How MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry Technology Contributes to Microbial Infection Control in Healthcare Settings
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. MALDI’s Historical Evolution
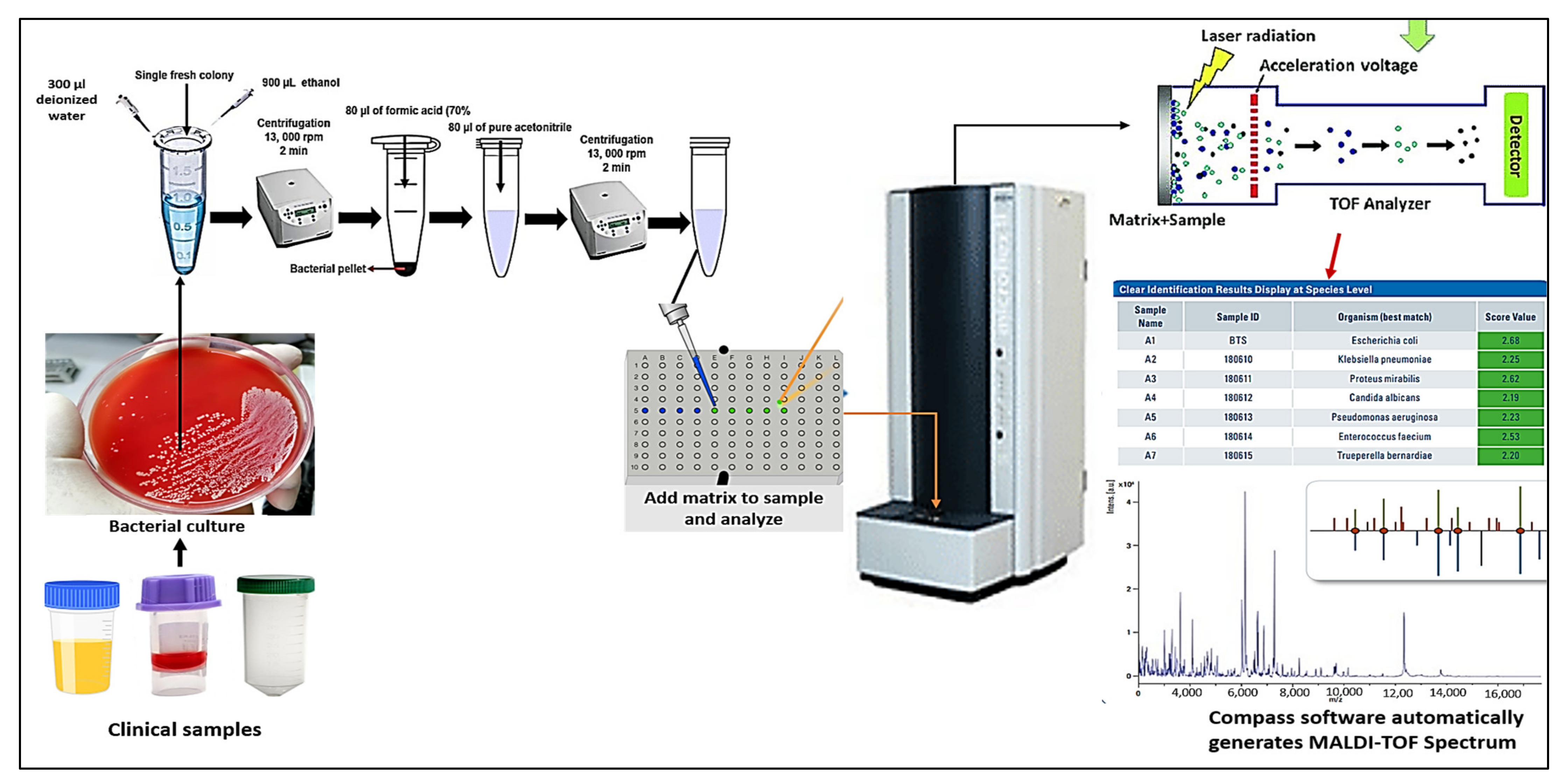
3. The Workflow of MALDI TOF Mass Spectrometry
4. Implications of MALDI-TOF MS for Microbial Recognition
4.1. Bacterial Identification
4.2. Yeasts and Filamentous Fungi Identification
4.3. Viral Identification
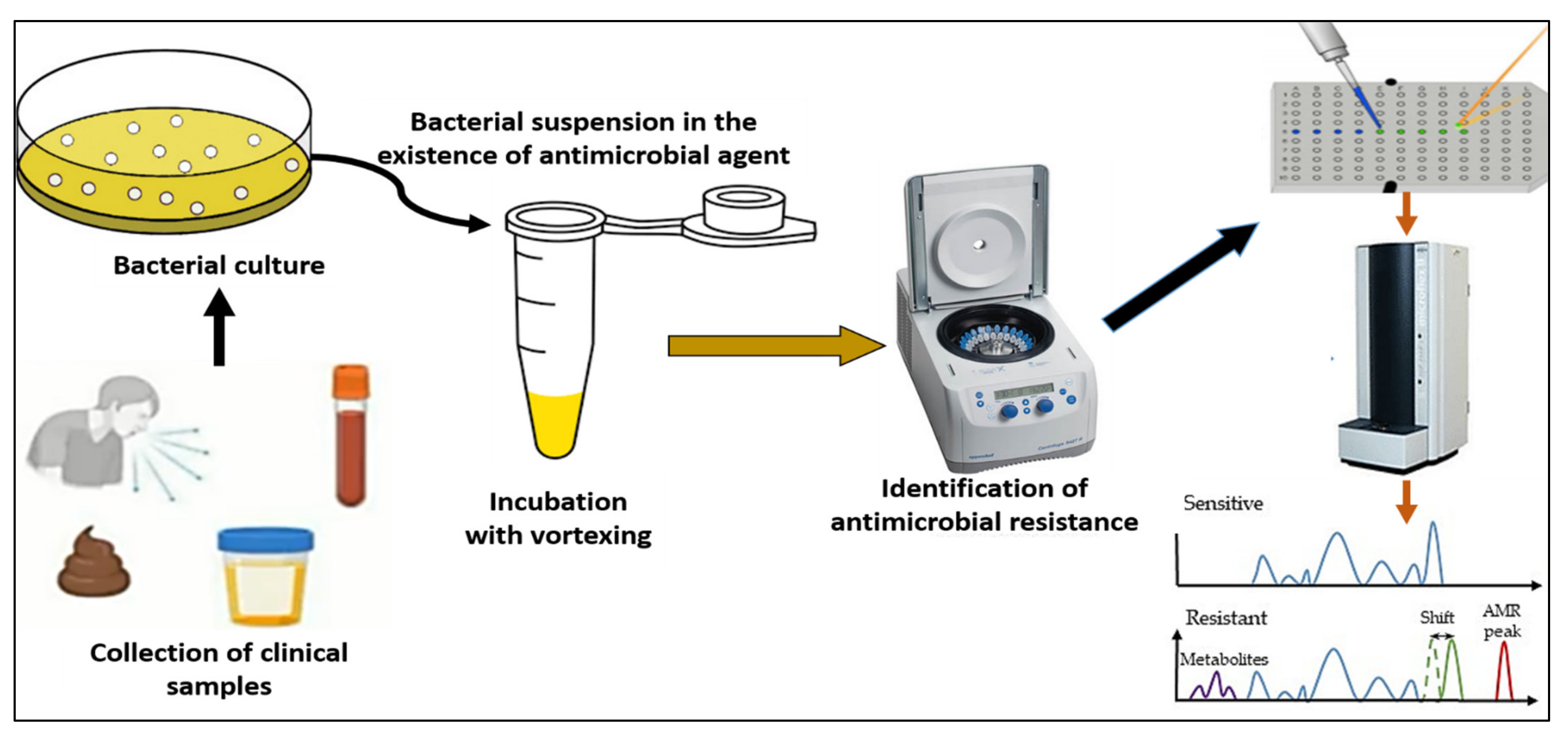
4.4. Detection of Antibiotic Resistance
4.5. The Advantages and Drawbacks of MALDI-TOF MS Technology
5. Outlooks for the Future
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, W.; Le, J.; Chen, Y.; Cai, Y.; Hong, Z.; Chai, Y. Recent advances in microfluidic devices for bacteria and fungus research. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 112, 175–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbehiry, A.; Marzouk, E.; Moussa, I.M.; Dawoud, T.M.; Mubarak, A.S.; Al-Sarar, D.; Alsubki, R.A.; Alhaji, J.H.; Hamada, M.; Abalkhail, A. Acinetobacter baumannii as a community foodborne pathogen: Peptide mass fingerprinting analysis, genotypic of biofilm formation and phenotypic pattern of antimicrobial resistance. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 1158–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rychert, J. Benefits and limitations of MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry for the identification of microorganisms. J. Infect. Epidemiol. 2019, 2, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartley, M.G.; El-Maaytah, M.; McKenzie, C.; Greenman, J. The tongue microbiota of low odour and malodorous individuals. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 1996, 9, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardi, S.; Continenza, M.A.; Al-Ahmad, A.; Karygianni, L.; Follo, M.; Filippi, A.; Macchiarelli, G. Streptococcus spp. and Fusobacterium nucleatum in tongue dorsum biofilm from halitosis patients: A fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) and confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) study. New Microbiol. 2019, 42, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hannig, C.; Follo, M.; Hellwig, E.; Al-Ahmad, A. Visualization of adherent micro-organisms using different techniques. J. Med. Microbiol. 2010, 59, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ercole, S.; Tripodi, D.; Marzo, G.; Bernardi, S.; Continenza, M.A.; Piattelli, A.; Iaculli, F.; Mummolo, S. Microleakage of bacteria in different implant-abutment assemblies: An in vitro study. J. Appl. Biomater. Funct. Mater. 2015, 13, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardi, S.; Bianchi, S.; Botticelli, G.; Rastelli, E.; Tomei, A.; Palmerini, M.; Continenza, M.; Macchiarelli, G. Scanning electron microscopy and microbiological approaches for the evaluation of salivary microorganisms behaviour on anatase titanium surfaces: In vitro study. Morphologie 2018, 102, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orioles, M.; Galeotti, M.; Saccà, E.; Bulfoni, M.; Corazzin, M.; Bianchi, S.; Torge, D.; Macchiarelli, G.; Magi, G.E.; Schmidt, J.G. Effect of temperature on transfer of Midichloria-like organism and development of red mark syndrome in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquaculture 2022, 560, 738577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Váradi, L.; Luo, J.L.; Hibbs, D.E.; Perry, J.D.; Anderson, R.J.; Orenga, S.; Groundwater, P. Methods for the detection and identification of pathogenic bacteria: Past, present, and future. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 4818–4832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlMasoud, N.; Muhamadali, H.; Chisanga, M.; AlRabiah, H.; Lima, C.A.; Goodacre, R. Discrimination of bacteria using whole organism fingerprinting: The utility of modern physicochemical techniques for bacterial typing. Analyst 2021, 146, 770–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramadan, A.A. Bacterial typing methods from past to present: A comprehensive overview. Gene Rep. 2022, 29, 101675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curry, A.; Appleton, H.; Dowsett, B. Application of transmission electron microscopy to the clinical study of viral and bacterial infections: Present and future. Micron 2006, 37, 91–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biel, S.S.; Gelderblom, H.R. Diagnostic electron microscopy is still a timely and rewarding method. J. Clin. Virol. 1999, 13, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, A.; Alby, K.; Kerr, A.; Jones, M.; Gilligan, P. Cost savings realized by implementation of routine microbiological identification by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 2473–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahi, P.; Prakash, O.; Shouche, Y. Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass-spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) based microbial identifications: Challenges and scopes for microbial ecologists. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanno, D.; Saito, K.; Ohashi, K.; Toyokawa, M.; Yamadera, Y.; Shimura, H. Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization-Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry with Time-of-Flight Peak Analysis for Rapid and Accurate Detection of Group B Streptococcus in Pregnant Women. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e01732-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welker, M.; Van Belkum, A.; Girard, V.; Charrier, J.-P.; Pincus, D. An update on the routine application of MALDI-TOF MS in clinical microbiology. Expert Rev. Proteom. 2019, 16, 695–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oviaño, M.; Rodríguez-Sánchez, B. MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry in the 21st century clinical microbiology laboratory. Enferm. Infecc. Y Microbiol. Clin. 2021, 39, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, K.; Waki, H.; Ido, Y.; Akita, S.; Yoshida, Y.; Yoshida, T.; Matsuo, T. Protein and polymer analyses up to m/z 100,000 by laser ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 1988, 2, 151–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karas, M.; Hillenkamp, F. Laser desorption ionization of proteins with molecular masses exceeding 10,000 daltons. Anal. Chem. 1988, 60, 2299–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseinian, H.; Ortega, E.O.; López, M.J.R.; Vera, A.R.; Hosseini, S. Characterization Techniques for Mass Spectrometry Analysis. In Material Characterization Techniques and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 47–69. [Google Scholar]
- Gandhi, K.; Sharma, N.; Gautam, P.B.; Sharma, R.; Mann, B.; Pandey, V. Mass Spectroscopy. In Advanced Analytical Techniques in Dairy Chemistry; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 199–217. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, R. MALDI-TOF MS for the diagnosis of infectious diseases. Clin. Chem. 2015, 61, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcaide, F.; Amlerová, J.; Bou, G.; Ceyssens, P.; Coll, P.; Corcoran, D.; Fangous, M.-S.; González-Álvarez, I.; Gorton, R.; Greub, G.; et al. How to: Identify non-tuberculous Mycobacterium species using MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2018, 24, 599–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitt, B.H.; Cunningham, S.A.; Dailey, A.L.; Gustafson, D.R.; Patel, R. Identification of anaerobic bacteria by Bruker Biotyper matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry with on-plate formic acid preparation. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 782–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassagne, C.; Ranque, S.; Normand, A.