Kinetics of Humoral Immunity against SARS-CoV-2 in Healthcare Workers after the Third Dose of BNT162b2 mRNA Vaccine
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Detection of Antibodies Anti-(S) RBD
2.4. Detection of Antibodies Anti-Nucleoprotein (N)
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Ethical Aspects
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Haas, E.J.; Angulo, F.J.; McLaughlin, J.M.; Anis, E.; Singer, S.R.; Khan, F.; Brooks, N.; Smaja, M.; Mircus, G.; Pan, K.; et al. Impact and effectiveness of mRNA BNT162b2 vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 infections and COVID-19 cases, hospitalisations, and deaths following a nationwide vaccination campaign in Israel: An observational study using national surveillance data. Lancet 2021, 397, 1819–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krammer, F. A correlate of protection for SARS-CoV-2 vaccines is urgently needed. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1147–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Liang, B.; Chen, C.; Wang, H.; Fang, Y.; Shen, S.; Yang, X.; Wang, B.; Chen, L.; Chen, Q.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection induces sustained humoral immune responses in convalescent patients following symptomatic COVID-19. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Donno, A.; Lobreglio, G.; Panico, A.; Grassi, T.; Bagordo, F.; Bozzetti, M.P.; Massari, S.; Siculella, L.; Damiano, F.; Guerra, F.; et al. IgM and IgG profiles reveal peculiar features of humoral immunity response to SARS-CoV-2 infection. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chemaitelly, H.; Ayoub, H.; AlMukdad, S.; Coyle, P.; Tang, P.; Yassine, H.M.; Al-Khatib, H.A.; Smatti, M.K.; Hasan, M.R.; Al-Kanaani, Z.; et al. Protection from previous natural infection compared with mRNA vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 infection and severe COVID-19 in Qatar: A retrospective cohort study. Lancet Microbe 2022, 22, 00287-7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panico, A.; Lobreglio, G.; Bagordo, F.; Zizza, A.; De Donno, A.; Rosato, C.; Lazzari, R.; Chicone, M.; Indino, F.; Recchia, V.; et al. Antibody response in healthcare workers before and after the third dose of anti-SARS-CoV-2 vaccine: A pilot study. Vaccines 2022, 10, 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo Sasso, B.; Agnello, L.; Giglio, R.V.; Gambino, C.M.; Ciaccio, A.M.; Vidali, M.; Ciaccio, M. Longitudinal analysis of anti-SARS-CoV-2 S-RBD IgG antibodies before and after the third dose of the BNT162b2 vaccine. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feikin, D.R.; Higdon, M.M.; Abu-Raddad, L.J.; Andrews, N.; Araos, R.; Goldberg, Y.; Groome, M.J.; Huppert, A.; O’Brien, K.L.; Smith, P.G.; et al. Duration of effectiveness of vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 infection and COVID-19 disease: Results of a systematic review and meta-regression. Lancet 2022, 399, 924–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilz, S.; Theiler-Schwetz, V.; Trummer, C.; Krause, R.; Ioannidis, J.P.A. SARS-CoV-2 reinfections: Overview of efficacy and duration of natural and hybrid immunity. Environ. Res. 2022, 209, 