Proteomic and Bioinformatic Analysis of Streptococcus suis Human Isolates: Combined Prediction of Potential Vaccine Candidates
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains and Culture Conditions
2.2. Bacterial Surface “Shaving” and Peptide Extraction
2.3. LC-MS/MS Analysis
2.4. Protein Identification and Database Searches
2.5. Computational Prediction of Protein Subcellular Localization
2.6. Data and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Bacterial Surface “Shaving” and Protein Identification
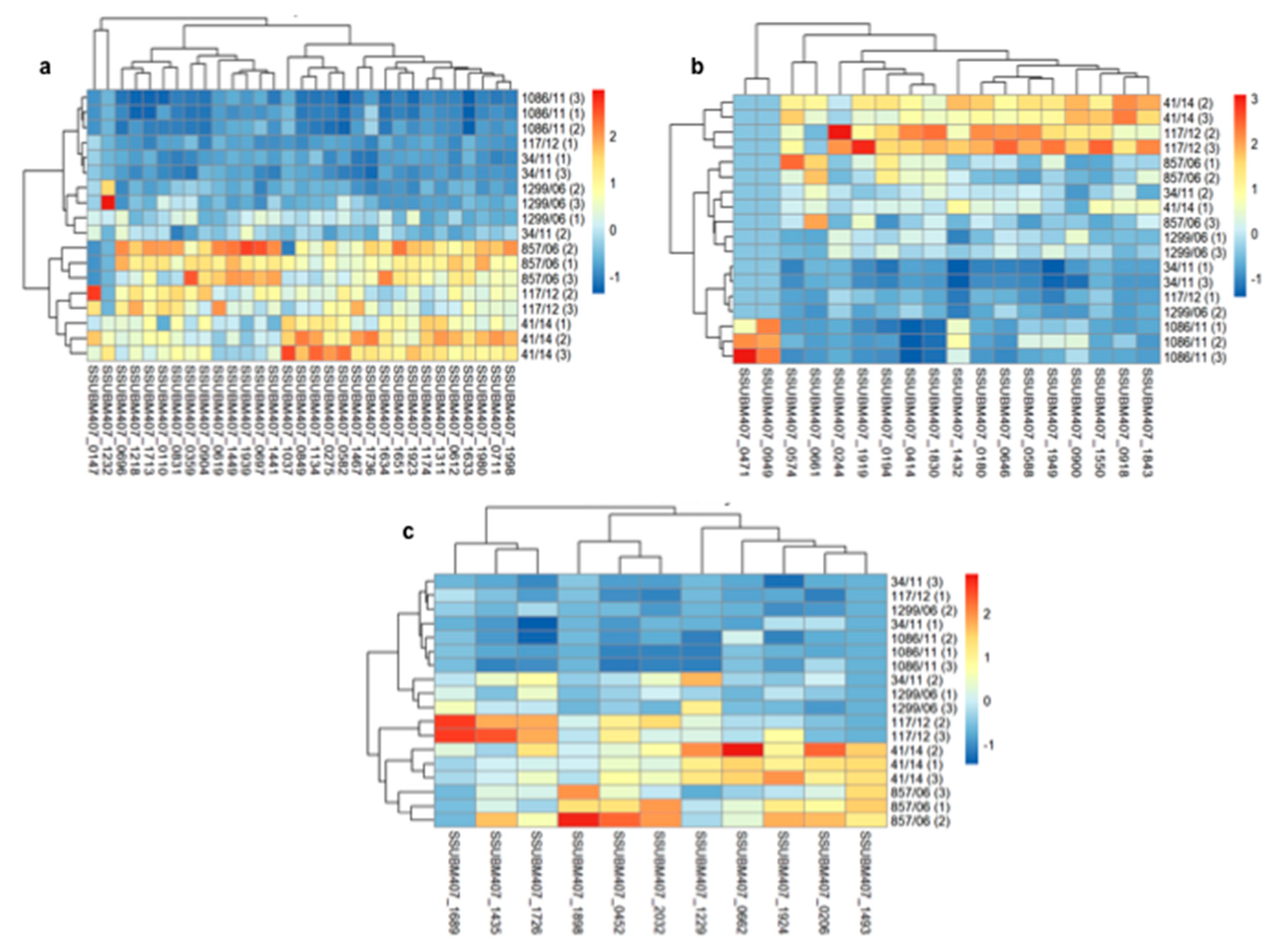
3.2. Analysis of Differences in Surface Protein Abundances among the Clinical Isolates
3.3. Prediction of New Potential Vaccine Candidates
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Vötsch, D.; Willenborg, M.; Weldearegay, Y.B.; Valentin-Weigand, P. Streptococcus suis—The “Two Faces” of a Pathobiont in the Porcine Respiratory Tract. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottschalk, M.; Xu, J.; Calzas, C.; Segura, M. Streptococcus suis: A new emerging or an old neglected zoonotic pathogen? Future Microbiol. 2010, 5, 371–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lun, Z.R.; Wang, Q.P.; Chen, X.G.; Li, A.X.; Zhu, X.Q. Streptococcus suis: An emerging zoonotic pathogen. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2007, 7, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinert, L.A.; Chaudhuri, R.R.; Wang, J.; Peters, S.E.; Corander, J.; Jombart, T.; Baig, A.; Howell, K.J.; Vehkala, M.; Valimaki, N.; et al. Genomic signatures of human and animal disease in the zoonotic pathogen Streptococcus suis. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kerdsin, A.; Takeuchi, D.; Nuangmek, A.; Akeda, Y.; Gottschalk, M.; Oishi, K. Genotypic Comparison between Streptococcus suis Isolated from Pigs and Humans in Thailand. Pathogens 2020, 9, E50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nghia, H.D.; Ho, D.T.; Tu, L.E.; Le, T.P.; Wolbers, M.; Thai, C.Q.; Cao, Q.T.; Hoang, N.V.; Nguyen, V.M.; Nga, T.V.; et al. Risk factors of Streptococcus suis infection in Vietnam. A case-control study. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takeuchi, D.; Kerdsin, A.; Pienpringam, A.; Loetthong, P.; Samerchea, S.; Luangsuk, P.; Khamisara, K.; Wongwan, N.; Areeratana, P.; Chiranairadul, P.; et al. Population-based study of Streptococcus suis infection in humans in Phayao Province in northern Thailand. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Segura, M.; Fittipaldi, N.; Calzas, C.; Gottschalk, M. Critical Streptococcus suis Virulence Factors: Are They All Really Critical? Trends Microbiol. 2017, 25, 585–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wertheim, H.F.; Nghia, H.D.; Taylor, W.; Schultsz, C. Streptococcus suis: An emerging human pathogen. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 48, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goyette-Desjardins, G.; Auger, J.P.; Xu, J.; Segura, M.; Gottschalk, M. Streptococcus suis, an important pig pathogen and emerging zoonotic agent-an update on the worldwide distribution based on serotyping and sequence typing. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2014, 3, e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baums, C.G.; Kock, C.; Beineke, A.; Bennecke, K.; Goethe, R.; Schroder, C.; Waldmann, K.H.; Valentin-Weigand, P. Streptococcus suis bacterin and subunit vaccine immunogenicities and protective efficacies against serotypes 2 and 9. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2009, 16, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Büttner, N.; Beineke, A.; de Buhr, N.; Lilienthal, S.; Merkel, J.; Waldmann, K.H.; Valentin-Weigand, P.; Baums, C.G. Streptococcus suis serotype 9 bacterin immunogenicity and protective efficacy. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2012, 146, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segura, M. Streptococcus suis vaccines: Candidate antigens and progress. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2015, 14, 1587–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grandi, G. Genomics and proteomics in reverse vaccines. Methods Biochem. Anal. 2006, 49, 379–393. [Google Scholar]
