Abstract
Background/Objectives: The CDC has recommended immunizations to protect infants during the respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) season, which varies annually and geographically. Seasonal differences in RSV hospitalizations among infants are not well studied. Methods: This retrospective cohort study identified infants < 12 months old hospitalized with RSV from the PINC AI Healthcare Database during the 2018–2023 surveillance years (1 July–30 June). Monthly RSV hospitalizations were stratified by U.S. census division and age group (<3, 3–5, 6–8, 9–11 months). Patient characteristics, healthcare resource utilization (HCRU), and cost were compared between typical in-season months (October–March) and typical off-season months (April–September) for RSV hospitalizations. Results: Among 20,531 hospitalizations for RSV (mean age: 4.1 months, 56.4% male), 22% (n = 4510) were off-season; 83% occurred in June–September across US census divisions. Infants < 3 months accounted for 46% (n = 2054) of off-season hospitalizations. Seasonal patterns were similar across age groups. Off-season hospitalizations were associated with longer hospital length of stay (6.9 vs. 4.9 days) and more supplemental oxygen (59.1% vs. 55.5%), intensive care unit admission (30.1% vs. 26.8%), and mechanical ventilation/airflow usage (20.3% vs. 16.3%). Mean hospitalization costs were 40% higher during off-season ($17,911 vs. $12,757). In the surveillance years before (2018–2020) and after (2022–2023) the COVID-19 pandemic, off-season costs and HCRU were consistently higher than in-season. Conclusions: There is an unmet need among the 1 in 5 infants with off-season RSV hospitalizations, which are associated with higher HCRU and costs. Current recommendations on RSV preventives offer limited protection for infants exposed to RSV outside the typical season.
1. Introduction
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is the primary cause of infant lower respiratory tract illness. The most common cause of inpatient admission among United States (US) children under the age of 2 years, the mean annual RSV hospitalization rate among infants < 1 year of age has been estimated to be 20 per 1000 [1,2]. More than 50% of RSV hospitalizations occur within the first 3 months of life and over 75% occur by 6 months of age [3].
In 2023, two new immunization products were licensed and recommended for the prevention of RSV disease among infants, though most infants do not need both. A maternal RSV prefusion F protein-based vaccine (RSVpreF) administered to pregnant persons 32 through 36 weeks’ gestation prevents RSV disease in infants aged through 6 months [4]. Alternatively, nirsevimab, a long-acting monoclonal antibody, is administered to infants aged <8 months who are born during or entering their first RSV season and lasts through at least 5 months [5].
The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) recommended seasonal administration of each prevention option timed to the typical national onset and offset of the RSV season. Surveillance data informed the recommendation according to the timing of high transmission rates occurring throughout the year. Maternal RSVpreF vaccination is recommended from September through January and nirsevimab is recommended from October through March [4,5,6,7,8]. While the timing of these seasonal recommendations is for most of the continental US, annual and geographic variability in RSV seasonality exists [8,9,10].
However, it remains unclear how the temporal and geographic patterns of RSV seasonality may vary among infants < 1 year old and whether any inequities exist according to the timing of birth out of season [6,8,11,12]. Given the current recommendations for seasonal administration of infant RSV preventions, understanding the clinical and economic burden of RSV hospitalizations among infants < 1 year occurring off-season is of importance. This study aimed to characterize and assess the seasonal patterns of hospitalization due to RSV among infants < 12 months of age. In addition, the economic burden of RSV hospitalizations occurring during the RSV season (i.e., 1 October–31 March) and off-season (i.e., 1 April–30 September) was investigated.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Data Source
This descriptive retrospective cohort study identified infants < 12 months of age hospitalized with RSV using the PINC AI Healthcare Database (PHD). The PHD is a hospital-based data source with >1190 contributing hospitals representing approximately 25% of annual hospital admissions and 326 million unique patients across the US. The regional and rural–urban distribution of PHD hospitals is similar to American Hospital Association member hospitals [13]. All data are de-identified and fully compliant with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA).
2.2. Study Population
Infants < 1 year of age hospitalized with RSV during July 2018–June 2023 were identified by a primary or secondary discharge diagnosis or a positive RSV lab test result. International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-10-CM) diagnosis codes for RSV included B97.4, J12.1, J21.0, and J20.5. Hospital lab test records were also searched to identify positive RSV lab tests. To assess trends in RSV hospitalization by infant age in months, RSV patients were required to have a “newborn” record, defined as a diagnosis code for liveborn infants according to place of birth (ICD-10-CM: Z38.00–Z38.8), since the PHD’s default patient demographic information only reports age by year. The infant’s age in months was estimated by calculating the number of months from the “newborn” record to the RSV hospitalization record. All qualified RSV hospitalizations for infants < 12 months of age were included in the study.
2.3. Outcomes
Patient demographic, hospital, and clinical characteristics were evaluated during the RSV hospitalization. Chronic medical conditions were identified by ICD-10-CM diagnosis codes present during RSV hospitalizations. Healthcare resource utilization (HCRU) and costs evaluated included total inpatient cost, hospitalization length of stay (LOS), inpatient pharmacy usage and costs, as well as the frequency, duration, and costs of intensive care unit (ICU) admission, mechanical ventilation/airflow (MVAF) usage, and supplemental oxygen usage. ICU admissions were identified by hospital chargemaster, Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System (HCPCS) and Current Procedural Terminology, fourth edition (CPT-4) procedure codes; MVAF was identified by hospital chargemaster, ICD-10 procedure codes (ICD-10-PCS), HCPCS, and CPT-4 codes; and supplemental oxygen was identified by hospital chargemaster and ICD-10-PCS. The duration of healthcare resource usage was measured based on the distinct number of days with a recorded corresponding service day and a relevant standard charge code or code during the inpatient encounter. Costs were assessed among patients with available cost data for the service category. All costs are inflation adjusted to 2024 US dollars using Consumer Price Index Medical Care component data.
2.4. Data Analyses
RSV hospitalizations were stratified by seasonality, surveillance year, age group, and geographic region for analysis. RSV seasonality was defined according to current ACIP recommendations for the prevention of RSV among infants with admission dates during 1 October–31 March being in-season and those during 1 April–30 September being off-season [5]. Based on admission date, hospitalizations were stratified into 5 surveillance years defined as the period of 1 July–30 June of the following year. Age groups included infants 0–2, 3–5, 6–8, and 9–11 months at hospitalization. Additional evaluations were conducted among infants 0, 1, and 2 months of age. Geographic stratifications were based on hospital location within the 9 US census divisions.
Patient demographic, hospital, and clinical characteristics, as well as HCRU and costs were assessed for the overall study population (infants < 12 months of age) and compared between all in-season and off-season RSV hospitalizations (July 2018–June 2023). HCRU and costs were also evaluated for in-season and off-season hospitalizations during the pre-COVID (July 2018–June 2020) and post-COVID (July 2022–June 2023) periods. HCRU and costs were further stratified among infants born within or outside an RSV season to evaluate the potential burden of a subgroup that is not eligible for any RSV prevention despite the current recommendation on RSV prevention. Infants born within an RSV season (i.e., between 1 October–31 March) were defined as in-season births and those born outside an RSV season were defined as off-season births. The seasonality of RSV cases among all infants < 1 year, regardless of an identifiable age in months, was evaluated as a sensitivity analysis.
