A Bioconjugate Vaccine Against Extra-Intestinal Pathogenic Escherichia coli (ExPEC)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials & Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains, Plasmids, Primers, and Growth Conditions
2.2. Plasmid Construction
2.3. Experimental Animals
2.4. LPS and OPS Extraction
2.5. Purification of Target Glycoproteins
2.6. Western Blot Analysis
2.7. Agglutination Assay
2.8. Animal Immunization and Challenge
2.9. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.10. Lethal Dose Challenge of E. coli O1, E. coli O2, E. coli O6, or E. coli O25 Infection in BALB/c Mouse Model
2.11. Sublethal Dose of E. coli O1, E. coli O2, E. coli O6, or E. coli O25 Infection in BALB/c Mouse Model
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. The Construction of the OPSECO1, OPSECO2, OPSECO6, and OPSECO25 Synthesis Plasmid and Its Functional Validation in E. coli
3.2. Synthesis of Candidate Bioconjugate Vaccines in Engineered E. coli
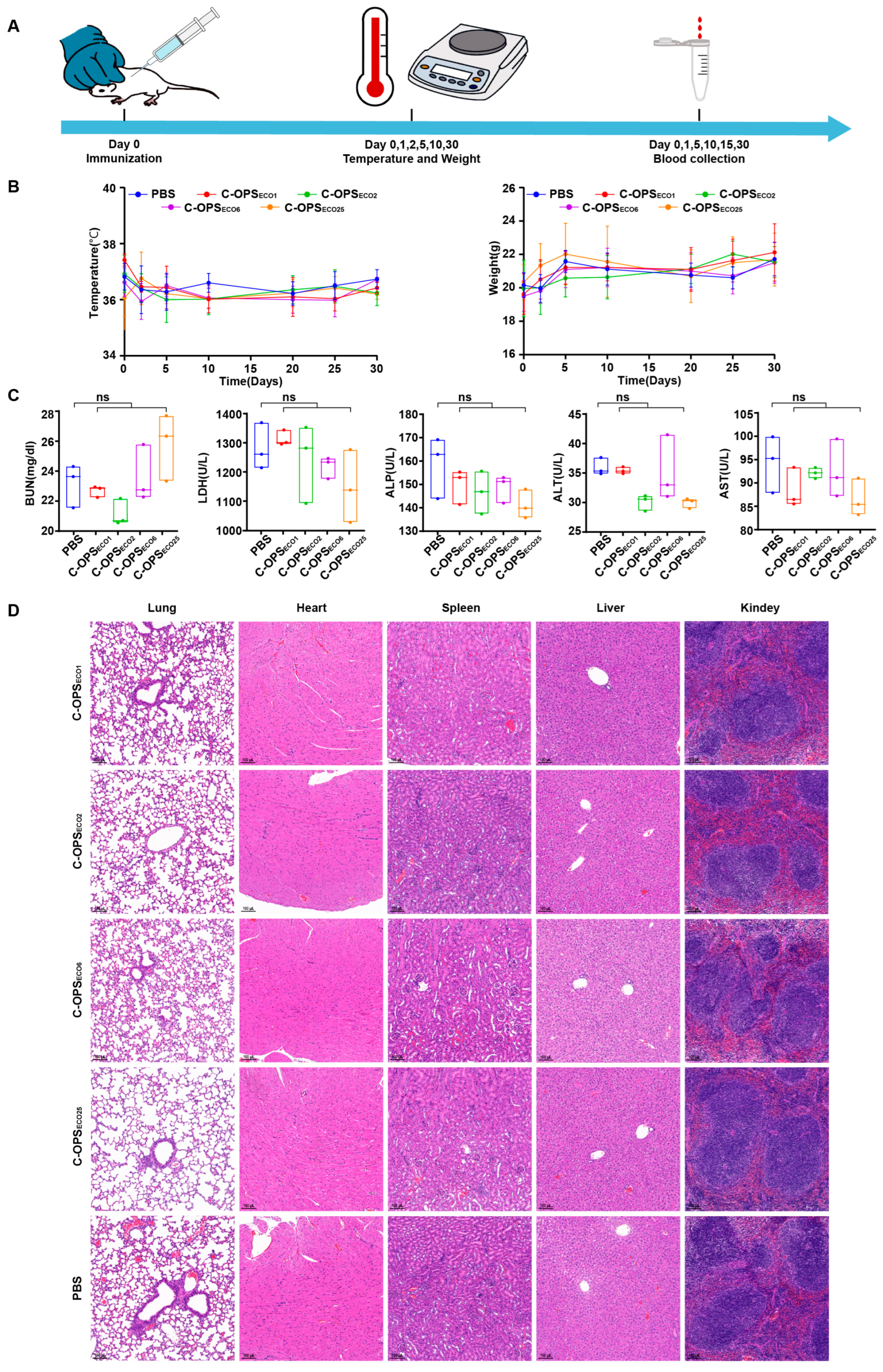
3.3. Safety Evaluation of Bioconjugate Vaccine
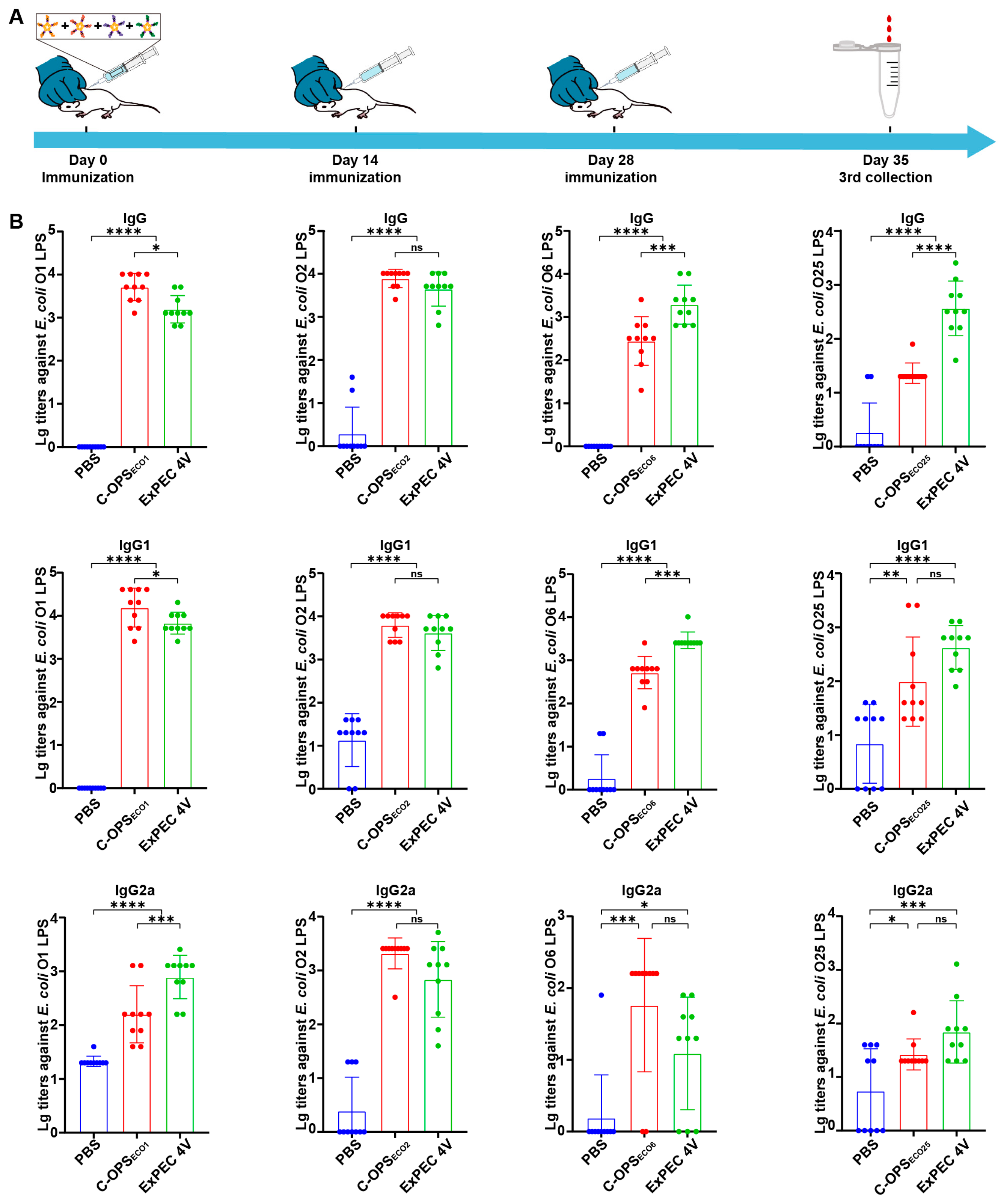
3.4. Evaluation of Specific Antibodies After Immunization with C-OPSECO1, C-OPSECO2, C-OPSECO6, or C-OPSECO25
3.5. Evaluation of Specific Antibodies After Immunization with ExPEC 4V
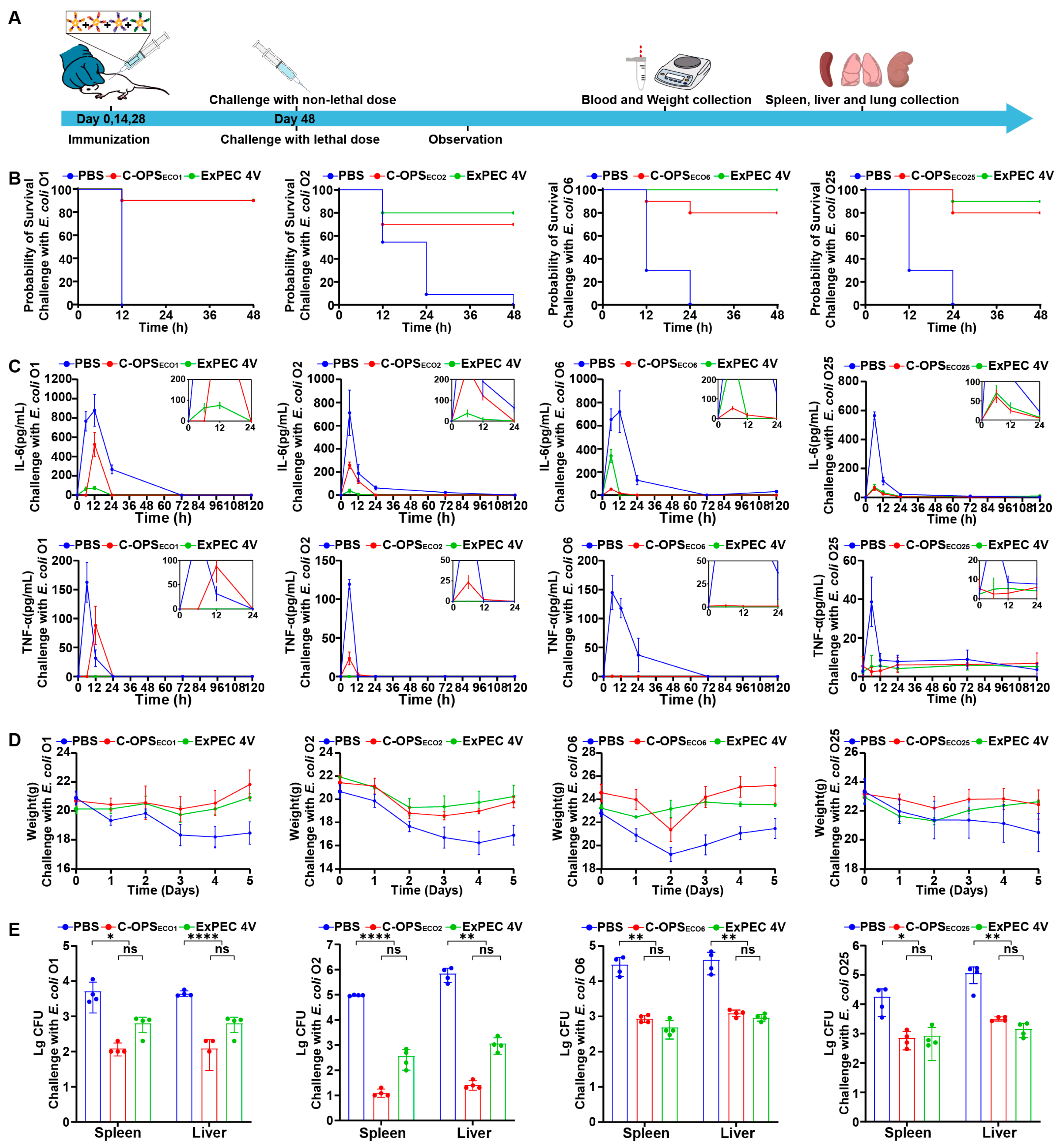
3.6. Evaluation of Bioconjugate Vaccine-Induced Protection After Infection with Varying Doses in Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ExPEC | Extra-intestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli |
| MDR | Multidrug-resistant |
| PGCT | Protein glycan coupling technology |
| O-AGC | O-antigen gene cluster |
| OPS | O-antigen polysaccharide |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| OST | Oligosaccharyltransferase |
| IPTG | Isopropyl-β-D-thiogalactopyranoside |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| CTB | Cholera toxin B subunit |
References
- Poolman, J.T.; Wacker, M. Extraintestinal Pathogenic Escherichia coli, a Common Human Pathogen: Challenges for Vaccine Development and Progress in the Field. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 213, 6–13. [Google Scholar]
- Dale, A.P.; Woodford, N. Extra-Intestinal Pathogenic Escherichia coli (Expec): Disease, Carriage and Clones. J. Infect. 2015, 71, 615–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.; Kim, J.-H.; Lee, Y. Virulence Factors Associated with Escherichia coli Bacteremia and Urinary Tract Infection. Ann. Lab. Med. 2022, 42, 203–212. [Google Scholar]
