Vaccination with Plasmids Encoding the Fusion Proteins D-S1, D-S1N and O-SN from SARS-CoV-2 Induces an Effective Humoral and Cellular Immune Response in Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
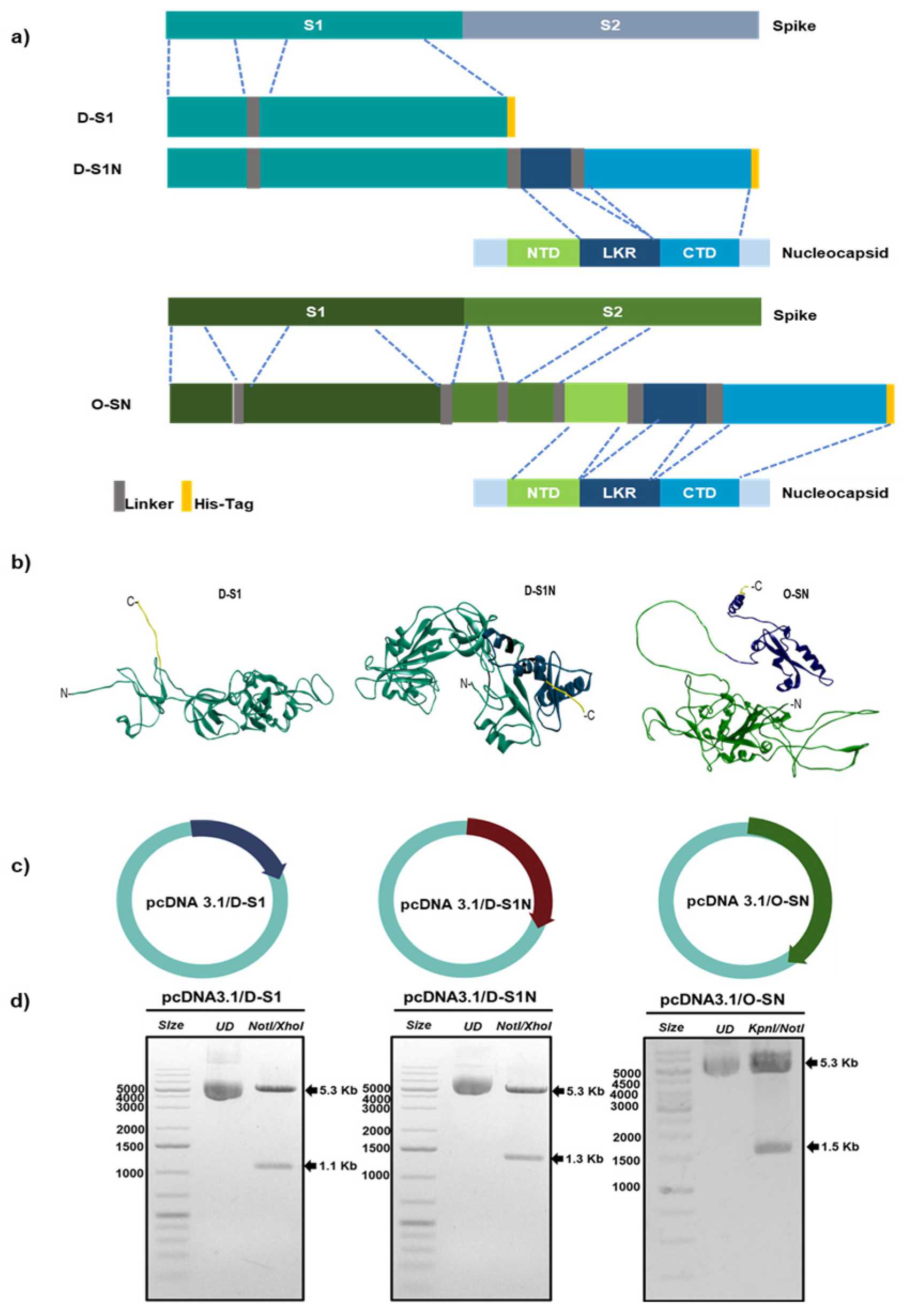
2.1. Design of Fusion Proteins
2.2. Bioinformatic Analysis
2.3. Gene Syntheses and Plasmid Construction
2.4. Expression of Fusion Proteins
2.5. Western Blotting
2.6. Immunofluorescence
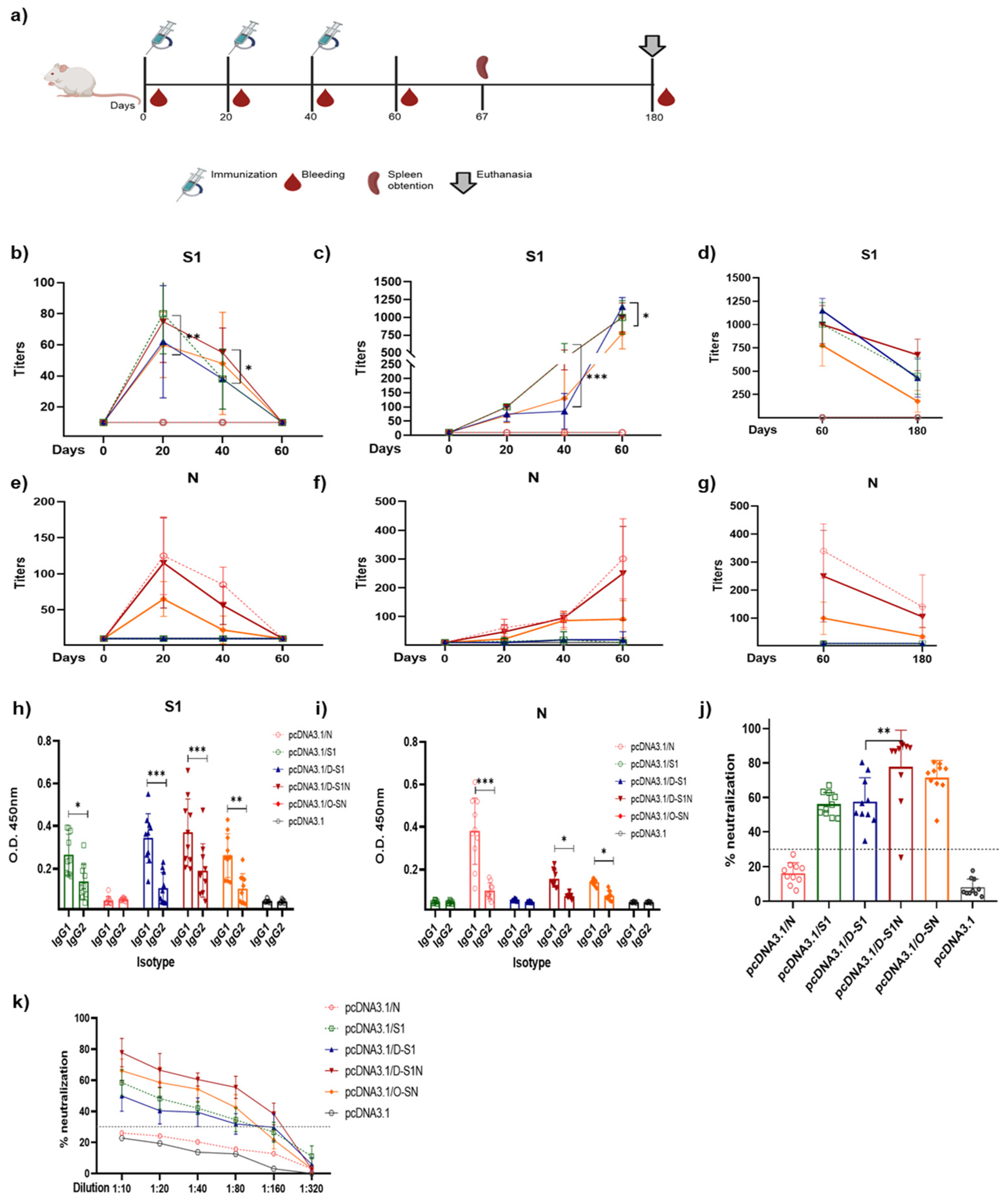
2.7. Immunization
2.8. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
2.9. Surrogate Virus Neutralization Test
2.10. Determination of IFN-γ Production
2.11. Proliferation Test
2.12. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Fusion Proteins D-S1, D-S1N, and O-SN Are Immunogenic According to Bioinformatic Approaches
3.2. Evaluation of Fusion Protein Expression in Eukaryotic Cells
3.3. Different Doses of Naked DNA Induce a Humoral Immune Response in Mice
3.4. Immunization with pcDNA3.1/D-S1, pcDNA3.1/D-S1N, and pcDNA3.1/O-SN Induce Specific Humoral Immune Responses
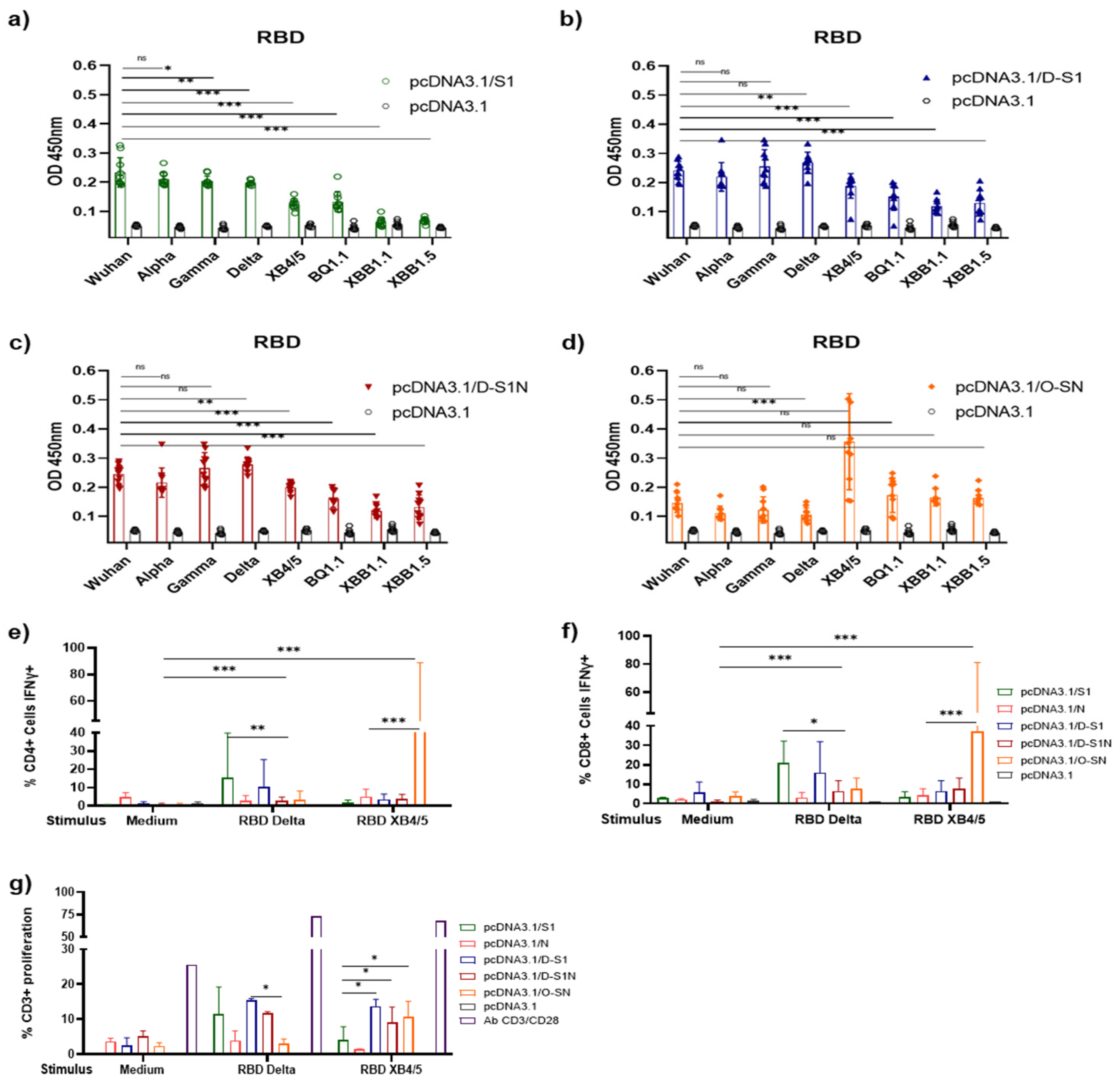
3.5. DNA Immunization with pcDNA3.1/D-S1, pcDNA3.1/D-S1N, and pcDNA3.1/O-SN Induces Specific Cellular Immune Responses
3.6. Antibodies Induced by DNA Immunization Recognized SARS-CoV-2 Viral Proteins in Infected Cells
3.7. DNA Immunization with pcDNA3.1/D-S1, pcDNA3.1/D-S1N, and pcDNA3.1/O-SN Elicited Cross-Reaction with RBD of SARS-CoV-2 VOCs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, P.; Yang, X.L.; Wang, X.G.; Hu, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Si, H.R.; Zhu, Y.; Li, B.; Huang, C.L.; et al. A Pneumonia Outbreak Associated with a New Coronavirus of Probable Bat Origin. Nature 2020, 579, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. WHO COVID-19 Dashboard. Available online: https://data.who.int/dashboards/covid19/cases?n=c (accessed on 1 November 2024).
- Wu, A.; Peng, Y.; Huang, B.; Ding, X.; Wang, X.; Niu, P.; Meng, J.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; et al. Genome Composition and Divergence of the Novel Coronavirus (2019-NCoV) Originating in China. Cell Host Microbe 2020, 27, 325–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, M.; Kleine-Weber, H.; Schroeder, S.; Krüger, N.; Herrler, T.; Erichsen, S.; Schiergens, T.S.; Herrler, G.; Wu, N.H.; Nitsche, A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor. Cell 2020, 181, 271–280.