Enhanced Effects of ISA 207 Adjuvant via Intradermal Route in Foot-and-Mouth Disease Vaccine for Pigs
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell and Virus
2.2. Preparation of Experimental Vaccines
2.3. Animal Experimentation
2.3.1. Comparison of the Effects of Different Adjuvants for ID Vaccination in Specific Pathogen-Free Mini Pigs
2.3.2. Comparison of the Effect of Adjuvant ISA 207 in Different Delivery Conditions in SPF Mini Pigs
2.3.3. ID Vaccination in the Field Setting Using Selected Adjuvants and a Needle-Free Device with Pigs from an Ordinary Farm
2.4. Quantification of FMDV RNA in Serum and Nasal Swabs
2.5. ELISA for Detecting FMDV Specific Sero-Conversion
2.6. Virus Neutralization Test
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Immunogenicity of ID Administration Using the FMDV Antigen with Eight Different Adjuvants (Exp 1)
3.2. Clinical Score and Protection, in the Immunized and Challenged Pigs (Exp 2)
3.3. Serological Response in Domestic Pigs Vaccinated Using Selected Adjuvants with a Needle-Free ID Injector (Exp 3)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ibrahim Eel, S.; Gamal, W.M.; Hassan, A.I.; Mahdy Sel, D.; Hegazy, A.Z.; Abdel-Atty, M.M. Comparative study on the immunopotentiator effect of ISA 201, ISA 61, ISA 50, ISA 206 used in trivalent foot and mouth disease vaccine. Vet. World 2015, 8, 1189–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexandersen, S.; Zhang, Z.; Donaldson, A.I.; Garland, A.J. The pathogenesis and diagnosis of foot-and-mouth disease. J. Comp. Pathol. 2003, 129, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiratsudakul, A.; Sekiguchi, S. The implementation of cattle market closure strategies to mitigate the foot-and-mouth disease epidemics: A contact modeling approach. Res. Vet. Sci. 2018, 121, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saravanan, S.; Umapathi, V.; Priyanka, M.; Hosamani, M.; Sreenivasa, B.P.; Patel, B.H.M.; Narayanan, K.; Sanyal, A.; Basagoudanavar, S.H. Hematological and serum biochemical profile in cattle experimentally infected with foot-and-mouth disease virus. Vet. World 2020, 13, 426–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamal, S.M.; Belsham, G.J. Foot-and-mouth disease: Past, present and future. Vet. Res. 2013, 44, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, L.L.; Grubman, M.J. Foot and mouth disease virus vaccines. Vaccine 2009, 27 (Suppl. 4), D90–D94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saiz, M.; Nunez, J.I.; Jimenez-Clavero, M.A.; Baranowski, E.; Sobrino, F. Foot-and-mouth disease virus: Biology and prospects for disease control. Microbes Infect. 2002, 4, 1183–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Lee, K.N.; Ko, Y.J.; Kim, S.M.; Lee, H.S.; Shin, Y.K.; Sohn, H.J.; Park, J.Y.; Yeh, J.Y.; Lee, Y.H.; et al. Control of foot-and-mouth disease during 2010-2011 epidemic, South Korea. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2013, 19, 655–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.H.; Lee, K.N.; Kim, S.M.; Lee, G.; Moon, Y.; Kim, B.; Lee, J.S.; Park, J.H. Needleless intradermal vaccination for foot-and-mouth disease induced granuloma-free effective protection in pigs. J. Vet. Sci. 2019, 20, e29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Mattoo, S.U.S.; Jeong, C.G.; Kim, S.C.; Nazki, S.; Lee, G.; Park, Y.S.; Park, S.Y.; Yang, M.S.; Kim, B.; et al. Intradermal Inoculation of Inactivated Foot-and-Mouth Disease Vaccine Induced Effective Immune Responses Comparable to Conventional Intramuscular Injection in Pigs. Vaccines 2024, 12, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pak, S.