Anti-Idiotypic mRNA Vaccine to Treat Autoimmune Disorders
Abstract
:1. Introduction
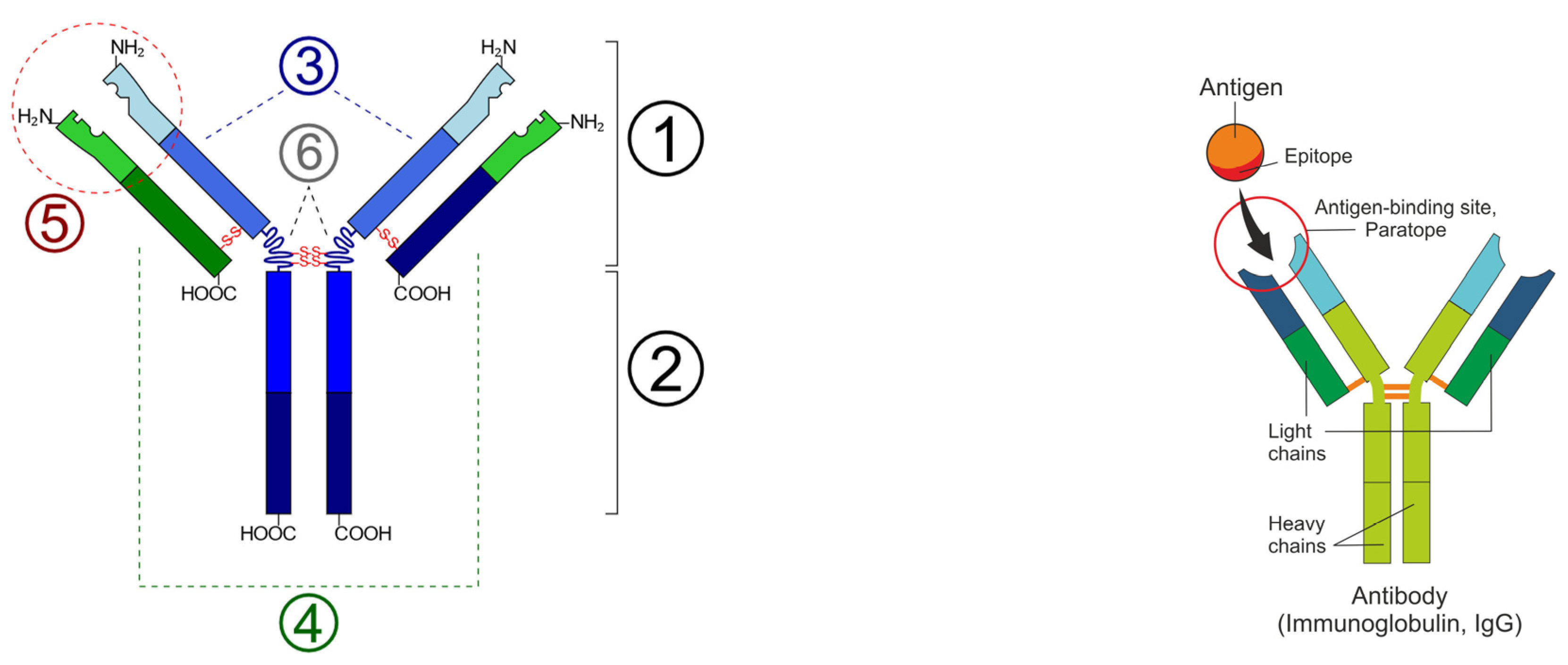
2. Anti-Idiotypic Antibodies
3. Nucleoside Vaccines
3.1. DNA Vaccine
3.2. mRNA Vaccines
3.3. mRNA Design
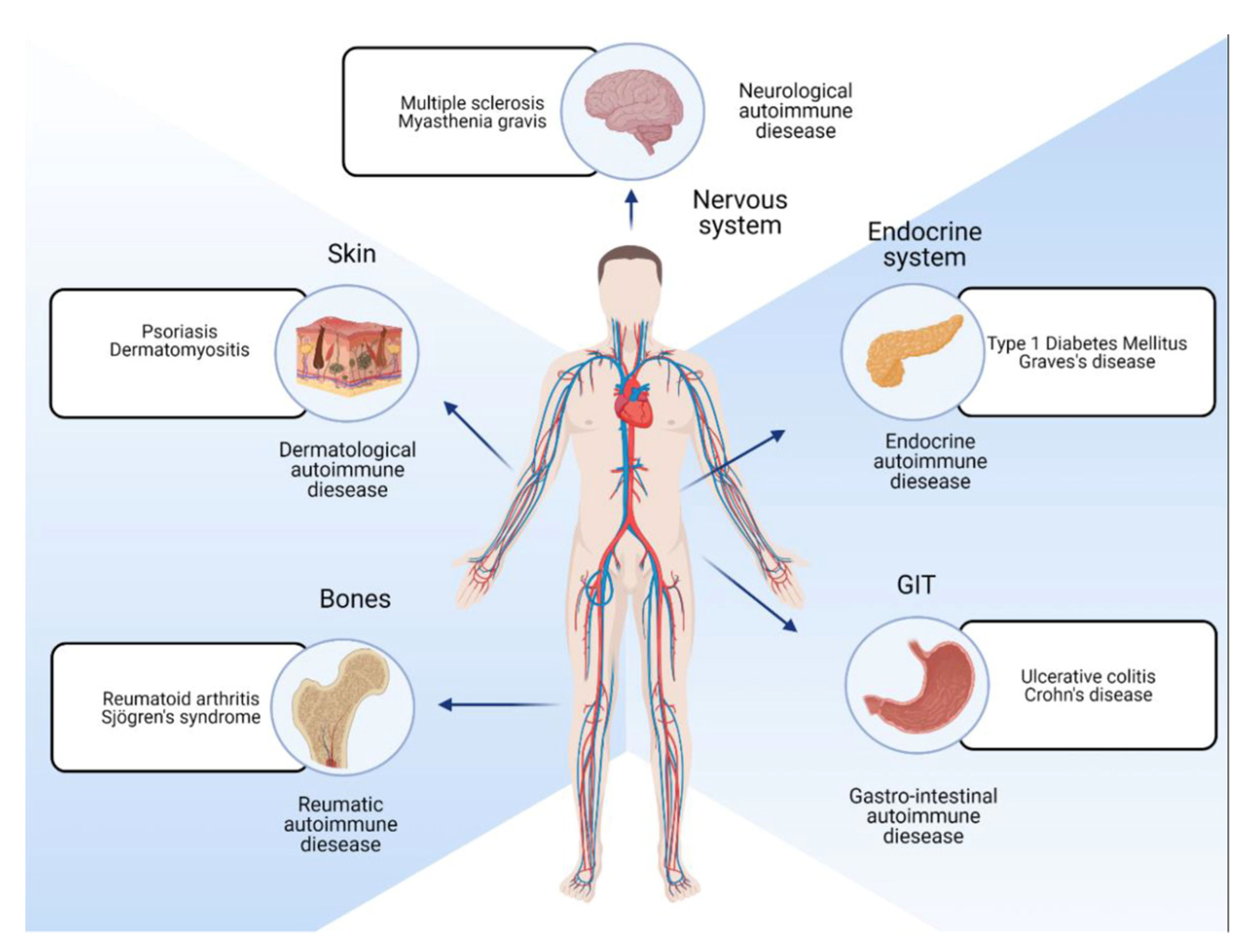
4. Disease Targets
mRNA Delivery
5. Regulatory
6. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cawein, A.; Emini, E.; Watson, M.; Dailey, J.; Donnelly, J.; Tresnan, D.; Evans, T.; Plotkin, S.; Gruber, W. Human capital gaps in vaccine development: An issue for global vaccine development and global health. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2017, 1395, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilleman, M.R.; Buynak, E.B.; Roehm, R.R.; Tytell, A.A.; Bertland, A.U.; Lampson, G.P. Purified and inactivated human hepatitis B vaccine: Progress report. Am. J. Med. Sci. 1975, 270, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadoff, J.; Struyf, F.; Douoguih, M. A plain language summary of how well the single-dose Janssen vaccine works and how safe it is. Future Virol. 2021, 16, 725–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voysey, M.; Clemens, S.A.C.; Madhi, S.A.; Weckx, L.Y.; Folegatti, P.M.; Aley, P.K.; Angus, B.; Baillie, V.L.; Barnabas, S.L.; Bhorat, Q.E.; et al. Safety and efficacy of the ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine (AZD1222) against SARS-CoV-2: An interim analysis of four randomised controlled trials in Brazil, South Africa, and the UK. Lancet 2021, 397, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardi, N.; Hogan, M.J.; Porter, F.W.; Weissman, D. mRNA vaccines—A new era in vaccinology. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2018, 17, 261–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polack, F.P.; Thomas, S.J.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Perez, J.L.; Perez Marc, G.; Moreira, E.D.; Zerbini, C.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2603–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, T. Personalized Anti-Cancer Vaccine Combining mRNA and Immunotherapy Tested in Melanoma Trial. Nature, 16 August 2023. Available online: https://www.nature.com/articles/d41591-023-00072-0 (accessed on 1 November 2023).
- Institute, G.A. Autoimmune Disease List. Available online: https://www.autoimmuneinstitute.org/resources/autoimmune-disease-list/2023 (accessed on 1 November 2023).
- Weissman, K.K.a.D. Noble Lecture Physiology and Medicine. Available online: https://youtu.be/gPdUnYjvWxo2023 (accessed on 1 November 2023).