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zost, S.J.; Gilchuk, P.; Chen, R.E.; Case, J.B.; Reidy, J.X.; Trivette, A.; Nargi, R.S.; Sutton, R.E.; Suryadevara, N.; Chen, E.C.; et al. Rapid Isolation and Profiling of a Diverse Panel of Human Monoclonal Antibodies Targeting the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1422–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapuente, D.; Winkler, T.H.; Tenbusch, M. B-Cell and Antibody Responses to SARS-CoV-2: Infection, Vaccination, and Hybrid Immunity. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2024, 21, 144–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padron-Regalado, E. Vaccines for SARS-CoV-2: Lessons from Other Coronavirus Strains. Infect. Dis. Ther. 2020, 9, 255–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, A.; Khattri, A.; Verma, V. Structural and Antigenic Variations in the Spike Protein of Emerging SARS-CoV-2 Variants. PLoS Pathog. 2022, 18, e1010260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadj Hassine, I. COVID-19 Vaccines and Variants of Concern: A Review. Rev. Med. Virol. 2022, 32, e2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callaway, E. The next Generation of Coronavirus Vaccines: A Graphical Guide. Nature 2023, 614, 22–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendoza-Ramírez, N.J.; García-Cordero, J.; Shrivastava, G.; Cedillo-Barrón, L. The Key to Increase Immunogenicity of Next-Generation COVID-19 Vaccines Lies in the Inclusion of the SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein. J. Immunol. Res. 2024, 2024, 9313267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, J.; Qureshi, R.; Sagurthi, S.R.; Qureshi, I.A. Designing of Nucleocapsid Protein Based Novel Multi-Epitope Vaccine Against SARS-CoV-2 Using Immunoinformatics Approach. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2021, 27, 941–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, O.W.; Chia, A.; Tan, A.T.; Jadi, R.S.; Leong, H.N.; Bertoletti, A.; Tan, Y.J. Memory T Cell Responses Targeting the SARS Coronavirus Persist up to 11 Years Post-Infection. Vaccine 2016, 34, 2008–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Du, N.; Lei, Y.; Dorje, S.; Qi, J.; Luo, T.; Gao, G.F.; Song, H. Structures of the SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid and Their Perspectives for Drug Design. EMBO J. 2020, 39, e105938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, E.K.V.B.; Bomfim, C.G.; Barbosa, A.P.; Noda, P.; Noronha, I.L.; Fernandes, B.H.V.; Machado, R.R.G.; Durigon, E.L.; Catanozi, S.; Rodrigues, L.G.; et al. Immunization with SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein Triggers a Pulmonary Immune Response in Rats. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0268434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dangi, T.; Sanchez, S.; Class, J.; Richner, M.; Visvabharathy, L.; Chung, Y.R.; Bentley, K.; Stanton, R.J.; Koralnik, I.J.; Richner, J.M.; et al. Improved Control of SARS-CoV-2 by Treatment with a Nucleocapsid-Specific Monoclonal Antibody. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132, e162282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thura, M.; En Sng, J.X.; Ang, K.H.; Li, J.; Gupta, A.; Hong, J.M.; Hong, C.W.; Zeng, Q. Targeting Intra-Viral Conserved Nucleocapsid (N) Proteins as Novel Vaccines against SARS-CoVs. Biosci. Rep. 2021, 41, BSR20211491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Wang, W.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Yang, C.; Jia, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, M.; Zeng, W.; Huang, X.; et al. Developing Next-Generation Protein-Based Vaccines Using High-Affinity Glycan Ligand-Decorated Glyconanoparticles. Adv. Sci. (Weinh.) 2023, 10, 2204598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matchett, W.E.; Joag, V.; Stolley, J.M.; Shepherd, F.K.; Quarnstrom, C.F.; Mickelson, C.K.; Wijeyesinghe, S.; Soerens, A.G.; Becker, S.; Thiede, J.M.; et al. Nucleocapsid Vaccine Elicits Spike-Independent SARS-CoV-2 Protective Immunity. J. Immunol. 2021, 207, 376–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabdano, S.O.; Ruzanova, E.A.; Pletyukhina, I.V.; Saveliev, N.S.; Kryshen, K.L.; Katelnikova, A.E.; Beltyukov, P.P.; Fakhretdinova, L.N.; Safi, A.S.; Rudakov, G.O.; et al. Immunogenicity and In Vivo Protective Effects of Recombinant Nucleocapsid-Based SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine Convacell®. Vaccines 2023, 11, 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dangi, T.; Class, J.; Palacio, N.; Richner, J.M.; Penaloza MacMaster, P. Combining Spike- and Nucleocapsid-Based Vaccines Improves Distal Control of SARS-CoV-2. Cell Rep. 2021, 36, 109664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza-Ramírez, N.J.; García-Cordero, J.; Martínez-Frías, S.P.; Roa-Velázquez, D.; Luria-Pérez, R.; Bustos-Arriaga, J.; Hernández-Lopez, J.; Cabello-Gutiérrez, C.; Zúñiga-Ramos, J.A.; Morales-Ríos, E.; et