Effect of Childhood Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccination on Invasive Disease Serotypes in Serbia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Collection, Identification, and Conservation of Isolates
2.2. Serotyping and Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
2.3. Multilocus Sequence Typing
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
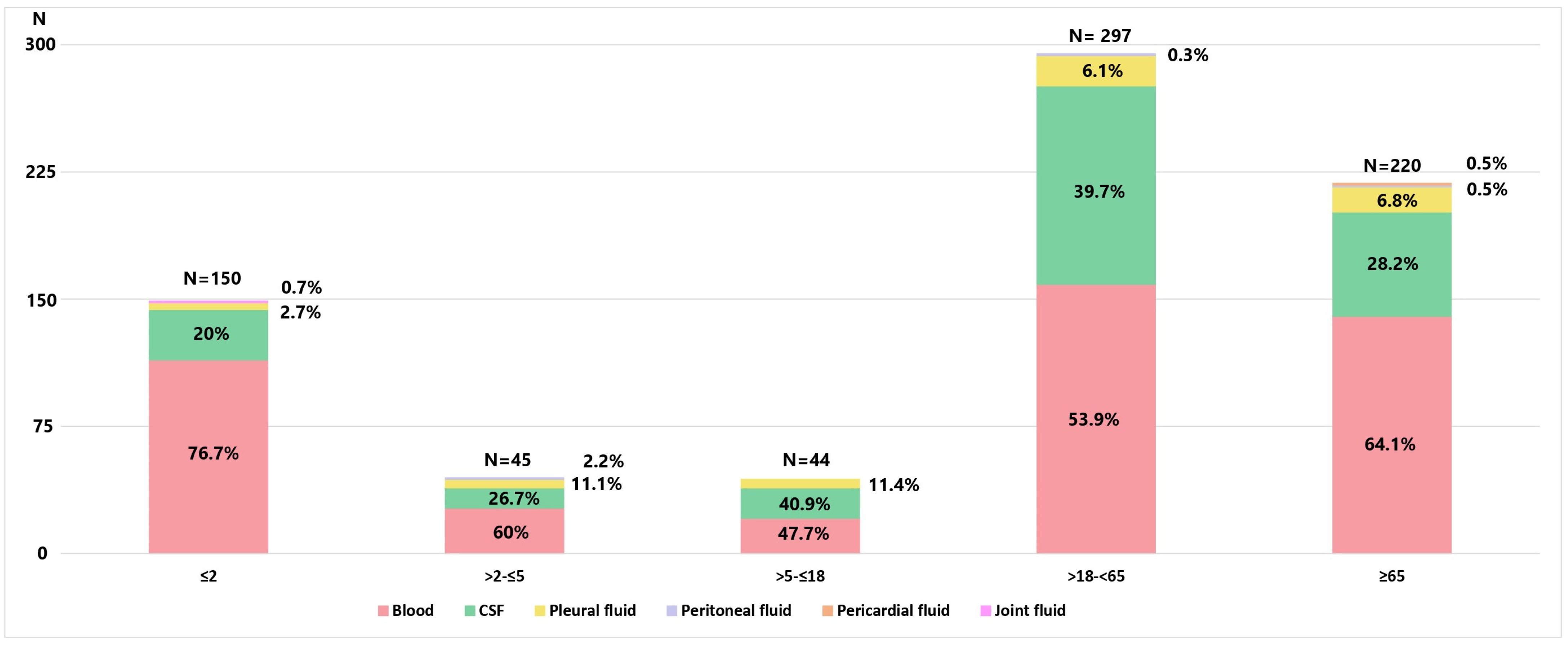
3.1. Bacterial Isolates and Patients’ Characteristics
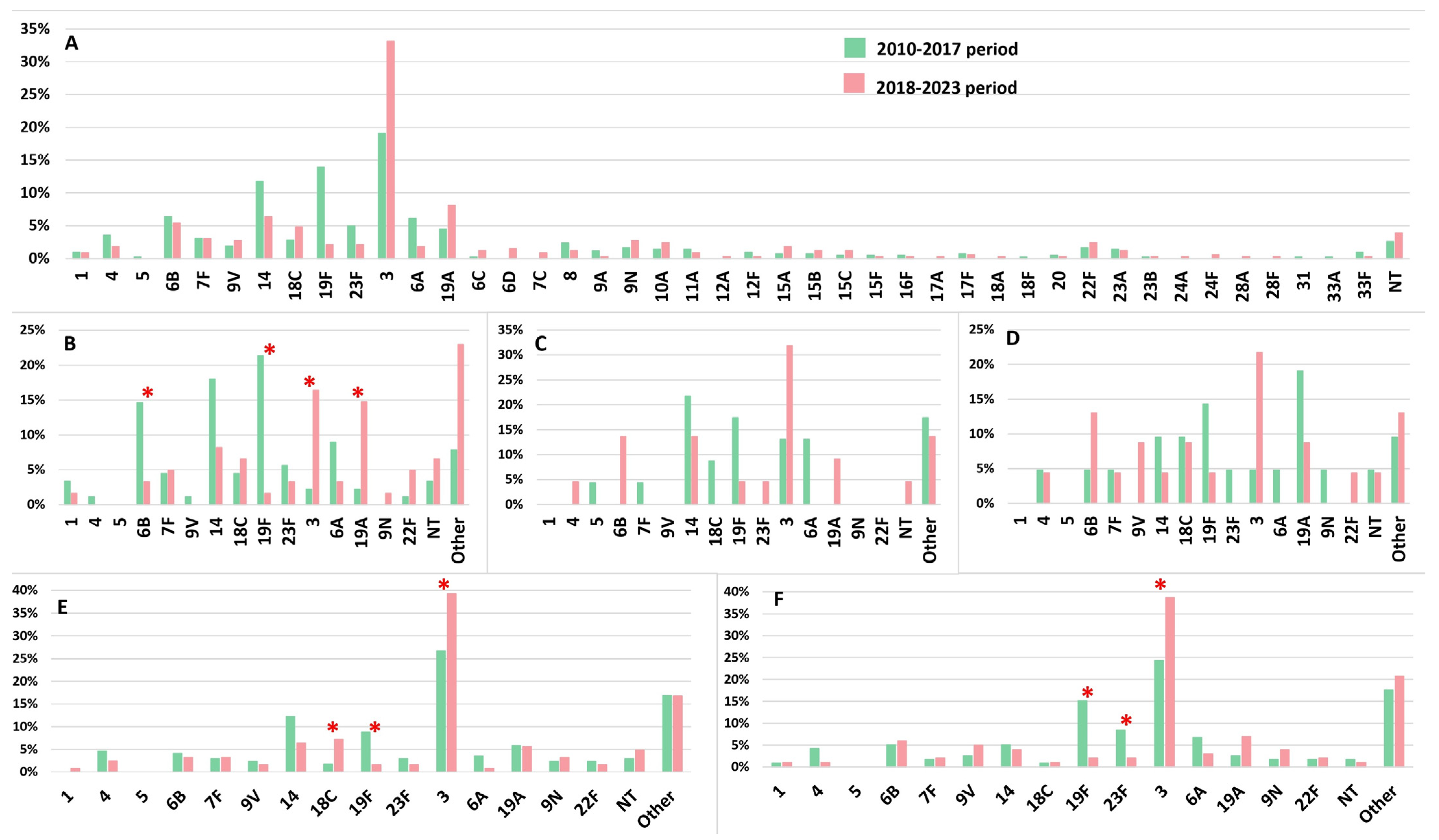
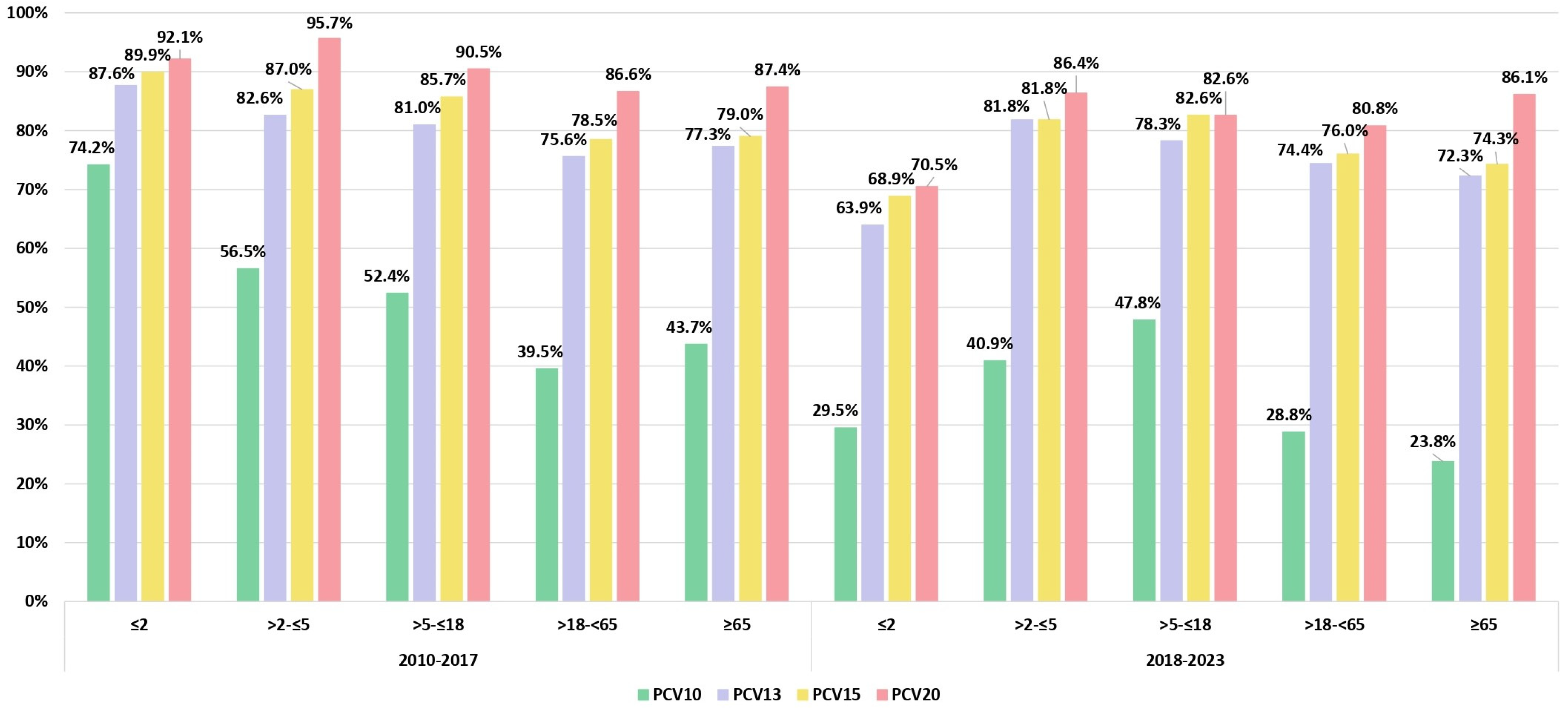
3.2. Serotype Distribution and Serotype Vaccine Coverage Over the Two Study Periods
3.3. Antimicrobial Susceptibility
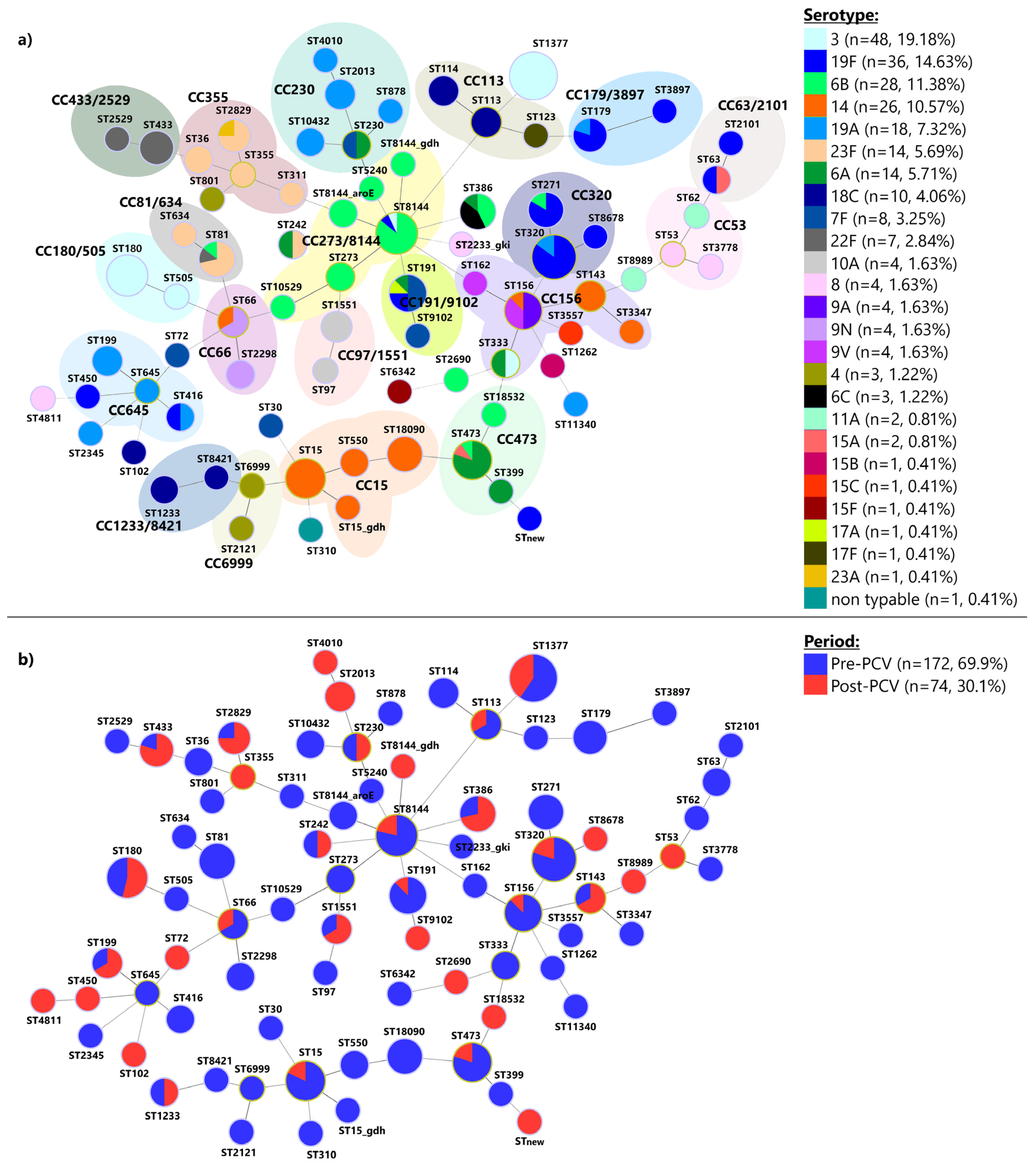
3.4. Multilocus Sequence Typing
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/pneumococcal/php/surveillance/index.html (accessed on 1 July 2024).