Patient and hospital characteristics as well as HCRU and cost outcomes were summarized using descriptive statistics. For categorical variables, the frequency and percentage of patients in each category were presented. Percentages were based on the total number of relevant patients without ‘unknown’ or missing values. For continuous variables, data were presented as means with standard deviations (SD) and medians. Analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Chi-squared tests were used as statistical comparisons for continuous and categorical variables, respectively. All data analyses were performed using statistical software SAS version 9.4 (SAS Institute; Cary, NC, USA).
3. Results
3.1. Study Population Characteristics
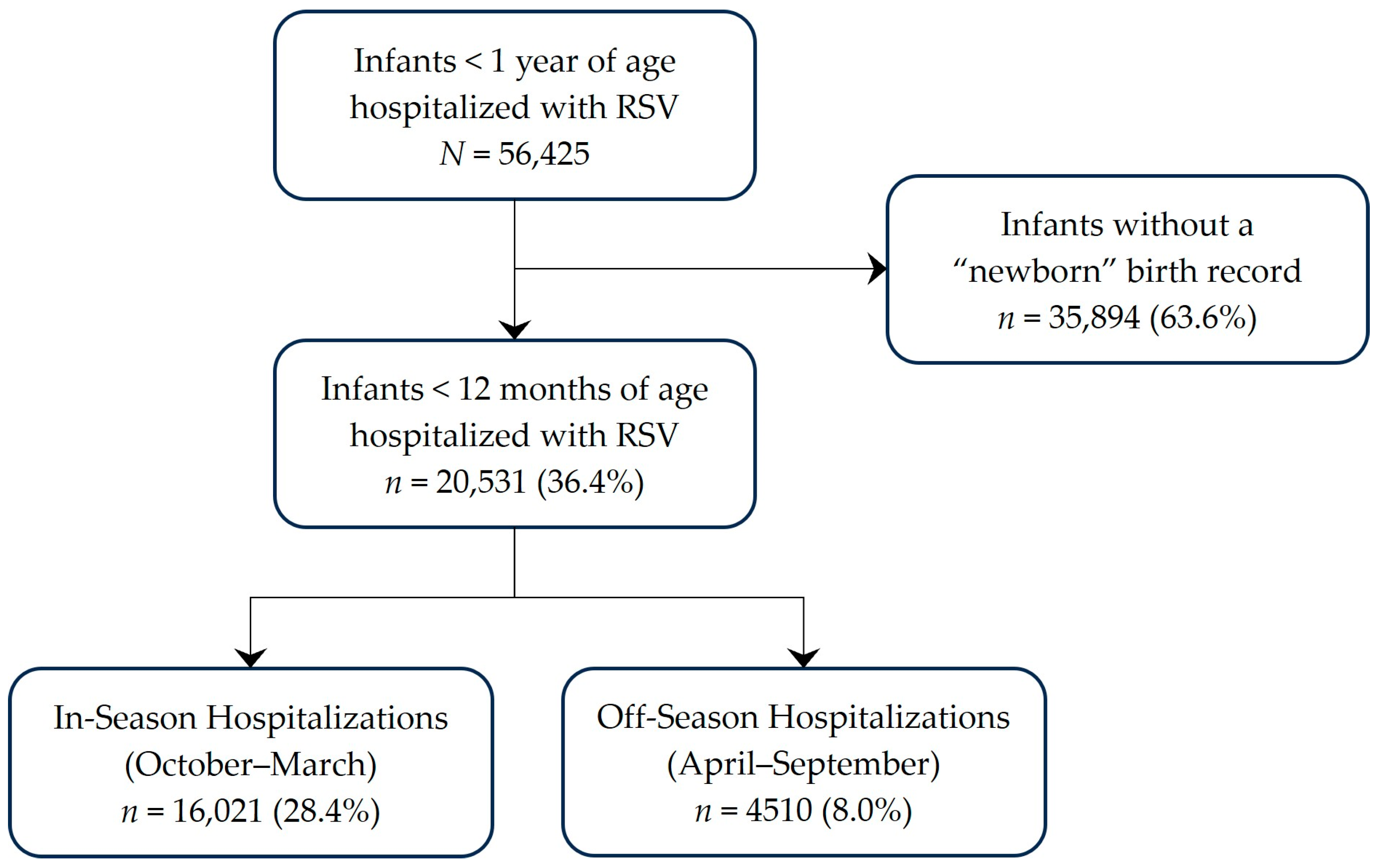
Among infants < 1 year of age hospitalized with RSV during July 2018–June 2023, 36% (n = 20,531) were determined to be <12 months of age when hospitalized (Figure 1). Approximately one-fifth of these RSV hospitalizations occurred outside the typical RSV season, which runs from 1 October–31 March. Of these off-season hospitalizations, 2774 (61.5%) occurred during the pandemic surveillance years. The demographic and clinical characteristics of infants < 12 months of age when hospitalized with RSV are reported in Table 1. Although patient age and sex distribution were similar between off-season and in-season hospitalizations, there were some differences in the demographic and clinical profiles of infants who were hospitalized in-season and off-season. A greater proportion of infants hospitalized off-season were Black, hospitalized in the South, and had congenital heart disease or other respiratory conditions during the RSV hospitalization; a smaller proportion were Hispanic, had Medicaid, and had pneumonia while hospitalized with RSV.
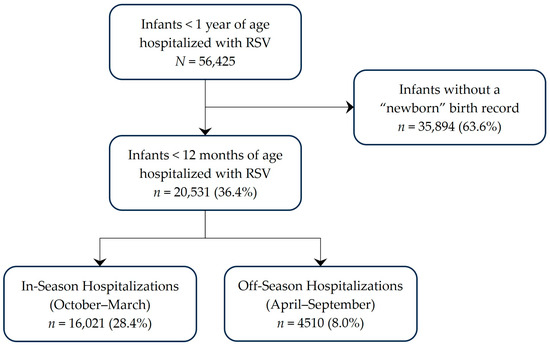
Figure 1.
Study Population.

Table 1.
Patient Demographic, Clinical, and Hospital Characteristics among Infants < 12 months.
