All Eyes on the Prefusion-Stabilized F Construct, but Are We Missing the Potential of Alternative Targets for Respiratory Syncytial Virus Vaccine Design?
Abstract
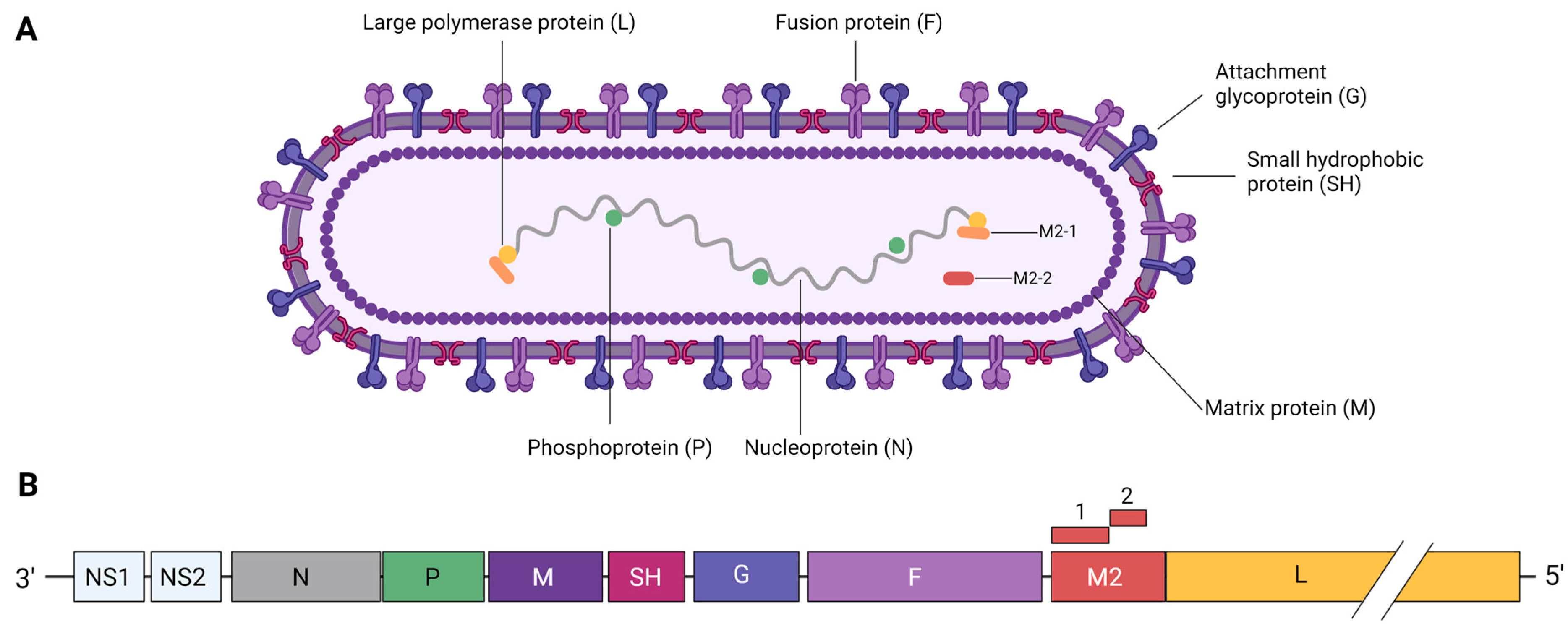
1. Introduction
2. RSV Structure
3. History of the Development of RSV Vaccines
4. Contemporary RSV Vaccine Landscape with Emphasis on Vaccines’ Constructs
4.1. F Protein
4.1.1. Full-Length F Protein
4.1.2. Prefusion-Stabilized Soluble F Protein
4.1.3. Prefusogenic F Protein
4.1.4. Specific Antigenic Sites of the F Protein
4.2. G Protein
4.3. SH Protein
4.4. N Protein
4.5. Multiple Viral Proteins and Complete Virus Particles
4.6. Vaccines with Unknown Antigen Design
5. Immunoprophylaxis
6. Current Challenges
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Graham, B.S. The Journey to RSV Vaccines—Heralding an Era of Structure-Based Design. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 579–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, T.; McAllister, D.A.; O’Brien, K.L.; Simoes, E.A.F.; Madhi, S.A.; Gessner, B.D.; Polack, F.P.; Balsells, E.; Acacio, S.; Aguayo, C.; et al. Global, regional, and national disease burden estimates of acute lower respiratory infections due to respiratory syncytial virus in young children in 2015: A systematic review and modelling study. Lancet 2017, 390, 946–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rima, B.; Collins, P.; Easton, A.; Fouchier, R.; Kurath, G.; Lamb, R.; Lee, B.; Maisner, A.; Rota, P.; Wang, L.; et al. ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profile: Pneumoviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mufson, M.A.; Orvell, C.; Rafnar, B.; Norrby, E. Two distinct subtypes of human respiratory syncytial virus. J. Gen. Virol. 1985, 66, 2111–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullender, W.M. Respiratory Syncytial Virus Genetic and Antigenic Diversity. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2000, 13, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Blau, D.; Caballero, M.; Feikin, D.; Gill, C.; Madhi, S.; Omer, S.; Simões, E.; Campbell, H.; et al. Global, regional, and national disease burden estimates of acute lower respiratory infections due to respiratory syncytial virus in children younger than 5 years in 2019: A systematic analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 2047–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glezen, W.P.; Taber, L.H.; Frank, A.L.; Kasel, J.A. Risk of primary infection and reinfection with respiratory syncytial virus. Am. J. Dis. Child. 1986, 140, 543–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, C.B.; Weinberg, G.G.; Iwane, M.K.; Blumkin, A.K.; Edwards, K.M.; Staat, M.A.; Auinger, P.; Griffin, M.R.; Poehling, K.A.; Erdman, D.; et al. The burden of respiratory syncytial virus infection in young children. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 588–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesman Saey, T. Here’s What We Know about Upcoming Vaccines and Antibodies against RSV. Available online: https://www.sciencenews.org/article/vaccines-antibodies-rsv-virus (accessed on 23 June 2023).
- Nair, H.; Nokes, D.J.; Gessner, B.D.; Dherani, M.; Madhi, S.A.; Singleton, R.J.; O’Brien, K.L.; Roca, A.; Wright, P.F.; Bruce, N.; et al. Global burden of acute lower respiratory infections due to respiratory syncytial virus in young children: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 2010, 375, 1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resch, B.; Manzoni, P.; Lanari, M. Severe respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) infection in infants with neuromuscular diseases and immune deficiency syndromes. Paediatr. Respir. Rev. 2009, 10, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckhaus, A.A.; Castro-Rodriguez, J.A. Down Syndrome and the Risk of Severe RSV Infection: A Meta-analysis. Pediatrics 2018, 142, e20180225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulkow, L.R.; Singleton, R.J.; Karron, R.A.; Harrison, L.H. Risk factors for severe respiratory syncytial virus infection among Alaska native children. Pediatrics 2002, 109, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srikantiah, P.; Vora, P.; Klugman, K.P. Assessing the Full Burden of Respiratory Syncytial Virus in Young Infants in Low- and Middle-Income Countries: The Importance of Community Mortality Studies. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 73 (Suppl. S3), S177–S179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, H.; Brooks, W.A.; Katz, M.; Roca, A.; Berkley, J.; Madhi, S.; Simmerman, J.; Gordon, A.; Sato, M.; Howie, S.; et al. Global burden of respiratory infections due to seasonal influenza in young children: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 2011, 378, 1917–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, K.M.; Bloom, H.H.; Mufson, M.A.; Chanock, R.M. Natural reinfection of adults by respiratory syncytial virus. Possible relation to mild upper respiratory disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 1962, 267, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazur, N.I.; Terstappen, J.; Baral, R.; Bardají, A.; Beutels, P.; Buchholz, U.J.; Cohen, C.; Crowe, J.E.; Cutland, C.L.; Eckert, L.; et al. Respiratory syncytial virus prevention within reach: The vaccine and monoclonal antibody landscape. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2023, 23, e2–e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ackerson, B.; Tseng, H.F.; Sy, L.S.; Solano, Z.; Slezak, J.; Luo, Y.; Fischetti, C.A.; Shinde, S. Severe Morbidity and Mortality Associated with Respiratory Syncytial Virus Versus Influenza Infection in Hospitalized Older Adults. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2019, 69, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korsten, K.; Adriaenssens, N.; Coenen, S.; Butler, C.; Ravanfar, B.; Rutter, H.; Allen, J.; Falsey, A.; Pirçon, J.Y.; Gruselle, O.; et al. Burden of respiratory syncytial virus infection in community-dwelling older adults in Europe (RESCEU): An international prospective cohort study. Eur. Respir. J. 2021, 57, 2002688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, N.W.; Binnicker, M.J.; Harris, D.M.; Chirila, R.M.; Brumble, L.; Mandrekar, J.; Hata, D.J. Morbidity and mortality among patients with respiratory syncytial virus infection: A 2-year retrospective review. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2016, 85, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falsey, A.; Hennessey, P.; Formica, M.; Cox, C.; Walsh, E. Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection in Elderly and High-Risk Adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 1749–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widmer, K.; Zhu, Y.; Williams, J.V.; Griffin, M.R.; Edwards, K.M.; Talbot, H.K. Rates of hospitalizations for respiratory syncytial virus, human metapneumovirus, and influenza virus in older adults. J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 206, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Center of Disease Control. RSV Surveillance and Research|CDC. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/rsv/research/index.html#ref04 (accessed on 3 July 2023).