-C.; Fourquet, P.; Thiebault, S.; Planard, C.; Hendrickx, M.; Piarroux, R. Mould routine identification in the clinical laboratory by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, T.-Y.; Chiang-Ni, C.; Teng, S.-H. Current status of MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry in clinical microbiology. J. Food Drug Anal. 2019, 27, 404–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbehiry, A.; Aldubaib, M.; Al Rugaie, O.; Marzouk, E.; Abaalkhail, M.; Moussa, I.; El-Husseiny, M.H.; Abalkhail, A.; Rawway, M. Proteomics-based screening and antibiotic resistance assessment of clinical and sub-clinical Brucella species: An evolution of brucellosis infection control. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0262551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Jin, Y.; Zhao, G.; Liu, J.; Zhou, X.; Yang, J.; Wang, J.; Cui, Y.; Hu, X.; Li, Y. Improvement of matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry for identification of clinically important Candida species. Clin. Lab. 2014, 60, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florio, W.; Baldeschi, L.; Rizzato, C.; Tavanti, A.; Ghelardi, E.; Lupetti, A. Detection of antibiotic-resistance by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry: An expanding area. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 572909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florio, W.; Tavanti, A.; Ghelardi, E.; Lupetti, A. MALDI-TOF MS applications to the detection of antifungal resistance: State of the art and future perspectives. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolk, D.M.; Clark, A.E. Matrix-assisted laser desorption time of flight mass spectrometry. Clin. Lab. Med. 2018, 38, 471–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singhal, N.; Kumar, M.; Kanaujia, P.K.; Virdi, J.S. MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry: An emerging technology for microbial identification and diagnosis. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karas, M.; Bachmann, D.; Hillenkamp, F. Influence of the wavelength in high-irradiance ultraviolet laser desorption mass spectrometry of organic molecules. Anal. Chem. 1985, 57, 2935–2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cain, T.C.; Lubman, D.M.; Weber, W.J., Jr. Differentiation of bacteria using protein profiles from matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 1994, 8, 1026–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, R.; Wilkes, J.; Rafii, F.; Sutherland, J.; Persons, C.; Voorhees, K.; Lay, J., Jr. Rapid identification of intact whole bacteria based on spectral patterns using matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization with time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 1996, 10, 1227–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claydon, M.A.; Davey, S.N.; Edwards-Jones, V.; Gordon, D.B. The rapid identification of intact microorganisms using mass spectrometry. Nat. Biotechnol. 1996, 14, 1584–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchida, S.; Nakayama, T. MALDI-Based Mass Spectrometry in Clinical Testing: Focus on Bacterial Identification. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seng, P.; Drancourt, M.; Gouriet, F.; La Scola, B.; Fournier, P.-E.; Rolain, J.M.; Raoult, D. Ongoing revolution in bacteriology: Routine identification of bacteria by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 49, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, K.C.; Patel, R. Systems for identification of bacteria and fungi. In Manual of Clinical Microbiology; ASM Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2015; pp. 29–43. [Google Scholar]
