Molecular, Physical, and Technical Performance Response After a Competitive Match in Male Professional Soccer Players
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants and Study Plan
2.2. Global Positioning System (GPS) Measurement
2.3. Plasma Oxidative Stress Measurements
2.4. Plasma Protein Carbonylation Analysis
2.5. Salivary IgA Western Blot Analysis
2.6. Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry (GC–MS) Analysis of Plasma Samples
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participants’ Characteristics
3.2. GPS Analysis
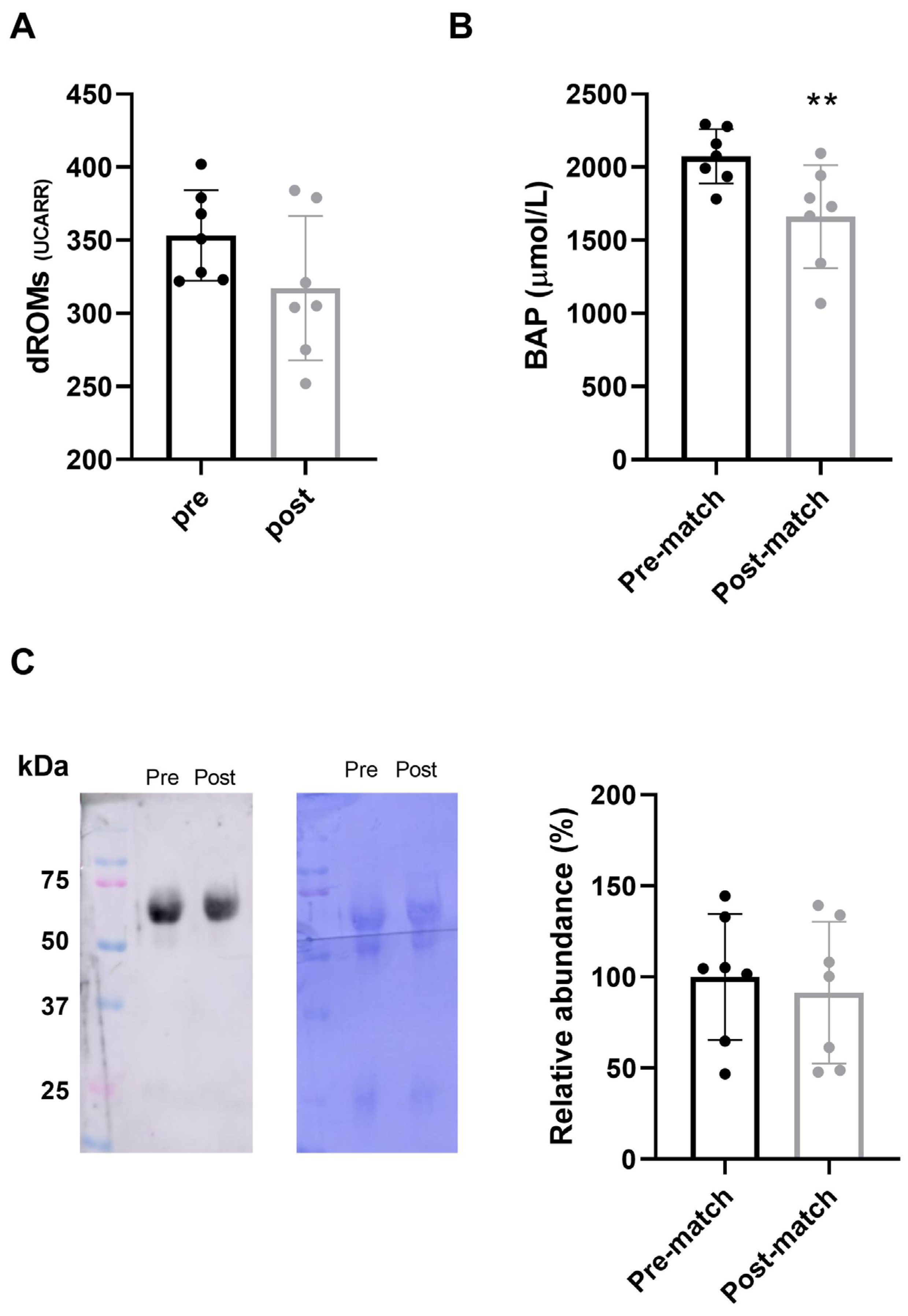
3.3. Plasma Oxidative Stress Analysis
3.4. IgA Levels in Saliva Samples
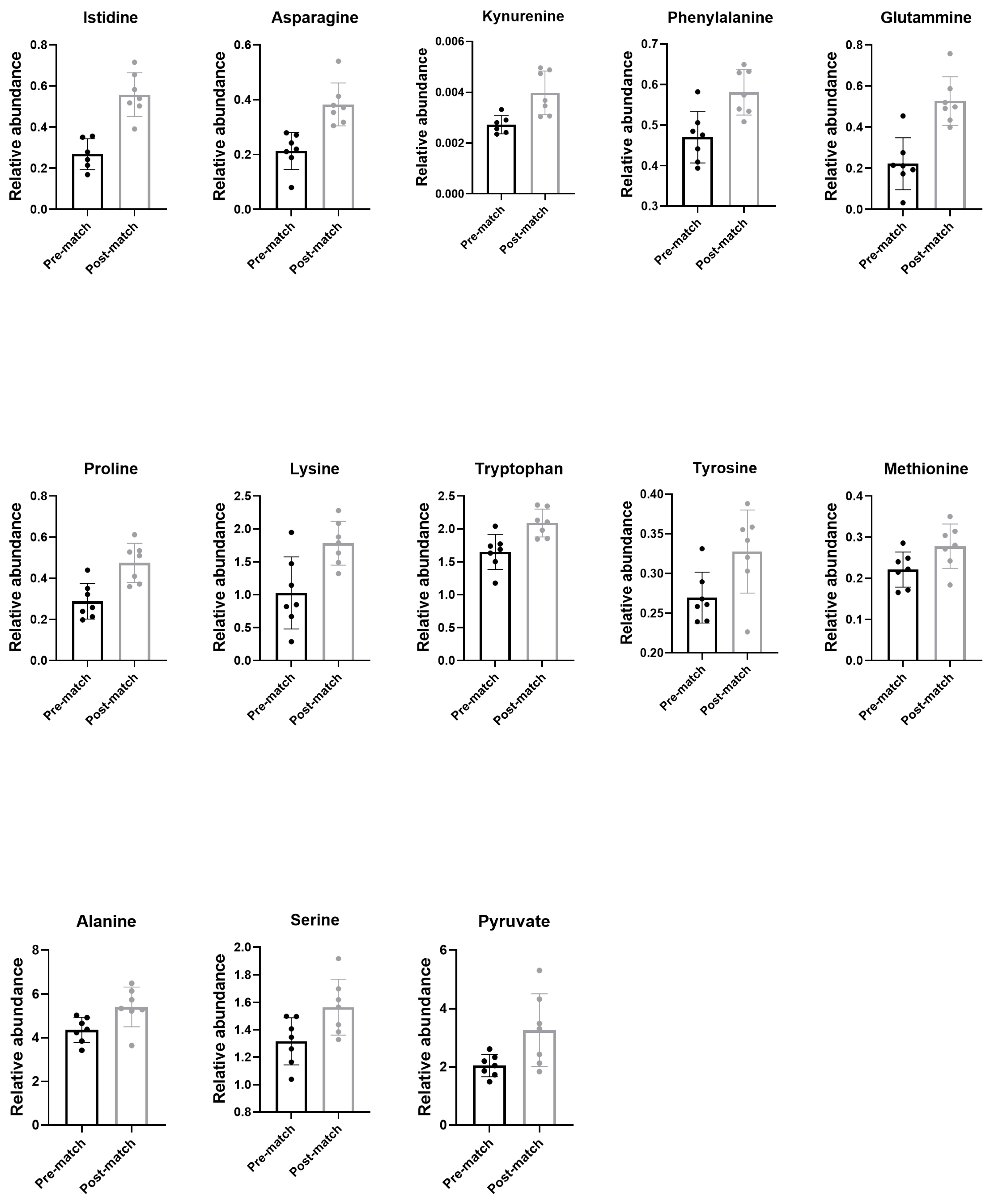
3.5. Metabolomic Analysis Using Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry (GC/MS)
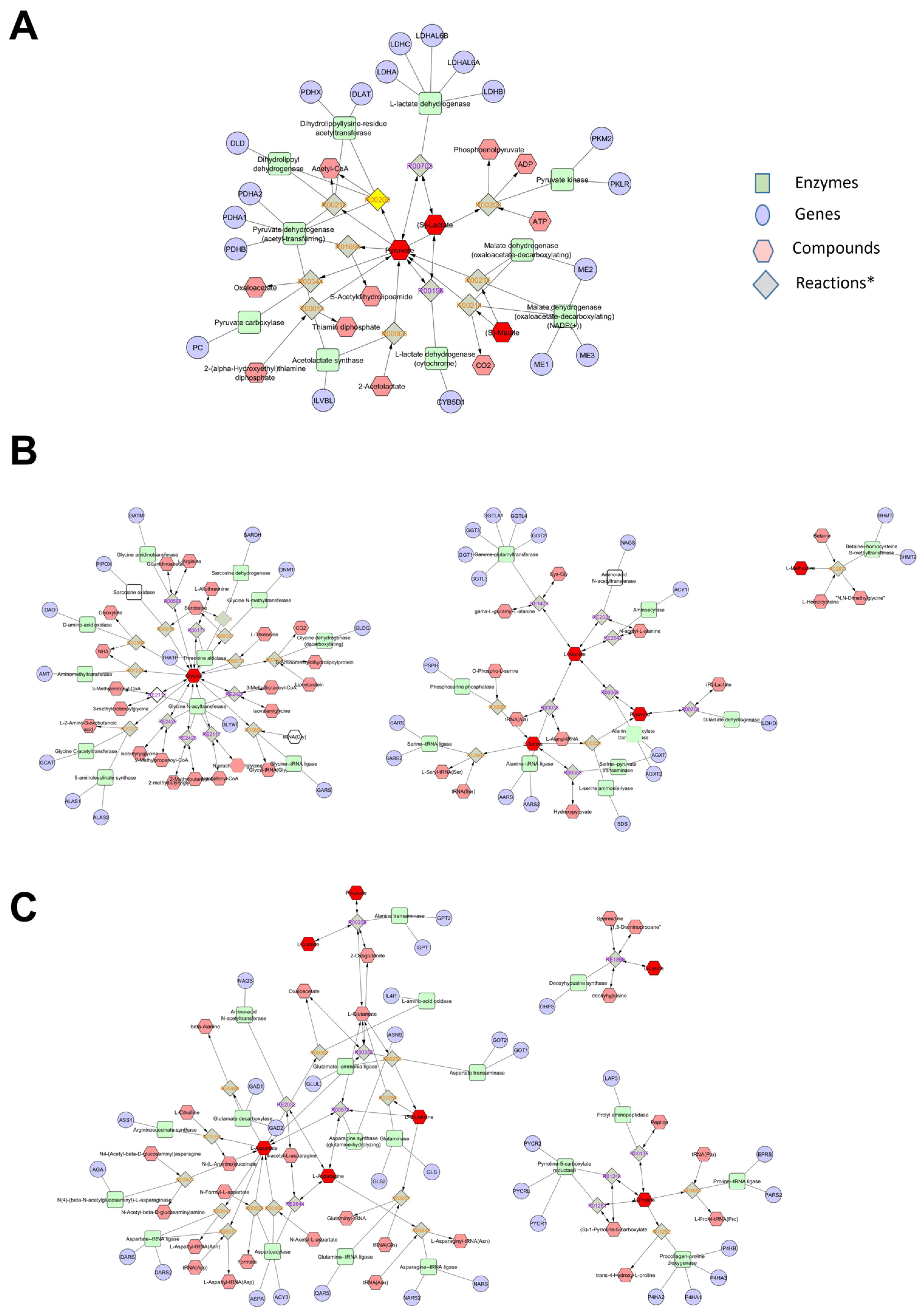
3.6. Metabolomic Interaction Network
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bangsbo, J.; Iaia, F.M.; Krustrup, P. Metabolic Response and Fatigue in Soccer. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2007, 2, 111–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aslan, A.; Acikada, C.; Güvenç, A.; Gören, H.; Hazir, T.; Ozkara, A. Metabolic Demands of Match Performance in Young Soccer Players. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2012, 11, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alghannam, A.F. Metabolic Limitations of Performance and Fatigue in Football. Asian J. Sports Med. 2012, 3, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nédélec, M.; McCall, A.; Carling, C.; Legall, F.; Berthoin, S.; Dupont, G. Recovery in Soccer. Sports Med. 2012, 42, 997–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Castillo, Í.M.; Rueda, R.; Bouzamondo, H.; López-Chicharro, J.; Mihic, N. Biomarkers of Post-Match Recovery in Semi-Professional and Professional Football (Soccer). Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1167449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luti, S.; Militello, R.; Fiaschi, T.; Magherini, F.; Gamberi, T.; Parri, M.; Marzocchini, R.; Pratesi, S.; Soldaini, R.; Modesti, A.; et al. Preliminary Results Indicate That Regular Training Induces High Protection against Oxidative Stress in Basketball Players Compared to Soccer. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 18526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Militello, R.; Pinto, G.; Illiano, A.; Luti, S.; Magherini, F.; Amoresano, A.; Modesti, P.A.; Modesti, A. Modulation of Plasma Proteomic Profile by Regular Training in Male and Female Basketball Players: A Preliminary Study. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 813447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, G.A. Lactate as a Fulcrum of Metabolism. Redox Biol. 2020, 35, 101454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Militello, R.; Luti, S.; Parri, M.; Marzocchini, R.; Soldaini, R.; Modesti, A.; Modesti, P.A. Redox Homeostasis and Metabolic Profile in Young Female Basketball Players during In-Season Training. Healthcare 2021, 9, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, G.; Militello, R.; Amoresano, A.; Modesti, P.A.; Modesti, A.; Luti, S. Relationships between Sex and Adaptation to Physical Exercise in Young Athletes: A Pilot Study. Healthcare 2022, 10, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selmi, O.; Ouergui, I.; Muscella, A.; Levitt, D.E.; Suzuki, K.; Bouassida, A. Monitoring Mood State to Improve Performance in Soccer Players: A Brief Review. Front. Psychol. 2023, 14, 1095238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, D.; Malone, S.; Collins, K.; Mourot, L.; Beato, M.; Coratella, G. Metabolic Power in Hurling with Respect to Position and Halves of Match-Play. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0225947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nobari, H.; Sögüt, M.; Oliveira, R.; Pérez-Gómez, J.; Suzuki, K.; Zouhal, H. Wearable Inertial Measurement Unit to Accelerometer-Based Training Monotony and Strain during a Soccer Season: A within-Group Study for Starters and Non-Starters. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 8007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinhardt, L.; Schwesig, R.; Lauenroth, A.; Schulze, S.; Kurz, E. Enhanced Sprint Performance Analysis in Soccer: New Insights from a GPS-Based Tracking System. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0217782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hennessy, L.; Jeffreys, I. The Current Use of GPS, Its Potential, and Limitations in Soccer. Strength. Cond. J. 2018, 40, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bestwick-Stevenson, T.; Toone, R.; Neupert, E.; Edwards, K.; Kluzek, S. Assessment of Fatigue and Recovery in Sport: Narrative Review. Int. J. Sports Med. 2022, 43, 1151–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petri, C.; Mascherini, G.; Izzicupo, P.; Rosati, D.; Cerboneschi, M.; Smeazzetto, S.; Arrones, L.S. Gut Microbiota and Physical Activity Level: Characterization from Sedentary to Soccer Players. Biol. Sport 2024, 41, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luti, S.; Militello, R.; Pinto, G.; Illiano, A.; Amoresano, A.; Chiappetta, G.; Marzocchini, R.; Modesti, P.A.; Pratesi, S.; Pazzagli, L.; et al. Chronic Training Induces Metabolic and Proteomic Response in Male and