Sucralose Promotes Benzo(a)Pyrene-Induced Renal Toxicity in Mice by Regulating P-glycoprotein
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Experiments
2.2. Antibodies, Chemicals and Reagents
2.3. Cell Culture and Cell Viability Assay
2.4. Biochemical Analysis
2.5. Histology Staining
2.6. Cellular Oxidative Stress Assay
2.7. B[a]P Accumulation and Efflux Assay
2.8. Cell Transient Transfection (PGP siRNA)
2.9. Molecular Docking
2.10. Western Blotting Assay
2.11. RNA Extraction, cDNA Synthesis, and RT-qPCR
2.12. Cellular Thermal Shift Assay (CETSA)
2.13. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
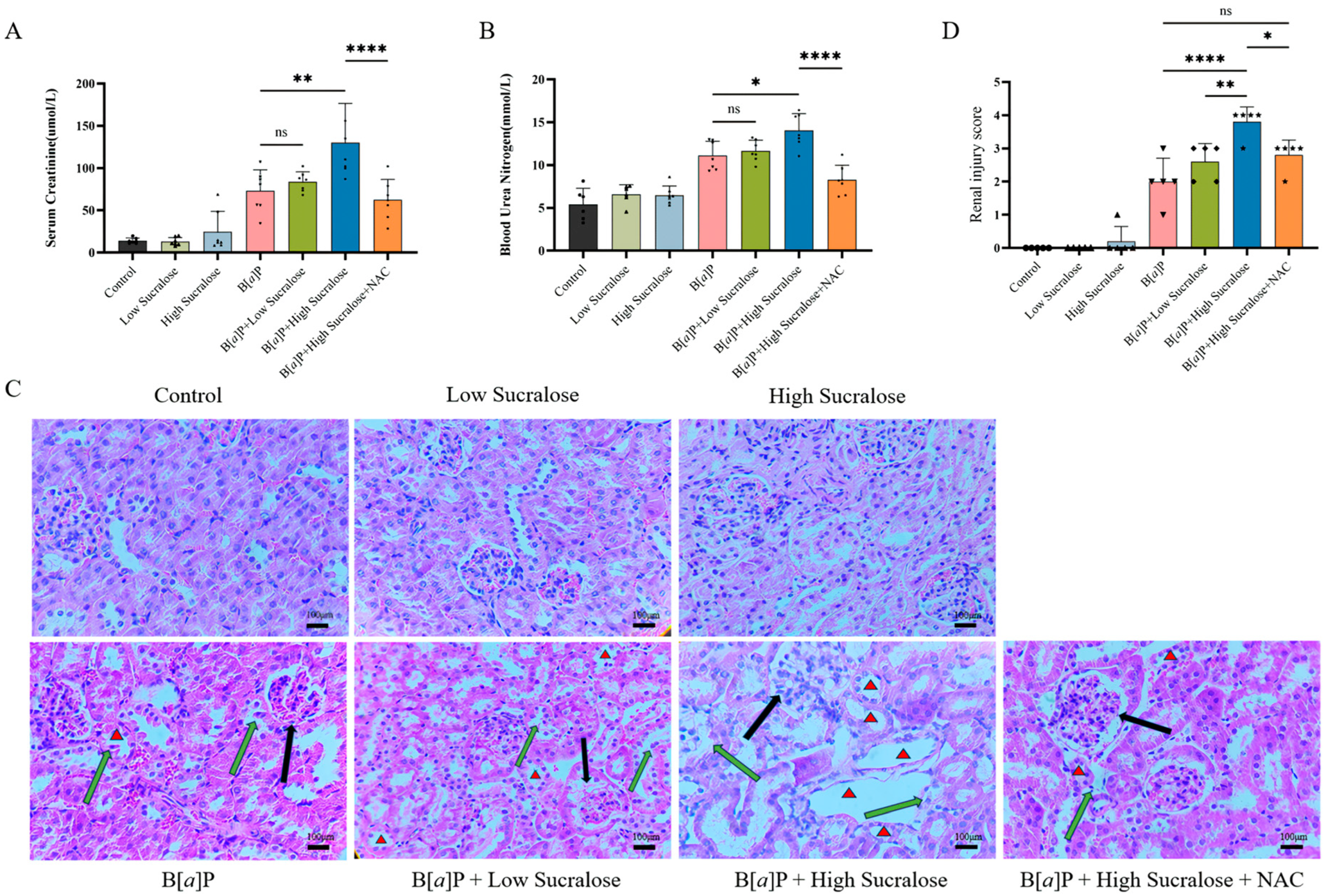
3.1. Sucralose Enhanced B[a]P-Induced Subchronic Kidney Injury
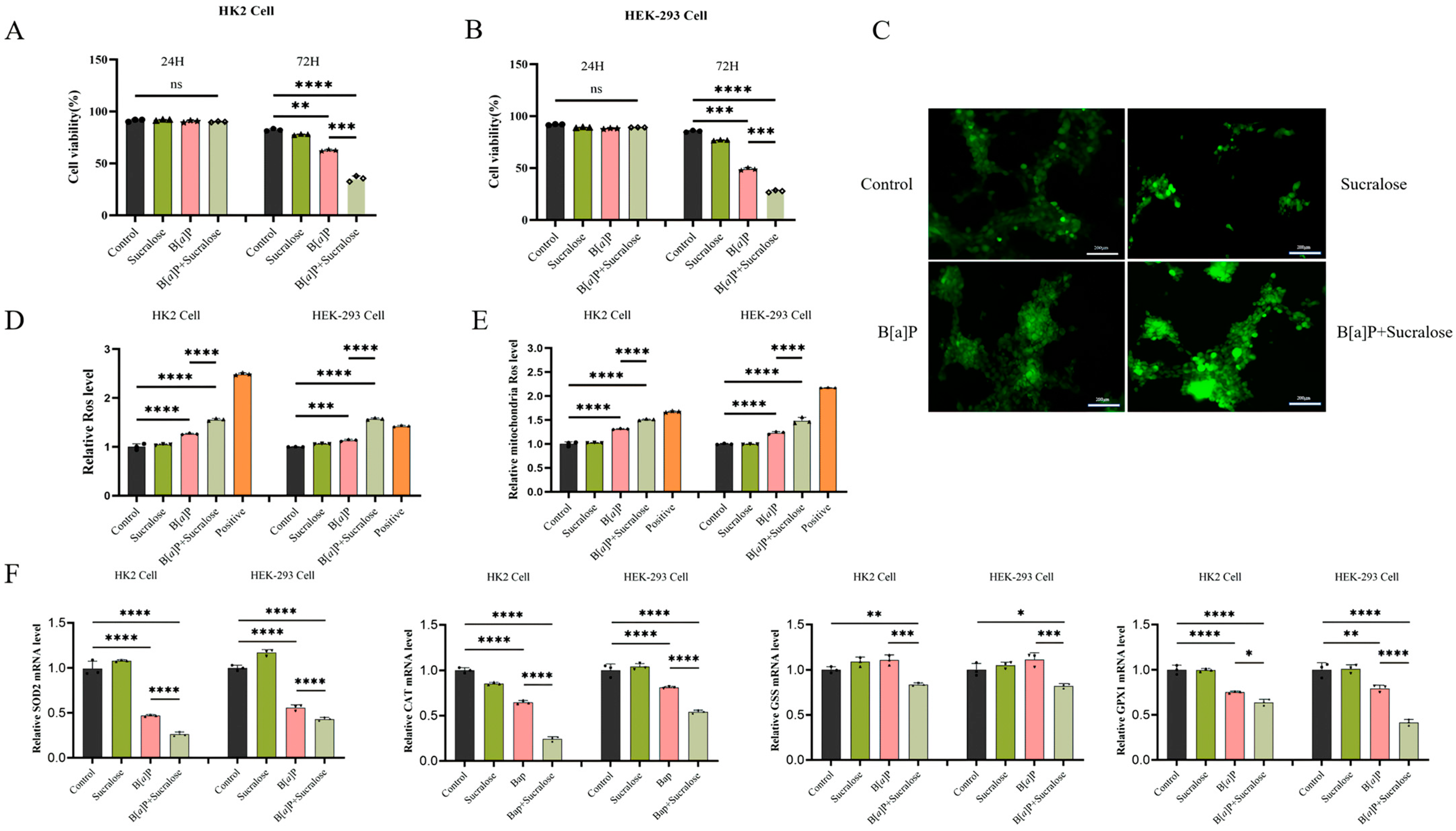
3.2. Sucralose Sensitized B[a]P-Induced Cell Growth Inhibition and ROS Production
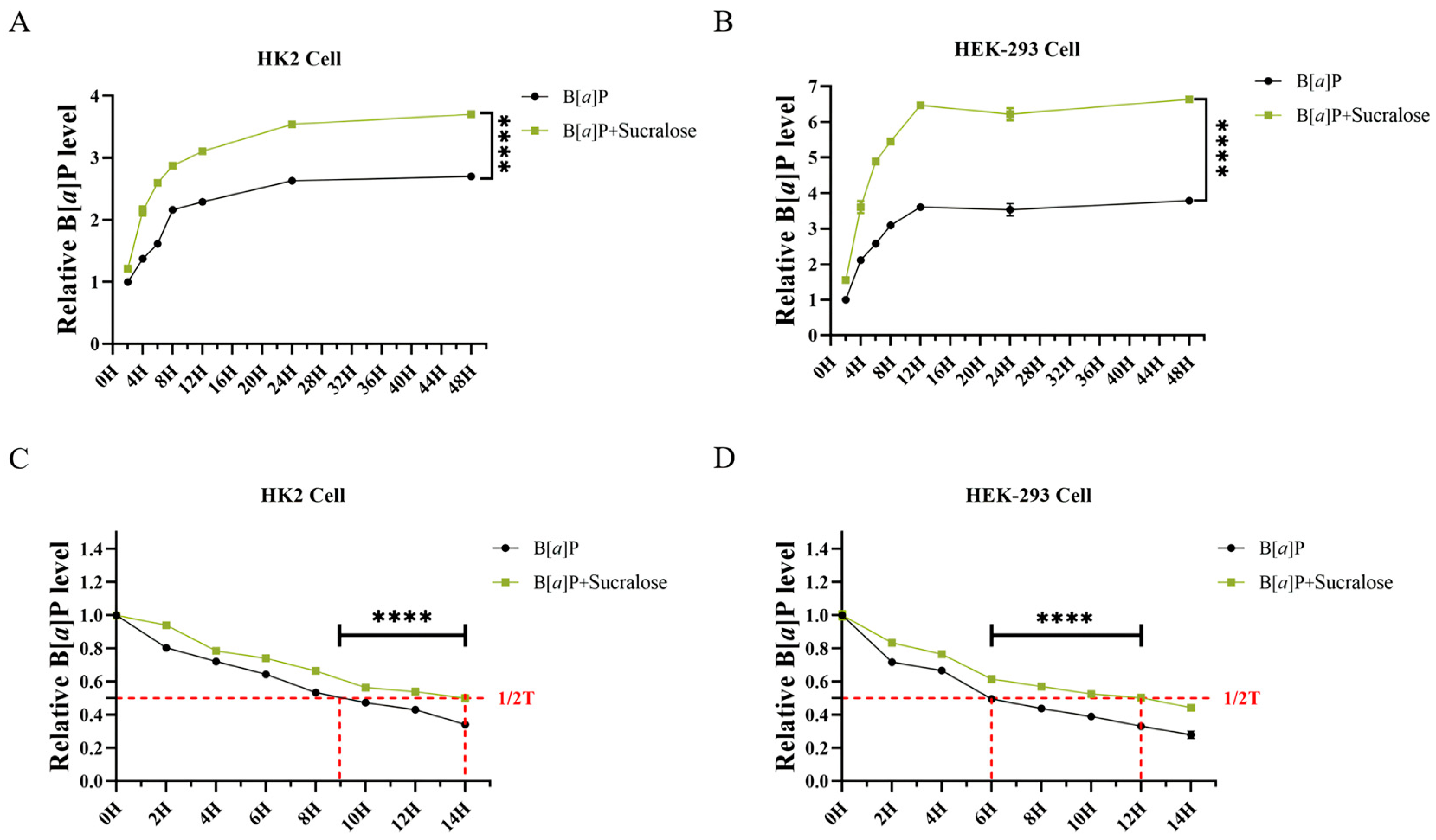
3.3. Sucralose Promotes B[a]P Intracellular Accumulation and Retention in Renal Cells
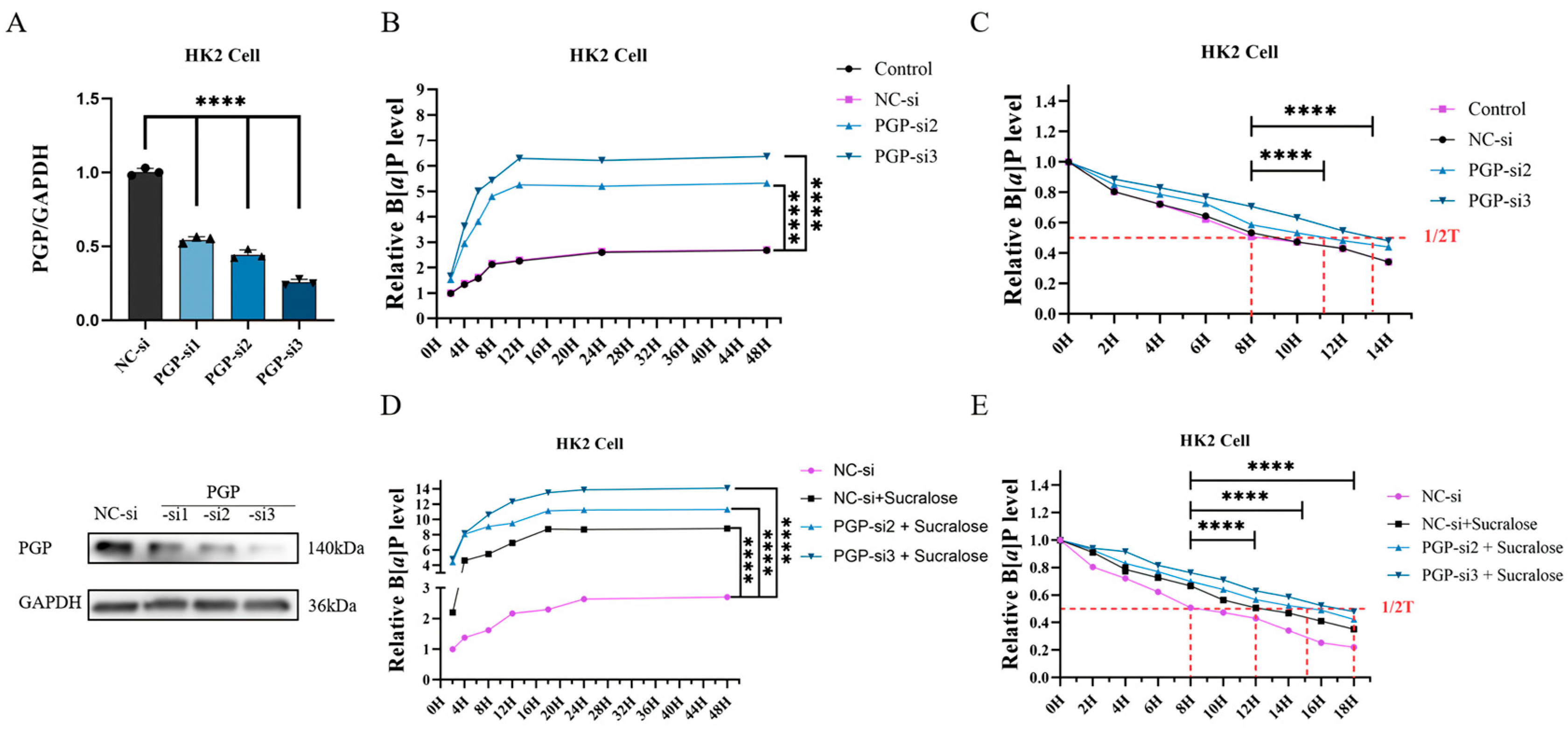
3.4. Knockdown of PGP Protein Further Promotes Sucralose-Induced B[a]P Accumulation
3.5. Sucralose Inhibits B[a]P Efflux by Binding Specifically to PGP
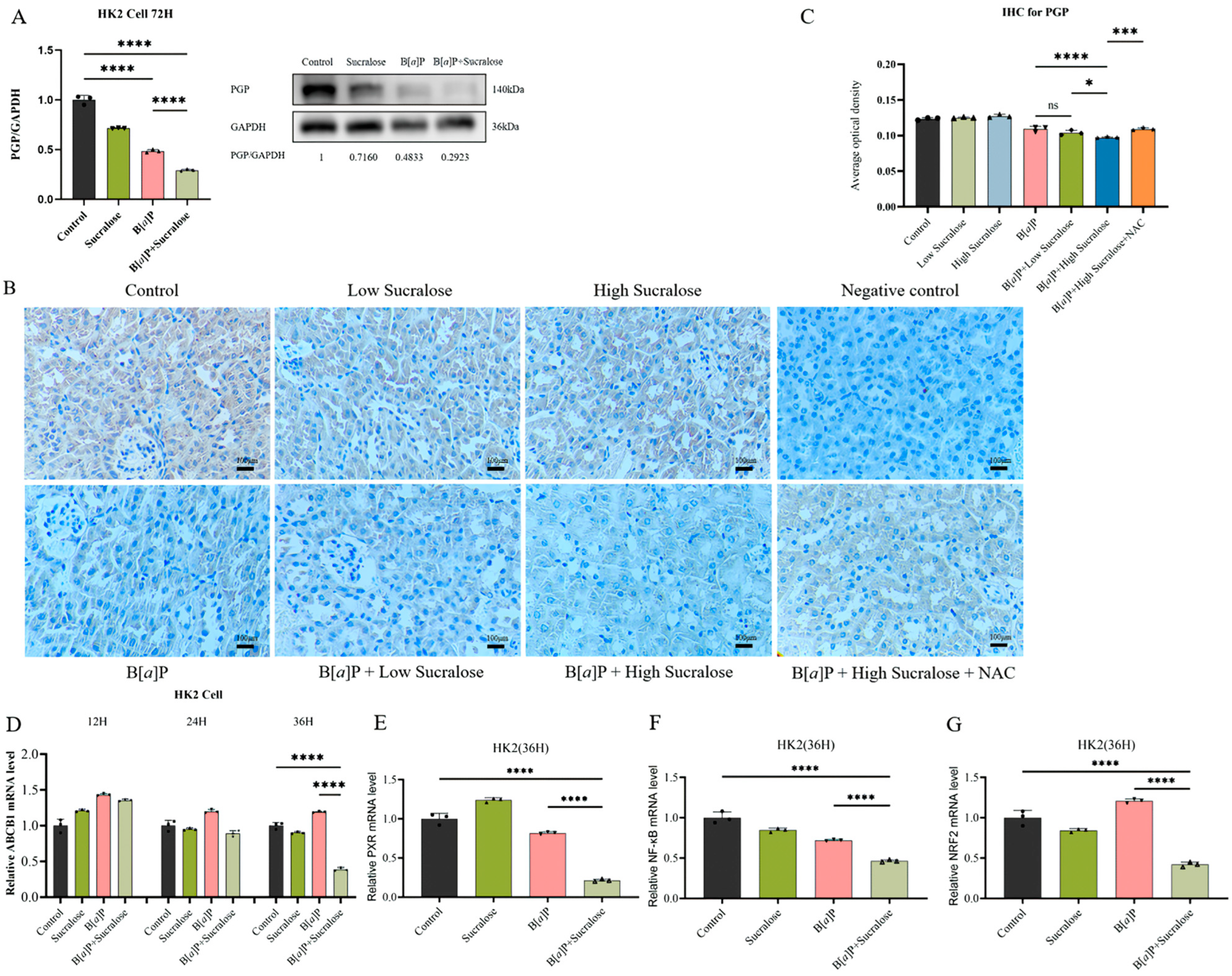
3.6. Sucralose Combined with B[a]P Inhibits the Expression of PGP and Its Upstream Transcription Factors in the Long Run
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stolte, S.; Steudte, S.; Schebb, N.H.; Willenberg, I.; Stepnowski, P. Ecotoxicity of Artificial Sweeteners and Stevioside. Environ. Int. 2013, 60, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Zhang, Q.; Cao, M.; Wu, L.; Cao, J.; Fang, F.; Li, C.; Xue, Z.; Feng, Q. Ecotoxicity and Environmental Fates of Newly Recognized Contaminants-Artificial Sweeteners: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 653, 1149–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Praveena, S.M.; Cheema, M.S.; Guo, H.-R. Non-Nutritive Artificial Sweeteners as an Emerging Contaminant in Environment: A Global Review and Risks Perspectives. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 170, 699–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, M.-S.; Ha, S.