- Radbruch, A.; Muehlinghaus, G.; Luger, E.O.; Inamine, A.; Smith, K.G.; Dörner, T.; Hiepe, F. Competence and competition: The challenge of becoming a long-lived plasma cell. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 6, 741–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGonagle, D.; McDermott, M.F. A proposed classification of the immunological diseases. PLoS Med. 2006, 3, e297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firestein, G.S. Evolving concepts of rheumatoid arthritis. Nature 2003, 423, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, A.; Diamond, B. Autoimmune diseases. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 345, 340–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, Y.; Morita, T.; Kumanogoh, A. Efficacy and risk of mRNA vaccination in patients with autoimmune inflammatory rheumatic diseases. Inflamm. Regen. 2023, 43, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UniProt or SwissProt-Reviewed Human Autoantibodies. Available online: https://www.uniprot.org/uniprotkb?query=autoantibodies&facets=model_organism%3A9606%2Creviewed%3Atrue2023 (accessed on 1 November 2023).
- Cooper, G.S. Unraveling the etiology of systemic autoimmune diseases: Peering into the preclinical phase of disease. J. Rheumatol. 2009, 36, 1853–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mills, K.H. TLR-dependent T cell activation in autoimmunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 807–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutterotti, A.; Hayward-Koennecke, H.; Sospedra, M.; Martin, R. Antigen-Specific Immune Tolerance in Multiple Sclerosis-Promising Approaches and How to Bring Them to Patients. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 640935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina, V.; Shoenfeld, Y. Infection, vaccines and other environmental triggers of autoimmunity. Autoimmunity 2005, 38, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, G.S.; Miller, F.W.; Pandey, J.P. The role of genetic factors in autoimmune disease: Implications for environmental research. Environ. Health Perspect. 1999, 107 (Suppl. S5), 693–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehman, H.K. Autoimmunity and Immune Dysregulation in Primary Immune Deficiency Disorders. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2015, 15, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulton, V.R. Sex Hormones in Acquired Immunity and Autoimmune Disease. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaheen, W.A.; Quraishi, M.N.; Iqbal, T.H. Gut microbiome and autoimmune disorders. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2022, 209, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, J.C.; Szczepanski, L.; Szechinski, J.; Filipowicz-Sosnowska, A.; Emery, P.; Close, D.R.; Stevens, R.M.; Shaw, T. Efficacy of B-cell-targeted therapy with rituximab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 2572–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardemann, H.; Hammersen, J.; Nussenzweig, M.C. Human Autoantibody Silencing by Immunoglobulin Light Chains. J. Exp. Med. 2004, 200, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, J.; Perkovic, V.; Foote, C.V.; Craig, M.E.; Craig, J.C.; Strippoli, G.F. Antihypertensive agents for preventing diabetic kidney disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012, 12, Cd004136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakano, M.; Iida, K.; Nyunoya, H.; Iida, H. Determination of structural regions important for Ca2+ uptake activity in Arabidopsis MCA1 and MCA2 expressed in yeast. Plant Cell Physiol. 2011, 52, 1915–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, J. Autoimmune Disorders. Available online: https://www.msdmanuals.com/professional/immunology-allergic-disorders/allergic,-autoimmune,-and-other-hypersensitivity-disorders/autoimmune-disorders2022 (accessed on 1 November 2023).
- He, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Huang, H.; Liu, J.; Kang, Z.; Lee, S.T. Photoluminescent Fe3O4/carbon nanocomposite with magnetic property. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2011, 356, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pertea, M.; Salzberg, S.L. Between a chicken and a grape: Estimating the number of human genes. Genome Biol. 2010, 11, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Divoux, A.; Xie, H.; Li, J.L.; Karastergiou, K.; Perera, R.J.; Chang, R.J.; Fried, S.K.; Smith, S.R. MicroRNA-196 Regulates HOX Gene Expression in Human Gluteal Adipose Tissue. Obesity 2017, 25, 1375–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandelman, J.S.; Byrne, M.T.; Mistry, A.M.; Polikowsky, H.G.; Diggins, K.E.; Chen, H.; Lee, S.J.; Arora, M.; Cutler, C.; Flowers, M.; et al. Machine learning reveals chronic graft-versus-host disease phenotypes and stratifies survival after stem cell transplant for hematologic malignancies. Haematologica 2019, 104, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghobadinezhad, F.; Ebrahimi, N.; Mozaffari, F.; Moradi, N.; Beiranvand, S.; Pournazari, M.; Rezaei-Tazangi, F.; Khorram, R.; Afshinpour, M.; Robino, R.A.; et al. The emerging role of regulatory cell-based therapy in autoimmune disease. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1075813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prajeeth, C.K.; Dittrich-Breiholz, O.; Talbot, S.R.; Robert, P.A.; Huehn, J.; Stangel, M. IFN-γ Producing Th1 Cells Induce Different Transcriptional Profiles in Microglia and Astrocytes. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2018, 12, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satokari, R. High Intake of Sugar and the Balance between Pro- and Anti-Inflammatory Gut Bacteria. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremain, A.C.; Wallace, R.P.; Lorentz, K.M.; Thornley, T.B.; Antane, J.T.; Raczy, M.R.; Reda, J.W.; Alpar, A.T.; Slezak, A.J.; Watkins, E.A.; et al. Synthetically glycosylated antigens for the antigen-specific suppression of established immune responses. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2023, 7, 1142–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rico, M.J.; Hall, R.P. Idiotypes, anti-idiotypes, and autoimmunity. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1988, 19, 579–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoenfeld, Y. The idiotypic network in autoimmunity: Antibodies that bind antibodies that bind antibodies. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, 17–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, S.Y.; Chia, Y.C.; Yee, H.R.; Fang Cheng, A.Y.; Anjum, C.E.; Kenisi, Y.; Chan, M.K.; Wong, M.B. Immunomodulatory potential of anti-idiotypic antibodies for the treatment of autoimmune diseases. Future Sci. OA 2020, 7, Fso648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hampe, C.S. Protective role of anti-idiotypic antibodies in autoimmunity--lessons for type 1 diabetes. Autoimmunity 2012, 45, 320–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, A.; Ojogho, O.; Franco, E.; Baron, P.; Iwaki, Y.; Escher, A. Pro-apoptotic DNA vaccination ameliorates new onset of autoimmune diabetes in NOD mice and induces foxp3+ regulatory T cells in vitro. Vaccine 2006, 24, 5036–5046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahin, U.; Karikó, K.; Türeci, Ö. mRNA-based therapeutics--developing a new class of drugs. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2014, 13, 759–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houseley, J.; Tollervey, D. The many pathways of RNA degradation. Cell 2009, 136, 763–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, A.; Medzhitov, R. Control of adaptive immunity by the innate immune system. Nat. Immunol. 2015, 16, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, T.R.F.; Patel, A.; Ramos, S.; Elwood, D.; Zhu, X.; Yan, J.; Gary, E.N.; Walker, S.N.; Schultheis, K.; Purwar, M.; et al. Immunogenicity of a DNA vaccine candidate for COVID-19. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottlieb, P.; Utz, P.J.; Robinson, W.; Steinman, L. Clinical optimization of antigen specific modulation of type 1 diabetes with the plasmid DNA platform. Clin. Immunol. 2013, 149, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coban, C.; Kobiyama, K.; Aoshi, T.; Takeshita, F.; Horii, T.; Akira, S.; Ishii, K.J. Novel strategies to improve DNA vaccine immunogenicity. Curr. Gene Ther. 2011, 11, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, B.; Li, Z.; Nath, A. Nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors and human immunodeficiency virus proteins cause axonal injury in human dorsal root ganglia cultures. J. Neurovirol. 2007, 13, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wardell, C.M.; Levings, M.K. mRNA vaccines take on immune tolerance. Nat. Biotechnol. 2021, 39, 419–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roep, B.O.; Solvason, N.; Gottlieb, P.A.; Abreu, J.R.F.; Harrison, L.C.; Eisenbarth, G.S.; Yu, L.; Leviten, M.; Hagopian, W.A.; Buse, J.B.; et al. Plasmid-encoded proinsulin preserves C-peptide while specifically reducing proinsulin-specific CD8(+) T cells in type 1 diabetes. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 191ra182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, M.; Peng, X.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Liu, J.; She, Q.; Tan, J.; Lou, C.; Liao, Z.; et al. mRNA vaccine in cancer therapy: Current advance and future outlook. Clin. Transl. Med. 2023, 13, e1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bluestone, J.A.; Buckner, J.H.; Fitch, M.; Gitelman, S.E.; Gupta, S.; Hellerstein, M.K.; Herold, K.C.; Lares, A.; Lee, M.R.; Li, K.; et al. Type 1 diabetes immunotherapy using polyclonal regulatory T cells. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 315ra189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Li, J.J.; Liu, T.; Brian, O.; Li, J. Infectious disease mRNA vaccines and a review on epitope prediction for vaccine design. Brief. Funct. Genom. 2021, 20, 289–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, T.; Narsaria, U.; Basak, S.; Deb, D.; Castiglione, F.; Mueller, D.M.; Srivastava, A.P. A candidate multi-epitope vaccine against SARS-CoV-2. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poland, G.A.; Ovsyannikova, I.G.; Kennedy, R.B. SARS-CoV-2 immunity: Review and applications to phase 3 vaccine candidates. Lancet 2020, 396, 1595–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalzik, F.; Schreiner, D.; Jensen, C.; Teschner, D.; Gehring, S.; Zepp, F. mRNA-Based Vaccines. Vaccines 2021, 9, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lurie, D.J.; Li, H.; Petryakov, S.; Zweier, J.L. Development of a PEDRI free-radical imager using a 0.38 T clinical MRI system. Magn. Reson. Med. 2002, 47, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kariko, K.; Buckstein, M.; Ni, H.; Weissman, D. Suppression of RNA recognition by Toll-like receptors: The impact of nucleoside modification and the evolutionary origin of RNA. Immunity 2005, 23, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, B.R.; Muramatsu, H.; Nallagatla, S.R.; Bevilacqua, P.C.; Sansing, L.H.; Weissman, D.; Kariko, K. Incorporation of pseudouridine into mRNA enhances translation by diminishing PKR activation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, 5884–5892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morais, P.; Adachi, H.; Yu, Y.T. The Critical Contribution of Pseudouridine to mRNA COVID-19 Vaccines. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 789427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolgin, E. CureVac COVID Vaccine Let-Down Spotlights mRNA Design Challenges. 2021. Available online: https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-021-01661-0 (accessed on 1 November 2023).
