Effects of Heart Failure Therapies on Atrial Fibrillation: Biological and Clinical Perspectives
Abstract
:1. Introduction
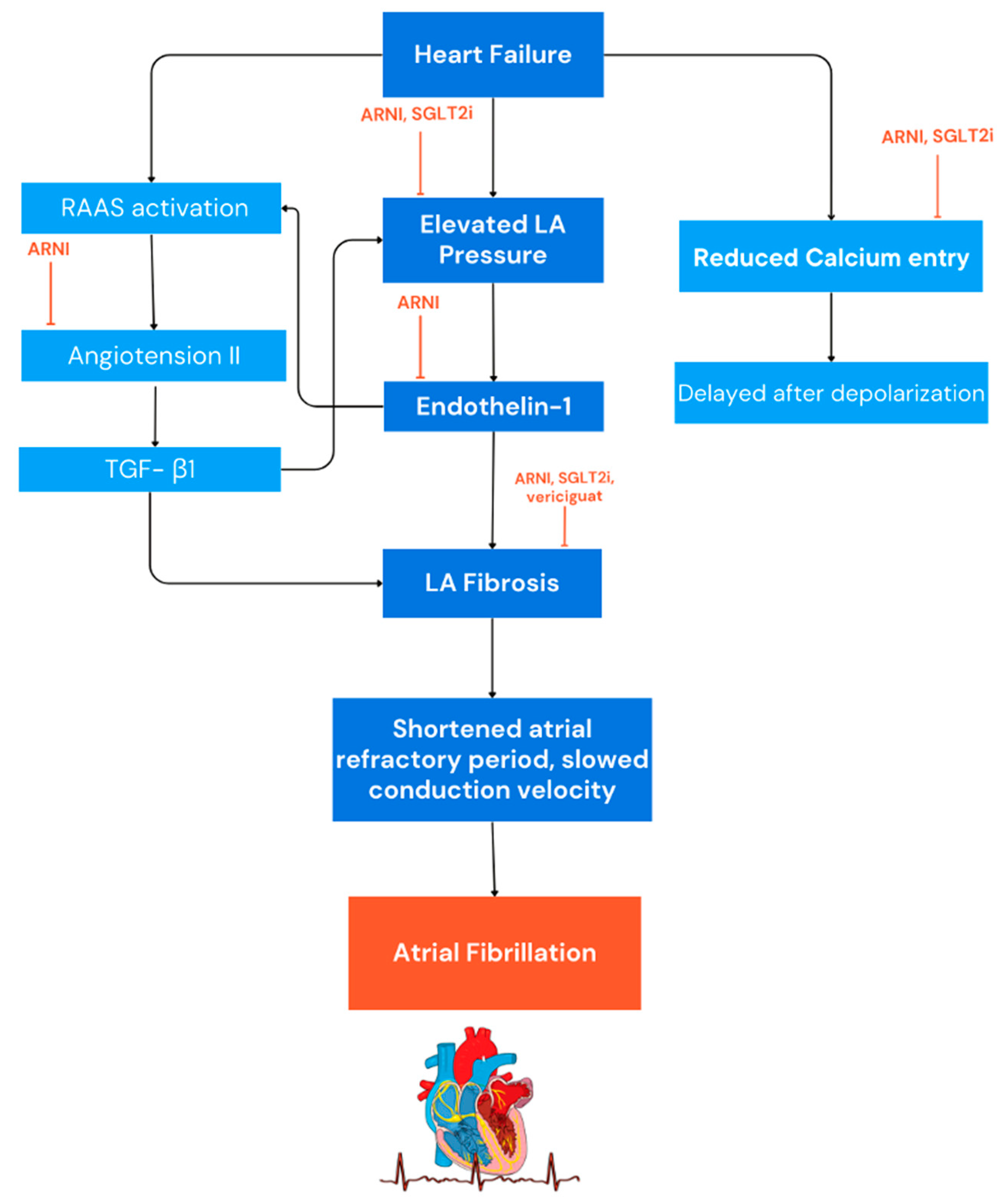
2. AF Electrogenesis in HF
3. Oxidative Stress and Atrial Fibrillation
4. Historical Use of Digitalis and NO Donors in HF Management
5. Angiotensin Receptor Neprilysin Inhibitors (ARNI)
6. Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter 2 Inhibitors (SGLT2i)
6.1. Dapagliflozin
6.2. Empagliflozin
6.3. Meta-Analyses Evaluating the Impact of SGLT2i on AF Occurrence
6.4. Putative Physio-Pathological Mechanism Explaining the Impact of SGLT2i on AF Occurrence
7. Vericiguat
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McDonagh, T.A.; Metra, M.; Adamo, M.; Gardner, R.S.; Baumbach, A.; Böhm, M.; Burri, H.; Butler, J.; Čelutkienė, J.; Chioncel, O.; et al. 2021 ESC Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute and Chronic Heart Failure. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 3599–3726, Erratum in Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 4901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahim, B.; Kapelios, C.J.; Savarese, G.; Lund, L.H. Global Public Health Burden of Heart Failure: An Updated Review. Card. Fail. Rev. 2023, 9, e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, J.D.; O’Meara, E.; Böhm, M.; Savarese, G.; Kelly, P.R.; Vardeny, O.; Allen, L.A.; Lancellotti, P.; Gottlieb, S.S.; Samad, Z.; et al. Implications of Atrial Fibrillation for Guideline-Directed Therapy in Patients with Heart Failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2024, 83, 932–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stolfo, D.; Lund, L.H.; Benson, L.; Hage, C.; Sinagra, G.; Dahlström, U.; Savarese, G. Persistent High Burden of Heart Failure Across the Ejection Fraction Spectrum in a Nationwide Setting. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2022, 11, 26708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conte, M.; Petraglia, L.; Poggio, P.; Valerio, V.; Cabaro, S.; Campana, P.; Comentale, G.; Attena, E.; Russo, V.; Pilato, E.; et al. Inflammation and Cardiovascular Diseases in the Elderly: The Role of Epicardial Adipose Tissue. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 844266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conte, M.; Petraglia, L.; Cabaro, S.; Valerio, V.; Poggio, P.; Pilato, E.; Attena, E.; Russo, V.; Ferro, A.; Formisano, P.; et al. Epicardial Adipose Tissue and Cardiac Arrhythmias: Focus on Atrial Fibrillation. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 932262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, L.J.; Antwi-Boasiako, S.; Ferrall, J.; Wold, L.E.; Mohler, P.J.; El Refaey, M. Genetic and Non-Genetic Risk Factors Associated with Atrial Fibrillation. Life Sci. 2022, 299, 120529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.-H.; Yang, Y.-Q. Atrial Fibrillation: Focus on Myocardial Connexins and Gap Junctions. Biology 2022, 11, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinno, H.; Derakhchan, K.; Libersan, D.; Merhi, Y.; Leung, T.K.; Nattel, S. Atrial Ischemia Promotes Atrial Fibrillation in Dogs. Circulation 2003, 107, 1930–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Andrea, A.; Ilardi, F.; D’Ascenzi, F.; Bandera, F.; Benfari, G.; Esposito, R.; Malagoli, A.; Mandoli, G.E.; Santoro, C.; Russo, V.; et al. Impaired Myocardial Work Efficiency in Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2021, 22, 1312–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisi, V.; Conte, M.; Petraglia, L.; Grieco, F.V.; Bruzzese, D.; Caruso, A.; Grimaldi, M.G.; Campana, P.; Gargiulo, P.; Paolillo, S.; et al. Echocardiographic Epicardial Adipose Tissue Thickness for Risk Stratification of Patients with Heart Failure. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmiero, G.; Florio, M.T.; Rubino, M.; Nesti, M.; Marchel, M.; Russo, V. Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy in Patients with Heart Failure. Heart Fail. Clin. 2021, 17, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morton, J.B.; Sanders, P.; Vohra, J.K.; Sparks, P.B.; Morgan, J.G.; Spence, S.J.; Grigg, L.E.; Kalman, J.M. Effect of Chronic Right Atrial Stretch on Atrial Electrical Remodeling in Patients with an Atrial Septal Defect. Circulation 2003, 107, 1775–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, P.; Morton, J.B.; Davidson, N.C.; Spence, S.J.; Vohra, J.K.; Sparks, P.B.; Kalman, J.M. Electrical Remodeling of the Atria in Congestive Heart Failure. Circulation 2003, 108, 1461–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Fareh, S.; Leung, T.K.; Nattel, S. Promotion of Atrial Fibrillation by Heart Failure in Dogs. Circulation 1999, 100, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buxton, A.E.; Waxman, H.L.; Marchlinski, F.E.; Josephson, M.E. Atrial Conduction: Effects of Extrastimuli with and without Atrial Dysrhythmias. Am. J. Cardiol. 