-D.; Choi, S.-H.; Bae, D.-H. Assessment of Korean Consumer Exposure to Sodium Saccharin, Aspartame and Stevioside. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2013, 30, 1238–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, M.; Khanna, S.K.; Das, M. Usage of Saccharin in Food Products and Its Intake by the Population of Lucknow, India. Food Addit. Contam. 2006, 23, 1265–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, A.; Renwick, A.G.; Sims, J.; Snodin, D.J. Sucralose Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics in Man. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2000, 38 (Suppl. 2), S31–S41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kıralan, S. Phthalate and Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon Levels in Liquid Ingredients of Packaged Fish Sold in Turkish Markets. J. Oleo Sci. 2020, 69, 851–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.-Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, X.-C.; Gao, S.-H.; Qu, L.-W.; Yu, H.; Fang, W.-F.; Zhou, Y.-C.; Liang, F.; Zhang, C.; et al. The Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Mediates Tobacco-Induced PD-L1 Expression and Is Associated with Response to Immunotherapy. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Xu, Y.; Ji, W.; Song, L.; Dai, C.; Zhan, L. Effects of Exposure to Benzo[a]Pyrene on Metastasis of Breast Cancer Are Mediated through ROS-ERK-MMP9 Axis Signaling. Toxicol. Lett. 2015, 234, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diggs, D.L.; Myers, J.N.; Banks, L.D.; Niaz, M.S.; Hood, D.B.; Roberts, L.J.; Ramesh, A. Influence of Dietary Fat Type on Benzo(a)Pyrene [B(a)P] Biotransformation in a B(a)P-Induced Mouse Model of Colon Cancer. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2013, 24, 2051–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khattab, S.A.; Hussien, W.F.; Raafat, N.; Ahmed Alaa El-Din, E. Modulatory Effects of Catechin Hydrate on Benzo[a]Pyrene-Induced Nephrotoxicity in Adult Male Albino Rats. Toxicol. Res. 2021, 10, 542–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanigawara, Y. Role of P-Glycoprotein in Drug Disposition. Ther. Drug Monit. 