- Niazi, S.K.; Magoola, M. mRNA and Synthesis-Based Therapeutic Proteins: A Non-Recombinant Affordable Option. Biologics 2023, 3, 355–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Mao, M.; Wang, L.J. Integrated clustering signature of genomic heterogeneity, stemness and tumor microenvironment predicts glioma prognosis and immunotherapy response. Aging 2023, 15, 9086–9104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawlings, D.J.; Metzler, G.; Wray-Dutra, M.; Jackson, S.W. Altered B cell signalling in autoimmunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 421–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sage, P.T.; Sharpe, A.H. T follicular regulatory cells. Immunol. Rev. 2016, 271, 246–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, H. Selfie: Autoimmunity, boon or bane. J. Immunoass. Immunochem. 2017, 38, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bluestone, J.A.; Tang, Q. T(reg) cells-the next frontier of cell therapy. Science 2018, 362, 154–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackay, I.R.; Rowley, M.J. Autoimmune epitopes: Autoepitopes. Autoimmun. Rev. 2004, 3, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravetch, J.V.; Bolland, S. IgG Fc receptors. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2001, 19, 275–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janeway, C.; Janeway, C. Immunobiology: The Immune System in Health and Disease, 5th ed.; Garland Pub: New York, NY, USA, 2001; p. xviii. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, J.; Malik, D.; Raina, A. Immuno-informatics approach for B-cell and T-cell epitope based peptide vaccine design against novel COVID-19 virus. Vaccine 2021, 39, 1087–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, V.; Tiwari, A.; Varadwaj, P. Prediction of suitable T and B cell epitopes for eliciting immunogenic response against SARS-CoV-2 and its mutant. Netw. Model. Anal. Health Inform. Bioinform. 2021, 11, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jerram, S.T.; Leslie, R.D. The Genetic Architecture of Type 1 Diabetes. Genes 2017, 8, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rich, S.S. Genetics and its potential to improve type 1 diabetes care. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2017, 24, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyaga, D.M.; Vickers, M.H.; Jefferies, C.; Perry, J.K.; O’Sullivan, J.M. The genetic architecture of type 1 diabetes mellitus. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2018, 477, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaida, K. Guillain-Barré Syndrome. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1190, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saverino, S.; Falorni, A. Autoimmune Addison’s disease. Best. Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 34, 101379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalmau, J.; Armangué, T.; Planagumà, J.; Radosevic, M.; Mannara, F.; Leypoldt, F.; Geis, C.; Lancaster, E.; Titulaer, M.J.; Rosenfeld, M.R.; et al. An update on anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis for neurologists and psychiatrists: Mechanisms and models. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 1045–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sammaritano, L.R. Antiphospholipid syndrome. Best. Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2020, 34, 101463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nissen, M.S.; Ryding, M.; Meyer, M.; Blaabjerg, M. Autoimmune Encephalitis: Current Knowledge on Subtypes, Disease Mechanisms and Treatment. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2020, 19, 584–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nista, E.C.; De Lucia, S.S.; Manilla, V.; Schepis, T.; Pellegrino, A.; Ojetti, V.; Pignataro, G.; Zileri Dal Verme, L.; Franceschi, F.; Gasbarrini, A.; et al. Autoimmune Pancreatitis: From Pathogenesis to Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marino, S.; Marino, L.; Greco, F.; Venti, V.; Fontana, A.; Timpanaro, T.; Taibi, R.; Pustorino, E.; Barbagallo, M.; Pavone, P. Bickerstaff’s brainstem encephalitis in childhood: A literature overview. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 12802–12807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, C.; Vinay, K.; Borradori, L.; Amber, K.T. Insights Into the Pathogenesis of Bullous Pemphigoid: The Role of Complement-Independent Mechanisms. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 912876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catassi, C.; Verdu, E.F.; Bai, J.C.; Lionetti, E. Coeliac disease. Lancet 2022, 399, 2413–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stino, A.M.; Naddaf, E.; Dyck, P.J.; Dyck, P.J.B. Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy-Diagnostic pitfalls and treatment approach. Muscle Nerve 2021, 63, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, H.; Lamberts, A.; Borradori, L.; Alberti-Violetti, S.; Barry, R.J.; Caproni, M.; Carey, B.; Carrozzo, M.; Caux, F.; Cianchini, G.; et al. European guidelines (S3) on diagnosis and management of mucous membrane pemphigoid, initiated by the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology—Part I. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2021, 35, 1750–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reunala, T.; Hervonen, K.; Salmi, T. Dermatitis Herpetiformis: An Update on Diagnosis and Management. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2021, 22, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nombel, A.; Fabien, N.; Coutant, F. Dermatomyositis With Anti-MDA5 Antibodies: Bioclinical Features, Pathogenesis and Emerging Therapies. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 773352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahreini, F.; Rayzan, E.; Rezaei, N. MicroRNAs and Diabetes Mellitus Type 1. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2022, 18, e021421191398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnelly, A.M.; Halbert, A.R.; Rohr, J.B. Discoid lupus erythematosus. Australas. J. Dermatol. 1995, 36, 3–10; quiz 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, J.; Dubey, S. Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis: A review. Autoimmun. Rev. 2023, 22, 103219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyamoto, D.; Gordilho, J.O.; Santi, C.G.; Porro, A.M. Epidermolysis bullosa acquisita. An. Bras. Dermatol. 2022, 97, 409–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, P.M.; Jones, V.A.; Murray, T.N.; Amber, K.T. A Review Comparing International Guidelines for the Management of Bullous Pemphigoid, Pemphigoid Gestationis, Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid, and Epidermolysis Bullosa Acquisita. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2020, 21, 557–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reggiani, F.; L’Imperio, V.; Calatroni, M.; Pagni, F.; Sinico, R.A. Goodpasture syndrome and anti-glomerular basement membrane disease. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2023, 41, 964–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moshkelgosha, S.; So, P.W.; Diaz-Cano, S.; Banga, J.P. Preclinical models of Graves’ disease and associated secondary complications. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2015, 21, 2414–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-García, A.; Sales-Sanz, M. Treatment of Graves’ ophthalmopathy. Med. Clin. 2021, 156, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasti, A.K.; Selmi, C.; Sarmiento-Monroy, J.C.; Vega, D.A.; Anaya, J.M.; Gershwin, M.E. Guillain-Barré syndrome: Causes, immunopathogenic mechanisms and treatment. Expert. Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2016, 12, 1175–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikulska, A.A.; Karaźniewicz-Łada, M.; Filipowicz, D.; Ruchała, M.; Główka, F.K. Metabolic Characteristics of Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis Patients and the Role of Microelements and Diet in the Disease Management-An Overview. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheckel, C.J.; Go, R.S. Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia: Diagnosis and Differential Diagnosis. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2022, 36, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gesualdo, L.; Di Leo, V.; Coppo, R. The mucosal immune system and IgA nephropathy. Semin. Immunopathol. 2021, 43, 657–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Audia, S.; Mahévas, M.; Samson, M.; Godeau, B.; Bonnotte, B. Pathogenesis of immune thrombocytopenia. Autoimmun. Rev. 2017, 16, 620–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascuzzi, R.M.; Bodkin, C.L. Myasthenia Gravis and Lambert-Eaton Myasthenic Syndrome: New Developments in Diagnosis and Treatment. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2022, 18, 3001–3022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, L.; Gardner, J.T., 2nd; Dao, H., Jr. Updates in the Diagnosis and Management of Linear IgA Disease: A Systematic Review. Medicina 2021, 57, 818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almaani, S.; Meara, A.; Rovin, B.H. Update on Lupus Nephritis. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 12, 825–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calle-Botero, E.; Abril, A. Lupus Vasculitis. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2020, 22, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keri, K.C.; Blumenthal, S.; Kulkarni, V.; Beck, L.; Chongkrairatanakul, T. Primary membranous nephropathy: Comprehensive review and historical perspective. Postgrad. Med. J. 2019, 95, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, A.; De Virgilio, A.; Rizzo, M.I.; Gallo, A.; Magliulo, G.; Fusconi, M.; Ruoppolo, G.; Tombolini, M.; Turchetta, R.; de Vincentiis, M. Microscopic polyangiitis: Advances in diagnostic and therapeutic approaches. Autoimmun. Rev. 2015, 14, 837–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilhus, N.E.; Verschuuren, J.J. Myasthenia gravis: Subgroup classification and therapeutic strategies. Lancet Neurol. 