- Branche, A.R.; Saiman, L.; Walsh, E.E.; Falsey, A.R.; Sieling, W.D.; Greendyke, W.; Peterson, D.R.; Vargas, C.Y.; Phillips, M.; Finelli, L. Incidence of Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection Among Hospitalized Adults, 2017–2020. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2022, 74, 1004–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mclaughlin, J.M.; Khan, F.; Begier, E.; Swerdlow, D.L.; Jodar, L.; Falsey, A.R. Rates of Medically Attended RSV Among US Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2022, 9, ofac300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savic, M.; Penders, Y.; Shi, T.; Branche, A.; Pirçon, J.Y. Respiratory syncytial virus disease burden in adults aged 60 years and older in high-income countries: A systematic literature review and meta-analysis. Influ. Other Respir. Viruses 2022, 17, e13031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battles, M.B.; McLellan, J.S. Respiratory syncytial virus entry and how to block it. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, D.; Gao, Y.; Liang, B. Structural Insights into the Respiratory Syncytial Virus RNA Synthesis Complexes. Viruses 2021, 13, 834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conley, M.J.; Short, J.M.; Burns, A.M.; Streetley, J.; Hutchings, J.; Bakker, S.E.; Power, B.J.; Jaffery, H.; Haney, J.; Zanetti, G.; et al. Helical ordering of envelope-associated proteins and glycoproteins in respiratory syncytial virus. EMBO J. 2022, 41, e109728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahriari, S.; Gordon, J.; Ghildyal, R. Host cytoskeleton in respiratory syncytial virus assembly and budding. Virol. J. 2016, 13, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghildyal, R.; Ho, A.; Jans, D.A. Central role of the respiratory syncytial virus matrix protein in infection. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2006, 30, 692–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahriari, S.; Wei, K.J.; Ghildyal, R. Respiratory Syncytial Virus Matrix (M) Protein Interacts with Actin In Vitro and in Cell Culture. Viruses 2018, 10, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, P.L.; Hill, M.G.; Cristina, J.; Grosfeld, H. Transcription elongation factor of respiratory syncytial virus, a nonsegmented negative-strand RNA virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, M.S.; Brazas, R.M.; Holtzman, M.J. Respiratory syncytial virus nonstructural proteins NS1 and NS2 mediate inhibition of Stat2 expression and alpha/beta interferon responsiveness. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 9315–9319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thornhill, E.M.; Verhoeven, D. Respiratory Syncytial Virus’s Non-structural Proteins: Masters of Interference. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, E.H.; Kolokoltsov, A.A.; Davey, R.A.; Nichols, J.E.; Norbert, J.R., Jr. Respiratory Syncytial Virus F Envelope Protein Associates with Lipid Rafts without a Requirement for Other Virus Proteins. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 12160–12170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, S.W.; Ng, L.; Lin, X.; Gong, X.; Torres, J. Structure and ion channel activity of the human respiratory syncytial virus (hRSV) small hydrophobic protein transmembrane domain. Protein Sci. 2008, 17, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLellan, J.S.; Ray, W.C.; Peeples, M.E. Structure and Function of RSV Surface Glycoproteins. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2013, 372, 83–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mastrangelo, P.; Chin, A.A.; Tan, S.; Jeon, A.H.; Ackerley, C.A.; Siu, K.K.; Lee, J.E.; Hegele, R.G. Identification of RSV Fusion Protein Interaction Domains on the Virus Receptor, Nucleolin. Viruses 2021, 13, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heminway, B.R.; Yu, Y.; Tanaka, Y.; Perrine, K.G.; Gustafson, E.; Bernstein, J.M.; Galinski, M.S. Analysis of respiratory syncytial virus F, G, and SH proteins in cell fusion. Virology 1994, 200, 801–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldman, S.A.; Audet, S.; Beeler, J.A. The Fusion Glycoprotein of Human Respiratory Syncytial Virus Facilitates Virus Attachment and Infectivity via an Interaction with Cellular Heparan Sulfate. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 6442–6447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, S.; Kaliaber-Franco, R.; Paradiso, P.R. Demonstration that glycoprotein G is the attachment protein of respiratory syncytial virus. J. Gen. Virol. 1987, 68 Pt 9, 2521–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, P.L.; Huang, Y.T.; Wertz, G.W. Nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding the fusion (F) glycoprotein of human respiratory syncytial virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 81, 7683–7687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolt, G.; Pedersen, L.Ø.; Birkeslund, H.H. Cleavage of the respiratory syncytial virus fusion protein is required for its surface expression: Role of furin. Virus Res. 2000, 68, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Day, N.D.; Branigan, P.J.; Liu, C.; Gutshall, L.L.; Luo, J.; Melero, J.A.; Sarisky, R.T.; Del Vecchio, A.M. Contribution of cysteine residues in the extracellular domain of the F protein of human respiratory syncytial virus to its function. Virol. J. 2006, 3, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruber, C.; Levine, S. Respiratory syncytial virus polypeptides. III. The envelope-associated proteins. J. Gen. Virol. 1983, 64 Pt 4, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leemans, A.; Boeren, M.; Van der Gucht, W.; Martinet, W.; Caljon, G.; Maes, L.; Cos, P.; Delputte, P. Characterization of the role of N-glycosylation sites in the respiratory syncytial virus fusion protein in virus replication, syncytium formation and antigenicity. Virus Res. 2019, 266, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilman, M.S.A.; Moin, S.M.; Mas, V.; Chen, M.; Patel, N.K.; Kramer, K.; Zhu, Q.; Kabeche, S.C.; Kumar, A.; Palomo, C.; et al. Characterization of a Prefusion-Specific Antibody That Recognizes a Quaternary, Cleavage-Dependent Epitope on the RSV Fusion Glycoprotein. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1005035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melero, J.A.; Mas, V.; McLellan, J.S. Structural, antigenic and immunogenic features of respiratory syncytial virus glycoproteins relevant for vaccine development. Vaccine 2017, 35, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilman, M.S.A.; Furmanova-Hollenstein, P.; Pascual, G.; van ‘t Wout, A.B.; Langedijk, J.P.M.; McLellan, J.S. Transient opening of trimeric prefusion RSV F proteins. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Stobart, C.C.; Hotard, A.L.; Moore, M.L. An overview of respiratory syncytial virus. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, B.S.; Modjarrad, K.; McLellan, J.S. Novel antigens for RSV vaccines. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2015, 35, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krivitskaya, V.; Komissarova, K.; Pisareva, M.; Sverlova, M.; Fadeev, A.; Petrova, E.; Timonina, V.; Sominina, A.; Danilenko, D. Respiratory Syncytial Virus G Protein Sequence Variability among Isolates from St. Petersburg, Russia, during the 2013–2014 Epidemic Season. Viruses 2021, 13, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, V.A.; Hoet, B.; Hochrein, H.; De Moerlooze, L. The Quest for a Respiratory Syncytial Virus Vaccine for Older Adults: Thinking beyond the F Protein. Vaccines 2023, 11, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mas, V.; Nair, H.; Campbell, H.; Melero, J.A.; Williams, T.C. Antigenic and sequence variability of the human respiratory syncytial virus F glycoprotein compared to related viruses in a comprehensive dataset. Vaccine 2018, 36, 6660–6673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngwuta, J.O.; Chen, M.; Modjarrad, K.; Joyce, M.G.; Kanekiyo, M.; Kumar, A.; Yassine, H.M.; Moin, S.M.; Killikelly, A.M.; Chuang, G.Y.; et al. Prefusion F–specific antibodies determine the magnitude of RSV neutralizing activity in human sera. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 309ra162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mousa, J.J.; Kose, N.; Matta, P.; Gilchuk, P.; Crowe, J.E. A novel pre-fusion conformation-specific neutralizing epitope on the respiratory syncytial virus fusion protein. Nat. Microbiol. 2017, 2, 16271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magro, M.; Mas, V.; Chappell, K.; Vázquez, M.; Cano, O.; Luque, D.; Terrón, M.C.; Melero, J.A.; Palomo, C. Neutralizing antibodies against the preactive form of respiratory syncytial virus fusion protein offer unique possibilities for clinical intervention. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 3089–3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Killikelly, A.M.; Kanekiyo, M.; Graham, B.S. Pre-fusion F is absent on the surface of formalin-inactivated respiratory syncytial virus. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLellan, J.S. Neutralizing epitopes on the respiratory syncytial virus fusion glycoprotein. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2015, 11, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLellan, J.S.; Chen, M.; Leung, S.; Graepel, K.W.; Du, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, T.; Baxa, U.; Yasuda, E.; Beaumont, T.; et al. Structure of RSV fusion glycoprotein trimer bound to a prefusion-specific neutralizing antibody. Science 2013, 340, 1113–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baglivo, S.J.; Polack, F.P. The long road to protect infants against severe RSV lower respiratory tract illness. F1000Research 2019, 8, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanock, R.; Roizman, B.; Myers, R. Recovery from infants with respiratory illness of a virus related to chimpanzee coryza agent (CCA). I. Isolation, properties and characterization. Am. J. Hyg. 2023, 66, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.W.; Canchola, J.G.; Brandt, C.D.; Pyles, G.; Chanock, R.M.; Jensen, K.; Parrott, R.H. Respiratory syncytial virus disease in infants despite prior administration of antigenic inactivated vaccine. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1969, 89, 422–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, M.F.; Coviello, S.; Monsalvo, A.C.; Melendi, G.A.; Hernandez, J.Z.; Batalle, J.P.; Diaz, L.; Trento, A.; Chang, H.Y.; Mitzner, W.; et al. Lack of antibody affinity maturation due to poor Toll-like receptor stimulation leads to enhanced respiratory syncytial virus disease. Nat. Med. 2008, 15, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, B.R.; Walsh, E.E. Formalin-inactivated respiratory syncytial virus vaccine induces antibodies to the fusion glycoprotein that are deficient in fusion-inhibiting activity. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1988, 26, 1595–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widjaja, I.; Wicht, O.; Luytjes, W.; Leenhouts, K.; Rottier, P.J.M.; Kuppeveld, F.J.M.; Haijema, B.J.; Haan, C.A.M. Characterization of Epitope-Specific Anti-Respiratory Syncytial Virus (Anti-RSV) Antibody Responses after Natural Infection and after Vaccination with Formalin-Inactivated RSV. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 5965–5977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, J.A.; Andreu, L.D.; Carreno, C.; Whyte, P.; Taylor, G.; Melero, J.A. Conformational constraints of conserved neutralizing epitopes from a major antigenic area of human respiratory syncytial virus fusion glycoprotein. J. Gen. Virol. 1993, 74 Pt 12, 2567–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, S.; Oliver, C.; Prince, G.A.; Hemming, V.G.; Pfarr, D.S.; Wang, S.C.; Dormitzcr, M.; O’Grady, J.; Koenig, S.; Tamura, J.K.; et al. Development of a humanized monoclonal antibody (MEDI-493) with potent in vitro and in vivo activity against respiratory syncytial virus. J. Infect. Dis. 1997, 176, 1215–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beeler, J.A.; van Wyke Coelingh, K. Neutralization epitopes of the F glycoprotein of respiratory syncytial virus: Effect of mutation upon fusion function. J. Virol. 1989, 63, 2941–2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resch, B. Product review on the monoclonal antibody palivizumab for prevention of respiratory syncytial virus infection. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2017, 13, 2138–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, J. Development of a potent respiratory syncytial virus-speci¢c monoclonal antibody for the prevention of serious lower respiratory tract disease in infants. Respir. Med. 2002, 96, S31–S35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meissner, H.C.; Long, S.S. Revised Indications for the Use of Palivizumab and Respiratory Syncytial Virus Immune Globulin Intravenous for the Prevention of Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infections. Pediatrics 2003, 112, 1447–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Synagis® (Palivizumab) Efficacy and Safety. Available online: https://synagishcp.com/synagis-palivizumab-efficacy.html (accessed on 5 July 2023).