al. Combination of Recombinant Proteins S1/N and RBD/N as Potential Vaccine Candidates. Vaccines 2023, 11, 864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wussow, F.; Kha, M.; Kim, T.; Ly, M.; Yll-Pico, M.; Kar, S.; Lewis, M.G.; Chiuppesi, F.; Diamond, D.J. Synthetic Multiantigen MVA Vaccine COH04S1 and Variant-Specific Derivatives Protect Syrian Hamsters from SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Subvariants. NPJ Vaccines 2023, 8, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCafferty, S.; Haque, A.K.M.A.; Vandierendonck, A.; Weidensee, B.; Plovyt, M.; Stuchlíková, M.; François, N.; Valembois, S.; Heyndrickx, L.; Michiels, J.; et al. A Dual-Antigen Self-Amplifying RNA SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine Induces Potent Humoral and Cellular Immune Responses and Protects against SARS-CoV-2 Variants through T Cell-Mediated Immunity. Mol. Ther. 2022, 30, 2968–2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, B.A.S.; Hodel, K.V.S.; Fonseca, L.M.D.S.; Mascarenhas, L.A.B.; Andrade, L.P.C.d.S.; Rocha, V.P.C.; Soares, M.B.P.; Berglund, P.; Duthie, M.S.; Reed, S.G.; et al. The Importance of RNA-Based Vaccines in the Fight against COVID-19: An Overview. Vaccines 2021, 9, 1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafaati, M.; Saidijam, M.; Soleimani, M.; Hazrati, F.; Mirzaei, R.; Amirheidari, B.; Tanzadehpanah, H.; Karampoor, S.; Kazemi, S.; Yavari, B.; et al. A Brief Review on DNA Vaccines in the Era of COVID-19. Future Virol. 2021, 17, 49–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maslow, J.N.; Kwon, I.; Kudchodkar, S.B.; Kane, D.; Tadesse, A.; Lee, H.; Park, Y.K.; Muthumani, K.; Roberts, C.C. DNA Vaccines for Epidemic Preparedness: SARS-CoV-2 and Beyond. Vaccines 2023, 11, 1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordero-Ortiz, M.; Reséndiz-Sandoval, M.; Dehesa-Canseco, F.; Solís-Hernández, M.; Pérez-Sánchez, J.; Martínez-Borges, C.; Mata-Haro, V.; Hernández, J. Development of a Multispecies Double-Antigen Sandwich ELISA Using N and RBD Proteins to Detect Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2. Animals 2023, 13, 3487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, F.; Li, Z.; Wang, H.; An, M.; Li, Y.; Pang, N.; Ding, J. Bioinformatics Analysis of EgA31 and EgG1Y162 Proteins for Designing a Multi-Epitope Vaccine against Echinococcus Granulosus. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2019, 73, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sha, T.; Li, Z.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, X.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, F.; Ding, J. Bioinformatics Analysis of Candidate Proteins Omp2b, P39 and BLS for Brucella Multivalent Epitope Vaccines. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 147, 104318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Cordero, J.; Mendoza-Ramírez, J.; Fernández-Benavides, D.; Roa-Velazquez, D.; Filisola-Villaseñor, J.; Martínez-Frías, S.P.; Sanchez-Salguero, E.S.; Miguel-Rodríguez, C.E.; Montero, J.L.M.; Torres-Ruiz, J.J.; et al. Recombinant Protein Expression and Purification of N, S1, and RBD of SARS-CoV-2 from Mammalian Cells and Their Potential Applications. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özcengiz, E.; Keser, D.; Özcengiz, G.; Çelik, G.; Özkul, A.; İnçeh, F.N. Two Formulations of Coronavirus Disease-19 Recombinant Subunit Vaccine Candidate Made up of S1 Fragment Protein P1, S2 Fragment Protein P2, and Nucleocapsid Protein Elicit Strong Immunogenicity in Mice. Immun. Inflamm. Dis. 2022, 10, e748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaemi, A.; Roshani Asl, P.; Zargaran, H.; Ahmadi, D.; Hashimi, A.A.; Abdolalipour, E.; Bathaeian, S.; Miri, S.M. Recombinant COVID-19 Vaccine Based on Recombinant RBD/Nucleoprotein and Saponin Adjuvant Induces Long-Lasting Neutralizing Antibodies and Cellular Immunity. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 974364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, J.T.; Azevedo, P.; Fumagalli, M.J.; Hojo-Souza, N.S.; Salazar, N.; Almeida, G.G.; Oliveira, L.I.; Faustino, L.; Antonelli, L.R.; Marçal, T.G.; et al. Promotion of Neutralizing Antibody-Independent Immunity to Wild-Type and SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern Using an RBD-Nucleocapsid Fusion Protein. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mekonnen, D.; Mengist, H.M.; Jin, T. SARS-CoV-2 Subunit Vaccine Adjuvants and Their Signaling Pathways. Expert. Rev. Vaccines 2022, 21, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogostin, B.H.; McHugh, K.J. Novel Vaccine Adjuvants as Key Tools for Improving Pandemic Preparedness. Bioengineering 2021, 8, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rump, A.; Risti, R.; Kristal, M.L.; Reut, J.; Syritski, V.; Lookene, A.; Ruutel Boudinot, S. Dual ELISA