1984, 54, 755–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sparks, P.B.; Mond, H.G.; Vohra, J.K.; Jayaprakash, S.; Kalman, J.M. Electrical Remodeling of the Atria Following Loss of Atrioventricular Synchrony. Circulation 1999, 100, 1894–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaccioli, G.; Bassi, G.; Lugi, C.; Parente, E.; D’andrea, A.; Proietti, R.; Imbalzano, E.; Al Turki, A.; Russo, V. Smartphone and New Tools for Atrial Fibrillation Diagnosis: Evidence for Clinical Applicability. Minerva Cardiol. Angiol. 2022, 70, 616–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, F.H.; Levin, E.R.; Gardner, D.G.; Samson, W.K. Natriuretic Peptides. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 339, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarzani, R.; Allevi, M.; Di Pentima, C.; Schiavi, P.; Spannella, F.; Giulietti, F. Role of Cardiac Natriuretic Peptides in Heart Structure and Function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mujović, N.; Dobrev, D.; Marinković, M.; Russo, V.; Potpara, T.S. The Role of Amiodarone in Contemporary Management of Complex Cardiac Arrhythmias. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 151, 104521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Andrea, A.; Ilardi, F.; Palermi, S.; Riegler, L.; Miele, T.; Giallauria, F.; D’Alto, M.; Russo, V.; Cice, G. Multimodality Imaging in Decompensated Heart Failure. Eur. Heart J. Suppl. 2023, 25, C292–C300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goetze, J.P.; Bruneau, B.G.; Ramos, H.R.; Ogawa, T.; de Bold, M.K.; de Bold, A.J. Cardiac Natriuretic Peptides. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2020, 17, 698–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staerk, L.; Sherer, J.A.; Ko, D.; Benjamin, E.J.; Helm, R.H. Atrial Fibrillation: Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, and Clinical Outcomes. Circ. Res. 2017, 120, 1501–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denham, N.C.; Pearman, C.M.; Caldwell, J.L.; Madders, G.W.P.; Eisner, D.A.; Trafford, A.W.; Dibb, K.M. Calcium in the Pathophysiology of Atrial Fibrillation and Heart Failure. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, H1002–H1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Wagoner, D.R.; Pond, A.L.; McCarthy, P.M.; Trimmer, J.S.; Nerbonne, J.M. Outward K+ Current Densities and Kv1.5 Expression Are Reduced in Chronic Human Atrial Fibrillation. Circ. Res. 1997, 80, 772–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, L.; Feng, J.; Gaspo, R.; Li, G.R.; Wang, Z.; Nattel, S. Ionic Remodeling Underlying Action Potential Changes in a Canine Model of Atrial Fibrillation. Circ. Res. 1997, 81, 512–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckstein, J.; Verheule, S.; de Groot, N.; Allessie, M.; Schotten, U. Mechanisms of Perpetuation of Atrial Fibrillation in Chronically Dilated Atria. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2008, 97, 435–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korantzopoulos, P.; Letsas, K.; Fragakis, N.; Tse, G.; Liu, T. Oxidative Stress and Atrial Fibrillation: An Update. Free Radic. Res. 2018, 52, 1199–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihm, M.J.; Yu, F.; Carnes, C.A.; Reiser, P.J.; McCarthy, P.M.; Van Wagoner, D.R.; Bauer, J.A. Impaired Myofibrillar Energetics and Oxidative Injury during Human Atrial Fibrillation. Circulation 2001, 104, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Wagoner, D.R. Electrophysiological Remodeling in Human Atrial Fibrillation. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2003, 26, 1572–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Wagoner, D.R. Molecular Basis of Atrial Fibrillation: A Dream or a Reality? J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2003, 14, 667–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carnes, C.A.; Chung, M.K.; Nakayama, T.; Nakayama, H.; Baliga, R.S.; Piao, S.; Kanderian, A.; Pavia, S.; Hamlin, R.L.; McCarthy, P.M.; et al. Ascorbate Attenuates Atrial Pacing-Induced Peroxynitrite Formation and Electrical Remodeling and Decreases the Incidence of Postoperative Atrial Fibrillation. Circ. Res. 2001, 89, e32–e38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhalla, N.S.; Temsah, R.M. Sarcoplasmic Reticulum and Cardiac Oxidative Stress: An Emerging Target for Heart Disease. Expert. Opin. Ther. Targets 2001, 5, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korantzopoulos, P.; Kolettis, T.M.; Galaris, D.; Goudevenos, J.A. The Role of Oxidative Stress in the Pathogenesis and Perpetuation of Atrial Fibrillation. Int. J. Cardiol. 2007, 115, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corradi, D.; Callegari, S.; Manotti, L.; Ferrara, D.; Goldoni, M.; Alinovi, R.; Pinelli, S.; Mozzoni, P.; Andreoli, R.; Asimaki, A.; et al. Persistent Lone Atrial Fibrillation: Clinicopathologic Study of 19 Cases. Heart Rhythm. 2014, 11, 1250–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elahi, M.M.; Flatman, S.; Matata, B.M. Tracing the Origins of Postoperative Atrial Fibrillation: The Concept of Oxidative Stress-Mediated Myocardial Injury Phenomenon. Eur. J. Cardiovasc. Prev. Rehabil. 2008, 15, 735–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakkar, M.; Ascione, R.; James, A.F.; Angelini, G.D.; Suleiman, M.S. Inflammation, Oxidative Stress and Postoperative Atrial Fibrillation in Cardiac Surgery. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 154, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.M.; Guzik, T.J.; Zhang, Y.H.; Zhang, M.H.; Kattach, H.; Ratnatunga, C.; Pillai, R.; Channon, K.M.; Casadei, B. A Myocardial Nox2 Containing NAD(P)H Oxidase Contributes to Oxidative Stress in Human Atrial Fibrillation. Circ. Res. 2005, 97, 629–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Santulli, G.; Reiken, S.R.; Yuan, Q.; Osborne, B.W.; Chen, B.X.; Marks, A.R. Mitochondrial Oxidative Stress Promotes Atrial Fibrillation. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrichs, K.; Baldus, S.; Klinke, A. Fibrosis in Atrial Fibrillation—Role of Reactive Species and MPO. Front. Physiol. 2012, 3, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudolph, V.; Andrié, R.P.; Rudolph, T.K.; Friedrichs, K.; Klinke, A.; Hirsch-Hoffmann, B.; Schwoerer, A.P.; Lau, D.; Fu, X.; Klingel, K.; et al. Myeloperoxidase Acts as a Profibrotic Mediator of Atrial Fibrillation. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 470–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ndrepepa, G.; Kastrati, A. Gamma-Glutamyl Transferase and Cardiovascular Disease. Ann. Transl. Med. 2016, 4, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, X.; Korantzopoulos, P.; Wang, S.; Li, G. Uric Acid Levels and Atrial Fibrillation in Hypertensive Patients. Intern. Med. 2011, 50, 799–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Liu, T.; Korantzopoulos, P.; Letsas, K.P.; Zhang, E.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Qiu, J.; Li, J.; Li, G. Association between Serum Uric Acid and Atrial Fibrillation Recurrence Following Catheter Ablation: A Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Cardiol. 2016, 204, 103–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamariz, L.; Hernandez, F.; Bush, A.; Palacio, A.; Hare, J.M. Association between Serum Uric Acid and Atrial Fibrillation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Heart Rhythm. 2014, 11, 1102–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korantzopoulos, P.; Letsas, K.P.; Liu, T. Xanthine Oxidase and Uric Acid in Atrial Fibrillation. Front. Physiol. 2012, 3, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaugai, S.; Meng, W.Y.; Sepehry, A.A. Effects of RAAS Blockers on Atrial Fibrillation Prophylaxis: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 21, 388–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Digitalis Investigation Group. The Effect of Digoxin on Mortality and Morbidity in Patients with Heart Failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 1997, 336, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, P.W.; Lam, C.S.P.; Anstrom, K.J.; Ezekowitz, J.; Hernandez, A.F.; O’Connor, C.M.; Pieske, B.; Ponikowski, P.; Shah, S.J.; Solomon, S.D.; et al. Effect of Vericiguat vs. Placebo on Quality of Life in Patients with Heart Failure and Preserved Ejection Fraction: The VITALITY-HFpEF Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2020, 324, 1512–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voors, A.A.; Dorhout, B.; van der Meer, P. The Potential