Synthetic Neuraminidase Vaccine Induces Cross-Species and Multi-Subtype Protection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Research Ethics
2.2. Influenza Viruses
2.3. Immunogen Design and Vaccine Production
2.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.5. Western Blot
2.6. Mouse Vaccinations and Sample Collections
2.7. Influenza Virus Microneutralization
2.8. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.9. Enzyme-Linked Lectin Assay (ELLA)
2.10. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Spot (ELISpot)
2.11. Mouse Challenge Studies
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Design of N1 Centralized Consensus Sequence and Construction of Vaccine
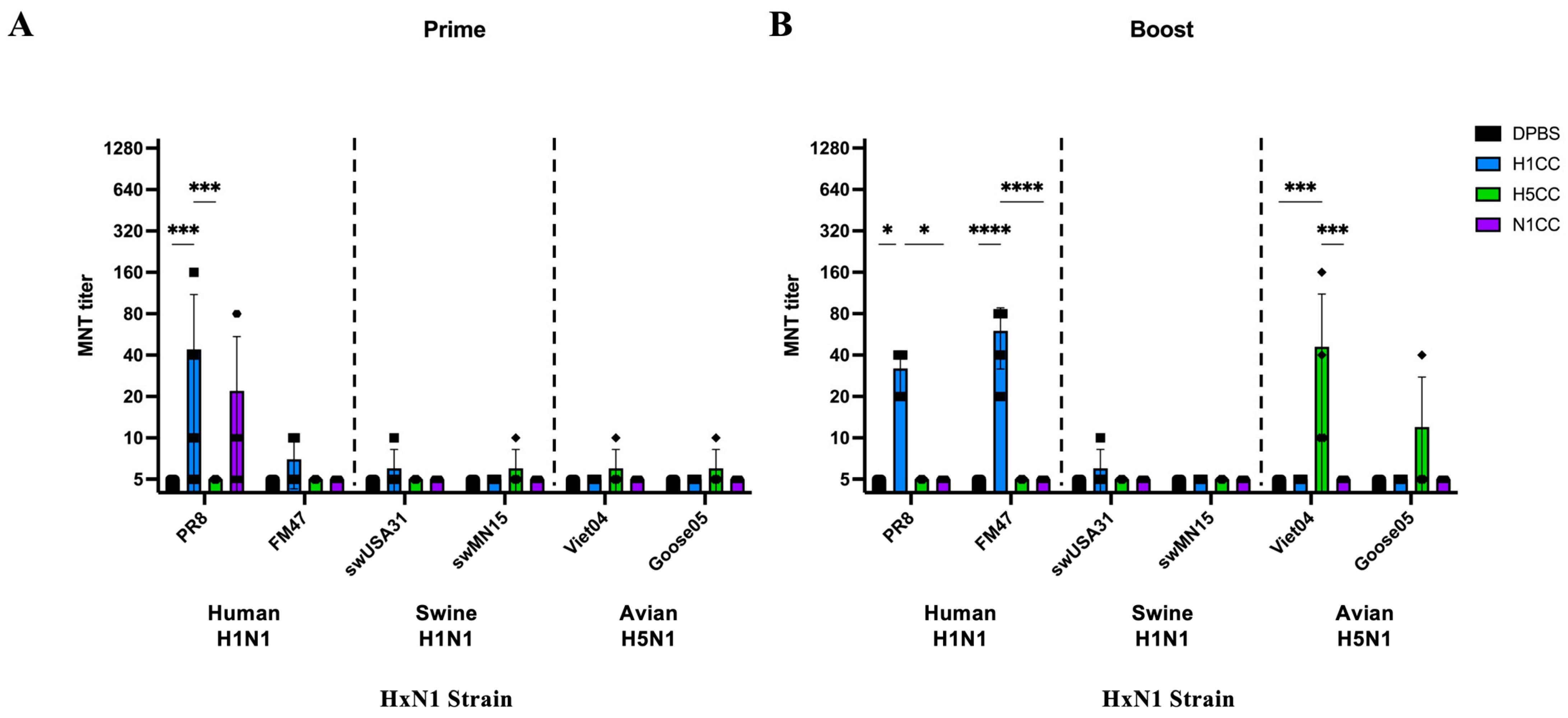
3.2. Functional Antibody Assessment
3.3. Induction of T-Cell Responses
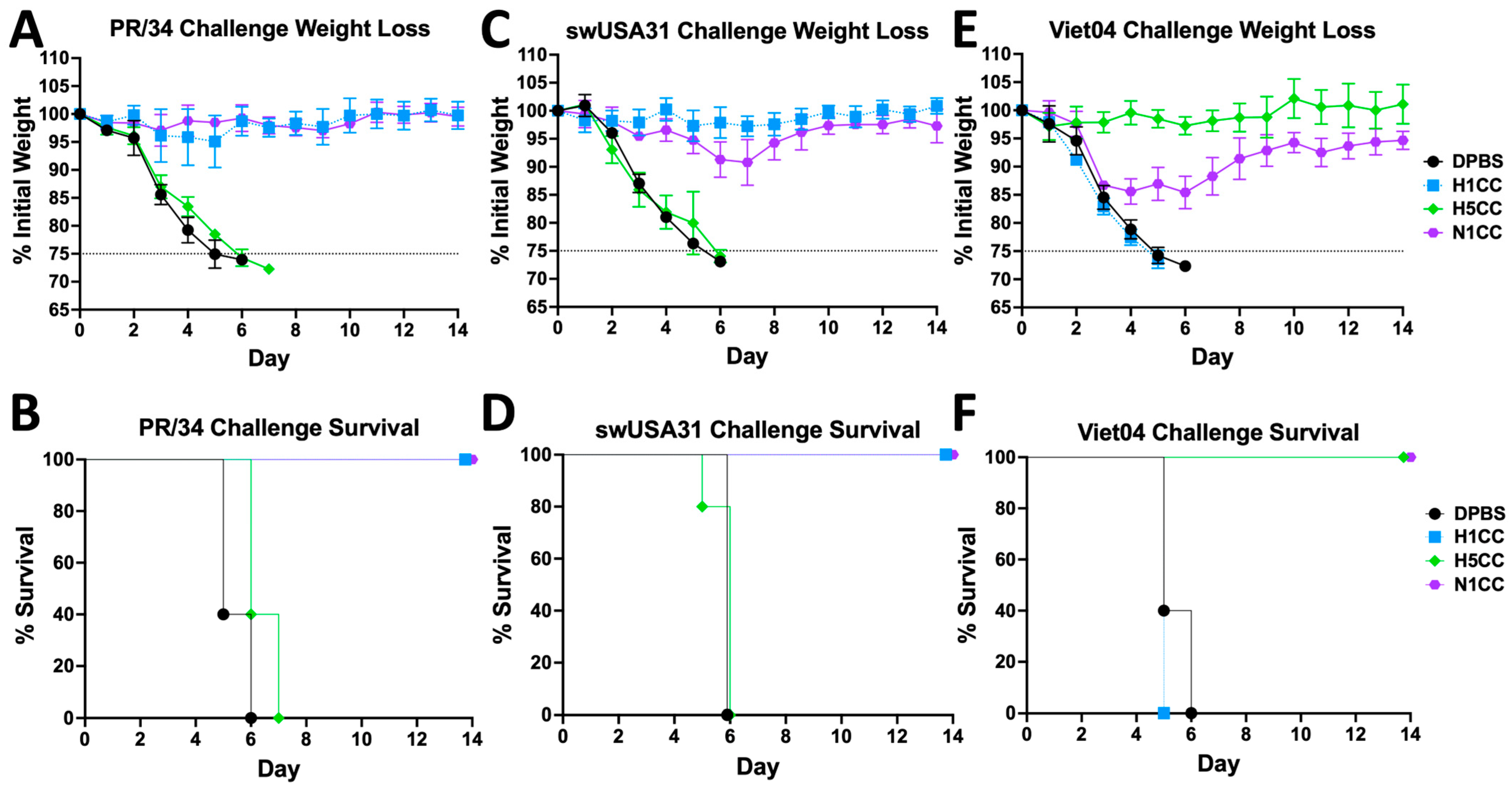
3.4. Protection from HxN1 Challenge
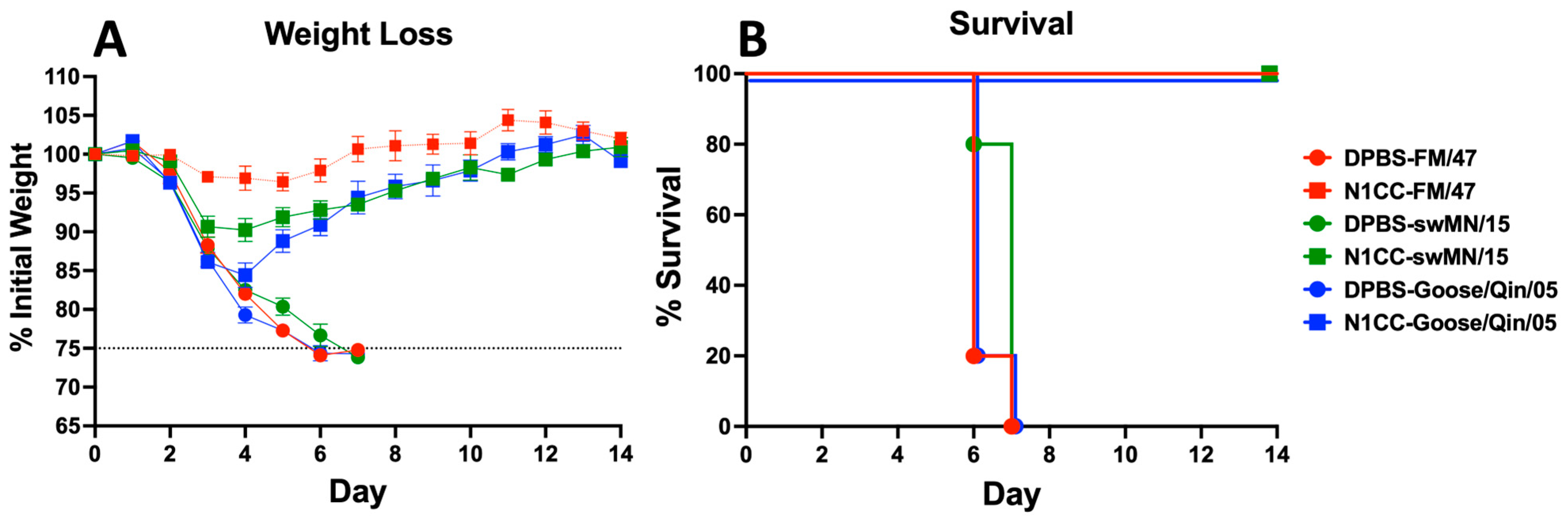
3.5. Strength and Breadth of Ad-N1CC Protection