- Zagursky, R.J.; Anderson, A.S. Application of genomics in bacterial vaccine discovery: A decade in review. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2008, 8, 632–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamczyk-Poplawska, M.; Markowicz, S.; Jagusztyn-Krynicka, E.K. Proteomics for development of vaccine. J. Proteom. 2011, 74, 2596–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagusztyn-Krynicka, E.K.; Dadlez, M.; Grabowska, A.; Roszczenko, P. Proteomic technology in the design of new effective antibacterial vaccines. Expert Rev. Proteom. 2009, 6, 315–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doro, F.; Liberatori, S.; Rodríguez-Ortega, M.J.; Rinaudo, C.D.; Rosini, R.; Mora, M.; Scarselli, M.; Altindis, E.; D’Aurizio, R.; Stella, M.; et al. Surfome analysis as a fast track to vaccine discovery: Identification of a novel protective antigen for group B Streptococcus hyper-virulent strain COH1. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2009, 8, 1728–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olaya-Abril, A.; Gómez-Gascón, L.; Jiménez-Munguía, I.; Obando, I.; Rodríguez-Ortega, M.J. Another turn of the screw in shaving Gram-positive bacteria: Optimization of proteomics surface protein identification in Streptococcus pneumoniae. J. Proteom. 2012, 75, 3733–3746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olaya-Abril, A.; Jiménez-Munguía, I.; Gómez-Gascón, L.; Obando, I.; Rodríguez-Ortega, M.J. A Pneumococcal Protein Array as a Platform to Discover Serodiagnostic Antigens Against Infection. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2015, 14, 2591–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodríguez-Ortega, M.J.; Norais, N.; Bensi, G.; Liberatori, S.; Capo, S.; Mora, M.; Scarselli, M.; Doro, F.; Ferrari, G.; Garaguso, I.; et al. Characterization and identification of vaccine candidate proteins through analysis of the group A Streptococcus surface proteome. Nat. Biotechnol. 2006, 24, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solis, N.; Cain, J.A.; Cordwell, S.J. Comparative analysis of Staphylococcus epidermidis strains utilizing quantitative and cell surface shaving proteomics. J. Proteom. 2016, 130, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solis, N.; Larsen, M.R.; Cordwell, S.J. Improved accuracy of cell surface shaving proteomics in Staphylococcus aureus using a false-positive control. Proteomics 2010, 10, 2037–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Solis, N.; Parker, B.L.; Kwong, S.M.; Robinson, G.; Firth, N.; Cordwell, S.J. Staphylococcus aureus surface proteins involved in adaptation to oxacillin identified using a novel cell shaving approach. J. Proteome Res. 2014, 13, 2954–2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Gascón, L.; Luque, I.; Olaya-Abril, A.; Jiménez-Munguía, I.; Orbegozo-Medina, R.A.; Peralbo, E.; Tarradas, C.; Rodríguez-Ortega, M.J. Exploring the pan-surfome of Streptococcus suis: Looking for common protein antigens. J. Proteom. 2012, 75, 5654–5666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olaya-Abril, A.; Jiménez-Munguía, I.; Gómez-Gascón, L.; Obando, I.; Rodríguez-Ortega, M.J. Identification of potential new protein vaccine candidates through pan-surfomic analysis of pneumococcal clinical isolates from adults. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gómez-Gascón, L.; Luque, I.; Tarradas, C.; Olaya-Abril, A.; Astorga, R.J.; Huerta, B.; Rodríguez-Ortega, M.J. Comparative immunosecretome analysis of prevalent Streptococcus suis serotypes. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2018, 57, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rappuoli, R. Reverse vaccinology. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2000, 3, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rappuoli, R. Reverse vaccinology, a genome-based approach to vaccine development. Vaccine 2001, 19, 2688–2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Ortega, M.J. “Shaving” Live Bacterial Cells with Proteases for Proteomic Analysis of Surface Proteins. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1722, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UniProt. Available online: https://www.uniprot.org/proteomes/UP000009077 (accessed on 17 July 2019).
- Zhou, M.; Boekhorst, J.; Francke, C.; Siezen, R.J. LocateP: Genome-scale subcellular-location predictor for bacterial proteins. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Krogh, A.; Larsson, B.; von Heijne, G.; Sonnhammer, E.L. Predicting transmembrane protein topology with a hidden Markov model: Application to complete genomes. J. Mol. Biol. 2001, 305, 567–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Almagro Armenteros, J.J.; Tsirigos, K.D.; Sonderby, C.K.; Petersen, T.N.; Winther, O.; Brunak, S.; von Heijne, G.; Nielsen, H. SignalP 5.0 improves signal peptide predictions using deep neural networks. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 420–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juncker, A.S.; Willenbrock, H.; Von Heijne, G.; Brunak, S.; Nielsen, H.; Krogh, A. Prediction of lipoprotein signal peptides in Gram-negative bacteria. Protein Sci. 2003, 12, 1652–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehisa, M.; Sato, Y. KEGG Mapper for inferring cellular functions from protein sequences. Protein Sci. 2020, 29, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Doytchinova, I.A.; Flower, D.R. VaxiJen: A server for prediction of protective antigens, tumour antigens and subunit vaccines. BMC Bioinform. 2007, 8, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Garibaldi, M.; Rodríguez-Ortega, M.J.; Mandanici, F.; Cardaci, A.; Midiri, A.; Papasergi, S.; Gambadoro, O.; Cavallari, V.; Teti, G.; Beninati, C. Immunoprotective activities of a Streptococcus suis pilus subunit in murine models of infection. Vaccine 2010, 28, 3609–3616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Ortega, M.J.; Luque, I.; Tarradas, C.; Bárcena, J.A. Overcoming function annotation errors in the Gram-positive pathogen Streptococcus suis by a proteomics-driven approach. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Navarre, W.W.; Schneewind, O. Surface proteins of gram-positive bacteria and mechanisms of their targeting to the cell wall envelope. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 1999, 63, 174–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Solis, N.; Cordwell, S.J. Current methodologies for proteomics of bacterial surface-exposed and cell envelope proteins. Proteomics 2011, 11, 3169–3189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaudo, C.D.; Telford, J.L.; Rappuoli, R.; Seib, K.L. Vaccinology in the genome era. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 2515–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gómez-Gascón, L.; Cardoso-Toset, F.; Amarilla, P.S.; Tarradas, C.; Carrasco, L.; Olaya-Abril, A.; Jiménez-Munguía, I.; Rodríguez-Ortega, M.J.; Luque, I. A new recombinant SsnA protein combined with aluminum hydroxide protects mouse against Streptococcus suis. Vaccine 2014, 32, 6992–6999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Gascón, L.; Cardoso-Toset, F.; Tarradas, C.; Gómez-Laguna, J.; Maldonado, A.; Nielsen, J.; Olaya-Abril, A.; Rodríguez-Ortega, M.J.; Luque, I. Characterization of the immune response and evaluation of the protective capacity of rSsnA against Streptococcus suis infection in pigs. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2016, 47, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olaya-Abril, A.; Jiménez-Munguía, I.; Gómez-Gascón, L.; Rodríguez-Ortega, M.J. Surfomics: Shaving live organisms for a fast proteomic identification of surface proteins. J. Proteom. 2014, 97, 164–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, M.; Bensi, G.; Capo, S.; Falugi, F.; Zingaretti, C.; Manetti, A.G.; Maggi, T.; Taddei, A.R.; Grandi, G.; Telford, J.L. Group A Streptococcus produce pilus-like structures containing protective antigens and Lancefield T antigens. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 15641–15646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pizza, M.; Scarlato, V.; Masignani, V.; Giuliani, M.M.; Arico, B.; Comanducci, M.; Jennings, G.T.; Baldi, L.; Bartolini, E.; Capecchi, B.; et al. Identification of vaccine candidates against serogroup B meningococcus by whole-genome sequencing. Science 2000, 287, 1816–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, M.; Telford, J.L. Genome-based approaches to vaccine development. J. Mol. Med. 2010, 88, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Gottschalk, M.; Esgleas, M.; Lacouture, S.; Dubreuil, J.D.; Willson, P.; Harel, J. Immunization with recombinant Sao protein confers protection against Streptococcus suis infection. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2007, 14, 937–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Martinez, G.; Gottschalk, M.; Lacouture, S.; Willson, P.; Dubreuil, J.D.; Jacques, M.; Harel, J. Identification of a surface protein of Streptococcus suis and evaluation of its immunogenic and protective capacity in pigs. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mandanici, F.; Gómez-Gascón, L.; Garibaldi, M.; Olaya-Abril, A.; Luque, I.; Tarradas, C.; Mancuso, G.; Papasergi, S.; Bárcena, J.A.; Teti, G.; et al. A surface protein of Streptococcus suis serotype 2 identified by proteomics protects mice against infection. J. Proteom. 2010, 73, 2365–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Chen, B.; Li, R.; Mu, X.; Han, L.; Zhou, H.; Chen, H.; Meilin, J. Identification of a surface protective antigen, HP0197 of Streptococcus suis serotype 2. Vaccine 2009, 27, 5209–5213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Xia, J.; Tan, C.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, C.; Chen, H.; Bei, W. Evaluation of the immunogenicity and the protective efficacy of a novel identified immunogenic protein, SsPepO, of Streptococcus suis serotype 2. Vaccine 2011, 29, 6514–6519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, A.A.; van den Berg, A.J.; Loeffen, P.L. Protection of experimentally infected pigs by suilysin, the thiol-activated haemolysin of Streptococcus suis. Vet. Rec. 1996, 139, 225–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wisselink, H.J.; Vecht, U.; Stockhofe-Zurwieden, N.; Smith, H.E. Protection of pigs against challenge with virulent Streptococcus suis serotype 2 strains by a muramidase-released protein and extracellular factor vaccine. Vet. Rec. 2001, 148, 473–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Greeff, A.; Wisselink, H.J.; de Bree, F.M.; Schultsz, C.; Baums, C.G.; Thi, H.N.; Stockhofe-Zurwieden, N.; Smith, H.E. Genetic diversity of Streptococcus suis isolates as determined by comparative genome hybridization. BMC Microbiol. 