The Salmonella Paratyphi A O-Antigen Glycoconjugate Vaccine Is Able to Induce Antibodies with Bactericidal Activity Against a Panel of Clinical Isolates
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains
2.2. Conjugates Formulation
2.3. Animal Studies
2.4. Ethics and 3R Statement
2.5. O-Antigen Extraction and Characterization
2.6. Flow Cytometry Binding Assay
2.7. Luminescence-Based Serum Bactericidal Assay
3. Results
3.1. S. Paratyphi A Isolates Express OAg with Different Levels of O-Acetylation, Glucosylation, and Molecular Weight
3.2. Sera Raised Against O:2 CRM197 Conjugates Are Able to Bind and Kill Clinical Isolates with Different OAg Characteristics
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- The global burden of typhoid and paratyphoid fevers: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 369–381. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crump, J.A.; Sjölund-Karlsson, M.; Gordon, M.A.; Parry, C.M. Epidemiology, Clinical Presentation, Laboratory Diagnosis, Antimicrobial Resistance, and Antimicrobial Management of Invasive Salmonella Infections. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 28, 901–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, A.J.; Kashef Hamadani, B.H.; Kumaran, E.A.P.; Rao, P.; Longbottom, J.; Harriss, E.; Moore, C.E.; Dunachie, S.; Basnyat, B.; Baker, S.; et al. Drug-resistant enteric fever worldwide, 1990 to 2018: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Med. 2020, 18, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, J.; Thada, P.K.; Hashmi, M.F.; DeVos, E. Typhoid Fever. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing LLC.: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Deen, J.; von Seidlein, L.; Andersen, F.; Elle, N.; White, N.J.; Lubell, Y. Community-acquired bacterial bloodstream infections in developing countries in south and southeast Asia: A systematic review. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2012, 12, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pieters, Z.; Saad, N.J.; Antillón, M.; Pitzer, V.E.; Bilcke, J. Case Fatality Rate of Enteric Fever in Endemic Countries: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 67, 628–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maskey, A.P.; Day, J.N.; Phung, Q.T.; Thwaites, G.E.; Campbell, J.I.; Zimmerman, M.; Farrar, J.J.; Basnyat, B. Salmonella enterica serovar Paratyphi A and S. enterica serovar Typhi cause indistinguishable clinical syndromes in Kathmandu, Nepal. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2006, 42, 1247–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ochiai, R.L.; Wang, X.; von Seidlein, L.; Yang, J.; Bhutta, Z.A.; Bhattacharya, S.K.; Agtini, M.; Deen, J.L.; Wain, J.; Kim, D.R.; et al. Salmonella paratyphi A rates, Asia. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2005, 11, 1764–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fangtham, M.; Wilde, H. Emergence of Salmonella paratyphi A as a major cause of enteric fever: Need for early detection, preventive measures, and effective vaccines. J. Travel Med. 2008, 15, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parry, C.M.; Vinh, H.; Chinh, N.T.; Wain, J.; Campbell, J.I.; Hien, T.T.; Farrar, J.J.; Baker, S. The influence of reduced susceptibility to fluoroquinolones in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi on the clinical response to ofloxacin therapy. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2011, 5, e1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walia, M.; Gaind, R.; Mehta, R.; Paul, P.; Aggarwal, P.; Kalaivani, M. Current perspectives of enteric fever: A hospital-based study from India. Ann. Trop. Paediatr. 2005, 25, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burki, T. Typhoid conjugate vaccine gets WHO prequalification. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, P.D.; Liang, Y.; Meiring, J.E.; Chasweka, N.; Patel, P.; Misiri, T.; Mwakiseghile, F.; Wachepa, R.; Banda, H.C.; Shumba, F.; et al. Efficacy of typhoid conjugate vaccine: Final analysis of a 4-year, phase 3, randomised controlled trial in Malawian children. Lancet 2024, 403, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steele, A.D.; Carey, M.E.; Kumar, S.; MacLennan, C.A.; Ma, L.F.; Diaz, Z.; Zaidi, A.K.M. Typhoid Conjugate Vaccines and Enteric Fever Control: Where to Next? Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71 (Suppl. S2), S185–S190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibani, M.M. Towards a marketplace for Vi polysaccharide-conjugate typhoid vaccines. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, 435–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darton, T.C.; Meiring, J.E.; Tonks, S.; Khan, M.A.; Khanam, F.; Shakya, M.; Thindwa, D.; Baker, S.; Basnyat, B.; Clemens, J.D.; et al. The STRATAA study protocol: A programme to assess the burden of enteric fever in Bangladesh, Malawi and Nepal using prospective population census, passive surveillance, serological studies and healthcare utilisation surveys. BMJ Open 2017, 7, e016283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, B.Q.; Yang, J.; Wang, X.Y.; Gong, J.; von Seidlein, L.; Wang, M.L.; Lin, M.; Liao, H.Z.; Ochiai, R.L.; Xu, Z.Y.; et al. Trends and disease burden of enteric fever in Guangxi province, China, 1994–2004. Bull. World Health Organ. 2010, 88, 689–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacLennan, C.A.; Stanaway, J.; Grow, S.; Vannice, K.; Steele, A.D. Salmonella Combination Vaccines: Moving Beyond Typhoid. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2023, 10 (Suppl. S1), S58–S66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Micoli, F.; Bjarnarson, S.P.; Arcuri, M.; Aradottir Pind, A.A.; Magnusdottir, G.J.; Necchi, F.; Di Benedetto, R.; Carducci, M.; Schiavo, F.; Giannelli, C.; et al. Short Vi-polysaccharide abrogates T-independent immune response and hyporesponsiveness elicited by long Vi-CRM(197) conjugate vaccine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 24443–24449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcuri, M.; Di Benedetto, R.; Cunningham, A.F.; Saul, A.; MacLennan, C.A.; Micoli, F. The influence of conjugation variables on the design and immunogenicity of a glycoconjugate vaccine against Salmonella Typhi. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0189100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfini, R.; Carducci, M.; Massai, L.; De Simone, D.; Mariti, M.; Rossi, O.; Rondini, S.; Micoli, F.; Giannelli, C. Design of a Glycoconjugate Vaccine Against Salmonella Paratyphi A. Vaccines 2024, 12, 1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravenscroft, N.; Cescutti, P.; Gavini, M.; Stefanetti, G.; MacLennan, C.A.; Martin, L.B.; Micoli, F. Structural analysis of the O-acetylated O-polysaccharide isolated from Salmonella paratyphi A and used for vaccine preparation. Carbohydr. Res. 2015, 404, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konadu, E.; Shiloach, J.; Bryla, D.A.; Robbins, J.B.; Szu, S.C. Synthesis, characterization, and immunological properties in mice of conjugates composed of detoxified lipopolysaccharide of Salmonella paratyphi A bound to tetanus toxoid with emphasis on the role of O acetyls. Infect. Immun. 1996, 64, 2709–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mylona, E.; Pereira-Dias, J.; Keane, J.A.; Karkey, A.; Dongol, S.; Khokhar, F.; Tran, T.A.; Cormie, C.; Higginson, E.; Baker, S. Phenotypic variation in the lipopolysaccharide O-antigen of Salmonella Paratyphi A and implications for vaccine development. Vaccine 2024, 42, 126404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Necchi, F.; Saul, A.; Rondini, S. Development of a high-throughput method to evaluate serum bactericidal activity using bacterial ATP measurement as survival readout. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0172163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mylona, E.; Pham Thanh, D.; Keane, J.A.; Dongol, S.; Basnyat, B.; Dolecek, C.; Voong Vinh, P.; Tran Vu Thieu, N.; Nguyen Thi Nguyen, T.; Karkey, A.; et al. A retrospective investigation of the population structure and geospatial distribution of Salmonella Paratyphi A in Kathmandu, Nepal. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2024, 18, e0011864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobinson, H.C.; Gibani, M.M.; Jones, C.; Thomaides-Brears, H.B.; Voysey, M.; Darton, T.C.; Waddington, C.S.; Campbell, D.; Milligan, I.; Zhou, L.; et al. Evaluation of the Clinical and Microbiological Response to Salmonella Paratyphi A Infection in the First Paratyphoid Human Challenge Model. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 64, 1066–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francesca Micoli, C.G.; Di Benedetto, R. Vaccine Delivery Technology. In Methods in Molecular Biology; Walker, J.M., Ed.; Humana: New York, NY, USA, 2021; p. 590. [Google Scholar]
- Micoli, F.; Alfini, R.; Giannelli, C. Methods for Assessment of OMV/GMMA Quality and Stability. Methods Mol. Biol. 2022, 2414, 227–279. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, L.B.; Khanam, F.; Qadri, F.; Khalil, I.; Sikorski, M.J.; Baker, S. Vaccine value profile for Salmonella enterica serovar Paratyphi A. Vaccine 2023, 41 (Suppl. S2), S114–S133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooda, Y.; Tanmoy, A.M.; Saha, S.K.; Saha, S. Genomic Surveillance of Salmonella Paratyphi A: Neglected No More? Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2023, 10 (Suppl. S1), S53–S57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, S.I.A.; Nguyen, T.N.T.; Khanam, F.; Thomson, N.R.; Dyson, Z.A.; Taylor-Brown, A.; Chowdhury, E.K.; Dougan, G.; Baker, S.; Qadri, F. Genetic diversity of Salmonella Paratyphi A isolated from enteric fever patients in Bangladesh from 2008 to 2018. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0009748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClelland, M.; Sanderson, K.E.; Clifton, S.W.; Latreille, P.; Porwollik, S.; Sabo, A.; Meyer, R.; Bieri, T.; Ozersky, P.; McLellan, M.; et al. Comparison of genome degradation in Paratyphi A and Typhi, human-restricted serovars of Salmonella enterica that cause typhoid. Nat. Genet. 2004, 36, 1268–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Puyvelde, S.; Gasperini, G.; Biggel, M.; Phoba, M.F.; Raso, M.M.; de Block, T.; Vanheer, L.N.; Deborggraeve, S.; Vandenberg, O.; Thomson, N.; et al. Genetic and Structural Variation in the O-Antigen of Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium Isolates Causing Bloodstream Infections in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. mBio 2022, 13, e0037422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Micoli, F.; Rondini, S.; Alfini, R.; Lanzilao, L.; Necchi, F.; Negrea, A.; Rossi, O.; Brandt, C.; Clare, S.; Mastroeni, P.; et al. Comparative immunogenicity and efficacy of equivalent outer membrane vesicle and glycoconjugate vaccines against nontyphoidal Salmonella. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 10428–10433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giersing, B.K.; Isbrucker, R.; Kaslow, D.C.; Cavaleri, M.; Baylor, N.; Maiga, D.; Pavlinac, P.B.; Riddle, M.S.; Kang, G.; MacLennan, C.A. Clinical and regulatory development strategies for Shigella vaccines intended for children younger than 5 years in low-income and middle-income countries. Lancet Glob. Health 2023, 11, e1819–e1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.; Tennant, S.M.; Simon, R.; Cross, A.S. Progress towards the development of Klebsiella vaccines. Expert. Rev. Vaccines 2019, 18, 681–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kintz, E.; Heiss, C.; Black, I.; Donohue, N.; Brown, N.; Davies, M.R.; Azadi, P.; Baker, S.; Kaye, P.M.; van der Woude, M. Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhi Lipopolysaccharide O-Antigen Modification Impact on Serum Resistance and Antibody Recognition. Infect. Immun. 2017, 85, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, G.L.; Attridge, S.R.; Morona, R. Regulation of Salmonella typhimurium lipopolysaccharide O antigen chain length is required for virulence; identification of FepE as a second Wzz. Mol. Microbiol. 2003, 47, 1395–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rondini, S.; Micoli, F.; Lanzilao, L.; Gavini, M.; Alfini, R.; Brandt, C.; Clare, S.; Mastroeni, P.; Saul, A.; MacLennan, C.A. Design of glycoconjugate vaccines against invasive African Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. Infect. Immun. 2015, 83, 996–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baliban, S.M.; Yang, M.; Ramachandran, G.; Curtis, B.; Shridhar, S.; Laufer, R.S.; Wang, J.Y.; Van Druff, J.; Higginson, E.E.; Hegerle, N.; et al. Development of a glycoconjugate vaccine to prevent invasive Salmonella Typhimurium infections in sub-Saharan Africa. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvis, F.G.; Mesenko, M.T.; Martin, D.G.; Perrine, T.D. Physiochemical properties of the Vi antigen before and after mild alkaline hydrolysis. J. Bacteriol. 