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Krammer, F.; Smith, G.J.D.; Fouchier, R.A.M.; Peiris, M.; Kedzierska, K.; Doherty, P.C.; Palese, P.; Shaw, M.L.; Treanor, J.; Webster, R.G.; et al. Influenza. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2018, 4, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Le Sage, V.; Lowen, A.C.; Lakdawala, S.S. Block the Spread: Barriers to Transmission of Influenza Viruses. Annu. Rev. Virol. 2023, 10, 347–370. [Google Scholar]
- Long, J.S.; Mistry, B.; Haslam, S.M.; Barclay, W.S. Host and viral determinants of influenza A virus species specificity. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 67–81. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, W.; Loving, C.L.; Driver, J.P. From Snoot to Tail: A Brief Review of Influenza Virus Infection and Immunity in Pigs. J. Immunol. 2023, 211, 1187–1194. [Google Scholar]
- Leguia, M.; Garcia-Glaessner, A.; Muñoz-Saavedra, B.; Juarez, D.; Barrera, P.; Calvo-Mac, C.; Jara, J.; Silva, W.; Ploog, K.; Amaro, L.; et al. Highly pathogenic avian influenza A (H5N1) in marine mammals and seabirds in Peru. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 5489. [Google Scholar]
- Markin, A.; Zanella, G.C.; Arendsee, Z.W.; Zhang, J.; Krueger, K.M.; Gauger, P.C.; Baker, A.L.V.; Anderson, T.K. Reverse-zoonoses of 2009 H1N1 pandemic influenza A viruses and evolution in United States swine results in viruses with zoonotic potential. PLoS Pathog. 2023, 19, e1011476. [Google Scholar]
- Venkatesan, P. Avian influenza spillover into mammals. Lancet Microbe 2023, 4, e492. [Google Scholar]
- Lipsitch, M.; Barclay, W.; Raman, R.; Russell, C.J.; A Belser, J.; Cobey, S.; Kasson, P.M.; O Lloyd-Smith, J.; Maurer-Stroh, S.; Riley, S.; et al. Viral factors in influenza pandemic risk assessment. eLife 2016, 5, e18491. [Google Scholar]
- Current H5N1 Bird Flu Situation in Mammals. 2024. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/bird-flu/situation-summary/mammals.html (accessed on 11 April 2024).
