New-Onset Acute Kidney Disease Post COVID-19 Vaccination
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Clinical Characteristics of Patients
3. Clinical Characteristics and Follow-Up of Patients by Disease
3.1. Minimal Change Disease (MCD)
3.2. IgA Nephropathy (IgAN)
3.3. Membranous Nephropathy (MN)
3.4. Anti-Glomerular Basement Membrane (Anti-GBM) and Anti-Neutrophil Cytoplasmic Autoantibodies (ANCA) Vasculitis
3.5. Acquired Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (aTTP)
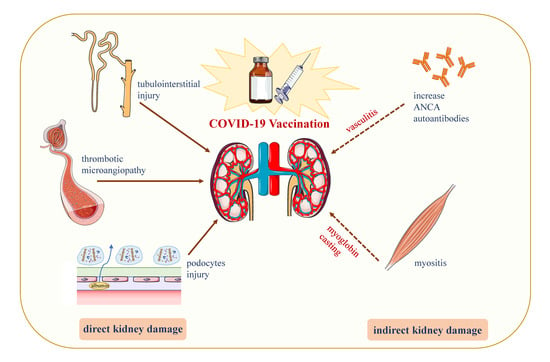
4. Inducing AKD through COVID-19 Vaccine: Hypotheses
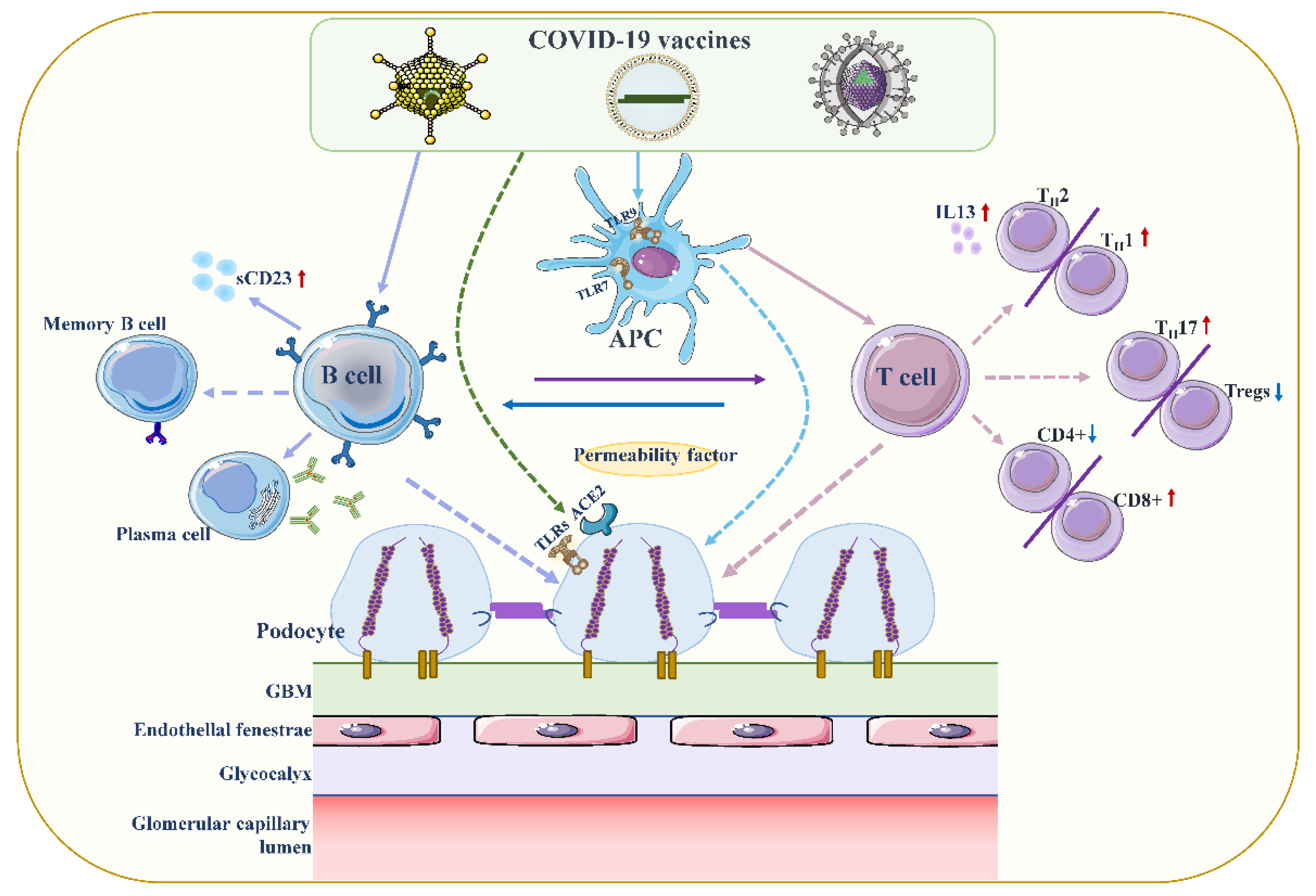
4.1. Podocyte Damage
4.2. Increased Production of Anti-Neutrophil Cytoplasmic Autoantibodies (ANCAs)
4.3. Vaccine-Induced Thrombotic Thrombocytopenia (VITT)
4.4. Direct Induction of Myositis
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AAV | ANCA-associated vasculitis |
| ACE2 | angiotensin conversion enzyme 2 |
| ADAMTS13 | A Disintegrin And Metalloproteinase with a ThromboSpondin type 1 motif, member 13 |
| AIN | acute interstitial nephritis |
| AKD | acute kidney disease |
| AKI | acute kidney injury |
| ANCA | anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibodies |
| anti-GBM | anti-glomerular basement membrane |
| anti-PLA2R | anti-phospholipase A2 receptor |
| APLs | antiphospholipid antibodies |
| aTTP | acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura |
| CKD | chronic kidney disease |
| COVID-19 | coronavirus disease 2019 |
| CR | complete remission |
| CTL | cytotoxic T-lymphocyte |
| CNS | central nervous system |
| CyC | cyclophosphamide |
| PF4 | platelet factor 4 |
| GN | glomerulonephritis |
| IgAN | IgA nephropathy |
| KDIGO | Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes |
| MCD | minimal change disease |
| MN | membranous nephropathy |
| MPO | myeloperoxidase |
| NAs | nucleic acids |
| PLEX | plasma exchange |
| PR | partial remission |
| PR3 | proteinase 3 |
| RAAS | renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system |
| RASB | renin-angiotensin system blockade |
| RRT | renal replacement therapy |
| RTX | rituximab |
| SARS-CoV-2 | severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 |
| Scr | serum creatinine |
| TAC | tacrolimus |
| TLRs | toll-like receptors |
| TLR2 | toll-like receptor 2 |
| TLR9 | toll-like receptor 9 |
| VITT | vaccine-induced immune thrombotic thrombocytopenia |
| VWF | von Willebrand factor |
References
- Sahin, U.; Muik, A.; Vogler, I.; Derhovanessian, E.; Kranz, L.M.; Vormehr, M.; Quandt, J.; Bidmon, N.; Ulges, A.; Baum, A.; et al. BNT162b2 vaccine induces neutralizing antibodies and poly-specific T cells in humans. Nature 2021, 595, 572–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, O.; Sultan, A.A.; Ding, H.; Triggle, C.R. A Review of the Progress and Challenges of Developing a Vaccine for COVID-19. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 585354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiolet, T.; Kherabi, Y.; MacDonald, C.J.; Ghosn, J.; Peiffer-Smadja, N. Comparing COVID-19 vaccines for their characteristics, efficacy and effectiveness against SARS-CoV-2 and variants of concern: A narrative review. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2021, 28, 202–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolff, J.A.; Malone, R.W.; Williams, P.; Chong, W.; Acsadi, G.; Jani, A.; Felgner, P.L. Direct gene transfer into mouse muscle in vivo. Science 1990, 247 Pt 1, 1465–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polack, F.P.; Thomas, S.J.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Perez, J.L.; Perez Marc, G.; Moreira, E.D.; Zerbini, C.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2603–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.J.; Moreira, E.D., Jr.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Perez, J.L.; Perez Marc, G.; Polack, F.P.; Zerbini, C.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine through 6 Months. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1761–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emary, K.R.W.; Golubchik, T.; Aley, P.K.; Ariani, C.V.; Angus, B.; Bibi, S.; Blane, B.; Bonsall, D.; Cicconi, P.; Charlton, S.; et al. Efficacy of ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 (AZD1222) vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 variant of concern 202012/01 (B.1.1.7). an exploratory analysis of a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2021, 397, 1351–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voysey, M.; Clemens, S.A.C.; Madhi, S.A.; Weckx, L.Y.; Folegatti, P.M.; Aley, P.K.; Angus, B.; Baillie, V.L.; Barnabas, S.L.; Bhorat, Q.E.; et