M2e/NP Dual Epitope-Displaying Nanoparticles Enhance Cross-Protection of Recombinant HA Influenza Vaccine: A Universal Boosting Strategy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Viruses, Competent Cells, and Animals
2.2. NP Protein T-Cell Epitope Prediction
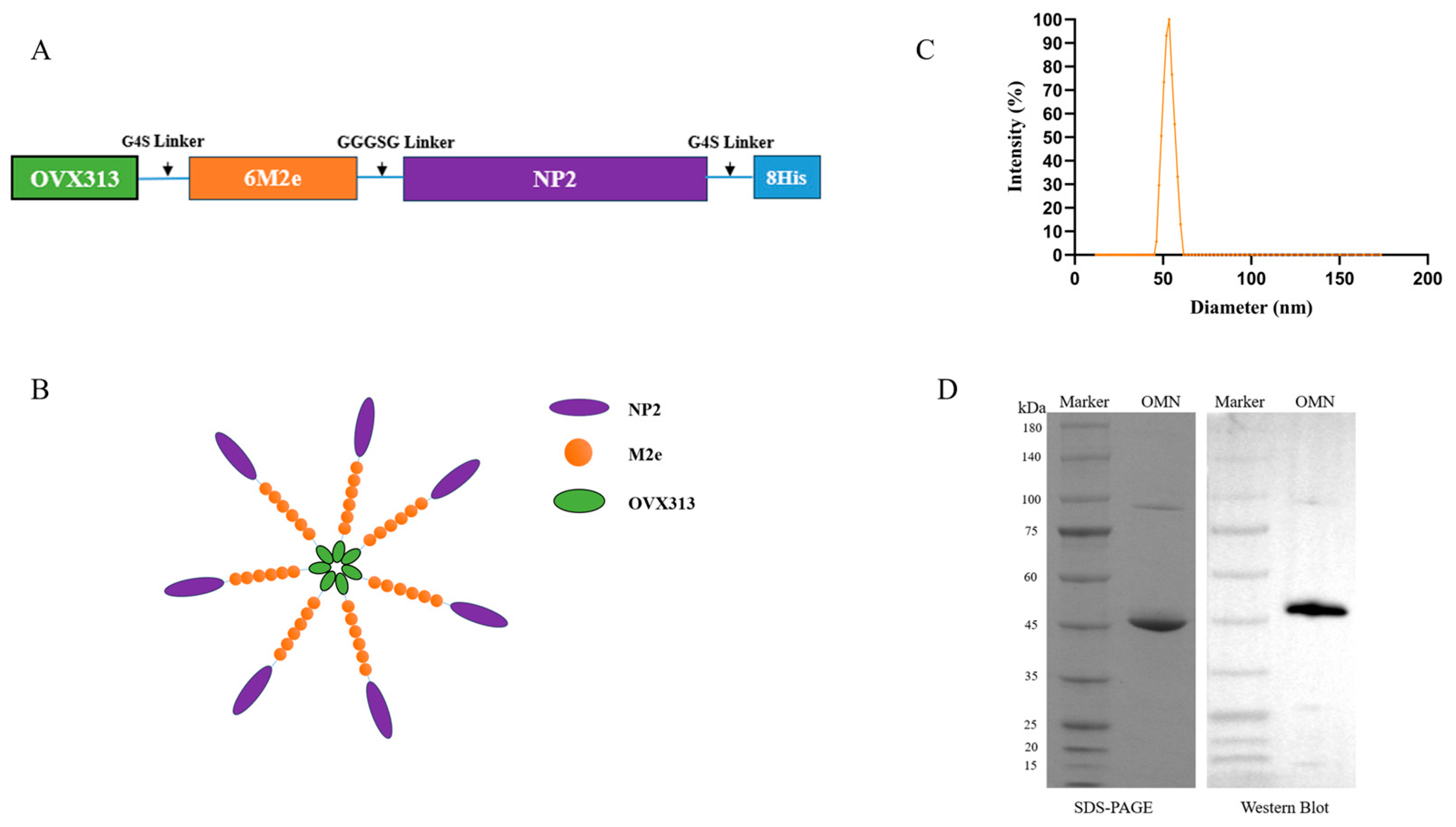
2.3. Construction of OMN Protein Expression Vector
2.4. OMN Protein Expression and Purification
2.5. SDS-PAGE, Western Blot, and Dynamic Light Scattering
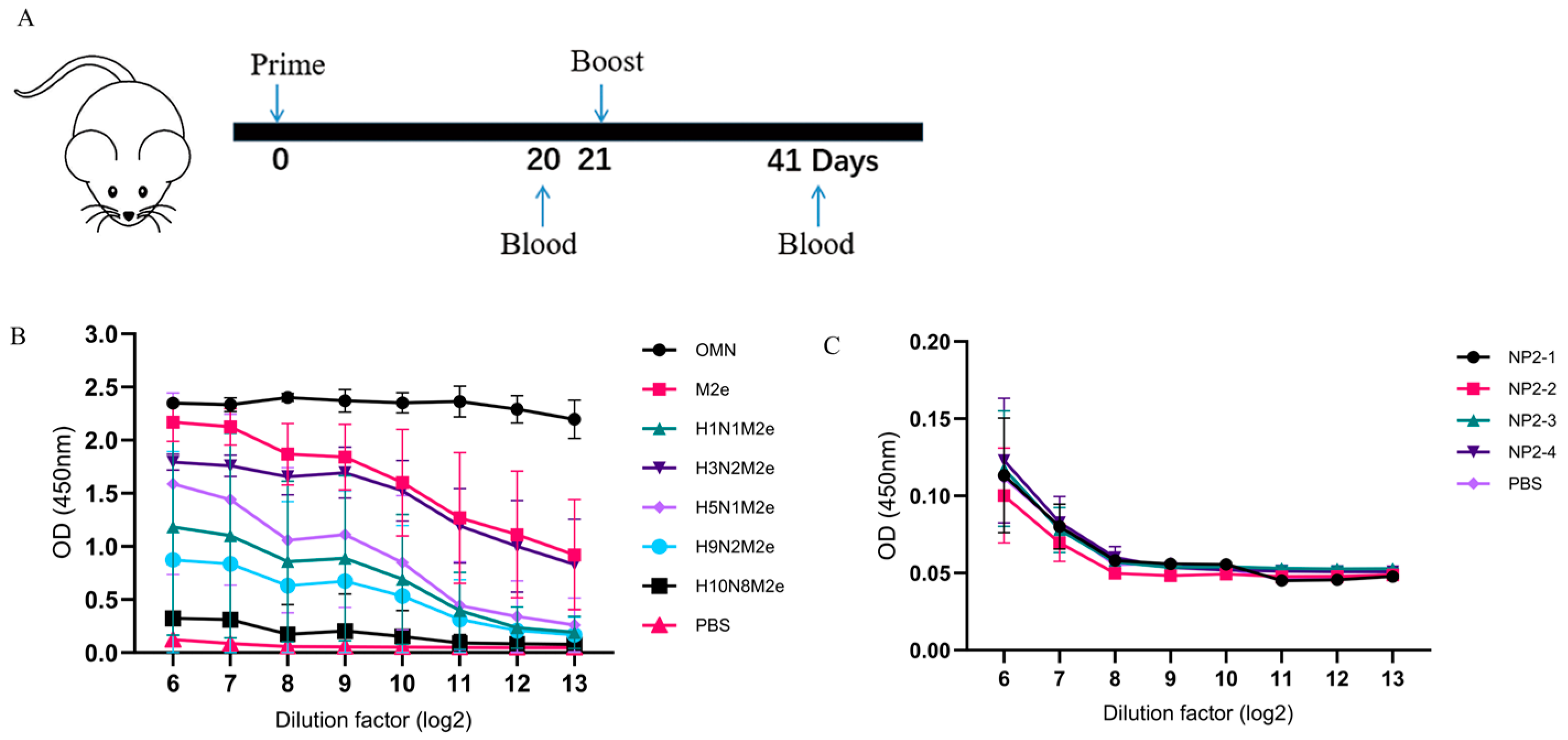
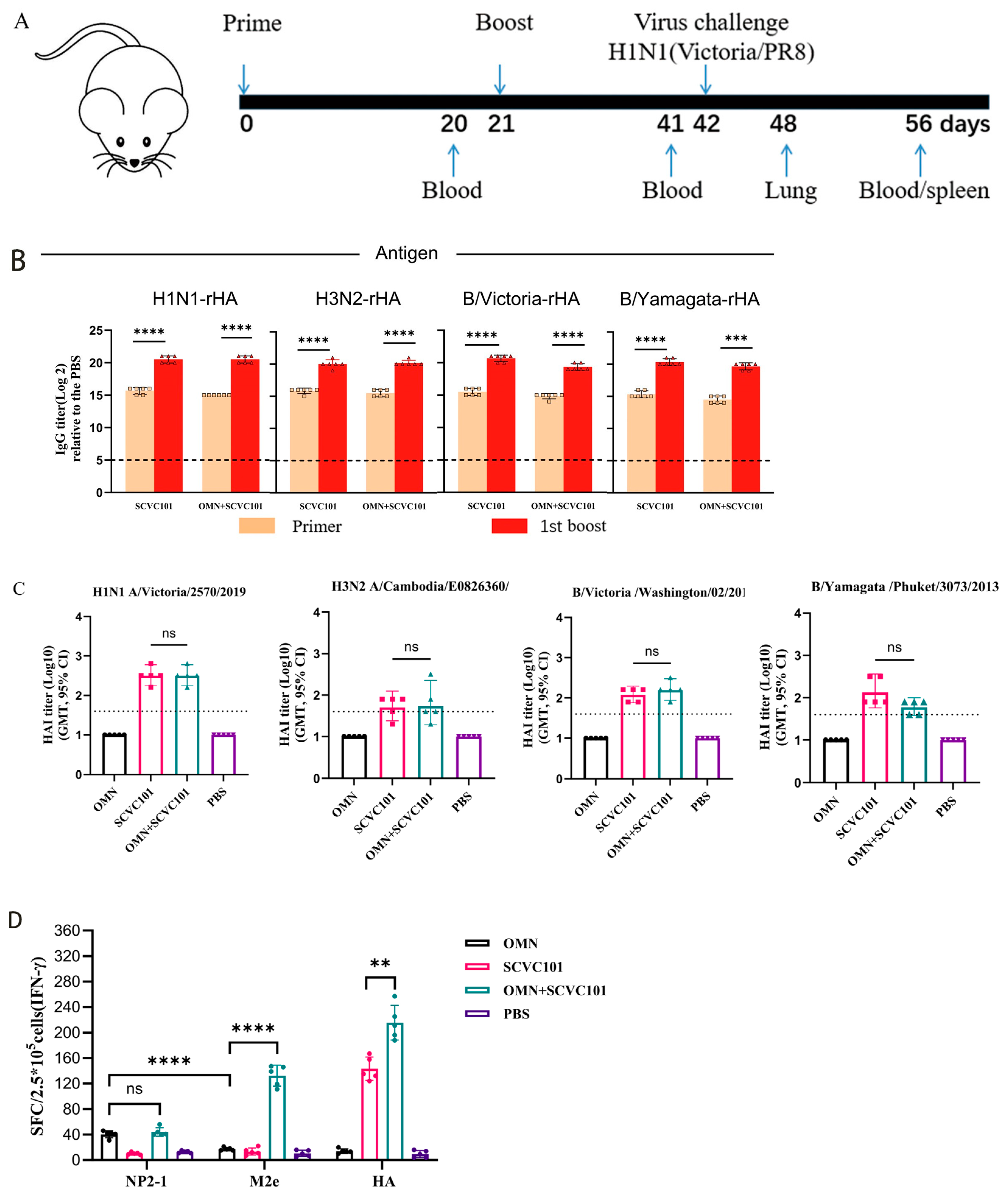
2.6. Immunization and Viral Infection Challenge in Mice
2.7. ELISA
2.8. ELISpot
2.9. Hemagglutinin Inhibition (HAI) Assay
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Selection of T-Cell Epitopes from NP Proteins
3.2. Expression and Characterization of OMN Nanoparticles
3.3. OMN Nanoparticle-Induced Broad Spectrum M2e Antibodies
3.4. Co-Immunization of SCVC101 and OMN-Induced Strong Cellular Immune Responses
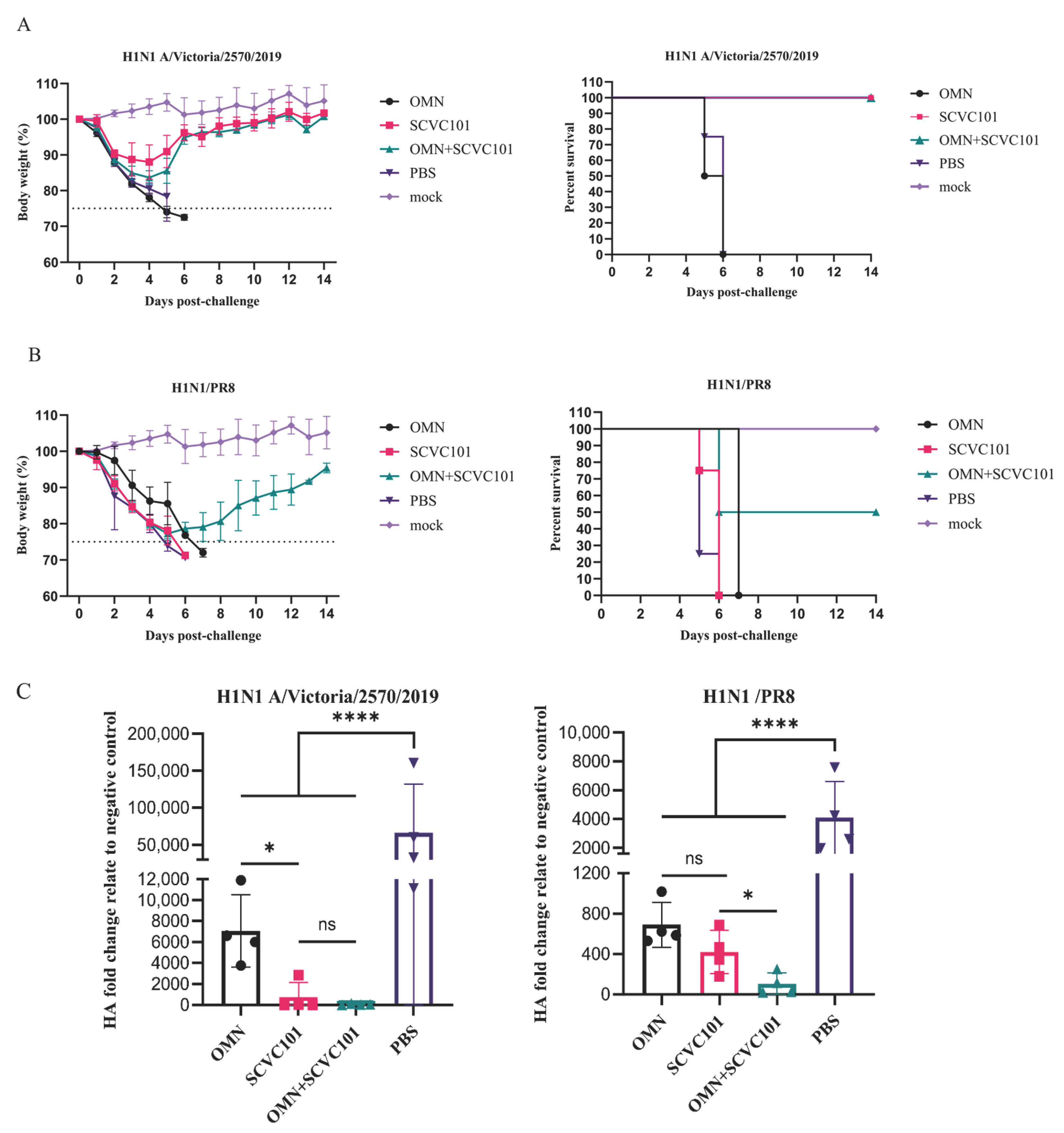
3.5. (SCVC101+OMN) Immunization Enhanced Protection Against H1N1 Influenza Virus Infection in Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ellebedy, A.H.; Krammer, F.; Li, G.-M.; Miller, M.S.; Chiu, C.; Wrammert, J.; Chang, C.Y.; Davis, C.W.; McCausland, M.; Elbein, R.; et al. Induction of broadly cross-reactive antibody responses to the influenza HA stem region following H5N1 vaccination in humans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 13133–13138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zambon, M.C. Epidemiology and pathogenesis of influenza. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 1999, 44, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Welsh, J.P.; Swartz, J.R. Production and stabilization of the trimeric influenza hemagglutinin stem domain for potentially broadly protective influenza vaccines. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staneková, Z.; Varečková, E. Conserved epitopes of influenza A virus inducing protective immunity and their prospects for universal vaccine development. Virol. J. 2010, 7, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Bakkouri, K.; Descamps, F.; De Filette, M.; Smet, A.; Festjens, E.; Birkett, A.; Van Rooijen, N.; Verbeek, S.; Fiers, W.; Saelens, X. Universal Vaccine Based on Ectodomain of Matrix Protein 2 of Influenza A: Fc Receptors and Alveolar Macrophages Mediate Protection. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 1022–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Filette, M.; Ramne, A.; Birkett, A.; Lycke, N.; Löwenadler, B.; Jou, W.M.; Saelens, X.; Fiers, W. The universal influenza vaccine M2e-HBc administered intranasally in combination with the adjuvant CTA1-DD provides complete protection. Vaccine 2006, 24, 544–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Lao, G.; Liu, R.; Feng, J.; Long, F.; Peng, T. The race toward a universal influenza vaccine: Front runners and the future directions. Antivir. Res. 2023, 210, 105505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnell, J.R.; Chou, J.J. Structure and mechanism of the M2 proton channel of influenza A virus. Nature 2008, 451, 591–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Zhang, M.; Mozdzanowska, K.; Zharikova, D.; Hoff, H.; Wunner, W.; Couch, R.B.; Gerhard, W. Influenza A virus infection engenders a poor antibody response against the ectodomain of matrix protein 2. Virol. J. 2006, 3, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepanova, L.A.; Kotlyarov, R.Y.; Kovaleva, A.A.; Potapchuk, M.V.; Korotkov, A.V.; Sergeeva, M.V.; Kasianenko, M.A.; Kuprianov, V.V.; Ravin, N.V.; Tsybalova, L.M.; et al. Protection against Multiple Influenza A Virus Strains Induced by Candidate Recombinant Vaccine Based on Heterologous M2e Peptides Linked to Flagellin. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.-H.; Yang, F.-R.; Yu, H.; Zhou, Y.-J.; Li, G.-X.; Huang, M.; Wen, F.; Tong, G. An M2e-based synthetic peptide vaccine for influenza A virus confers heterosubtypic protection from lethal virus challenge. Virol. J. 2013, 10, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, L.; Ibañez, L.I.; Bossche, V.V.D.; Roose, K.; Youssef, S.A.; de Bruin, A.; Fiers, W.; Saelens, X. Protection against Influenza A Virus Challenge with M2e-Displaying Filamentous Escherichia coli Phages. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, P.G.; Keating, R.; Hulse-Post, D.J.; Doherty, P.C. Cell-mediated Protection in Influenza Infection. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2006, 12, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.-Y.; Kang, J.-O.; Chang, J. Nucleoprotein vaccine induces cross-protective cytotoxic T lymphocytes against both lineages of influenza B virus. Clin. Exp. Vaccine Res. 2019, 8, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, S.L.; Price, G.E. Cross-protective immunity to influenza A viruses. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2010, 9, 1325–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.M.; Simon, J.K.; Baker, J.R., Jr. Applications of nanotechnology for immunology. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 592–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lung, P.; Yang, J.; Li, Q. Nanoparticle formulated vaccines: Opportunities and challenges. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 5746–5763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanekiyo, M.; Wei, C.-J.; Yassine, H.M.; McTamney, P.M.; Boyington, J.C.; Whittle, J.R.R.; Rao, S.S.; Kong, W.-P.; Wang, L.; Nabel, G.J. Self-assembling influenza nanoparticle vaccines elicit broadly neutralizing H1N1 antibodies. Nature 2013, 499, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Campo, J.; Pizzorno, A.; Djebali, S.; Bouley, J.; Haller, M.; Pérez-Vargas, J.; Lina, B.; Boivin, G.; Hamelin, M.-E.; Nicolas, F.; et al. OVX836 a recombinant nucleoprotein vaccine inducing cellular responses and protective efficacy against multiple influenza A subtypes. NPJ Vaccines 2019, 4, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmeyer, T.; Schmelz, S.; Degiacomi, M.T.; Peraro, M.D.; Daneschdar, M.; Scrima, A.; Heuvel, J.v.D.; Heinz, D.W.; Kolmar, H. Arranged Sevenfold: Structural Insights into the C-Terminal Oligomerization Domain of Human C4b-Binding Protein. J. Mol. Biol. 2013, 425, 1302–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foged, C.; Brodin, B.; Frokjaer, S.; Sundblad, A. Particle size and surface charge affect particle uptake by human dendritic cells in an in vitro model. Int. J. Pharm. 