2000, 22, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fromm, M.F. P-Glycoprotein: A Defense Mechanism Limiting Oral Bioavailability and CNS Accumulation of Drugs. Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2000, 38, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fromm, M.F. Importance of P-Glycoprotein at Blood-Tissue Barriers. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2004, 25, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, G.C.; Lopaczynska, J.; Poore, C.M.; Phang, J.M. A New Functional Role for P-Glycoprotein: Efflux Pump for Benzo(Alpha)Pyrene in Human Breast Cancer MCF-7 Cells. Cancer Res. 1992, 52, 6692–6695. [Google Scholar]
- Danner, L.; Malard, F.; Valdes, R.; Olivier-Van Stichelen, S. Non-Nutritive Sweeteners Acesulfame Potassium and Sucralose Are Competitive Inhibitors of the Human P-Glycoprotein/Multidrug Resistance Protein 1 (PGP/MDR1). Nutrients 2023, 15, 1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barangi, S.; Mehri, S.; Moosavi, Z.; Hayesd, A.W.; Reiter, R.J.; Cardinali, D.P.; Karimi, G. Melatonin Inhibits Benzo(a)Pyrene-Induced Apoptosis through Activation of the Mir-34a/Sirt1/Autophagy Pathway in Mouse Liver. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 196, 110556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labib, S.; Yauk, C.; Williams, A.; Arlt, V.M.; Phillips, D.H.; White, P.A.; Halappanavar, S. Subchronic Oral Exposure to Benzo(a)Pyrene Leads to Distinct Transcriptomic Changes in the Lungs That Are Related to Carcinogenesis. Toxicol. Sci. 2012, 129, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Hao, R.; Rong, X.; Dou, Q.P.; Tan, X.; Li, G.; Li, F.; Li, D. Secoisolariciresinol Diglucoside Mitigates Benzo[a]Pyrene-Induced Liver and Kidney Toxicity in Mice via miR-101a/MKP-1-Mediated P38 and ERK Pathway. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2022, 159, 112733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Roche, L.; Rodeiro, I.; Riera, M.; Herrera, J.A.; Venturi, I.; Hernández, Y.; Fernández, G.; Pérez, C.L.; Rodriguez, J.C.; Fernández, M.D.; et al. Chemoprotective Effects of Ulva Lactuca (Green Seaweed) Aqueous-Ethanolic Extract against Subchronic Exposure to Benzo(a)Pyrene by CYP1A1 Inhibition in Mice. Phytother. Res. 2019, 33, 958–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Li, Q.; Liu, H.; Ma, S.; Long, C.; Li, G.; Yu, Y. Urinary Monohydroxylated Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in the General Population from 26 Provincial Capital Cities in China: Levels, Influencing Factors, and Health Risks. Environ. Int. 2022, 160, 107074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zani, F.; Blagih, J.; Gruber, T.; Buck, M.D.; Jones, N.; Hennequart, M.; Newell, C.L.; Pilley, S.E.; Soro-Barrio, P.; Kelly, G.; et al. The Dietary Sweetener Sucralose Is a Negative Modulator of T Cell-Mediated Responses. Nature 2023, 615, 705–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.; Bin, J.-L.; Liao, X.-W.; Wu, Y.; Tang, Y.; Lu, P.-Z.; Zhu, G.-Z.; Cui, Q.-R.; Dan, Y.Y.; Yang, G.-H.; et al. The Prognostic Role of ACSL4 in Postoperative Adjuvant TACE-Treated HCC: Implications for Therapeutic Response and Mechanistic Insights. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2024, 43, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Liu, Y.; Wei, Q.; Huo, Y.; Liu, K.; Liu, F.; Dong, Z. Tubular p53 regulates multiple genes to mediate AKI. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 25, 2278–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nosol, K.; Romane, K.; Irobalieva, R.N.; Alam, A.; Kowal, J.; Fujita, N.; Locher, K.P. Cryo-EM Structures Reveal Distinct Mechanisms of Inhibition of the Human Multidrug Transporter ABCB1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 26245–26253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberhardt, J.; Santos-Martins, D.; Tillack, A.F.; Forli, S. AutoDock Vina 1.2.0: New Docking Methods, Expanded Force Field, and Python Bindings. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2021, 61, 3891–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindranath, P.A.; Forli, S.; Goodsell, D.S.; Olson, A.J.; Sanner, M.F. AutoDockFR: Advances in Protein-Ligand Docking with Explicitly Specified Binding Site Flexibility. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2015, 11, e1004586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomize, M.A.; Pogozheva, I.D.; Joo, H.; Mosberg, H.I.; Lomize, A.L. OPM Database and PPM Web Server: Resources for Positioning of Proteins in Membranes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, D370–D376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sylvetsky, A.C.; Bauman, V.; Blau, J.E.; Garraffo, H.M.; Walter, P.J.; Rother, K.I. Plasma Concentrations of Sucralose in Children and Adults. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2017, 99, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Chen, X.; Yang, G.; Wang, Q.; Wang, J.; Xiong, W.; Yuan, J. BaP-Induced DNA Damage Initiated P53-Independent Necroptosis via the Mitochondrial Pathway Involving Bax and Bcl-2. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2013, 32, 1245–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Pan, Z.; Yu, Q.; Mo, X.; Song, N.; Yan, M.; Zouboulis, C.C.; Xia, L.; Ju, Q. Benzo(a)Pyrene Induces Interleukin (IL)-6 Production and Reduces Lipid Synthesis in Human SZ95 Sebocytes via the Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Signaling Pathway. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2016, 43, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holme, J.A.; Gorria, M.; Arlt, V.M.; Ovrebø, S.; Solhaug, A.; Tekpli, X.; Landvik, N.E.; Huc, L.; Fardel, O.; Lagadic-Gossmann, D. Different Mechanisms Involved in Apoptosis Following Exposure to Benzo[a]Pyrene in F258 and Hepa1c1c7 Cells. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2007, 167, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.G.; Hien, T.T.; Han, E.H.; Hwang, Y.P.; Choi, J.H.; Kang, K.W.; Kwon, K.; Kim, B.-H.; Kim, S.K.; Song, G.Y.; et al. Metformin Inhibits P-Glycoprotein Expression via the NF-κB Pathway and CRE Transcriptional Activity through AMPK Activation. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 162, 1096–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bharathiraja, P.; Baskar, S.; Prasad, N.R. Solasodine Downregulates ABCB1 Overexpression in Multidrug Resistant Cancer Cells via Inhibiting Nrf2/Keap1 Signaling Pathway. J. Cell. Biochem. 