al. Safety and efficacy of the ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine (AZD1222) against SARS-CoV-2. an interim analysis of four randomised controlled trials in Brazil, South Africa, and the UK. Lancet 2021, 397, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa Clemens, S.A.; Weckx, L.; Clemens, R.; Almeida Mendes, A.V.; Ramos Souza, A.; Silveira, M.B.V.; da Guarda, S.N.F.; de Nobrega, M.M.; de Moraes Pinto, M.I.; Gonzalez, I.G.S.; et al. Heterologous versus homologous COVID-19 booster vaccination in previous recipients of two doses of CoronaVac COVID-19 vaccine in Brazil (RHH-001). a phase 4, non-inferiority, single blind, randomised study. Lancet 2022, 399, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baden, L.R.; El Sahly, H.M.; Essink, B.; Kotloff, K.; Frey, S.; Novak, R.; Diemert, D.; Spector, S.A.; Rouphael, N.; Creech, C.B.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klomjit, N.; Alexander, M.P.; Fervenza, F.C.; Zoghby, Z.; Garg, A.; Hogan, M.C.; Nasr, S.H.; Minshar, M.A.; Zand, L. COVID-19 Vaccination and Glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int. Rep. 2021, 6, 2969–2978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levey, A.S.; Eckardt, K.U.; Tsukamoto, Y.; Levin, A.; Coresh, J.; Rossert, J.; De Zeeuw, D.; Hostetter, T.H.; Lameire, N.; Eknoyan, G. Definition and classification of chronic kidney disease. a position statement from Kidney Disease. Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO). Kidney Int. 2005, 67, 2089–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kellum, J.A.; Lameire, N.; Group, K.A.G.W. Diagnosis, evaluation, and management of acute kidney injury. a KDIGO summary (Part 1). Crit. Care 2013, 17, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chawla, L.S.; Bellomo, R.; Bihorac, A.; Goldstein, S.L.; Siew, E.D.; Bagshaw, S.M.; Bittleman, D.; Cruz, D.; Endre, Z.; Fitzgerald, R.L.; et al. Acute kidney disease and renal recovery. consensus report of the Acute Disease Quality Initiative (ADQI) 16 Workgroup. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2017, 13, 241–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hirsch, J.S.; Ng, J.H.; Ross, D.W.; Sharma, P.; Shah, H.H.; Barnett, R.L.; Hazzan, A.D.; Fishbane, S.; Jhaveri, K.D.; Northwell, C.-R.C.; et al. Acute kidney injury in patients hospitalized with COVID-19. Kidney Int. 2020, 98, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leclerc, S.; Royal, V.; Lamarche, C.; Laurin, L.P. Minimal Change Disease With Severe Acute Kidney Injury Following the Oxford-AstraZeneca COVID-19 Vaccine. A Case Report. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2021, 78, 607–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.H.; Han, M.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, M.S.; Jung, H.Y.; Choi, J.Y.; Cho, J.H.; Kim, C.D.; Kim, Y.L.; Park, S.H. New-onset Nephrotic Syndrome after Janssen COVID-19 Vaccination. a Case Report and Literature Review. J. Korean Med. Sci 2021, 36, e218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebedev, L.; Sapojnikov, M.; Wechsler, A.; Varadi-Levi, R.; Zamir, D.; Tobar, A.; Levin-Iaina, N.; Fytlovich, S.; Yagil, Y. Minimal Change Disease Following the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 Vaccine. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2021, 78, 142–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maas, R.J.; Gianotten, S.; van der Meijden, W.A.G. An Additional Case of Minimal Change Disease Following the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 Vaccine. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2021, 78, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Agati, V.D.; Kudose, S.; Bomback, A.S.; Adamidis, A.; Tartini, A. Minimal change disease and acute kidney injury following the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine. Kidney Int. 2021, 100, 461–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzworth, A.; Couchot, P.; Cruz-Knight, W.; Brucculeri, M. Minimal change disease following the Moderna mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 vaccine. Kidney Int. 2021, 100, 463–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weijers, J.; Alvarez, C.; Hermans, M.M.H. Post-vaccinal minimal change disease. Kidney Int. 2021, 100, 459–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, S.; Fugo, K.; Yamazaki, K.; Terawaki, H. Minimal change disease soon after Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccination. Clin. Kidney J. 2021, 14, 2606–2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanna, J.; Ingram, A.; Shao, T. Minimal Change Disease After First Dose of Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 