- Garegnani, L.; Styrmisdóttir, L.; Rodriguez, P.R.; Liquitay, C.M.E.; Esteban, I.; Franco, J.V.A. Palivizumab for preventing severe respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) infection in children. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2021, 11, CD013757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, S.; Abu Raya, B.; Baraldi, E.; Flanagan, K.; Martinon Torres, F.; Tsolia, M.; Zielen, S. RSV Prevention in All Infants: Which Is the Most Preferable Strategy? Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 880368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, B.S.; Gilman, M.S.A.; McLellan, J.S. Structure-Based Vaccine Antigen Design. Annu. Rev. Med. 2019, 70, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krarup, A.; Truan, D.; Furmanova-Hollenstein, O.; Bogaert, L.; Bouchier, P.; Bisschop, I.J.M.; Widjojoatmodjo, M.N.; Zahn, R.; Schuitemaker, H.; McLellan, J.S.; et al. A highly stable prefusion RSV F vaccine derived from structural analysis of the fusion mechanism. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, X.; Xu, S.; Lu, Y.; Luo, Z.; Yan, Y.; Wang, C.; Ji, J. Development of mRNA vaccines against respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2022, 68, 37–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crank, M.C.; Ruckwardt, T.J.; Chen, M.; Morabito, K.M.; Phung, E.; Costner, P.J.; Holman, L.S.A.; Hickman, S.P.; Berkowitz, N.M.; Gordon, I.J.; et al. A proof of concept for structure-based vaccine design targeting RSV in humans. Science 2019, 365, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilman, M.S.A.; Castellanos, C.A.; Chen, M.; Ngwuta, J.O.; Goodwin, E.; Moin, S.M.; Mas, V.; Melero, J.A.; Wright, P.F.; Graham, B.S.; et al. Rapid profiling of RSV antibody repertoires from the memory B cells of naturally infected adult donors. Sci. Immunol. 2016, 1, eaaj1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLellan, J.S.; Chen, M.; Joyce, M.G.; Sastry, M.; Stewart-Jones, G.B.E.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Chen, L.; Srivatsan, S.; Zheng, A.; et al. Structure-Based Design of a Fusion Glycoprotein Vaccine for Respiratory Syncytial Virus. Science 2013, 342, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langedijk, A.C.; Bont, L.J. Respiratory syncytial virus infection and novel interventions. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 21, 734–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiegand, M.A.; Gori-Savellini, G.; Gandolfo, C.; Papa, G.; Kaufmann, C.; Felder, E.; Ginori, A.; Disanto, M.G.; Spina, D.; Grazia Cusi, M. A Respiratory Syncytial Virus Vaccine Vectored by a Stable Chimeric and Replication-Deficient Sendai Virus Protects Mice without Inducing Enhanced Disease. J. Virol. 2017, 91, 2298–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinkenburg, O.; Vogelmeier, C.; Bossow, S.; Neubert, W.J.; Lutz, R.B.; Ungerechts, G.; Lauer, U.M.; Bitzer, M.; Bals, R. Recombinant Sendai virus for efficient gene transfer to human airway epithelium. Exp. Lung Res. 2004, 30, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonemitsu, Y.; Kitson, C.; Ferrari, S.; Farley, R.; Griesenbach, U.; Judd, D.; Steel, R.; Scheid, P.; Zhu, J.; Jeffery, P.K.; et al. Efficient gene transfer to airway epithelium using recombinant Sendai virus. Nat. Biotechnol. 2000, 18, 970–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, S.; Griesenbach, U.; Iida, A.; Farley, R.; Wright, A.M.; Zhu, J.; Munkonge, F.M.; Smith, S.N.; You, J.; Ban, H.; et al. Sendai virus-mediated CFTR gene transfer to the airway epithelium. Gene Ther. 2007, 14, 1371–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Villenave, R.; Touzelet, O.; Thavagnanam, S.; Sarlang, S.; Parker, J.; Skibinski, G.; Heaney, L.G.; McKaigue, J.P.; Coyle, P.V.; Shields, M.D.; et al. Cytopathogenesis of Sendai Virus in Well-Differentiated Primary Pediatric Bronchial Epithelial Cells. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 11718–11728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID). A Safety and Immunogenicity Study of Intranasal Sendai Virus Vectored Respiratory Syncytial Virus (SeVRSV) Vaccine in Healthy Adults. Available online: https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03473002 (accessed on 30 July 2023).
- Blue Lake Biotechnology. A Study of BLB-201 RSV Vaccine in Infants and Children. Available online: https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05655182 (accessed on 30 July 2023).
- Blue Lake Biotechnology. Blue Lake Biotechnology Announces Positive Interim Phase 1 Data for BLB201 Intranasal RSV Vaccine; Blue Lake Biotechnology: San Jose, CA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Blue Lake Biotechnology. Phase 1 Study of BLB-201 Vaccine in Healthy Young and Older Adults—2023. Available online: https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05281263 (accessed on 30 July 2023).
- GSK. US FDA Approves GSK’s Arexvy, The World’s First Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Vaccine for Older Adults|GSK. Available online: https://www.gsk.com/en-gb/media/press-releases/us-fda-approves-gsk-s-arexvy-the-world-s-first-respiratory-syncytial-virus-rsv-vaccine-for-older-adults/ (accessed on 10 July 2023).
- Leroux-Roels, I.; Davis, M.G.; Steenackers, K.; Essink, B.; Vandermeulen, C.; Fogarty, C.; Andrews, C.P.; Kerwin, E.; David, M.P.; Fissette, L.; et al. Safety and Immunogenicity of a Respiratory Syncytial Virus Prefusion F (RSVPreF3) Candidate Vaccine in Older Adults: Phase 1/2 Randomized Clinical Trial. J. Infect. Dis. 2023, 227, 761–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandya, M.C.; Callahan, S.M.; Savchenko, K.G.; Stobart, C.C. A Contemporary View of Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Biology and Strain-Specific Differences. Pathogens 2019, 8, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacconay, L.; De Smedt, J. The RSVPreF3-AS01 vaccine elicits broad neutralization of contemporary and antigenically distant respiratory syncytial virus strains. Sci. Transl. Med. 2023, 15, eadg6050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, H.Y.; Englund, J.A. Maternal immunization. Birth Defects Res. 2017, 109, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, K.; Roy, E.; Arifeen, S.E.; Rahman, M.; Raqib, R.; Wilson, E.; Omer, S.B.; Shahid, N.S.; Breiman, R.F.; Steinhoff, M.C. Effectiveness of Maternal Influenza Immunization in Mothers and Infants. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 1555–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Switzer, C.; D’Heilly, C.; Macina, D. Immunological and Clinical Benefits of Maternal Immunization Against Pertussis: A Systematic Review. Infect. Dis. Ther. 2019, 8, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GSK. A Phase III Double-Blind Study to Assess Safety and Efficacy of an RSV Maternal Unadjuvanted Vaccine, in Pregnant Women and Infants Born to Vaccinated Mothers. Available online: https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04605159 (accessed on 5 July 2023).
- Boytchev, H. Maternal RSV vaccine: Further analysis is urged on preterm births. BMJ 2023, 381, p1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetter, K. When Will an RSV Vaccine Be Available? CNN. 18 May 2023. Available online: https://edition.cnn.com/2023/05/18/health/rsv-vaccine-covid-health-wellness/index.html (accessed on 10 July 2023).