2015, 14, 1023–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wingerchuk, D.M.; Banwell, B.; Bennett, J.L.; Cabre, P.; Carroll, W.; Chitnis, T.; de Seze, J.; Fujihara, K.; Greenberg, B.; Jacob, A.; et al. International consensus diagnostic criteria for neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders. Neurology 2015, 85, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlé, A.; Pedersen, I.B.; Knudsen, N.; Perrild, H.; Ovesen, L.; Jørgensen, T.; Laurberg, P. Thyroid volume in hypothyroidism due to autoimmune disease follows a unimodal distribution: Evidence against primary thyroid atrophy and autoimmune thyroiditis being distinct diseases. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 94, 833–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loehrer, P.A.; Zieger, L.; Simon, O.J. Update on Paraneoplastic Cerebellar Degeneration. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melchionda, V.; Harman, K.E. Pemphigus vulgaris and pemphigus foliaceus: An overview of the clinical presentation, investigations and management. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2019, 44, 740–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, M.; Thio, J.; Thomas, R.S.; Phillips, J. Pernicious anaemia. BMJ 2020, 369, m1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Findlay, A.R.; Goyal, N.A.; Mozaffar, T. An overview of polymyositis and dermatomyositis. Muscle Nerve 2015, 51, 638–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, L.M. Clinical practice. Primary ovarian insufficiency. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 606–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsen, T.H.; Folseraas, T.; Thorburn, D.; Vesterhus, M. Primary sclerosing cholangitis—A comprehensive review. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 1298–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trapnell, B.C.; Nakata, K.; Bonella, F.; Campo, I.; Griese, M.; Hamilton, J.; Wang, T.; Morgan, C.; Cottin, V.; McCarthy, C. Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2019, 5, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carapetis, J.R.; Beaton, A.; Cunningham, M.W.; Guilherme, L.; Karthikeyan, G.; Mayosi, B.M.; Sable, C.; Steer, A.; Wilson, N.; Wyber, R.; et al. Acute rheumatic fever and rheumatic heart disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2016, 2, 15084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akiyama, M.; Kaneko, Y. Pathogenesis, clinical features, and treatment strategy for rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease. Autoimmun. Rev. 2022, 21, 103056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Careta, M.F.; Romiti, R. Localized scleroderma: Clinical spectrum and therapeutic update. An. Bras. Dermatol. 2015, 90, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brito-Zerón, P.; Retamozo, S.; Ramos-Casals, M. Sjögren syndrome. Med. Clin. 2023, 160, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newsome, S.D.; Johnson, T. Stiff person syndrome spectrum disorders; more than meets the eye. J. Neuroimmunol. 2022, 369, 577915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Punukollu, M.; Mushet, N.; Linney, M.; Hennessy, C.; Morton, M. Neuropsychiatric manifestations of Sydenham’s chorea: A systematic review. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 2016, 58, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadler, J.E. Pathophysiology of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood 2017, 130, 1181–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damase, T.R.; Sukhovershin, R.; Boada, C.; Taraballi, F.; Pettigrew, R.I.; Cooke, J.P. The Limitless Future of RNA Therapeutics. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 628137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Zaks, T.; Langer, R.; Dong, Y. Lipid nanoparticles for mRNA delivery. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2021, 6, 1078–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Berg, A.I.S.; Yun, C.O.; Schiffelers, R.M.; Hennink, W.E. Polymeric delivery systems for nucleic acid therapeutics: Approaching the clinic. J. Control Release 2021, 331, 121–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichmuth, A.M.; Oberli, M.A.; Jaklenec, A.; Langer, R.; Blankschtein, D. mRNA vaccine delivery using lipid nanoparticles. Ther. Deliv. 2016, 7, 319–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saiding, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, S.; Xiao, F.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhen, X.; Khan, M.M.; Chen, W.; Koo, S.; et al. Nano-bio interactions in mRNA nanomedicine: Challenges and opportunities for targeted mRNA delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2023, 203, 115116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naik, R.; Peden, K. Regulatory Considerations on the Development of mRNA Vaccines. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2022, 440, 187–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerriaud, M.; Kohli, E. RNA-based drugs and regulation: Toward a necessary evolution of the definitions issued from the European union legislation. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 1012497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services; Food and Drug Administration; Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research. Guidance for human somatic cell therapy and gene therapy. Hum. Gene Ther. 2001, 12, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Disease | Autoantibody |