2011, 11, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dalsass, M.; Brozzi, A.; Medini, D.; Rappuoli, R. Comparison of Open-Source Reverse Vaccinology Programs for Bacterial Vaccine Antigen Discovery. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| Clinical Isolate | Province of Origin | Source |
|---|---|---|
| 117/12 | Ciudad Real | Blood |
| 1299/06 | Huelva | Cerebrospinal fluid |
| 1086/11 | Lugo | Blood |
| 34/11 | Asturias | Cerebrospinal fluid |
| 857/06 | Córdoba | Cerebrospinal fluid |
| 41/14 | Vitoria | Blood |
| Protein Category a | Number of Identified Proteins | Number of Predicted Proteins in S. suis BM407 Genome | Identified/Predicted (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lipoprotein | 31 | 40 | 77.5 |
| Cell wall | 18 | 20 | 90 |
| Secreted | 11 | 18 | 61.1 |
| Membrane (1 TMD) | 45 | 110 | 40.9 |
| Multi-transmembrane | 26 | 369 | 7.1 |
| Total | 131 | 557 | 23.5 |
| Locus | Protein Annotation | 117/12 | 1299/06 | 1086/11 | 34/11 | 857/06 | 41/14 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lipoproteins a | |||||||
| SSUBM407_0110 | Zinc-binding protein AdcA | × | × | × | × | × | × |
| SSUBM407_0147 | Putative endopeptidase | × | × | × | × | ||
| SSUBM407_0275 | Extracellular solute-binding protein | × | × | × | × | × | × |
| SSUBM407_0359 | Putative penicillin-binding protein 1A | × | × | × | × | × | × |
| SSUBM407_0582 | Putative lipoprotein | × | × | × | × | × | × |
| SSUBM407_0612 | Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase | × | × | × | × | × | × |
| SSUBM407_0619 | Extracellular solute-binding protein | × | × | × | × | × | |
| SSUBM407_0696 | Putative lipoprotein | × | × | × | × | × | × |
| SSUBM407_0697 | Putative lipoprotein | × | × | × | × | × | × |
| SSUBM407_0711 | Foldase protein PrsA | × | × | × | × | × | × |
| SSUBM407_0831 | Putative phosphate ABC transporter, extracellular phosphate-binding lipoprotein | × | × | × | × | ||
| SSUBM407_0849 | Putative lipoprotein | × | × | × | × | × | × |
| SSUBM407_0904 | Putative extracellular amino acid-binding protein | × | × | × | × | × | |
| SSUBM407_1037 | Putative lipoprotein | × | × | × | × | × | × |
| SSUBM407_1134 | Putative D-alanyl-D-alanine carboxypeptidase | × | × | × | × | × | × |
| SSUBM407_1174 | Putative lipoprotein | × | × | × | × | × | × |
| SSUBM407_1218 | Putative ferrichrome-binding protein | × | × | × | × | × | × |
| SSUBM407_1232 | Putative exported protein | × | × | ||||
| SSUBM407_1311 | Putative amino acid ABC transporter, extracellular amino acid-binding protein | × | × | × | × | × | × |
| SSUBM407_1441 | Branched-chain amino acid ABC transporter, amino acid-binding protein | × | × | × | × | × | × |
| SSUBM407_1449 | Multiple sugar-binding protein | × | × | × | × | × | × |
| SSUBM407_1467 | Streptococcal histidine triad-family protein | × | × | × | × | × | × |
| SSUBM407_1633 | FAD:protein FMN transferase | × | × | × | × | × | |
| SSUBM407_1634 | Putative lipoprotein | × | × | × | × | × | × |
| SSUBM407_1651 | Lipoprotein | × | × | × | × | × | × |
| SSUBM407_1713 | Putative lipoprotein | × | × | × | × | × | × |
| SSUBM407_1736 | Putative oligopeptide-binding protein OppA | × | × | × | × | × | × |
| SSUBM407_1923 | Putative amino-acid ABC transporter extracellular-binding protein | × | × | × | × | × | × |
| SSUBM407_1939 | Extracellular metal cation-binding protein | × | × | × | × | × | × |
| SSUBM407_1980 | Maltodextrin-binding protein | × | × | × | × | × | × |
