A Liposome-Based Nanoparticle Vaccine Induces Effective Immunity Against EBV Infection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Plasmids Construction and Recombinant Protein Expression and Purification
2.3. Native-PAGE, SDS-PAGE and Western Blotting (WB)
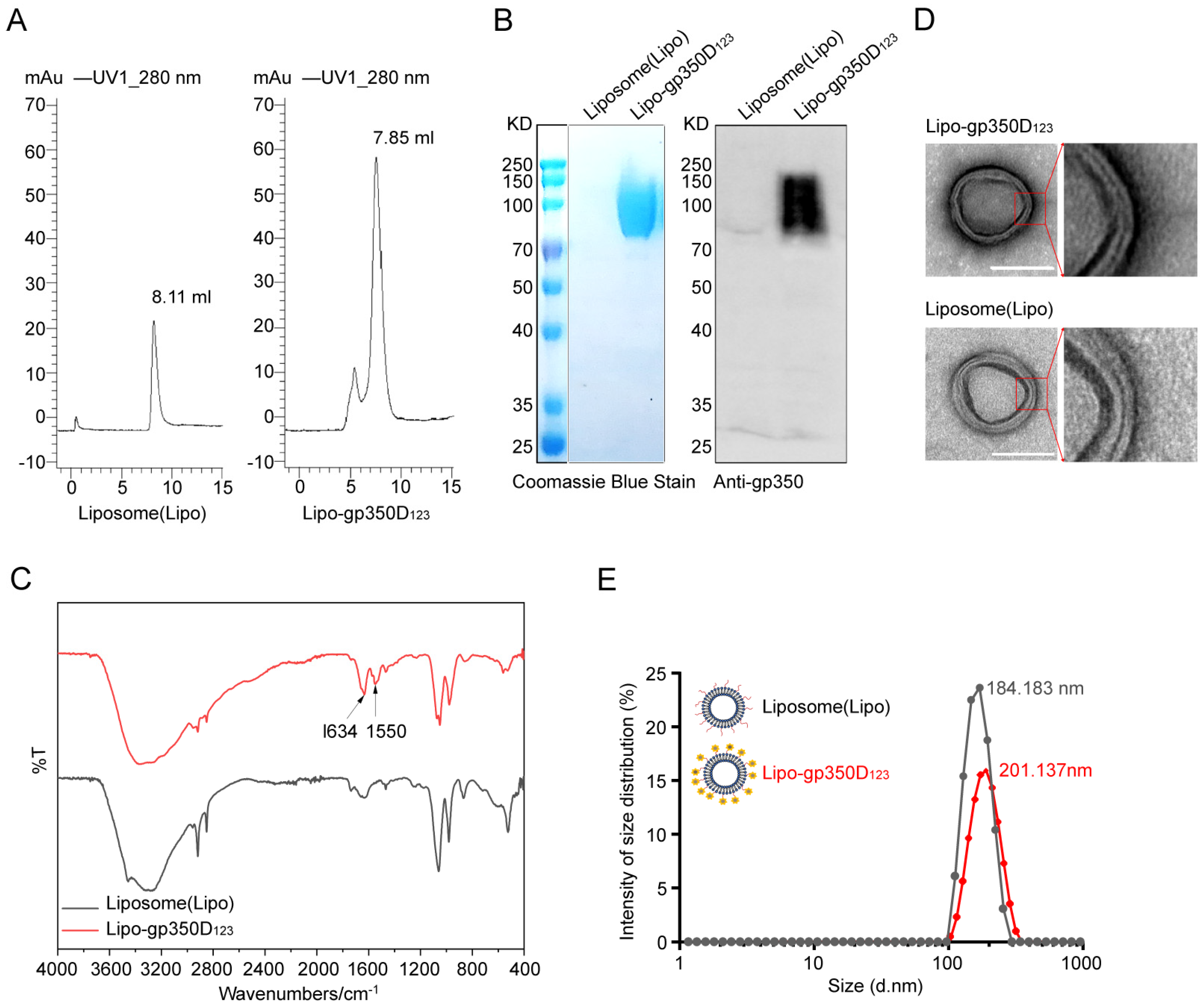
2.4. Synthesis of Liposomes, and Assembly with Antigen Proteins
2.5. Attenuated Total Reflectance (ATR) and Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) Detection
2.6. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.7. Immunization Assay
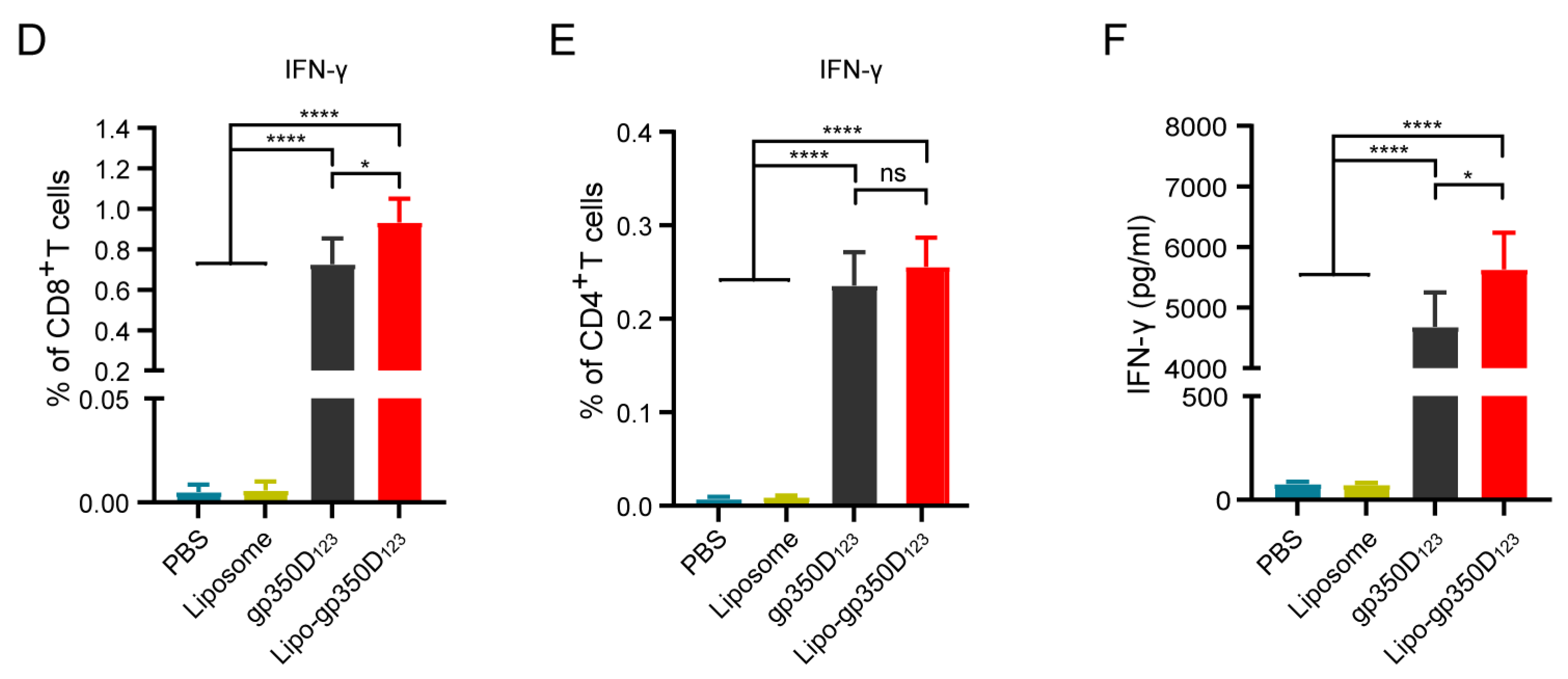
2.8. Splenocyte Isolation and Intracellular Cytokine Staining (ICCS)
2.9. Indirect Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.10. Production and Purification of EBV-GFP Reporter Virus
2.11. EBV Infection Blocking Experiment
2.12. Histopathology Analysis
2.13. Data Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Rational Molecular Design of Liposome-Based Vaccine
3.2. Characterization of Lipo-gp350D123 Nanoparticle
3.3. Immunogenicity of the Lipo-gp350D123 Nanoparticle Vaccine
3.4. Lipo-gp350D123 Nanoparticle Vaccine Induced Effective Neutralizing Antibody Response
3.5. Lipo-gp350D123 Nanoparticle Vaccine Demonstrates Favorable Safety in Balb/c Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, T.C.; Mann, R.B.; Charache, P.; Hayward, S.D.; Staal, S.; Lambe, B.C.; Ambinder, R.F. Detection Of EBV Gene-Expression in reed-sternberg cells of Hodgkins-Disease. Int. J. Cancer 1990, 46, 801–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunmire, S.K.; Verghese, P.S.; Balfour, H.H., Jr. Primary Epstein-Barr virus infection. J. Clin. Virol. 2018, 102, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damania, B.; Kenney, S.C.; Raab-Traub, N. Epstein-Barr virus: Biology and clinical disease. Cell 2022, 185, 3652–3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bräuninger, A.; Schmitz, R.; Bechtel, D.; Renné, C.; Hausmann, M.L.; Küppers, R. Molecular biology of Hodgkin’s and Reed/Sternberg cells in Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Int. J. Cancer 2006, 118, 1853–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, L.S.; Yap, L.F.; Murray, P.G. Epstein-Barr virus: More than 50 years old and still providing surprises. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 16, 789–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J.I.; Mocarski, E.S.; Raab-Traub, N.; Corey, L.; Nabel, G.J. The need and challenges for development of an Epstein-Barr virus vaccine. Vaccine 2013, 31 (Suppl. S2), B194–B196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjornevik, K.; Cortese, M.; Healy, B.C.; Kuhle, J.; Mina, M.J.; Leng, Y.; Elledge, S.J.; Niebuhr, D.W.; Scher, A.I.; Munger, K.L.; et al. Longitudinal analysis reveals high prevalence of Epstein-Barr virus associated with multiple sclerosis. Science 2022, 375, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanz, T.V.; Brewer, R.C.; Ho, P.P.; Moon, J.S.; Jude, K.M.; Fernandez, D.; Fernandes, R.A.; Gomez, A.M.; Nadj, G.S.; Bartley, C.M.; et al. Clonally expanded B cells in multiple