Design of a Glycoconjugate Vaccine Against Salmonella Paratyphi A
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. O:2 Production, Purification, and Characterization
2.3. Partial O:2 De-O-Acetylation Through Ammonia Treatment
2.4. Conjugation of S. Paratyphi A O:2 with CRM197
2.5. O:2–CRM197 Conjugates Characterization
2.5.1. Conjugate MW Determination
2.5.2. S. Paratyphi A O-Antigen Quantification
2.5.3. Protein Quantification
2.5.4. Free CRM197 Determination in Conjugates
2.5.5. Free Polysaccharide Quantification in Conjugates
2.5.6. Determination of the OAc Content of the O:2 and O:2–CRM197 Conjugates Through the Micro Hestrin Assay
2.6. Immunogenicity Study in Animal Models
2.7. Formulation Preparation
2.8. Stability Test
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of O:2–CRM197 Glycoconjugates
3.2. Immunogenicity of O:2–CRM197 Conjugates in Mice
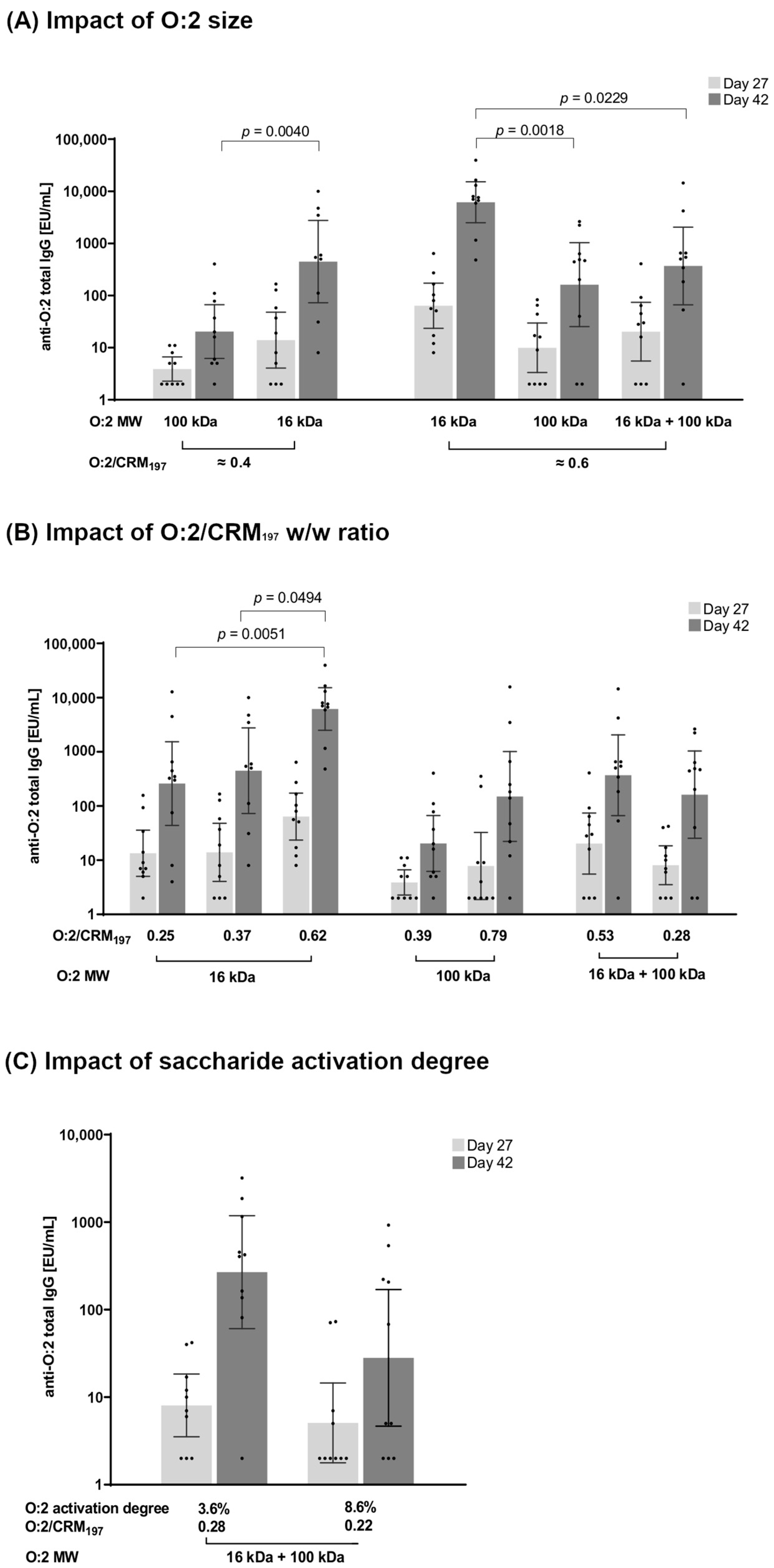
3.2.1. Effect of O:2 Size
3.2.2. Effect of O:2/CRM197 Ratio
3.2.3. Effect of O:2 Activation Degree
3.2.4. Effect of O-Acetylation Levels
3.3. Immunogenicity of O:2–CRM197 Conjugates in Rabbits
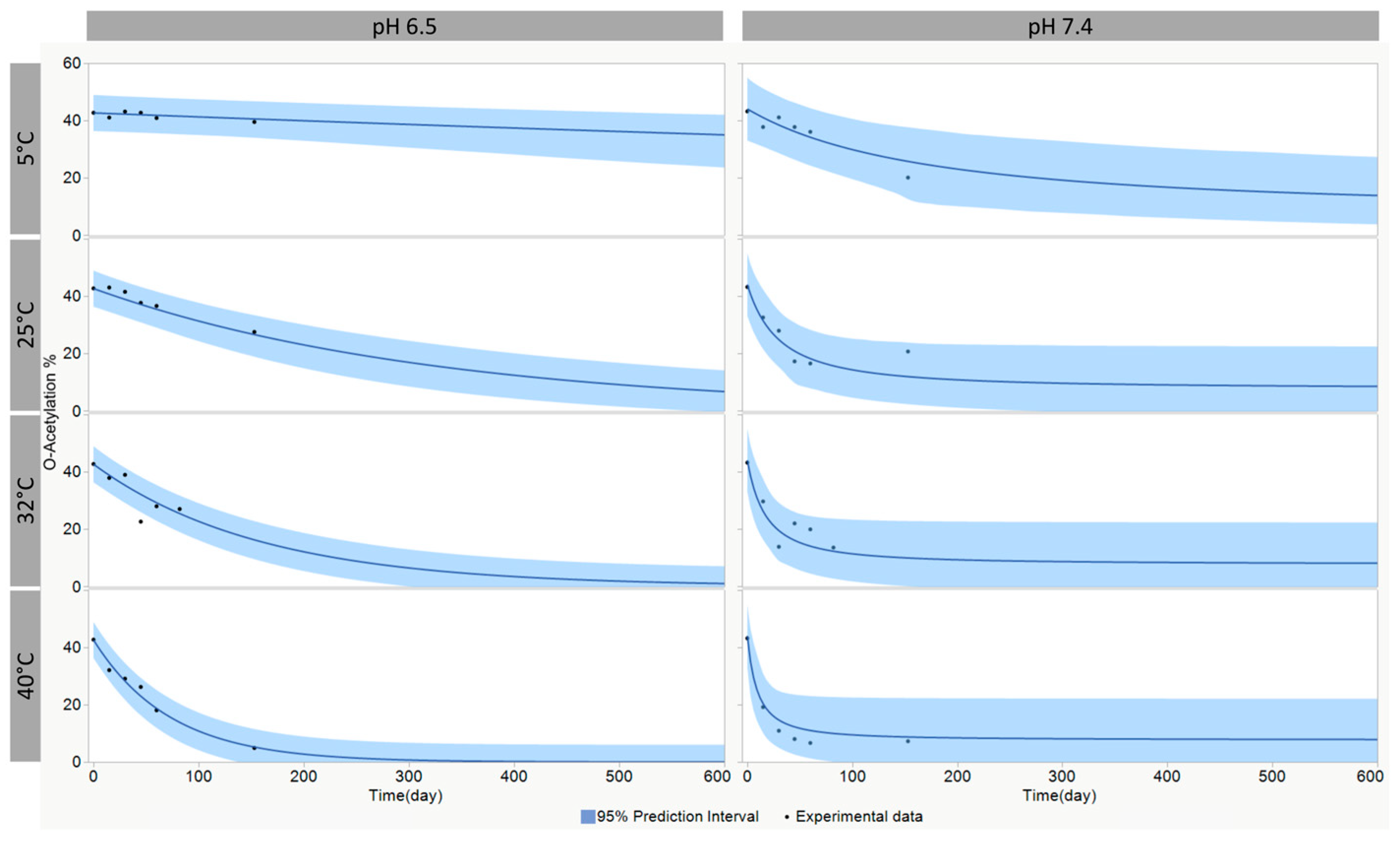
3.4. Modeling of the O-Acetylation Stability
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: A systematic analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 629–655. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sallam, M.; Snygg, J.; Allam, D.; Kassem, R. From Protection to Prevention: Redefining Vaccines in the Context of Antimicrobial Resistance. Cureus 2024, 16, e60551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasso-Agopsowicz, M.; Sparrow, E.; Cameron, A.M.; Sati, H.; Srikantiah, P.; Gottlieb, S.; Bentsi-Enchill, A.; Le Doare, K.; Hamel, M.; Giersing, B.K.; et al. The role of vaccines in reducing antimicrobial resistance: A review of potential impact of vaccines on AMR and insights across 16 vaccines and pathogens. Vaccine 2024, 42, S1–S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zavaleta-Monestel, E.; Hasselmyr Hasselmyr, S.; García-Montero, J.; Arguedas-Chacón, S.; Rojas-Chinchilla, C.; Díaz-Madriz, J.P. The Impact of Vaccination as a Strategy to Combat Bacterial Antimicrobial Resistance. Cureus 2024, 16, e65840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, P.D.; Liang, Y.; Meiring, J.E.; Chasweka, N.; Patel, P.; Misiri, T.; Mwakiseghile, F.; Wachepa, R.; Banda, H.C.; Shumba, F.; et al. Efficacy of typhoid conjugate vaccine: Final analysis of a 4-year, phase 3, randomised controlled trial in Malawian children. Lancet 2024, 403, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Typhoid vaccines: WHO position paper, March 2018—Recommendations. Vaccine 2019, 37, 214–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micoli, F.; Bjarnarson, S.P.; Arcuri, M.; Aradottir