3.2. Seasonal Distribution of RSV Hospitalizations
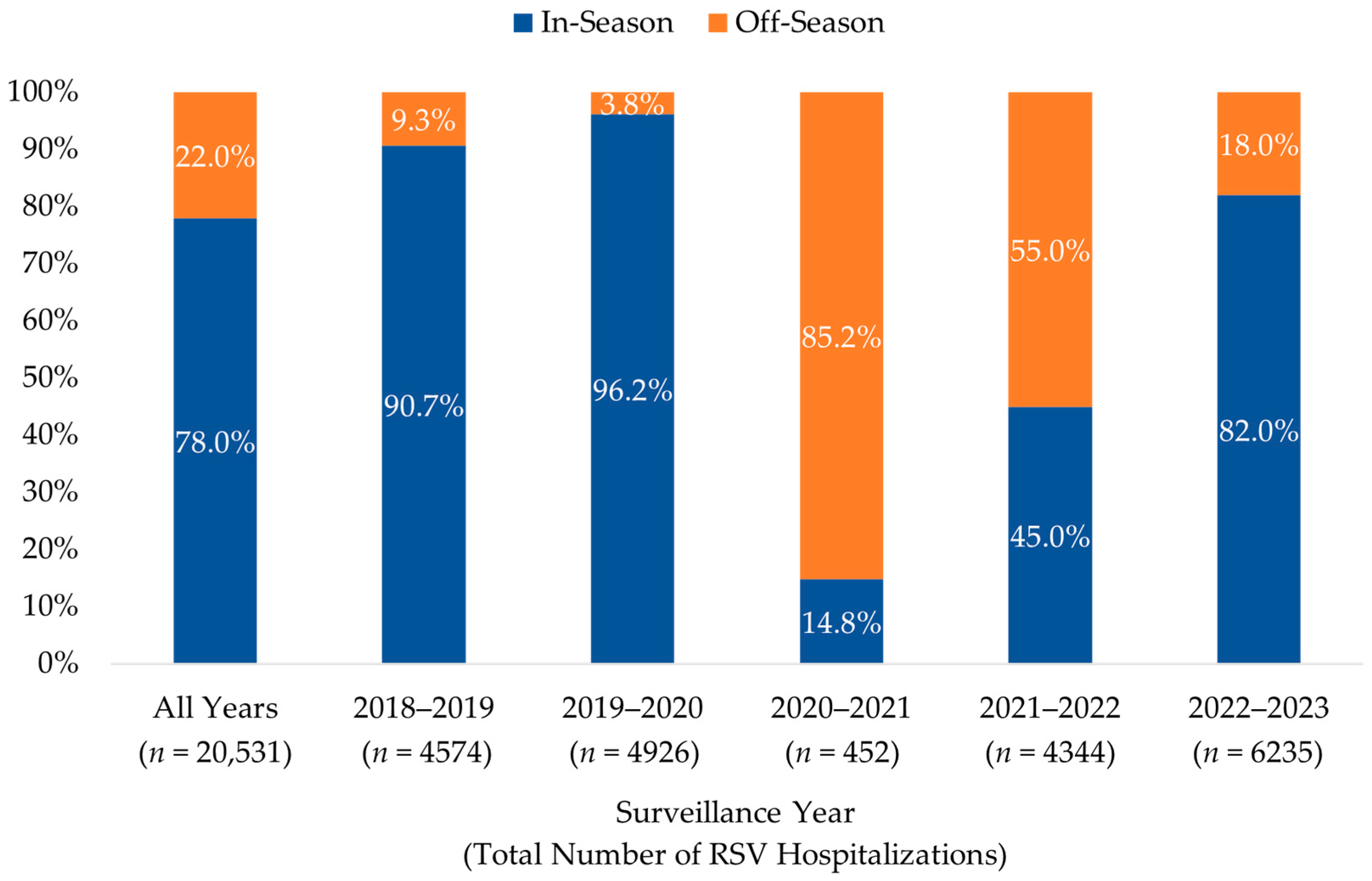
The distribution of in- and off-season RSV hospitalizations among infants < 12 months of age during each of the five surveillance years is illustrated in Figure 2. The seasonal distribution of RSV hospitalizations was significantly impacted by the COVID-19 pandemic, particularly during the first of the two pandemic surveillance years (July 2020–June 2021), where 85.2% (n = 385) of cases occurred during months typically considered to be off-season. Although the number of cases returned to pre-pandemic (2018–2020) levels during the second year, 55.0% (n = 2389) of hospitalizations occurred during the off-season months. Post-pandemic RSV hospitalization levels during July 2022–June 2023 were higher than pre-pandemic levels during the July 2018–June 2019 surveillance year, with a greater proportion occurring in the off-season (18.0% vs. 9.3%). Sensitivity analysis showed consistent seasonal patterns among all infants < 1 year of age.
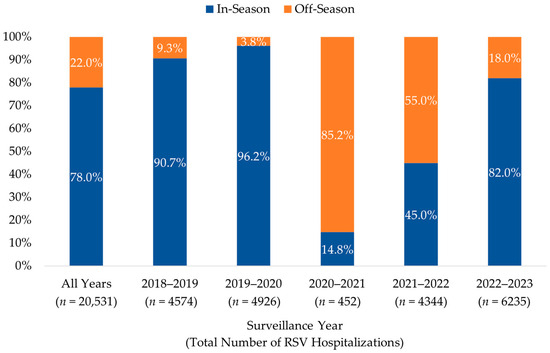
Figure 2.
Distribution of RSV Hospitalizations by Surveillance Year among Infants < 12 months, 2018–2023. The percentage of infants with an RSV hospitalization during (in-season, 1 October–31 March) and outside (off-season, 1 April–30 September) a typical RSV season are shown for each surveillance year (1 July to 30 June of the next year).
