Continuous HIV-1 Escape from Autologous Neutralization and Development of Cross-Reactive Antibody Responses Characterizes Slow Disease Progression of Children
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Patients’ Characteristics and Samples
2.2. Ethical Permission
2.3. PBMC-Based Neutralization Assay
2.4. TZMbl Neutralization Assay
2.5. Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity Assay
2.6. ELISA Assay for Reactivity to Tetanus and Diphteria Toxoids, and HIV-1 Gp4
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Persistent Autologous Neutralizing Activity Is Common in Slow Progressing Children
3.2. Neutralization against Heterologous Virus Evolves in Children with Slow Disease Progression
3.3. Titers of Antibodies Mediating ADCC against gp120 Coated Target Cells Increase with Age
3.4. Lack of HIV-1 Neutralization Capacity Does Not Correlate with Impaired Antibody Responses in General
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gray, G.E.; Huang, Y.; Grunenberg, N.; Laher, F.; Roux, S.; Andersen-Nissen, E.; De Rosa, S.C.; Flach, B.; Randhawa, A.K.; Jensen, R.; et al. Immune correlates of the Thai RV144 HIV vaccine regimen in South Africa. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, eaax1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanche, S.; Mayaux, M.-J.; Rouzioux, C.; Teglas, J.-P.; Firtion, G.; Monpoux, F.; Cicaru-Vigneron, N.; Meier, F.; Tricoire, J.; Courpotin, C.; et al. Relation of the course of HIV Infection in children to the severity of the disease in their mothers at delivery. N. Engl. J. Med. 1994, 330, 308–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarlatti, G. Paediatric HIV infection. Lancet 1996, 348, 863–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tovo, P.; Gabiano, C.; Palomba, E.; de Martino, M.; Galli, L.; Cappello, N.; D’Elia, R.; Ruga, E.; Loy, A.; Plebani, A.; et al. Prognostic factors and survival in children with perinatal HIV-1 infection. Lancet 1192, 339, 1249–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, J.; Abrahamsson, B.; Nagy, K.; Aurelius, E.; Gaines, H.; Nyström, G. Rapid development of isolate-specific neutralizing antibodies after primary HIV-1 infection and consequent emergence of virus variants which resist neutralization by autologous sera. AIDS 1990, 4, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunnik, E.M.; Pisas, L.; van Nuenen, A.C.; Schuitemaker, H. Autologous neutralizing humoral immunity and evolution of the viral envelope in the course of subtype b human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 7932–7941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Richman, D.D.; Wrin, T.; Little, S.J.; Petropoulos, C.J. Rapid evolution of the neutralizing antibody response to HIV type 1 infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 4144–4149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gray, E.S.; Taylor, N.; Wycuff, D.; Moore, P.L.; Tomaras, G.D.; Wibmer, C.K.; Puren, A.; De Camp, A.; Gilbert, P.B.; Wood, B.; et al. Antibody specificities associated with neutralization breadth in plasma from human immunodeficiency virus type 1 subtype c-infected blood donors. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 8925–8937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Gils, M.J.; Euler, Z.; Schweighardt, B.; Wrin, T.; Schuitemaker, H. Prevalence of cross-reactive HIV-1-neutralizing activity in HIV-1-infected patients with rapid or slow disease progression. AIDS 2009, 23, 2405–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Euler, Z.; van Gils, M.J.; Bunnik, E.M.; Phung, P.; Schweighardt, B.; Wrin, T.; Schuitemaker, H. Cross-reactive neutralizing humoral immunity does not protect from HIV type 1 disease progression. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 201, 1045–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Broliden, K.; Sievers, E.; Tovo, P.A.; Moschese, V.; Scarlatti, G.; Broliden, P.A.; Fundaro, C.; Rossi, P. Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity and neutralizing activity in sera of HIV-1-infected mothers and their children. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1993, 93, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, S.S.; Andrabi, R.; Kumar, R.; Lodha, R.; Kabra, S.K.; Vajpayee, M.; Luthra, K. Antibodies that cross-neutralize the tier-2 pseudoviruses are produced in antiretroviral-naïve HIV-1-infected children from northern India. Arch. Virol. 2012, 157, 1797–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Perre, P.; Lepage, P.; Simonon, A.; Desgranges, C.; Hitimana, D.-G.; Bazubagira, A.; Van Goethem, C.; Kleinschmidt, A.; Bex, F.; Broliden, K.; et al. Biological markers associated with prolonged survival in african children maternally infected by the human immunodeficiency virus type 1. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 1992, 8, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goo, L.; Chohan, V.; Nduati, R.; Overbaugh, J. Early development of broadly neutralizing antibodies in HIV-1-infected infants. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 655–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ditse, Z.; Muenchhoff, M.; Adland, E.; Jooste, P.; Goulder, P.; Moore, P.L.; Morris, L. HIV-1 subtype c-infected children with exceptional neutralization breadth exhibit polyclonal responses targeting known epitopes. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e00878-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fouda, G.G.; De Paris, K.; Levy, O.; Marchant, A.; Gray, G.; Permar, S.; Marovich, M.; Singh, A. Immunological mechanisms of inducing HIV immunity in infants. Vaccine 2020, 38, 411–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muenchhoff, M.; Adland, E.; Karimanzira, O.; Crowther, C.; Pace, M.; Csala, A.; Leitman, E.; Moonsamy, A.; McGregor, C.; Hurst, J.; et al. Nonprogressing HIV-infected children share fundamental immunological features of nonpathogenic SIV infection. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 358ra125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Milligan, C.; Richardson, B.A.; John-Stewart, G.; Nduati, R.; Overbaugh, J. Passively acquired Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity (ADCC) activity in HIV-infected infants is associated with reduced mortality. Cell Host Microbe 2015, 17, 500–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tranchat, C.; Van de Perre, P.; Simonon-Sorel, A.; Karita, E.; Benchaïb, M.; Lepage, P.; Desgranges, C.; Boyer, V.; répo, C. Maternal humoral factors associated with perinatal human immunodeficiency virus type-1 transmission in a cohort from Kigali, Rwanda, 1988–1994. J. Infect. 1999, 39, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ljunggren, K.; Moschese, V.; Broliden, P.-A.; Giaquinto, C.; Quinti, I.; Fenyö, E.-M.; Wahren, B.; Rossi, P.; Jondal, M. Antibodies mediating cellular cytotoxicity and neutralization correlate with a better clinical stage in children born to human immunodeficiency virus-infected mothers. J. Infect. Dis. 1990, 161, 198–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarlatti, G. Mother-to-child transmission of HIV-1: Advances and controversies of the twentieth centuries. AIDS Rev. 2004, 6, 67–78. [Google Scholar]
- Baan, E.; de Ronde, A.; Stax, M.; Sanders, R.W.; Luchters, S.; Vyankandondera, J.; Lange, J.M.; Pollakis, G.; Paxton, W.A. HIV-1 autologous antibody neutralization associates with mother to child transmission. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dickover, R.; Garratty, E.; Yusim, K.; Miller, C.; Korber, B.; Bryson, Y. Role of maternal autologous neutralizing antibody in selective perinatal transmission of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 escape variants. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 6525–6533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Omenda, M.M.; Milligan, C.; Odem-Davis, K.; Nduati, R.; Richardson, B.A.; Lynch, J.; John-Stewart, G.; Overbaugh, J. Evidence for efficient vertical transfer of maternal HIV-1 envelope-specific neutralizing antibodies but no association of such antibodies with reduced infant infection. J. Acquir. Immune. Defic. Syndr. 2013, 64, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Russell, E.S.; Kwiek, J.J.; Keys, J.; Barton, K.; Mwapasa, V.; Montefiori, D.C.; Meshnick, S.R.; Swanstrom, R. The genetic bottleneck in vertical transmission of subtype C HIV-1 is not driven by selection of especially neutralization-resistant virus from the maternal viral population. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 8253–8262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baba, T.W.; Liska, V.; Hofmann-Lehmann, R.; Vlasak, J.; Xu, W.; Ayehunie, S.; Cavacini, L.A.; Posner, M.R.; Katinger, H.; Stiegler, G.; et al. Human neutralizing monoclonal antibodies of the IgG1 subtype protect against mucosal simian-human immunodeficiency virus infection. Nat. Med. 2000, 6, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrantelli, F.; Buckley, K.A.; Rasmussen, R.A.; Chalmers, A.; Wang, T.; Li, P.-L.; Williams, A.L.; Hofmann-Lehmann, R.; Montefiori, D.C.; Cavacini, L.A.; et al. Time dependence of protective post-exposure prophylaxis with human monoclonal antibodies against pathogenic SHIV challenge in newborn macaques. Virology 2007, 358, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmad, N.; Baroudy, B.M.; Baker, R.C.; Chappey, C. Genetic analysis of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope V3 region isolates from mothers and infants after perinatal transmission. J. Virol. 