sclerosis bind EBV EBNA1 and GlialCAM. Nature 2022, 603, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedeschi, V.; Vitulano, C.; Cauli, A.; Paladini, F.; Piga, M.; Mathieu, A.; Sorrentino, R.; Fiorillo, M.T. The Ankylosing Spondylitis-associated HLA-B*2705 presents a B*0702-restricted EBV epitope and sustains the clonal amplification of cytotoxic T cells in patients. Mol. Med. 2016, 22, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedeschi, V.; Alba, J.; Paladini, F.; Paroli, M.; Cauli, A.; Mathieu, A.; Sorrentino, R.; D’Abramo, M.; Fiorillo, M.T. Unusual Placement of an EBV Epitope into the Groove of the Ankylosing Spondylitis-Associated HLA-B27 Allele Allows CD8+ T Cell Activation. Cells 2019, 8, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.; Kim, S.J.; Park, S.; Yoo, K.H.; Ki, C.S.; Ko, Y.; Kim, W.S. Significance of circulating Epstein-Barr virus DNA monitoring after remission in patients with extranodal natural killer T cell lymphoma. Ann. Hematol. 2018, 97, 1427–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J.I.; Fauci, A.S.; Varmus, H.; Nabel, G.J. Epstein-Barr Virus: An Important Vaccine Target for Cancer Prevention. Sci. Transl. Med. 2011, 3, 107fs7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Martel, C.; Ferlay, J.; Franceschi, S.; Vignat, J.; Bray, F.; Forman, D.; Plummer, M. Global burden of cancers attributable to infections in 2008: A review and synthetic analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shannon-Lowe, C.D.; Neuhierl, B.; Baldwin, G.; Rickinson, A.B.; Delecluse, H.J. Resting B cells as a transfer vehicle for Epstein-Barr virus infection of epithelial cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 7065–7070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, T.; Kondo, Y.; Sugimoto, A.; Kawashima, D.; Saito, S.; Isomura, H.; Kanda, T.; Tsurumi, T. Epigenetic histone modification of Epstein-Barr virus BZLF1 promoter during latency and reactivation in Raji cells. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 4752–4761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, T.; Tsurumi, T. Switching of EBV cycles between latent and lytic states. Rev. Med. Virol. 2014, 24, 142–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laichalk, L.L.; Hochberg, D.; Babcock, G.J.; Freeman, R.B.; Thorley-Lawson, D.A. The dispersal of mucosal memory B cells: Evidence from persistent EBV infection. Immunity 2002, 16, 745–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.A.; Herbert, A.P.; Barlow, P.N.; Holers, V.M.; Hannan, J.P. Molecular basis of the interaction between complement receptor type 2 (CR2/CD21) and Epstein-Barr virus glycoprotein gp350. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 11217–11227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, T.; Johannessen, I.; Dombagoda, D.; Sengupta, C.; Burns, D.M.; Bird, P.; Hale, G.; Mieli-Vergani, G.; Crawford, D.H. A mouse monoclonal antibody against Epstein-Barr virus envelope glycoprotein 350 prevents infection both in vitro and in vivo. J. Infect. Dis. 2006, 194, 584–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sairenji, T.; Bertoni, G.; Medveczky, M.M.; Medveczky, P.G.; Nguyen, Q.V.; Humphreys, R.E. Inhibition of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) release from P3HR-1 and B95-8 cell lines by monoclonal antibodies to EBV membrane antigen gp350/220. J. Virol. 