Identification of Interleukin (IL)-33 Inhibitory Constituents from Canavalia gladiata Pods
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Liquid Chromatography Quadrupole Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry Conditions
2.3. Plant Material
2.4. Extraction and Isolation
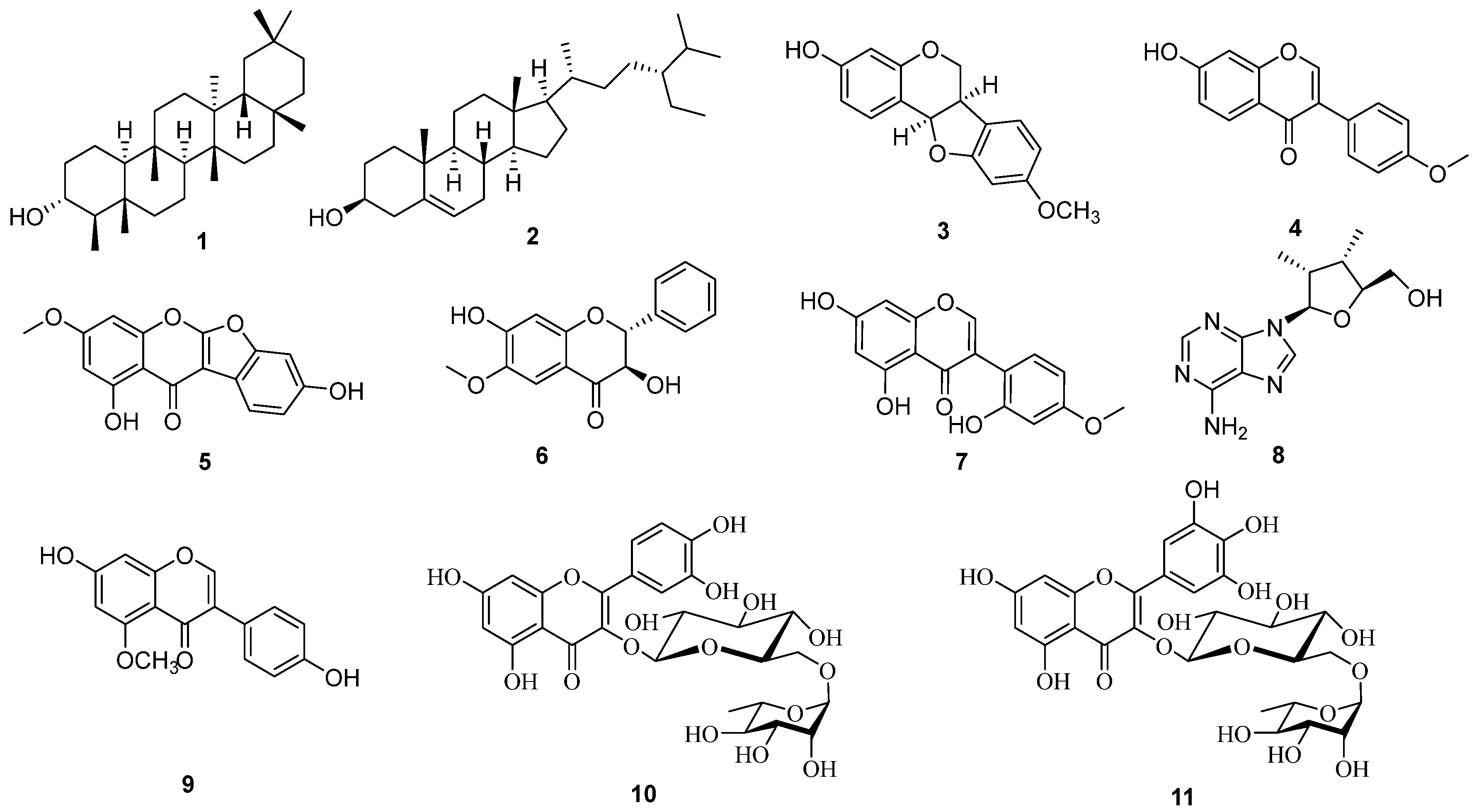
2.5. Physical and Spectroscopic Data of Bioactive Compounds
2.6. IL-33 Protein Expression and Purification
2.7. The Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay Technique
2.8. Molecular Docking Simulation
2.9. Molecular Dynamic Simulation
2.10. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Screening Secondary Metabolites Using Liquid Chromatography Quadrupole Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry Conditions for Target Isolation
3.2. Extraction and Purification of Bioactive Compounds from C. gladiata
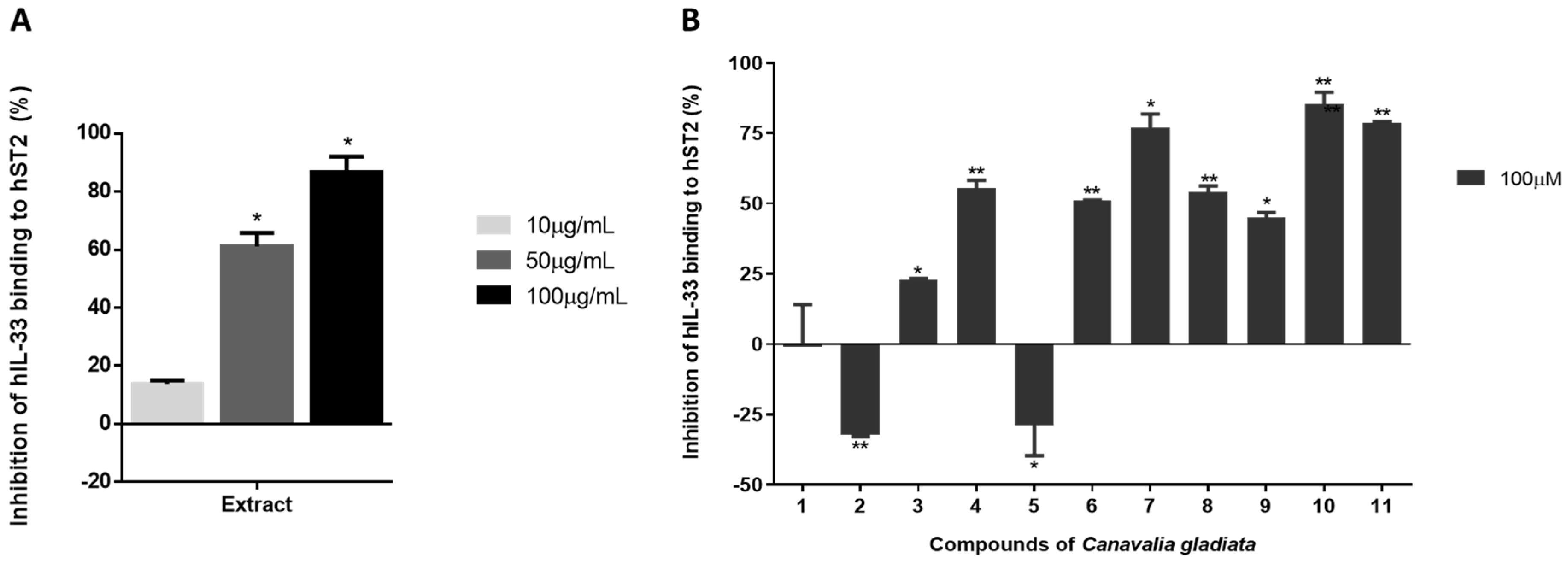
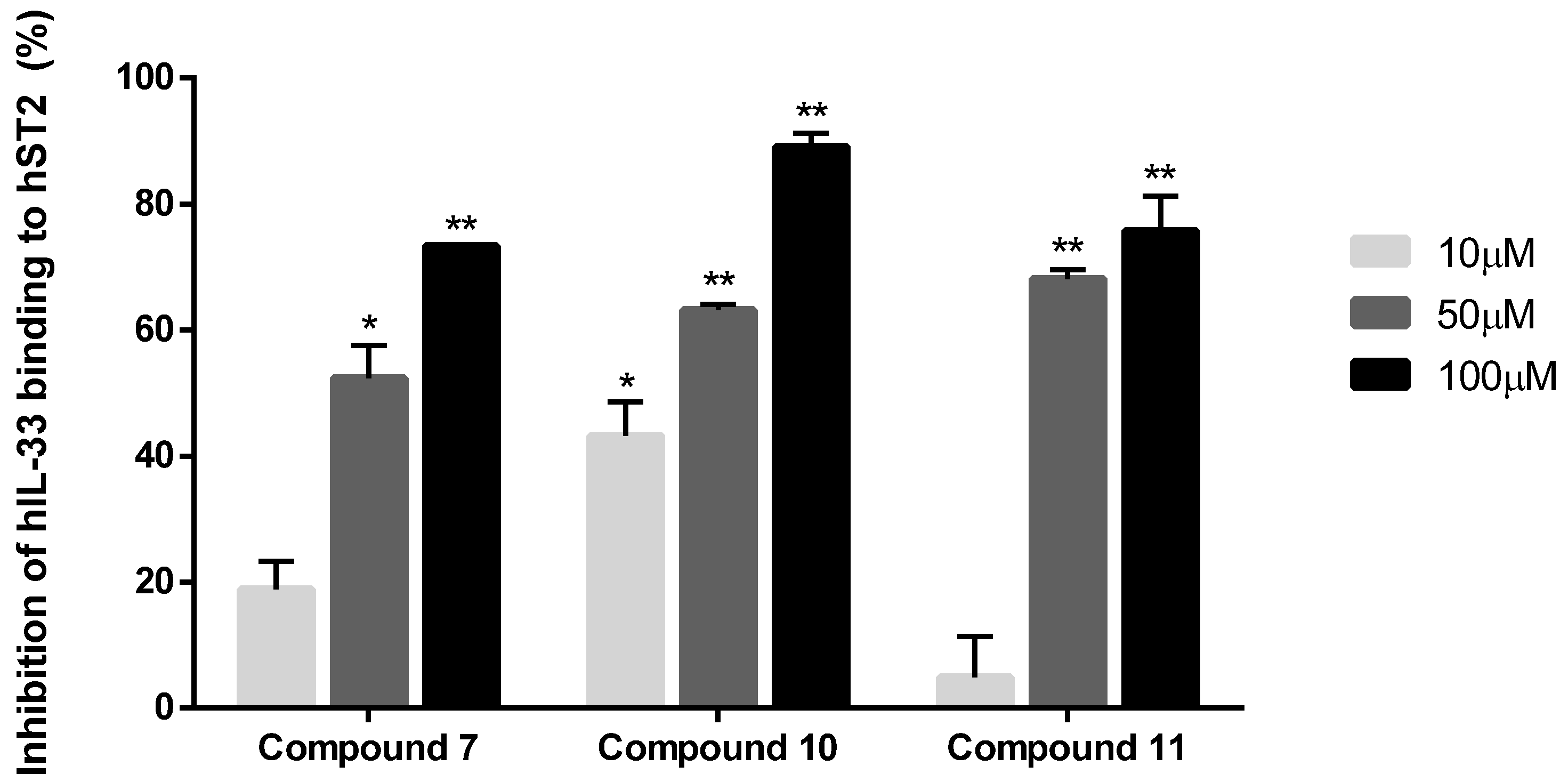
3.3. In Vitro Evaluation of IL-33/ST2 Interaction with Isolated Compounds Using ELISA
3.4. In Silico Evaluation of Pharmacological Effects
3.4.1. Molecular Docking Simulation
3.4.2. Molecular Dynamic Simulation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kubo, T.; Morita, H.; Sugita, K.; Akdis, C.A. Introduction to mechanisms of allergic diseases. In Middleton’s Allergy Essentials; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Sleeman, K.E.; De Brito, M.; Etkind, S.; Nkhoma, K.; Guo, P.; Higginson, I.J.; Gomes, B.; Harding, R. The escalating global burden of serious health-related suffering: Projections to 2060 by world regions, age groups, and health conditions. Lancet Glob. Health 2019, 7, e883–e892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paller, A.; Jaworski, J.C.; Simpson, E.L.; Boguniewicz, M.; Russell, J.J.; Block, J.K.; Tofte, S.; Dunn, J.D.; Feldman, S.R.; Clark, A.R. Major comorbidities of atopic dermatitis: Beyond allergic disorders. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2018, 19, 821–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcon, R.M.G.; Caoili, S.E.C. Immunologic, genetic, and ecological interplay of factors involved in allergic diseases. Front. Allergy 2023, 4, 1215616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Guo, M.; Ge, X.; Chen, F.; Lei, P. IL-33/ST2 Axis: A potential therapeutic target in neurodegenerative diseases. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, S.M.; Subbannayya, Y.; Rex, D.; Raju, R.; Chatterjee, O.; Advani, J.; Radhakrishnan, A.; Keshava Prasad, T.; Wani, M.R.; Pandey, A. A network map of IL-33 signaling pathway. J. Cell Commun. Signal. 2018, 12, 615–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saluja, R.; Zoltowska, A.; Ketelaar, M.E.; Nilsson, G. IL-33 and Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin in mast cell functions. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 778, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisniewski, J.A.; Borish, L. Novel cytokines and cytokine-producing T cells in allergic disorders. In Allergy and Asthma Proceedings, 2011; OceanSide Publications: Providence, RI, USA, 2011; p. 83. [Google Scholar]
- Saba, J.B.; Turnquist, H.t.R. The Reparative Roles of IL-33. Transplantation 2023, 107, 1069–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, M.; Anderson, E.L.; Squillace, D.L.; Patil, N.; Maniak, P.J.; Iijima, K.; Kita, H.; O’Grady, S.M. Oxidative stress serves as a key checkpoint for IL-33 release by airway epithelium. Allergy 2017, 72, 1521–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Yu, Q.; Nie, H.; Yin, C.; Liu, B. IL-33/ST2 signaling in pain and itch: Cellular and molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potentials. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 165, 115143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekanayake, S.; Jansz, E.; Nair, B.M. Literature review of an underutilized legume: Canavalia gladiata L. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2000, 55, 305–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, R.Y.; Lui, W.Y.; Corke, H. Sword bean (Canavalia gladiata) as a source of antioxidant phenolics. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 51, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, H.J.; Kim, E.H.; Lee, H.J.; Cho, J.Y.; Moon, J.H. New caryophyllene-type sesquiterpene and flavonol tetraglycoside with sixteen known compounds from sword bean (Canavalia gladiata). Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2020, 29, 1343–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.K.; Vinh, L.B.; Nam, M.H.; Lee, K.Y. Identification of compounds using HPLC-QTOF-MS online antioxidant activity mapping from aerial parts of Ligularia stenocephala. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2023, 66, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Naskar, R.; Acharya, S.; Vinh, L.B.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, Y.H.; Kang, J.S.; Hwang, I. Inotodiol, an antiasthmatic agent with efficacy and safety, preferentially impairs membrane-proximal signaling for mast cell activation. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 117, 109854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinh, L.B.; Han, Y.K.; Park, S.Y.; Kim, Y.J.; Phong, N.V.; Kim, E.; Ahn, B.G.; Jung, Y.W.; Byun, Y.; Jeon, Y.H. Identification of triterpenoid saponin inhibitors of interleukin (IL)-33 signaling from the roots of Astragalus membranaceus. J. Funct. Foods 2023, 101, 105418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, R.; Wang, Y.; Xu, J.; He, X. Anti-proliferative and anti-inflammatory prenylated isoflavones and coumaronochromones from the fruits of Ficus altissima. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 113, 104996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazuma, K.; Noda, N.; Suzuki, M. Malonylated flavonol glycosides from the petals of Clitoria ternatea. Phytochemistry 2003, 62, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turk, A.; Lee, S.; Yeon, S.W.; Ryu, S.H.; Han, Y.K.; Kim, Y.J.; Ko, S.M.; Kim, B.S.; Hwang, B.Y.; Lee, K.Y. Adenosine deaminase inhibitory activity of medicinal plants: Boost the production of cordycepin in Cordyceps militaris. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakkar, R.; Lee, R.T. The IL-33/ST2 pathway: Therapeutic target and novel biomarker. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 827–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.W.; Zhang, C.; Reher, R.; Wang, M.; Alexander, K.L.; Nothias, L.-F.; Han, Y.K.; Shin, H.; Lee, K.Y.; Lee, K.H. DeepSAT: Learning molecular structures from nuclear magnetic resonance data. J. Cheminformatics 2023, 15, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hawary, S.; El-Gohary, H.; Gonaid, M.; El-Sayed, R.; Sleem, A. Phytochemical and biological investigation of pentacyclic triterpenes isolated from Pyrus calleryana Decne growing in Egypt. Bull. Fac. Pharm. Cairo Univ. 2003, 41, 145–157. [Google Scholar]
- Morales, G.; Sierra, P.; Mancilla, A.; Paredes, A.; Loyola, L.A.; Gallardo, O.; Borquez, J. Secondary metabolites from four medicinal plants from northern Chile: Antimicrobial activity and biotoxicity against Artemia salina. J. Chil. Chem. Soc. 2003, 48, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, C.W.; Choi, Y.H.; Cha, M.R.; Yoo, D.S.; Kim, Y.S.; Yon, G.H.; Hong, K.S.; Kim, Y.H.; Ryu, S.Y. Yeast α-glucosidase inhibition by isoflavones from plants of Leguminosae as an in vitro alternative to acarbose. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 9988–9993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frasinyuk, M.S.; Zhang, W.; Wyrebek, P.; Yu, T.; Xu, X.; Sviripa, V.M.; Bondarenko, S.P.; Xie, Y.; Ngo, H.X.; Morris, A.J. Developing antineoplastic agents that target peroxisomal enzymes: Cytisine-linked isoflavonoids as inhibitors of hydroxysteroid 17-beta-dehydrogenase-4 (HSD17B4). Org. Biomol. Chem. 2017, 15, 7623–7629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.P.; Hu, J.; Wang, J.H.; Lou, F.-C. A new coumaronochromone from Sophora japonica. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2002, 4, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, W.L.; Chang, F.R.; Hsieh, T.J.; Wu, Y.C. The constituents of Euchresta formosana. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2002, 49, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuncbilek, M.; Kucukdumlu, A.; Guven, E.B.; Altiparmak, D.; Cetin-Atalay, R. Synthesis of novel 6-substituted amino-9-(β-D-ribofuranosyl) purine analogs and their bioactivities on human epithelial cancer cells. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 28, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulesh, N.; Vasilevskaya, N.; Veselova, M.; Denisenko, V.; Fedoreev, S. Minor polyphenols from Maackia amurensis wood. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2008, 44, 712–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharbert, S.; Holzmann, N.; Hofmann, T. Identification of the astringent taste compounds in black tea infusions by combining instrumental analysis and human bioresponse. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 3498–3508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Ma, C.; Park, S.; Shin-, Y.; Lee, T.; Paek, J.; Hoon Kim, K.; Jang, G.; Cho, H.; Son, S. Rational design, synthesis and evaluation of oxazolo [4, 5-c]-quinolinone analogs as novel interleukin-33 inhibitors. Chem. Asian J. 2021, 16, 3702–3712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osbourn, M.; Soares, D.C.; Vacca, F.; Cohen, E.S.; Scott, I.C.; Gregory, W.F.; Smyth, D.J.; Toivakka, M.; Kemter, A.M.; Le Bihan, T. HpARI protein secreted by a helminth parasite suppresses interleukin-33. Immunity 2017, 47, 739–751.