2025, 126, e30674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ji, H.; Ni, S.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Wu, X.; Tian, J.; Chen, J. Antimalarial Activity and Sensitization of Chrysosplenetin against Artemisinin-Resistant Genotype Plasmodium Berghei K173 Potentially via Dual-Mechanism of Maintaining Host P-Glycoprotein Homeostasis Mediated by NF-κB P52 or PXR/CAR Signaling Pathways and Regulating Heme/Haemozoin Metabolism. Phytother. Res. 2023, 37, 2939–2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.I.A.; Nawaz, H.; Nadeem, N. Historical and Current Perspectives on the Human Consumption of Non-Nutritive Sweeteners (NNS). J. Akhtar Saeed Med. Dent. Coll. 2023, 5, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathaus, M.; Azem, L.; Livne, R.; Ron, S.; Ron, I.; Hadar, R.; Efroni, G.; Amir, A.; Braun, T.; Haberman, Y.; et al. Long-Term Metabolic Effects of Non-Nutritive Sweeteners. Mol. Metab. 2024, 88, 101985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riboli, E.; Beland, F.A.; Lachenmeier, D.W.; Marques, M.M.; Phillips, D.H.; Schernhammer, E.; Afghan, A.; Assunção, R.; Caderni, G.; Corton, J.C.; et al. Carcinogenicity of Aspartame, Methyleugenol, and Isoeugenol. Lancet Oncol. 2023, 24, 848–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debras, C.; Chazelas, E.; Srour, B.; Druesne-Pecollo, N.; Esseddik, Y.; Szabo de Edelenyi, F.; Agaësse, C.; De Sa, A.; Lutchia, R.; Gigandet, S.; et al. Artificial Sweeteners and Cancer Risk: Results from the NutriNet-Santé Population-Based Cohort Study. PLoS Med. 2022, 19, e1003950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalenberg, J.R.; Patel, B.P.; Denis, R.; Veldhuizen, M.G.; Nakamura, Y.; Vinke, P.C.; Luquet, S.; Small, D.M. Short-Term Consumption of Sucralose with, but Not without, Carbohydrate Impairs Neural and Metabolic Sensitivity to Sugar in Humans. Cell Metab. 2020, 31, 493–502.