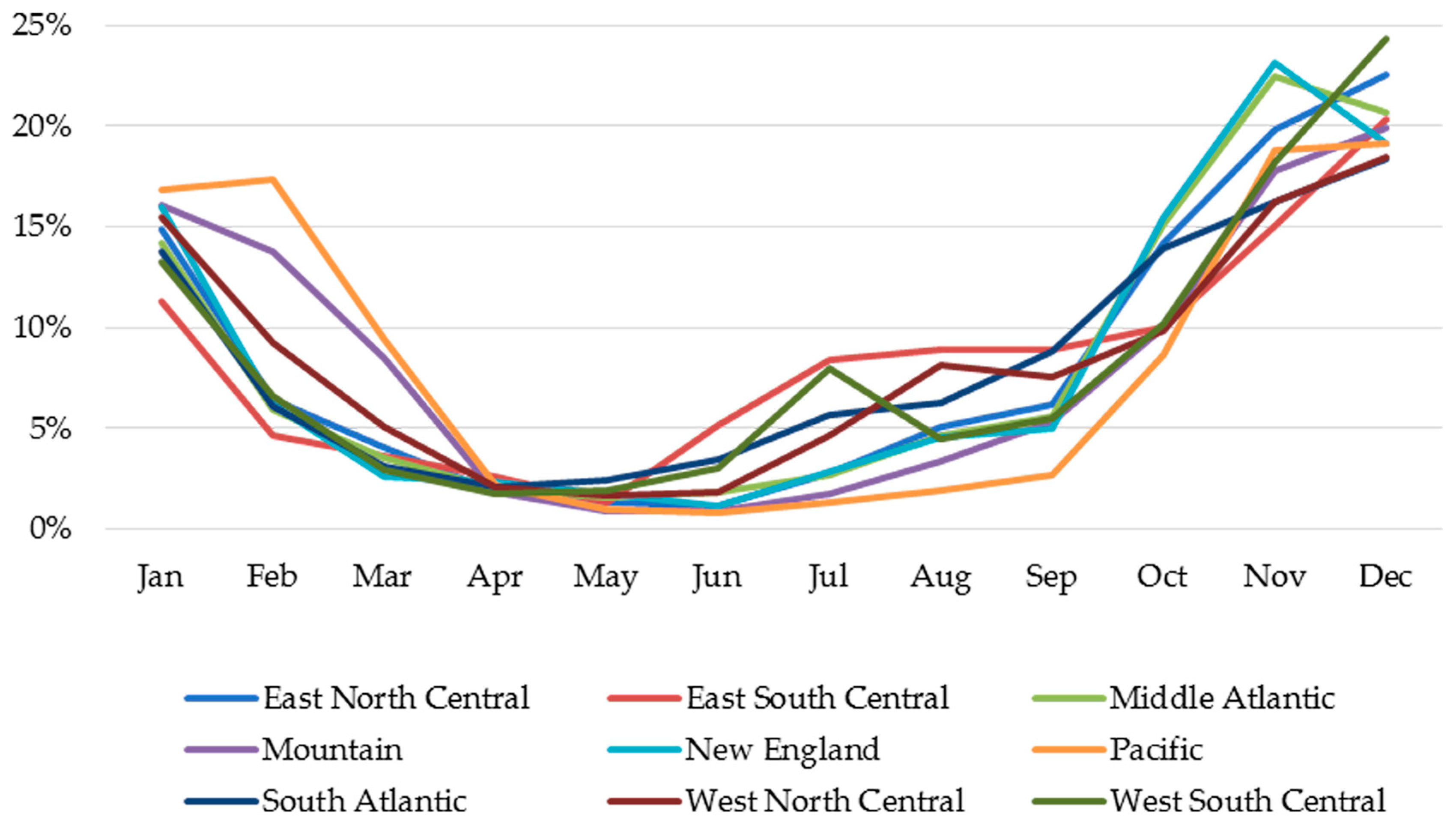
The monthly distribution of RSV hospitalizations among infants < 12 months of age across all surveillance years, stratified by the nine US census divisions, is illustrated in Figure 3. Seasonal distributions varied geographically from 9.9% of cases in the Pacific division to 35.1% of cases in the East South Central division occurring during off-season months. Of the RSV hospitalizations that occurred during the off-season, 83% of these cases occurred in June–September, ranging across various divisions from 67.9% in the Pacific division to 89.0% in the East South Central division.
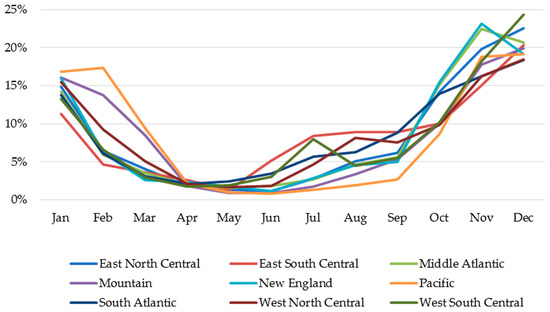
Figure 3.
Monthly Distribution of RSV Hospitalizations Stratified by Geographic Region Across All Study Years.
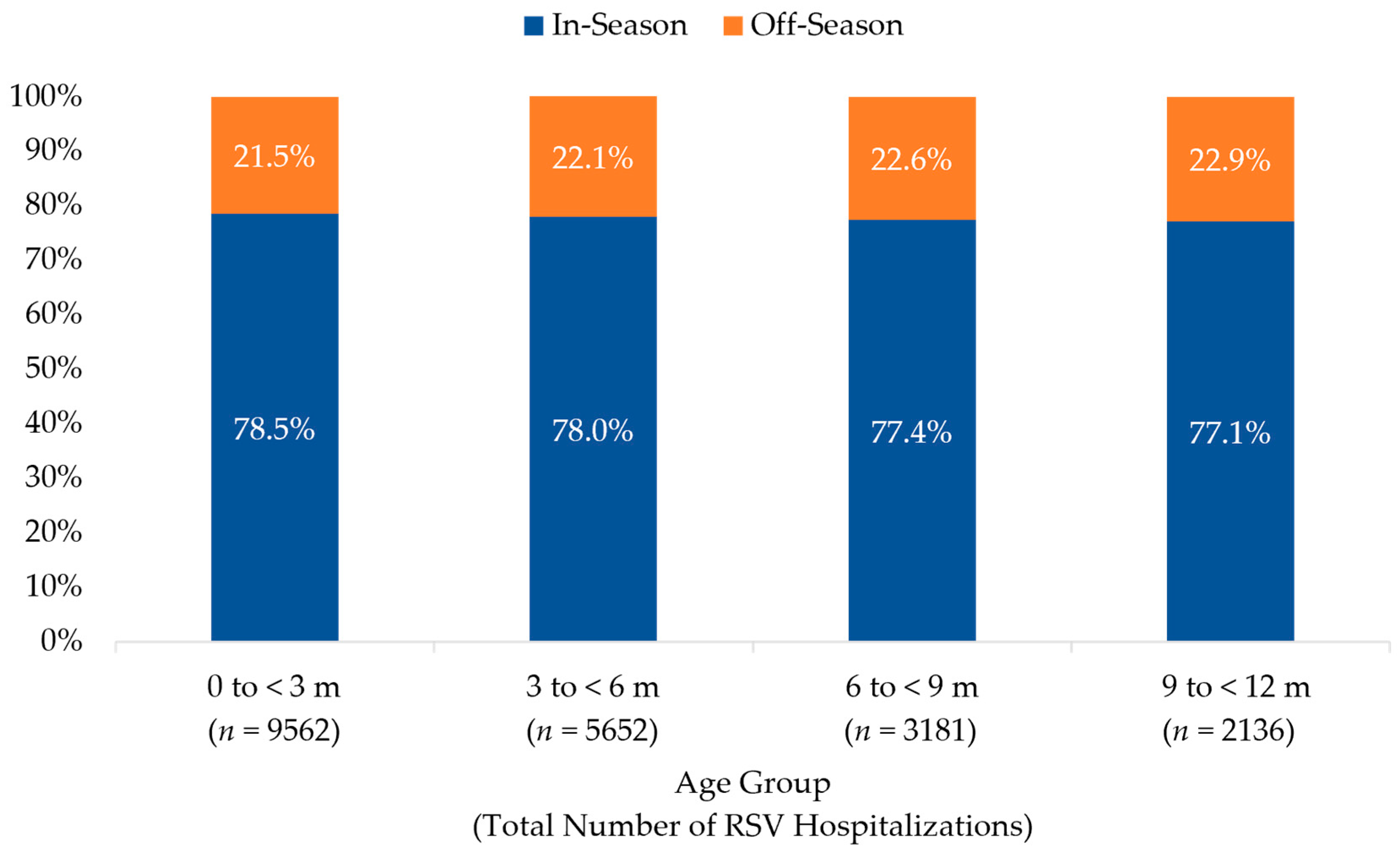
The distribution of in- and off-season RSV hospitalizations among infants < 12 months of age across all surveillance years, stratified by age group, is illustrated in Figure 4. The seasonality of RSV hospitalizations did not vary by age group. Infants < 3 months of age accounted for the 46.6% (n = 9562) of all RSV hospitalizations; 30.6% (n = 2923) of these infants were <1 month of age when hospitalized with RSV and 39.2% (n = 3746) were 1 to <2 months of age. Of all off-season hospitalizations for RSV, 45.5% (n = 2054) were among infants < 3 months of age; 32.1% (n = 660) of these infants were <1 month, and 38.1% (n = 782) were 1 to <2 months of age when hospitalized.