|---|---|
| Acute motor axonal neuropathy [76] | ANCA, Anti-mitochondrial antibodies |
| Addison’s disease [77] | 21-hydroxylase antibodies |
| Anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis [78] | Anti-GM1 |
| Antiphospholipid syndrome [79] | Antiphospholipid antibodies |
| Autoimmune Encephalitis [80] | Anti-NMDA receptor |
| Autoimmune Pancreatitis [81] | IgG4, Anti-CA2 antibodies |
| Bickerstaff’s encephalitis [82] | Various, depending on subtype (e.g., NMDA receptor antibodies, LGI1 antibodies) |
| Bullous pemphigoid [83] | Anti-BP180, Anti-BP230 |
| Celiac disease [84] | ANA, ASMA, anti-LKM1 |
| Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy [85] | Anti-GQ1b |
| Cicatricial pemphigoid [86] | Anti-BP180, Anti-BP230 |
| Dermatitis herpetiformis [87] | Anti-tissue transglutaminase |
| Dermatomyositis [88] | Anti-Jo1, Anti-Mi2, Anti-SRP, Anti-TIF1 |
| Diabetes mellitus type 1 [89] | Anti-insulin, anti-IA-2, anti-GAD, anti-ZnT8 antibodies |
| Discoid lupus erythematosus [90] | ANA, Anti-dsDNA, Anti-Sm |
| Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA) [91] | Anti-streptolysin O (ASO), anti-DNase B |
| Epidermolysis bullosa acquisita [92] | Anti-type VII collagen |
| Gestational pemphigoid [93] | Anti-BP180, Anti-BP230 |
| Goodpasture syndrome [94] | p-ANCA/MPO-ANCA |
| Granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA) [91] | ANCA |
| Graves’ disease [95] | TSI, TPO, TG antibodies |
| Graves’ ophthalmopathy [96] | TSH receptor antibodies |
| Guillain-Barré syndrome [97] | Various, including anti-MAG |
| Hashimoto’s thyroiditis [98] | TPO, TG antibodies |
| Hemolytic anemia [99] | Anti-red blood cell antibodies |
| IgA nephropathy [100] | Anti-GBM antibodies |
| Immune thrombocytopenia [101] | Anti-platelet antibodies |
| Lambert–Eaton myasthenic syndrome [102] | Various, including anti-GM1, anti-GD1a |
| Linear IgA disease [103] | Anti-epidermal basement membrane IgA |
| Lupus nephritis [104] | Anti-PLA2R antibodies |
| Lupus vasculitis | c-ANCA/PR3-ANCA |
| Lupus vasculitis [105] | ANA, anti-dsDNA, anti-Smith, others |
| Membranous nephropathy [106] | IgA autoantibodies |
| Microscopic polyangiitis (MPA) [107] | ANA, anti-dsDNA, anti-Smith, others |
| Myasthenia gravis | Anti-VGCC |
| Myasthenia gravis [108] | Anti-acetylcholine receptor, Anti-MuSK |
| Neuromyelitis optica [109] | Anti-AQP4, Anti-AChR, anti-MuSK; AQP4-IgG (NMO-IgG) |
| Ord’s thyroiditis [110] | TPO, TG antibodies |
| Paraneoplastic cerebellar degeneration [111] | Anti-Yo, Anti-Hu, Anti-Ri, others |
| Pemphigus vulgaris [112] | Anti-desmoglein 3, Anti-desmoglein 1 |
| Pernicious anemia [113] | Anti-tissue transglutaminase antibodies (tTG), Endomysial antibodies (EMA), Deamidated gliadin peptide (DGP) |
| Polymyositis [114] | Anti-Jo-1, Anti-SRP, others |
| Premature ovarian failure [115] | Anti-ovarian antibodies, Anti-adrenal antibodies |
| Primary sclerosing cholangitis [116] | Anti-dsDNA, Anti-Sm, Anti-nuclear antibodies |
| Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis [117] | Anti-GM-CSF antibodies |
| Rheumatic heart disease [118] | Anti-IF, Anti-parietal cell |
| Rheumatoid lung disease [119] | Rheumatoid factor, Anti-CCP antibodies |
| Scleroderma (systemic sclerosis) [120] | ANA, anti-Scl-70, anti-centromere |
| Sjögren syndrome [121] | Anti-SSA/Ro, Anti-SSB/La antibodies |
| Stiff-person syndrome [122] | Anti-GAD, anti-amphiphysin |
| Sydenham’s chorea [123] | Anti-basal ganglia |
| Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura [124] | ADAMTS13 autoantibodies |
| No. | Start | End | Peptide | Length |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 21 | 31 | RTCPKPDDLPF | 11 |
| 2 | 40 | 58 | FYEPGEEITYSCKPGYVSR | 19 |
| 5 | 119 | 135 | ADSAKCTEEGKWSPELP | 17 |
| 6 | 139 | 149 | PITCPPPSIPT | 11 |
| 7 | 157 | 166 | KPSAGNNSLY | 10 |
| 10 | 191 | 197 | HGNWTKL | 7 |
| 11 | 205 | 225 | CPFPSRPDNGFVNYPAKPTLY | 21 |
| 13 | 237 | 247 | GYSLDGPEEIE | 11 |
| 18 | 304 | 315 | EKKCSYTEDAQC | 12 |
| RTCPKPDDLPF-GSGSGSGS-FYEPGEEITYSCKPGYVSR-GSGSGSGS-ADSAKCTEEGKWSPELP-GSGSGSGS-PITCPPPSIPT-GSGSGSGS-KPSAGNNSLY-GSGSGSGS-HGNWTKL-GSGSGSGS-CPFPSRPDNGFVNYPAKPTLY-GSGSGSGS-GYSLDGPEEIE-GSGSGSGS-EKKCSYTEDAQC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Niazi, S.K. Anti-Idiotypic mRNA Vaccine to Treat Autoimmune Disorders. Vaccines 2024, 12, 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12010009
Niazi SK. Anti-Idiotypic mRNA Vaccine to Treat Autoimmune Disorders. Vaccines. 2024; 12(1):9. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12010009
Chicago/Turabian StyleNiazi, Sarfaraz K. 2024. "Anti-Idiotypic mRNA Vaccine to Treat Autoimmune Disorders" Vaccines 12, no. 1: 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12010009
APA StyleNiazi, S. K. (2024). Anti-Idiotypic mRNA Vaccine to Treat Autoimmune Disorders. Vaccines, 12(1), 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12010009