Role of Valsartan + AHU377 (LCZ696) in the Treatment of Heart Failure. Expert. Opin. Investig. Drugs 2013, 22, 1041–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMurray, J.J.V.; Packer, M.; Desai, A.S.; Gong, J.; Lefkowitz, M.P.; Rizkala, A.R.; Rouleau, J.L.; Shi, V.C.; Solomon, S.D.; Swedberg, K.; et al. Angiotensin–Neprilysin Inhibition versus Enalapril in Heart Failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 993–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMurray, J.J.V.; Packer, M.; Desai, A.S.; Gong, J.; Lefkowitz, M.P.; Rizkala, A.R.; Rouleau, J.; Shi, V.C.; Solomon, S.D.; Swedberg, K.; et al. Dual Angiotensin Receptor and Neprilysin Inhibition as an Alternative to Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibition in Patients with Chronic Systolic Heart Failure: Rationale for and Design of the Prospective Comparison of ARNI with ACEI to Determine Impact on Global Mortality and Morbidity in Heart Failure Trial (PARADIGM-HF). Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2013, 15, 1062–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, A.S.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Packer, M.; Swedberg, K.; Rouleau, J.L.; Chen, F.; Gong, J.; Rizkala, A.R.; Brahimi, A.; Claggett, B.; et al. Effect of the Angiotensin-Receptor-Neprilysin Inhibitor LCZ696 Compared with Enalapril on Mode of Death in Heart Failure Patients. Eur. Heart J. 2015, 36, 1990–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Veldhuisen, D.J.; Linssen, G.C.M.; Jaarsma, T.; van Gilst, W.H.; Hoes, A.W.; Tijssen, J.G.P.; Paulus, W.J.; Voors, A.A.; Hillege, H.L. B-Type Natriuretic Peptide and Prognosis in Heart Failure Patients with Preserved and Reduced Ejection Fraction. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013, 61, 1498–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martens, P.; Nuyens, D.; Rivero-Ayerza, M.; Van Herendael, H.; Vercammen, J.; Ceyssens, W.; Luwel, E.; Dupont, M.; Mullens, W. Sacubitril/Valsartan Reduces Ventricular Arrhythmias in Parallel with Left Ventricular Reverse Remodeling in Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction. Clin. Res. Cardiol. 2019, 108, 1074–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Diego, C.; González-Torres, L.; Núñez, J.M.; Centurión Inda, R.; Martin-Langerwerf, D.A.; Sangio, A.D.; Chochowski, P.; Casasnovas, P.; Blazquéz, J.C.; Almendral, J. Effects of Angiotensin-Neprilysin Inhibition Compared to Angiotensin Inhibition on Ventricular Arrhythmias in Reduced Ejection Fraction Patients under Continuous Remote Monitoring of Implantable Defibrillator Devices. Heart Rhythm. 2018, 15, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, V.; Ammendola, E.; Gasperetti, A.; Bottino, R.; Schiavone, M.; Masarone, D.; Pacileo, G.; Nigro, G.; Golino, P.; Lip, G.Y.H.; et al. Add-on Therapy with Sacubitril/Valsartan and Clinical Outcomes in CRT-D Nonresponder Patients. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2022, 79, 472–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, V.; Bottino, R.; Rago, A.; Papa, A.A.; Liccardo, B.; Proietti, R.; Manna, V.; Golino, P.; D’Onofrio, A.; Nigro, G. The Effect of Sacubitril/Valsartan on Device Detected Arrhythmias and Electrical Parameters among Dilated Cardiomyopathy Patients with Reduced Ejection Fraction and Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vecchis, R.; Paccone, A.; Di Maio, M. Favorable Effects of Sacubitril/Valsartan on the Peak Atrial Longitudinal Strain in Patients with Chronic Heart Failure and a History of One or More Episodes of Atrial Fibrillation: A Retrospective Cohort Study. J. Clin. Med. Res. 2020, 12, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Chen, Y.; Qin, F.; Du, H.; Gan, C.; Zhou, B.; Wang, N.; Xiao, M.; Ou, Z.; Zhao, W.; et al. Effect of Sacubitril-Valsartan on Restoration and Maintenance of Sinus Rhythm in Patients with Persistent Atrial Fibrillation. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 870203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Zhuo, C.; Xia, Q.; Jiang, J.; Wu, B.; Zhou, D.; Shu, Z.; Zhao, J.; Chen, M.; Chen, H.; et al. Sacubitril/Valsartan Can Reduce Atrial Fibrillation Recurrence After Catheter Ablation in Patients with Persistent Atrial Fibrillation. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 2023, 37, 549–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, M.; Yamada, T.; Mizuno, H.; Minamiguchi, H.; Konishi, S.; Ohtani, T.; Yamaguchi, O.; Okuyama, Y.; Uematsu, M.; Sakata, Y. Impact of Atrial Fibrillation Ablation on Cardiac Sympathetic Nervous System in Patients with and without Heart Failure. Int. J. Cardiol. 