- GSK. Efficacy Study of GSK’s Investigational Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Vaccine in Adults Aged 60 Years and above. Available online: https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04886596 (accessed on 10 July 2023).
- Che, Y.; Gribenko, A.V.; Song, X.; Handke, L.D.; Efferen, K.S.; Tompkins, K.; Kodali, S.; Nunez, L.; Prasad, A.K.; Phelan, L.M.; et al. Rational design of a highly immunogenic prefusion-stabilized F glycoprotein antigen for a respiratory syncytial virus vaccine. Sci. Transl. Med. 2023, 15, eade6422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfizer. Pfizer Announces Positive Top-Line Data of Phase 3 Global Maternal Immunization Trial for Its Bivalent Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Vaccine Candidate|Pfizer. Pfizer. Available online: https://www.pfizer.com/news/press-release/press-release-detail/pfizer-announces-positive-top-line-data-phase-3-global (accessed on 10 July 2023).
- Pfizer. Respiratory Syncytial Virus Bivalent Stabilized Prefusion F Subunit Vaccine (RSVpreF)—VRBPAC Briefing Document; Pfizer: Albany, GA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Pfizer. 2023. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04424316 (accessed on 7 July 2023).
- European Medicines Agency. First RSV Vaccine to Protect Infants up to 6 Months of Age and Older Adults|European Medicines Agency. European Medicines Agency (EMA). Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/news/first-rsv-vaccine-protect-infants-6-months-age-older-adults (accessed on 27 July 2023).
- Kampmann, B.; Madhi, S.A.; Munjal, I.; Simões, E.A.; Pahud, B.A.; Llapur, C.; Baker, J.; Marc, G.P.; Radley, D.; Shittu, E.; et al. Bivalent Prefusion F Vaccine in Pregnancy to Prevent RSV Illness in Infants. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 1451–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simões, E.A.F.; Center, K.J.; Tita, A.T.N.; Swanson, K.A.; Radley, D.; Houghton, J.; McGrory, S.B.; Gomme, E.; Anderson, M.; Roberts, J.P.; et al. Prefusion F Protein–Based Respiratory Syncytial Virus Immunization in Pregnancy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 1615–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Study to Evaluate the Efficacy, Immunogenicity, and Safety of RSVpreF in Adults. Available online: https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05035212 (accessed on 10 July 2023).
- Walsh, E.E.; Pérez Marc, G.; Zareba, A.M.; Falsey, A.R.; Jiang, Q.; Patton, M.; Polack, F.P.; Llapur, C.; Doreski, P.A.; Ilangovan, K.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of a Bivalent RSV Prefusion F Vaccine in Older Adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 1465–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moderna. A Study to Evaluate the Safety and Efficacy of mRNA-1345 Vaccine Targeting Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) in Adults ≥60 Years of Age. Available online: https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05127434 (accessed on 10 July 2023).
- Moderna. Announces mRNA-, M.M.1345, an Investigational Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Vaccine, Has Met Primary Efficacy Endpoints in Phase 3 Trial in Older Adults. Moderna. Available online: https://investors.modernatx.com/news/news-details/2023/Moderna-Announces-mRNA-1345-an-Investigational-Respiratory-Syncytial-Virus-RSV-Vaccine-Has-Met-Primary-Efficacy-Endpoints-in-Phase-3-Trial-in-Older-Adults/default.aspx (accessed on 10 July 2023).
- Safety, M.A. Tolerability, and Immunogenicity Study of mRNA-1345 and mRNA-1365 in Participants Aged 5 Months to <24 Months. Available online: https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05743881 (accessed on 28 July 2023).
- Stuart, A.S.V.; Virta, M.; Williams, K.; Seppa, I.; Hartvickson, R.; Greenland, M.; Omoruyi, E.; Bastian, R.; Haazen, W.; Heijnen, E.; et al. Phase 1/2a Safety and Immunogenicity of an Adenovirus 26 Vector Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Vaccine Encoding Prefusion F in Adults 18–50 Years and RSV-Seropositive Children 12–24 Months. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 227, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen Vaccines & Prevention. A Study of an Adenovirus Serotype 26 Pre-Fusion Conformation-Stabilized F Protein (Ad26. RSV. preF) Based Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Vaccine in the Prevention of Lower Respiratory Tract Disease in Adults Aged 60 Years and Older. Available online: https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04908683 (accessed on 10 July 2023).
- Saeland, E.; van der Fits, L.; Bolder, R.; Heemskerk-van der Meer, M.; Drijver, J.; van Polanen, Y.; Vaneman, C.; Tettero, L.; Serroyen, J.; Zahn, R.C.; et al. Immunogenicity and protective efficacy of adenoviral and subunit RSV vaccines based on stabilized prefusion F protein in pre-clinical models. Vaccine 2022, 40, 934–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen. Janssen Announces Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Adult Vaccine Candidate Maintains High Efficacy Regardless of Lower Respiratory Tract Disease Severity|Janssen. Available online: https://www.janssen.com/janssen-announces-respiratory-syncytial-virus-rsv-adult-vaccine-candidate-maintains-high-efficacy#_edn1 (accessed on 28 July 2023).
- Goodman, B. Johnson & Johnson Halts Development of RSV Vaccine in Midst of Late-Stage Clinical Trials|CNN. CNN. 29 March 2023. Available online: https://edition.cnn.com/2023/03/29/health/janssen-rsv-vaccine-trial/index.html (accessed on 28 July 2023).
- Johnson & Johnson. Janssen Provides Portfolio Update. Johnson & Johnson. Available online: https://www.jnj.com/janssen-provides-portfolio-update (accessed on 28 July 2023).
- Johnson, J. 2023 Results. Apr. 2023. Available online: https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20230418005360/en/Johnson-Johnson-Reports-Q1-2023-Results (accessed on 10 July 2023).
- Janssen Vaccines & Prevention. A Study to Evaluate the Safety, Tolerability and Immunogenicity of an Investigational RSV Vaccine Candidate (Ad26.RSV.preF) in Adults 18 to 50 Years of Age, and RSV-Seropositive Toddlers 12 to 24 Months of Age. Available online: https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03303625?term=Janssen&cond=RSV+Infection&draw=3&rank=15 (accessed on 28 July 2023).
- Ruckwardt, T.J.; Morabito, K.M.; Phung, E.; Crank, M.C.; Costner, P.J.; Holman, L.A.; Zhao, Z.; Chang, L.A.; Hickman, S.P.; Berkowitz, N.M.; et al. Safety, tolerability, and immunogenicity of the respiratory syncytial virus prefusion F subunit vaccine DS-Cav1: A phase 1, randomised, open-label, dose-escalation clinical trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, 1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NIAID. Dose, Safety, Tolerability and Immunogenicity of a Stabilized Prefusion RSV F Subunit Protein Vaccine, VRC-RSVRGP084-00-VP (DS-Cav1), alone or with Alum Adjuvant, in Healthy Adults. Available online: https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03049488 (accessed on 5 July 2023).
- Icosavax. Icosavax Initiates Phase 2 Trial of IVX-A12 Against RSV and hMPV in Older Adults—Icosavax, Inc. Available online: https://ir.icosavax.com/news-releases/news-release-details/icosavax-initiates-phase-2-trial-ivx-a12-against-rsv-and-hmpv/ (accessed on 29 July 2023).
- Clinical Trials Arena. Icosavax Announces Initiation of Pneumonia Vaccine Trial in Adults; Clinical Trials Arena: London, UK, 2023; Available online: https://www.clinicaltrialsarena.com/news/icosavax-phase-ii-pneumonia-adults/ (accessed on 29 July 2023).
- Marcandalli, J.; Fiala, B.; Ols, S.; Perotti, M.; de van der Schueren, W.; Snijder, J.; King, N.P.; Hodge, E.; Benhaim, M.; Ravichandran, R.; et al. Induction of Potent Neutralizing Antibody Responses by a Designed Protein Nanoparticle Vaccine for Respiratory Syncytial Virus. Cell 2019, 176, 1420–1431.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Icosavax. Safety and Immunogenicity of IVX-A12 in Healthy Older Adults. Available online: https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05664334 (accessed on 29 July 2023).
- Krzyzaniak, M.A.; Zumstein, M.T.; Gerez, J.A.; Picotti, P.; Helenius, A. Host Cell Entry of Respiratory Syncytial Virus Involves Macropinocytosis Followed by Proteolytic Activation of the F Protein. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Lee, Y.; Klenow, L.; Coyle, E.M.; Tang, J.; Ravichandran, S.; Khurana, S.; Golding, H.; Ravichandran, S.; Tang, J.; et al. Protective antigenic sites identified in respiratory syncytial virus fusion protein reveals importance of p27 domain. EMBO Mol. Med. 2021, 14, e13847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuentes, S.; Hahn, M.; Chilcote, K.; Chemaly, R.F.; Shah, D.P.; Ye, X.; Avadhanula, V.; Piedra, P.A.; Golding, H.; Khurana, S. Antigenic Fingerprinting of Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV)-A–Infected Hematopoietic Cell Transplant Recipients Reveals Importance of Mucosal Anti–RSV G Antibodies in Control of RSV Infection in Humans. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 221, 636–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novavax. A Study to Evaluate the Efficacy of an RSV F Vaccine in Older Adults. Available online: https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02608502 (accessed on 10 July 2023).
- Novavax. A Study to Determine the Safety and Efficacy of the RSV F Vaccine to Protect Infants via Maternal Immunization. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT02624947 (accessed on 10 July 2023).