Female Basketball Players: Salivary Modifications during In-Season Training Programs. Healthcare 2023, 11, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filetti, C.; Ruscello, B.; Ascenzi, G.; Di Mascio, M.; D’ottavio, S. Physical Performance Metrics in Elite Soccer: Do Power and Acceleration Metrics Provide Insight into Positional Demands and Match-Related Fatigue in the 4-3-3 System? J. Sports Med. Phys. Fitness 2019, 59, 1640–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, P.S.; Di Mascio, M.; Peart, D.; Olsen, P.; Sheldon, B. High-Intensity Activity Profiles of Elite Soccer Players at Different Performance Levels. J. Strength. Cond. Res. 2010, 24, 2343–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, P.S.; Carling, C.; Archer, D.; Roberts, J.; Dodds, A.; Di Mascio, M.; Paul, D.; Gomez Diaz, A.; Peart, D.; Krustrup, P. The Effect of Playing Formation on High-Intensity Running and Technical Profiles in English FA Premier League Soccer Matches. J. Sports Sci. 2011, 29, 821–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aquino, R.; Carling, C.; Palucci Vieira, L.H.; Martins, G.; Jabor, G.; Machado, J.; Santiago, P.; Garganta, J.; Puggina, E. Influence of Situational Variables, Team Formation, and Playing Position on Match Running Performance and Social Network Analysis in Brazilian Professional Soccer Players. J. Strength. Cond. Res. 2020, 34, 808–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magherini, F.; Abruzzo, P.M.; Puglia, M.; Bini, L.; Gamberi, T.; Esposito, F.; Veicsteinas, A.; Marini, M.; Fiorillo, C.; Gulisano, M.; et al. Proteomic Analysis and Protein Carbonylation Profile in Trained and Untrained Rat Muscles. J. Proteomics 2012, 75, 978–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luti, S.; Militello, R.; Pinto, G.; Illiano, A.; Marzocchini, R.; Santi, A.; Becatti, M.; Amoresano, A.; Gamberi, T.; Pellegrino, A.; et al. Chronic Lactate Exposure Promotes Cardiomyocyte Cytoskeleton Remodelling. Heliyon 2024, 10, e24719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliva-Lozano, J.M.; Granero-Gil, P.; Panascì, M. Changes in Physical Performance Throughout Professional Soccer Match-Play. J. Strength. Cond. Res. 2024, 38, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aktitiz, S.; Koşar, Ş.N.; Turnagöl, H.H. Effects of Acute and Multi-Day Low-Dose Sodium Bicarbonate Intake on High-Intensity Endurance Exercise Performance in Male Recreational Cyclists. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2024, 124, 2111–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, J.L.; Gleeson, M.; Pyne, D.B.; Callister, R.; Clancy, R.L. Variation of Salivary Immunoglobulins in Exercising and Sedentary Populations. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2005, 37, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujika, I.; Halson, S.; Burke, L.M.; Balagué, G.; Farrow, D. An Integrated, Multifactorial Approach to Periodization for Optimal Performance in Individual and Team Sports. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2018, 13, 538–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalen, T.; Jørgen, I.; Gertjan, E.; Geir Havard, H.; Ulrik, W. Player Load, Acceleration, and Deceleration During Forty-Five Competitive Matches of Elite Soccer. J. Strength. Cond. Res. 2016, 30, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aquino, R.; Vieira, L.H.P.; Carling, C.; Martins, G.H.M.; Alves, I.S.; Puggina, E.F. Effects of Competitive Standard, Team Formation and Playing Position on Match Running Performance of Brazilian Professional Soccer Players. Int. J. Perform. Anal. Sport. 2017, 17, 695–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souglis, A.; Bogdanis, G.C.; Chryssanthopoulos, C.; Apostolidis, N.; Geladas, N.D. Time Course of Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Muscle Damage Markers for 5 Days After a Soccer Match: Effects of Sex and Playing Position. J. Strength. Cond. Res. 2018, 32, 2045–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kon, M.; Taniguchi, K.; Ebi, Y.; Nakagaki, K. Effects of High-Intensity Interval Exercise under Hyperoxia on HSP27 and Oxidative Stress Responses. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2021, 283, 103544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colombo, G.; Clerici, M.; Garavaglia, M.E.; Giustarini, D.; Rossi, R.; Milzani, A.; Dalle-Donne, I. A Step-by-Step Protocol for Assaying Protein Carbonylation in Biological Samples. J. Chromatogr. B 2016, 1019, 178–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas Echeverri, J.C.; Milkovska-Stamenova, S.; Hoffmann, R. A Workflow towards the Reproducible Identification and Quantitation of Protein Carbonylation Sites in Human Plasma. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, H.; John, A.; Shafarin, J.; Howarth, F.C. Exercise-Induced Alterations in Pancreatic Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial Function in Type 2 Diabetic Goto-Kakizaki Rats. Physiol. Rep. 2016, 4, e12751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidi, F.; Magherini, F.; Gamberi, T.; Bini, L.; Puglia, M.; Marzocchini, R.; Ranaldi, F.; Modesti, P.A.; Gulisano, M.; Modesti, A. Plasma Protein Carbonylation and Physical Exercise. Mol. Biosyst. 