Pind, A.A.; Magnusdottir, G.J.; Necchi, F.; Di Benedetto, R.; Carducci, M.; Schiavo, F.; Giannelli, C.; et al. Short Vi-polysaccharide abrogates T-independent immune response and hyporesponsiveness elicited by long Vi-CRM(197) conjugate vaccine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 24443–24449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rondini, S.; Micoli, F.; Lanzilao, L.; Hale, C.; Saul, A.J.; Martin, L.B. Evaluation of the immunogenicity and biological activity of the Citrobacter freundii Vi-CRM197 conjugate as a vaccine for Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2011, 18, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcuri, M.; Di Benedetto, R.; Cunningham, A.F.; Saul, A.; MacLennan, C.A.; Micoli, F. The influence of conjugation variables on the design and immunogenicity of a glycoconjugate vaccine against Salmonella Typhi. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0189100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, S.I.A.; Nguyen, T.N.T.; Khanam, F.; Thomson, N.R.; Dyson, Z.A.; Taylor-Brown, A.; Chowdhury, E.K.; Dougan, G.; Baker, S.; Qadri, F. Genetic diversity of Salmonella Paratyphi A isolated from enteric fever patients in Bangladesh from 2008 to 2018. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0009748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The global burden of typhoid and paratyphoid fevers: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 369–381. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; McCann, A.; Weill, F.X.; Blin, C.; Nair, S.; Wain, J.; Dougan, G.; Achtman, M. Transient Darwinian selection in Salmonella enterica serovar Paratyphi A during 450 years of global spread of enteric fever. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 12199–12204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zellweger, R.M.; Basnyat, B.; Shrestha, P.; Prajapati, K.G.; Dongol, S.; Sharma, P.K.; Koirala, S.; Darton, T.C.; Dolecek, C.; Thompson, C.N.; et al. A 23-year retrospective investigation of Salmonella Typhi and Salmonella Paratyphi isolated in a tertiary Kathmandu hospital. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0006051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irfan, S.; Hasan, Z.; Qamar, F.N.; Ghanchi, N.; Ashraf, J.; Kanji, A.; Razzak, S.A.; Greig, D.; Nair, S.; Hasan, R. Correction: Ceftriaxone resistant Salmonella enterica serovar Paratyphi A identified in a case of enteric fever: First case report from Pakistan. BMC Infect. Dis. 2023, 23, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Micoli, F.; Rondini, S.; Gavini, M.; Lanzilao, L.; Medaglini, D.; Saul, A.; Martin, L.B. O:2-CRM(197) conjugates against Salmonella Paratyphi A. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konadu, E.; Shiloach, J.; Bryla, D.A.; Robbins, J.B.; Szu, S.C. Synthesis, characterization, and immunological properties in mice of conjugates composed of detoxified lipopolysaccharide of Salmonella paratyphi A bound to tetanus toxoid with emphasis on the role of O acetyls. Infect. Immun. 1996, 64, 2709–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konadu, E.Y.; Lin, F.Y.; Hó, V.A.; Thuy, N.T.; Van Bay, P.; Thanh, T.C.; Khiem, H.B.; Trach, D.D.; Karpas, A.B.; Li, J.; et al. Phase 1 and phase 2 studies of Salmonella enterica serovar paratyphi A O-specific polysaccharide-tetanus toxoid conjugates in adults, teenagers, and 2- to 4-year-old children in Vietnam. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 1529–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLennan, C.A.; Stanaway, J.; Grow, S.; Vannice, K.; Steele, A.D. Salmonella Combination Vaccines: Moving Beyond Typhoid. Open Forum. Infect. Dis. 2023, 10, S58–S66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chettri, D.; Chirania, M.; Boro, D.; Verma, A.K. Glycoconjugates: Advances in modern medicines and human health. Life Sci. 2024, 348, 122689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantino, P.; Rappuoli, R.; Berti, F. The design of semi-synthetic and synthetic glycoconjugate vaccines. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2011, 6, 1045–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berti, F.; Adamo, R. Antimicrobial glycoconjugate vaccines: An overview of classic and modern approaches for protein modification. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 9015–9025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravenscroft, N.; Cescutti, P.; Gavini, M.; Stefanetti, G.; MacLennan, C.A.; Martin, L.B.; Micoli, F. Structural analysis of the O-acetylated O-polysaccharide isolated from Salmonella paratyphi A and used for vaccine preparation. Carbohydr. Res. 2015, 404, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nappini, R.; Alfini, R.; Durante, S.; Salvini, L.; Raso, M.M.; Palmieri, E.; Di Benedetto, R.; Carducci, M.; Rossi, O.; Cescutti, P.; et al. Modeling 1-Cyano-4-dimethylaminopyridine Tetrafluoroborate (CDAP) Chemistry to Design Glycoconjugate Vaccines with Desired Structural and Immunological Characteristics. Vaccines 2024, 12, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Put, R.M.F.; Metz, B.; Pieters, R.J. Carriers and Antigens: New Developments in Glycoconjugate Vaccines. Vaccines 2023, 11, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micoli, F.; Giannelli, C.; Di Benedetto, R. O-Antigen Extraction, Purification, and Chemical Conjugation to a Carrier Protein. Methods Mol. Biol. 2021, 2183, 267–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raso, M.M.; Vassallo, O.; Micoli, F.; Giannelli, C. Comparison and Optimization of Quantification Methods for Shigella flexneri Serotype 6 O-antigen Containing Galacturonic Acid and Methyl-Pentose. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitri, K.; Kuttel, M.M.; De Benedetto, G.; Lockyer, K.; Gao, F.; Hansal, P.; Rudd, T.R.; Beamish, E.; Rijpkema, S.; Ravenscroft, N.; et al. O-acetylation of typhoid capsular polysaccharide confers polysaccharide rigidity and immunodominance by masking additional epitopes. Vaccine 2019, 37, 3866–3875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanetti, G.; Rondini, S.; Lanzilao, L.; Saul, A.; MacLennan, C.A.; Micoli, F. Impact of conjugation chemistry on the immunogenicity of S. Typhimurium conjugate vaccines. Vaccine 2014, 32, 6122–6129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micoli, F.; Alfini, R.; Giannelli, C. Methods for Assessment of OMV/GMMA Quality and Stability. Methods Mol. Biol. 2022, 2414, 227–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hestrin, S. The reaction of acetylcholine and other carboxylic acid derivatives with hydroxylamine, and its analytical application. J. Biol. Chem. 1949, 180, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasperini, G.; Massai, L.; De Simone, D.; Raso, M.M.; Palmieri, E.; Alfini, R.; Rossi, O.; Ravenscroft, N.; Kuttel, M.M.; Micoli, F. O-Antigen decorations in Salmonella enterica play a key role in eliciting functional immune responses against heterologous serovars in animal models. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1347813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Necchi, F.; Saul, A.; Rondini, S. Setup of luminescence-based serum bactericidal assay against Salmonella Paratyphi A. J. Immunol. Methods 2018, 461, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mylona, E.; Sanchez-Garrido, J.; Hoang Thu, T.N.; Dongol, S.; Karkey, A.; Baker, S.; Shenoy, A.R.; Frankel, G. Very long O-antigen chains of Salmonella Paratyphi A inhibit inflammasome activation and pyroptotic cell death. Cell Microbiol. 2021, 23, e13306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campa, C.; Pronce, T.; Paludi, M.; Weusten, J.; Conway, L.; Savery, J.; Richards, C.; Clénet, D. Use of Stability Modeling to Support Accelerated Vaccine Development and Supply. Vaccines 2021, 9, 1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Burden of Disease Collaborative Network. Global Burden of Disease Study 2019; Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME): Seattle, DC, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Baliban, S.M.; Lu, Y.J.; Malley, R. Overview of the Nontyphoidal and Paratyphoidal Salmonella Vaccine Pipeline: Current Status and Future Prospects. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, S151–S154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanetti, G.; MacLennan, C.A.; Micoli, F. Impact and Control of Sugar Size in Glycoconjugate Vaccines. Molecules 2022, 27, 6432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berti, F.; De Ricco, R.; Rappuoli, R. Role of O-Acetylation in the Immunogenicity of Bacterial Polysaccharide Vaccines. Molecules 2018, 23, 1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micoli, F.; Stefanetti, G.; MacLennan, C.A. Exploring the variables influencing the immune response of traditional and innovative glycoconjugate vaccines. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2023, 10, 1201693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svenson, S.B.; Lindberg, A.A. Artificial Salmonella vaccines: Salmonella typhimurium O-antigen-specific oligosaccharide-protein conjugates elicit protective antibodies in rabbits and mice. Infect. Immun. 1981, 32, 490–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rondini, S.; Micoli, F.; Lanzilao, L.; Gavini, M.; Alfini, R.; Brandt, C.; Clare, S.; Mastroeni, P.; Saul, A.; MacLennan, C.A. Design of glycoconjugate vaccines against invasive African Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. Infect. Immun. 2015, 83, 996–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Xiong, K.; Chen, Z.; Hu, X.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Rao, X.; Cong, Y. Construction of an attenuated Salmonella enterica serovar Paratyphi A vaccine strain harboring defined mutations in htrA and yncD. Microbiol. Immunol. 2015, 59, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roland, K.L.; Tinge, S.A.; Kochi, S.K.; Thomas, L.J.; Killeen, K.P. Reactogenicity and immunogenicity of live attenuated Salmonella enterica serovar Paratyphi A enteric fever vaccine candidates. Vaccine 2010, 28, 3679–3687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santander, J.; Curtiss, R., 3rd. Salmonella enterica Serovars Typhi and Paratyphi A are avirulent in newborn and infant mice even when expressing virulence plasmid genes of Salmonella Typhimurium. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries 2010, 4, 723–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| O:2 | Source | MW (Mp) | Glucosylation % | O-acetylation % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O:2[16kDa+100kDa] | ED199 ΔtolR strain | 100 kDa + 16 kDa (mix) | 79.0 | 60.0 |
| O:2[100kDa] O:2[16kDa] | ED199 ΔtolR strain (populations isolated by SEC) | only 100 kDa only 16 kDa | 83.2 85.2 | 47.8 44.0 |
| Nr | Conjugate | O:2 Size (kDa) | Conjugation Conditions (Weight Proportion) | O:2 Activation * | Conjugate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PS | CRM197 | CDAP | % | O:2/CRM197 w/w Ratio ** | |||
| 1 | O:2[16kDa]–CRM197 | 16 | 1 | 2 | 0.2 | nd | 0.25 |