1995, 69, 1001–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumar, A.; Smith, C.E.P.; Giorgi, E.E.; Eudailey, J.; Martinez, D.R.; Yusim, K.; Douglas, A.O.; Stamper, L.; McGuire, E.; LaBranche, C.C.; et al. Infant transmitted/founder HIV-1 viruses from peripartum transmission are neutralization resistant to paired maternal plasma. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1006944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, X.; Parast, A.B.; Richardson, B.A.; Nduati, R.; John-Stewart, G.; Mbori-Ngacha, D.; Rainwater, S.M.J.; Overbaugh, J. Neutralization escape variants of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 are transmitted from mother to infant. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 835–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Doepker, L.E.; Simonich, C.A.; Ralph, D.; Shipley, M.M.; Garrett, M.; Gobillot, T.; Vigdorovich, V.; Sather, D.N.; Nduati, R.; Matsen, F.A.; et al. Diversity and function of maternal HIV-1-specific antibodies at the time of vertical transmission. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e01594-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mabuka, J.; Goo, L.; Omenda, M.M.; Nduati, R.; Overbaugh, J. HIV-1 maternal and infant variants show similar sensitivity to broadly neutralizing antibodies, but sensitivity varies by subtype. AIDS 2013, 27, 1535–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Russell, E.S.; Ojeda, S.; Fouda, G.G.; Meshnick, S.R.; Montefiori, D.; Permar, S.R.; Swanstrom, R. Short communication: HIV type 1 subtype C variants transmitted through the bottleneck of breastfeeding are sensitive to new generation broadly neutralizing antibodies directed against quaternary and CD4-binding site epitopes. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 2013, 29, 511–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thenin, S.; Samleerat, T.; Tavernier, E.; Ngo-Giang-Huong, N.; Jourdain, G.; Lallemant, M.; Barin, F.; Braibant, M. Envelope glycoproteins of Human Immunodeficiency Virus type 1 variants issued from mother–infant pairs display a wide spectrum of biological properties. Virology 2012, 426, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lynch, J.B.; Nduati, R.; Blish, C.A.; Richardson, B.A.; Mabuka, J.M.; Jalalian-Lechak, Z.; John-Stewart, G.; Overbaugh, J. The breadth and potency of passively acquired human immunodeficiency virus type 1-specific neutralizing antibodies do not correlate with the risk of infant infection. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 5252–5261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geffin, R.; Hutto, C.; Andrew, C.; Scott, G.B. A longitudinal assessment of autologous neutralizing antibodies in children perinatally infected with human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Virology 2003, 310, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scarlatti, G.; Hodara, V.; Rossi, P.; Muggiasca, L.; Bucceri, A.; Albert, J.; Fenyö, E.M. Transmission