| SSUBM407_1998 | Putative fumarate reductase flavoprotein subunit | × | × | × | × | × | × |
| Cell wall proteins | |||||||
| SSUBM407_0180 | Putative surface-anchored protein | × | × | × | × | × | × |
| SSUBM407_0194 | Putative surface-anchored protein | × | × | × | × | × | × |
| SSUBM407_0244 | Putative surface-anchored protein | × | × | × | × | × | × |
| SSUBM407_0414 | Major pilus subunit | × | × | × | × | × | × |
| SSUBM407_0471 | Putative glucan-binding surface-anchored protein | × | |||||
| SSUBM407_0574 | Putative surface-anchored dipeptidase | × | × | × | × | × | × |
| SSUBM407_0588 | Putative surface-anchored protein | × | × | × | × | × | × |
| SSUBM407_0646 | Putative surface-anchored zinc carboxypeptidase | × | × | × | × | × | × |
| SSUBM407_0661 | Putative surface-anchored protein | × | × | × | × | × | × |
| SSUBM407_0918 | Putative 5′-nucleotidase | × | × | × | × | × | × |
| SSUBM407_0949 | Putative glucan-binding surface-anchored protein | × | |||||
| SSUBM407_1432 | Putative surface-anchored 5′-nucleotidase | × | × | × | × | × | × |
| SSUBM407_1550 | Putative surface-anchored protein | × | × | × | × | ||
| SSUBM407_1830 | Surface-anchored DNA nuclease | × | × | × | × | × | × |
| SSUBM407_1843 | Putative surface-anchored serine protease | × | × | × | × | × | × |
| SSUBM407_1919 | Putative surface-anchored amylopullulanase | × | × | × | × | × | × |
| SSUBM407_1949 | Putative surface-anchored 2′,3′-cyclic-nucleotide 2′-phosphodiesterase | × | × | × | × | × | × |
| SSUBM407_0900 | Putative IgA-specific zinc metalloproteinase | × | × | × | × | × | × |
| Multi-transmembrane proteins | |||||||
| SSUBM407_0015 | ATP-dependent zinc metalloprotease FtsH | × | × | ||||
| SSUBM407_0177 | Putative glycerophosphodiester phosphodiesterase | × | |||||
| SSUBM407_0233 | Putative membrane protein | × | |||||
| SSUBM407_0240 | Glycerol facilitator-aquaporin | × | |||||
| SSUBM407_0279 | Putative cation-transporting ATPase | × | × | × | × | ||
| SSUBM407_0454 | Putative permease | × | × | ||||
| SSUBM407_0552 | Cell division protein FtsX | × | |||||
| SSUBM407_0579 | ABC transporter permease protein | × | × | × | × | × | |
| SSUBM407_0621 | DNA translocase FtsK | × | |||||
| SSUBM407_0673 | Putative glycosyl transferase | × | × | ||||
| SSUBM407_0687 | Putative sulfatase | × | × | ||||
| SSUBM407_0762 | Putative membrane protein | × | × | × | × | × | |
| SSUBM407_0896 | Putative glutamine ABC transporter, glutamine-binding protein/permease protein | × | × | × | × | × | × |
| SSUBM407_1196 | Putative membrane protein | × | |||||
| SSUBM407_1297 | Putative chain length determinant protein | × | × | × | × | × | |
| SSUBM407_1298 | Integral membrane regulatory protein Wzg | × | × | × | × | × | × |
| SSUBM407_1333 | Large-conductance mechanosensitive channel | × | |||||
| SSUBM407_1406 | Putative peptidoglycan biosynthesis protein | × | |||||
| SSUBM407_1578 | Acyltransferase family protein | × | × | × | |||
| SSUBM407_1659 | Putative mannose-specific phosphotransferase system (PTS), IID component | × | |||||
| SSUBM407_1682 | Enoyl-CoA hydratase/isomerase family protein | × | × | × | × | × | × |
| SSUBM407_1747 | Glutamine ABC transporter, glutamine-binding protein/permease protein | × | × | × | × | × | × |
| SSUBM407_1834 | Nicotinamide mononucleotide transporter | × | |||||
| SSUBM407_1894 | ABC transporter ATP-binding membrane protein | × | |||||
| SSUBM407_1895 | ABC transporter ATP-binding membrane protein | × | |||||
| SSUBM407_1994 | Putative beta-glucosidase | × | |||||
| Membrane proteins (1 TMD) | |||||||
| SSUBM407_0010 | Putative septum formation initiator protein | × | |||||