- Madhi, S.A.; Polack, F.P.; Piedra, P.A.; Munoz, F.M.; Trenholme, A.A.; Simões, E.A.; Fries, L.F.; Swamy, G.K.; Agrawal, S.; Ahmed, K.; et al. Respiratory Syncytial Virus Vaccination during Pregnancy and Effects in Infants. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 426–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pharmaceutical Technology. Unsuccessful Phase III Could Determine Novavax RSV Vaccine Failure. Pharmaceutical Technology. Available online: https://www.pharmaceutical-technology.com/comment/novavax-rsv-vaccine-failure/ (accessed on 10 July 2023).
- Patel, N.; Tian, J.-H.; Flores, R.; Jacobson, K.; Walker, M.; Portnoff, A.; Gueber-Xabier, M.; Massare, M.J.; Glenn, G.; Ellingsworth, L.; et al. Flexible RSV Prefusogenic Fusion Glycoprotein Exposes Multiple Neutralizing Epitopes that May Collectively Contribute to Protective Immunity. Vaccines 2020, 8, 607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krueger, S.; Curtis, J.E.; Scott, D.R.; Grishaev, A.; Glenn, G.; Smith, G.; Ellingsworth, L.; Borisov, O.; Maynard, E.L. Structural Characterization and Modeling of a Respiratory Syncytial Virus Fusion Glycoprotein Nanoparticle Vaccine in Solution. Mol. Pharm. 2021, 18, 359–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novavax. Novavax Announces Topline RSV F Vaccine Data from Two Clinical Trials in Older Adults—15 September 2016. Available online: https://ir.novavax.com/press-releases/2016-09-25-Novavax-Announces-Topline-RSV-F-Vaccine-Data-from-Two-Clinical-Trials-in-Older-Adults (accessed on 10 July 2023).
- Zuniga, A.; Rassek, O.; Vrohlings, M.; Marrero-Nodarse, A.; Moehle, K.; Robinson, J.A.; Ghasparian, A. An epitope-specific chemically defined nanoparticle vaccine for respiratory syncytial virus. npj Vaccines 2021, 6, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virometix. Pipeline—Virometix AG—2023. Available online: https://virometix.com/pipeline/ (accessed on 29 July 2023).
- Pharmaceutical Technology. V-306 by Virometix for Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Infections: Likelihood of Approval. Pharmaceutical Technology. Available online: https://www.pharmaceutical-technology.com/data-insights/v-306-virometix-respiratory-syncytial-virus-rsv-infections-likelihood-of-approval/ (accessed on 29 July 2023).
- Virometix. Phase 1 Study to Evaluate the Safety and Immunogenicity of a Candidate Vaccine against Respiratory Syncytial Virus. Available online: https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04519073 (accessed on 29 July 2023).
- Hervé, P.L.; Dhelft, V.; Zuniga, A.; Ghasparian, A.; Rassek, O.; Yim, K.C.; Donne, N.; Lambert, P.-H.; Benhamou, P.-H.; Mondoulet, L.; et al. Epicutaneous immunization using synthetic virus-like particles efficiently boosts protective immunity to respiratory syncytial virus. Vaccine 2021, 39, 4555–4563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wertz, G.W.; Collins, P.L.; Huang, Y.; Gruber, C.; Levine, S.; Ball, L.A. Nucleotide sequence of the G protein gene of human respiratory syncytial virus reveals an unusual type of viral membrane protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1985, 82, 4075–4079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, X. Genetic variability of subgroup A and B respiratory syncytial virus strains circulating in southwestern China from 2009 to 2011. Arch. Virol. 2013, 158, 1487–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, P.R.; Spriggs, M.K.; Olmsted, R.A.; Collins, P.L. The G glycoprotein of human respiratory syncytial viruses of subgroups A and B: Extensive sequence divergence between antigenically related proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 5625–5629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karron, R.A.; Buonagurio, D.A.; Georgiu, A.F.; Whitehead, S.S.; Adamus, J.E.; Clements-Mann, M.L.; Harris, D.O.; Randolph, V.B.; Udem, S.A.; Murphy, B.R.; et al. Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) SH and G proteins are not essential for viral replication in vitro: Clinical evaluation and molecular characterization of a cold-passaged, attenuated RSV subgroup B mutant. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 13961–13966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, J.; Hotard, A.L.; Currier, M.G.; Lee, S.; Stobart, C.C.; Moore, M.L. Respiratory Syncytial Virus Attachment Glycoprotein Contribution to Infection Depends on the Specific Fusion Protein. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedechkin, S.O.; George, N.L.; Castrejon, A.M.N.; Dillen, J.R.; Kauvar, L.M.; DuBois, R.M. Conformational Flexibility in Respiratory Syncytial Virus G Neutralizing Epitopes. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e01879-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, H.G.; Ritschel, T.; Pascual, G.; Brakenhoff, J.P.J.; Keogh, E.; Furmanova-Hollenstein, P.; Lanckacker, E.; Wadia, J.S.; Gilman, M.S.A.; Williamson, R.A.; et al. Structural basis for recognition of the central conserved region of RSV G by neutralizing human antibodies. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1006935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedechkin, S.O.; George, N.L.; Wolff, J.T.; Kauvar, L.M.; DuBois, R.M. Structures of respiratory syncytial virus G antigen bound to broadly neutralizing antibodies. Sci. Immunol. 2018, 3, eaar3534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, E.E.; Hruska, J. Monoclonal antibodies to respiratory syncytial virus proteins: Identification of the fusion protein. J. Virol. 1983, 47, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pharmaceutical Technology. BARS-13 by Beijing Advaccine Biotechnology for Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Infections: Likelihood of Approval. Pharmaceutical Technology. Available online: https://www.pharmaceutical-technology.com/data-insights/bars-13-beijing-advaccine-biotechnology-respiratory-syncytial-virus-rsv-infections-likelihood-of-approval/ (accessed on 15 July 2023).
- Su, C.; Zhong, Y.; Zhao, G.; Hou, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, B. RSV pre-fusion F protein enhances the G protein antibody and anti-infectious responses. npj Vaccines 2022, 7, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Advaccine. A First in Human Study to Evaluate the Safety and Immune Response to a Vaccine for the Treatment of a Respiratory Virus, When Administered Into the Arm in Healthy Adult Participants. Available online: https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04851977 (accessed on 15 July 2023).
- Advaccine. Advaccine Announces First Participants Dosed in Phase 2 Study of ADV110 Evaluating Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Vaccine Candidate in Australia. BioSpace. Available online: https://www.biospace.com/article/releases/advaccine-announces-first-participants-dosed-in-phase-2-study-of-adv110-evaluating-respiratory-syncytial-virus-rsv-vaccine-candidate-in-australia/ (accessed on 15 July 2023).
- Advaccine. Safety and Efficacy of BARS13 in the Elderly. Available online: https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04681833 (accessed on 15 July 2023).
- Fuentes, S.; Tran, K.C.; Luthra, P.; Teng, M.N.; He, B. Function of the Respiratory Syncytial Virus Small Hydrophobic Protein. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 8361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, S.W.; Tan, E.; Lin, X.; Yu, D.; Wang, J.; Tan, G.M.Y.; Vararattanavech, A.; Yeo, C.Y.; Soon, C.H.; Soong, T.W.; et al. The Small Hydrophobic Protein of the Human Respiratory Syncytial Virus Forms Pentameric Ion Channels. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 24671–24689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, M.; García-Barreno, B.; Melero, J.A.; Carrasco, L.; Guinea, R. Membrane Permeability Changes Induced in Escherichia coli by the SH Protein of Human Respiratory Syncytial Virus. Virology 1997, 235, 342–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Triantafilou, K.; Kar, S.; Vakakis, E.; Kotecha, S.; Triantafilou, M. Human respiratory syncytial virus viroporin SH: A viral recognition pathway used by the host to signal inflammasome activation. Thorax 2013, 68, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rixon, H.W.M.L.; Brown, G.; Aitken, J.; McDonald, T.; Graham, S.; Sugrue, R.J. The small hydrophobic (SH) protein accumulates within lipid-raft structures of the Golgi complex during respiratory syncytial virus infection. J. Gen. Virol. 2004, 85 Pt 5, 1153–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schepens, B.; Sedeyn, K.; Vande Ginste, L.; De Baets, S.; Schotsaert, M.; Roose, K.; Houspie, L.; Van Ranst, M.; Gilbert, B.; van Rooijen, N.; et al. Protection and mechanism of action of a novel human respiratory syncytial virus vaccine candidate based on the extracellular domain of small hydrophobic protein. EMBO Mol. Med. 2014, 6, 1436–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schepens, B.; De Baets, S.; Sedyen, K.; Bogaert, P.; Gilbert, B.; Piedra, P.A.; Fiers, W.; Saelens, X. She’s a novel target for RSV vaccination. In Proceedings of the 8th Respiratory Syncytial Virus Symposium, Santa Fe, NM, USA, 27–30 September 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Torrey, H.L.; Kaliaperumal, V.; Bramhecha, Y.; Weir, G.M.; Falsey, A.R.; Walsh, E.E.; Langley, J.M.; Schepens, B.; Saelens, X.; Stanford, M.M. Evaluation of the protective potential of antibody and T cell responses elicited by a novel preventative vaccine towards respiratory syncytial virus small hydrophobic protein. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2020, 16, 2007–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schepens, B.; Schotsaert, M.; Saelens, X. Small hydrophobic protein of respiratory syncytial virus as a novel vaccine antigen. Immunotherapy 2015, 7, 203–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ImmunoVaccine. A Study to Evaluate the Safety and Reactogenicity of DPX-RSV(A), a Respiratory Syncytial Virus Vaccine. Available online: https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02472548 (accessed on 16 July 2023).