1988, 62, 2614–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanekiyo, M.; Bu, W.; Joyce, M.G.; Meng, G.; Whittle, J.R.; Baxa, U.; Yamamoto, T.; Narpala, S.; Todd, J.P.; Rao, S.S.; et al. Rational Design of an Epstein-Barr Virus Vaccine Targeting the Receptor-Binding Site. Cell 2015, 162, 1090–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanner, J.E.; Hu, J.; Alfieri, C. Construction and Characterization of a Humanized Anti-Epstein-Barr Virus gp350 Antibody with Neutralizing Activity in Cell Culture. Cancers 2018, 10, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasari, V.; McNeil, L.K.; Beckett, K.; Solomon, M.; Ambalathingal, G.; Thuy, T.L.; Panikkar, A.; Smith, C.; Steinbuck, M.P.; Jakubowski, A.; et al. Lymph node targeted multi-epitope subunit vaccine promotes effective immunity to EBV in HLA-expressing mice. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 4371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, B.; Zhang, X.; Krummenacher, C.; Song, S.; Gao, L.; Zhang, H.; Xu, M.; Feng, L.; Feng, Q.; Zeng, M.; et al. Immunization with Fc-Based Recombinant Epstein-Barr Virus gp350 Elicits Potent Neutralizing Humoral Immune Response in a BALB/c Mice Model. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, W.; Joyce, M.G.; Nguyen, H.; Banh, D.V.; Aguilar, F.; Tariq, Z.; Yap, M.L.; Tsujimura, Y.; Gillespie, R.A.; Tsybovsky, Y.; et al. Immunization with Components of the Viral Fusion Apparatus Elicits Antibodies That Neutralize Epstein-Barr Virus in B Cells and Epithelial Cells. Immunity 2019, 50, 1305–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.B.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.P.; Li, Y.; Zhao, B.; Feng, G.K.; Du, Y.; Xiong, D.; Zhong, Q.; Liu, W.L.; et al. Neuropilin 1 is an entry factor that promotes EBV infection of nasopharyngeal epithelial cells. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sathiyamoorthy, K.; Jiang, J.; Hu, Y.X.; Rowe, C.L.; Mohl, B.S.; Chen, J.; Jiang, W.; Mellins, E.D.; Longnecker, R.; Zhou, Z.H.; et al. Assembly and architecture of the EBV B cell entry triggering complex. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Hong, J.; Zhong, L.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, Q.; Chen, H.; Wei, D.; Li, R.; Zhang, W.; et al. Protective anti-gB neutralizing antibodies targeting two vulnerable sites for EBV-cell membrane fusion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2202371119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Kang, Y.F.; Fang, X.Y.; Liu, Y.N.; Bu, G.L.; Wang, A.J.; Li, Y.; Zhu, Q.Y.; Zhang, H.; Xie, C.; et al. A gB nanoparticle vaccine elicits a protective neutralizing antibody response against EBV. Cell Host Microbe 2023, 31, 1882–1897E10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanekiyo, M.; Joyce, M.G.; Gillespie, R.A.; Gallagher, J.R.; Andrews, S.F.; Yassine, H.M.; Wheatley, A.K.; Fisher, B.E.; Ambrozak, D.R.; Creanga, A.; et al. Mosaic nanoparticle display of diverse influenza virus hemagglutinins elicits broad B cell responses. Nat. Immunol. 