112911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Chen, Z.; Azman, A.S.; Sun, R.; Lu, W.; Zheng, N.; Zhou, J.; Wu, Q.; Deng, X.; Zhao, Z.; et al. Neutralizing antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 variants induced by natural infection or vaccination: A systematic review and pooled meta-analysis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 74, 734–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazit, S.; Shlezinger, R.; Perez, G.; Lotan, R.; Peretz, A.; Ben-Tov, A.; Herzel, E.; Alapi, H.; Cohen, D.; Muhsen, K.; et al. Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Naturally Acquired Immunity versus Vaccine-induced Immunity, Reinfections versus Breakthrough Infections: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2022, 75, e545–e551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, E.G.; Lustig, Y.; Cohen, C.; Fluss, R.; Indenbaum, V.; Amit, S.; Doolman, R.; Asraf, K.; Mendelson, E.; Ziv, A.; et al. Waning Immune Humoral Response to BNT162b2 COVID-19 Vaccine over 6 Months. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, e84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doria-Rose, N.; Suthar, M.S.; Makowski, M.; O’Connell, S.; McDermott, A.B.; Flach, B.; Ledgerwood, J.E.; Mascola, J.R.; Graham, B.S.; Lin, B.C.; et al. Antibody persistence through 6 months after the second dose of mRNA-1273 vaccine for COVID-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 2259–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barouch, D.H.; Stephenson, K.E.; Sadoff, J.; Yu, J.; Chang, A.; Gebre, M.; McMahan, K.; Liu, J.; Chandrashekar, A.; Patel, S.; et al. Durable humoral and cellular immune responses 8 months after Ad26. COV2.S vaccination. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 951–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandolfo, C.; Anichini, G.; Mugnaini, M.; Bocchia, M.; Terrosi, C.; Sicuranza, A.; Savellini, G.G.; Gozzetti, A.; Franchi, F.; Cusi, M.G. Overview of anti-SARS-CoV-2 immune response six months after BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine. Vaccines 2022, 10, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naaber, P.; Tserel, L.; Kangro, K.; Sepp, E.; Jürjenson, V.; Adamson, A.; Haljasmägi, L.; Rumm, A.P.; Maruste, R.; Kärner, J.; et al. Dynamics of antibody response to BNT162b2 vaccine after six months: A longitudinal prospective study. Lancet Reg. Health Eur. 2021, 10, 100208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, Y.; Mandel, M.; Bar-On, Y.M.; Bodenheimer, O.; Freedman, L.; Haas, E.J.; Milo, R.; Alroy-Preis, S.; Ash, N.; Huppert, A. Waning immunity after the BNT162b2 vaccine in Israel. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, e85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groβ, R.; Zanoni, M.; Seidel, A.; Conzelmann, C.; Gilg, A.; Krnavek, D.; Erdemci-Evin, S.; Mayer, B.; Hoffmann, M.; Pohlmann, S.; et al. Heterologous ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 and BNT162b2 prime-boost vaccination elicits potent neutralizing antibody responses and T cell reactivity against prevalent SARS-CoV-2 variants. EBioMedicine 2021, 75, 103761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.M.S.; Mok, C.K.P.; Leung, W.Y.; Ng, S.S.; Chan, C.K.; Ko, F.W.; Chen, C.; Yiu, K.; Lam, B.H.S.; Lau, E.H.Y.; et al. Neutralizing antibodies against the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant BA.1 following homologous and heterologous CoronaVac or BNT162b2 vaccination. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 486–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ainsworth, M.; Andersson, M.; Auckland, K.; Baillie, J.K.; Barnes, E.; Beer, S.; Beveridge, A.; Bibi, S.; Blackwell, L.; Borak, M.; et al. Performance characteristics of five immunoassays for SARS-CoV-2: A head-to-head benchmark comparison. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 1390–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earle, K.A.; Ambrosino, D.M.; Fiore-Gartland, A.; Goldblatt, D.; Gilbert, P.B.; Siber, G.R.; Dull, P.; Plotkin, S.A. Evidence for antibody as a protective correlate for COVID-19 vaccines. Vaccine 2021, 39, 4423–4428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoury, D.S.; Cromer, D.; Reynaldi, A.; Schlub, T.E.; Wheatley, A.K.; Juno, J.A.; Subbarao, K.; Kent, S.J.; Triccas, J.A.; Davenport, M.P. Neutralizing antibody levels are highly predictive of immune protection from symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1205–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayak, K.; Gottimukkala, K.; Kumar, S.; Reddy, E.S.; Edara, V.V.; Kauffman, R.; Floyd, K.; Mantus, G.; Savargaonkar, D.; Goel, P.K.; et al. Characterization of neutralizing versus binding antibodies and memory B cells in COVID-19 recovered individuals from India. Virology 2021, 558, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lustig, Y.; Sapir, E.; Regev-Yochay, G.; Cohen, C.; Fluss, R.; Olmer, L.; Indenbaum, V.; Mandelboim, M.; Doolman, R.; Amit, S.; et al. BNT162b2 COVID-19 vaccine and correlates of humoral immune responses and dynamics: A prospective, single-centre, longitudinal cohort study in health-care workers. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, 999–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brisotto, G.; Muraro, E.; Montico, M.; Corso, C.; Evangelista, C.; Casarotto, M.; Caffau, C.; Vettori, R.; Cozzi, M.R.; Zanussi, S.; et al. IgG antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 decay but persist 4 months after vaccination in a cohort of healthcare workers. Clin. Chim. Acta 2021, 523, 476–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatopoulou, M.; Tsamadias, V.; Theodosopoulos, T.; Demeridou, S.; Kaparos, G.; Memos, N.; Konstadoulakis, M.; Baka, S. Rapid decay of anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in infection-naïve healthcare workers four months after vaccination. Germs 2021, 11, 625–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malipiero, G.; D’Agaro, P.; Segat, L.; Moratto, A.; Villalta, D. Long-term decay of anti-RBD IgG titers after BNT162b2 vaccination is not mirrored by loss of neutralizing bioactivity against SARS-CoV-2. Clin. Chim. Acta 2022, 524, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matusali, G.; Sberna, G.; Meschi, S.; Gramigna, G.; Colavita, F.; Lapa, D.; Francalancia, M.; Bettini, A.; Capobianchi, M.R.; Puro, V.; et al. Differential dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 binding and functional antibodies upon BNT162b2 vaccine: A 6-month follow-up. Viruses 2022, 14, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliakim-Raz, N.; Leibovici-Weisman, Y.; Stemmer, A.; Ness, A.; Awwad, M.; Ghantous, N.; Stemmer, S.M. Antibody Titers before and after a third dose of the SARS-CoV-2 BNT162b2 vaccine in adults aged ≥60 years. JAMA 2021, 326, 2203–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilboa, M.; Mandelboim, M.; Indenbaum, V.; Lustig, Y.; Cohen, C.; Rahav, G.; Asraf, K.; Amit, S.; Jaber, H.; Nemet, I.; et al. Early immunogenicity and safety of the third dose of BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 vaccine among adults older than 60 years; real world experience. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 225, 785–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blain, H.; Tuaillon, E.; Gamon, L.; Pisoni, A.; Miot, S.; Picot, M.C. Strong decay of SARS-CoV-2 spike antibodies after 2 BNT162b2 vaccine doses and high antibody response to a third dose in nursing home residents. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2022, 23, 750–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bar-On, Y.M.; Goldberg, Y.; Mandel, M.; Bodenheimer, O.; Freedman, L.; Kalkstein, N.; Mizrahi, B.; Alroy-Preis, S.; Ash, N.; Milo, R.; et al. Protection of BNT162b2 vaccine booster against COVID-19 in Israel. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1393–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patalon, T.; Saciuk, Y.; Peretz, A.; Perez, G.; Lurie, Y.; Maor, Y.; Gazit, S. Waning effectiveness of the third dose of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- L’Huillier, A.G.; Meyer, B.; Andrey, D.O.; Arm-Vernez, I.; Baggio, S.; Didierlaurent, A.; Eberhardt, C.S.; Eckerle, I.; Grasset-Salomon, C.; Huttner, A.; et al. Antibody persistence in the first six months following SARS-CoV-2 infection among hospital workers: A prospective longitudinal study. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2021, 27, e1–e784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, A.S.; Jones, F.K.; Nodoushani, A.; Kelly, M.; Becker, M.; Slater, D.; Mills, R.; Teng, E.; Kamruzzaman, M.; Garcia-Beltran, W.F.; et al. Persistence and decay of human antibody responses to the receptor binding domain of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein in COVID-19 patients. Sci. Immunol. 2020, 5, eabe0367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prendecki, M.; Clarke, C.; Brown, J.; Cox, A.; Gleeson, S.; Guckian, M.; Randell, P.; Pria, A.D.; Lightstone, L.; Xu, X.N.; et al. Effect of previous SARS-CoV-2 infection on humoral and T-cell responses to single-dose BNT162b2 vaccine. Lancet 2021, 397, 1178–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sariol, C.A.; Pantoja, P.; Serrano-Collazo, C.; Rosa-Arocho, T.; Armina-Rodríguez, A.; Cruz, L.; Stone, E.T.; Arana, T.; Climent, C.; Latoni, G.; et al. Function is more reliable than quantity to follow up the humoral response to the receptor-binding domain of SARS-CoV-2-Spike protein after natural infection or COVID-19 vaccination. Viruses 2021, 13, 1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, N.; Tessier, E.; Stowe, J.; Gower, C.; Kirsebom, F.; Simmons, R.; Gallagher, E.; Thelwall, S.; Groves, N.; Dabrera, G.; et al. Duration of Protection against Mild and Severe Disease by Covid-19 Vaccines. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 340–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, R.R.; Apostolidis, S.A.; Painter, M.M.; Mathew, D.; Pattekar, A.; Kuthuru, O.; Gouma, S.; Hicks, P.; Meng, W.; Rosenfeld, A.M.; et al. Distinct antibody and memory B cell responses in SARS-CoV-2 naïve and recovered individuals after mRNA vaccination. Sci. Immunol. 2021, 6, eabi6950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonura, F.; De Grazia, S.; Bonura, C.; Sanfilippo, G.L.; Giammanco, G.M.; Amodio, E.; Ferraro, D. Differing kinetics of anti-spike protein IgGs and neutralizing antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 after Comirnaty (BNT162b2) immunization. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 132, 3987–3994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellini, R.; Venuti, A.; Pimpinelli, F.; Abril, E.; Blandino, G.; Campo, F.; Conti, L.; De Virgilio, A.; De Marco, F.; Di Domenico, E.G.; et al. Initial observations on age, gender, BMI and hypertension in antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 BNT162b2 vaccine. E Clin. Med. 2021, 36, 100928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrotri, M.; Fragaszy, E.; Nguyen, V.; Navaratnam, A.M.D.; Geismar, C.; Beale, S.; Kovar, J.; Byrne, T.E.; Fong, W.L.E.; Patel, P.; et al. Spike-antibody responses to COVID-19 vaccination by demographic and clinical factors in a prospective community cohort study. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padoan, A.; Cosma, C.; Bonfante, F.; della Rocca, F.; Barbaro, F.; Santarossa, C.; Dall’Olmo, L.; Pagliari, M.; Bortolami, A.; Cattelan, A.; et al. Neutralizing antibody titers six months after Comirnaty vaccination: Kinetics and comparison with SARS-CoV-2 immunoassays. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2021, 60, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaebler, C.; Wang, Z.; Lorenzi, J.C.C.; Muecksch, F.; Finkin, S.; Tokuyama, M.; Cho, A.; Jankovic, M.; Schaefer-Babajew, D.; Oliveira, T.Y.; et al. Evolution of antibody immunity to SARS-CoV-2. Nature 2021, 591, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melgaço, J.G.; Azamor, T.; Ano Bom, A.P.D. Protective immunity after COVID-19 has been questioned: What can we do without SARS-CoV-2-IgG detection? Cell Immunol. 2020, 353, 104114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geers, D.; Shamier, M.C.; Bogers, S.; den Hartog, G.; Gommers, L.; Nieuwkoop, N.N.; Schmitz, K.S.; Rijsbergen, L.C.; van Osch, J.A.T.; Dijkhuizen, E.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern partially escape humoral but not T-cell responses in COVID-19 convalescent donors and vaccinees. Sci. Immunol. 2021, 6, eabj1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, U.; Muik, A.; Derhovanessian, E.; Vogler, I.; Kranz, L.M.; Vormehr, M.; Baum, A.; Pascal, K.; Quandt, J.; Maurus, D.; et al. COVID-19 vaccine BNT162b1 elicits human antibody and T(H)1 T cell responses. Nature 2020, 586, 594–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grifoni, A.; Weiskopf, D.; Ramirez, S.I.; Mateus, J.; Dan, J.M.; Moderbacher, C.R.; Rawlings, S.A.; Sutherland, A.; Premkumar, L.; Jadi, R.S.; et al. Targets of T cell responses to SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus in humans with COVID-19 disease and unexposed individuals. Cell 2020, 181, 1489–1501.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Variables | ||