- Longhi, C.; Maurizi, L.; Conte, A.L.; Marazzato, M.; Comanducci, A.; Nicoletti, M.; Zagaglia, C. Extraintestinal Pathogenic Escherichia coli: Beta-Lactam Antibiotic and Heavy Metal Resistance. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, P.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, F.; Li, X.; Liu, H.; Ishfaq, M.; Xu, G.; Zhang, X. Antimicrobial Resistance and Virulence Profiles of Mcr-1-Positive Escherichia coli Isolated from Swine Farms in Heilongjiang Province of China. J. Food Prot. 2020, 83, 2209–2215. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shafiq, M.; Rahman, H.; Qasim, M.; Ayub, N.; Hussain, S.; Khan, J.; Naeem, M. Prevalence of Plasmid-Mediated Ampc Beta-Lactamases in Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumonia at Tertiary Care Hospital of Islamabad, Pakistan. Eur. J. Microbiol. Immunol. 2013, 3, 267–271. [Google Scholar]
- Arconada Nuin, E.; Vilken, T.; Xavier, B.B.; Doua, J.; Morrow, B.; Geurtsen, J.; Go, O.; Spiessens, B.; Sarnecki, M.; Poolman, J.; et al. A Microbiological and Genomic Perspective of Globally Collected Escherichia coli from Adults Hospitalized with Invasive E. coli Disease. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2024, 79, 2142–2151. [Google Scholar]
- Kalynych, S.; Morona, R.; Cygler, M. Progress in Understanding the Assembly Process of Bacterial O-Antigen. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 38, 1048–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Furevi, A.; Perepelov, A.V.; Guo, X.; Cao, H.; Wang, Q.; Reeves, P.R.; Knirel, Y.A.; Wang, L.; Widmalm, G. Structure and Genetics of Escherichia coli O Antigens. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2020, 44, 655–683. [Google Scholar]
- Kaper, J.B.; Nataro, J.P.; Mobley, H.L. Pathogenic Escherichia coli. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 2, 123–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weerdenburg, E.; Davies, T.; Morrow, B.; Zomer, A.L.; Hermans, P.; Go, O.; Spiessens, B.; Hoven, T.v.D.; van Geet, G.; Aitabi, M.; et al. Global Distribution of O Serotypes and Antibiotic Resistance in Extraintestinal Pathogenic Escherichia coli Collected from the Blood of Patients with Bacteremia across Multiple Surveillance Studies. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2023, 76, e1236–e1243. [Google Scholar]