2015, 199, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KANG, K.; KIM, T.H.; PARK, J.; UHM, J.S.; JOUNG, B.; HWANG, C.; LEE, M.; PAK, H. Long-Term Changes in Heart Rate Variability After Radiofrequency Catheter Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation: 1-Year Follow-Up Study with Irrigation Tip Catheter. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2014, 25, 693–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuechterlein, K.; AlTurki, A.; Ni, J.; Martínez-Sellés, M.; Martens, P.; Russo, V.; Backelin, C.N.; Huynh, T. Real-World Safety of Sacubitril/Valsartan in Women and Men with Heart Failure and Reduced Ejection Fraction: A Meta-Analysis. CJC Open 2021, 3, S202–S208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vecchis, R.; Paccone, A.; Di Maio, M. Sacubitril/Valsartan Therapy for 14 Months Induces a Marked Improvement of Global Longitudinal Strain in Patients with Chronic Heart Failure: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Cardiol. Res. 2019, 10, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Lou, Q.; Liu, G.; Lv, J.; Yun, F.; Li, T.; Yang, W.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, L.; Bai, N.; et al. Sacubitril/Valsartan Attenuates Atrial Electrical and Structural Remodelling in a Rabbit Model of Atrial Fibrillation. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 881, 173120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-M.; Wu, T.-J.; Zhou, S.; Doshi, R.N.; Lee, M.-H.; Ohara, T.; Fishbein, M.C.; Karagueuzian, H.S.; Chen, P.-S.; Chen, L.S. Nerve Sprouting and Sympathetic Hyperinnervation in a Canine Model of Atrial Fibrillation Produced by Prolonged Right Atrial Pacing. Circulation 2001, 103, 22–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swissa, M.; Zhou, S.; Paz, O.; Fishbein, M.C.; Chen, L.S.; Chen, P.-S. Canine Model of Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation and Paroxysmal Atrial Tachycardia. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2005, 289, H1851–H1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, X.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, K.; Song, W.; Ma, J.; Zhou, Y.; Liang, E.; Fu, H.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Evaluation of the Efficacy of Sacubitril/Valsartan on Radiofrequency Ablation in Patients with Hypertension and Persistent Atrial Fibrillation. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nespoux, J.; Vallon, V. SGLT2 Inhibition and Kidney Protection. Clin. Sci. 2018, 132, 1329–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonseca-Correa, J.I.; Correa-Rotter, R. Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors Mechanisms of Action: A Review. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 777861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahinya, M.; Khan, Z. Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) Inhibitor Therapy for the Primary and Secondary Prevention of Heart Failure in Patients with and without Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review. Cureus 2023, 15, e37388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, A.W.-C.; Chan, C.-C.; Chen, S.-W.; Kao, Y.-W.; Huang, C.-Y.; Chan, Y.-H.; Chu, P.-H. The Risk of New-Onset Atrial Fibrillation in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Treated with Sodium Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors versus Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2020, 19, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, A.K.; Okaj, I.; Kaur, H.; Belley-Cote, E.P.; Wang, J.; Oraii, A.; Benz, A.P.; Johnson, L.S.B.; Young, J.; Wong, J.A.; et al. Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter Inhibitors and Atrial Fibrillation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2021, 10, e022222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonora, B.M.; Raschi, E.; Avogaro, A.; Fadini, G.P. SGLT-2 Inhibitors and Atrial Fibrillation in the Food and Drug Administration Adverse Event Reporting System. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2021, 20, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zinman, B.; Wanner, C.; Lachin, J.M.; Fitchett, D.; Bluhmki, E.; Hantel, S.; Mattheus, M.; Devins, T.; Johansen, O.E.; Woerle, H.J.; et al. Empagliflozin, Cardiovascular Outcomes, and Mortality in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 2117–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Yu, B.; Tan, X.; Wang, B.; Lu, Y.; Wang, N. SGLT2 Inhibition, Circulating Metabolites, and Atrial Fibrillation: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2023, 22, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T.; Aizawa, Y.; Yuasa, S.; Fujita, S.; Ikeda, Y.; Okabe, M. The Effect of Dapagliflozin Treatment on Epicardial Adipose Tissue Volume and P-Wave Indices: An Ad-Hoc Analysis of the Previous Randomized Clinical Trial. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2020, 27, 1348–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaribeygi, H.; Sathyapalan, T.; Atkin, S.L.; Sahebkar, A. Molecular Mechanisms Linking Oxidative Stress and Diabetes Mellitus. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 8609213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aso, Y.; Kato, K.; Sakurai, S.; Kishi, H.; Shimizu, M.; Jojima, T.; Iijima, T.; Maejima, Y.; Shimomura, K.; Usui, I. Impact of Dapagliflozin, an SGLT2 Inhibitor, on Serum Levels of Soluble Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2019, 73, e13335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, K.-F.; Chen, Y.-L.; Chiou, T.T.-Y.; Chu, T.-H.; Li, L.-C.; Ng, H.-Y.; Lee, W.-C.; Lee, C.-T. Emergence of SGLT2 Inhibitors as Powerful Antioxidants in Human Diseases. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nassif, M.E.; Windsor, S.L.; Tang, F.; Khariton, Y.; Husain, M.; Inzucchi, S.E.; McGuire, D.K.; Pitt, B.; Scirica, B.M.; Austin, B.; et al. Dapagliflozin Effects on Biomarkers, Symptoms, and Functional Status in Patients with Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction. Circulation 2019, 140, 1463–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMurray, J.J.V.; Solomon, S.D.; Inzucchi, S.E.; Køber, L.; Kosiborod, M.N.; Martinez, F.A.; Ponikowski, P.; Sabatine, M.S.; Anand, I.S.; Bělohlávek, J.; et al. Dapagliflozin in Patients with Heart Failure and Reduced Ejection Fraction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 1995–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heerspink, H.J.L.; Stefánsson, B.V.; Correa-Rotter, R.; Chertow, G.M.; Greene, T.; Hou, F.-F.; Mann, J.F.E.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Lindberg, M.; Rossing, P.; et al. Dapagliflozin in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1436–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiviott, S.D.; Raz, I.; Bonaca, M.P.; Mosenzon, O.; Kato, E.T.; Cahn, A.; Silverman, M.G.; Zelniker, T.A.; Kuder, J.F.; Murphy, S.A.; et al. Dapagliflozin and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zelniker, T.A.; Bonaca, M.P.; Furtado, R.H.M.; Mosenzon, O.; Kuder, J.F.; Murphy, S.A.; Bhatt, D.L.; Leiter, L.A.; McGuire, D.K.; Wilding, J.P.H.; et al. Effect of Dapagliflozin on Atrial Fibrillation in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Circulation 2020, 141, 1227–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, S.D.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Claggett, B.; de Boer, R.A.; DeMets, D.; Hernandez, A.F.; Inzucchi, S.E.; Kosiborod, M.N.; Lam, C.S.P.; Martinez, F.; et al. Dapagliflozin in Heart Failure with Mildly Reduced or Preserved Ejection Fraction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 1089–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vardeny, O.; Desai, A.S.; Jhund, P.S.; Fang, J.C.; Claggett, B.; de Boer, R.A.; Hernandez, A.F.; Inzucchi, S.E.; Kosiborod, M.N.; Lam, C.S.P.; et al. Dapagliflozin and Mode of Death in Heart Failure with Improved Ejection Fraction. JAMA Cardiol. 2024, 9, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, J.H.; Kondo, T.; Jhund, P.S.; Comin-Colet, J.; de Boer, R.A.; Desai, A.S.; Hernandez, A.F.; Inzucchi, S.E.; Janssens, S.P.; Kosiborod, M.N.; et al. Atrial Fibrillation and Dapagliflozin Efficacy in Patients with Preserved or Mildly Reduced Ejection Fraction. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2022, 80, 1705–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, S.; Erlinge, D.; Storey, R.F.; McGuire, D.K.; de Belder, M.; Eriksson, N.; Andersen, K.; Austin, D.; Arefalk, G.; Carrick, D.; et al. Dapagliflozin in Myocardial Infarction without Diabetes or Heart Failure. NEJM Evid. 2023, 3, EVIDoa2300286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anker, S.D.; Butler, J.; Filippatos, G.; Ferreira, J.P.; Bocchi, E.; Böhm, M.; Brunner-La Rocca, H.-P.; Choi, D.