-H.C.A.S.-I. Economic burden of foot-and-mouth disease vaccination-induced injection site lesions in slaughtered pigs and its causal relationship. J. Prev. Vet. Med. 2015, 39, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabrizi, F.; Andrulli, S.; Bacchini, G.; Corti, M.; Locatelli, F. Intradermal versus intramuscular hepatitis b re-vaccination in non-responsive chronic dialysis patients: A prospective randomized study with cost-effectiveness evaluation. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 1997, 12, 1204–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vannier, P.; Cariolet, R. Vaccination of pigs against Aujeszky’s disease by the intradermal route using live attenuated and inactivated virus vaccines. Zentralbl Vet. B 1989, 36, 515–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoft, D.F.; Blazevic, A.; Abate, G.; Hanekom, W.A.; Kaplan, G.; Soler, J.H.; Weichold, F.; Geiter, L.; Sadoff, J.C.; Horwitz, M.A. A new recombinant bacille Calmette-Guerin vaccine safely induces significantly enhanced tuberculosis-specific immunity in human volunteers. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 198, 1491–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shmeleva, E.V.; Gomez de Aguero, M.; Wagner, J.; Enright, A.J.; Macpherson, A.J.; Ferguson, B.J.; Smith, G.L. Smallpox vaccination induces a substantial increase in commensal skin bacteria that promote pathology and influence the host response. PLoS Pathog. 2022, 18, e1009854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eble, P.L.; Weerdmeester, K.; van Hemert-Kluitenberg, F.; Dekker, A. Intradermal vaccination of pigs against FMD with 1/10 dose results in comparable vaccine efficacy as intramuscular vaccination with a full dose. Vaccine 2009, 27, 1272–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Luduec, J.B.; Debeer, S.; Piras, F.; Andreoni, C.; Boudet, F.; Laurent, P.; Kaiserlian, D.; Dubois, B. Intradermal vaccination with un-adjuvanted sub-unit vaccines triggers skin innate immunity and confers protective respiratory immunity in domestic swine. Vaccine 2016, 34, 914–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandya, M.; Pacheco, J.M.; Bishop, E.; Kenney, M.; Milward, F.; Doel, T.; Golde, W.T. An alternate delivery system improves vaccine performance against foot-and-mouth disease virus (FMDV). Vaccine 2012, 30, 3106–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, L.; Borghetti, P.; Gozio, S.; De Angelis, E.; Ballotta, L.; Smeets, J.; Blanchaert, A.; Martelli, P. Evaluation of the immune response induced by intradermal vaccination by using a needle-less system in comparison with the intramuscular route in conventional pigs. Res. Vet. Sci. 2011, 90, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.W.; Cho, G.; Kim, H.; Lee, G.; Lim, T.G.; Kwak, H.Y.; Park, J.H.; Park, S.H. Immunogenicity and Protection against Foot-and-Mouth Disease Virus in Swine Intradermally Vaccinated with a Bivalent Vaccine of Foot-and-Mouth Disease Virus Type O and A. Vaccines 2023, 11, 815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishnan, M.A. Determination of 50% endpoint titer using a simple formula. World J. Virol. 