- Huttner, A.; Hatz, C.; Dobbelsteen, G.v.D.; Abbanat, D.; Hornacek, A.; Frölich, R.; Dreyer, A.M.; Martin, P.; Davies, T.; Fae, K.; et al. Safety, Immunogenicity, and Preliminary Clinical Efficacy of a Vaccine against Extraintestinal Pathogenic Escherichia coli in Women with a History of Recurrent Urinary Tract Infection: A Randomised, Single-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Phase 1b Trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 528–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghattas, M.; Dwivedi, G.; Lavertu, M.; Alameh, M.-G. Vaccine Technologies and Platforms for Infectious Diseases: Current Progress, Challenges, and Opportunities. Vaccines 2021, 9, 1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollard, A.J.; Perrett, K.P.; Beverley, P.C. Maintaining Protection against Invasive Bacteria with Protein-Polysaccharide Conjugate Vaccines. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avery, O.T.; Goebel, W.F. Chemo-Immunological Studies on Conjugated Carbohydrate-Proteins: V. The Immunological Specifity of an Antigen Prepared by Combining the Capsular Polysaccharide of Type Iii Pneumococcus with Foreign Protein. J. Exp. Med. 1931, 54, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- MacCalman, T.E.; Phillips-Jones, M.K.; Harding, S.E. Glycoconjugate Vaccines: Some Observations on Carrier and Production Methods. Biotechnol. Genet. Eng. Rev. 2019, 35, 93–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Stefanetti, G.; Berti, F.; Kasper, D.L. Polysaccharide Structure Dictates Mechanism of Adaptive Immune Response to Glycoconjugate Vaccines. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jefferies, J.M.; Macdonald, E.; Faust, S.N.; Clarke, S.C. 13-Valent Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine (Pcv13). Hum. Vaccines 2011, 7, 1012–1018. [Google Scholar]
- Feldman, M.F.; Wacker, M.; Hernandez, M.; Hitchen, P.G.; Marolda, C.L.; Kowarik, M.; Morris, H.R.; Dell, A.; Valvano, M.A.; Aebi, M. Engineering N-Linked Protein Glycosylation with Diverse O Antigen Lipopolysaccharide Structures in Escherichia coli. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 3016–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, C.M.; Feldman, M.F. Glycoengineering Bioconjugate Vaccines, Therapeutics, and Diagnostics in E. coli. Glycobiology 2019, 29, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuccui, J.; Thomas, R.M.; Moule, M.G.; D’Elia, R.V.; Laws, T.R.; Mills, D.C.; Williamson, D.; Atkins, T.P.; Prior, J.L.; Wren, B.W.; et al. Exploitation of Bacterial N-Linked Glycosylation to Develop a Novel Recombinant Glycoconjugate Vaccine against Francisella tularensis. Open Biol. 2013, 3, 130002. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Z.; Zhang, H.; Li, L.; Chen, M.; Wang, P.G. Direct Cloning of Bacterial Surface Polysaccharide Gene Cluster for One-Step Production of Glycoconjugate Vaccine. ACS Infect. Dis. 2019, 5, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nothaft, H.; Szymanski, C.M. Protein Glycosylation in Bacteria: Sweeter Than Ever. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 765–778. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wacker, M.; Linton, D.; Hitchen, P.G.; Nita-Lazar, M.; Haslam, S.M.; North, S.J.; Panico, M.; Morris, H.R.; Dell, A.; Wren, B.W.; et al. N-Linked Glycosylation in Campylobacter Jejuni and Its Functional Transfer into E. coli. Science 2002, 298, 1790–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.; Sun, P.; Liu, B.; Liang, H.; Peng, Z.; Dong, Y.; Wang, D.; Liu, X.; Wang, B.; Zeng, M.; et al. Biosynthesis of Conjugate Vaccines Using an O-Linked Glycosylation System. mBio 2016, 7, e00443-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faridmoayer, A.; Fentabil, M.A.; Haurat, M.F.; Yi, W.; Woodward, R.; Wang, P.G.; Feldman, M.F. Extreme Substrate Promiscuity of the Neisseria Oligosaccharyl Transferase Involved in Protein O-Glycosylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 34596–34604. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, P.; Pan, C.; Zeng, M.; Liu, B.; Liang, H.; Wang, D.; Liu, X.; Wang, B.; Lyu, Y.; Wu, J.; et al. Design and Production of Conjugate Vaccines against S. paratyphi a Using an O-Linked Glycosylation System in Vivo. NPJ Vaccines 2018, 3, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Pan, C.; Sun, P.; Feng, E.; Wu, J.; Zhu, L.; Wang, H. Application of an O-Linked Glycosylation System in Yersinia enterocolitica Serotype O:9 to Generate a New Candidate Vaccine against Brucella Abortus. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Pan, C.; Wang, K.; Guo, Y.; Sun, Y.; Li, X.; Sun, P.; Wu, J.; Wang, H.; Zhu, L. Preparation of a Klebsiella Pneumoniae Conjugate Nanovaccine Using Glycol-Engineered Escherichia coli. Microb. Cell Fact. 2023, 22, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dow, J.M.; Mauri, M.; Scott, T.A.; Wren, B.W. Improving Protein Glycan Coupling Technology (Pgct) for Glycoconjugate Vaccine Production. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2020, 19, 507–527. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, L.; Chirman, D.; Clark, J.R.; Xing, Y.; Santos, H.H.; Vaughan, E.E.; Maresso, A.W. Vaccines against Extraintestinal Pathogenic Escherichia coli (Expec): Progress and Challenges. Gut Microbes 2024, 16, 2359691. [Google Scholar]
- Hachen, H.J. Oral Immunotherapy in Paraplegic Patients with Chronic Urinary Tract Infections: A Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. J. Urol. 1990, 143, 759–763. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hopkins, W.J.; Elkahwaji, J.; Beierle, L.M.; Leverson, G.E.; Uehling, D.T. Vaginal Mucosal Vaccine for Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections in Women: Results of a Phase 2 Clinical Trial. J. Urol. 2007, 177, 1349–1353. [Google Scholar]
- Eldridge, G.R.; Hughey, H.; Rosenberger, L.; Martin, S.M.; Shapiro, A.M.; D’antonio, E.; Krejci, K.G.; Shore, N.; Peterson, J.; Lukes, A.S.; et al. Safety and Immunogenicity of an Adjuvanted Escherichia coli Adhesin Vaccine in Healthy Women with and without Histories of Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections: Results from a First-in-Human Phase 1 Study. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2021, 17, 1262–1270. [Google Scholar]
- Hasanzadeh, S.; Habibi, M.; Shokrgozar, M.A.; Cohan, R.A.; Ahmadi, K.; Karam, M.R.A.; Bouzari, S. In Silico Analysis and in Vivo Assessment of a Novel Epitope-Based Vaccine Candidate against Uropathogenic Escherichia coli. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16258. [Google Scholar]
- Reigstad, C.S.; Hultgren, S.J.; Gordon, J.I. Functional Genomic Studies of Uropathogenic Escherichia coli and Host Urothelial Cells When Intracellular Bacterial Communities Are Assembled. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 21259–212567. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Li, Z.; Jia, R.; Hou, Y.; Yin, J.; Bian, X.; Li, A.; Muller, R.; Stewart, A.F.; Fu, J.; et al. Recet Direct Cloning and Redalphabeta Recombineering of Biosynthetic Gene Clusters, Large Operons or Single Genes for Heterologous Expression. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 1175–1190. [Google Scholar]