Vaccine. A Case Report and Review of Minimal Change Disease Related to COVID-19 Vaccine. Can. J. Kidney Health Dis. 2021, 8, 20543581211058271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unver, S.; Haholu, A.; Yildirim, S. Nephrotic syndrome and acute kidney injury following CoronaVac anti-SARS-CoV-2 vaccine. Clin. Kidney J. 2021, 14, 2608–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da, Y.; Goh, G.H.; Khatri, P. A case of membranous nephropathy following Pfizer-BioNTech mRNA vaccination against COVID-19. Kidney Int. 2021, 100, 938–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gueguen, L.; Loheac, C.; Saidani, N.; Khatchatourian, L. Membranous nephropathy following anti-COVID-19 mRNA vaccination. Kidney Int. 2021, 100, 1140–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudose, S.; Friedmann, P.; Albajrami, O.; D’Agati, V.D. Histologic correlates of gross hematuria following Moderna COVID-19 vaccine in patients with IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2021, 100, 468–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.Z.; Tan, R.Y.; Choo, J.C.J.; Lim, C.C.; Tan, C.S.; Loh, A.H.L.; Tien, C.S.; Tan, P.H.; Woo, K.T. Is COVID-19 vaccination unmasking glomerulonephritis? Kidney Int. 2021, 100, 469–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, C.; Herrera Hernandez, L.P.; Bu, L.; Kizilbash, S.; Najera, L.; Rheault, M.N.; Czyzyk, J.; Kouri, A.M. IgA nephropathy presenting as macroscopic hematuria in 2 pediatric patients after receiving the Pfizer COVID-19 vaccine. Kidney Int. 2021, 100, 705–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderegg, M.A.; Liu, M.; Saganas, C.; Montani, M.; Vogt, B.; Huynh-Do, U.; Fuster, D.G. De novo vasculitis after mRNA-1273 (Moderna) vaccination. Kidney Int. 2021, 100, 474–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacker, A.; Kung, V.; Andeen, N. Anti-GBM nephritis with mesangial IgA deposits after SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination. Kidney Int. 2021, 100, 471–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, M.; Diaz-Crespo, F.; Perez de Jose, A.; Verdalles, U.; Verde, E.; Almeida Ruiz, F.; Acosta, A.; Mijaylova, A.; Goicoechea, M. A case of ANCA-associated vasculitis after AZD1222 (Oxford-AstraZeneca) SARS-CoV-2 vaccination. casualty or causality? Kidney Int. 2021, 100, 937–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakroush, S.; Tampe, B. Case Report. ANCA-Associated Vasculitis Presenting With Rhabdomyolysis and Pauci-Immune Crescentic Glomerulonephritis After Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 mRNA Vaccination. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 762006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekar, A.; Campbell, R.; Tabbara, J.; Rastogi, P. ANCA glomerulonephritis after the Moderna COVID-19 vaccination. Kidney Int. 2021, 100, 473–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakoor, M.T.; Birkenbach, M.P.; Lynch, M. ANCA-Associated Vasculitis Following Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 Vaccine. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2021, 78, 611–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dube, G.K.; Benvenuto, L.J.; Batal, I. Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Autoantibody-Associated Glomerulonephritis Following the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 Vaccine. Kidney Int. Rep. 2021, 6, 3087–3089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feghali, E.J.; Zafar, M.; Abid, S.; Santoriello, D.; Mehta, S. De-novo Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-Associated Vasculitis Following the mRNA-1273 (Moderna) Vaccine for COVID-19. Cureus 2021, 13, e19616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillion, V.; Jadoul, M.; Demoulin, N.; Aydin, S.; Devresse, A. Granulomatous vasculitis after the AstraZeneca anti-SARS-CoV-2 vaccine. Kidney Int. 2021, 100, 706–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mira, F.S.; Costa Carvalho, J.; de Almeida, P.A.; Pimenta, A.C.; Alen Coutinho, I.; Figueiredo, C.; Rodrigues, L.; Sousa, V.; Ferreira, E.; Pinto, H.; et al. A Case of Acute Interstitial Nephritis After Two Doses of the BNT162b2 SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine. Int. J. Nephrol. Renov. Dis. 2021, 14, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancianti, N.; Guarnieri, A.; Tripodi, S.; Salvo, D.P.; Garosi, G. Minimal change disease following vaccination for SARS-CoV-2. J. Nephrol. 