2011, 7, 640–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peñailillo, L.; Maya, L.; Niño, G.; Torres, H.; Zbinden-Foncea, H. Salivary Hormones and IgA in Relation to Physical Performance in Football. J. Sports Sci. 2015, 33, 2080–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieman, D.C.; Henson, D.A.; Austin, M.D.; Brown, V.A. Immune Response to a 30-Minute Walk. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2005, 37, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, A.; Arsati, F.; Cury, P.R.; Franciscon, C.; de Oliveira, P.R.; de Araújo, V.C. Salivary Immunoglobulin A Response to a Match in Top-Level Brazilian Soccer Players. J. Strength. Cond. Res. 2009, 23, 1968–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, A.J.; Wherry, A.D.; Petersen, M.C.; Johnson, J.C.; Stuart, M.K.; Sexton, W.L. Salivary Immunoglobulin Aresponse to A Collegiate Rugby Game. J. Strength. Cond. Res. 2007, 21, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgans, R.; Orme, P.; Bezuglov, E.; Di Michele, R.; Moreira, A. The Immunological and Hormonal Responses to Competitive Match-Play in Elite Soccer Players. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 11784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Churchward-Venne, T.A.; Pinckaers, P.J.; Smeets, J.S.; Betz, M.W.; Senden, J.M.; Goessens, J.P.; Gijsen, A.P.; Rollo, I.; Verdijk, L.B.; van Loon, L.J. Dose-Response Effects of Dietary Protein on Muscle Protein Synthesis during Recovery from Endurance Exercise in Young Men: A Double-Blind Randomized Trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 112, 303–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henriksson, J. Effect of Exercise on Amino Acid Concentrations in Skeletal Muscle and Plasma. J. Exp. Biol. 1991, 160, 149–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blomstrand, E.; Hassmén, P.; EK, S.; Ekblom, B.; Newsholme, E.A. Influence of Ingesting a Solution of Branched-chain Amino Acids on Perceived Exertion during Exercise. Acta Physiol. Scand. 1997, 159, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassmén, P.; Blomstrand, E.; Ekblom, B.; Newsholme, E.A. Branched-Chain Amino Acid Supplementation during 30-Km Competitive Run: Mood and Cognitive Performance. Nutrition 1994, 10, 405–410. [Google Scholar]
- Strasser, B.; Geiger, D.; Schauer, M.; Gostner, J.; Gatterer, H.; Burtscher, M.; Fuchs, D. Probiotic Supplements Beneficially Affect Tryptophan–Kynurenine Metabolism and Reduce the Incidence of Upper Respiratory Tract Infections in Trained Athletes: A Randomized, Double-Blinded, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2016, 8, 752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strasser, B.; Geiger, D.; Schauer, M.; Gatterer, H.; Burtscher, M.; Fuchs, D. Effects of Exhaustive Aerobic Exercise on Tryptophan-Kynurenine Metabolism in Trained Athletes. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Portuguez, R.; Sutphin, G.L. Kynurenine Pathway, NAD+ Synthesis, and Mitochondrial Function: Targeting Tryptophan Metabolism to Promote Longevity and Healthspan. Exp. Gerontol. 2020, 132, 110841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castell, L.M.; Newsholme, E.A. Glutamine and the Effects of Exhaustive Exercise upon the Immune Response. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 1998, 76, 524–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusy, K.; Matysiak, J.; Zarębska, E.A.; Klupczyńska-Gabryszak, A.; Ciekot-Sołtysiak, M.; Plewa, S.; Kokot, Z.J.; Dereziński, P.; Zieliński, J. Changes in Plasma Concentration of Free Proteinogenic and Non-Proteinogenic Amino Acids in High-Performance Sprinters over a 6-Month Training Cycle. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 5300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusy, K.; Ciekot-Sołtysiak, M.; Matysiak, J.; Klupczyńska-Gabryszak, A.; Plewa, S.; Zarębska, E.A.; Kokot, Z.J.; Dereziński, P.; Zieliński, J. Changes in Plasma Free Amino Acid Profile in Endurance Athletes over a 9-Month Training Cycle. Metabolites 2024, 14, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felig, P.; Wahren, J. Amino Acid Metabolism in Exercising Man. J. Clin. Investig. 1971, 50, 2703–2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houten, S.M.; Herrema, H.; te Brinke, H.; Denis, S.; Ruiter, J.P.N.; van Dijk, T.H.; Argmann, C.A.; Ottenhoff, R.; Müller, M.; Groen, A.K.; et al. Impaired Amino Acid Metabolism Contributes to Fasting-Induced Hypoglycemia in Fatty Acid Oxidation Defects. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2013, 22, 5249–5261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikonen, J.N.; Joro, R.; Uusitalo, A.L.; Kyröläinen, H.; Kovanen, V.; Atalay, M.; Tanskanen-Tervo, M.M. Effects of Military Training on Plasma Amino Acid Concentrations and Their Associations with Overreaching. Exp. Biol. Med. 2020, 245, 1029–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancha, A.H.; Recco, M.B.; Abdalla, D.S.P.; Curi, R. Effect of Aspartate, Asparagine, and Carnitine Supplementation in the Diet on Metabolism of Skeletal Muscle during a Moderate Exercise. Physiol. Behav. 1995, 57, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisi, A.; Quaranta, F.; Masala, D.; Fagnani, F.; Di Salvo, V.; Casasco, M.; Pigozzi, F. Do Aspartate and Asparagine Acute Supplementation Influence the Onset of Fatigue in Intense Exercise? J. Sports Med. Phys. Fitness 2007, 47, 422–426. [Google Scholar]