2016, 5, 85–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norman, J.J.; Gupta, J.; Patel, S.R.; Park, S.; Jarrahian, C.; Zehrung, D.; Prausnitz, M.R. Reliability and accuracy of intradermal injection by Mantoux technique, hypodermic needle adapter, and hollow microneedle in pigs. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2014, 4, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, M.P.; Guzylack-Piriou, L.; Juillard, V.; Audonnet, J.C.; Doel, T.; Dawson, H.; Golde, W.T.; Gerber, H.; Peduto, N.; McCullough, K.C.; et al. Innate immune defenses induced by CpG do not promote vaccine-induced protection against foot-and-mouth disease virus in pigs. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2009, 16, 1151–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fowler, V.L.; Knowles, N.J.; Paton, D.J.; Barnett, P.V. Marker vaccine potential of a foot-and-mouth disease virus with a partial VP1 G-H loop deletion. Vaccine 2010, 28, 3428–3434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barteling, S.J.; Vreeswijk, J. Developments in foot-and-mouth disease vaccines. Vaccine 1991, 9, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H. Requirements for improved vaccines against foot-and-mouth disease epidemics. Clin. Exp. Vaccine Res. 2013, 2, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aucouturier, J.; Dupuis, L.; Ganne, V. Adjuvants designed for veterinary and human vaccines. Vaccine 2001, 19, 2666–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burakova, Y.; Madera, R.; McVey, S.; Schlup, J.R.; Shi, J. Adjuvants for Animal Vaccines. Viral Immunol. 2018, 31, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.H.; You, S.H.; Ko, M.K.; Jo, H.E.; Shin, S.H.; Jo, H.; Lee, M.J.; Kim, S.M.; Kim, B.; Lee, J.S.; et al. Improved immune responses and safety of foot-and-mouth disease vaccine containing immunostimulating components in pigs. J. Vet. Sci. 2020, 21, e74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oda, K.; Tsukahara, F.; Kubota, S.; Kida, K.; Kitajima, T.; Hashimoto, S. Emulsifier content and side effects of oil-based adjuvant vaccine in swine. Res. Vet. Sci. 2006, 81, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martelli, P.; Cordioli, P.; Alborali, L.G.; Gozio, S.; De Angelis, E.; Ferrari, L.; Lombardi, G.; Borghetti, P. Protection and immune response in pigs intradermally vaccinated against porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome (PRRS) and subsequently exposed to a heterologous European (Italian cluster) field strain. Vaccine 2007, 25, 3400–3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Rooij, E.M.; Haagmans, B.L.; de Visser, Y.E.; de Bruin, M.G.; Boersma, W.; Bianchi, A.T. Effect of vaccination route and composition of DNA vaccine on the induction of protective immunity against pseudorabies infection in pigs. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1998, 66, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christopher C., L. Chase, D., MS, PhD; C. Scanlon Daniels, DVM, MBA; Roberto Garcia, DVM, MS; Frank Milward, DVM, MS; Tiffany Nation, DVM, MS. Needle-free injection technology in swine: Progress toward vaccine efficacy and pork quality. J. Swine Health Prod. 2008, 16, 254–261. [Google Scholar]