2021, 34, 1039–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydin, M.F.; Yildiz, A.; Oruc, A.; Sezen, M.; Dilek, K.; Gullulu, M.; Yavuz, M.; Ersoy, A. Relapse of primary membranous nephropathy after inactivated SARS-CoV-2 virus vaccination. Kidney Int. 2021, 100, 464–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrin, P.; Bassand, X.; Benotmane, I.; Bouvier, N. Gross hematuria following SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in patients with IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2021, 100, 466–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yocum, A.; Simon, E.L. Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura after Ad26.COV2-S Vaccination. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2021, 49, 441.e443–441.e444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruhe, J.; Schnetzke, U.; Kentouche, K.; Prims, F.; Baier, M.; Herfurth, K.; Schlosser, M.; Busch, M.; Hochhaus, A.; Wolf, G. Acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura after first vaccination dose of BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine. Ann. Hematol. 2022, 101, 717–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osmanodja, B.; Schreiber, A.; Schrezenmeier, E.; Seelow, E. First diagnosis of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura after SARS-CoV-2 vaccine—Case report. BMC Nephrol. 2021, 22, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamarti, K.; Dar, K.; Reddy, A.; Gundlapalli, A.; Mourning, D.; Bajaj, K. Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura Presentation in an Elderly Gentleman Following COVID Vaccine Circumstances. Cureus 2021, 13, e16619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alislambouli, M.; Veras Victoria, A.; Matta, J.; Yin, F. Acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura following Pfizer COVID-19 vaccination. EJHaem 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, K.; Sakaki, A.; Matsuyama, Y.; Mushino, T.; Matsumoto, M.; Sonoki, T.; Tamura, S. Acquired Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura Following BNT162b2 mRNA Coronavirus Disease Vaccination in a Japanese Patient. Intern. Med. 2022, 61, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Missoum, S.; Lahmar, M.; Khellaf, G. Leukocytoclastic vasculitis and acute renal failure following inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine. Nephrol. Ther. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Rawahi, B.; BaTaher, H.; Jaffer, Z.; Al-Balushi, A.; Al-Mazrouqi, A.; Al-Balushi, N. Vaccine-induced immune thrombotic thrombocytopenia following AstraZeneca (ChAdOx1 nCOV-19) vaccine-A case report. Res. Pract. Thromb. Haemost 2021, 5, e12578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, J.H.; Kim, M.S.; Kim, Y.J.; Han, M.H.; Jung, H.Y.; Choi, J.Y.; Cho, J.H.; Kim, C.D.; Kim, Y.L.; Park, S.H. New-Onset Kidney Diseases after COVID-19 Vaccination. A Case Series. Vaccines 2022, 10, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vivarelli, M.; Massella, L.; Ruggiero, B.; Emma, F. Minimal Change Disease. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 12, 332–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Williams, M.A.; Bevan, M.J. Effector and memory CTL differentiation. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 25, 171–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mudd, P.A.; Minervina, A.A.; Pogorelyy, M.V.; Turner, J.S.; Kim, W.; Kalaidina, E.; Petersen, J.; Schmitz, A.J.; Lei, T.; Haile, A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination elicits a robust and persistent T follicular helper cell response in humans. Cell 2021, 185, 603–613.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, H.; Hollenbaugh, J.A.; Zand, M.S.; Holden-Wiltse, J.; Mosmann, T.R.; Perelson, A.S.; Wu, H.; Topham, D.J. Quantifying the early immune response and adaptive immune response kinetics in mice infected with influenza A virus. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 6687–6698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sette, A.; Crotty, S. Adaptive immunity to SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19. Cell 2021, 184, 861–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colucci, M.; Corpetti, G.; Emma, F.; Vivarelli, M. Immunology of idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2018, 33, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathieson, P.W. Immune dysregulation in minimal change nephropathy. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2003, 18 (Suppl. S6), vi26–vi29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le Berre, L.; Herve, C.; Buzelin, F.; Usal, C.; Soulillou, J.P.; Dantal, J. Renal macrophage activation and Th2 polarization precedes the development of nephrotic syndrome in Buffalo/Mna rats. Kidney Int. 2005, 68, 2079–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pardi, N.; Hogan, M.J.; Porter, F.W.; Weissman, D. mRNA vaccines—A new era in vaccinology. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2018, 17, 261–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sahin, U.; Muik, A.; Derhovanessian, E.; Vogler, I.; Kranz, L.M.; Vormehr, M.; Baum, A.; Pascal, K.; Quandt, J.; Maurus, D.; et al. COVID-19 vaccine BNT162b1 elicits human antibody and TH1 T cell responses. Nature 2020, 586, 594–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imanishi, T.; Ishihara, C.; Badr Mel, S.; Hashimoto-Tane, A.; Kimura, Y.; Kawai, T.; Takeuchi, O.; Ishii, K.J.; Taniguchi, S.; Noda, T.; et al. Nucleic acid sensing by T cells initiates Th2 cell differentiation. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Teijaro, J.R.; Farber, D.L. COVID-19 vaccines: Modes of immune activation and future challenges. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 21, 195–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.K.; Bhargava, R.; Shaukat, A.A.; Albert, E.; Leggat, J. Spectrum of podocytopathies in new-onset nephrotic syndrome following COVID-19 disease. a report of 2 cases. BMC Nephrol. 2020, 21, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabarre, P.; Dumas, G.; Dupont, T.; Darmon, M.; Azoulay, E.; Zafrani, L. Acute kidney injury in critically ill patients with COVID-19. Intens. Care Med. 2020, 46, 1339–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffs, L.S.; Nitschke, J.; Tervaert, J.W.; Peh, C.A.; Hurtado, P.R. Viral RNA in the influenza vaccine may have contributed to the development of ANCA-associated vasculitis in a patient following immunisation. Clin. Rheumatol. 2016, 35, 943–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uppal, N.N.; Kello, N.; Shah, H.H.; Khanin, Y.; De Oleo, I.R.; Epstein, E.; Sharma, P.; Larsen, C.P.; Bijol, V.; Jhaveri, K.D. De Novo ANCA-Associated Vasculitis With Glomerulonephritis in COVID-19. Kidney Int. Rep. 2020, 5, 2079–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlachoyiannopoulos, P.G.; Magira, E.; Alexopoulos, H.; Jahaj, E.; Theophilopoulou, K.; Kotanidou, A.; Tzioufas, A.G. Autoantibodies related to systemic autoimmune rheumatic diseases in severely ill patients with COVID-19. Ann. Rheum Dis. 2020, 79, 1661–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izci Duran, T.; Turkmen, E.; Dilek, M.; Sayarlioglu, H.; Arik, N. ANCA-associated vasculitis after COVID-19. Rheumatol. Int. 2021, 41, 1523–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunachalam, P.S.; Scott, M.K.D.; Hagan, T.; Li, C.; Feng, Y.; Wimmers, F.; Grigoryan, L.; Trisal, M.; Edara, V.V.; Lai, L.; et al. Systems vaccinology of the BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine in humans. Nature 2021, 596, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Summers, S.A.; Steinmetz, O.M.; Gan, P.Y.; Ooi, J.D.; Odobasic, D.; Kitching, A.R.; Holdsworth, S.R. Toll-like receptor 2 induces Th17 myeloperoxidase autoimmunity while Toll-like receptor 9 drives Th1 autoimmunity in murine vasculitis. Arthritis Rheum 2011, 63, 1124–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, N.; Admane, N.; Kumari, A.; Sood, D.; Grover, S.; Prajapati, V.K.; Chandra, R.; Grover, A. Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte elicited vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 employing immunoinformatics framework. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talotta, R.; Robertson, E.S. Antiphospholipid antibodies and risk of post-COVID-19 vaccination thrombophilia. The straw that breaks the camel’s back? Cytokine Growth Factor. Rev. 2021, 60, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Xu, Z.; Wang, P.; Li, X.M.; Shuai, Z.W.; Ye, D.Q.; Pan, H.F. New-onset autoimmune phenomena post-COVID-19 vaccination. Immunology 2021, 165, 386–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, K.Y.; Au, S.Y.; Fong, K.M. Thrombotic Thrombocytopenia after ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 Vaccination. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, e11. [Google Scholar]
- Pasin, F.; Calabrese, A.; Pelagatti, L. Immune thrombocytopenia following COVID-19 mRNA vaccine. casuality or causality? Intern. Emerg. Med. 2022, 17, 295–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, M.; Labelle, A.; Mazzetti, I.; Elbatarny, H.S.; Lillicrap, D. Adenovirus-induced thrombocytopenia. the role of von Willebrand factor and P-selectin in mediating accelerated platelet clearance. Blood 2007, 109, 2832–2839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichinger, S.; Warkentin, T.E.; Greinacher, A. Thrombotic Thrombocytopenia after ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 Vaccination. Reply. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, e11. [Google Scholar]