- Lancha, A.H.; Poortmans, J.R.; Pereira, L.O. The Effect of 5 Days of Aspartate and Asparagine Supplementation on Glucose Transport Activity in Rat Muscle. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2009, 27, 552–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Age (Year) | Height (cm) | Weight (kg) | BMI (kg/m2) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD 1 | 27 | 182 | 78.1 | 23.6 |
| CD 2 | 24 | 186 | 76.6 | 22.1 |
| SD 1 | 32 | 179 | 71 | 22.8 |
| SD 2 | 23 | 174 | 64.1 | 21.2 |
| MF 1 | 34 | 179 | 74.5 | 23.3 |
| MF 2 | 31 | 179 | 84.9 | 26.5 |
| ST 1 | 23 | 174.5 | 75.8 | 24.9 |
| Mean | 27.7 | 174.5 | 71 | 23.5 |
| Total Distance (m) | Sprint Running Distance > 25 km/h (m) | Distance Acceleration > 2 m/s2 | Metabolic Power (W/Kg) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Analyzed match | 10,113.4 ± 178.32 | 283.38 ± 132.80 | 176.84 ± 33.50 | 10.57 ± 0.85 |
| Serie A mean | 11,070.4 ± 188.20 | 241.05 ± 21.90 | 228.00 ± 7.00 | 10.50 ± 0.20 |
| Time Played (Minutes) | Total Distance (m) | Sprint Running Distance > 25 km/h (m) | Distance Acceleration > 2 m/s2 | Metabolic Power | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD 1 | 97.53 | 11,398.03 | 426.71 | 215.26 | 10.85 |
| CD 2 | 97.53 | 10,557.39 | 285.7 | 172.27 | 10.02 |
| Mean CD | 97.53 | 10,977.7 ± 594.42 | 356.2 ± 99.7 | 193.7 ± 30.4 | 10.6 ± 0.7 |
| SD 1 | 97.53 | 12,279.01 | 335.81 | 122 | 11.76 |
| SD 2 | 91.23 | 10,998.58 | 513.44 | 193.03 | 11.34 |
| Mean SD | 94.38 | 11,638.8 ± 905.4 | 424.62 ± 125.6 | 157.5 ± 50.22 | 11.5 ± 0.29 |
| MF 1 | 97.53 | 10,489.21 | 161.79 | 198.8 | 10.05 |
| MF 2 | 85.13 | 8621.21 | 154.46 | 141.44 | 9.28 |
| Mean MF | 91.33 | 9555.2 ± 660.4 | 158.12 ± 5.1 | 170.12 ± 40.5 | 9.66 ± 0.54 |
| ST 1 | 85 | 9993.88 | 201.98 | 210.57 | 11.25 |
| Metabolite Name | CAS Number ◘ | KEGG ID ° | Mean-Pre | Mean-Post | Difference + | p-Value Δ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L-alanine | 56-41-7 | C00041 | 4.361 | 5.414 | 1.053 | 0.023989 * |
| L-asparagine | 70-47-3 | C00152 | 0.2131 | 0.3830 | 0.1699 | 0.000937 * |
| L-aspartic acid | 56-84-8 | C00049 | 0.06905 | 0.09054 | 0.02149 | 0.082809 * |
| L-phenylalanine | 63-91-2 | C00079 | 0.4704 | 0.5812 | 0.1107 | 0.004835 * |
| L-glycine | 56-40-6 | C00037 | 3.056 | 3.292 | 0.2359 | 0.318085 |
| L-glutamic acid | 56-86-0 | C00025 | 0.9687 | 1.212 | 0.2434 | 0.138978 |
| L-glutamine | 56-85-9 | C00064 | 0.2220 | 0.5267 | 0.3047 | 0.000553 * |
| L-isoleucine | 73-32-5 | C00407 | 1.014 | 1.149 | 0.1354 | 0.468522 |
| L-histidine | 26,062-48-6 | C00135 | 0.2685 | 0.5578 | 0.2893 | 0.000168 * |
| L-leucine | 61-90-5 | C00123 | 1.925 | 2.204 | 0.2784 | 0.415897 |