- Available online: https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/376776/9789240093461-eng.pdf?sequence=1 (accessed on 1 May 2024).
- Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/vpd/pneumo/hcp/recommendations.html (accessed on 1 May 2024).
- Reyburn, R.; Tsatsaronis, A.; von Mollendorf, C.; Mulholland, K.; Russell, F.M. Systematic Review on the Impact of the Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine Ten Valent (PCV10) or Thirteen Valent (PCV13) on All-Cause, Radiologically Confirmed and Severe Pneumonia Hospitalisation Rates and Pneumonia Mortality in Children 0–9 Years Old. J. Glob. Health 2023, 13, 05002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waight, P.A.; Andrews, N.J.; Ladhani, S.N.; Sheppard, C.L.; Slack, M.P.E.; Miller, E. Effect of the 13-Valent Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine on Invasive Pneumococcal Disease in England and Wales 4 Years after Its Introduction: An Observational Cohort Study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2015, 15, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuck-Paim, C.; Taylor, R.J.; Alonso, W.J.; Weinberger, D.M.; Simonsen, L. Effect of Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine Introduction on Childhood Pneumonia Mortality in Brazil: A Retrospective Observational Study. Lancet Glob. Health 2019, 7, e249–e256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, S.S.; Diekema, D.J.; Heilmann, K.P.; Dohrn, C.L.; Riahi, F.; Doern, G.V. Changes in Pneumococcal Serotypes and Antimicrobial Resistance after Introduction of the 13-Valent Conjugate Vaccine in the United States. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 6484–6489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsaban, G.; Ben-Shimol, S. Indirect (Herd) Protection, Following Pneumococcal Conjugated Vaccines Introduction: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Vaccine 2017, 35, 2882–2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weil-Olivier, C.; van der Linden, M.; de Schutter, I.; Dagan, R.; Mantovani, L. Prevention of Pneumococcal Diseases in the Post-Seven Valent Vaccine Era: A European Perspective. BMC Infect. Dis. 2012, 12, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackenzie, G.A.; Plumb, I.D.; Sambou, S.; Saha, D.; Uchendu, U.; Akinsola, B.; Ikumapayi, U.N.; Baldeh, I.; Usuf, E.; Touray, K.; et al. Monitoring the Introduction of Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccines into West Africa: Design and Implementation of a Population-Based Surveillance System. PLoS Med. 2012, 9, e1001161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.batut.org.rs/index.php?category_id=140 (accessed on 1 May 2024).
- Available online: https://www.paragraf.rs/propisi/pravilnik-o-programu-obavezne-i-preporucene-imunizacije-stanovnistva-protiv-odredjenih-zaraznih-bolesti.html (accessed on 1 May 2024).