- Dobbelsteen, G.P.v.D.; Faé, K.C.; Serroyen, J.; Nieuwenhof, I.M.v.D.; Braun, M.; Haeuptle, M.A.; Sirena, D.; Schneider, J.; Alaimo, C.; Lipowsky, G.; et al. Immunogenicity and Safety of a Tetravalent E. coli O-Antigen Bioconjugate Vaccine in Animal Models. Vaccine 2016, 34, 4152–4160. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, J.R.; Owens, K.; Gajewski, A.; Kuskowski, M.A. Bacterial Characteristics in Relation to Clinical Source of Escherichia coli Isolates from Women with Acute Cystitis or Pyelonephritis and Uninfected Women. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 6064–6072. [Google Scholar]
- Sung, J.; Cheong, Y.; Kim, Y.-S.; Ahn, J.; Sohn, M.H.; Byun, S.; Seong, B.-L. Harnessing Pentameric Scaffold of Cholera Toxin B (Ctb) for Design of Subvirion Recombinant Dengue Virus Vaccine. Vaccines 2024, 12, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hempel, H.; Page, M.; Kemp, T.; Semper, A.; Brooks, T.; Pinto, L.A. The Importance of Using Who International Standards to Harmonise SARS-CoV-2 Serological Assays. Lancet Microbe 2024, 5, e301–e305. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hao, L.; Huang, W.; Guo, Y.; Liu, X.; Wu, J.; Zhu, L.; Pan, C.; Wang, H. A Bioconjugate Vaccine Against Extra-Intestinal Pathogenic Escherichia coli (ExPEC). Vaccines 2025, 13, 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13040362
Hao L, Huang W, Guo Y, Liu X, Wu J, Zhu L, Pan C, Wang H. A Bioconjugate Vaccine Against Extra-Intestinal Pathogenic Escherichia coli (ExPEC). Vaccines. 2025; 13(4):362. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13040362
Chicago/Turabian StyleHao, Linhui, Wenhua Huang, Yan Guo, Xiankai Liu, Jun Wu, Li Zhu, Chao Pan, and Hengliang Wang. 2025. "A Bioconjugate Vaccine Against Extra-Intestinal Pathogenic Escherichia coli (ExPEC)" Vaccines 13, no. 4: 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13040362
APA StyleHao, L., Huang, W., Guo, Y., Liu, X., Wu, J., Zhu, L., Pan, C., & Wang, H. (2025). A Bioconjugate Vaccine Against Extra-Intestinal Pathogenic Escherichia coli (ExPEC). Vaccines, 13(4), 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13040362