| L-lysine | 56-87-1 | C00047 | 1.027 | 1.783 | 0.7559 | 0.008950 * |
| L-methionine | 63-68-3 | C00073 | 0.2213 | 0.2780 | 0.05671 | 0.049442 * |
| L-proline | 147-85-3 | C00148 | 0.2885 | 0.4748 | 0.1863 | 0.002407 * |
| L-serine | 56-45-1 | C00065 | 1.316 | 1.565 | 0.2489 | 0.029811 * |
| L-tyrosine | 200-460-4 | C00082 | 0.2699 | 0.3278 | 0.05799 | 0.028104 * |
| L-threonine | 956-48-9 | C00102 | 0.4877 | 0.4689 | −0.01885 | 0.712030 |
| L-tryptophan | 73-22-3 | C00078 | 1650 | 2090 | 0.4400 | 0.005013 * |
| L-valine | 72-18-4 | C00183 | 3041 | 3265 | 0.2241 | 0.471524 |
| kynurenine | 2922-83-0 | C00328 | 0.002727 | 0.003975 | 0.001248 | 0.007081 * |
| Alpha-ketoglutaric acid | 328-50-7 | C00026 | 0.05269 | 0.05919 | 0.006503 | 0.301500 |
| Citric acid | 5949-29-1 | C00158 | 1.117 | 1.317 | 0.2004 | 0.211565 |
| Fumarate | 110-17-8 | C00122 | 0.02126 | 0.02053 | −0.0007238 | 0.811405 |
| Malate | 149-61-1 | C00149 | 0.03063 | 0.04747 | 0.01684 | 0.201045 |
| Succinate | 56-14-4 | C00042 | 0.1381 | 0.1128 | −0.02532 | 0.107247 |
| Pyruvate | 57-60-3 | C00022 | 2.040 | 3.262 | 1.221 | 0.029370 * |
| L-lactic acid | 79-33-4 | C00186 | 21.66 | 26.49 | 4.832 | 0.062270 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Modesti, A.; Militello, R.; Tanturli, A.; Santi, A.; Gulisano, M.; Petri, C.; Pengue, L.; Pellegrino, A.; Modesti, P.A.; Luti, S. Molecular, Physical, and Technical Performance Response After a Competitive Match in Male Professional Soccer Players. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 73. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14010073
Modesti A, Militello R, Tanturli A, Santi A, Gulisano M, Petri C, Pengue L, Pellegrino A, Modesti PA, Luti S. Molecular, Physical, and Technical Performance Response After a Competitive Match in Male Professional Soccer Players. Antioxidants. 2025; 14(1):73. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14010073
Chicago/Turabian StyleModesti, Alessandra, Rosamaria Militello, Alice Tanturli, Alice Santi, Massimo Gulisano, Cristian Petri, Luca Pengue, Alessio Pellegrino, Pietro Amedeo Modesti, and Simone Luti. 2025. "Molecular, Physical, and Technical Performance Response After a Competitive Match in Male Professional Soccer Players" Antioxidants 14, no. 1: 73. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14010073
APA StyleModesti, A., Militello, R., Tanturli, A., Santi, A., Gulisano, M., Petri, C., Pengue, L., Pellegrino, A., Modesti, P. A., & Luti, S. (2025). Molecular, Physical, and Technical Performance Response After a Competitive Match in Male Professional Soccer Players. Antioxidants, 14(1), 73. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14010073