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez-García, L.A.; Bueno-Hernández, N.; Cid-Soto, M.A.; De León, K.L.; Mendoza-Martínez, V.M.; Espinosa-Flores, A.J.; Carrero-Aguirre, M.; Esquivel-Velázquez, M.; León-Hernández, M.; Viurcos-Sanabria, R.; et al. Ten-Week Sucralose Consumption Induces Gut Dysbiosis and Altered Glucose and Insulin Levels in Healthy Young Adults. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John, A.; Raza, H. Azadirachtin Attenuates Carcinogen Benzo(a) Pyrene-Induced DNA Damage, Cell Cycle Arrest, Apoptosis, Inflammatory, Metabolic, and Oxidative Stress in HepG2 Cells. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Na, J.; Liu, X.; Jia, X.; Ren, M.; Chen, J.; Han, B.; Xu, J.; Li, N.; Li, Z.; et al. Co-Exposure to Phthalates and Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and the Risk of Gestational Hypertension in Chinese Women. Environ. Int. 2024, 185, 108562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Song, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, W.; Cen, Y.; You, M.; Yang, G. DBP and BaP Co-Exposure Induces Kidney Injury via Promoting Pyroptosis of Renal Tubular Epithelial Cells in Rats. Chemosphere 2023, 314, 137714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Xu, Y.; Tao, C.; Tong, J.; Luo, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, X.; Xu, T. Uncovering SOD3 and GPX4 as New Targets of Benzo[α]Pyrene-Induced Hepatotoxicity through Metabolomics and Chemical Proteomics. Redox Biol. 2023, 67, 102930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, L.; He, S.; Chen, Q.; Peng, F.; Peng, H.; Xie, M. Comparative Proteomic Analysis of Cellular Response of Human Airway Epithelial Cells (A549) to Benzo(a)Pyrene. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2011, 21, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lange, E.C.M. Potential Role of ABC Transporters as a Detoxification System at the Blood-CSF Barrier. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2004, 56, 1793–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katayama, K.; Kapoor, K.; Ohnuma, S.; Patel, A.; Swaim, W.; Ambudkar, I.S.; Ambudkar, S.V. Revealing the Fate of Cell Surface Human P-Glycoprotein (ABCB1): The Lysosomal Degradation Pathway. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1853, 2361–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Name | Sense (5′ to 3′) |