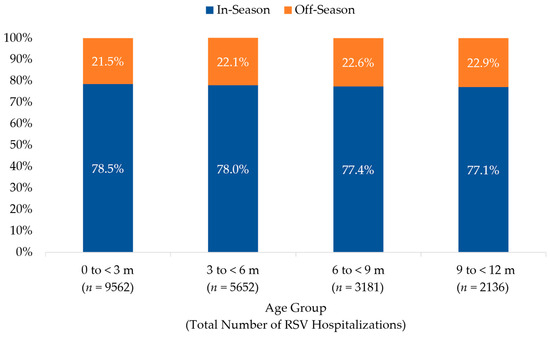
Figure 4.
Distribution of RSV Hospitalization by Age Group among Infants Age < 12 months, 2018–2023. The percentage of infants with an RSV hospitalization during (in-season, 1 October–31 March) and outside (off-season, 1 April–30 September) a typical RSV season are shown for each age group (in months).
3.3. HCRU and Costs
The HCRU and cost of all RSV hospitalizations during July 2018–June 2023, as well as a comparison of the HCRU and cost of RSV hospitalizations during in-season and off-season months are reported in Table 2. Off-season hospitalizations were associated with significantly longer mean hospital LOS (7 vs. 5 days, p < 0.0001), more ICU admissions (30.1% vs. 26.8%, p < 0.0001), MVAF use (20.3% vs. 16.3%, p < 0.0001), and supplemental oxygen use (59.1% vs. 55.5%, p < 0.0001). Furthermore, infants hospitalized during the off-season had longer ICU admissions and required more days with MVAF and supplemental oxygen use. Overall, mean total hospitalization costs were 40% higher during the off-season, primarily driven by ICU usage, which, unlike MVAF and oxygen use, was associated with significantly higher mean costs ($24,311 vs. $18,365, p = 0.0003).

Table 2.
In-Season and Off-Season HCRU and Costs.
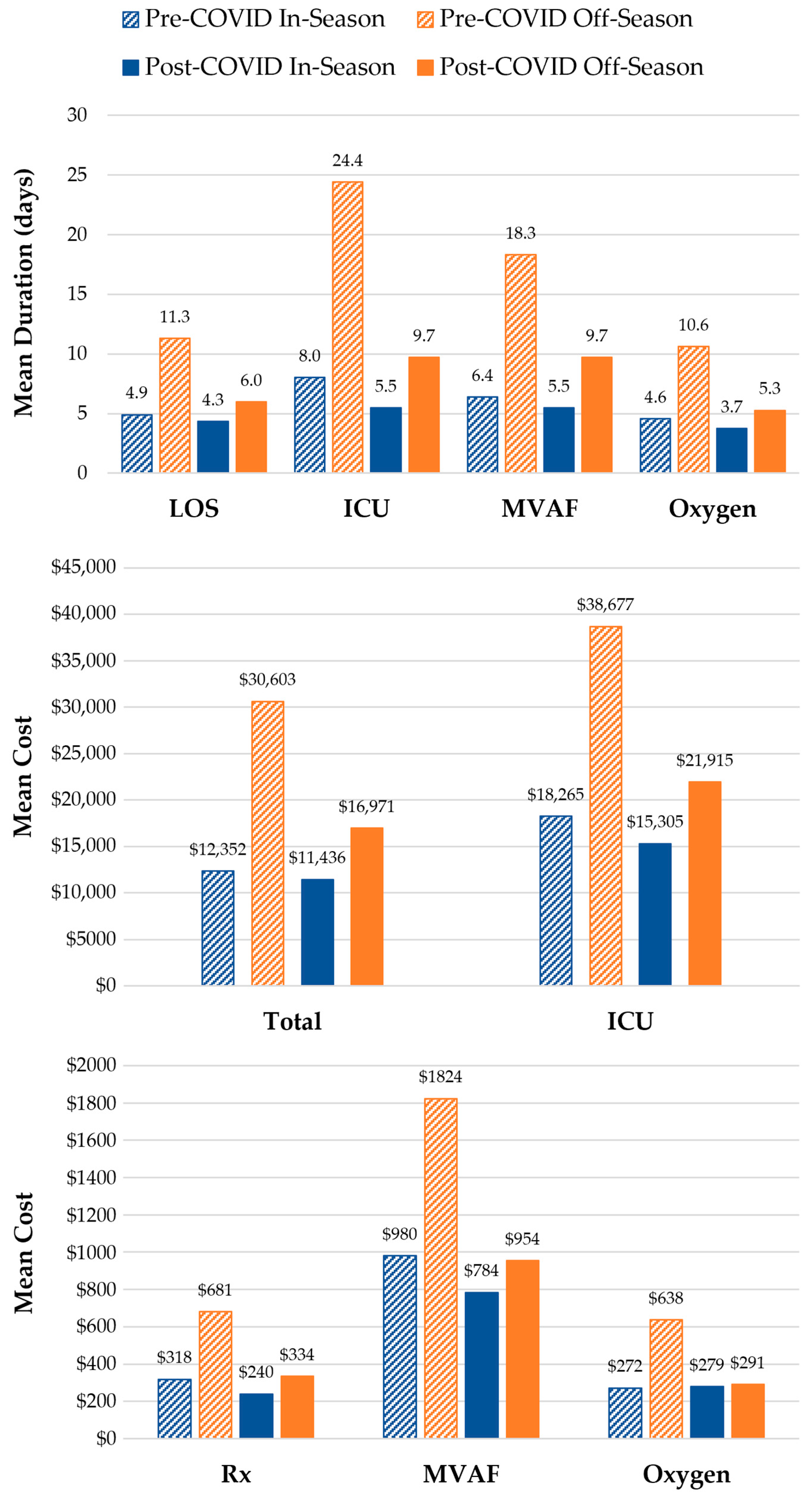
Comparisons of the HCRU and costs of in-season and off-season RSV hospitalizations during the pre-COVID (July 2018–June 2020) and post-COVID (July 2022–June 2023) periods are illustrated in Figure 5. In the two surveillance years prior to the COVID-19 pandemic (2018–2020), 9500 infants were hospitalized with RSV; 6.5% (n = 615) of these hospitalizations were during off-season months. Of all five surveillance years, the last post-pandemic year (2022–2023) had the highest number of cases (n = 6235), of which 18.0% (n = 1121) occurred during the off-season. The HCRU and costs of off-season RSV hospitalizations were consistently higher than in-season hospitalizations both prior to and after the COVID-19 pandemic surveillance years (July 2020–June 2022). Hospital LOS and the duration of ICU admissions, MVAF, and supplemental oxygen use were all longer for off-season hospitalizations during both the pre-COVID (2018–2020) and post-COVID (2022–2023) periods. However, while healthcare costs were higher for most services received during off-season hospitalizations within the pre-COVID (2018–2020) and post-COVID (2022–2023) periods, the cost of MVAF and supplemental oxygen use was comparable between in- and off-season hospitalizations during the post-COVID period.