2019, 20, 362–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Zou, F.; Yu, F.; Li, R.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Deng, J.; Chen, T.; Song, Z.; et al. Nanoparticle Vaccines Based on the Receptor Binding Domain (RBD) and Heptad Repeat (HR) of SARS-CoV-2 Elicit Robust Protective Immune Responses. Immunity 2020, 53, 1315–1330E9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, B.; Ding, M.; Song, S.; Kang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Xu, M.; Xiang, T.; Gao, L.; Feng, Q.; et al. A novel vaccine candidate based on chimeric virus-like particle displaying multiple conserved epitope peptides induced neutralizing antibodies against EBV infection. Theranostics 2020, 10, 5704–5718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.J.; Bu, W.; Nguyen, L.A.; Batchelor, J.D.; Kim, J.; Pittaluga, S.; Fuller, J.R.; Nguyen, H.; Chou, T.H.; Cohen, J.I.; et al. A bivalent Epstein-Barr virus vaccine induces neutralizing antibodies that block infection and confer immunity in humanized mice. Sci. Transl. Med. 2022, 14, eabf3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, L.; Zhang, W.; Liu, H.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Z.; Wen, Z.; Chen, L.; Chen, H.; Luo, Y.; Chen, Y.; et al. A cocktail nanovaccine targeting key entry glycoproteins elicits high neutralizing antibody levels against EBV infection. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 5310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.J.; Tian, J.; Qi, X.K.; Xiang, T.; He, G.P.; Zhang, H.; Yu, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, B.; Feng, Q.S.; et al. Epstein-Barr virus activates F-box protein FBXO2 to limit viral infectivity by targeting glycoprotein B for degradation. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1007208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.X.; Bu, G.L.; Liu, G.F.; Kong, X.W.; Sun, C.; Li, Z.Q.; Dai, D.L.; Sun, H.X.; Kang, Y.F.; Feng, G.K.; et al. mRNA-based Vaccines Targeting the T-cell Epitope-rich Domain of Epstein Barr Virus Latent Proteins Elicit Robust Anti-Tumor Immunity in Mice. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, e2302116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Ye, Z.; Huang, C.; Qiu, M.; Song, D.; Li, Y.; Xu, Q. Lipid nanoparticle-mediated lymph node-targeting delivery of mRNA cancer vaccine elicits robust CD8(+) T cell response. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2207841119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Narayanan, E.; Liu, Q.; Tsybovsky, Y.; Boswell, K.; Ding, S.; Hu, Z.; Follmann, D.; Lin, Y.; Miao, H.; et al. A multiclade env-gag VLP mRNA vaccine elicits tier-2 HIV-1-neutralizing antibodies and reduces the risk of heterologous SHIV infection in macaques. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 2234–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbeke, R.; Lentacker, I.; De Smedt, S.C.; Dewitte, H. The dawn of mRNA vaccines: The COVID-19 case. J. Control. Release 2021, 333, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parhiz, H.; Atochina-Vasserman, E.N.; Weissman, D. mRNA-based therapeutics: Looking beyond COVID-19 vaccines. Lancet 2024, 403, 1192–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanick, J.F.; Ashley, J.D.; Kiziltepe, T.; Bilgicer, B. A systematic analysis of peptide linker length and liposomal polyethylene glycol coating on cellular uptake of peptide-targeted liposomes. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 2935–2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hjalmsdottir, A.; Hasler, F.; Waeckerle-Men, Y.; Duda, A.; Lopez-Deber, M.P.; Pihlgren, M.; Vukicevic, M.; Kundig, T.M.; Johansen, P. T cell independent antibody responses with class switch and memory using peptides anchored on liposomes. NPJ Vaccines 2024, 9, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, L.; Luo, Z.; Wang, L.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yin, H.; You, J. Liposome Vaccine for Active Regulation of Cellular and Humoral Immunity. Mol. Pharm. 2023, 20, 5668–5681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID). Safety and Immunogenicity of an Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) gp350-Ferritin Nanoparticle Vaccine in Healthy Adults with or without EBV Infection. ClinicalTrials.gov. 2024. Available online: https://clinicalstudies.info.nih.gov/protocoldetails.aspx?id=21-I-0005&&query=Type%201 (accessed on 27 March 2025).
- ModernaTX, I. A Study of an Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) Candidate Vaccine, mRNA-1189, in 10- to 30-Year-Old Healthy Adolescents and Adults. ClinicalTrials.gov. 2024. Available online: https://www.centerwatch.com/clinical-trials/listings/NCT05164094/a-study-of-an-epstein-barr-virus-ebv-candidate-vaccine-mrna-1189-in-10-to-30-year-old-healthy-adolescents-and-adults (accessed on 27 March 2025).




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, P.; Yu, Z.; Jiang, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Shi, J.; Han, S.; Ma, L. A Liposome-Based Nanoparticle Vaccine Induces Effective Immunity Against EBV Infection. Vaccines 2025, 13, 360. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13040360
Li P, Yu Z, Jiang Z, Jiang Y, Shi J, Han S, Ma L. A Liposome-Based Nanoparticle Vaccine Induces Effective Immunity Against EBV Infection. Vaccines. 2025; 13(4):360. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13040360
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Ping, Zihang Yu, Ziyi Jiang, Yike Jiang, Jingjing Shi, Sanyang Han, and Lan Ma. 2025. "A Liposome-Based Nanoparticle Vaccine Induces Effective Immunity Against EBV Infection" Vaccines 13, no. 4: 360. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13040360
APA StyleLi, P., Yu, Z., Jiang, Z., Jiang, Y., Shi, J., Han, S., & Ma, L. (2025). A Liposome-Based Nanoparticle Vaccine Induces Effective Immunity Against EBV Infection. Vaccines, 13(4), 360. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13040360