- Greinacher, A.; Thiele, T.; Warkentin, T.E.; Weisser, K.; Kyrle, P.A.; Eichinger, S. Thrombotic Thrombocytopenia after ChAdOx1 nCov-19 Vaccination. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 2092–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greinacher, A.; Selleng, K.; Mayerle, J.; Palankar, R.; Wesche, J.; Reiche, S.; Aebischer, A.; Warkentin, T.E.; Muenchhoff, M.; Hellmuth, J.C.; et al. Anti-platelet factor 4 antibodies causing VITT do not cross-react with SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. Blood 2021, 138, 1269–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theodorou, D.J.; Theodorou, S.J.; Axiotis, A.; Gianniki, M.; Tsifetaki, N. COVID-19 vaccine-related myositis. QJM 2021, 114, 424–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Case | Authors | Age/Sex | Country (Race) | Medical History | Vaccine | Onset (Day) | Baseline-Scr (mg/dL) | After Vaccine-Scr (mg/dL) (Day) | Newly HT/Worse | Symptoms | Diagnosis | Treatments | Outcomes | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type | Manufacturer | Onset after Which Dose | |||||||||||||
| New Case | |||||||||||||||
| 1 | Leclerc et al. [16] | 71/M | Canada | dyslipidemia treated with rosuvastatin | Vector | AstraZeneca | 1st | D1 | 0.7 | 10.6 (D14) | III | edema | MCD | HD, mPSL 1 g/day 1–3 day, PSL 60 mg/day | CR. Scr was 1.2 mg/dL, UPCR 28 mg/mmol at D81 |
| 2 | Lim et al. [17] | 51/M | Korea | None | Vector | Janssen | 1st | D7 | NA | 1.54 (D28) | I | edema | MCD | mPSL 64 mg/day | CR. Scr was 0.95 mg/dL, UPCR was 0.2 g/g at D57 |
| 3 | Lebedev et al. [18] | 50/M | Israel | None | mRNA | Pfizer-BioNTech | 1st | D4 | 0.78 | 2.31 (D10) | III | edema, abdominal pain, diarrhea | MCD with ATI | PSL 80 mg/day | CR. Scr was 0.97 mg/dL, UACR was 155 mg/g at D37 |
| 4 | Maas et al. [19] | 80s/M | Netherlands | VTE | mRNA | Pfizer-BioNTech | 1st | D7 | NA | 1.43 (D7) | II | edema | MCD with ATI | PSL 80 mg/day | CR. UPCR was 0.68 g/g after 10 days of PSL |
| 5 | D’Agati et al. [20] | 77/M | USA (Caucasian) | T2DM | mRNA | Pfizer-BioNTech | 1st | D7 | 1.0–1.3 | 2.33 (D14) | I | edema | MCD with ATI | mPSL 1 g/day 1–3 day, PSL 60 mg/day | NR. Scr was 3.74 mg/dL, UTP was 18.8 g/day at D35 |
| 6 | Holzworth et al. [21] | 63/F | USA | HT | mRNA | Moderna | 1st | <D7 | 0.7 | 1.48 (>D28) | III | edema, dyspnea | MCD with ATI and AIN | mPSL 500 mg/day 1–3 day, PSL 1 mg/kg/day | NA |
| 7 | Weijers et al. [22] | 61/F | Netherlands | AIH, hypothyroidism | mRNA | Pfizer-BioNTech | 1st | D1 | 0.7–0.8 | 1.47 (D4) | NA | edema | MCD | HD, steroids 1 mg/kg/day | CR. Scr was <1 mg/dL at D77, UTP was 0 g/day at D58 |
| 8 | Kobayashi et al. [23] | 75/M | Japan | edema and hydrocele testicle after 1st vaccine | mRNA | Pfizer-BioNTech | 2nd | D2 | 0.96 | 1.24 (D7) | I | edema | MCD | mPSL 1 g/day 1–3 day, PSL 1 mg/kg/day | CR was achieved within D42 |
| 9 | Lim et al. [52] | 51/M | Korea | None | Vector | Janssen | 1st | D7 | Normal | 1.54 (D21) 1.96 (D33) | NA | edema | MCD | high-dose steroid | CR was achieved after 3 weeks of treatment |
| 10 | Hanna et al. [24] | 60/M | Canada | None | mRNA | Pfizer-BioNTech | 1st | D10 | 0.89 | 1.34 (D45) | II | edema, dyspnea | MCD with ATI | PSL 80 mg/day | R. Scr was 1.03 mg/dL at 11 weeks |
| 11 | Klomjit et al. [11] | 83/M | USA (Caucasian) | NA | mRNA | Moderna | 2nd | D28 | 1.19 | 2.19 | NA | AKI | MCD, ATN | high-dose steroid | R. Scr was 1.2 mg/dL during last follow-up |
| 12 | Da et al. [26] | 70/M | Singapore | edema after 1st vaccine | mRNA | Pfizer-BioNTech | 2nd | D1 | NA | 1.28 | I | edema | MN (anti-PLA2R-) | irbesartan, frusemide, warfarin | NR within D60 |
| 13 | Gueguen et al. [27] | 76/M | France | HT, UV-treated cutaneous mycosis fungoid | mRNA | Pfizer-BioNTech | 1st | D4 | 0.86 | 1.14 | NA | edema | MN (anti-PLA2R 1:800) | RASB | PR. |
| mRNA | Moderna | 2nd | D2 | 1.14 | 1.15 | NA | edema | MN | RTX 1 g 1–14 day | PR. | |||||
| 14 | Kudose et al. [28] | 50/F | USA (Caucasian) | HT, obesity, APS | mRNA | Moderna | 2nd | D2 | 1.3 | 1.7 | NA | gross hematuria, fever, body aches | IgAN (M1E0S1T1C1) | conservative | CR. hematuria resolved within D5 |
| 15 | Kudose et al. [28] | 19/M | USA (Caucasian) | microhematuria | mRNA | Moderna | 2nd | D2 | Normal | 1.2 | NA | gross hematuria | IgAN (M1E1S1T0C0) | conservative | CR. hematuria resolved within D2 |
| 16 | Tan et al. [29] | 41/F | Chinese | GDM | mRNA | Pfizer-BioNTech | 2nd | D1 | Normal | 1.73 (D2) | I | gross hematuria, headache, myalgia | IgAN with fibrocellular and fibrous crescents | pulse mPSL, PSL, CyC | NA |