- Vrioni, G.; Tsiamis, C.; Oikonomidis, G.; Theodoridou, K.; Kapsimali, V.; Tsakris, A. MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry technology for detecting biomarkers of antimicrobial resistance: Current achievements and future perspectives. Ann. Transl. Med. 2018, 6, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeletti, S. Matrix assisted laser desorption time of flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) in clinical microbiology. J. Microbiol. Methods 2017, 138, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, F. Proteome-based bacterial identification using matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS): A revolutionary shift in clinical diagnostic microbiology. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta-Proteins Proteom. 2015, 1854, 528–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posteraro, B.; De Carolis, E.; Vella, A.; Sanguinetti, M. MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry in the clinical mycology laboratory: Identification of fungi and beyond. Expert Rev. Proteom. 2013, 10, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bizzini, A.; Durussel, C.; Bille, J.; Greub, G.; Prod’Hom, G. Performance of matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry for identification of bacterial strains routinely isolated in a clinical microbiology laboratory. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 1549–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastin, B.; Bird, P.; Benzinger, M.J.; Crowley, E.; Agin, J.; Goins, D.; Sohier, D.; Timke, M.; Shi, G.; Kostrzewa, M. Confirmation and identification of Salmonella spp., Cronobacter spp., and other Gram-negative organisms by the Bruker MALDI biotyper method: Collaborative study, first action 2017.09. J. AOAC Int. 2018, 101, 1593–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martiny, D.; Busson, L.; Wybo, I.; El Haj, R.A.; Dediste, A.; Vandenberg, O. Comparison of the Microflex LT and Vitek MS systems for routine identification of bacteria by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 1313–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, C.; Passet, V.; Rakotondrasoa, A.; Brisse, S. Identification of Klebsiella pneumoniae, Klebsiella quasipneumoniae, Klebsiella variicola and related phylogroups by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alby, K.; Gilligan, P.H.; Miller, M.B. Comparison of matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight (MALDI-TOF) mass spectrometry platforms for the identification of Gram-negative rods from patients with cystic fibrosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 3852–3854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couturier, M.R.; Mehinovic, E.; Croft, A.C.; Fisher, M.A. Identification of HACEK clinical isolates by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization–time of flight mass spectrometry. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 1104–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, E.; Bakhalek, Y.; Taha, M.-K. Identification of Neisseria meningitidis by MALDI-TOF MS may not be reliable. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2019, 25, 717–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oviaño, M.; Gómara, M.; Barba, M.J.; Revillo, M.J.; Barbeyto, L.P.; Bou, G. Towards the early detection of β-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae by MALDI-TOF MS analysis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2017, 72, 2259–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrıguez-Sánchez, B.; Marın, M.; Sánchez-Carrillo, C.; Cercenado, E.; Ruiz, A.; Rodrıguez-Créixems, M.; Bouza, E. Improvement of matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry identification of difficult-toidentify bacteria and its impact in the workflow of a clinical microbiology laboratory. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2014, 79, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marín, M.; Cercenado, E.; Sánchez-Carrillo, C.; Ruiz, A.; González, Á.G.; Rodríguez-Sánchez, B.; Bouza, E. Accurate differentiation of Streptococcus pneumoniae from other species within the Streptococcus mitis group by peak analysis using MALDI-TOF MS. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harju, I.; Lange, C.; Kostrzewa, M.; Maier, T.; Rantakokko-Jalava, K.; Haanperä, M. Improved differentiation of Streptococcus pneumoniae and other S. mitis group streptococci by MALDI Biotyper using an improved MALDI Biotyper database content and a novel result interpretation algorithm. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 914–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Sánchez, B.; Alcalá, L.; Marín, M.; Ruiz, A.; Alonso, E.; Bouza, E. Evaluation of MALDI-TOF MS (matrix-assisted laser desorption-ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry) for routine identification of anaerobic bacteria. Anaerobe 2016, 42, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veloo, A.; Jean-Pierre, H.; Justesen, U.; Morris, T.; Urban, E.; Wybo, I.; Kostrzewa, M.; Friedrich, A.; Shah, H.; Nagy, E. Validation of a for anaerobic bacteria optimized MALDI-TOF MS biotyper database: The ENRIA project. Anaerobe 2018, 54, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinne, S.; Saad, J.; Morsli, M.; Hamidou, Z.H.; Tazerart, F.; Drancourt, M.; Baron, S.A. Rapid Identification of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Complex Using Mass Spectrometry: A Proof of Concept. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 753969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, J.; Corcoran, G.; O’Reilly, B.; O’Mahony, J.; Lucey, B. Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization–Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) for Investigation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Complex Outbreaks: A Type Dream? J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 58, e02077-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostrzewa, M.; Nagy, E.; Schröttner, P.; Pranada, A.B. How MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry can aid the diagnosis of hard-to-identify pathogenic bacteria—the rare and the unknown. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2019, 19, 667–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, A.F. Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight for fungal identification. Clin. Lab. Med. 2021, 41, 267–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zvezdanova, M.; Escribano, P.; Ruiz, A.; Martínez-Jiménez, M.; Peláez, T.; Collazos, A.; Guinea, J.; Bouza, E.; Rodríguez-Sánchez, B. Increased species-assignment of filamentous fungi using MALDI-TOF MS coupled with a simplified sample processing and an in-house library. Med. Mycol. 2019, 57, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Normand, A.; Becker, P.; Gabriel, F.; Cassagne, C.; Accoceberry, I.; Gari-Toussaint, M.; Hasseine, L.; De Geyter, D.; Pierard, D.; Surmont, I. Validation of a new web application for identification of fungi by use of matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 2661–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanguinetti, M.; Posteraro, B. Identification of molds by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, R. A moldy application of MALDI: MALDI-ToF mass spectrometry for fungal identification. J. Fungi 2019, 5, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.-F.; Hou, X.; Xiao, M.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, J.-W.; Zhou, M.-L.; Huang, J.-J.; Zhang, J.-J.; Xu, Y.-C.; Hsueh, P.-R. Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time of flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) analysis for the identification of pathogenic microorganisms: A review. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjoholm, M.I.; Dillner, J.; Carlson, J. Multiplex detection of human herpesviruses from archival specimens by using matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 540–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Guan, Q.; Huan, Y.; Liu, Z.; Qi, J.; Ge, S. Development of high-throughput genotyping method of all 18 HR HPV based on the MALDI-TOF MS platform and compared with the Roche Cobas 4800 HPV assay using clinical specimens. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiu, L.; Zhang, C.; Wu, Z.; Peng, J. Establishment and application of a universal coronavirus screening method using MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshinari, T.; Hayashi, K.; Hirose, S.; Ohya, K.; Ohnishi, T.; Watanabe, M.; Taharaguchi, S.; Mekata, H.; Taniguchi, T.; Maeda, T. Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption and Ionization Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry Analysis for the Direct Detection of SARS-CoV-2 in Nasopharyngeal Swabs. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 4218–4226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.J.; Falk, B.; Fenselau, C.; Jackman, J.; Ezzell, J. Viral characterization by direct analysis of capsid proteins. Anal. Chem. 1998, 70, 3863–3867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderaro, A.; Arcangeletti, M.C.; Rodighiero, I.; Buttrini, M.; Montecchini, S.; Simone, R.V.; Medici, M.C.; Chezzi, C.; De Conto, F. Identification of different respiratory viruses, after a cell culture step, by matrix assisted laser desorption/ionization time of flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS). Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krokhin, O.; Li, Y.; Andonov, A.; Feldmann, H.; Flick, R.; Jones, S.; Stroeher, U.; Bastien, N.; Dasuri, K.V.; Cheng, K. Mass Spectrometric Characterization of Proteins from the SARS Virus: A Preliminary Report* S. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2003, 2, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, N.K.; Howard, T.; Walsh, R.; Pepper, J.; Loegering, J.; Phinney, B.; Salemi, M.R.; Rashidi, H.H. Novel application of automated machine learning with MALDI-TOF-MS for rapid high-throughput screening of COVID-19: A proof of concept. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazari, L.C.; Zerbinati, R.M.; Rosa-Fernandes, L.; Santiago, V.F.; Rosa, K.F.; Angeli, C.B.; Schwab, G.; Palmieri, M.; Sarmento, D.J.; Marinho, C.R. MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry of saliva samples as a prognostic tool for COVID-19. J. Oral Microbiol. 2022, 14, 2043651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camarasa, C.G.; Cobo, F. Application of MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry in clinical virology. In The Use of Mass Spectrometry Technology (MALDI-TOF) in Clinical Microbiology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 167–180. [Google Scholar]
- Roca, I.; Akova, M.; Baquero, F.; Carlet, J.; Cavaleri, M.; Coenen, S.; Cohen, J.; Findlay, D.; Gyssens, I.; Heure, O. The global threat of antimicrobial resistance: Science for intervention. New Microbes New Infect. 2015, 6, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idelevich, E.; Sparbier, K.; Kostrzewa, M.; Becker, K. Rapid detection of antibiotic resistance by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry using a novel direct-on-target microdroplet growth assay. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2018, 24, 738–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Roberts, D.; Wood, K.E.; Light, B.; Parrillo, J.E.; Sharma, S.; Suppes, R.; Feinstein, D.; Zanotti, S.; Taiberg, L. Duration of hypotension before initiation of effective antimicrobial therapy is the critical determinant of survival in human septic shock. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 34, 1589–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerremans, J.; Verboom, P.; Stijnen, T.; Roijen, L.H.-V.; Goessens, W.; Verbrugh, H.; Vos, M. Rapid identification and antimicrobial susceptibility testing reduce antibiotic use and accelerate pathogen-directed antibiotic use. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2008, 61, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oviaño, M.; Bou, G. Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry for the rapid detection of antimicrobial resistance mechanisms and beyond. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 32, e00037-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oviaño, M.; Sparbier, K.; Barba, M.J.; Kostrzewa, M.; Bou, G. Universal protocol for the rapid automated detection of carbapenem-resistant Gram-negative bacilli directly from blood cultures by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionisation time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF/MS). Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2016, 48, 655–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrabák, J. Detection of carbapenemases using matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) meropenem hydrolysis assay. In Sepsis; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 91–96. [Google Scholar]
- Camara, J.E.; Hays, F.A. Discrimination between wild-type and ampicillin-resistant Escherichia coli by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 389, 1633–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bizzini, A.; Jaton, K.; Romo, D.; Bille, J.; Prod’hom, G.; Greub, G. Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization–time of flight mass spectrometry as an alternative to 16S rRNA gene sequencing for identification of difficult-to-identify bacterial strains. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 693–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Justesen, U.S.; Holm, A.; Knudsen, E.; Andersen, L.B.; Jensen, T.G.; Kemp, M.; Skov, M.N.; Gahrn-Hansen, B.; Møller, J.K. Species identification of clinical isolates of anaerobic bacteria: A comparison of two matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization–time of flight mass spectrometry systems. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 4314–4318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Rotz, M.; Dierig, A.; Heininger, U.; Chrobak, C.; Baettig, V.; Egli, A. Case report: When two and ½ men go camping…. BMC Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 102. [Google Scholar]
- Pappas, P.G.; Kauffman, C.A.; Andes, D.R.; Clancy, C.J.; Marr, K.A.; Ostrosky-Zeichner, L.; Reboli, A.C.; Schuster, M.G.; Vazquez, J.A.; Walsh, T.J. Clinical practice guideline for the management of candidiasis: 2016 update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 62, e1–e50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garey, K.W.; Rege, M.; Pai, M.P.; Mingo, D.E.; Suda, K.J.; Turpin, R.S.; Bearden, D.T. Time to initiation of fluconazole therapy impacts mortality in patients with candidemia: A multi-institutional study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2006, 43, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pincus, D.; Orenga, S.; Chatellier, S. Yeast identification—Past, present, and future methods. Med. Mycol. 2007, 45, 97–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.; Ellis, B.; Lee, R.; Stamper, P.; Zhang, S.; Carroll, K. Prospective evaluation of a matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization–time of flight mass spectrometry system in a hospital clinical microbiology laboratory for identification of bacteria and yeasts: A bench-by-bench study for assessing the impact on time to identification and cost-effectiveness. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 3301–3308. [Google Scholar]