| SSUBM407_0017 | Cell shape-determining protein MreC | × | × | × | × | × | × |
| SSUBM407_0019 | Putative amidase | × | × | × | × | × | × |
| SSUBM407_0116 | Putative penicillin-binding protein 1B | × | × | × | × | × | × |
| SSUBM407_0169 | Putative membrane protein | × | |||||
| SSUBM407_0203 | Signal peptidase I | × | × | × | × | × | |
| SSUBM407_0366 | Ribonuclease Y | × | |||||
| SSUBM407_0531 | Glycosyl hydrolases family protein | × | × | × | × | × | |
| SSUBM407_0599 | Sensor histidine kinase | × | |||||
| SSUBM407_0603 | Penicillin-binding protein 2b | × | × | × | × | ||
| SSUBM407_0686 | Streptococcal histidine triad-family protein | × | × | × | × | × | × |
| SSUBM407_0768 | ATP synthase subunit b | × | |||||
| SSUBM407_0777 | Putative competence associated endonuclease | × | × | × | × | × | × |
| SSUBM407_0856 | Sortase SrtA | × | × | × | × | × | × |
| SSUBM407_1034 | Putative lipoprotein | × | |||||
| SSUBM407_1039 | Putative membrane protein | × | × | × | × | ||
| SSUBM407_1048 | Putative membrane protein | × | × | × | |||
| SSUBM407_1080 | Spermidine/putrescine extracellular binding protein | × | × | × | × | × | × |
| SSUBM407_1087 | Putative polysaccharide deacetylase | × | × | × | × | × | × |
| SSUBM407_1116 | Putative exported protein | × | |||||
| SSUBM407_1215 | Putative acyltransferase | × | |||||
| SSUBM407_1225 | Putative D-alanyl-lipoteichoic acid biosynthesis protein | × | × | × | × | ||
| SSUBM407_1315 | Signal peptidase I | × | × | × | × | ||
| SSUBM407_1355 | Flotillin family protein | × | |||||
| SSUBM407_1368 | Putative exported protein | × | |||||
| SSUBM407_1403 | Septation ring formation regulator EzrA | × | × | ||||
| SSUBM407_1468 | Putative membrane protein | × | × | ||||
| SSUBM407_1494 | Putative exported protein | × | |||||
| SSUBM407_1524 | Peptidoglycan GlcNAc deacetylase | × | × | × | × | × | |
| SSUBM407_1536 | GDSL-like lipase/acylhydrolase protein | × | × | × | × | × | |
| SSUBM407_1544 | Putative neutral zinc metallopeptidase | × | × | × | × | × | |
| SSUBM407_1564 | Endopeptidase La | × | × | × | × | × | |
| SSUBM407_1622 | Putative penicillin binding protein 2x | × | × | × | × | × | × |
| SSUBM407_1750 | Putative membrane protein | × | |||||
| SSUBM407_1847 | Penicillin-binding protein 2a | × | × | × | × | × | × |
| SSUBM407_1955a | Putative accessory pilus subunit | × | × | × | × | × | |
| SSUBM407_0137 | Putative exported protein | × | × | × | × | × | |
| SSUBM407_0299 | Streptococcal histidine triad-family protein | × | × | × | × | × | |
| SSUBM407_0558 | Thiol-activated cytolysin (suilysin) | × | × | × | × | × | × |
| SSUBM407_0564 | GTPase Era | × | × | × | × | × | × |
| SSUBM407_0596 | Putative glutamine-binding protein | × | × | × | × | × | × |
| SSUBM407_0725 | Putative gluconate 5-dehydrogenase | × | |||||
| SSUBM407_1737 | Putative D-alanyl-D-alanine carboxypeptidase | × | × | × | × | × | × |
| SSUBM407_2015 | Putative exported protein | × | × | × | × | × | × |
| SSUBM407_1318 | Putative Mac family protein | × | × | × | × | × | × |
| Secreted proteins | |||||||
| SSUBM407_0206 | Putative exported protein | × | × | × | × | × | × |
| SSUBM407_0452 | Putative exported protein | × | × | × | × | × | × |
| SSUBM407_0662 | Putative N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanine amidase | × | × | × | × | × | × |
| SSUBM407_1229 | Putative exported protein | × | × | × | × | × | |
| SSUBM407_1435 | Putative exported protein | × | × | × | × | × | × |
| SSUBM407_1493 | Putative exported protein | × | × | ||||
| SSUBM407_1689 | Putative exported protein | × | × | × | × | × | × |
| SSUBM407_1726 | LytR family regulatory protein | × | × | × | × | × | × |
| SSUBM407_1898 | UTP-glucose-1-phosphate uridylyltransferase | × | × | × | × | × | × |