| 17 | Hanna et al. [30] | 17/M | USA (Caucasian) | foamy urine | mRNA | Pfizer-BioNTech | 2nd | <D1 | Normal | 1.78 (D6) | I | gross hematuria | IgAN (M1E1S1T1C1) | pulse mPSL | R. Scr improved (duration not reported) |
| 18 | Anderegg et al. [31] | 39/M | Switzerland | HT | mRNA | Moderna | 2nd | immediately | NA | AKI | NA | flu-like symptoms, fever, macrohematuria | severe crescentic IgAN | high-dose glucocorticoids, CyC | R. Scr was normalized within several weeks |
| 19 | Klomjit et al. [11] | 38/M | USA (Caucasian) | NA | mRNA | Pfizer-BioNTech | 2nd | D14 | 1.3 | 1.6 | NA | gross hematuria | IgAN | conservative | NA |
| 20 | Klomjit et al. [11] | 44/M | USA (Caucasian) | NA | mRNA | Moderna | 1st | D14 | 1.1 | 2.5 | NA | AKI | IgAN, AIN | high-dose steroid | NR. Scr was 3.6 mg/dL during last follow-up |
| 21 | Klomjit et al. [11] | 66/M | USA (Caucasian) | NA | mRNA | Moderna | 1st | D14 | 1.1 | 1.5 | NA | gross hematuria | IgAN | PSL | R. Scr was 1.4 mg/dL during last follow-up |
| 22 | Klomjit et al. [11] | 62/M | USA (Caucasian) | NA | mRNA | Pfizer-BioNTech | 2nd | D42 | 1.0 | 2.2 | NA | AKI | IgAN | conservative | R. Scr was 2.0 mg/dL during last follow-up |
| 23 | Tan et al. [29] | 60/F | Malay | hyperlipidemia | mRNA | Pfizer-BioNTech | 2nd | D1 | Normal | 6.11 (D39) | III | gross hematuria | Anti-GBM nephritis | pulse mPSL, PSL, CyC, PLEX | NA |
| 24 | Sacke et al. [32] | older/F | USA | None | mRNA | Moderna | 2nd | D14 | Normal | 7.8 | NA | fever, gross hematuria, anorexia, nausea | Anti-GBM with mesangial IgA deposits | mPSL, CyC, PLEX | NR. remained HD dependent |
| 25 | Klomjit et al. [11] | 77/M | USA (Caucasian) | NA | mRNA | Pfizer-BioNTech | 1st | D7 | 1 | 1.8 | + | HT | Atypical anti-GBM nephritis | PSL, mycophenolate | NR. Scr was 2.9 mg/dL during last follow-up |
| 26 | Sekar et al. [35] | 52/M | USA (Caucasian) | HT | mRNA | Moderna | 2nd | D1 | 1.11 | 8.41 (D14) | NA | headache, weakness | PR3-ANCA vasculitis | RTX, CyC, PSL, HD | NR. remained HD dependent |
| 27 | Anderegg et al. [31] | 81/M | Switzerland | sustained flu-like symptoms after 1st vaccine | mRNA | Moderna | 2nd | <D1 | NA | AKI | NA | flu-like symptoms worsened | PR3-ANCA vasculitis | high-dose glucocorticoids, CyC, PLEX | R. renal function improved within D21 |
| 28 | Feghali et al. [38] | 58/M | USA (Caucasian) | None | mRNA | Moderna | 2nd | D4 | NA | 4.1 | NA | hematuria, proteinuria | PR3-ANCA vasculitis | mPSL 1 g 1–3 day, PSL 60 mg/kg/day, RTX, CyC, PLEX | R. Scr was 1.5 mg/dL after 10 weeks of diagnosis |
| 29 | Villa et al. [33] | 63/M | Spain | None | Vector | AstraZeneca | 1st | D2 | Normal | 2.9 (D7) | NA | flu-like syndrome, hemoptysis | MPO-ANCA vasculitis | high-dose glucocorticoids, CyC | NR. Scr was 2.08 mg/dL at D49 |
| 30 | Hakroush et al. [34] | 79/F | Italy (Caucasian) | HT, degenerative disc disease | mRNA | Pfizer-BioNTech | 2nd | D14 | 0.71 | 1.38 (D14) 6.57 (D24) | NA | weakness, upper thigh pain | MPO-ANCA vasculitis, ATI | mPSL 250 mg/day 1–3 day, PSL 1 mg/kg/day, CyC | R. Scr was normalized within D47 |
| 31 | Klomjit et al. [11] | 82/F | USA (Caucasian) | NA | mRNA | Moderna | 2nd | D28 | 0.8 | 2.5 | NA | AKI, hematuria, proteinuria | MPO-ANCA vasculitis | High-dose steroid, RTX | R. Scr was 2.3 mg/dL during last follow-up |
| 32 | Shakoor et al. [36] | 78/F | USA | T2DM, HT, atrial fibrillation | mRNA | Pfizer-BioNTech | 1st | <D7 | 0.77 | 1.31 (D16) | NA | nausea, vomiting, diarrhea | AKI | None | CR. improved spontaneously |
| mRNA | Pfizer-BioNTech | 2nd | D6 | Normal | 3.54 (D6) | NA | lethargy, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea | MPO-ANCA vasculitis | mPSL 1–3 day, PSL 1 mg/kg/day, RTX | R. Scr was 1.71 mg/dL at 1-month follow-up | |||||
| 33 | Dube et al. [37] | 29/F | USA | congenital diffuse cystic lung disease | mRNA | Pfizer-BioNTech | 2nd | D16 | 0.8 | 1.25 (D16) 1.91 (D49) | Normal | NA | MPO-ANCA vasculitis | mPSL 500 mg 1–3 day, PSL 1 mg/kg/day, RTX, CyC | R. Scr was 1.01 mg/dL at D133 |
| 34 | Gillion et al. [39] | 77/M | Belgium | None | Vector | AstraZeneca | 1st | D28 | 1.2 | 2.7 | NA | fever, night sweat | ANCA-negative granulomatous vasculitis | mPSL | R. Scr was normalized within D56 |
| 35 | Mira et al. [40] | 45/F | Portugal (Caucasian) | total thyroidectomy | mRNA | Pfizer-BioNTech | 2nd | D1 | 0.85 | 18.4 (D8) | Normal | anorexia, nausea, vomiting, urine output reduction | AIN, ATI | HD, mPSL 500 mg/day 1–3 day, PSL 1 mg/kg/day | R. Scr was 1.02 mg/dL at D37 |
| 36 | Unver et al. [25] | 67/F | Turkey | T2DM, MCD in PR | Inactivated | Sinovac Life Science | 2nd | D10 | 0.8 | 4.2 (D26) | III | edema, headache | AIN, ATI | mPSL 500 mg/day 1–3 day, PSL 1 mg/kg/day, cyclosporine A | PR. Scr was 1.12 mg/dL at D60, UTP was 3 g/day at D115 |