Using SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein Produced in E. Coli and CHO Cells Reveals Epitope Masking by N-Glycosylation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 534, 457–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, X.; Liu, Y.; Lei, X.; Li, P.; Mi, D.; Ren, L.; Guo, L.; Guo, R.; Chen, T.; Hu, J.; et al. Characterization of Spike Glycoprotein of SARS-CoV-2 on Virus Entry and Its Immune Cross-Reactivity with SARS-CoV. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Rcheulishvili, N.; Cai, J.; Liu, C.; Xie, F.; Hu, X.; Yang, N.; Hou, M.; Papukashvili, D.; He, Y.; et al. Development of DNA Vaccine Candidate against SARS-CoV-2. Viruses 2022, 14, 1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozak, M.; Hu, J. DNA Vaccines: Their Formulations, Engineering and Delivery. Vaccines 2024, 12, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledesma-Feliciano, C.; Chapman, R.; Hooper, J.W.; Elma, K.; Zehrung, D.; Brennan, M.B.; Spiegel, E.K. Improved DNA Vaccine Delivery with Needle-Free Injection Systems. Vaccines 2023, 11, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babuadze, G.G.; Fausther-Bovendo, H.; deLaVega, M.A.; Lillie, B.; Naghibosadat, M.; Shahhosseini, N.; Joyce, M.A.; Saffran, H.A.; Lorne Tyrrell, D.; Falzarano, D.; et al. Two DNA Vaccines Protect against Severe Disease and Pathology Due to SARS-CoV-2 in Syrian Hamsters. NPJ Vaccines 2022, 7, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, A.; Verma, M.; Shin, A.; Zakin, L.; Sieling, P.; Tanaka, S.; Balint, J.; Dinkins, K.; Adisetiyo, H.; Morimoto, B.; et al. Intranasal plus Subcutaneous Prime Vaccination with a Dual Antigen COVID-19 Vaccine Elicits T-Cell and Antibody Responses in Mice. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koerber, N.; Priller, A.; Yazici, S.; Bauer, T.; Cheng, C.C.; Mijočević, H.; Wintersteller, H.; Jeske, S.; Vogel, E.; Feuerherd, M.; et al. Dynamics of Spike-and Nucleocapsid Specific Immunity during Long-Term Follow-up and Vaccination of SARS-CoV-2 Convalescents. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dan, J.M.; Mateus, J.; Kato, Y.; Hastie, K.M.; Yu, E.D.; Faliti, C.E.; Grifoni, A.; Ramirez, S.I.; Haupt, S.; Frazier, A.; et al. Immunological Memory to SARS-CoV-2 Assessed for up to 8 Months after Infection. Science 2021, 371, eabf4063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, L.