- Hanquet, G.; Krizova, P.; Dalby, T.; Ladhani, S.N.; Nuorti, J.P.; Danis, K.; Mereckiene, J.; Knol, M.J.; Winje, B.A.; Ciruela, P.; et al. Serotype Replacement after Introduction of 10-Valent and 13-Valent Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccines in 10 Countries, Europe. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2022, 28, 137–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillespie, S.H.; Ullman, C.; Smith, M.D.; Emery, V. Detection of Streptococcus pneumoniae in sputum samples by PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1994, 32, 1038–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajic, I.; Kabic, J.; Kekic, D.; Jovicevic, M.; Milenkovic, M.; Mitic Culafic, D.; Trudic, A.; Ranin, L.; Opavski, N. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing: A Comprehensive Review of Currently Used Methods. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Breakpoint Tables for Interpretation of MICs and Zone Diameters. Version 13.0. Available online: http://www.eucast.org (accessed on 23 October 2023).
- Mohanty, S.; Johnson, K.D.; Yu, K.C.; Watts, J.A.; Gupta, V. A Multicenter Evaluation of Trends in Antimicrobial Resistance Among Streptococcus Pneumoniae Isolates From Adults in the United States. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2022, 9, ofac420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.-C.; Kuo, K.-C.; Lee, C.-H.; Hsieh, Y.-C.; Tsai, M.-H.; Huang, C.-T.; Huang, Y.-C. The Antimicrobial Susceptibility in Adult Invasive Pneumococcal Disease in the Era of Pneumococcus Vaccination: A Hospital-Based Observational Study in Taiwan. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2020, 53, 836–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cillóniz, C.; Rodríguez-Hurtado, D.; Torres, A. Characteristics and Management of Community-Acquired Pneumonia in the Era of Global Aging. Med. Sci. 2018, 6, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enright, M.C.; Spratt, B.G. A Multilocus Sequence Typing Scheme for Streptococcus Pneumoniae: Identification of Clones Associated with Serious Invasive Disease. Microbiology 1998, 144, 3049–3060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francisco, A.P.; Vaz, C.; Monteiro, P.T.; Melo-Cristino, J.; Ramirez, M.; Carriço, J.A. PHYLOViZ: Phylogenetic Inference and Data Visualization for Sequence Based Typing Methods. BMC Bioinform. 2012, 13, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setchanova, L.; Alexandrova, A.; Pencheva, D.; Sirakov, I.; Mihova, K.; Kaneva, R.; Mitov, I. Rise of Multidrug-Resistant Streptococcus Pneumoniae Clones Expressing Non-Vaccine Serotypes among Children Following Introduction of the 10-Valent Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine in Bulgaria. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2018, 15, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opavski, N.; Jovicevic, M.; Kabic, J.; Kekic, D.; Vasiljevic, Z.; Tosic, T.; Medic, D.; Laban, S.; Ranin, L.; Gajic, I. Serotype Distribution, Antimicrobial Susceptibility and Molecular Epidemiology of Invasive Streptococcus Pneumoniae in the Nine-Year Period in Serbia. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1244366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapidot, R.; Shea, K.; Yildirim, I.; Cabral, H.; Pelton, S.; Massachusetts Department of Public Health. Characteristics of Serotype 3 Invasive Pneumococcal Disease before and after Universal Childhood Immunization with PCV13 in Massachusetts. Pathogens 2020, 9, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sings, H.L.; Gessner, B.D.; Wasserman, M.D.; Jodar, L. Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine Impact on Serotype 3: A Review of Surveillance Data. Infect. Dis. Ther. 2021, 10, 521–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouldali, N.; Varon, E.; Levy, C.; Angoulvant, F.; Georges, S.; Ploy, M.-C.; Kempf, M.; Cremniter, J.; Cohen, R.; Bruhl, D.L.; et al. Invasive Pneumococcal Disease Incidence in Children and Adults in France during the Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine Era: An Interrupted Time-Series Analysis of Data from a 17-Year National Prospective Surveillance Study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oyewole, O.R.