- Langley, J.M.; Macdonald, L.D.; Weir, G.M.; Mackinnon-Cameron, D.; Ye, L.; Mcneil, S.; Schepens, B.; Saelens, X.; Stanford, M.M.; Halperin, S.A. A Respiratory Syncytial Virus Vaccine Based on the Small Hydrophobic Protein Ectodomain Presented With a Novel Lipid-Based Formulation Is Highly Immunogenic and Safe in Adults: A First-in-Humans Study. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 218, 378–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Omari, K.; Dhaliwal, B.; Ren, J.; Abrescia, N.G.A.; Lockyer, M.; Powell, K.L.; Hawkins, A.R.; Stammers, D.K. Structures of respiratory syncytial virus nucleocapsid protein from two crystal forms: Details of potential packing interactions in the native helical form. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. F Struct. Biol. Cryst. Commun. 2011, 67 Pt 10, 1179–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, S.E.; Duquerroy, S.; Galloux, M.; Loney, C.; Conner, E.; Eléouet, J.F.; Rey, F.A.; Bhella, D. The respiratory syncytial virus nucleoprotein-RNA complex forms a left-handed helical nucleocapsid. J. Gen. Virol. 2013, 94 Pt 8, 1734–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhella, D.; Ralph, A.; Murphy, L.B.; Yeo, R.P. Significant differences in nucleocapsid morphology within the Paramyxoviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2002, 83 Pt 8, 1831–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roux, X.; Dubuquoy, C.; Durand, G.; Tran-Tolla, T.L.; Castagné, N.; Bernard, J.; Petit-Camurdan, A.; Eléouët, J.F.; Riffault, S. Sub-Nucleocapsid Nanoparticles: A Nasal Vaccine against Respiratory Syncytial Virus. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goulder, P.J.R.; Lechner, F.; Klenerman, P.; McIntosh, K.; Walker, B.D. Characterization of a novel respiratory syncytial virus-specific human cytotoxic T-lymphocyte epitope. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 7694–7697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venter, M.; Rock, M.; Puren, A.J.; Tiemessen, C.T.; Crowe, J.E. Respiratory syncytial virus nucleoprotein-specific cytotoxic T-cell epitopes in a South African population of diverse HLA types are conserved in circulating field strains. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 7319–7329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherrie, A.H.; Anderson, K.; Wertz, G.W.; Openshaw, P.J. Human cytotoxic T cells stimulated by antigen on dendritic cells recognize the N, SH, F, M, 22K, and 1b proteins of respiratory syncytial virus. J. Virol. 1992, 66, 2102–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dave, V.P.; Allan, J.E.; Slobod, K.S.; Smith, F.S.; Ryan, K.W.; Takimoto, T.; Power, U.F.; Portner, A.; Hurwitz, J.L. Viral cross-reactivity and antigenic determinants recognized by human parainfluenza virus type 1-specific cytotoxic T-cells. Virology 1994, 199, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrosi, C.; Di Genova, G.; Savellini, G.G.; Correale, P.; Blardi, P.; Cusi, M.G. Immunological characterization of respiratory syncytial virus N protein epitopes recognized by human cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Viral Immunol. 2007, 20, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bangham, C.R.; Openshaw, P.J.; Ball, L.A.; King, A.M.; Wertz, G.W.; Askonas, B.A. Human and murine cytotoxic T cells specific to respiratory syncytial virus recognize the viral nucleoprotein (N), but not the major glycoprotein (G), expressed by vaccinia virus recombinants. J. Immunol. 1986, 13, 3973–3977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussell, T.; Baldwin, C.J.; O’Garra, A.; Openshaw, P.J.M. CD8+ T cells control Th2-driven pathology during pulmonary respiratory syncytial virus infection. Eur. J. Immunol. 1997, 27, 3341–3349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, M.J.; Openshaw, P.J.M.; Askonas, B.A. Cytotoxic T cells clear virus but augment lung pathology in mice infected with respiratory syncytial virus. J. Exp. Med. 1988, 168, 1163–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, T.R.; Hong, S.; Van Kaer, L.; Koezuka, Y.; Graham, B.S. NK T Cells Contribute to Expansion of CD8+ T Cells and Amplification of Antiviral Immune Responses to Respiratory Syncytial Virus. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 4294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostler, T.; Ehl, S. Pulmonary T cells induced by respiratory syncytial virus are functional and can make an important contribution to long-lived protective immunity. Eur. J. Immunol. 2000, 32, 2562–2569. [Google Scholar]
- Graham, B.S.; Bunton, L.A.; Wright, P.F.; Karzon, D.T. Role of T lymphocyte subsets in the pathogenesis of primary infection and rechallenge with respiratory syncytial virus in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 1991, 88, 1026–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, P.L.; Fearns, R.; Graham, B.S. Respiratory syncytial virus: Virology, reverse genetics, and pathogenesis of disease. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2013, 372, 3–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samal, S.K.; Zamora, M. Nucleotide sequence analysis of a matrix and small hydrophobic protein dicistronic mRNA of bovine respiratory syncytial virus demonstrates extensive sequence divergence of the small hydrophobic protein from that of human respiratory syncytial virus. J. Gen. Virol. 1991, 72 Pt 7, 1715–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, A.M.; Stott, E.J.; Langer, S.J.; Young, K.K.; Ball, L.A.; Wertz, G.W. Recombinant vaccinia viruses carrying the N gene of human respiratory syncytial virus: Studies of gene expression in cell culture and immune response in mice. J. Virol. 1987, 61, 2885–2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, G.; Thomas, L.H.; Furze, J.M.; Cook, R.S.; Wyld, S.G.; Lerch, R.; Hardy, R.; Wertz, G.W. Recombinant vaccinia viruses expressing the F, G or N, but not the M2, protein of bovine respiratory syncytial virus (BRSV) induce resistance to BRSV challenge in the calf and protect against the development of pneumonic lesions. J. Gen. Virol. 1997, 78 Pt 12, 3195–3206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, C.A.; Scarselli, E.; Voysey, M.; Capone, S.; Vitelli, A.; Nicosia, A.; Cortese, R.; Thompson, A.J.; Sande, C.S.; De Lara, C.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of novel respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) vaccines based on the RSV viral proteins F, N and M2-1 encoded by simian adenovirus (PanAd3-RSV) and MVA (MVA-RSV); protocol for an open-label, dose-escalation, single-centre, phase 1 clinical trial in healthy adults. BMJ Open 2015, 5, e008748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan, K.; Rhodes, G.H.; Gershwin, L.J. DNA immunization against respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) in infant rhesus monkeys. Vaccine 2005, 23, 2928–2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boxus, M.; Tignon, M.; Roels, S.; Toussaint, J.F.; Walravens, K.; Benoit, M.A.; Coppe, P.; Letesson, J.J.; Letellier, C.; Kerkhofs, P.; et al. DNA Immunization with Plasmids Encoding Fusion and Nucleocapsid Proteins of Bovine Respiratory Syncytial Virus Induces a Strong Cell-Mediated Immunity and Protects Calves against Challenge. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 6879–6889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abarca, K.; Rey-Jurado, E.; Muñoz-Durango, N.; Vázquez, Y.; Soto, J.A.; Gálvez, N.M.S.; Valdés-Ferrada, J.; Iturriaga, C.; Urzúa, M.; Borzutzky, A.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity evaluation of recombinant BCG vaccine against respiratory syncytial virus in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase I clinical trial. EClinicalMedicine 2020, 27, 100517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, S.M.; González, P.A.; Cautivo, K.M.; Mora, J.E.; Leiva, E.D.; Tobar, H.E.; Fennelly, G.J.; Eugenin, E.A.; Jacobs, W.R.; Riedel, C.A.; et al. Protective T cell immunity against respiratory syncytial virus is efficiently induced by recombinant BCG. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 20822–20827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezende, C.A.F.; De Moraes, M.T.B.; Matos, D.C.D.S.; Mcintoch, D.; Armoa, G.R.G. Humoral response and genetic stability of recombinant BCG expressing hepatitis B surface antigens. J. Virol. Methods 2005, 125, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Liu, Q.; Liu, K.; Zhong, W.; Gao, S.; Jiang, L.; An, N. Immune response induced by recombinant Mycobacterium bovis BCG expressing ROP2 gene of Toxoplasma gondii. Parasitol. Int. 2007, 56, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Im, E.-J.; Saubi, N.; Virgili, G.; Sander, C.; Teoh, D.; Gatell, J.M.; McShane, H.; Joseph, J.; Hanke, T. Vaccine platform for prevention of tuberculosis and mother-to-child transmission of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 through breastfeeding. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 9408–9418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawahara, M.; Matsuo, K.; Honda, M. Intradermal and oral immunization with recombinant Mycobacterium bovis BCG expressing the simian immunodeficiency virus Gag protein induces long-lasting, antigen-specific immune responses in guinea pigs. Clin. Immunol. 2006, 119, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cayabyab, M.J.; Hovav, A.H.; Hsu, T.; Krivulka, G.R.; Lifton, M.A.; Gorgone, D.A.; Fennelly, G.J.; Haynes, B.F.; Jacobs, W.R., Jr.; Letvin, N.L. Generation of CD8+ T-Cell Responses by a Recombinant Nonpathogenic Mycobacterium smegmatis Vaccine Vector Expressing Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Env. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 1645–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, M.A.; Armôa, G.R.G.; Dellagostin, O.A.; McIntosh, D. Induction of humoral immunity in response to immunization with recombinant Mycobacterium bovis BCG expressing the S1 subunit of Bordetella pertussis toxin. Can. J. Microbiol. 2005, 51, 1015–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapeah, S.; Norazmi, M.N. Immunogenicity of a recombinant Mycobacterium bovis bacille Calmette-Guèrin expressing malarial and tuberculosis epitopes. Vaccine 2006, 24, 3646–3653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fennelly, G.J.; Flynn, J.A.L.; Meulen, V.T.; Liebert, U.G.; Bloom, B.R. Recombinant bacille Calmette-Guérin priming against measles. J. Infect. Dis. 1995, 172, 698–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dennehy, M.; Bourn, W.; Steele, D.; Williamson, A.L. Evaluation of recombinant BCG expressing rotavirus VP6 as an anti-rotavirus vaccine. Vaccine 2007, 25, 3646–3657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ota, M.O.C.; Vekemans, J.; Schlegel-Haueter, S.E.; Fielding, K.; Sanneh, M.; Kidd, M.; Newport, M.J.; Aaby, P.; Whittle, H.; Lambert, P.H.; et al. Influence of Mycobacterium bovis Bacillus Calmette-Guérin on Antibody and Cytokine Responses to Human Neonatal Vaccination 1. 2002. Available online: http://journals.aai.org/jimmunol/article-pdf/168/2/919/1145586/919.pdf (accessed on 30 July 2023).