|---|---|
| NC-si | UUCUCCGAACGUGUCACGU |
| PGP-si1 | CAAUGUUUCGCUAUUCAAA |
| PGP-si2 | GGAGGAGCAAAGAAGAAGA |
| PGP-si3 | GGAAUGUUCUUUCAGUCAA |
| Genes | Accession Number | Forward Primer Sequence | Reverse Primer Sequence |
|---|---|---|---|
| ABCB1 | NM_001348946 | GTCCCAGGAGCCCATCCT | CCCGGCTGTTGTCTCCATA |
| NRF2 | NM_006164 | TCAGCGACGGAAAGAGTATGA | CCACTGGTTTCTGACTGGATGT |
| NF-κB | NM_003998 | AACAGAGAGGATTTCGTTTCCG | TTTGACCTGAGGGTAAGACTTCT |
| PXR | NM_003889 | AAGCCCAGTGTCAACGCAG | GGGTCTTCCGGGTGATCTC |
| SOD2 | NM_001322816 | GCTCCGGTTTTGGGGTATCTG | GCGTTGATGTGAGGTTCCAG |
| CAT | NM_001752 | TGGAGCTGGTAACCCAGTAGG | CCTTTGCCTTGGAGTATTTGGTA |
| GSS | NM_000178 | GGGAGCCTCTTGCAGGATAAA | GAATGGGGCATAGCTCACCAC |
| GPX1 | NM_000581 | CAGTCGGTGTATGCCTTCTCG | GAGGGACGCCACATTCTCG |
| ACTB | NM_001101 | GGACTTCGAGCAAGAGATGG | AGCACTGTGTTGGCGTACAG |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, J.; Feng, J.; Bai, Y.; Yao, Z.-S.; Wu, X.-Y.; Hong, X.-Y.; Lu, G.-D.; Xue, K. Sucralose Promotes Benzo(a)Pyrene-Induced Renal Toxicity in Mice by Regulating P-glycoprotein. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 474. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14040474
Hu J, Feng J, Bai Y, Yao Z-S, Wu X-Y, Hong X-Y, Lu G-D, Xue K. Sucralose Promotes Benzo(a)Pyrene-Induced Renal Toxicity in Mice by Regulating P-glycoprotein. Antioxidants. 2025; 14(4):474. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14040474
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Jun, Ji Feng, Yan Bai, Zhi-Sheng Yao, Xiao-Yu Wu, Xin-Yu Hong, Guo-Dong Lu, and Kun Xue. 2025. "Sucralose Promotes Benzo(a)Pyrene-Induced Renal Toxicity in Mice by Regulating P-glycoprotein" Antioxidants 14, no. 4: 474. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14040474
APA StyleHu, J., Feng, J., Bai, Y., Yao, Z.-S., Wu, X.-Y., Hong, X.-Y., Lu, G.-D., & Xue, K. (2025). Sucralose Promotes Benzo(a)Pyrene-Induced Renal Toxicity in Mice by Regulating P-glycoprotein. Antioxidants, 14(4), 474. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14040474