- Pupo, G.M.; Lan, R.; Reeves, P.R. Multiple independent origins of Shigella clones of Escherichia coli and convergent evolution of many of their characteristics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 10567–10572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paauw, A.; Jonker, D.; Roeselers, G.; Heng, J.M.; Mars-Groenendijk, R.H.; Trip, H.; Molhoek, E.M.; Jansen, H.-J.; van der Plas, J.; de Jong, A.L. Rapid and reliable discrimination between Shigella species and Escherichia coli using MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2015, 305, 446–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khot, P.D.; Fisher, M.A. Novel approach for differentiating Shigella species and Escherichia coli by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization–time of flight mass spectrometry. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 3711–3716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branda, J.; Fritsche, T.; Burnham, C.; Butler-Wu, S.; Doern, C.; Fedorko, D.; Frana, T.; Gawoski, J.; Ginocchio, C.; Hamula, C. Methods for the identification of cultured microorganisms using matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. In CLSI Guideline; CLSI: Wayne, PA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson, R.; Gonzales-Siles, L.; Boulund, F.; Svensson-Stadler, L.; Skovbjerg, S.; Karlsson, A.; Davidson, M.; Hulth, S.; Kristiansson, E.; Moore, E.R. Proteotyping: Proteomic characterization, classification and identification of microorganisms—A prospectus. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 38, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Body, B.A.; Beard, M.A.; Slechta, E.S.; Hanson, K.E.; Barker, A.P.; Babady, N.E.; McMillen, T.; Tang, Y.-W.; Brown-Elliott, B.A.; Iakhiaeva, E. Evaluation of the Vitek MS v3.0 matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry system for identification of Mycobacterium and Nocardia species. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 56, e00237-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rychert, J.; Slechta, E.S.; Barker, A.P.; Miranda, E.; Babady, N.E.; Tang, Y.-W.; Gibas, C.; Wiederhold, N.; Sutton, D.; Hanson, K.E. Multicenter evaluation of the Vitek MS v3.0 system for the identification of filamentous fungi. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 56, e01353-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alizadeh, M.; Yousefi, L.; Pakdel, F.; Ghotaslou, R.; Rezaee, M.A.; Khodadadi, E.; Oskouei, M.A.; Barhaghi, M.H.S.; Kafil, H.S. MALDI-TOF Mass Spectroscopy Applications in Clinical Microbiology. Adv. Pharmacol. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 2021, 9928238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Elbehiry, A.; Aldubaib, M.; Abalkhail, A.; Marzouk, E.; ALbeloushi, A.; Moussa, I.; Ibrahem, M.; Albazie, H.; Alqarni, A.; Anagreyyah, S.; et al. How MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry Technology Contributes to Microbial Infection Control in Healthcare Settings. Vaccines 2022, 10, 1881. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10111881
Elbehiry A, Aldubaib M, Abalkhail A, Marzouk E, ALbeloushi A, Moussa I, Ibrahem M, Albazie H, Alqarni A, Anagreyyah S, et al. How MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry Technology Contributes to Microbial Infection Control in Healthcare Settings. Vaccines. 2022; 10(11):1881. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10111881
Chicago/Turabian StyleElbehiry, Ayman, Musaad Aldubaib, Adil Abalkhail, Eman Marzouk, Ahmad ALbeloushi, Ihab Moussa, Mai Ibrahem, Hamad Albazie, Abdullah Alqarni, Sulaiman Anagreyyah, and et al. 2022. "How MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry Technology Contributes to Microbial Infection Control in Healthcare Settings" Vaccines 10, no. 11: 1881. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10111881
APA StyleElbehiry, A., Aldubaib, M., Abalkhail, A., Marzouk, E., ALbeloushi, A., Moussa, I., Ibrahem, M., Albazie, H., Alqarni, A., Anagreyyah, S., Alghamdi, S., & Rawway, M. (2022). How MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry Technology Contributes to Microbial Infection Control in Healthcare Settings. Vaccines, 10(11), 1881. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10111881