- Castrucci, M.R. Factors affecting immune responses to the influenza vaccine. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2018, 14, 637–646. [Google Scholar]
- McLean, H.Q.; Petrie, J.G.; Hanson, K.E.; Meece, J.K.; Rolfes, M.A.; Sylvester, G.C.; Neumann, G.; Kawaoka, Y.; Belongia, E.A. Interim Estimates of 2022-23 Seasonal Influenza Vaccine Effectiveness—Wisconsin, October 2022-February 2023. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2023, 72, 201–205. [Google Scholar]
- Wohlbold, T.J.; Krammer, F. In the shadow of hemagglutinin: A growing interest in influenza viral neuraminidase and its role as a vaccine antigen. Viruses 2014, 6, 2465–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullard, B.L.; Weaver, E.A. Strategies Targeting Hemagglutinin as a Universal Influenza Vaccine. Vaccines 2021, 9, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, S.M.; Newhams, M.M.; Halasa, N.B.; Feldstein, L.R.; Novak, T.; Weiss, S.L.; Coates, B.M.; E Schuster, J.; Schwarz, A.J.; Maddux, A.B.; et al. Vaccine Effectiveness Against Life-Threatening Influenza Illness in US Children. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2022, 75, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, K.; Weber, Z.A.; Yang, D.H.; Klein, N.P.; DeSilva, M.B.; Dascomb, K.; Irving, S.A.; Naleway, A.L.; Rao, S.; Gaglani, M.; et al. Vaccine Effectiveness Against Pediatric Influenza-A-Associated Urgent Care, Emergency Department, and Hospital Encounters During the 2022-2023 Season: VISION Network. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2023, 78, 746–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kissling, E.; Pozo, F.; Martínez-Baz, I.; Buda, S.; Vilcu, A.; Domegan, L.; Mazagatos, C.; Dijkstra, F.; Latorre-Margalef, N.; Filipović, S.K.; et al. Influenza vaccine effectiveness against influenza A subtypes in Europe: Results from the 2021-2022 I-MOVE primary care multicentre study. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses 2023, 17, e13069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, E.A.; Rubrum, A.M.; Webby, R.J.; Barry, M.A. Protection against divergent influenza H1N1 virus by a centralized influenza hemagglutinin. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webby, R.J.; Weaver, E.A. Centralized Consensus Hemagglutinin Genes Induce Protective Immunity against H1, H3 and H5 Influenza Viruses. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingel, A.; Bullard, B.L.; Weaver, E.A. Efficacy of an Adenoviral Vectored Multivalent Centralized Influenza Vaccine. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petro-Turnquist, E.M.; Bullard, B.L.; Pekarek, M.J.; Weaver, E.A. Adenoviral-Vectored Centralized Consensus Hemagglutinin Vaccine Provides Broad Protection against H2 Influenza a Virus. Vaccines 2022, 10, 926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.-J.; Crank, M.C.; Shiver, J.; Graham, B.S.; Mascola, J.R.; Nabel, G.J. Next-generation influenza vaccines: Opportunities and challenges. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2020, 19, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-Y.; Yeh, Y.-C.; Chan, J.-T.; Yang, Y.-C.; Yang, J.-R.; Liu, M.-T.; Wu, H.-S.; Hsiao, P.-W. A VLP Vaccine Induces Broad-Spectrum Cross-Protective Antibody Immunity against H5N1 and H1N1 Subtypes of Influenza A Virus. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42363. [Google Scholar]
- Quan, F.-S.; Kim, M.-C.; Lee, B.-J.; Song, J.-M.; Compans, R.W.; Kang, S.-M. Influenza M1 VLPs containing neuraminidase induce heterosubtypic cross-protection. Virology 2012, 430, 127–135. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.-C.; Lin, C.-Y.; Tsou, Y.-T.; Jan, J.-T.; Wu, S.-C. Cross-Reactive Neuraminidase-Inhibiting Antibodies Elicited by Immunization with Recombinant Neuraminidase Proteins of H5N1 and Pandemic H1N1 Influenza A Viruses. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 7224–7234. [Google Scholar]