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, X. Neutralizing Antibodies for the Prevention and Treatment of COVID-19. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 2293–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guimaraes, L.C.; Costa, P.A.C.; Scalzo Júnior, S.R.A.; Ferreira, H.A.S.; Braga, A.C.S.; de Oliveira, L.C.; Figueiredo, M.M.; Shepherd, S.; Hamilton, A.; Queiroz-Junior, C.M.; et al. Nanoparticle-Based DNA Vaccine Protects against SARS-CoV-2 Variants in Female Preclinical Models. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, Z.; Lai, X.; Sun, J.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Dai, J.; Liu, D.; Li, Y.; Li, F.; Wang, Y.; et al. Mapping and Role of T Cell Response in SARS-CoV-2-Infected Mice. J. Exp. Med. 2021, 218, e20202187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajnik, R.L.; Plante, J.A.; Liang, Y.; Alameh, M.G.; Tang, J.; Bonam, S.R.; Zhong, C.; Adam, A.; Scharton, D.; Rafael, G.H.; et al. Dual Spike and Nucleocapsid MRNA Vaccination Confer Protection against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron and Delta Variants in Preclinical Models. Sci. Transl. Med. 2022, 14, eabq1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.; Shi, L.; Cai, L.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Li, H.; Liang, J.; Gu, Q.; Ji, G.; Li, J.; et al. A Two-Adjuvant Multiantigen Candidate Vaccine Induces Superior Protective Immune Responses against SARS-CoV-2 Challenge. Cell Rep. 2021, 37, 110112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mambelli, F.; Marinho, F.V.; Andrade, J.M.; de Araujo, A.C.V.S.C.; Abuna, R.P.F.; Fabri, V.M.R.; Santos, B.P.O.; da Silva, J.S.; de Magalhães, M.T.Q.; Homan, E.J.; et al. Recombinant Bacillus Calmette-Guérin Expressing SARS-CoV-2 Chimeric Protein Protects K18-HACE2 Mice against Viral Challenge. J. Immunol. 2023, 210, 1925–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiuppesi, F.; Nguyen, V.H.; Park, Y.; Contreras, H.; Karpinski, V.; Faircloth, K.; Nguyen, J.; Kha, M.; Johnson, D.; Martinez, J.; et al. Synthetic Multiantigen MVA Vaccine COH04S1 Protects against SARS-CoV-2 in Syrian Hamsters and Non-Human Primates. NPJ Vaccines 2022, 7, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, K.L.; Gourdine, T.; Fletcher, P.; Clancy, C.S.; Marzi, A. Protection from COVID-19 with a VSV-Based Vaccine Expressing the Spike and Nucleocapsid Proteins. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1025500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfizer COVID-19 Bivalent (COMIRNATY Original/Omicron BA.4-5 COVID-19 Vaccine) Booster Dose Vaccine|Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA). Available online: https://www.tga.gov.au/products/covid-19/covid-19-vaccines/covid-19-vaccine-provisional-registrations/pfizer-covid-19-bivalent-comirnaty-originalomicron-ba4-5-covid-19-vaccine-booster-dose-vaccine (accessed on 16 February 2024).





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mendoza-Ramírez, N.J.; García-Cordero, J.; Hernández-Galicia, G.; Moreno-Licona, N.J.; Hernandez, J.; Cabello-Gutierrez, C.; Zúñiga-Ramos, J.A.; Morales-Rios, E.; Pérez-Tapia, S.M.; Ortiz-Navarrete, V.; et al. Vaccination with Plasmids Encoding the Fusion Proteins D-S1, D-S1N and O-SN from SARS-CoV-2 Induces an Effective Humoral and Cellular Immune Response in Mice. Vaccines 2025, 13, 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13020134
Mendoza-Ramírez NJ, García-Cordero J, Hernández-Galicia G, Moreno-Licona NJ, Hernandez J, Cabello-Gutierrez C, Zúñiga-Ramos JA, Morales-Rios E, Pérez-Tapia SM, Ortiz-Navarrete V, et al. Vaccination with Plasmids Encoding the Fusion Proteins D-S1, D-S1N and O-SN from SARS-CoV-2 Induces an Effective Humoral and Cellular Immune Response in Mice. Vaccines. 2025; 13(2):134. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13020134
Chicago/Turabian StyleMendoza-Ramírez, Noe Juvenal, Julio García-Cordero, Gabriela Hernández-Galicia, Nicole Justine Moreno-Licona, Jesus Hernandez, Carlos Cabello-Gutierrez, Joaquín Alejandro Zúñiga-Ramos, Edgar Morales-Rios, Sonia Mayra Pérez-Tapia, Vianney Ortiz-Navarrete, and et al. 2025. "Vaccination with Plasmids Encoding the Fusion Proteins D-S1, D-S1N and O-SN from SARS-CoV-2 Induces an Effective Humoral and Cellular Immune Response in Mice" Vaccines 13, no. 2: 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13020134
APA StyleMendoza-Ramírez, N. J., García-Cordero, J., Hernández-Galicia, G., Moreno-Licona, N. J., Hernandez, J., Cabello-Gutierrez, C., Zúñiga-Ramos, J. A., Morales-Rios, E., Pérez-Tapia, S. M., Ortiz-Navarrete, V., Espinosa-Cantellano, M., Fernández-Benavides, D. A., & Cedillo-Barrón, L. (2025). Vaccination with Plasmids Encoding the Fusion Proteins D-S1, D-S1N and O-SN from SARS-CoV-2 Induces an Effective Humoral and Cellular Immune Response in Mice. Vaccines, 13(2), 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13020134