-A.; Lang, P.; Albrich, W.C.; Wissel, K.; Leib, S.L.; Casanova, C.; Hilty, M. The Impact of Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine (PCV) Coverage Heterogeneities on the Changing Epidemiology of Invasive Pneumococcal Disease in Switzerland, 2005–2019. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandileone, M.-C.C.; Almeida, S.C.G.; Minamisava, R.; Andrade, A.-L. Distribution of Invasive Streptococcus Pneumoniae Serotypes before and 5 Years after the Introduction of 10-Valent Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine in Brazil. Vaccine 2018, 36, 2559–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, S.C.G.; Lo, S.W.; Hawkins, P.A.; Gladstone, R.A.; Cassiolato, A.P.; Klugman, K.P.; Breiman, R.F.; Bentley, S.D.; McGee, L.; Brandileone, M.-C.d.C. Genomic Surveillance of Invasive Streptococcus Pneumoniae Isolates in the Period Pre-PCV10 and Post-PCV10 Introduction in Brazil. Microb. Genom. 2021, 7, 000635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jokinen, J.; Rinta-Kokko, H.; Siira, L.; Palmu, A.A.; Virtanen, M.J.; Nohynek, H.; Virolainen-Julkunen, A.; Toropainen, M.; Nuorti, J.P. Impact of Ten-Valent Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccination on Invasive Pneumococcal Disease in Finnish Children—A Population-Based Study. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinta-Kokko, H.; Palmu, A.A.; Auranen, K.; Nuorti, J.P.; Toropainen, M.; Siira, L.; Virtanen, M.J.; Nohynek, H.; Jokinen, J. Long-Term Impact of 10-Valent Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccination on Invasive Pneumococcal Disease among Children in Finland. Vaccine 2018, 36, 1934–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savulescu, C.; Krizova, P.; Lepoutre, A.; Mereckiene, J.; Vestrheim, D.F.; Ciruela, P.; Ordobas, M.; Guevara, M.; McDonald, E.; Morfeldt, E.; et al. Effect of High-Valency Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccines on Invasive Pneumococcal Disease in Children in SpIDnet Countries: An Observational Multicentre Study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2017, 5, 648–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepoutre, A.; Varon, E.; Georges, S.; Dorléans, F.; Janoir, C.; Gutmann, L.; Lévy-Bruhl, D. Impact of the Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccines on Invasive Pneumococcal Disease in France, 2001–2012. Vaccine 2015, 33, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skoczyńska, A.; Kuch, A.; Sadowy, E.; Waśko, I.; Markowska, M.; Ronkiewicz, P.; Matynia, B.; Bojarska, A.; Wasiak, K.; Gołębiewska, A.; et al. Recent Trends in Epidemiology of Invasive Pneumococcal Disease in Poland. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2015, 34, 779–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, L.R.; Hanquet, G.; Sepúlveda-Pachón, I.T.; Theilacker, C.; Baay, M.; Slack, M.P.E.; Jodar, L.; Gessner, B.D. Effects of PCV10 and PCV13 on Pneumococcal Serotype 6C Disease, Carriage, and Antimicrobial Resistance. Vaccine 2024, 42, 2983–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahm, M.H.; Oliver, M.B.; Siira, L.; Kaijalainen, T.; Lambertsen, L.M.; Virolainen, A. A Report of Streptococcus Pneumoniae Serotype 6D in Europe. J. Med. Microbiol. 2011, 60, 46–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tin Tin Htar, M.; Christopoulou, D.; Schmitt, H.-J. Pneumococcal Serotype Evolution in Western Europe. BMC Infect. Dis. 2015, 15, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desmet, S.; Peetermans, W.; Lagrou, K. Switch in Childhood Pneumococcal Vaccine in Belgium. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 945–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medic, D.; Bozic Cvijan, B.; Bajcetic, M. Impact of Antibiotic Consumption on Antimicrobial Resistance to Invasive Hospital Pathogens. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anti-Microbial Resistance Surveillance in Europe 2023–2021 Data; European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control and World Health Organization: Stockholm, Sweden, 2023.