-J.; Chopra, V.; Chuquiure-Valenzuela, E.; et al. Empagliflozin in Heart Failure with a Preserved Ejection Fraction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1451–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filippatos, G.; Farmakis, D.; Butler, J.; Zannad, F.; Ferreira, J.P.; Ofstad, A.P.; Iwata, T.; Brueckmann, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Packer, M.; et al. Empagliflozin in Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction with and without Atrial Fibrillation. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2023, 25, 970–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Böhm, M.; Slawik, J.; Brueckmann, M.; Mattheus, M.; George, J.T.; Ofstad, A.P.; Inzucchi, S.E.; Fitchett, D.; Anker, S.D.; Marx, N.; et al. Efficacy of Empagliflozin on Heart Failure and Renal Outcomes in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation: Data from the EMPA-REG OUTCOME Trial. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2020, 22, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Liu, Y.; Hidru, T.H.; Yang, X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, C.; Li, K.H.C.; Tang, Y.; Wei, Y.; Tse, G.; et al. Protective Effects of Sodium-Glucose Transporter 2 Inhibitors on Atrial Fibrillation and Atrial Flutter: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trials. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 619586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, R.-J.; Wang, Y.; Tang, J.-N.; Duan, J.-Y.; Yuan, M.-Y.; Zhang, J.-Y. Association of SGLT2 Inhibitors with Risk of Atrial Fibrillation and Stroke in Patients with and without Type 2 Diabetes: A Systemic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2022, 79, e145–e152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.-L.; Lip, G.Y.H.; Feng, Q.; Fei, Y.; Tse, Y.-K.; Wu, M.; Ren, Q.; Tse, H.-F.; Cheung, B.-M.Y.; Yiu, K.-H. Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors (SGLT2i) and Cardiac Arrhythmias: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2021, 20, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sfairopoulos, D.; Liu, T.; Zhang, N.; Tse, G.; Bazoukis, G.; Letsas, K.; Goudis, C.; Milionis, H.; Vrettos, A.; Korantzopoulos, P. Association between Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors and Incident Atrial Fibrillation/Atrial Flutter in Heart Failure Patients with Reduced Ejection Fraction: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Heart Fail. Rev. 2022, 28, 925–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rau, M.; Thiele, K.; Hartmann, N.-U.K.; Schuh, A.; Altiok, E.; Möllmann, J.; Keszei, A.P.; Böhm, M.; Marx, N.; Lehrke, M. Empagliflozin Does Not Change Cardiac Index nor Systemic Vascular Resistance but Rapidly Improves Left Ventricular Filling Pressure in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized Controlled Study. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2021, 20, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiele, K.; Rau, M.; Grebe, J.; Korbinian Hartmann, N.-U.; Altiok, E.; Böhm, M.; Keszei, A.P.; Marx, N.; Lehrke, M. Empagliflozin Improves Left Atrial Strain in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: Data From a Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Study. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2023, 16, e015176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koizumi, T.; Watanabe, M.; Yokota, T.; Tsuda, M.; Handa, H.; Koya, J.; Nishino, K.; Tatsuta, D.; Natsui, H.; Kadosaka, T.; et al. Empagliflozin Suppresses Mitochondrial Reactive Oxygen Species Generation and Mitigates the Inducibility of Atrial Fibrillation in Diabetic Rats. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2023, 10, 1005408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puglisi, S.; Rossini, A.; Poli, R.; Dughera, F.; Pia, A.; Terzolo, M.; Reimondo, G. Effects of SGLT2 Inhibitors and GLP-1 Receptor Agonists on Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 738848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trum, M.; Riechel, J.; Schollmeier, E.; Lebek, S.; Hegner, P.; Reuthner, K.; Heers, S.; Keller, K.; Wester, M.; Klatt, S.; et al. Empagliflozin Inhibits Increased Na Influx in Atrial Cardiomyocytes of Patients with HFpEF. Cardiovasc. Res. 2024, cvae095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, P.W.; Pieske, B.; Anstrom, K.J.; Ezekowitz, J.; Hernandez, A.F.; Butler, J.; Lam, C.S.P.; Ponikowski, P.; Voors, A.A.; Jia, G.; et al. Vericiguat in Patients with Heart Failure and Reduced Ejection Fraction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1883–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponikowski, P.; Alemayehu, W.; Oto, A.; Bahit, M.C.; Noori, E.; Patel, M.J.; Butler, J.; Ezekowitz, J.A.; Hernandez, A.F.; Lam, C.S.P.; et al. Vericiguat in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation and Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction: Insights from the VICTORIA Trial. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2021, 23, 1300–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, Q.; Li, L.; Liu, G.; Li, T.; Zhang, L.; Zang, Y.; Zhan, C.; Wang, H.; Li, W. Vericiguat Reduces Electrical and Structural Remodeling in a Rabbit Model of Atrial Fibrillation. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. Ther. 2023, 28, 10742484231185252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Authors | Study Design | Patients, n | Clinical Setting | Outcomes | Follow-Up | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wang et al. [62] | Prospective, RCT | 76 | HF with EF > 30% | AF recurrence rate | 12 months | 21.7% p < 0.001 |
| Russo et al. [59] | Prospective | 167 | HFrEF | Reduction in AF episodes | 12 months | −9%; p = 0.03 |
| Zang et al. [70] | Prospective | 140 | CHF | Recurrence rate of AF in HF patients | 12 months | 30%; p = 0.005 |
| De Vecchis et al. [60] | Retrospective | 40 | CHF | Improving PALS | 12 months | 26.5%; p < 0.001 |
| Decreased risk of AF relapses, n (%) | 87.5%; p = 0.001 | |||||
| Chen et al. [61] | Retrospective | 76 | CHF | Ineffective ECV, n (%) | 30 days | 25%; p = 0.02 |
| Authors | Enrolled Patients, n | Characteristics | SGLT2i | Outcomes | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Li et al. [95] | 66,685 | T2DM, T1DM, CKD, HFrEF, HFpEF, or a combination | Dapagliflozin | Incidence of AF | −29% p = 0.003 |
| Canagliflozin | −20% p = 0.19 | ||||
| Empagliflozin | +15% p = 0.59 | ||||
| Sotagliflozin | −49% p = 0.63 | ||||
| Ertugliflozin | +8% p = 0.76 | ||||
| Pandey et al. [75] | 75,279 | DM, CKD, CVD, HFrEF | Dapagliflozin Canagliflozin Empagliflozin Sotagliflozin Ertugliflozin | SAEs AF/AFL | −25% p < 0.0001 |
| Composite of HF hospitalisation/urgent visit or cardiovascular death in patients with AF at baseline | −30% p = 0.0005 | ||||
| Li H et al. [97] | 52,115 | DM, CKD, HF | Dapagliflozin Canagliflozin Empagliflozin Ertugliflozin | Incidence of AF | −18% p hetero |
| Incidence of embolic stroke | −68% p hetero | ||||
| Incidence of AFL | −17% p hetero | ||||
| Incidence of cardiac arrest | −17% p hetero | ||||
| Incidence of AF/AFL | −18% p hetero | ||||
| Incidence of VT | −27% p hetero | ||||
| Zheng et al. [96] | 63,604 | T2DM, HFrEF, CKD, CVD | Dapagliflozin Canagliflozin Empagliflozin Ertugliflozin | Incidence of AF | −18% p = 0.002 |
| Incidence of stroke | −1% p = 0.877 | ||||
| Sfairopoulos et al. [98] | 9467 | HFrEF | Dapagliflozin | Incidence of AF | −31% p = 0.12 |
| Incidence of AF/AFL | −18% p = 0.38 | ||||
| Empagliflozin | Incidence of AF | −45% p = 0.01 | |||
| Incidence of AF/AFL | −50% p = 0.002 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mauriello, A.; Ascrizzi, A.; Roma, A.S.; Molinari, R.; Caturano, A.; Imbalzano, E.; D’Andrea, A.; Russo, V. Effects of Heart Failure Therapies on Atrial Fibrillation: Biological and Clinical Perspectives. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 806. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox13070806
Mauriello A, Ascrizzi A, Roma AS, Molinari R, Caturano A, Imbalzano E, D’Andrea A, Russo V. Effects of Heart Failure Therapies on Atrial Fibrillation: Biological and Clinical Perspectives. Antioxidants. 2024; 13(7):806. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox13070806
Chicago/Turabian StyleMauriello, Alfredo, Antonia Ascrizzi, Anna Selvaggia Roma, Riccardo Molinari, Alfredo Caturano, Egidio Imbalzano, Antonello D’Andrea, and Vincenzo Russo. 2024. "Effects of Heart Failure Therapies on Atrial Fibrillation: Biological and Clinical Perspectives" Antioxidants 13, no. 7: 806. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox13070806
APA StyleMauriello, A., Ascrizzi, A., Roma, A. S., Molinari, R., Caturano, A., Imbalzano, E., D’Andrea, A., & Russo, V. (2024). Effects of Heart Failure Therapies on Atrial Fibrillation: Biological and Clinical Perspectives. Antioxidants, 13(7), 806. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox13070806