2005, 298, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Campo, J.; Bouley, J.; Chevandier, M.; Rousset, C.; Haller, M.; Indalecio, A.; Guyon-Gellin, D.; Le Vert, A.; Hill, F.; Djebali, S.; et al. OVX836 Heptameric Nucleoprotein Vaccine Generates Lung Tissue-Resident Memory CD8+ T-Cells for Cross-Protection Against Influenza. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 678483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Withanage, K.; De Coster, I.; Cools, N.; Viviani, S.; Tourneur, J.; Chevandier, M.; Lambiel, M.; Willems, P.; Le Vert, A.; Nicolas, F.; et al. Phase 1 Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Dose-Escalating Study to Evaluate OVX836, a Nucleoprotein-Based Influenza Vaccine: Intramuscular Results. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 226, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.; Du, Y.; Chen, L.; Su, W.; Wei, H.; Liu, A.; Jiang, X.; Guo, J.; Dai, C.; Xu, Y.; et al. A quadrivalent recombinant influenza Hemagglutinin vaccine induced strong protective immune responses in animal models. Vaccine 2024, 42, 126008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Du, Y.; Peng, T. SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Variant is Expected to Retain Most of the Spike Protein Specific Dominant T-Cell Epitopes Presented by COVID-19 Vaccines—Worldwide, 2021. China CDC Wkly. 2022, 4, 381–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zykova, A.A.; Blokhina, E.A.; Kotlyarov, R.Y.; Stepanova, L.A.; Tsybalova, L.M.; Kuprianov, V.V.; Ravin, N.V. Highly Immunogenic Nanoparticles Based on a Fusion Protein Comprising the M2e of Influenza A Virus and a Lipopeptide. Viruses 2020, 12, 1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, E.; Wu, C.; Chan, K.; Eckle, S.; Bharadwaj, M.; Zou, Q.M.; Kedzierska, K.; Chen, W. Nucleoprotein of influenza A virus is a major target of immunodominant CD8+ T-cell responses. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2013, 91, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Guan, J.; Handel, A.; Tscharke, D.C.; Sidney, J.; Sette, A.; Wakim, L.M.; Sng, X.Y.X.; Thomas, P.G.; Croft, N.P.; et al. Quantification of epitope abundance reveals the effect of direct and cross-presentation on influenza CTL responses. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, H.Q.; Belongia, E.A. Influenza Vaccine Effectiveness: New Insights and Challenges. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2021, 11, a038315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Chang, J. Cross-protective efficacy and safety of an adenovirus-based universal influenza vaccine expressing nucleoprotein, hemagglutinin, and the ectodomain of matrix protein 2. Vaccine 2024, 42, 3505–3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erbelding, E.J.; Post, D.J.; Stemmy, E.J.; Roberts, P.C.; Augustine, A.D.; Ferguson, S.; Paules, C.I.; Graham, B.S.; Fauci, A.S. A Universal Influenza Vaccine: The Strategic Plan for the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 218, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Zheng, B.-J.; Lu, L.; Zhou, Y.; Jiang, S.; Du, L. Advancements in the development of subunit influenza vaccines. Microbes Infect. 2015, 17, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, K.; Ying, G.; Yan, Z.; Shanshan, Y.; Lei, Z.; Hongjun, L.; Maosheng, S. Progress on adenovirus-vectored universal influenza vaccines. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2015, 11, 1209–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravin, N.V.; Blokhina, E.A.; Kuprianov, V.V.; Stepanova, L.A.; Shaldjan, A.A.; Kovaleva, A.A.; Tsybalova, L.M.; Skryabin, K.G. Development of a candidate influenza vaccine based on virus-like particles displaying influenza M2e peptide into the immunodominant loop region of hepatitis B core antigen: Insertion of multiple copies of M2e increases immunogenicity and protective efficiency. Vaccine 2015, 33, 3392–3397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Zhu, H.; Xia, X.; Liang, Z.; Ma, X.; Sun, B. Vaccine adjuvants: Understanding the structure and mechanism of adjuvanticity. Vaccine 2019, 37, 3167–3178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egli, A.; Santer, D.M.; O’Shea, D.; Barakat, K.; Syedbasha, M.; Vollmer, M.; Baluch, A.; Bhat, R.; Groenendyk, J.; Joyce, M.A.; et al. IL-28B is a Key Regulator of B- and T-Cell Vaccine Responses against Influenza. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Q.; Luo, W.; Mallajosyula, V.; Bo, Y.; Guo, J.; Xie, J.; Sun, M.; Verma, R.; Li, C.; Constantz, C.M.; et al. A TLR7-nanoparticle adjuvant promotes a broad immune response against heterologous strains of influenza and SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Mater. 2023, 22, 380–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goff, P.H.; Hayashi, T.; Martínez-Gil, L.; Corr, M.; Crain, B.; Yao, S.; Cottam, H.B.; Chan, M.; Ramos, I.; Eggink, D.; et al. Synthetic Toll-Like Receptor 4 (TLR4) and TLR7 Ligands as Influenza Virus Vaccine Adjuvants Induce Rapid, Sustained, and Broadly Protective Responses. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 3221–3235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Davies, J.E.; Dollinger, E.P.; Pone, E.J.; Felgner, J.; Liang, L.; Strohmeier, S.; Jan, S.; Albin, T.J.; Jain, A.; Nakajima, R.; et al. Magnitude and breadth of antibody cross-reactivity induced by recombinant influenza hemagglutinin trimer vaccine is enhanced by combination adjuvants. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 9198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
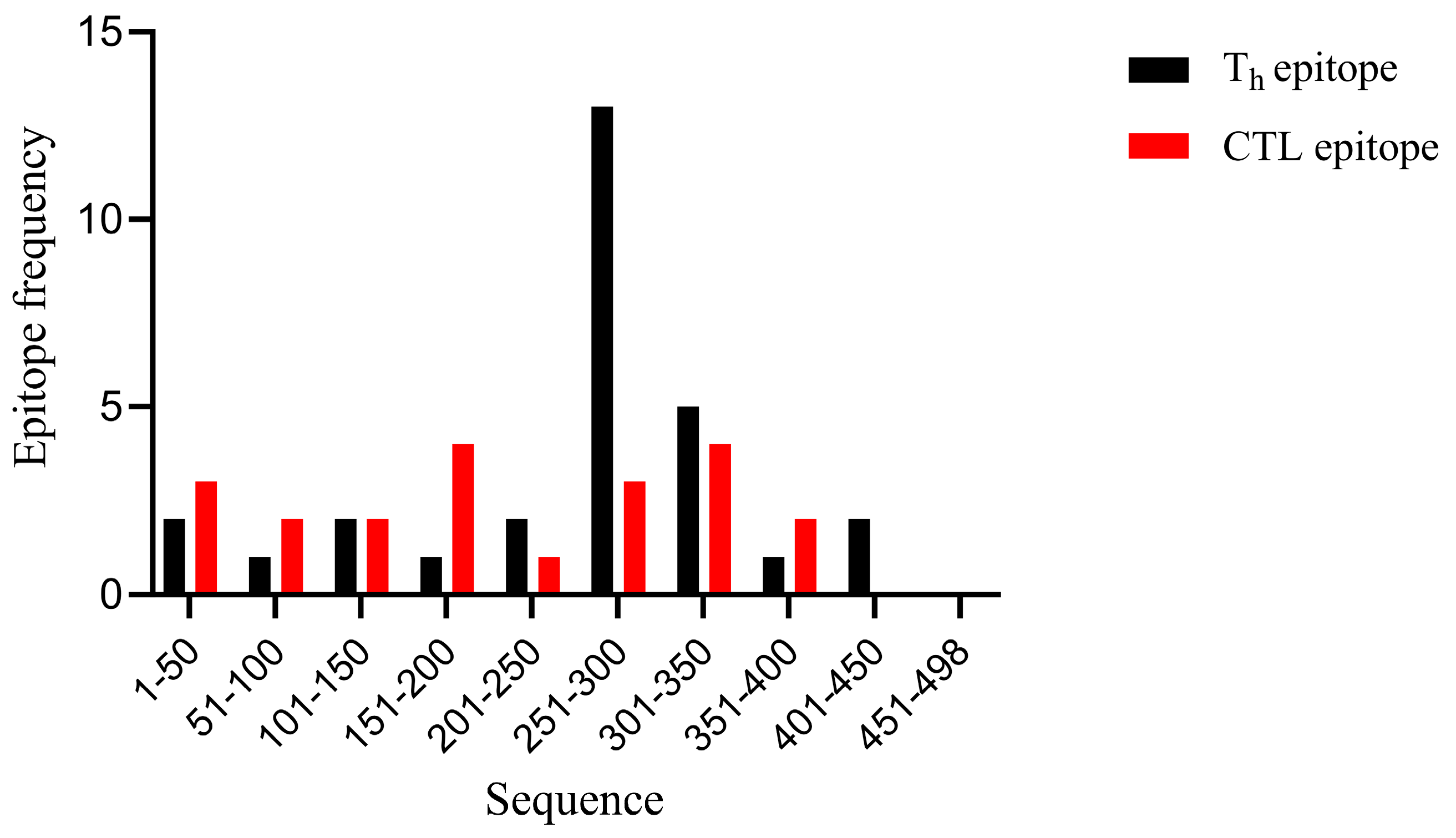

| NetCTL1.2 | IEDB-MHC I | SYFPEITHI | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Start Site | CTL Epitope Sequences | Score | Start Site | CTL Epitope Sequences | Score | Start Site | CTL Epitope Sequences | Score |
| 258 | FLARSALIL | 1.19 | 158 | GMDPRMCSL | 0.54 | 185 | GIGTMVMEL | 25 |
| 135 | HMMIWHSNL | 1.13 | 307 | LQNSQIYSL | 0.52 | 258 | FLARSALIL | 24 |
| 158 | GMDPRMCSL | 1.07 | 55 | RLIQNSLTI | 0.48 | 55 | RLIQNSLTI | 23 |
| 373 | NMGSSTLEL | 1.07 | 258 | FLARSALIL | 0.36 | 158 | GMDPRMCSL | 23 |
| 55 | RLIQNSLTI | 0.98 | 48 | KLSDHEGRL | 0.36 | 336 | AAFEDLRLL | 23 |
| 307 | LQNSQIYSL | 0.95 | 189 | MVMELIRMI | 0.30 | 373 | NMGSSTLEL | 23 |
| 189 | MVMELIRMI | 0.94 | 225 | ILKGKFQTA | 0.25 | 48 | KLSDHEGRL | 22 |
| 357 | KLSTRGVQI | 0.84 | 373 | NMGSSTLEL | 0.23 | 256 | LIFLARSAL | 22 |
| 328 | LVWMACHSA | 0.78 | 31 | KMIDGIGRF | 0.19 | 342 | RLLSFIRGT | 22 |