of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 (HIV-1) from Mother to Child Correlates with Viral Phenotype. Virology 1993, 197, 624–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarlatti, G.; Lombardi, V.; Plebani, A.; Principi, N.; Vegni, C.; Ferraris, G.; Bucceri, A.; Fenyö, E.M.; Wigzell, H.; Rossi, P.; et al. Polymerase chain reaction, virus isolation and antigen assay in HIV-1-antibody-positive mothers and their children. AIDS 1991, 5, 1173–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarlatti, G.; Tresoldi, E.; Björndal, Å.; Fredriksson, R.; Colognesi, C.; Deng, H.K.; Malnati, M.S.; Plebani, A.; Siccardi, A.G.; Littman, D.R.; et al. In vivo evolution of HIV-1 co-receptor usage and sensitivity to chemokine-mediated suppression. Nat. Med. 1997, 3, 1259–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarlatti, G.; Leitner, T.; Halapi, E.; Wahlberg, J.; Marchisio, P.; Clerici-Schoeller, M.A.; Wigzell, H.; Fenyö, E.M.; Albert, J.; Uhlén, M.; et al. Comparison of variable region 3 sequences of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 from infected children with the RNA and DNA sequences of the virus populations of their mothers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 1721–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Control Center for Disease. 1994 revised classification system for human immunodeficiency virus infection in children less than 13 years of age. Recomm. Rep. 1994, 43, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Cavarelli, M.; Karlsson, I.; Zanchetta, M.; Antonsson, L.; Plebani, A.; Giaquinto, C.; Fenyö, E.M.; De Rossi, A.; Scarlatti, G. HIV-1 with multiple CCR5/CXCR4 chimeric receptor use is predictive of immunological failure in infected children. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarlatti, G.; Albert, J.; Rossi, P.; Hodara, V.; Biraghi, P.; Muggiasca, L.; Fenyö, E.M. Mother-to-child transmission of human immunodeficiency virus type 1: Correlation with neutralizing antibodies against primary isolates. J. Infect. Dis. 1993, 168, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenyö, E.M.; Heath, A.; Dispinseri, S.; Holmes, H.; Lusso, P.; Zolla-Pazner, S.; Donners, H.; Heyndrickx, L.; Alcami, J.; Bongertz, V.; et al. International network for comparison of HIV neutralization assays: The NeutNet report. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e4505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarzotti-Kelsoe, M.; Bailer, R.T.; Turk, E.; Lin, C.; Bilska, M.; Greene, K.M.; Gao, H.; Todd, C.A.; Ozaki, D.A.; Seaman, M.S.; et al. Optimization and validation of the TZM-bl assay for standardized assessments of neutralizing antibodies against HIV-1. J. Immunol. Methods 2014, 409, 131–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heyndrickx, L.; Heath, A.; Sheik-Khalil, E.; Alcami, J.; Bongertz, V.; Jansson, M.; Malnati, M.; Montefiori, D.; Moog, C.; Morris, L.; et al. International network for comparison of HIV neutralization assays: The NeutNet report II. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollara, J.; Hart, L.; Brewer, F.; Pickeral, J.; Packard, B.Z.; Hoxie, J.A.; Komoriya, A.; Ochsenbauer, C.; Kappes, J.C.; Roederer, M.; et al. High-throughput quantitative analysis of HIV-1 and SIV-specific ADCC-mediating antibody responses. Cytom. Part A 2011, 79, 603–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McFarland, E.J.; Johnson, D.C.; Muresan, P.; Fenton, T.; Tomaras, G.D.; McNamara, J.; Read, J.S.; Douglas, S.D.; Deville, J.; Gurwith, M.; et al. HIV-1 vaccine induced immune responses in newborns of HIV-1 infected mothers. AIDS 2006, 20, 1481–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halapi, E.; Leitner, T.; Jansson, M.; Scarlatti, G.; Orlandi, P.; Plebani, A.; Romiti, L.; Albert, J.; Wigzell, H.; Rossi, P. Correlation between HIV sequence evolution, specific immune response and clinical outcome in vertically infected infants. AIDS 1997, 11, 1709–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pensieroso, S.; Cagigi, A.; Palma, P.; Nilsson, A.; Capponi, C.; Freda, E.; Bernardi, S.; Thorstensson, R.; Chiodi, F.; Rossi, P. Timing of HAART defines the integrity of memory B cells and the longevity of humoral responses in HIV-1 vertically-infected children. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 7939–7944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moir, S.; Buckner, C.M.; Ho, J.; Wang, W.; Chen, J.; Waldner, A.J.; Posada, J.G.; Kardava, L.; O’Shea, M.A.; Kottilil, S.; et al. B cells in early and chronic HIV infection: Evidence for preservation of immune function associated with early initiation of antiretroviral therapy. Blood 2010, 116, 5571–5579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doria-Rose, N.A.; Klein, R.M.; Daniels, M.G.; O’Dell, S.; Nason, M.; Lapedes, A.; Bhattacharya, T.; Migueles, S.A.; Wyatt, R.T.; Korber, B.T.; et al. Breadth of human immunodeficiency virus-specific neutralizing activity in sera: Clustering analysis and association with clinical variables. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Simek, M.D.; Rida, W.; Priddy, F.H.; Pung, P.; Carrow, E.; Laufer, D.S.; Lehrman, J.K.; Boaz, M.; Tarragona-Fiol, T.; Miiro, G.; et al. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 elite neutralizers: Individuals with broad and potent neutralizing activity identified by using a high-throughput neutralization assay together with an analytical selection algorithm. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 7337–7348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Naiman, N.E.; Slyker, J.; Richardson, B.A.; John-Stewart, G.; Nduati, R.; Overbaugh, J.M. Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity targeting CD4-inducible epitopes predicts mortality in HIV-infected infants. EBioMedicine 2019, 47, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
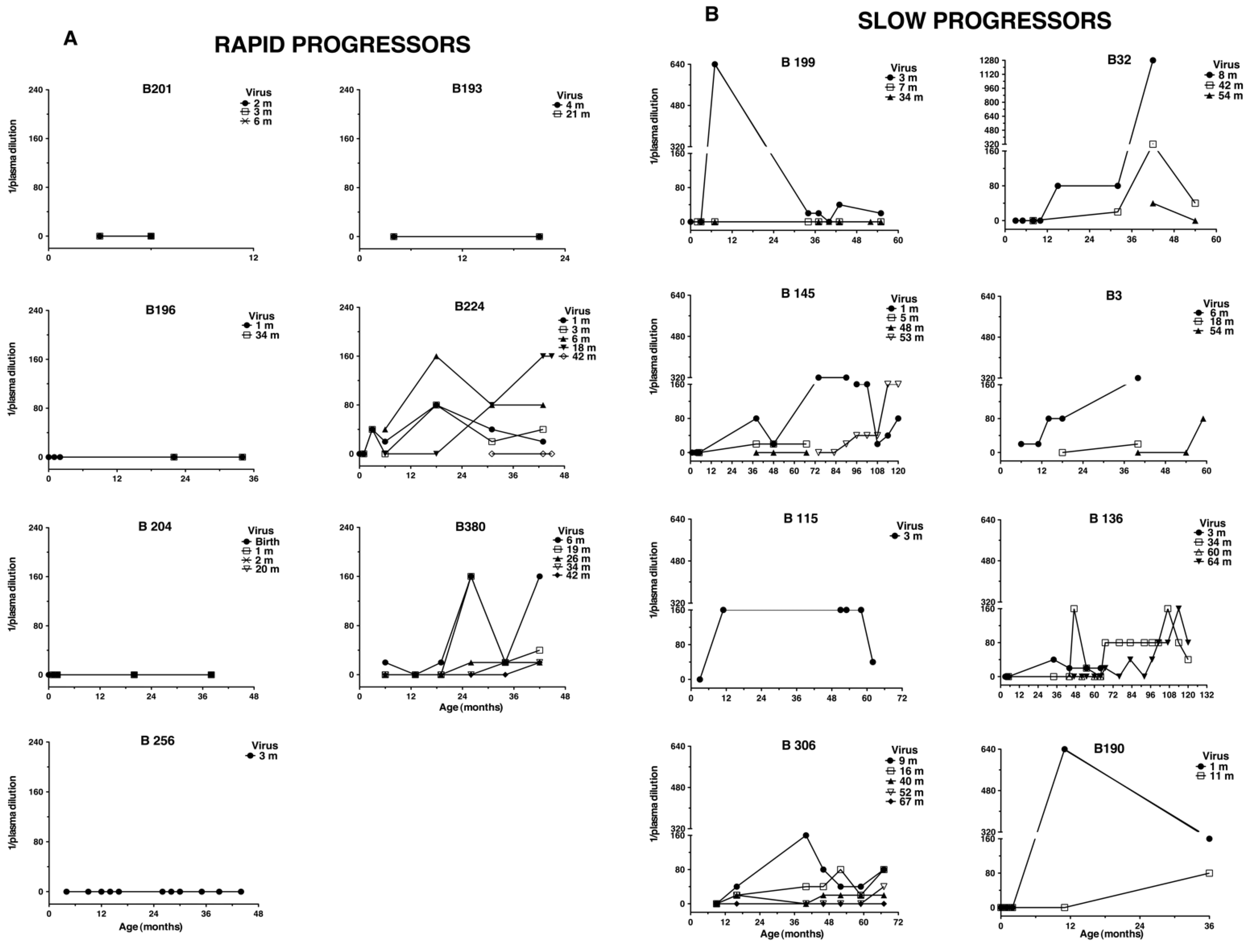
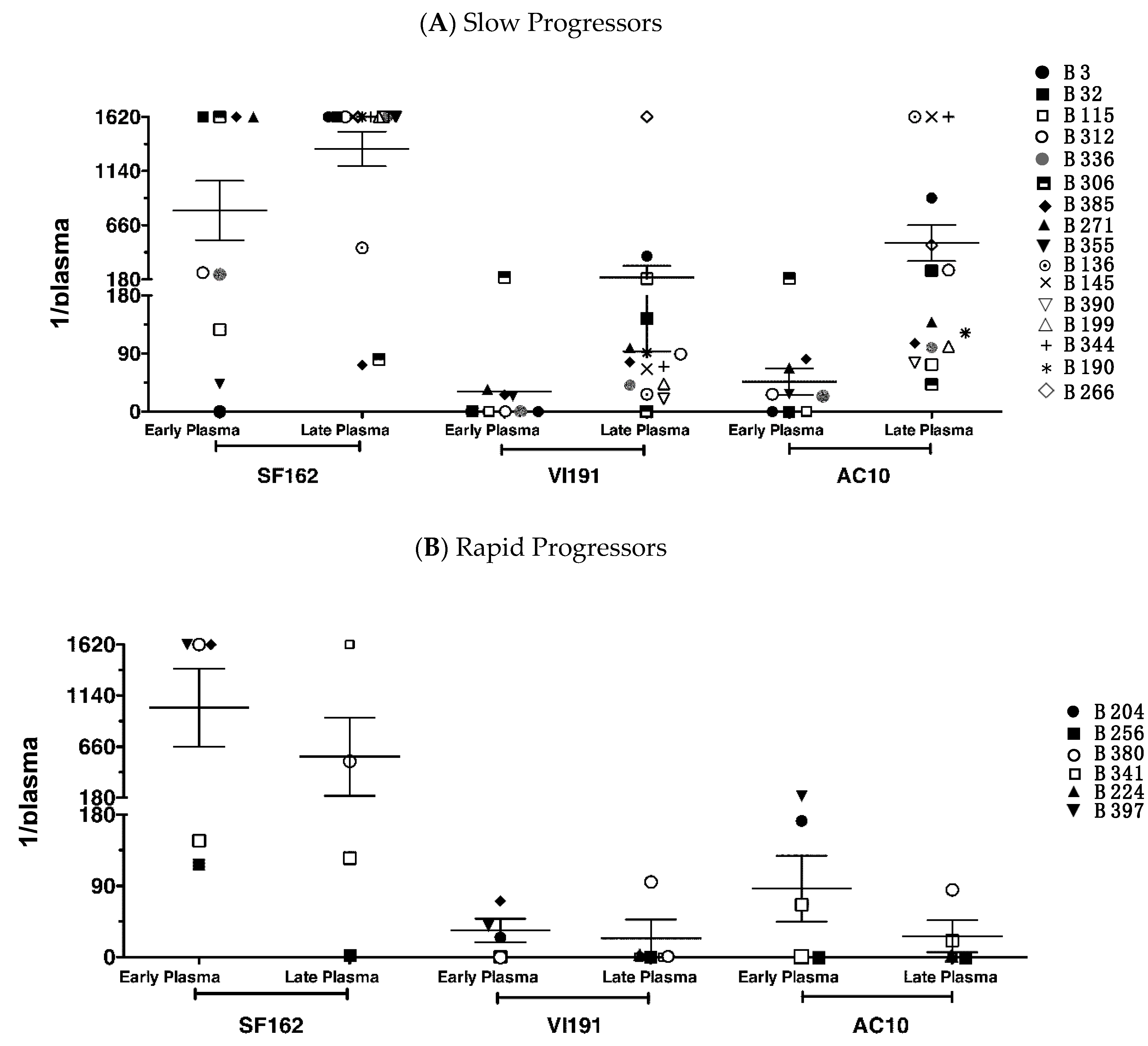


| Group of Disease Progression | Child Code | Age at First HIV Diagnosis (b) | Age at Category Diagnosed (c) | First CXCR4-Virus Isolation (d) | Therapy Start (e) | Death | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CDC 3 | CDC B | CDC C | ||||||
| Rapid Progressor | ||||||||
| B193 | 4 | 6 | 6 | 12 | 21 | 12 | 28 | |