- Hanekom, W.A. The immune response to BCG vaccination of newborns. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2005, 1062, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flynn, J.L.; Chan, J. Immunology of Tuberculosis. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2001, 19, 93–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cautivo, K.M.; Bueno, S.M.; Cortes, C.M.; Wozniak, A.; Riedel, C.A.; Kalergis, A.M. Efficient lung recruitment of respiratory syncytial virus-specific Th1 cells induced by recombinant bacillus Calmette-Guérin promotes virus clearance and protects from infection. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 7633–7645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Céspedes, P.F.; Rey-Jurado, E.; Espinoza, J.A.; Rivera, C.A.; Canedo-Marroquín, G.; Bueno, S.M.; Kalergis, A.M. A single, low dose of a cGMP recombinant BCG vaccine elicits protective T cell immunity against the human respiratory syncytial virus infection and prevents lung pathology in mice. Vaccine 2017, 35, 757–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soto, J.A.; Gálvez, N.M.S.; Rivera, C.A.; Palavecino, C.E.; Céspedes, P.F.; Rey-Jurado, E.; Bueno, S.M.; Kalergis, A.M. Recombinant BCG Vaccines Reduce Pneumovirus-Caused Airway Pathology by Inducing Protective Humoral Immunity. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pontificia Universidad Catolica de Chile. A Study to Assess Safety, Tolerability and Immunogenicity of the Live Attenuated hRSV Vaccine rBCG-N-hRSV (EVA-VRS01). Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT03213405?term=NCT03213405&rank=1 (accessed on 30 July 2023).
- Bavarian Nordic. MVA-BN-RSV Vaccine Trial. Available online: https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05238025 (accessed on 7 July 2023).
- Bavarian Nordic. Bavarian Nordic Provides Update on RSV Vaccine Programme. Available online: https://www.bavarian-nordic.com/investor/news/news.aspx?news=6808 (accessed on 28 November 2023).
- Stobart, C.C.; Rostad, C.A.; Ke, Z.; Dillard, R.S.; Hampton, C.M.; Strauss, J.D.; Yi, H.; Hotard, A.L.; Meng, J.; Pickles, R.J.; et al. A live RSV vaccine with engineered thermostability is immunogenic in cotton rats despite high attenuation. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meissa Vaccines. Technology: AttenuBlock for Optimized Immunity. Meissa Vaccines. Available online: https://www.meissavaccines.com/technology (accessed on 14 July 2023).
- Meissa Vaccines. Safety and Immunogenicity of an Intranasal Vaccine for Respiratory Syncytial Virus in Seronegative Children 6–36 Months. Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04909021?cond=RSV&term=Meissa&rank=2 (accessed on 14 July 2023).
- Meissa Vaccines. Vaccine Pipeline: RSV and Intranasal COVID-19 Vaccine Candidates. Meissa Vaccines. Available online: https://www.meissavaccines.com/vaccine-pipeline (accessed on 14 July 2023).
- Codagenix. Codagenix Initiates Dosing in Phase 1 Study of Intranasal, Live-Attenuated RSV Vaccine, CodaVaxTM- RSV, in a Pediatric Population. Codagenix. Available online: https://codagenix.com/codagenix-initiates-dosing-in-phase-1-study-of-intranasal-live-attenuated-rsv-vaccine-codavax-rsv-in-pediatric-patients/ (accessed on 29 July 2023).
- Le Nouën, C.; McCarty, T.; Brown, M.; Smith, M.L.; Lleras, R.; Dolan, M.A.; Mehedi, M.; Yang, L.; Luongo, C.; Liang, B.; et al. Genetic stability of genome-scale deoptimized RNA virus vaccine candidates under selective pressure. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E386–E395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, S.; Stauft, C.B.; Kalkeri, R.; Koidei, F.; Kushnir, A.; Tasker, S.; Coleman, J.R. A codon-pair deoptimized live-attenuated vaccine against respiratory syncytial virus is immunogenic and efficacious in non-human primates. Vaccine 2020, 38, 2943–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codagenix. Safety and Immunogenicity of CodaVax-RSV in Seropositive and Seronegative Children. Available online: https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04919109 (accessed on 29 July 2023).
- Verdijk, P.; van der Plas, J.L.; van Brummelen, E.M.J.; Jeeninga, R.E.; de Haan, C.A.M.; Roestenberg, M.; Burggraaf, J.; Kamerling, I.M.C. First-in-human administration of a live-attenuated RSV vaccine lacking the G-protein assessing safety, tolerability, shedding and immunogenicity: A randomized controlled trial. Vaccine 2020, 38, 6088–6095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widjojoatmodjo, M.N.; Boes, J.; van Bers, M.; van Remmerden, Y.; Roholl, P.J.M.; Luytjes, W. A highly attenuated recombinant human respiratory syncytial virus lacking the G protein induces long-lasting protection in cotton rats. Virol. J. 2010, 7, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dacchi Sankyo. A Dose Finding Study of VN-0200. Available online: https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05547087 (accessed on 30 July 2023).
- Sanofi. Study of an Live-Attenuated Respiratory Syncytial Virus Vaccine in Infants and Toddlers. Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05687279 (accessed on 11 October 2023).
- Sanofi. Study of a Respiratory Syncytial Virus mRNA Candidate With 2 Different Lipid Nanoparticle-based Formulations in Adults Aged 18 to 50 Years and 60 Years and Older. Available online: https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05639894 (accessed on 30 July 2023).
- Sanofi. Pipeline Charts as Communicated at Q2 2023; Sanofi: Paris, France, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Sanofi. Innovation to Drive Sustainable Growth in Vaccines; Sanofi: Paris, France, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Ananworanich, J.; Heaton, P.M. Bringing Preventive RSV Monoclonal Antibodies to Infants in Low- and Middle-Income Countries: Challenges and Opportunities. Vaccines 2021, 9, 961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, S.S.; Pickering, K.L.; Prober, G.C. Passive immunization. In Principles and Practice of Pediatric Infectious Diseases; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; p. 42. Available online: https://books.google.be/books?id=TN2Gu2Af1BIC&printsec=copyright&redir_esc=y#v=onepage&q&f=false (accessed on 10 July 2023).
- AstraZeneca. Nirsevimab Unanimously Recommended by FDA Advisory Committee for the Prevention of RSV Lower Respiratory Tract Disease in Infants. AstraZeneca. Available online: https://www.astrazeneca.com/media-centre/press-releases/2023/nirsevimab-recommended-for-infant-rsv-protection.html (accessed on 10 July 2023).
- Merck. Efficacy and Safety of Clesrovimab (MK-1654) in Infants (MK-1654-004). ClinicalTrials.gov. Available online: https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04767373 (accessed on 10 July 2023).
- Messina, A.; Germano, C.; Avellis, V.; Tavella, E.; Dodaro, V.; Massaro, A.; Vitale, R.; Masturzo, B.; Manzoni, P. New strategies for the prevention of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). Early Hum. Dev. 2022, 174, 105666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, S.; Park, S.; Sohn, M.H.; Jo, M.; Ko, B.J.; Na, J.H.; Yoo, H.; Jeong, A.L.; Ha, K.; Woo, J.R.; et al. An Fc variant with two mutations confers prolonged serum half-life and enhanced effector functions on IgG antibodies. Exp. Mol. Med. 2022, 54, 1850–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcotte, H.; Hammarström, L. Passive Immunization: Toward Magic Bullets. Mucosal Immunol. 2015, 2, 1403–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hause, A.M.; Henke, D.M.; Avadhanula, V.; Shaw, C.A.; Tapia, L.I.; Piedra, P.A. Sequence variability of the respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) fusion gene among contemporary and historical genotypes of RSV/A and RSV/B. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0175792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, A.; Chen, Z.; Cox, K.S.; Su, H.P.; Callahan, C.; Fridman, A.; Zhang, L.; Patel, S.B.; Cejas, P.J.; Swoyer, R.; et al. A potent broadly neutralizing human RSV antibody targets conserved site IV of the fusion glycoprotein. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merck. Clesrovimab (MK-1654) in Infants and Children at Increased Risk for Severe Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Disease (MK-1654-007). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04938830?term=NCT04938830&rank=1 (accessed on 31 July 2023).