1967, 94, 1406–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szewczyk, B.; Taylor, A. Immunochemical properties of Vi antigen from Salmonella typhi Ty2: Presence of two antigenic determinants. Infect. Immun. 1980, 29, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berti, F.; De Ricco, R.; Rappuoli, R. Role of O-Acetylation in the Immunogenicity of Bacterial Polysaccharide Vaccines. Molecules 2018, 23, 1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



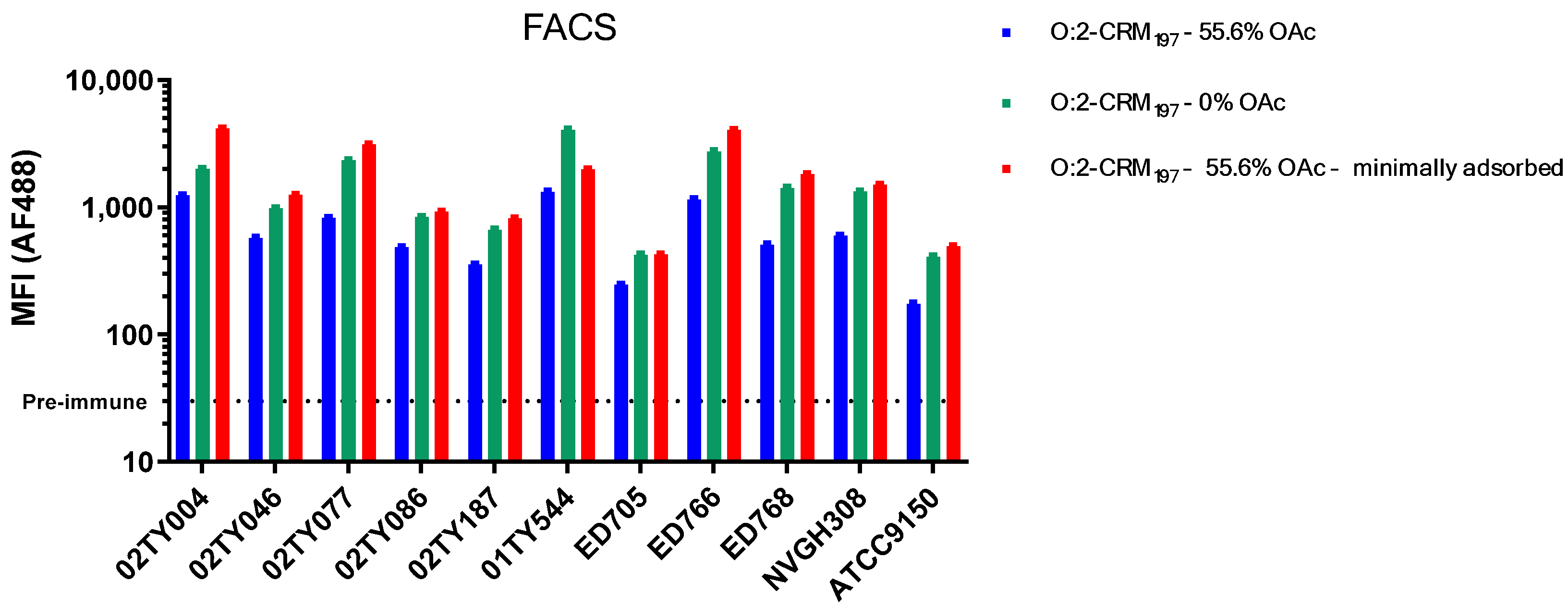
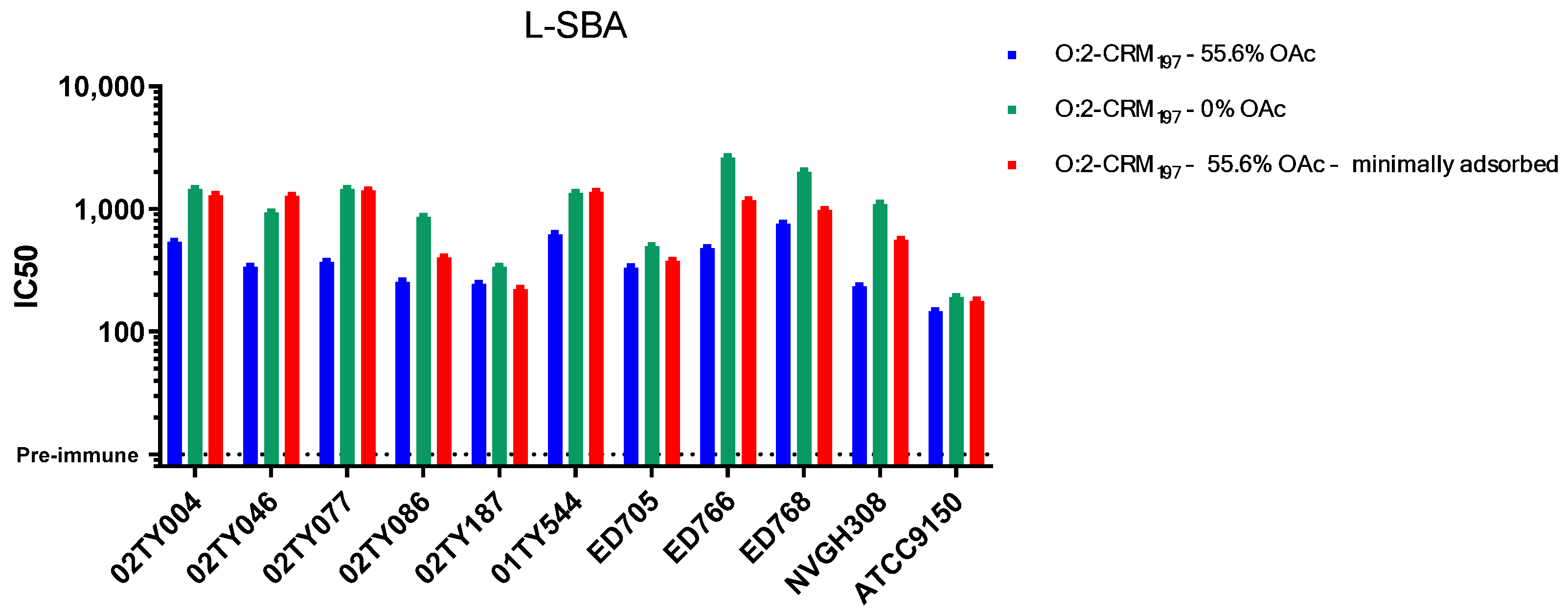
| Isolate ID | OAg µg/OD | Size (kDa) | %OAc * | %Glc * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HMW | MMW; Core | ||||
| 02TY004 | 307 | 111.3 | 11.4; 3.1 | 90 | 64 |
| 02TY046 | 396 | 94.4 | 2.4 | 61 | 76 |
| 02TY077 | 255 | 98.5 | 10.1; 2.6 | 75 | 88 |
| 02TY086 | 263 | 84.3 | 11.1; 2.5 | 94 | 51 |
| 02TY187 | 195 | 85.0 | 11.9; 2.5 | 54 | 51 |
| 01TY544 | 273 | 96.3 | 13.0; 3.2 | 87 | 89 |
| ED705 | 65 | 975 | 8.6; 2.7 | 73 | 49 |
| ED766 | 139 | 91.6 | 10.4; 2.7 | 100 | 79 |
| ED768 | 245 | 92.0 | 11.0; 2.5 | 37 | 95 |
| ATCC9150 | 44 | 99.7 | 6.6; 2.6 | 17 | 57 |
| NVGH308 | 219 | 86.1 | 2.5 | 61 | 78 |
| Entry n | Conjugate Formulation | O:2 O-Acetylation | Conjugate Adsorption on Alhydrogel | Osmolality mOsm/kg | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | O:2-CRM197–55.6% OAc | 55.6% | 98.1% | 278 | 7.76 |
| 2 | O:2-CRM197–not OAc | 0% | 99.0% | 298 | 7.45 |
| 3 | O:2-CRM197–55.6% OAc–minimally adsorbed | 55.6% | 14.1% | 282 | 7.67 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pinto, M.; Durante, S.; Carducci, M.; Massai, L.; Alfini, R.; Mylona, E.; Karkey, A.; Baker, S.; Micoli, F.; Giannelli, C.; et al. The Salmonella Paratyphi A O-Antigen Glycoconjugate Vaccine Is Able to Induce Antibodies with Bactericidal Activity Against a Panel of Clinical Isolates. Vaccines 2025, 13, 122. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13020122
Pinto M, Durante S, Carducci M, Massai L, Alfini R, Mylona E, Karkey A, Baker S, Micoli F, Giannelli C, et al. The Salmonella Paratyphi A O-Antigen Glycoconjugate Vaccine Is Able to Induce Antibodies with Bactericidal Activity Against a Panel of Clinical Isolates. Vaccines. 2025; 13(2):122. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13020122
Chicago/Turabian StylePinto, Marika, Salvatore Durante, Martina Carducci, Luisa Massai, Renzo Alfini, Elli Mylona, Abhilasha Karkey, Stephen Baker, Francesca Micoli, Carlo Giannelli, and et al. 2025. "The Salmonella Paratyphi A O-Antigen Glycoconjugate Vaccine Is Able to Induce Antibodies with Bactericidal Activity Against a Panel of Clinical Isolates" Vaccines 13, no. 2: 122. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13020122
APA StylePinto, M., Durante, S., Carducci, M., Massai, L., Alfini, R., Mylona, E., Karkey, A., Baker, S., Micoli, F., Giannelli, C., Rossi, O., & Rondini, S. (2025). The Salmonella Paratyphi A O-Antigen Glycoconjugate Vaccine Is Able to Induce Antibodies with Bactericidal Activity Against a Panel of Clinical Isolates. Vaccines, 13(2), 122. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13020122