- Redin, A.; Ciruela, P.; de Sevilla, M.F.; Gomez-Bertomeu, F.; Gonzalez-Peris, S.; Benitez, M.A.; Trujillo, G.; Diaz, A.; Jou, E.; Izquierdo, C.; et al. Serotypes and Clonal Composition of Streptococcus Pneumoniae Isolates Causing IPD in Children and Adults in Catalonia before 2013 to 2015 and after 2017 to 2019 Systematic Introduction of PCV13. Microbiol. Spectr. 2021, 9, e01150-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cleary, D.W.; Lo, S.W.; Kumar, N.; Bentley, S.D.; Faust, S.N.; Clarke, S.C. Comparative Genomic Epidemiology of Serotype 3 IPD and Carriage Isolates from Southampton, UK between 2005 and 2017. Microb. Genom. 2023, 9, 000945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mott, M.P.; Caierão, J.; Cunha, G.R.; Del Maschi, M.M.; Pizzutti, K.; D’Azevedo, P.; Dias, C.A.G. Emergence of Serotype 19A Streptococcus Pneumoniae after PCV10 Associated with a ST320 in Adult Population, in Porto Alegre, Brazil. Epidemiol. Infect. 2019, 147, e93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, Y.-C.; Lin, T.-L.; Chang, K.-Y.; Huang, Y.-C.; Chen, C.-J.; Lin, T.-Y.; Wang, J.-T. Expansion and Evolution of Streptococcus Pneumoniae Serotype 19A ST320 Clone as Compared to Its Ancestral Clone, Taiwan19F-14 (ST236). J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 208, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
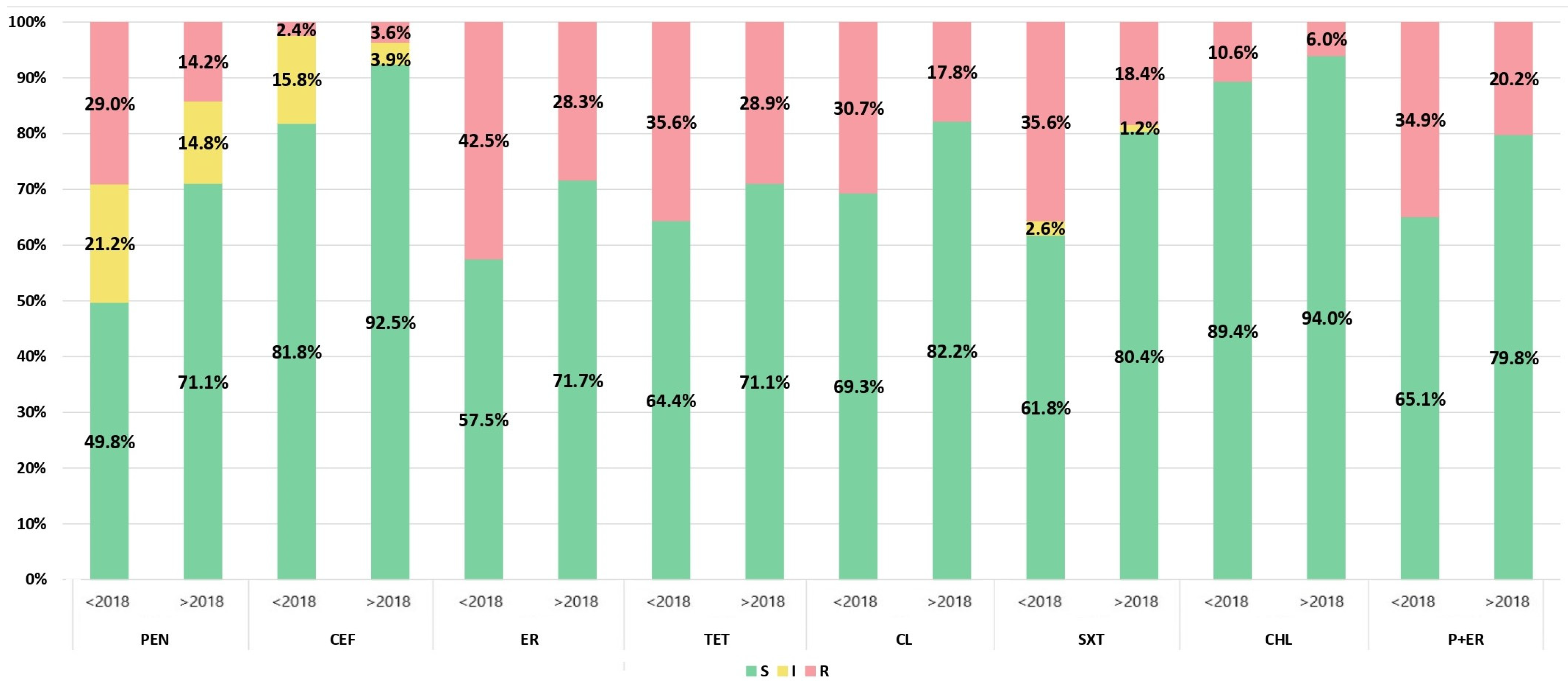
| Serotype | Period (N) | PEN | CEF | ER | TET | CL | SXT | CHL | P+ER | MDR | XDR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 2010–2017 (81) | 9.9% | 2.5% | 4.9% | 6.2% | 3.7% | 3.7% | 1.2% | 1.2% | 1.2% | 1.2% |
| 2018–2023 (110) | 4.5% | 0.0% | 5.5% | 10.9% | 1.8% | 0.9% | 1.8% | 0.0% | 1.8% | 0.0% | |
| 6A | 2010–2017 (26) | 80.8% | 11.5% | 76.9% | 23.1% | 19.2% | 11.5% | 0.0% | 65.4% | 19.2% | 3.8% |
| 2018–2023 (6) | 100.0% | 16.7% | 100.0% | 50.0% | 16.7% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 100.0% | 50.0% | 0.0% | |
| 6B | 2010–2017 (27) | 96.3% | 40.7% | 70.4% | 70.4% | 66.7% | 74.1% | 44.4% | 66.7% | 29.6% | 48.1% |
| 2018–2023 (18) | 66.7% | 5.5% | 61.1% | 55.5% | 50.0% | 50.0% | 50.0% | 50.0% | 33.3% | 33.3% | |
| 14 | 2010–2017 (50) | 94.0% | 30.0% | 62.0% | 34.0% | 56.0% | 90.0% | 20.0% | 58.0% | 28.0% | 34.0% |
| 2018–2023 (21) | 76.2% | 28.6% | 57.1% | 33.3% | 52.4% | 61.9% | 9.5% | 52.4% | 33.3% | 28.6% | |
| 18C | 2010–2017 (15) | 13.3% | 0.0% | 20.0% | 6.7% | 0.0% | 33.3% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% |
| 2018–2023 (16) | 25.0% | 6.3% | 50.0% | 18.8% | 6.3% | 31.3% | 0.0% | 12.5% | 12.5% | 0.0% | |