|---|---|---|
| Gender Male Female | 10 (29.4) 24 (70.6) | N (%) N (%) |
| Age ≥50 <50 | 47.0 ± 11.5 15 (44.1) 19 (55.9) | Mean ± SD (years) N (%) N (%) |
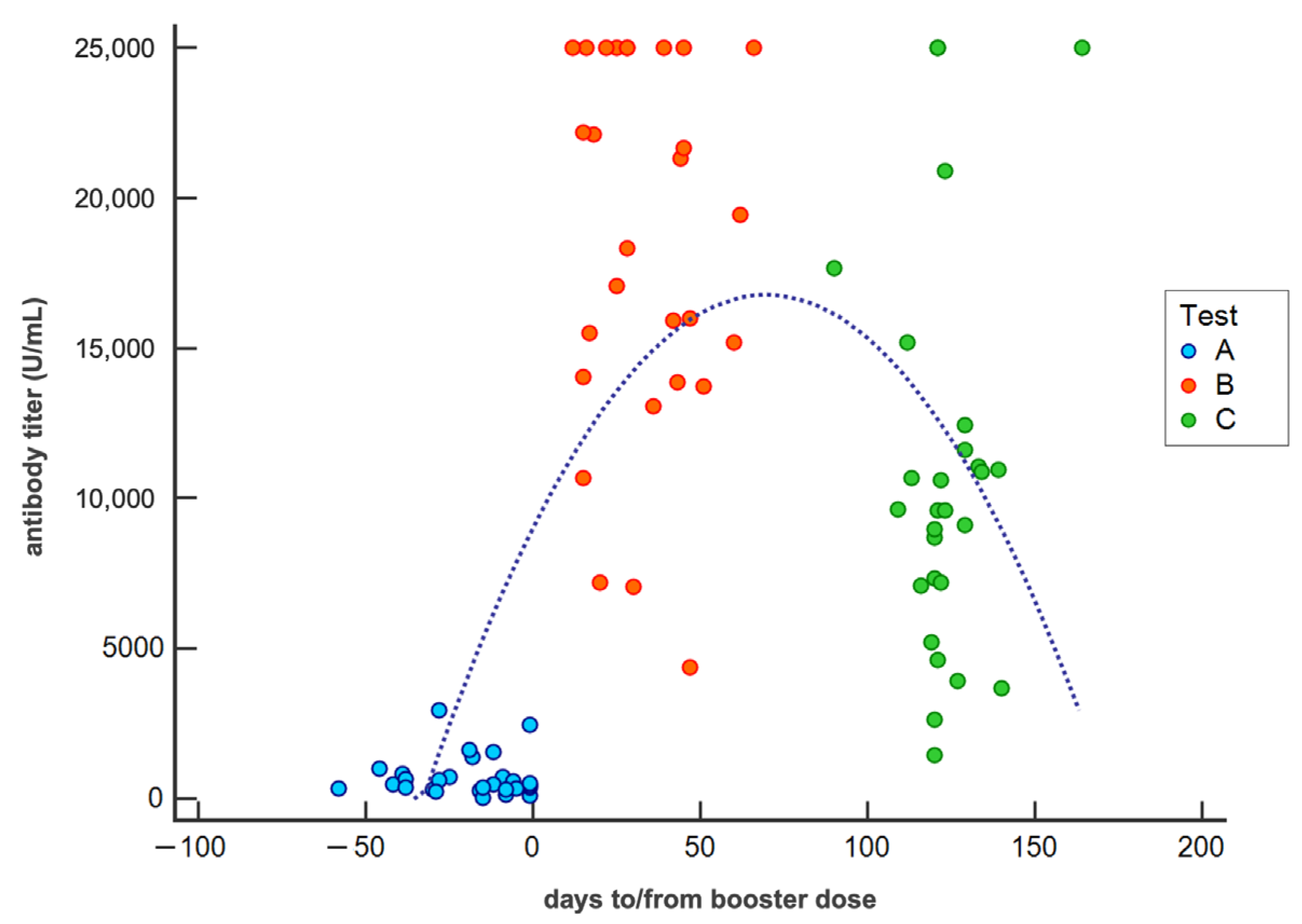
| Antibody titer at test A | 763.1 ± 687.8 | Mean ± SD (U/mL) |
| Antibody titer at test B | 17679.0 ± 6420.0 | Mean ± SD (U/mL) |
| Antibody titer at test C | 10919.2 ± 6528.6 | Mean ± SD (U/mL) |
| Antibody titer at test C in COVID-19 subjects | 24004.5 ± 1938.3 | Mean ± SD (U/mL) |
| Interval test A-3rd dose | 20 ± 16 | Mean ± SD (days) |
| Interval 3rd dose-test B | 34 ± 16 | Mean ± SD (days) |
| Interval 3rd dose-test C | 124 ± 12 | Mean ± SD (days) |
| COVID-19 Subjects | Age | Gender | Interval Test A-3rd Dose (days) | Antibody Titer Test A (U/mL) | Interval 3rd Dose-Test B (days) | Antibody Titer Test B (U/mL) | Interval 3rd Dose-COVID-19 Positivity (days) | Interval 3rd Dose-Test C (days) | Antibody Titer Test C (U/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| COVID#1 | 61 | M | 8 | 750 | 65 | 6651 | 75 | 147 | 23,870 |
| COVID#2 | 55 | M | 35 | 508 | 14 | 25,000 | 74 | 138 | 25,000 |
| COVID#3 | 55 | F | 42 | 490 | 26 | 13,770 | 70 | 127 | 25,000 |
| COVID#4 | 59 | F | 42 | 2362 | 18 | 13,871 | 89 | 126 | 20,157 |
| COVID#5 | 42 | F | 5 | 567 | 49 | 25,000 | 61 | 121 | 25,000 |
| COVID#6 | 51 | F | 11 | 808 | 46 | 25,000 | 56 | 120 | 25,000 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grassi, T.; Lobreglio, G.; Panico, A.; Rosato, C.; Zizza, A.; Lazzari, R.; Chicone, M.; Indino, F.; Bagordo, F. Kinetics of Humoral Immunity against SARS-CoV-2 in Healthcare Workers after the Third Dose of BNT162b2 mRNA Vaccine. Vaccines 2022, 10, 1948. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10111948
Grassi T, Lobreglio G, Panico A, Rosato C, Zizza A, Lazzari R, Chicone M, Indino F, Bagordo F. Kinetics of Humoral Immunity against SARS-CoV-2 in Healthcare Workers after the Third Dose of BNT162b2 mRNA Vaccine. Vaccines. 2022; 10(11):1948. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10111948
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrassi, Tiziana, Giambattista Lobreglio, Alessandra Panico, Chiara Rosato, Antonella Zizza, Roberta Lazzari, Michele Chicone, Floriano Indino, and Francesco Bagordo. 2022. "Kinetics of Humoral Immunity against SARS-CoV-2 in Healthcare Workers after the Third Dose of BNT162b2 mRNA Vaccine" Vaccines 10, no. 11: 1948. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10111948
APA StyleGrassi, T., Lobreglio, G., Panico, A., Rosato, C., Zizza, A., Lazzari, R., Chicone, M., Indino, F., & Bagordo, F. (2022). Kinetics of Humoral Immunity against SARS-CoV-2 in Healthcare Workers after the Third Dose of BNT162b2 mRNA Vaccine. Vaccines, 10(11), 1948. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10111948







