy metabolism by astrocytes: An update. Glia 2007, 55, 1251–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfrieger, F.W.; Barres, B.A. Synaptic efficacy enhanced by glial cells in vitro. Science 1997, 277, 1684–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eroglu, C.; Barres, B.A. Regulation of synaptic connectivity by glia. Nature 2010, 468, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itoh, K.; Wakabayashi, N.; Katoh, Y.; Ishii, T.; Igarashi, K.; Engel, J.D.; Yamamoto, M. Keap1 represses nuclear activation of antioxidant responsive elements by Nrf2 through binding to the amino-terminal Neh2 domain. Genes. Dev. 1999, 13, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wild, A.C.; Moinova, H.R.; Mulcahy, R.T. Regulation of gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase subunit gene expression by the transcription factor Nrf2. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 33627–33636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyapaul, J.; Jaiswal, A.K. Nrf2 and c-Jun regulation of antioxidant response element (ARE)-mediated expression and induction of gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase heavy subunit gene. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2000, 59, 1433–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, A.K. Regulation of genes encoding NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductases. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2000, 29, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.; Sherratt, P.J.; Huang, H.C.; Yang, C.S.; Pickett, C.B. Increased protein stability as a mechanism that enhances Nrf2-mediated transcriptional activation of the antioxidant response element. Degradation of Nrf2 by the 26 S proteasome. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 4536–4541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayes, J.D.; McMahon, M. NRF2 and KEAP1 mutations: Permanent activation of an adaptive response in cancer. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2009, 34, 176–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.; Nioi, P.; Pickett, C.B. The Nrf2-antioxidant response element signaling pathway and its activation by oxidative stress. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 13291–13295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eggler, A.L.; Liu, G.; Pezzuto, J.M.; van Breemen, R.B.; Mesecar, A.D. Modifying specific cysteines of the electrophile-sensing human Keap1 protein is insufficient to disrupt binding to the Nrf2 domain Neh2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 10070–10075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.D. Mechanistic studies of the Nrf2-Keap1 signaling pathway. Drug Metab. Rev. 2006, 38, 769–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaspar, J.W.; Niture, S.K.; Jaiswal, A.K. Nrf2:INrf2 (Keap1) signaling in oxidative stress. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2009, 47, 1304–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muz, B.; Kontny, E.; Marcinkiewicz, J.; Maslinski, W. Heme oxygenase-1 participates in the anti-inflammatory activity of taurine chloramine. Amino Acids 2008, 35, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun Jang, J.; Piao, S.; Cha, Y.N.; Kim, C. Taurine chloramine activates Nrf2, increases HO-1 expression, and protects cells from death caused by hydrogen peroxide. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2009, 45, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Jang, J.S.; Cho, M.R.; Agarawal, S.R.; Cha, Y.N. Taurine chloramine induces heme oxygenase-1 expression via Nrf2 activation in murine macrophages. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2010, 10, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, S.; Cha, Y.N.; Kim, C. Taurine chloramine protects RAW 264.7 macrophages against hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis by increasing antioxidants. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2011, 49, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.W.; Kim, C. Inhibition of LPS-induced NO production by taurine chloramine in macrophages is mediated though Ras-ERK-NF-kappaB. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2005, 70, 1352–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinkova-Kostova, A.T.; Holtzclaw, W.D.; Cole, R.N.; Itoh, K.; Wakabayashi, N.; Katoh, Y.; Yamamoto, M.; Talalay, P. Direct evidence that sulfhydryl groups of Keap1 are the sensors regulating induction of phase 2 enzymes that protect against carcinogens and oxidants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 11908–11913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulsen, C.E.; Carroll, K.S. Cysteine-mediated redox signaling: Chemistry, biology, and tools for discovery. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 4633–4679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, S. Neuroprotective function of high glycolytic activity in astrocytes: Common roles in stroke and neurodegenerative diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, S.; Mashima, K. Neuroprotection and disease modification by astrocytes and microglia in Parkinson disease. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baranano, D.E.; Snyder, S.H. Neural roles for heme oxygenase: Contrasts to nitric oxide synthase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 10996–11002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.H.; Kim, S.W.; Jin, Y.; Kim, I.D.; Lee, J.K. Ethyl pyruvate-mediated Nrf2 activation and hemeoxygenase 1 induction in astrocytes confer protective effects via autocrine and paracrine mechanisms. Neurochem. Int. 2012, 61, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Kim, S.W.; Lee, H.K.; Kim, I.D.; Lee, H.; Lee, J.K. Anti-oxidative effects of 4-hydroxybenzyl alcohol in astrocytes confer protective effects in autocrine and paracrine manners. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Kim, S.W.; Lee, H.K.; Kim, I.D.; Lee, H.; Lee, J.K. Anti-Zn(2+)-Toxicity of 4-hydroxybenzyl alcohol in astrocytes and neurons contribute to a robust neuroprotective effects in the postischemic brain. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 38, 615–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen-Roetling, J.; Song, W.; Schipper, H.M.; Regan, C.S.; Regan, R.F. Astrocyte overexpression of heme oxygenase-1 improves outcome after intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke 2015, 46, 1093–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Hong, J.; Zhang, H.; Zheng, W.; Yang, Y. Astrocyte-derived exosomes protect hippocampal neurons after traumatic brain injury by suppressing mitochondrial oxidative stress and apoptosis. Aging 2021, 13, 21642–21658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ockaili, R.; Natarajan, R.; Salloum, F.; Fisher, B.J.; Jones, D.; Fowler, A.A., 3rd; Kukreja, R.C. HIF-1 activation attenuates postischemic myocardial injury: Role for heme oxygenase-1 in modulating microvascular chemokine generation. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2005, 289, H542–H548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubulus, D.; Mathes, A.; Pradarutti, S.; Raddatz, A.; Heiser, J.; Pavlidis, D.; Wolf, B.; Bauer, I.; Rensing, H. Hemin arginate-induced heme oxygenase 1 expression improves liver microcirculation and mediates an anti-inflammatory cytokine response after hemorrhagic shock. Shock 2008, 29, 583–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carratu, P.; Pourcyrous, M.; Fedinec, A.; Leffler, C.W.; Parfenova, H. Endogenous heme oxygenase prevents impairment of cerebral vascular functions caused by seizures. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2003, 285, H1148–H1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfieri, A.; Srivastava, S.; Siow, R.C.M.; Cash, D.; Modo, M.; Duchen, M.R.; Fraser, P.A.; Williams, S.C.R.; Mann, G.E. Sulforaphane preconditioning of the Nrf2/HO-1 defense pathway protects the cerebral vasculature against blood-brain barrier disruption and neurological deficits in stroke. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2013, 65, 1012–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitvitsky, V.; Garg, S.K.; Banerjee, R. Taurine biosynthesis by neurons and astrocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 32002–32010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, J.X. Antioxidant defense of the brain: A role for astrocytes. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 1997, 75, 1149–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dringen, R.; Kussmaul, L.; Gutterer, J.M.; Hirrlinger, J.; Hamprecht, B. The glutathione system of peroxide detoxification is less efficient in neurons than in astroglial cells. J. Neurochem. 1999, 72, 2523–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belanger, M.; Magistretti, P.J. The role of astroglia in neuroprotection. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2009, 11, 281–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, A.; Kang, M.I.; Okawa, H.; Ohtsuji, M.; Zenke, Y.; Chiba, T.; Igarashi, K.; Yamamoto, M. Oxidative stress sensor Keap1 functions as an adaptor for Cul3-based E3 ligase to regulate proteasomal degradation of Nrf2. Mol. Cell Biol. 2004, 24, 7130–7139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theodore, M.; Kawai, Y.; Yang, J.; Kleshchenko, Y.; Reddy, S.P.; Villalta, F.; Arinze, I.J. Multiple nuclear localization signals function in the nuclear import of the transcription factor Nrf2. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 8984–8994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, T.; Warabi, E.; Mann, G.E. Stress activated MAP kinases and cyclin-dependent kinase 5 mediate nuclear translocation of Nrf2 via Hsp90alpha-Pin1-Dynein motor transport machinery. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baird, L.; Yamamoto, M. The molecular mechanisms regulating the KEAP1-NRF2 pathway. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 40, e00099-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Lv, Y.F.; Zhao, J.L.; You, Q.D.; Jiang, Z.Y. Regulation of Nrf2 by phosphorylation: Consequences for biological function and therapeutic implications. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2021, 168, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marino, S.M.; Gladyshev, V.N. Analysis and functional prediction of reactive cysteine residues. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 4419–4425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Seol, S.-I.; Kang, I.S.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, J.-K.; Kim, C. Taurine Chloramine-Mediated Nrf2 Activation and HO-1 Induction Confer Protective Effects in Astrocytes. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 169. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox13020169
Seol S-I, Kang IS, Lee JS, Lee J-K, Kim C. Taurine Chloramine-Mediated Nrf2 Activation and HO-1 Induction Confer Protective Effects in Astrocytes. Antioxidants. 2024; 13(2):169. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox13020169
Chicago/Turabian StyleSeol, Song-I, In Soon Kang, Ji Seok Lee, Ja-Kyeong Lee, and Chaekyun Kim. 2024. "Taurine Chloramine-Mediated Nrf2 Activation and HO-1 Induction Confer Protective Effects in Astrocytes" Antioxidants 13, no. 2: 169. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox13020169
APA StyleSeol, S.-I., Kang, I. S., Lee, J. S., Lee, J.-K., & Kim, C. (2024). Taurine Chloramine-Mediated Nrf2 Activation and HO-1 Induction Confer Protective Effects in Astrocytes. Antioxidants, 13(2), 169. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox13020169