- Sparrow, E.; Adetifa, I.; Chaiyakunapruk, N.; Cherian, T.; Fell, D.B.; Graham, B.S.; Innis, B.; Kaslow, D.C.; Karron, R.A.; Nair, H.; et al. WHO preferred product characteristics for monoclonal antibodies for passive immunization against respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) disease in infants—Key considerations for global use. Vaccine 2022, 40, 3506–3510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bill & Melinda Gates Medical Research Institute. Safety, Tolerability, and Pharmacokinetics of RSV Monoclonal Antibody RSM01 in Healthy Adults. Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05118386 (accessed on 31 July 2023).
- mAbxience. Exploratory Study to Estimate the Prophylactic Efficacy of Palivizumab in Healthy Adult Participants Inoculated With RSV. Available online: https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04540627 (accessed on 31 July 2023).
- Trinomab Biotech. A Study of TNM001 in Chinese Healthy Preterm and Term Infants. Available online: https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05630573 (accessed on 31 July 2023).
- Pharmaceutical Technology. TNM-001 by Zhuhai Trinomab Biotechnology for Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Infections: Likelihood of Approval. Pharmaceutical Technology. Available online: https://www.pharmaceutical-technology.com/data-insights/tnm-001-zhuhai-trinomab-biotechnology-respiratory-syncytial-virus-rsv-infections-likelihood-of-approval/ (accessed on 31 July 2023).
- Trinomab Technology. Product Development. Available online: https://trinomab.com/en-us/list/95.html (accessed on 28 November 2023).
- Karron, R.A.; Black, R.E. Determining the burden of respiratory syncytial virus disease: The known and the unknown. Lancet 2017, 390, 917–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trento, A.; Rodríguez-Fernández, R.; González-Sánchez, M.I.; González-Martínez, F.; Mas, V.; Vázquez, M.; Palomo, C.; Melero, J.A. The complexity of antibody responses elicited against the respiratory syncytial virus glycoproteins in hospitalized children younger than 2 years. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunatilaka, A.; Giles, M.L. Maternal RSV vaccine development. Where to from here. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2021, 17, 4542–4548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapikian, A.Z.; Mitchell, R.H.; Chanock, R.M.; Shvedoff, R.A.; Stewart, C.E. An epidemiologic study of altered clinical reactivity to respiratory syncytial (RS) virus infection in children previously vaccinated with an inactivated RS virus vaccine. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1969, 89, 405–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludlow, M. Respiratory syncytial virus infection in the modern era. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2023, 36, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, B.; Hassan, F.; Harrison, C.J.; Dien Bard, J.; Dunn, J.; Kehl, S.; Selvarangan, R. A multi-center study to determine genetic variations in the fusion gene of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) from children <2 years of age in the U.S. J. Clin. Virol. 2022, 154, 105223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mabilo, P.; Mthiyane, H.; Simane, A.; Subramoney, K.; Treurnicht, F.K. Characterisation of RSV Fusion Proteins from South African Patients with RSV Disease, 2019 to 2020. Viruses 2022, 14, 2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, G.L.; Drysdale, S.B.; Snape, M.D.; O’Connor, D.; Brown, A.; MacIntyre-Cockett, G.; Mellado-Gomez, E.; de Cesare, M.; Bonsall, D.; Ansari, M.A.; et al. Distinct patterns of within-host virus populations between two subgroups of human respiratory syncytial virus. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffin, M.P.; Yuan, Y.; Takas, T.; Domachowske, J.B.; Madhi, S.A.; Manzoni, P.; Simões, E.A.F.; Esser, M.T.; Khan, A.A.; Dubovsky, F.; et al. Single-Dose Nirsevimab for Prevention of RSV in Preterm Infants. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simões, E.A.F.; Forleo-Neto, E.; Geba, G.P.; Kamal, M.; Yang, F.; Cicirello, H.; Houghton, M.R.; Rideman, R.; Zhao, Q.; Benvin, S.L.; et al. Suptavumab for the Prevention of Medically Attended Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection in Preterm Infants. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 73, e4400–e4408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, C.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, H.; Fang, F.; Chen, M.; Yuan, Z.; Teng, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhang, X. Analysis of circulating respiratory syncytial virus A strains in Shanghai, China identified a new and increasingly prevalent lineage within the dominant ON1 genotype. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 966235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Liu, H.; Tabor, D.E.; Tovchigrechko, A.; Qi, Y.; Ruzin, A.; Esser, M.T.; Jin, H. Emergence of new antigenic epitopes in the glycoproteins of human respiratory syncytial virus collected from a US surveillance study, 2015–2017. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, W.K.; Schadenhofer, A.; Habierski, A.; Kaiser, F.K.; Saletti, G.; Ganzenmueller, T.; Hage, E.; Haid, S.; Pietschmann, T.; Hansen, G.; et al. Reverse genetics systems for contemporary isolates of respiratory syncytial virus enable rapid evaluation of antibody escape mutants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2026558118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Gucht, W.; Stobbelaar, K.; Govaerts, M.; Mangodt, T.; Barbezange, C.; Leemans, A.; De Winter, B.; Van Gucht, S.; Caljon, G.; Maes, L.; et al. Isolation and Characterization of Clinical RSV Isolates in Belgium during the Winters of 2016–2018. Viruses 2019, 11, 1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levitz, R.; Gao, Y.; Dozmorov, I.; Song, R.; Wakeland, E.K.; Kahn, J.S. Distinct patterns of innate immune activation by clinical isolates of respiratory syncytial virus. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Jiang, M.; Wang, F.; Qian, Y.; Song, Q.; Sun, Y.; Zhu, R.; Wang, F.; Qu, D.; Cao, L.; et al. Immune escaping of the novel genotypes of human respiratory syncytial virus based on gene sequence variation. Front. Immunol. 2023, 13, 1084139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stokes, K.L.; Chi, M.H.; Sakamoto, K.; Newcomb, D.C.; Currier, M.G.; Huckabee, M.M.; Lee, S.; Goleniewska, K.; Pretto, C.; Williams, J.V.; et al. Differential Pathogenesis of Respiratory Syncytial Virus Clinical Isolates in BALB/c Mice. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 5782–5793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagliardi, T.B.; Criado, M.F.; Proença-Módena, J.L.; Saranzo, A.M.; Iwamoto, M.A.; De Paula, F.E.; Cardoso, R.S.; Delcaro, L.S.; Silva, M.L.; Câmara, A.A.; et al. Syncytia Induction by Clinical Isolates of Human Respiratory Syncytial Virus A. Intervirology 2017, 60, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, T.M.; Roddam, P.L.; Harrison, L.M.; A Aitken, J.; DeVincenzo, J.P. Viral Specific Factors Contribute to Clinical Respiratory Syncytial Virus Disease Severity Differences in Infants. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 4, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villenave, R.; O’Donoghue, D.; Thavagnanam, S.; Touzelet, O.; Skibinski, G.; Heaney, L.G.; McKaigue, J.P.; Coyle, P.V.; Shields, M.D.; Power, U.F. Differential cytopathogenesis of respiratory syncytial virus prototypic and clinical isolates in primary pediatric bronchial epithelial cells. Virol. J. 2011, 8, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levitz, R.; Wattier, R.; Phillips, P.; Solomon, A.; Lawler, J.; Lazar, I.; Weibel, C.; Kahn, J.S. Induction of IL-6 and CCL5 (RANTES) in human respiratory epithelial (A549) cells by clinical isolates of respiratory syncytial virus is strain specific. Virol. J. 2012, 9, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, C.B.; Walsh, E.E.; Schnabel, K.C.; Long, C.E.; McConnochie, K.M.; Hildreth, S.W.; Anderson, L.J. Occurrence of groups A and B of respiratory syncytial virus over 15 years: Associated epidemiologic and clinical characteristics in hospitalized and ambulatory children. J. Infect. Dis. 1990, 162, 1283–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broberg, E.K.; Waris, M.; Johansen, K.; Snacken, R.; Penttinen, P.; Trebbien, R.; Emborg, H.D.; Krause, T.G.; Fischer, T.K.; Kuznetsova, N.; et al. Seasonality and geographical spread of respiratory syncytial virus epidemics in 15 European countries, 2010 to 2016. Eurosurveillance 2018, 23, 17-00284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, L.A.; Holland, S.C.; Smith, M.F.; Leonard, V.R.; Murugan, V.; Nordstrom, L.; Mulrow, M.; Salgado, R.; White, M.; Lim, E.S. Genomic Sequencing Surveillance and Antigenic Site Mutations of Respiratory Syncytial Virus in Arizona, USA. medRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schaerlaekens, S.; Jacobs, L.; Stobbelaar, K.; Cos, P.; Delputte, P. All Eyes on the Prefusion-Stabilized F Construct, but Are We Missing the Potential of Alternative Targets for Respiratory Syncytial Virus Vaccine Design? Vaccines 2024, 12, 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12010097
Schaerlaekens S, Jacobs L, Stobbelaar K, Cos P, Delputte P. All Eyes on the Prefusion-Stabilized F Construct, but Are We Missing the Potential of Alternative Targets for Respiratory Syncytial Virus Vaccine Design? Vaccines. 2024; 12(1):97. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12010097
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchaerlaekens, Sofie, Lotte Jacobs, Kim Stobbelaar, Paul Cos, and Peter Delputte. 2024. "All Eyes on the Prefusion-Stabilized F Construct, but Are We Missing the Potential of Alternative Targets for Respiratory Syncytial Virus Vaccine Design?" Vaccines 12, no. 1: 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12010097
APA StyleSchaerlaekens, S., Jacobs, L., Stobbelaar, K., Cos, P., & Delputte, P. (2024). All Eyes on the Prefusion-Stabilized F Construct, but Are We Missing the Potential of Alternative Targets for Respiratory Syncytial Virus Vaccine Design? Vaccines, 12(1), 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12010097






