Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease Challenges and Its Antiviral Therapeutics
1. Introduction
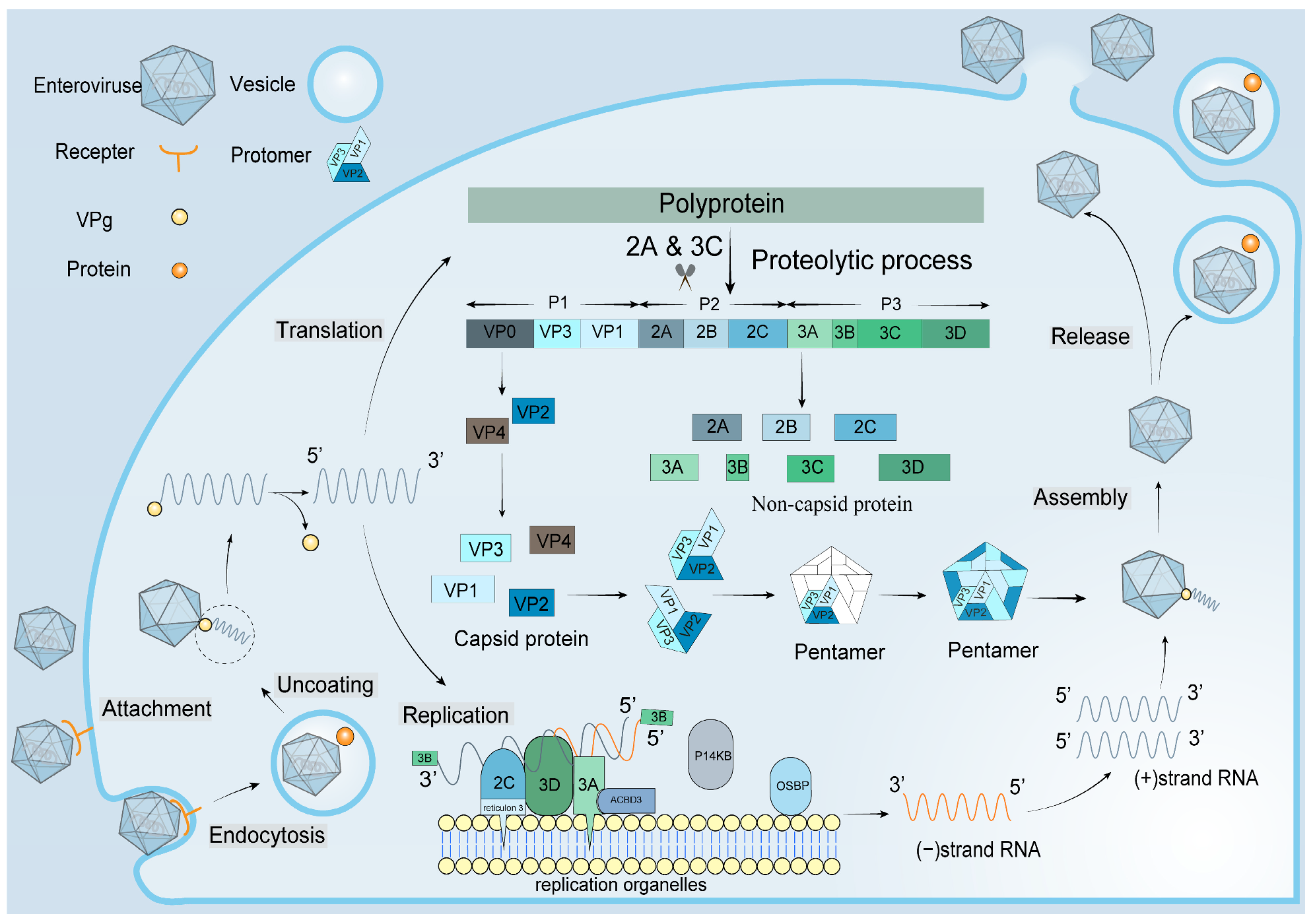
2. Recent Development in the Design of Antiviral Agents
2.1. Antiviral Agents Targeting the Five-Fold Axis
2.2. Antiviral Agents Targeting the Hydrophobic Pocket
2.3. Antiviral Agents Targeting Non-Structural Proteins of EVs
2.4. Antiviral Agents Targeting Internal Ribosome Entry Site (IRES)
3. Prospects and Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xie, Y.; Hu, Q.; Jiang, W.; Ji, W.; Chen, S.; Jin, Y.; Duan, G. Laboratory Indicators for Identifying Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease Severity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Vaccines 2022, 10, 1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Hu, Y.; Zheng, M. Enterovirus A71 antivirals: Past, present, and future. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2022, 12, 1542–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhu, S.; Guo, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, D.; Yan, D.; Tan, X.; Tang, L.; Zhu, H.; Yang, Z.; et al. Retrospective seroepidemiology indicated that human enterovirus 71 and coxsackievirus A16 circulated wildly in central and southern China before large-scale outbreaks from 2008. Virol. J. 2010, 7, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shah, J.; Sijun, L.; Hui, Z.; Zeb, F.; Haq, I.U.; Ullah, A. Neurological Complications of Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease In Children: A Review. J. Ayub Med. Coll. Abbottabad 2020, 32, 562–569. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aswathyraj, S.; Arunkumar, G.; Alidjinou, E.K.; Hober, D. Hand, foot and mouth disease (HFMD): Emerging epidemiology and the need for a vaccine strategy. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2016, 205, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Yu, J.; Hao, F.; He, H.; Shi, X.; Hu, J.; Wang, L.; Du, C.; Zhang, X.; Sun, Y.; et al. Discovery of Potent EV71 Capsid Inhibitors for Treatment of HFMD. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 8, 841–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.L.; Shih, S.R.; Tolbert, B.S.; Brewer, G. Enterovirus A71 Vaccines. Vaccines 2021, 9, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, S.; Abd-Aziz, N.; Saw, W.T.; Liew, S.Y.; Yusoff, K.; Shafee, N. Recombinant Enterovirus 71 Viral Protein 1 Fused to a Truncated Newcastle Disease Virus NP (NPt) Carrier Protein. Vaccines 2020, 8, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, K.; Koike, S. Cellular receptors for enterovirus A71. J. Biomed. Sci. 2020, 27, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.W.; Chan, Y.F.; Sim, K.M.; Tan, E.L.; Poh, C.L. Inhibition of enterovirus 71 (EV-71) infections by a novel antiviral peptide derived from EV-71 capsid protein VP1. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, C.W.; Sam, I.C.; Lee, V.S.; Wong, H.V.; Chan, Y.F. VP1 residues around the five-fold axis of enterovirus A71 mediate heparan sulfate interaction. Virology 2017, 501, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.W.; Poh, C.L.; Sam, I.C.; Chan, Y.F. Enterovirus 71 uses cell surface heparan sulfate glycosaminoglycan as an attachment receptor. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 611–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lalani, S.; Tan, S.H.; Tan, K.O.; Lim, H.X.; Ong, K.C.; Wong, K.T.; Poh, C.L. Molecular mechanism of L-SP40 peptide and in vivo efficacy against EV-A71 in neonatal mice. Life Sci. 2021, 287, 120097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, Y.; McLaughlin, N.P.; Pan, J.; Goldstein, S.; Hafenstein, S.; Shimizu, H.; Winkler, J.D.; Bergelson, J.M. The Suramin Derivative NF449 Interacts with the 5-fold Vertex of the Enterovirus A71 Capsid to Prevent Virus Attachment to PSGL-1 and Heparan Sulfate. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1005184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Lee, H.; Thibaut, H.J.; Lanko, K.; Rivero-Buceta, E.; Bator, C.; Martinez-Gualda, B.; Dallmeier, K.; Delang, L.; Leyssen, P.; et al. Viral engagement with host receptors blocked by a novel class of tryptophan dendrimers that targets the 5-fold-axis of the enterovirus-A71 capsid. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1007760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hsieh, C.F.; Jheng, J.R.; Lin, G.H.; Chen, Y.L.; Ho, J.Y.; Liu, C.J.; Hsu, K.Y.; Chen, Y.S.; Chan, Y.F.; Yu, H.M.; et al. Rosmarinic acid exhibits broad anti-enterovirus A71 activity by inhibiting the interaction between the five-fold axis of capsid VP1 and cognate sulfated receptors. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 1194–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Zeng, S.; Ji, X.; Meng, X.; Lei, N.; Yang, H.; Mu, X. Type I Interferon-Induced TMEM106A Blocks Attachment of EV-A71 Virus by Interacting With the Membrane Protein SCARB2. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 817835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, T.; Jia, Q.; Wong, S.M.; Chua, K.B. In Vitro and In Vivo Inhibition of the Infectivity of Human Enterovirus 71 by a Sulfonated Food Azo Dye, Brilliant Black BN. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e00061-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hsieh, C.F.; Chen, Y.L.; Lin, G.H.; Chan, Y.F.; Hsieh, P.W.; Horng, J.T. 3,4-Dicaffeoylquinic Acid from the Medicinal Plant Ilex kaushue Disrupts the Interaction Between the Five-Fold Axis of Enterovirus A-71 and the Heparan Sulfate Receptor. J. Virol. 2022, 96, e0054221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossmann, M.G.; He, Y.; Kuhn, R.J. Picornavirus-receptor interactions. Trends. Microbiol. 2002, 10, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plevka, P.; Perera, R.; Yap, M.L.; Cardosa, J.; Kuhn, R.J.; Rossmann, M.G. Structure of human enterovirus 71 in complex with a capsid-binding inhibitor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 5463–5467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Muckelbauer, J.K.; Kremer, M.; Minor, I.; Diana, G.; Dutko, F.J.; Groarke, J.; Pevear, D.C.; Rossmann, M.G. The structure of coxsackievirus B3 at 3.5 A resolution. Structure 1995, 3, 653–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rossmann, M.G. Viral cell recognition and entry. Protein Sci. 1994, 3, 1712–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heim, A.; Pfetzing, U.; Muller, G.; Grumbach, I.M. Antiviral activity of WIN 54954 in coxsackievirus B2 carrier state infected human myocardial fibroblasts. Antiviral Res. 1998, 37, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, S.R.; Tsai, M.C.; Tseng, S.N.; Won, K.F.; Shia, K.S.; Li, W.T.; Chern, J.H.; Chen, G.W.; Lee, C.C.; Lee, Y.C.; et al. Mutation in enterovirus 71 capsid protein VP1 confers resistance to the inhibitory effects of pyridyl imidazolidinone. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 3523–3529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pevear, D.C.; Tull, T.M.; Seipel, M.E.; Groarke, J.M. Activity of pleconaril against enteroviruses. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1999, 43, 2109–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tijsma, A.; Franco, D.; Tucker, S.; Hilgenfeld, R.; Froeyen, M.; Leyssen, P.; Neyts, J. The capsid binder Vapendavir and the novel protease inhibitor SG85 inhibit enterovirus 71 replication. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 6990–6992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, C.