| 2 | O:2[16kDa]–CRM197 | 16 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.2 | nd | 0.37 |
| 3 | O:2[16kDa]–CRM197 | 16 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.5 | nd | 0.62 |
| 4 | O:2[100kDa]–CRM197 | 100 | 1 | 2 | 0.2 | nd | 0.39 |
| 5 | O:2[100kDa]–CRM197 | 100 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.2 | nd | 0.79 |
| 6 | O:2[100kDa]–CRM197 | 100 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.5 | nd | 0.65 |
| 7 | O:2[16kDa+100kDa]–CRM197 | 16 + 100 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.2 | nd | 0.53 |
| 8 | O:2[16kDa+100kDa]–CRM197 | 16 + 100 | 1 | 2 | 0.2 | 3.6 | 0.28 |
| 9 | O:2[16kDa+100kDa]–CRM197 | 16 + 100 | 1 | 2 | 0.5 | 8.6 | 0.22 |
| A (1/s) | E (J/mol) | n | Yinitial (T0) | Yend (T∞) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O-acetylation pH 6.5 | 1.176 × 106 | 77,149.5 | 1 | 42.7 | 2.2 × 10−5 |
| O-acetylation pH 7.4 | 9330 | 59,286.1 | 1.7 | 44.0 | 7.7 |
| Nr | O:2 Size (kDa) | Conjugate | Conjugate O:2/CRM197 w/w Ratio | OAc Level % | Free O:2 % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 16 kDa + 100 kDa | O:2[54% OAc]–CRM197 | 0.69 | 54 | 4.7 |
| 2 | 16 kDa + 100 kDa | O:2[45.2% OAc]–CRM197 | 0.49 | 45.2 | 2.8 |
| 3 | 16 kDa + 100 kDa | O:2[35.3% OAc]–CRM197 | 0.42 | 35.3 | 3.6 |
| 4 | 16 kDa + 100 kDa | O:2[18.5% OAc]–CRM197 | 0.41 | 18.5 | 2.9 |
| 5 | 16 kDa + 100 kDa | O:2[0% OAc]–CRM197 | 0.38 | 0 | 2.5 |
| 6 | 16 kDa | O:2[58.5% OAc]–CRM197 | 0.39 | 58.5 | 6.1 |
| 7 | 16 kDa | O:2[25.2% OAc]–CRM197 | 0.36 | 25.2 | 5.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alfini, R.; Carducci, M.; Massai, L.; De Simone, D.; Mariti, M.; Rossi, O.; Rondini, S.; Micoli, F.; Giannelli, C. Design of a Glycoconjugate Vaccine Against Salmonella Paratyphi A. Vaccines 2024, 12, 1272. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12111272
Alfini R, Carducci M, Massai L, De Simone D, Mariti M, Rossi O, Rondini S, Micoli F, Giannelli C. Design of a Glycoconjugate Vaccine Against Salmonella Paratyphi A. Vaccines. 2024; 12(11):1272. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12111272
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlfini, Renzo, Martina Carducci, Luisa Massai, Daniele De Simone, Marco Mariti, Omar Rossi, Simona Rondini, Francesca Micoli, and Carlo Giannelli. 2024. "Design of a Glycoconjugate Vaccine Against Salmonella Paratyphi A" Vaccines 12, no. 11: 1272. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12111272
APA StyleAlfini, R., Carducci, M., Massai, L., De Simone, D., Mariti, M., Rossi, O., Rondini, S., Micoli, F., & Giannelli, C. (2024). Design of a Glycoconjugate Vaccine Against Salmonella Paratyphi A. Vaccines, 12(11), 1272. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12111272