- Cheung, M.; Chang, C.; Rathnasinghe, R.; Rossignol, E.; Zhang, Y.; Ferrari, A.; Patel, H.; Huang, Y.; Guillen, M.S.; Scalzo, T.; et al. Self-amplifying mRNA seasonal influenza vaccines elicit mouse neutralizing antibody and cell-mediated immunity and protect ferrets. NPJ Vaccines 2023, 8, 150. [Google Scholar]
- Kitikoon, P.; Knetter, S.M.; Mogler, M.A.; Morgan, C.L.; Hoehn, A.; Puttamreddy, S.; Strait, E.L.; Segers, R.P. Quadrivalent neuraminidase RNA particle vaccine protects pigs against homologous and heterologous strains of swine influenza virus infection. Vaccine 2023, 41, 6941–6951. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Zhao, T.; Wang, L.; Yang, Z.; Luo, C.; Li, M.; Luo, H.; Sun, C.; Yan, H.; Shu, Y. A mosaic influenza virus-like particles vaccine provides broad humoral and cellular immune responses against influenza A viruses. NPJ Vaccines 2023, 8, 132. [Google Scholar]
- McMahon, M.; Tan, J.; O’Dell, G.; Roubidoux, E.K.; Strohmeier, S.; Krammer, F. Immunity induced by vaccination with recombinant influenza B virus neuraminidase protein breaks viral transmission chains in guinea pigs in an exposure intensity-dependent manner. J. Virol. 2023, 97, e0105723. [Google Scholar]
- Werninghaus, I.C.; Hinke, D.M.; Fossum, E.; Bogen, B.; Braathen, R. Neuraminidase delivered as an APC-targeted DNA vaccine induces protective antibodies against influenza. Mol. Ther. 2023, 31, 2188–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Job, E.R.; Ysenbaert, T.; Smet, A.; Christopoulou, I.; Strugnell, T.; Oloo, E.O.; Oomen, R.P.; Kleanthous, H.; Vogel, T.U.; Saelens, X. Broadened immunity against influenza by vaccination with computationally designed influenza virus N1 neuraminidase constructs. NPJ Vaccines 2018, 3, 55. [Google Scholar]
- Skarlupka, A.L.; Bebin-Blackwell, A.-G.; Sumner, S.F.; Ross, T.M. Universal Influenza Virus Neuraminidase Vaccine Elicits Protective Immune Responses against Human Seasonal and Pre-pandemic Strains. J. Virol. 2021, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Wu, T.-L.; O Lasaro, M.; Latimer, B.P.; Parzych, E.M.; Bian, A.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Erikson, J.; Xiang, Z.; et al. A Universal Influenza A Vaccine Based on Adenovirus Expressing Matrix-2 Ectodomain and Nucleoprotein Protects Mice From Lethal Challenge. Mol. Ther. 2010, 18, 2182–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitelli, A.; Quirion, M.R.; Lo, C.-Y.; Misplon, J.A.; Grabowska, A.K.; Pierantoni, A.; Ammendola, V.; Price, G.E.; Soboleski, M.R.; Cortese, R.; et al. Vaccination to Conserved Influenza Antigens in Mice Using a Novel Simian Adenovirus Vector, PanAd3, Derived from the Bonobo Pan paniscus. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyushina, N.A.; Khalenkov, A.M.; Seiler, J.P.; Forrest, H.L.; Bovin, N.V.; Marjuki, H.; Barman, S.; Webster, R.G.; Webby, R.J. Adaptation of Pandemic H1N1 Influenza Viruses in Mice. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 8607–8616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, H.; Palmer, D.J.; Ng, P.; Barry, M.A. Evaluation of polyethylene glycol modification of first-generation and helper-dependent adenoviral vectors to reduce innate immune responses. Mol. Ther. 2005, 11, 66–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Couzens, L.; Eichelberger, M.C. Measuring Influenza Neuraminidase Inhibition Antibody Titers by Enzyme-linked Lectin Assay. J. Vis. Exp. 2016, 115, 54573. [Google Scholar]