| 48 | KLSDHEGRL | 0.76 | 357 | KLSTRGVQI | 0.19 | 60 | SLTIEKMVL | 21 |
| 185 | GIGTMVMEL | 0.72 | 185 | GIGTMVMEL | 0.17 | 262 | SALILRGSV | 21 |
| 342 | RLLSFIRGT | 0.68 | 342 | RLLSFIRGT | 0.13 | 357 | KLSTRGVQI | 21 |
| 41 | IQMCTELKL | 0.67 | 336 | AAFEDLRLL | 0.10 | 146 | ATYQRTRAL | 20 |
| 188 | TMVMELIRM | 0.62 | 135 | HMMIWHSNL | 0.08 | 189 | MVMELIRMI | 20 |
| IEDB-MHCII | RANKPEP | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Start Site | Th Epitope Sequences | Rank | Start Site | Th Epitope Sequences | Score |
| 254 | EDLIFLARSALILRGS | 0.44 | 385 | YWAIRTRSG | 19.60 |
| 253 | IEDLIFLARSALILRG | 0.50 | 97 | YRRVDGKWM | 16.63 |
| 255 | DLIFLARSALILRGSV | 0.59 | 10 | YEQMETDGD | 15.89 |
| 252 | EIEDLIFLARSALILR | 0.79 | 423 | STIMAAFTG | 15.64 |
| 256 | LIFLARSALILRGSVA | 0.94 | 164 | CSLMQGSTL | 15.52 |
| 304 | FKLLQNSQIYSLIRPN | 1.10 | 304 | FKLLQNSQI | 13.78 |
| 300 | GIDPFKLLQNSQIYSL | 1.10 | 207 | WRGENGRKT | 12.25 |
| 301 | IDPFKLLQNSQIYSLI | 1.10 | 25 | IRASVGKMI | 12.14 |
| 251 | AEIEDLIFLARSALIL | 1.20 | 258 | FLARSALIL | 11.75 |
| 302 | DPFKLLQNSQIYSLIR | 1.20 | 273 | KSCLPACAY | 11.62 |
| 303 | PFKLLQNSQIYSLIRP | 1.20 | 120 | WRQANNGED | 11.33 |
| 298 | LVGIDPFKLLQNSQIY | 1.40 | 219 | YDRMCNILK | 11.26 |
| 297 | SLVGIDPFKLLQNSQI | 1.40 | 148 | YQRTRALVR | 10.79 |
| 299 | VGIDPFKLLQNSQIYS | 1.40 | 445 | IRMMEGAKP | 10.45 |
| 257 | IFLARSALILRGSVAH | 1.70 | 341 | LRLLSFIRG | 10.05 |
| Influenza Strains | Subtype | M2e Amino Acid Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| M2e in OMN nanoparticles(A/Cambodia/e0826360/2020 (H3N2)) | H3N2 | SLLTEVETPIRNEWGSRSNDSSD |
| A/Puerto Rico/30/2022 | H1N1 | SLLTEVETPTRSEWECRCSGSND |
| A/Cambodia/e0826360/2020 | H3N2 | SLLTEVETPIRNEWGCRCNDSSD |
| A/Guangdong-Shenzhen/1/2011 | H5N1 | SLLTEVETPTRNEWECRCSDSSD |
| A/Jiangsu/602/2021 | H9N2 | SLLTEVETPTRTGWECNCSGSSD |
| A/Jiangxi-Donghu/346-2/2013 | H10N8 | SLLTEVETLTKTGWECNCSGSSD |
| Influenza Strains | Subtype | NP Amino Acid Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| A/Puerto Rico/30/2022 | H1N1 | NP2-1 (AEIEDLIFLARSALILRGSVAHKS) |
| NP2-2 (SLVGIDPFKLLQNSQVVSLMRPNEN) | ||
| NP2-3 (RVSSFIRGKKVIPRGKLSTRGVQIA) | ||