- Madapong, A.; Saeng-Chuto, K.; Chaikhumwang, P.; Tantituvanont, A.; Saardrak, K.; Pedrazuela Sanz, R.; Miranda Alvarez, J.; Nilubol, D. Immune response and protective efficacy of intramuscular and intradermal vaccination with porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus 1 (PRRSV-1) modified live vaccine against highly pathogenic PRRSV-2 (HP-PRRSV-2) challenge, either alone or in combination with of PRRSV-1. Vet. Microbiol. 2020, 244, 108655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temple, D.; Escribano, D.; Jimenez, M.; Mainau, E.; Ceron, J.J.; Manteca, X. Effect of the needle-free “intra dermal application of liquids” vaccination on the welfare of pregnant sows. Porc. Health Manag. 2017, 3, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
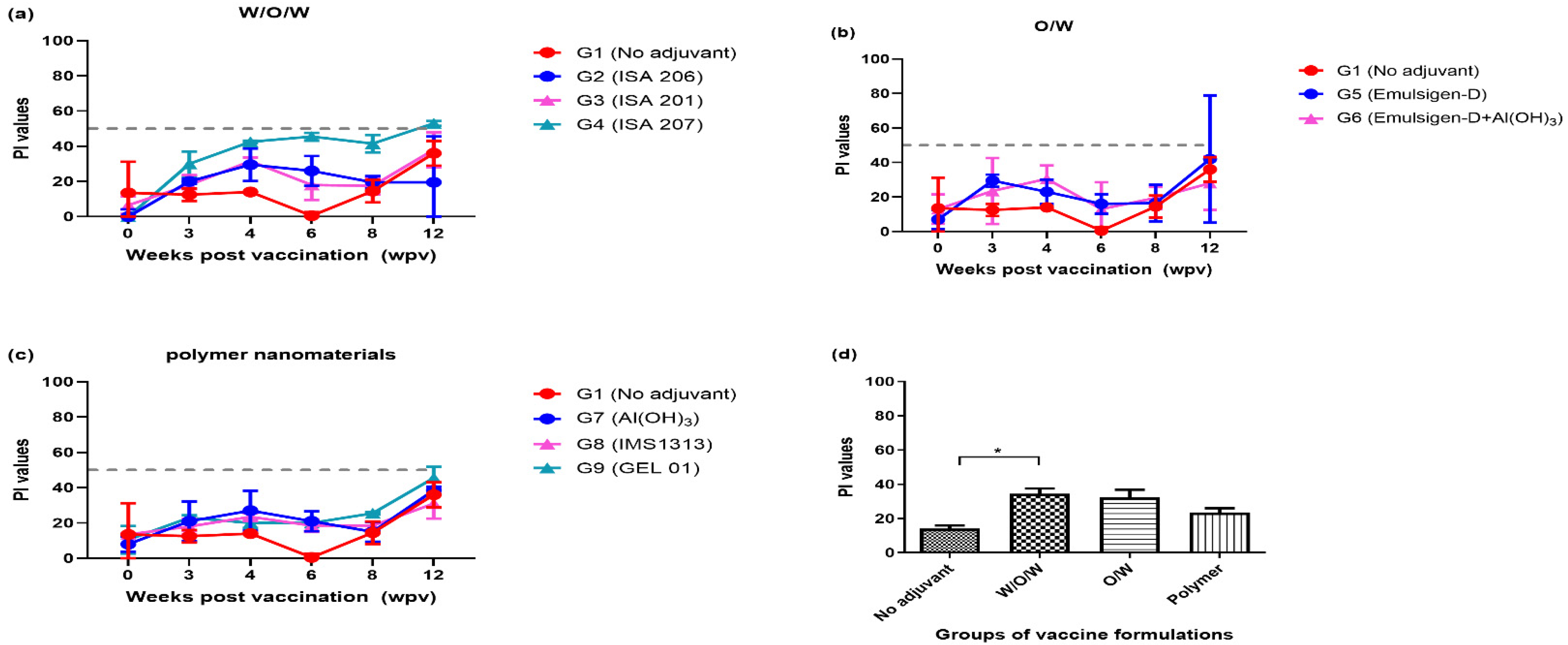

| Exp No. | Groups | Identification of Pigs | Antigen Payload (μg/head) | Adjuvants | Administration Route | Injected Volume/Dose (mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exp1 SPF/N | G1 | #26, #20 | 12 | No | ID | 0.2 |
| G2 | #19, #21 | 12 | ISA 206 | ID | 0.2 | |
| G3 | #23, #24 | 12 | ISA 201 | ID | 0.2 | |
| G4 | #25, #11 | 12 | ISA 207 | ID | 0.2 | |
| G5 | #8, #12 | 12 | Emulsigen-D | ID | 0.2 | |
| G6 | #27, #22 | 12 | Emulsigen-D + Al(OH)3 | ID | 0.2 | |
| G7 | #9, #15 | 12 | Al(OH)3 | ID | 0.2 | |
| G8 | #17, #13 | 12 | IMS1313 | ID | 0.2 | |
| G9 | #16, #14 | 12 | GEL 01 | ID | 0.2 | |
| Exp2 SPF/N | C1 | #77, #83, #89 | 12 | ISA 207 | ID | 0.2 |
| C2 | #78, #84, #90 | 1.2 | ISA 207 | ID | 0.2 | |
| C3 | #79, #85, #91 | 12 | ISA 207 | IM | 1 | |
| C4 | #80, #86, #74 | 1.2 | ISA 207 | IM | 1 | |
| C5 | #2 | No | ISA 207 | ID | 0.2 | |
| C6 | #3 | No | ISA 207 | IM | 1 | |
| Exp3 FP/NFD | F1 | #2, #3, #6, #9, #10 | 12 | ISA 207 | ID | 0.2 |
| F2 | #21, #22, #23, #27, #29 | 12 | ISA 201 | ID | 0.2 | |
| F3 | #14, #15, #16, #18, #19 | No | ISA 207 | ID | 0.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hwang, J.-h.; Lee, K.-N.; Kim, S.-M.; Kim, H.; Park, S.-H.; Kim, D.-W.; Cho, G.; Lee, Y.-H.; Lee, J.-S.; Park, J.-H. Enhanced Effects of ISA 207 Adjuvant via Intradermal Route in Foot-and-Mouth Disease Vaccine for Pigs. Vaccines 2024, 12, 963. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12090963
Hwang J-h, Lee K-N, Kim S-M, Kim H, Park S-H, Kim D-W, Cho G, Lee Y-H, Lee J-S, Park J-H. Enhanced Effects of ISA 207 Adjuvant via Intradermal Route in Foot-and-Mouth Disease Vaccine for Pigs. Vaccines. 2024; 12(9):963. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12090963
Chicago/Turabian StyleHwang, Ji-hyeon, Kwang-Nyeong Lee, Su-Mi Kim, Hyejin Kim, Sung-Han Park, Dong-Wan Kim, Giyoun Cho, Yoon-Hee Lee, Jong-Soo Lee, and Jong-Hyeon Park. 2024. "Enhanced Effects of ISA 207 Adjuvant via Intradermal Route in Foot-and-Mouth Disease Vaccine for Pigs" Vaccines 12, no. 9: 963. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12090963
APA StyleHwang, J. -h., Lee, K. -N., Kim, S. -M., Kim, H., Park, S. -H., Kim, D. -W., Cho, G., Lee, Y. -H., Lee, J. -S., & Park, J. -H. (2024). Enhanced Effects of ISA 207 Adjuvant via Intradermal Route in Foot-and-Mouth Disease Vaccine for Pigs. Vaccines, 12(9), 963. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12090963