| B196 | 1 (3d) | 6 | 6 | 34 | 1 | 9 | 44 | |
| B201 | 2 | 6 | - (c) | 6 | - | - | 9 | |
| B204 | 5d | 6 | 6 | - | 1 | - | 38 | |
| B224 | 1 (4d) | 6 | 8 | 44 | - | 8 | - | |
| B341 | 1 | 7 | 13 | - | na | 34 | - | |
| B380 | 1 | 9 | 9 | 15 | - | 4 | - | |
| B256 | 1.5 | 17 | - | 5 | na | 7 | 46 | |
| B397 | 1 | 24 | 0.5 | - | na | 28 | - | |
| Slow Progressor | ||||||||
| B32 | 3 | 28 | 28 | - | - | 28 | 96 | |
| B199 | 1 (7d) | 27 | 24 | - | 37 | 27 | 60 | |
| B3 | 6 | 55 | 44 | - | 54 | 54 | - | |
| B115 | 3 | 58 | 58 | - | 119 | 59 | - | |
| B136 | 1 | 60 | - | - | 60 | 64 | - | |
| B145 | 1 | 48 | 8 | 98 | 48 | 51 | - | |
| B266 | 1 | 44 | 42 | - | 19 | 26 | - | |
| B390 | 1 | 53 | - | - | na | 61 | - | |
| B385 | 1 | - | - | 6 | na | 7 | - | |
| B190 | 1 (3d) | - | - | - | - | 77 | - | |
| B271 | 1 (2d) | - | - | - | na | 72 | - | |
| B306 | 1 | - | 28 | - | - | 61 | - | |
| B312 | 1 | - | - | - | na | 61 | - | |
| B336 | 1 | - | - | - | na | 60 | - | |
| B344 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| B355 | 1 | - | 1.5 | 21.5 | na | 35 | - | |
| Plasma | Viral Isolate (a) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (b) | 3–54 (X4) (c) | 32–42 (R5) | 32–54 (R5) | 145-5 (R5) | |
| Rapid Progressor | |||||
| B193 | 24 | 0 | 40 | nd (d) | 0 |
| B224 | 31 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| B204 | 33 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| B256 | 39 | nd | 0 | nd | 0 |
| Slow Progressor | |||||
| B199 | 37 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| B32 | 32 | 0 | nd | nd | 0 |
| B145 | 38 | 80 | 0 | 0 | (80) (e) |
| B115 | 53 | 20 | 0 | 0 | 20 |
| B136 | 34 | 0 | 40 | 20 | 0 |
| B190 | 36 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dispinseri, S.; Cavarelli, M.; Tolazzi, M.; Plebani, A.M.; Jansson, M.; Scarlatti, G. Continuous HIV-1 Escape from Autologous Neutralization and Development of Cross-Reactive Antibody Responses Characterizes Slow Disease Progression of Children. Vaccines 2021, 9, 260. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9030260
Dispinseri S, Cavarelli M, Tolazzi M, Plebani AM, Jansson M, Scarlatti G. Continuous HIV-1 Escape from Autologous Neutralization and Development of Cross-Reactive Antibody Responses Characterizes Slow Disease Progression of Children. Vaccines. 2021; 9(3):260. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9030260
Chicago/Turabian StyleDispinseri, Stefania, Mariangela Cavarelli, Monica Tolazzi, Anna Maria Plebani, Marianne Jansson, and Gabriella Scarlatti. 2021. "Continuous HIV-1 Escape from Autologous Neutralization and Development of Cross-Reactive Antibody Responses Characterizes Slow Disease Progression of Children" Vaccines 9, no. 3: 260. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9030260
APA StyleDispinseri, S., Cavarelli, M., Tolazzi, M., Plebani, A. M., Jansson, M., & Scarlatti, G. (2021). Continuous HIV-1 Escape from Autologous Neutralization and Development of Cross-Reactive Antibody Responses Characterizes Slow Disease Progression of Children. Vaccines, 9(3), 260. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9030260