| SSUBM407_1924 | Putative amidase | × | × | × | × | × | × |
| SSUBM407_2032 | Serine protease | × | × | × | × | × | × |
| Locus | Protein Annotation | VaxiJen Score (Whole Protein Sequence) | VaxiJen Score (Selected Region) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SSUBM407_0015 | ATP-dependent zinc metalloprotease FtsH | 0.4769 | 0.4083 |
| SSUBM407_0177 | Putative glycerophosphodiester phosphodiesterase | 0.5947 | 0.736 |
| SSUBM407_0233 | Putative membrane protein | 0.5118 | 0.3818 |
| SSUBM407_0240 | Glycerol facilitator-aquaporin | 0.4743 | 0.0193; 0.6665 a |
| SSUBM407_0279 | Putative cation-transporting ATPase | 0.4129 | −0.7033 |
| SSUBM407_0454 | Putative permease | 0.3927 | 0.5403 |
| SSUBM407_0552 | Cell division protein FtsX | 0.3305 | 0.5012 |
| SSUBM407_0579 | ABC transporter permease protein | 0.5152 | 0.6518 |
| SSUBM407_0621 | DNA translocase FtsK | 0.6354 | 0.5652; 0.0679; 0.4148 b |
| SSUBM407_0673 | Putative glycosyl transferase | 0.406 | 0.4508; 0.4627; 1.0152 b |
| SSUBM407_0687 | Putative sulfatase | 0.4886 | −1.0353; 0.1934; 1.2694 b |
| SSUBM407_0762 | Putative membrane protein | 0.5909 | 0.5467; 0.4076 c |
| SSUBM407_0896 | Putative glutamine ABC transporter, glutamine-binding protein/permease protein | 0.4815 | 0.5710; 0.5193 d |
| SSUBM407_1196 | Putative membrane protein | 0.614 | 1.542 |
| SSUBM407_1297 | Putative chain length determinant protein | 0.429 | 0.5168 |
| SSUBM407_1298 | Integral membrane regulatory protein Wzg | 0.4806 | 0.4464 |
| SSUBM407_1333 | Large-conductance mechanosensitive channel | 0.1327 | −0.3111 |
| SSUBM407_1406 | Putative peptidoglycan biosynthesis protein | 0.4707 | 1.3646 |
| SSUBM407_1578 | Acyltransferase family protein | 0.5404 | 0.6473; 0.3350 c |
| SSUBM407_1659 | Putative mannose-specific phosphotransferase system (PTS), IID component | 0.5271 | 0.5209 |
| SSUBM407_1682 | Enoyl-CoA hydratase/isomerase family protein | 0.2805 | 0.3215; 0.3055 e |
| SSUBM407_1747 | Glutamine ABC transporter, glutamine-binding protein/permease protein | 0.4425 | 0.5469 |
| SSUBM407_1834 | Nicotinamide mononucleotide transporter | 0.3328 | 1.5844 |
| SSUBM407_1894 | ABC transporter ATP-binding membrane protein | 0.3206 | 1.0090; 0.4935; −0.0553; 0.2739 f |
| SSUBM407_1895 | ABC transporter ATP-binding membrane protein | 0.4377 | 1.4975; 0.4104 g |
| SSUBM407_1994 | Putative beta-glucosidase | 0.4664 | 0.5024; 0.3803 c |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Prados de la Torre, E.; Rodríguez-Franco, A.; Rodríguez-Ortega, M.J. Proteomic and Bioinformatic Analysis of Streptococcus suis Human Isolates: Combined Prediction of Potential Vaccine Candidates. Vaccines 2020, 8, 188. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines8020188
Prados de la Torre E, Rodríguez-Franco A, Rodríguez-Ortega MJ. Proteomic and Bioinformatic Analysis of Streptococcus suis Human Isolates: Combined Prediction of Potential Vaccine Candidates. Vaccines. 2020; 8(2):188. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines8020188
Chicago/Turabian StylePrados de la Torre, Esther, Antonio Rodríguez-Franco, and Manuel J. Rodríguez-Ortega. 2020. "Proteomic and Bioinformatic Analysis of Streptococcus suis Human Isolates: Combined Prediction of Potential Vaccine Candidates" Vaccines 8, no. 2: 188. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines8020188
APA StylePrados de la Torre, E., Rodríguez-Franco, A., & Rodríguez-Ortega, M. J. (2020). Proteomic and Bioinformatic Analysis of Streptococcus suis Human Isolates: Combined Prediction of Potential Vaccine Candidates. Vaccines, 8(2), 188. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines8020188