- Weaver, E.A. Dose Effects of Recombinant Adenovirus Immunization in Rodents. Vaccines 2019, 7, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh, P.; Long, H.; Tien, N.; Hien, N.; Mai, L.; Phong, L.; Van Tuan, L.; Van Tan, H.; Nguyen, N.; Van Tu, P.; et al. Risk factors for human infection with avian influenza A H5N1, Vietnam 2004. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2006, 12, 1841–1847. [Google Scholar]
- Ly, H. Highly pathogenic avian influenza H5N1 virus infections of dairy cattle and livestock handlers in the United States of America. Virulence 2024, 15, 2343931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, E.A. Vaccines within vaccines: The use of adenovirus types 4 and 7 as influenza vaccine vectors. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2014, 10, 544–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamlangdee, A.; Kingstad-Bakke, B.; Osorio, J.E. Mosaic H5 Hemagglutinin Provides Broad Humoral and Cellular Immune Responses against Influenza Viruses. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 6771–6783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-Q.; Lan, L.Y.-L.; Huang, M.; Henry, C.; Wilson, P.C. Hemagglutinin Stalk-Reactive Antibodies Interfere with Influenza Virus Neuraminidase Activity by Steric Hindrance. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e01526-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krammer, F.; Fouchier, R.A.M.; Eichelberger, M.C.; Webby, R.J.; Shaw-Saliba, K.; Wan, H.; Wilson, P.C.; Compans, R.W.; Skountzou, I.; Monto, A.S. NAction! How Can Neuraminidase-Based Immunity Contribute to Better Influenza Virus Vaccines? MBio 2018, 9, e02332-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Do, T.H.T.; Wheatley, A.K.; Kent, S.J.; Koutsakos, M. Influenza B virus neuraminidase: A potential target for next-generation vaccines? Expert Rev. Vaccines 2023, 23, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memoli, M.J.; Shaw, P.A.; Han, A.; Czajkowski, L.; Reed, S.; Athota, R.; Bristol, T.; Fargis, S.; Risos, K.; Powers, J.H.; et al. Evaluation of Antihemagglutinin and Antineuraminidase Antibodies as Correlates of Protection in an Influenza A/H1N1 Virus Healthy Human Challenge Model. MBio 2016, 7, e00417.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, K.; Paust, S. Dynamic Natural Killer Cell and T Cell Responses to Influenza Infection. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Chang, T.Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, S.; Matsuyama, S.; Yu, G.; Compans, R.W.; Li, J.-D.; Prausnitz, M.R.; et al. Heterosubtypic influenza protection elicited by double-layered polypeptide nanoparticles in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E7758–E7767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullard, B.L.; DeBeauchamp, J.; Pekarek, M.J.; Petro-Turnquist, E.; Vogel, P.; Webby, R.J.; Weaver, E.A. An epitope-optimized human H3N2 influenza vaccine induces broadly protective immunity in mice and ferrets. NPJ Vaccines 2022, 7, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, J.A.; Weber, T.; Cejas, P.J.; Cox, K.S.; Touch, S.; Austin, L.A.; Ou, Y.; Citron, M.P.; Luo, B.; Gindy, M.E.; et al. Characterization of humoral and cell-mediated immunity induced by mRNA vaccines expressing influenza hemagglutinin stem and nucleoprotein in mice and nonhuman primates. Vaccine 2022, 40, 4412–4423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, G.; Noda, T.; Kawaoka, Y. Emergence and pandemic potential of swine-origin H1N1 influenza virus. Nature 2009, 459, 931–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.C.F.; Bahl, J.; Joseph, U.; Butt, K.M.; Peck, H.A.; Koay, E.S.C.; Oon, L.L.E.; Barr, I.G.; Vijaykrishna, D.; Smith, G.J.D. Phylodynamics of H1N1/2009 influenza reveals the transition from host adaptation to immune-driven selection. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raha, J.R.; Kim, K.-H.; Bhatnagar, N.; Liu, R.; Le, C.T.T.; Park, B.R.; Grovenstein, P.; Pal, S.S.; Ko, E.-J.; Shin, C.H.; et al. Supplementation of seasonal vaccine with multi-subtype neuraminidase and M2 ectodomain virus-like particle improves protection against homologous and heterologous influenza viruses in aged mice. Antivir. Res. 2024, 225, 105877. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alvarado-Facundo, E.; Herrup, R.; Wang, W.; Colombo, R.E.; Collins, L.; Ganesan, A.; Hrncir, D.; Lalani, T.; Markelz, A.E.; Maves, R.C.; et al. Comparison of neuraminidase inhibiting antibody responses elicited by egg- and cell-derived influenza vaccines. Vaccine 2025, 46, 126669. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xie, R.; Edwards, K.M.; Wille, M.; Wei, X.; Wong, S.-S.; Zanin, M.; El-Shesheny, R.; Ducatez, M.; Poon, L.L.M.; Kayali, G.; et al. The episodic resurgence of highly pathogenic avian influenza H5 virus. Nature 2023, 622, 810–817. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Peacock, T.P.; Moncla, L.; Dudas, G.; VanInsberghe, D.; Sukhova, K.; Lloyd-Smith, J.O.; Worobey, M.; Lowen, A.C.; Nelson, M.I. The global H5N1 influenza panzootic in mammals. Nature 2025, 637, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Strain | Genbank Accession | Strain Name | Genbank Accession 2 |
| A/Brevig Mission/1/18 | AF250356.2 | A/Cam/46 | CY009598.1 |
| A/WSN/1933 | J02177.1 | A/Fort Monmouth/1/1947 | CY009614.1 |
| A/NWS/1933 | L25815.1 | A/Fort Warren/1/1950 | CY009334.1 |
| A/Puerto Rico/8/1934 | J02146.1 | A/FLW/1951 | CY147376.1 |
| A/Melbourne/35 | CY009326.1 | A/Denver/57 | CY008990.1 |
| A/Bel/1942 | CY009278.1 | A/USSR/90/1977 | CY121880.1 |
| A/AA/Marton/1943 | CY020287.1 | A/Singapore/6/1986 | CY020479.1 |
| Strain | Subtype | Abbr. | H1CC | H5CC | N1CC |
| A/Fort Monmouth/1/1947 | H1N1 | FM47 | 95.60% | 62.60% | 97.20% |
| A/Puerto Rico/8/1934 | H1N1 | PR8 | 92.60% | 63.80% | 92.50% |
| A/swine/USA/1976/1931 | H1N1 | swUSA31 | 88.20% | 64.10% | 89.30% |
| A/swine/Minnesota/A01489606/2015 | H1N1 | swMN15 | 82.90% | 62.70% | 84.40% |
| A/Vietnam/1203/2004 | H5N1 | Viet04 | 63.10% | 97.90% | 82.10% |
| A/bar-headed goose/Qinghai/1A/2005 | H5N1 | Goose05 | 63.00% | 97.70% | 82.10% |
| A/Thailand/4(SP-528)/2004 | H5N1 | Thai04 | 63.10% | 95.60% | 81.90% |
| A/New Caledonia/20/1999& | H1N1 | NC99 | 94.20% | 62.70% | 90.20% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pekarek, M.J.; Petro-Turnquist, E.M.; Jeanjaquet, N.E.; Hoagstrom, K.V.; LaMontia-Hankin, E.; Jahnke, L.; Madapong, A.; Weaver, E.A. Synthetic Neuraminidase Vaccine Induces Cross-Species and Multi-Subtype Protection. Vaccines 2025, 13, 364. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13040364
Pekarek MJ, Petro-Turnquist EM, Jeanjaquet NE, Hoagstrom KV, LaMontia-Hankin E, Jahnke L, Madapong A, Weaver EA. Synthetic Neuraminidase Vaccine Induces Cross-Species and Multi-Subtype Protection. Vaccines. 2025; 13(4):364. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13040364
Chicago/Turabian StylePekarek, Matthew J., Erika M. Petro-Turnquist, Nicholas E. Jeanjaquet, Kristine V. Hoagstrom, Enzo LaMontia-Hankin, Leigh Jahnke, Adthakorn Madapong, and Eric A. Weaver. 2025. "Synthetic Neuraminidase Vaccine Induces Cross-Species and Multi-Subtype Protection" Vaccines 13, no. 4: 364. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13040364
APA StylePekarek, M. J., Petro-Turnquist, E. M., Jeanjaquet, N. E., Hoagstrom, K. V., LaMontia-Hankin, E., Jahnke, L., Madapong, A., & Weaver, E. A. (2025). Synthetic Neuraminidase Vaccine Induces Cross-Species and Multi-Subtype Protection. Vaccines, 13(4), 364. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13040364