| 19A | 2010–2017 (19) | 47.4% | 21.1% | 42.1% | 42.1% | 31.6% | 47.4% | 0.0% | 31.6% | 42.1% | 10.5% |
| 2018–2023 (27) | 63.0% | 25.9% | 51.9% | 77.8% | 44.4% | 66.7% | 0.0% | 40.7% | 37.0% | 29.6% | |
| 19F | 2010–2017 (59) | 79.7% | 47.5% | 86.4% | 83.1% | 84.7% | 62.7% | 5.1% | 74.6% | 40.7% | 45.8% |
| 2018–2023 (7) | 57.1% | 42.9% | 57.1% | 71.4% | 57.1% | 42.9% | 0.0% | 57.1% | 14.3% | 42.9% | |
| 23F | 2010–2017 (21) | 81.0% | 33.3% | 61.9% | 71.4% | 19.0% | 52.4% | 38.1% | 57.1% | 38.1% | 33.3% |
| 2018–2023 (7) | 14.3% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 14.3% | 0.0% | 14.3% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 14.3% | 0.0% | |
| Other | 2010–2017 (129) | 27.9% | 5.4% | 24.0% | 24.0% | 12.4% | 22.5% | 8.5% | 16.3% | 16.3% | 4.7% |
| 2018–2023 (120) | 25.8% | 5.8% | 27.5% | 28.3% | 15.8% | 12.5% | 5.8% | 20.0% | 20.0% | 2.5% | |
| Total | 2010–2017 (434) | 50.2% | 18.2% | 42.5% | 35.6% | 30.7% | 38.2% | 10.6% | 34.9% | 21.0% | 17.5% |
| 2018–2023 (332) | 28.9% | 7.5% | 28.3% | 28.9% | 17.8% | 19.6% | 6.0% | 20.2% | 16.9% | 7.8% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Opavski, N.; Jovićević, M.; Kabić, J.; Kekić, D.; Gajić, I.; Study Group for Laboratory Surveillance of Invasive Pneumococcal Diseases. Effect of Childhood Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccination on Invasive Disease Serotypes in Serbia. Vaccines 2024, 12, 940. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12080940
Opavski N, Jovićević M, Kabić J, Kekić D, Gajić I, Study Group for Laboratory Surveillance of Invasive Pneumococcal Diseases. Effect of Childhood Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccination on Invasive Disease Serotypes in Serbia. Vaccines. 2024; 12(8):940. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12080940
Chicago/Turabian StyleOpavski, Nataša, Miloš Jovićević, Jovana Kabić, Dušan Kekić, Ina Gajić, and Study Group for Laboratory Surveillance of Invasive Pneumococcal Diseases. 2024. "Effect of Childhood Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccination on Invasive Disease Serotypes in Serbia" Vaccines 12, no. 8: 940. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12080940
APA StyleOpavski, N., Jovićević, M., Kabić, J., Kekić, D., Gajić, I., & Study Group for Laboratory Surveillance of Invasive Pneumococcal Diseases. (2024). Effect of Childhood Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccination on Invasive Disease Serotypes in Serbia. Vaccines, 12(8), 940. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12080940