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Musharrafieh, R.; Wang, J. A Novel Capsid Binding Inhibitor Displays Potent Antiviral Activity against Enterovirus D68. ACS Infect. Dis. 2019, 5, 1952–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Colibus, L.; Wang, X.; Spyrou, J.A.B.; Kelly, J.; Ren, J.; Grimes, J.; Puerstinger, G.; Stonehouse, N.; Walter, T.S.; Hu, Z.; et al. More-powerful virus inhibitors from structure-based analysis of HEV71 capsid-binding molecules. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2014, 21, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ho, J.Y.; Chern, J.H.; Hsieh, C.F.; Liu, S.T.; Liu, C.J.; Wang, Y.S.; Kuo, T.W.; Hsu, S.J.; Yeh, T.K.; Shih, S.R.; et al. In vitro and in vivo studies of a potent capsid-binding inhibitor of enterovirus 71. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2016, 71, 1922–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Pei, X.; Wang, C.; Niu, Y.; Xu, P.; Peng, Y. Substituted 3-benzylcoumarins 13 and 14 suppress enterovirus A71 replication by impairing viral 2A(pro) dependent IRES-driven translation. Antiviral. Res. 2018, 160, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Zhu, M.; Xiong, Q.; Wang, Y.; Xu, C.; Sun, J.; Wang, C.; Zhang, H.; Xu, P.; Peng, Y. Regulation of enterovirus 2A protease-associated viral IRES activities by the cell’s ERK signaling cascade: Implicating ERK as an efficiently antiviral target. Antiviral Res. 2017, 143, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falah, N.; Montserret, R.; Lelogeais, V.; Schuffenecker, I.; Lina, B.; Cortay, J.C.; Violot, S. Blocking human enterovirus 71 replication by targeting viral 2A protease. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2012, 67, 2865–2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.Y.; Huang, A.C.; Hour, M.J.; Huang, S.H.; Kung, S.H.; Chen, C.H.; Chen, I.C.; Chang, Y.S.; Lien, J.C.; Lin, C.W. Antiviral Potential of a Novel Compound CW-33 against Enterovirus A71 via Inhibition of Viral 2A Protease. Viruses 2015, 7, 3155–3171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Duan, H.; Liu, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Zhu, M.; Guo, J.; Zhao, Z.; Meng, L.; Peng, Y. The multi-targeted kinase inhibitor sorafenib inhibits enterovirus 71 replication by regulating IRES-dependent translation of viral proteins. Antiviral Res. 2014, 106, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Shen, L.; Wu, J.; Zou, X.; Gu, J.; Chen, J.; Mao, L. Enterovirus A71 Proteins: Structure and Function. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ulferts, R.; de Boer, S.M.; van der Linden, L.; Bauer, L.; Lyoo, H.R.; Mate, M.J.; Lichiere, J.; Canard, B.; Lelieveld, D.; Omta, W.; et al. Screening of a Library of FDA-Approved Drugs Identifies Several Enterovirus Replication Inhibitors That Target Viral Protein 2C. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 2627–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, C.; Yang, R.; Bai, P.; Zhang, X.Y.; Kong, J.; Yin, L.; Qiu, Y.; Zhou, X. Antiviral Peptides Targeting the Helicase Activity of Enterovirus Nonstructural Protein 2C. J. Virol. 2021, 95, e02324-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J. Pharmacological Characterization of the Mechanism of Action of R523062, a Promising Antiviral for Enterovirus D68. ACS Infect. Dis. 2020, 6, 2260–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, J.; Kye, S.; Quinn, K.K.; Cooper, P.; Damoiseaux, R.; Krogstad, P. Discovery of Structurally Diverse Small-Molecule Compounds with Broad Antiviral Activity against Enteroviruses. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 60, 1615–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, Q.; Xu, Z.; Jin, M.; Shu, T.; Chen, Y.; Feng, L.; Zhang, Q.; Lan, K.; Wu, S.; Zhou, H.B. Identification of dibucaine derivatives as novel potent enterovirus 2C helicase inhibitors: In vitro, in vivo, and combination therapy study. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 202, 112310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, F.D.; Monto, A.S.; DeLong, D.C.; Exelby, A.; Bryan, E.R.; Srivastava, S. Controlled trial of enviroxime against natural rhinovirus infections in a community. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1985, 27, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arita, M.; Kojima, H.; Nagano, T.; Okabe, T.; Wakita, T.; Shimizu, H. Phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase III beta is a target of enviroxime-like compounds for antipoliovirus activity. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 2364–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Palma, A.M.; Thibaut, H.J.; van der Linden, L.; Lanke, K.; Heggermont, W.; Ireland, S.; Andrews, R.; Arimilli, M.; Al-Tel, T.H.; De Clercq, E.; et al. Mutations in the nonstructural protein 3A confer resistance to the novel enterovirus replication inhibitor TTP-8307. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 1850–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, Q.; Yuan, S.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; He, G.; Zhang, S.; Altmeyer, R.; Zou, G. Discovery of itraconazole with broad-spectrum in vitro antienterovirus activity that targets nonstructural protein 3A. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 2654–2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, M.; Xu, B.; Ma, Y.; Shang, L.; Ye, S.; Wang, Y. Reversible covalent inhibitors suppress enterovirus 71 infection by targeting the 3C protease. Antiviral Res. 2021, 192, 105102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cao, L.; Zhai, Y.; Yin, Z.; Sun, Y.; Shang, L. Structure of the Enterovirus 71 3C Protease in Complex with NK-1.8k and Indications for the Development of Antienterovirus Protease Inhibitor. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e00298-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matthews, D.A.; Dragovich, P.S.; Webber, S.E.; Fuhrman, S.A.; Patick, A.K.; Zalman, L.S.; Hendrickson, T.F.; Love, R.A.; Prins, T.J.; Marakovits, J.T.; et al. Structure-assisted design of mechanism-based irreversible inhibitors of human rhinovirus 3C protease with potent antiviral activity against multiple rhinovirus serotypes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 11000–11007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yao, C.; Xi, C.; Hu, K.; Gao, W.; Cai, X.; Qin, J.; Lv, S.; Du, C.; Wei, Y. Inhibition of enterovirus 71 replication and viral 3C protease by quercetin. Virol. J. 2018, 15, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, B.; Liu, M.; Ma, S.; Ma, Y.; Liu, S.; Shang, L.; Zhu, C.; Ye, S.; Wang, Y. 4-Iminooxazolidin-2-One as a Bioisostere of Cyanohydrin Suppresses EV71 Proliferation by Targeting 3C(pro). Microbiol. Spectr. 2021, 9, e0102521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cao, L.; Zhai, Y.; Ma, J.; Nie, Q.; Li, T.; Yin, Z.; Sun, Y.; Shang, L. Inhibition of enterovirus 71 replication by an alpha-hydroxy-nitrile derivative NK-1.9k. Antiviral Res. 2017, 141, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, L.; Wang, Y.; Qing, J.; Shu, B.; Cao, L.; Lou, Z.; Gong, P.; Sun, Y.; Yin, Z. An adenosine nucleoside analogue NITD008 inhibits EV71 proliferation. Antiviral Res. 2014, 112, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Yang, J.; Zheng, B.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Huan, C.; Wang, S.; Chang, J.; Zhang, W. The Pyrimidine Analog FNC Potently Inhibits the Replication of Multiple Enteroviruses. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e00204-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, T.C.; Chang, H.Y.; Lin, P.F.; Chern, J.H.; Hsu, J.T.; Chang, C.Y.; Shih, S.R. Novel antiviral agent DTriP-22 targets RNA-dependent RNA polymerase of enterovirus 71. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 2740–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Velu, A.B.; Chen, G.W.; Hsieh, P.T.; Horng, J.T.; Hsu, J.T.; Hsieh, H.P.; Chen, T.C.; Weng, K.F.; Shih, S.R. BPR-3P0128 inhibits RNA-dependent RNA polymerase elongation and VPg uridylylation activities of Enterovirus 71. Antiviral Res. 2014, 112, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, S.R.; Sarnow, P. Enterovirus 71 contains a type I IRES element that functions when eukaryotic initiation factor eIF4G is cleaved. Virology 2003, 315, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, J.; Stein, D.A.; Lim, T.; Qiu, D.; Coughlin, S.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Blouch, R.; Moulton, H.M.; Iversen, P.L.; et al. Inhibition of coxsackievirus B3 in cell cultures and in mice by peptide-conjugated morpholino oligomers targeting the internal ribosome entry site. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 11510–11519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsai, F.J.; Lin, C.W.; Lai, C.C.; Lan, Y.C.; Lai, C.H.; Hung, C.H.; Hsueh, K.C.; Lin, T.H.; Chang, H.C.; Wan, L.; et al. Kaempferol inhibits enterovirus 71 replication and internal ribosome entry site (IRES) activity through FUBP and HNRP proteins. Food Chem. 2011, 128, 312–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Qiu, M.; Chen, D.; Zheng, N.; Jin, Y.; Wu, Z. Apigenin inhibits enterovirus 71 replication through suppressing viral IRES activity and modulating cellular JNK pathway. Antiviral Res. 2014, 109, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, H.Y.; Lu, W.W.; Wu, K.Y.; Lin, C.W.; Kung, S.H. Idarubicin is a broad-spectrum enterovirus replication inhibitor that selectively targets the virus internal ribosomal entry site. J. Gen. Virol. 2016, 97, 1122–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, J.Y.; Li, M.L.; Brewer, G. mRNA decay factor AUF1 binds the internal ribosomal entry site of enterovirus 71 and inhibits virus replication. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Davila-Calderon, J.; Patwardhan, N.N.; Chiu, L.Y.; Sugarman, A.; Cai, Z.; Penutmutchu, S.R.; Li, M.L.; Brewer, G.; Hargrove, A.E.; Tolbert, B.S. IRES-targeting small molecule inhibits enterovirus 71 replication via allosteric stabilization of a ternary complex. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, Z.Q.; Ng, Q.Y.; Ng, J.W.Q.; Mahendran, V.; Alonso, S. Recent progress and challenges in drug development to fight hand, foot and mouth disease. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2020, 15, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.R.; Chang, C.M.; Yeh, Y.C.; Huang, C.F.; Lin, F.M.; Huang, J.T.; Hsieh, C.C.; Wang, J.R.; Liu, H.S. Honeysuckle Aqueous Extracts Induced let-7a Suppress EV71 Replication and Pathogenesis In Vitro and In Vivo and Is Predicted to Inhibit SARS-CoV-2. Viruses 2021, 13, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Ji, W.; Chen, S.; Duan, G.; Jin, Y. Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease Challenges and Its Antiviral Therapeutics. Vaccines 2023, 11, 571. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11030571
Li Z, Ji W, Chen S, Duan G, Jin Y. Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease Challenges and Its Antiviral Therapeutics. Vaccines. 2023; 11(3):571. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11030571
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zijie, Wangquan Ji, Shuaiyin Chen, Guangcai Duan, and Yuefei Jin. 2023. "Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease Challenges and Its Antiviral Therapeutics" Vaccines 11, no. 3: 571. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11030571
APA StyleLi, Z., Ji, W., Chen, S., Duan, G., & Jin, Y. (2023). Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease Challenges and Its Antiviral Therapeutics. Vaccines, 11(3), 571. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11030571