| 37 | Lim et al. [52] | 44/M | Korea | T2DM, chronic hepatitis B infection, hyperlipidemia | mRNA | Moderna | 1st | D1 | 0.91 | 4.13 (D7) 4.94 (D21) | NA | gastrointestinal discomfort, anorexia | ATN | high-dose steroid | PR. Scr was 1.89 mg/dL, UPCR was 0.3 g/g at D42 |
| 38 | Lim et al. [52] | 77/F | Korea | T2DM, Chronic hepatitis B, hepatocellular carcinoma | mRNA | Pfizer-BioNTech | 2nd | D1 | 0.98 | 10.67 (D7) 11.15 (D14) | NA | severe nausea and vomiting | ATN with myoglobin tubular casts | HD | PR. Scr was 2.12 mg/dL, within 4 months |
| 39 | Missoum et al. [50] | 58/M | Algeria | HT | Inactivated | Sinovac Life Science | 1st | D9 | Normal | 8.9 | NA | fever, arthralgias, purpura | Leukocytoclastic vasculitis ATN | HD, prednisone | R. Scr was 2.8 mg/dL at D90 |
| 40 | Al Rawahi et al. [51] | 64/M | Sultanate of Oman | HT, hyperlipidemia | Vector | AstraZeneca | 1st | D7 | NA | 1.18 (D7) | I | fever, lethargy, abdominal pain | aTTP, VITT | argatroban, fondaparinux, hydrocortisone, immunoglobulin | R. renal function improved at D15 |
| 41 | Yocum et al. [44] | 62/F | USA | hyperlipidemia, GERD, hypothyroidism, HT | Vector | Janssen | 1st | D37 | NA | 2.19 (D37) 6 (D38) | III | altered mental status | aTTP, VITT, | PLEX, HD, mPSL, packed RBCs | NA |
| 42 | Osmanodja et al. [46] | 25/M | Germany | None | mRNA | Moderna | 1st | D2 | NA | 1.5 (D13) | NA | fever, headache, petechiae | aTTP | PLEX, PSL 250 mg 1–3 day, caplacizumab | R. Scr was 1 mg/dL at D27 |
| 43 | Alislambouli et al. [48] | 61/M | Korean-American | NA | mRNA | Pfizer-BioNTech | 1st | D5 | NA | 1.57 (D5) | NA | fever, confusion, headache, emesis, ecchymosis | aTTP | PLEX, mPSL 1 g 1–3 day, RTX | R. rapid and excellent response |
| 44 | Yoshida et al. [49] | 57/M | Japan | None | mRNA | Pfizer-BioNTech | 1st | D7 | NA | 1.57 (D14) | NA | fatigue, loss of appetite, jaundice | aTTP | PLEX, PSL, RTX | R. in good condition at D48 |
| 45 | Ruhe et al. [45] | 84/F | Germany | NA | mRNA | Pfizer-BioNTech | 1st | D16 | NA | 1.95 (D16) | III | partial hemiplegia, petechiae | aTTP | PLEX, RTX, corticosteroid | R. Scr was 0.6 mg/dL at D34 |
| 46 | Chamarti et al. [47] | 80/M | Hispanic | HT, T2DM, hyperlipidemia, gout, IDA | mRNA | Pfizer-BioNTech | 2nd | D12 | NA | 2.4 (D14) | I | generalized weakness, malaise | aTTP | PLEX, packed RBCs, platelets, prednisone | R. Scr was 1 mg/dL at D30 |
| 47 | Lim et al. [52] | 69/F | Korea | T2DM | Vector | AstraZeneca | 1st | D2 | 0.8 | 3.69 (D14) | general weakness, gastrointestinal discomfort | aTTP | None | CR Scr was 0.65 mg/dL, UPCR was 1.0 g/g at D56 | |
| Relapsed cases | |||||||||||||||
| 48 | Mancianti et al. [41] | 39/M | Italy (Caucasian) | MCD in remission for 37 years | mRNA | Pfizer-BioNTech | 1st | D3 | 0.9 | 1.8 (D8) | NA | edema | MCD | PSL 1 mg/kg/day | CR |
| 49 | Klomjit et al. [11] | 67/F | USA (Caucasian) | MCD | mRNA | Moderna | 2nd | D21 | 1 | 1.6 | NA | edema | MCD | high-dose steroid, RTX | R. Scr was 1.5 mg/dL, UTP was 0.07 g/day during last follow-up |
| 50 | Aydin et al. [42] | 66/F | Turkey | hyperlipidemia, DM, HT, MN in CR for 8 years | Inactivated | Sinovac Life Science | 1st | D14 | Normal | 2.78 (D14) | NA | edema | MN (anti-PLA2R 1:120.53) | NA | NA |
| 51 | Klomjit et al. [11] | 39/M | USA (Caucasian) | MN | mRNA | Pfizer-BioNTech | 2nd | D7 | 0.91 | 1.13 | NA | edema | MN (anti-PLA2R+) | TAC | R. Scr was 1.1 mg/dL, UTP was 5.7 g/day during last follow-up |
| 52 | Hanna et al. [30] | 13/M | USA (Caucasian) | IgAN, T1DM | mRNA | Pfizer-BioNTech | 2nd | <D1 | 0.54 | 1.31 (D2) | NA | gross hematuria, vomiting | IgAN (M0E0S0T0C0) | conservative | CR. hematuria and Scr resolved within D6 |
| 53 | Perrin et al. [43] | 41/F | France | IgAN, KT | mRNA | Pfizer-BioNTech | 1st | D2 | NA | Scr transiently increased | NA | gross hematuria | IgAN | conservative | CR. spontaneously resolved |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Rao, M.; Xu, G. New-Onset Acute Kidney Disease Post COVID-19 Vaccination. Vaccines 2022, 10, 742. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10050742
Li Y, Rao M, Xu G. New-Onset Acute Kidney Disease Post COVID-19 Vaccination. Vaccines. 2022; 10(5):742. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10050742
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yebei, Meiying Rao, and Gaosi Xu. 2022. "New-Onset Acute Kidney Disease Post COVID-19 Vaccination" Vaccines 10, no. 5: 742. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10050742
APA StyleLi, Y., Rao, M., & Xu, G. (2022). New-Onset Acute Kidney Disease Post COVID-19 Vaccination. Vaccines, 10(5), 742. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10050742