| NP2-4 (TMDSNTLELRSRYWAIRTRSGGNTN) | ||
| NP in OMN nanoparticles | H3N2 | NP2-1 (AEIEDLIFLARSALILRGSVAHKS) |
| NP2-2 (SLVGIDPFKLLQNSQIYSLIRPNEN) | ||
| NP2-3 (RLLSFIRGTKVSPRGKLSTRGVQIA) | ||
| NP2-4 (NMGSSTLELRSGYWAIRTRSGGNTN) | ||
| A/Guangdong-Shenzhen/1/2011 | H5N1 | NP2-1 (AEIEDLIFLARSALILRGSVAHKS) |
| NP2-2 (SLVGIDPFRLLQNSQVFSLIRPNEN) | ||
| NP2-3 (RVSSFIRGTRVVPRGQLSTRGVQIA) | ||
| NP2-4 (TMDSNTLELRSRYWAIRTRSGGNTN) | ||
| A/Jiangsu/602/2021 | H9N2 | NP2-1 (AEIEDLIFLARSALILRGSVAHKS) |
| NP2-2 (SLVGIDPFRLLQNSQVFSLIRPNEN) | ||
| NP2-3 (RVSSFIRGTRMVPRGQLSTRGVQIA) | ||
| NP2-4 (TMDSNTLELRSRYWAIRTRSGGNTN) | ||
| A/Jiangxi-Donghu/346-2/2013 | H10N8 | NP2-1 (AEIEDLIFLARSALILRGSVAHKS) |
| NP2-2 (SLVGIDPFRLLQNSQVFSLIRPNEN) | ||
| NP2-3 (RVSSFIRGTRMVPRGQLSTRGVQIA) | ||
| NP2-4 (AMDSNTLELRSRYWAIRTRSGGNTN) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, R.; Yang, L.; Feng, J.; Zhang, S.; Wu, L.; Du, Y.; Kong, D.; Xu, Y.; Peng, T. M2e/NP Dual Epitope-Displaying Nanoparticles Enhance Cross-Protection of Recombinant HA Influenza Vaccine: A Universal Boosting Strategy. Vaccines 2025, 13, 412. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13040412
Liu R, Yang L, Feng J, Zhang S, Wu L, Du Y, Kong D, Xu Y, Peng T. M2e/NP Dual Epitope-Displaying Nanoparticles Enhance Cross-Protection of Recombinant HA Influenza Vaccine: A Universal Boosting Strategy. Vaccines. 2025; 13(4):412. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13040412
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Rui, Lejun Yang, Jin Feng, Songchen Zhang, Liping Wu, Yingying Du, Dexin Kong, Yuhua Xu, and Tao Peng. 2025. "M2e/NP Dual Epitope-Displaying Nanoparticles Enhance Cross-Protection of Recombinant HA Influenza Vaccine: A Universal Boosting Strategy" Vaccines 13, no. 4: 412. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13040412
APA StyleLiu, R., Yang, L., Feng, J., Zhang, S., Wu, L., Du, Y., Kong, D., Xu, Y., & Peng, T. (2025). M2e/NP Dual Epitope-Displaying Nanoparticles Enhance Cross-Protection of Recombinant HA Influenza Vaccine: A Universal Boosting Strategy. Vaccines, 13(4), 412. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13040412