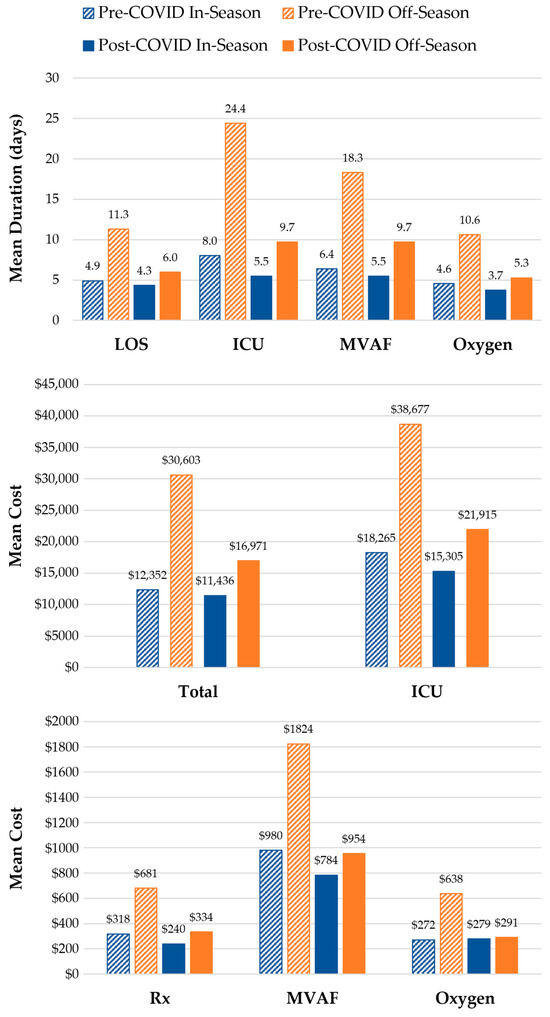
Figure 5.
In-Season and Off-Season HCRU and Costs during the Pre-COVID (July 2018–June 2020) and Post-COVID (July 2022–June 2023) Periods. Hospital LOS and total costs were evaluated for all RSV hospitalizations among infants < 12 months of age during (in-season, 1 October–31 March) and outside (off-season, 1 April–30 September) a typical RSV season. The duration of ICU admissions, MVAF, and supplemental oxygen usage were assessed among infants who received such services while hospitalized. Service costs were assessed among the subset of those who with available cost data. Pre-COVID in-season vs. off-season comparison: p < 0.0001 for all HCRU and costs except for the cost of MVAF (p = 0.003). Post-COVID in-season vs. off-season comparison: p < 0.0001 for all HCRU except for MVAF duration (p = 0.0003); p = 0.02 for Rx and ICU costs; p = 0.32 for MVAF costs; and p = 0.69 for supplemental oxygen costs.
The HCRU and costs of in-season and off-season RSV hospitalizations among infants born in-season and those born off-season are reported in Table 3. Although similar proportions of infants were born in- and off-season (48.0% vs. 52.0%), off-season RSV hospitalizations were more frequent among infants born off-season vs. in-season (25.6% vs. 18.1%). Mean off-season RSV hospitalization HCRU was 2.4- to 4.0-fold higher and mean costs were 1.7- to 2.9-fold higher among infants born in the RSV off-season compared to infants who were born in-season.

Table 3.
HCRU and Cost of In-Season and Off-Season RSV Hospitalizations among Infants Born Within or Outside an RSV Season.
4. Discussion
This large-scale, real-world database analysis showed that over one in five infants hospitalized with RSV were affected during the off-season, with rates varying by geography and year. Nearly half of these hospitalizations occurred among infants < 3 months of age; 32.1% of these infants were <1 month when hospitalized. Off-season hospitalizations with RSV were associated with longer hospital stays, higher ICU admission, a greater need for MVAF and supplemental oxygen for longer durations, and higher costs. Post-pandemic RSV hospitalization levels during the 2022–2023 surveillance year were higher than pre-pandemic levels during the 2018–2019 surveillance year, with a greater proportion occurring in the off-season. During both the 2018–2020 pre-pandemic and 2022–2023 post-pandemic surveillance years, off-season hospitalizations were generally associated with higher HCRU and costs than in-season hospitalizations. Compared to infants born in-season, more infants born during the off-season were hospitalized with RSV off-season and had more HCRU and higher costs.
Although the CDC’s analysis of surveillance data during 2017–2023 was not limited to pediatric patients, the reported variability in RSV season duration and geographic variation was consistent with our study’s findings [8]. Among 850 children hospitalized with RSV in Texas during May 2000–September 2006, 5.3% were admitted off-season between May and September [13]. In our study, 22.0% of hospitalizations were off-season between April and September. In contrast, only 2.9% of the 109,185 children < 24 months of age who were hospitalized for RSV during July 2017–November 2022 had an off-season hospitalization when variable RSV season durations were employed [9]. From among those <12 months of age, 54.7% of the off-season RSV hospitalizations occurred among infants < 4 months. A study of regional RSV activity during July 2010–June 2013 reported regional variations in the duration of RSV activity with seasons that typically began between October and January and ended between March and May [14]. Furthermore, 9.8% of pediatric RSV hospitalizations occurred outside of these regional activity seasons. Similar to our study, the frequency of off-season RSV hospitalizations varied by region, ranging from 5.6% to 22.4%.
In our study, 49.6% of the infants hospitalized in-season were born off-season, which was similar to the previously reported rate of 54% [15]. Previous studies have also reported a higher risk of hospitalization with RSV among infants born during a typical RSV season, as well as increased ICU admission rates, especially among preterm infants [15,16,17]. In our study, the proportion of infants born in- and off-season who had ICU admissions was similar (28.1% vs. 26.9%). However, the gestational age of 73.6% of the infants in our study was unknown. With only 23.0% (n = 2265) of infants born in-season and 25.2% (n = 2690) of infants born off-season identified as preterm, RSV hospitalization by preterm birth status was not evaluated in our study.
Numerous studies have investigated the HCRU and costs associated with pediatric RSV hospitalizations [18,19,20,21,22]. However, few have addressed the impact of RSV seasonality. In the study of children hospitalized with RSV in Texas, a greater proportion of patients with off-season hospitalizations received MVAF (8.9% vs. 3.0%, p = 0.05) compared to patients admitted in-season [13]. Another study of children < 24 months of age hospitalized for RSV reported more ICU admissions (38.9% vs. 26.5–31.5%, p < 0.001) and MVAF (15.8% vs. 8.4–12.0%, p < 0.001) during off-season vs. in-season hospitalizations [9]. Our study has demonstrated that off-season RSV hospitalizations are associated with higher HCRU and costs compared to in-season hospitalizations.