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majumdar, S.; Ghosh, A.; Saha, S. Modulating interleukins and their receptors interactions with small chemicals using in silico approach for asthma. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2018, 18, 1123–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, D.J. Drug discovery from natural sources. Curr. Pharmacol. Rep. 2023, 9, 67–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuneki, H.; Ma, E.-L.; Kobayashi, S.; Sekizaki, N.; Maekawa, K.; Sasaoka, T.; Wang, M.-W.; Kimura, I. Antiangiogenic activity of β-eudesmol in vitro and in vivo. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2005, 512, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
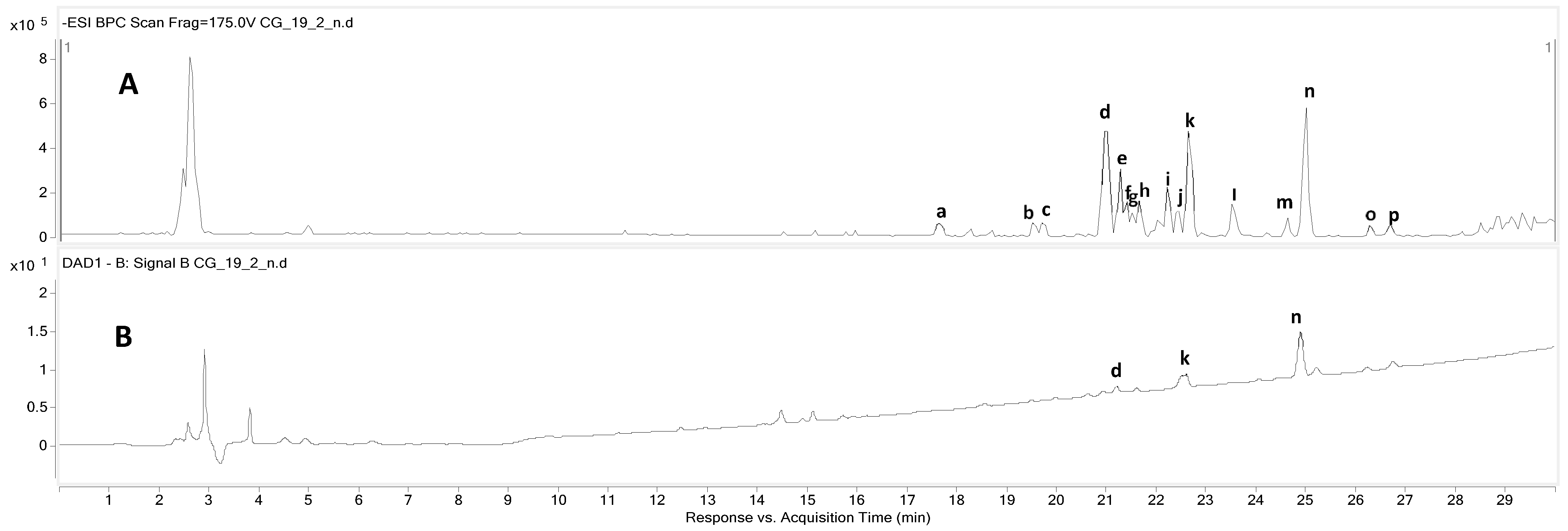


| Peak No. | Expected Compounds | tR (min) | Observed m/z | Calculated m/z | Molecular Formula [M-H]− | MS/MS Fragments (m/z) | UV (λmax, nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | Unidentified | 17.656 | 331.0809 | 331.0823 | C17H15O7 | 288 [M-43-H]− | |
| b | Unidentified | 19.588 | 283.0598 | 283.0612 | C16H11O5 | 268 [M-CH3-H]− | |
| c | Hydroxybenzoic acid | 19.716 | 137.0235 | 137.0244 | C7H5O3 | 93 [M-CO2-H]− | |
| d | Unidentified | 20.965 | 285.0757 | 285.0768 | C16H13O5 | 270 [M-CH3-H]− | 281, 339 |
| e | Genistein | 21.278 | 269.0442 | 269.0455 | C15H9O5 | 133 [M-C7H4O3-H]− | 285, 350 |
| f | Unidentified | 21.402 | 299.0545 | 299.0561 | C16H11O6 | 284 [M-CH3-H]− | |
| g | Unidentified | 21.527 | 301.0703 | 301.0718 | C16H13O6 | 165 [M-136-H]− | |
| h | Methoxykaempferol | 21.652 | 299.0547 | 299.0561 | C16H11O6 | - | |
| i | Unidentified | 22.214 | 301.0704 | 301.0718 | C16H13O6 | 125 [M-176-H]− | |
| j | Pseudobaptigenin | 22.464 | 281.0443 | 281.0455 | C16H9O5 | 253 [M-C2H4-H]− | |
| k | Formonetin | 22.651 | 267.0651 | 267.0663 | C16H11O4 | 252 [M-CH3-H]− | 284, 350 |
