The author wishes to make the following correction to this paper [1]. The H2O2 concentration of one experimental condition was mistyped in the index in Figure 7A,B. The correct Figure 7 is as follows:
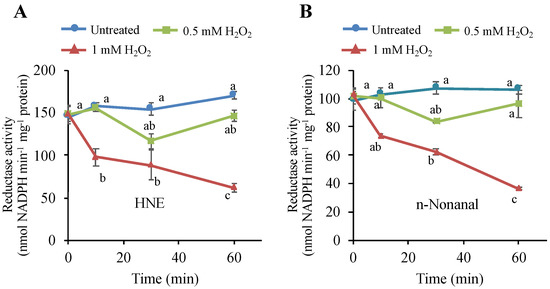
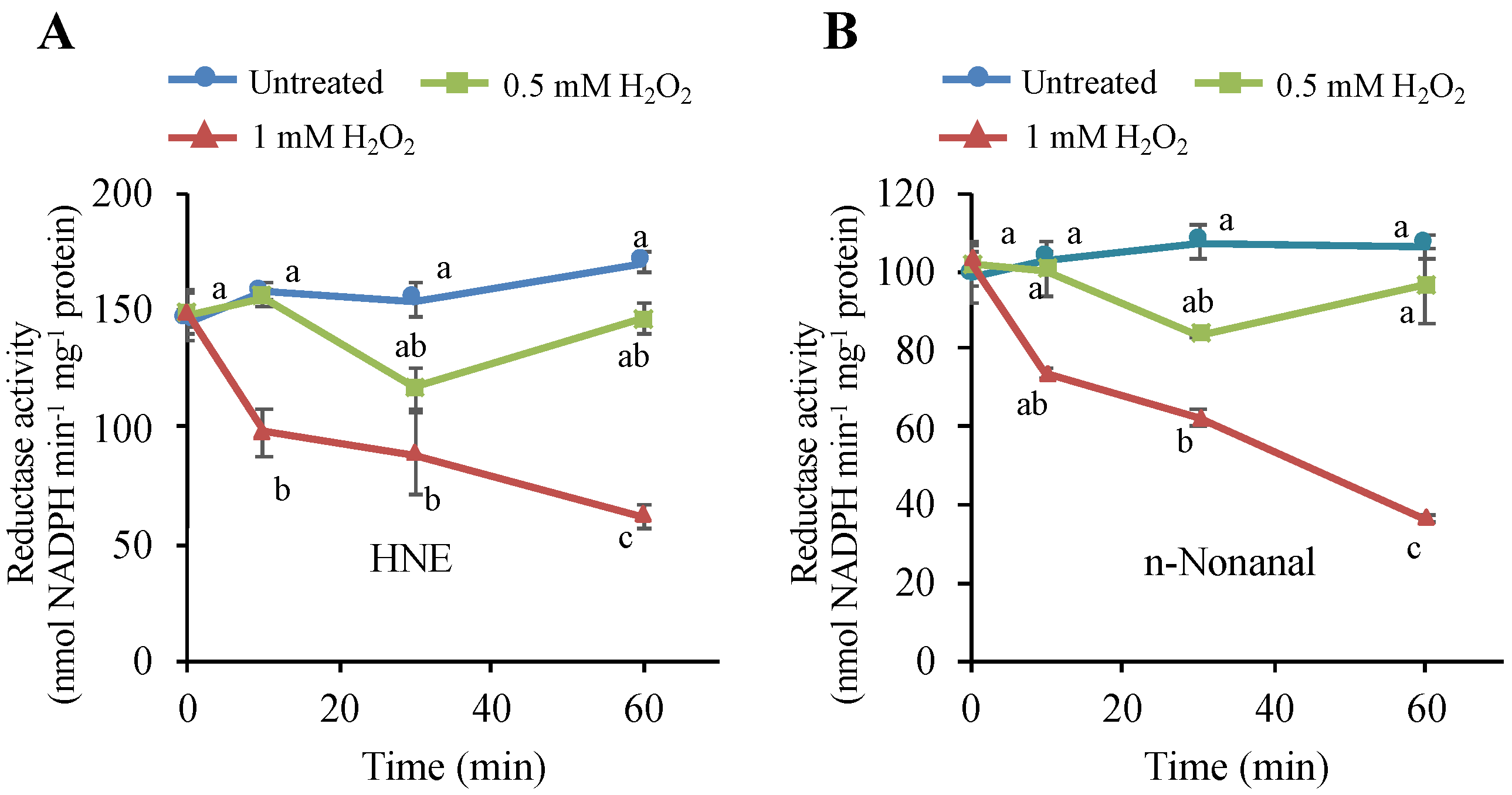
Figure 7.
Effects of H2O2 on the NADPH-dependent HNE-reducing and n-nonanal-reducing activities in tobacco BY-2 cells. Four-d cultured cells were treated with H2O2 at 0.5 mM and 1 mM, as in Figure 1. Then, cells were harvested at the indicated time point, and proteins were extracted as in the Materials and Methods section. The reductase activities for (A) HNE and (B) n-nonanal were determined as in the Materials and Methods section. Each point represents the mean of three independent experiments and the error bars of the SEM. Different letters represent significantly different values (p < 0.05 on Tukey test).
These changes have no material impact on the discussion and conclusions of the paper. The authors would like to apologize for any inconvenience caused to the readers by these changes.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Reference
- Biswas, M.S.; Terada, R.; Mano, J. Inactivation of Carbonyl-Detoxifying Enzymes by H2O2 Is a Trigger to Increase Carbonyl Load for Initiating Programmed Cell Death in Plants. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).