In our study, the pre-pandemic period included both the 2018–2019 and 2019–2020 surveillance years. For much of the 2019–2020 RSV season, monthly RSV-associated hospitalization rates among infants < 1 year of age were higher than those corresponding to the previous season, peaking at 281.8 and 211.5 per 100,000 during January 2020 and 2019, respectively [23]. However, by the start of the COVID-19 pandemic in March 2020, the RSV hospitalization rate had dropped below that of the 2018–2019 season (69.5 vs. 84.1 per 100,000) and was substantially lower during April 2020 (3.1 vs. 34.7 per 100,000), the last month of the RSV Hospitalization Surveillance Network (RSV-NET) surveillance period. A similar trend was seen in our study, where the percentage of RSV hospitalizations at the beginning of the RSV season was greater in 2020 than in 2019, before shifting in February (2020: 14.9%; 2019: 16.0%). As the 2019–2020 surveillance year progressed, the disparities in proportions widened (March: 5.9% vs. 10.1%; April: 0.5% vs. 4.0%; May: 0.1% vs. 1.8%; June: 0.02% vs. 1.1%). Correspondingly, while the number of in-season hospitalizations during the 2019–2020 surveillance year may be slightly lower, the number of off-season hospitalizations would be expected to be substantially reduced. As a result, the economic burden of off-season RSV hospitalizations during the pre-pandemic period may be underestimated. The low levels of RSV activity during the fall and winter of the 2020–2021 surveillance year may be attributed to the mitigation measures implemented at the start of the COVID-19 pandemic. Lockdowns, social distancing, and travel restrictions decreased exposure to RSV, reducing the incidence of infections that could lead to hospitalization. However, reduced exposure to RSV also resulted in decreased immunity, whether due to waning maternal immunity or declining herd immunity. This decreased immunity, as well as the easing of mitigation measures, may have contributed to the spikes in off-season RSV hospitalizations that occurred during the 2020–2022 pandemic surveillance years. Although the COVID-19 pandemic impacted RSV seasonality, the difference between in-season and off-season HCRU and costs persisted. The decrease in the magnitude of the difference during the post-COVID timeframe is likely the consequence of shorter hospital LOS during this period.
The findings of this study should be interpreted in the context of several limitations. First, since hospitalizations that occur outside the PHD catchment network are not recorded, it may not be representative of the entire population of hospitalized RSV patients in the US. However, the hospital-based PHD database captures approximately one in four hospitalizations in the US and includes hospitals across all census divisions [24]. In addition, the regional and urban-rural distribution of its member hospitals is comparable to the member hospitals of the American Hospital Association. Second, this administrative database is subject to potential coding and billing errors, and deidentification of patient records prevents validation of outcomes. In addition, identification of preterm infants was limited to ICD-10 codes, which may not be well-documented in claims data. Due to the limited laboratory clinical data available in the PHD, RSV diagnoses were not laboratory confirmed and cases with other viral illnesses identified as RSV may possibly have been included. Third, only a subpopulation of infants hospitalized with RSV had a “linked” newborn birth record, allowing us to estimate age in months. However, sensitivity analysis found that the distribution of all infants hospitalized due to RSV was comparable to the subpopulation of infants with birth records. Fourth, study outcomes were not adjusted for comorbid conditions that could potentially have increased the risk of off-season hospitalization and increased HCRU. Finally, the seasonal distribution of RSV hospitalizations during the pandemic surveillance years diverged from that of previous years, with significantly fewer cases during July 2020–June 2021. The COVID-19 pandemic also altered healthcare seeking behavior, which may have impacted HCRU and cost outcomes. The seasonal distribution of RSV hospitalizations during the 2022–2023 post-pandemic surveillance year appears to be returning to the pre-pandemic levels seen during the 2018–2019 surveillance year; further monitoring of the post-pandemic seasonality of RSV hospitalizations is needed to better inform and optimize prophylactic measures for infants at risk of RSV infection.
5. Conclusions
The current ACIP recommendations on seasonal administration of infant RSV prevention options were informed by historical surveillance data. Our study demonstrates that more than one-fifth of infants < 12 months of age had an off-season hospitalization with RSV. While RSV activity appears to be returning to pre-pandemic levels, these off-season cases continue to be associated with longer length of hospital stay, higher ICU admission, and higher costs. More importantly, infants born off-season who were subsequently hospitalized with RSV are unable to benefit from available preventive measures. Our study findings may have important implications for policy makers in their ongoing assessment of recommendations by informing about both implementation timing and how expansion of the vaccination window can reduce the clinical and economic burden of infant RSV occurring off-season and outside the window for current prevention options.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.W.L., J.L., J.J., S.J.P. and A.C.; Data curation, J.L. and J.J.; Formal analysis, J.L. and J.J.; Funding acquisition, A.W.L.; Investigation, J.L. and J.J.; Methodology, A.W.L., J.L., J.J., S.J.P. and A.C.; Project administration, A.W.L.; Software, J.L. and J.J.; Supervision, A.W.L.; Validation, J.L. and J.J.; Visualization, A.W.L., J.L., J.J., S.J.P. and A.C.; Writing—original draft, A.W.L. and J.L.; Writing—review and editing, A.W.L., J.J., S.J.P. and A.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was sponsored by Pfizer Inc. Editorial support provided by Novosys Health was funded by Pfizer.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets presented in this article are not readily available because the study used data that was acquired under a licensing agreement. Requests to access the datasets should be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
Editorial support was provided by Grace Lin at Novosys Health.