| l | Unidentified | 23.525 | 193.0854 | 193.0870 | C11H13O3 | 177 [M-16-H]− | |
| m | 5′-Hydroxy pseudobaptigenin | 24.649 | 297.0386 | 297.0405 | C16H9O6 | 269 [M-C2H4-H]− | |
| n | Biochanin A | 25.024 | 283.0593 | 283.0612 | C16H11O5 | 268 [M-CH3-H]− | 260 |
| o | Sophorophenolone | 26.273 | 297.0388 | 297.0405 | C16H9O6 | 282 [M-CH3-H]− | |
| p | Unidentified | 26.710 | 194.0808 | 194.0823 | C10H11NO3 | - |
| Compound | XP Dock Score (kcal/mol) | Hydrogen Bonding Interactions (Å) | Pi–Pi Stacking (Å) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | −12.383 | SER125 (2.73), SER127 (2.06), ASN226 (2.07, 2.65) | PHE230 (5.42) |
| 11 | −11.901 | SER125 (2.45), SER127 (2.09), ASP131 (1.88), ASN226 (1.88), VAL228 (2.52) | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vinh, L.B.; Shin, S.H.; Han, Y.K.; Kim, Y.J.; Cuong, N.C.; Oh, S.; Lee, K.Y. Identification of Interleukin (IL)-33 Inhibitory Constituents from Canavalia gladiata Pods. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 767. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox13070767
Vinh LB, Shin SH, Han YK, Kim YJ, Cuong NC, Oh S, Lee KY. Identification of Interleukin (IL)-33 Inhibitory Constituents from Canavalia gladiata Pods. Antioxidants. 2024; 13(7):767. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox13070767
Chicago/Turabian StyleVinh, Le Ba, Seung Hyuck Shin, Yoo Kyong Han, Young Jun Kim, Nguyen Cao Cuong, Soohwan Oh, and Ki Yong Lee. 2024. "Identification of Interleukin (IL)-33 Inhibitory Constituents from Canavalia gladiata Pods" Antioxidants 13, no. 7: 767. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox13070767
APA StyleVinh, L. B., Shin, S. H., Han, Y. K., Kim, Y. J., Cuong, N. C., Oh, S., & Lee, K. Y. (2024). Identification of Interleukin (IL)-33 Inhibitory Constituents from Canavalia gladiata Pods. Antioxidants, 13(7), 767. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox13070767