Conflicts of Interest
J.L. is an employee of Novosys Health, which received funding from Pfizer in connection with the development of this manuscript and study. A.W.L., J.J., S.J.P. and A.C. are employed by, and are shareholders of, Pfizer Inc.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| ACIP | Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices |
| ANOVA | Analysis of variance |
| CDC | Centers for Disease Control and Prevention |
| CPT-4 | Current Procedural Terminology, fourth edition |
| HCPCS | Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System |
| HCRU | Healthcare resource utilization |
| HIPAA | Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act |
| ICD-10-CM | International Classification of Diseases, tenth revision, clinical modification |
| ICD-10-PCS | International Classification of Diseases, tenth revision, procedure coding system |
| ICU | Intensive care unit |
| LOS | Length of stay |
| MVAF | Mechanical ventilation/airflow |
| PHD | PINC AI Healthcare Database |
| RSV | Respiratory syncytial virus |
| RSV-NET | RSV Hospitalization Surveillance Network |
| RSVpreF | RSV prefusion F protein-based vaccine |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| US | United States |
References
- Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Blau, D.M.; Caballero, M.T.; Feikin, D.R.; Gill, C.J.; Madhi, S.A.; Omer, S.B.; Simoes, E.A.F.; Campbell, H.; et al. Global, regional, and national disease burden estimates of acute lower respiratory infections due to respiratory syncytial virus in children younger than 5 years in 2019: A systematic analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 2047–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLaughlin, J.M.; Khan, F.; Schmitt, H.J.; Agosti, Y.; Jodar, L.; Simoes, E.A.F.; Swerdlow, D.L. Respiratory Syncytial Virus-Associated Hospitalization Rates among US Infants: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 225, 1100–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parikh, R.C.; McLaurin, K.K.; Margulis, A.V.; Mauskopf, J.; Ambrose, C.S.; Pavilack, M.; Candrilli, S.D. Chronologic Age at Hospitalization for Respiratory Syncytial Virus Among Preterm and Term Infants in the United States. Infect. Dis. Ther. 2017, 6, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming-Dutra, K.E.; Jones, J.M.; Roper, L.E.; Prill, M.M.; Ortega-Sanchez, I.R.; Moulia, D.L.; Wallace, M.; Godfrey, M.; Broder, K.R.; Tepper, N.K.; et al. Use of the Pfizer Respiratory Syncytial Virus Vaccine During Pregnancy for the Prevention of Respiratory Syncytial Virus-Associated Lower Respiratory Tract Disease in Infants: Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices—United States, 2023. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2023, 72, 1115–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, J.M.; Fleming-Dutra, K.E.; Prill, M.M.; Roper, L.E.; Brooks, O.; Sanchez, P.J.; Kotton, C.N.; Mahon, B.E.; Meyer, S.; Long, S.S.; et al. Use of Nirsevimab for the Prevention of Respiratory Syncytial Virus Disease Among Infants and Young Children: Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices—United States, 2023. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2023, 72, 920–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toepfer, A.P.; Amarin, J.Z.; Spieker, A.J.; Stewart, L.S.; Staat, M.A.; Schlaudecker, E.P.; Weinberg, G.A.; Szilagyi, P.G.; Englund, J.A.; Klein, E.J.; et al. Seasonality, Clinical Characteristics, and Outcomes of Respiratory Syncytial Virus Disease by Subtype Among Children Aged < 5 Years: New Vaccine Surveillance Network, United States, 2016–2020. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2024, 78, 1352–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Berger, N.; Davis, P.B.; Kaelber, D.C.; Volkow, N.; Xu, R. Time trend and seasonality in medically attended respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) infections in US children aged 0–5 years, January 2010–January 2023. Fam. Med. Community Health 2023, 11, e002453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamid, S.; Winn, A.; Parikh, R.; Jones, J.M.; McMorrow, M.; Prill, M.M.; Silk, B.J.; Scobie, H.M.; Hall, A.J. Seasonality of Respiratory Syncytial Virus—United States, 2017–2023. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2023, 72, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusma, J.D.; Macy, M.L.; Kociolek, L.K.; Davis, M.M.; Ramgopal, S. Seasonality in Respiratory Syncytial Virus Hospitalizations and Immunoprophylaxis. JAMA Health Forum 2023, 4, e231582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, E.B.; Wheatley, A.; Langley, G.; Gerber, S.; Haynes, A. Respiratory Syncytial Virus Seasonality—United States, 2014–2017. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2018, 67, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obando-Pacheco, P.; Justicia-Grande, A.J.; Rivero-Calle, I.; Rodriguez-Tenreiro, C.; Sly, P.; Ramilo, O.; Mejias, A.; Baraldi, E.; Papadopoulos, N.G.; Nair, H.; et al. Respiratory Syncytial Virus Seasonality: A Global Overview. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 217, 1356–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staadegaard, L.; Duckers, M.; van Summeren, J.; van Gameren, R.; Demont, C.; Bangert, M.; Li, Y.; Casalegno, J.S.; Caini, S.; Paget, J. Determining the timing of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) epidemics: A systematic review, 2016 to 2021; method categorisation and identification of influencing factors. Euro Surveill. 2024, 29, 2300244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quick, R.D.; Jesser, C.A.; Bell, A.C.; Fernandez, M.; Glomb, W.B.; McWilliams, B.C.; Murray, J.L.; Hauger, S.B. Hospitalizations Due to Respiratory Syncytial Virus Outside of the Typical Season. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. Pulmonol. 2012, 25, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glick, A.F.; Kjelleren, S.; Hofstetter, A.M.; Subramony, A. RSV Hospitalizations in Comparison With Regional RSV Activity and Inpatient Palivizumab Administration, 2010–2013. Hosp. Pediatr. 2017, 7, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mira-Iglesias, A.; Demont, C.; Lopez-Labrador, F.X.; Mengual-Chulia, B.; Garcia-Rubio, J.; Carballido-Fernandez, M.; Tortajada-Girbes, M.; Mollar-Maseres, J.; Schwarz-Chavarri, G.; Puig-Barbera, J.; et al. Role of age and birth month in infants hospitalized with RSV-confirmed disease in the Valencia Region, Spain. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses 2022, 16, 328–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gantenberg, J.R.; van Aalst, R.; Bhuma, M.R.; Limone, B.; Diakun, D.; Smith, D.M.; Nelson, C.B.; Bengtson, A.M.; Chaves, S.S.; La Via, W.V.; et al. Risk Analysis of Respiratory Syncytial Virus Among Infants in the United States by Birth Month. J. Pediatric. Infect. Dis. Soc. 2024, 13, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoes, E.A.; Anderson, E.J.; Wu, X.; Ambrose, C.S. Effects of Chronologic Age and Young Child Exposure on Respiratory Syncytial Virus Disease among US Preterm Infants Born at 32 to 35 Weeks Gestation. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowser, D.M.; Rowlands, K.R.; Hariharan, D.; Gervasio, R.M.; Buckley, L.; Halasa-Rappel, Y.; Glaser, E.L.; Nelson, C.B.; Shepard, D.S. Cost of Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infections in US Infants: Systematic Literature Review and Analysis. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 226, S225–S235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Finelli, L. Cost of Medically Attended RSV Among Medicaid Beneficiaries </=2 Years of Age by Underlying Risk Condition. J. Pediatric. Infect. Dis. Soc. 2023, 12, 590–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaurin, K.K.; Farr, A.M.; Wade, S.W.; Diakun, D.R.; Stewart, D.L. Respiratory syncytial virus hospitalization outcomes and costs of full-term and preterm infants. J. Perinatol. 2016, 36, 990–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, M.; Smitherman, L. Socioeconomic Impact of RSV Hospitalization. Infect. Dis. Ther. 2021, 10, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suh, M.; Movva, N.; Jiang, X.; Reichert, H.; Bylsma, L.C.; Fryzek, J.P.; Nelson, C.B. Respiratory Syncytial Virus Burden and Healthcare Utilization in United States Infants <1 Year of Age: Study of Nationally Representative Databases, 2011–2019. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 226, S184–S194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. RSV-NET. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/rsv/php/surveillance/rsv-net.html (accessed on 14 March 2025).
- PINC AI Applied Sciences. PINC AI Healthcare Database: Data That Informs and Performs (White Paper). Available online: https://offers.premierinc.com/rs/381-NBB-525/images/PINC_AI_Healthcare_Data_White_Paper.pdf (accessed on 1 October 2024).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).