Abstract
Background: Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) and cytomegalovirus (CMV) infections can have serious consequences during the period of aplasia and lymphopenia following hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT). Large pediatric cohort studies examining the effect of antiviral prophylaxis against these viruses are scarce. The present study aimed to analyse the potential effect of antiviral prophylaxis (acyclovir and famciclovir) on active post-transplant EBV and CMV infection in a pediatric cohort of allogeneic HSCT recipients. Methods: We used data from the TREASuRE cohort, consisting of 156 patients who had a first allogeneic HSCT, enrolled in four pediatric centers in Canada between July 2013 and March 2017. Follow-up was performed from the time of transplant up to 100 days post-transplant. Adjusted hazard ratio (HR) with 95% confidence intervals (CI) for the association between antiviral prophylaxis with acyclovir and/or famciclovir and EBV and CMV DNAemia was estimated using multivariate Cox regression models. Results: The post-transplant cumulative incidence of EBV and CMV DNAemia at 100 days of follow-up were, respectively, 34.5% (95% CI: 27.6–42.6) and 19.9% (95% CI: 14.5–27.1). For acyclovir, the adjusted hazard ratio (HR) for CMV and EBV DNAemia was 0.55 (95% CI: 0.24–1.26) and 1.41 (95% CI: 0.63–3.14), respectively. For famciclovir, the adjusted HR were 0.82 (95% CI: 0.30–2.29) and 0.79 (95% CI: 0.36–1.72) for CMV and EBV DNAemia, respectively. Conclusion: The antivirals famciclovir and acyclovir did not reduce the risk of post-transplant CMV and EBV DNAemia among HSCT recipients in our pediatric population.
1. Introduction
Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) is used for the treatment of malignant tumors and certain blood or immune system disorders [1,2,3,4]. The immunosuppressed state correlates with a significant risk of post-transplant infections, and these infections play a major role in treatment-related morbidity and post-transplant mortality in pediatric HSCT [5,6,7,8,9,10]. Among the most morbid viral infections are those caused by the human herpesviruses (HHV), namely herpes simplex viruses (HSV or HHV-1/2), varicella-zoster virus (VZV or HHV-3), Epstein–Barr virus (EBV or HHV-4), and cytomegalovirus (CMV or HHV-5) [11,12]. Active infection with HHV-6 (roseolavirus) and HHV-7 can also occur but is less common [1,11,12,13,14]. HHV-8 infection (associated with Kaposi’s sarcoma and Castleman’s disease) is infrequent in pediatric HSCT [15,16]. Active HHV infections can occur either during primary infection or following reactivation of latent virus [8], predominantly during the early post-transplant period when the patient’s cell-mediated immune response is severely compromised [9,10,11]. More than two-thirds of patients develop viral reactivation or primary HHV infections in the first 3 months after HSCT [12].
Antivirals are generally used systematically in clinical protocols to prevent reactivation of specific human herpesviruses, namely HSV, VZV, and CMV [17,18,19]. The Francophone Society of Bone Marrow Transplantation and Cell Therapy, and the European Conference on Leukemia recommend prophylaxis for HSV seropositive patients from the start of conditioning until the end of granulocytopenia and resolution of mucositis. Specific recommendations involve the use of intravenous acyclovir or famciclovir for 3 to 6 weeks after initiation of chemotherapy or grafting, or up to the end of aplasia [18,20]. Long-term prophylaxis with acyclovir (up to one-year post-transplant or until immunosuppressive drugs are discontinued) is also recommended for VZV seropositive HSCT recipients. Ganciclovir is recommended until day 100 post-HSCT to prevent active CMV infection in allogeneic HSCT recipients who are at risk (CMV seropositive recipient or CMV seropositive donor) of engraftment failure [21,22]. Although active EBV infection is very common and may lead to serious complications such as post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder (PTLD), the International Medical Societies do not recommend the use of antiviral prophylaxis for EBV as there is no proven clinically effective antiviral against this virus [23].
Viral blood monitoring can also be done for early detection of viral DNA and pre-emptive treatment. In this case, valaciclovir and famciclovir are preferred for the oral treatment of HSV and VZV in pediatric HSCT recipients with stable localized disease [18]. Intravenous ganciclovir can also be used for the treatment of CMV disease during the year following HSCT [21,22]. Although there are no recognized clinically effective antivirals against EBV, qPCR monitoring is usually performed to assess pre-emptive treatment of patients showing significant spikes in viral load with the anti-CD20 monoclonal (rituximab) thereby preventing the development of PTLD [18].
Overall, the prophylactic efficacy of acyclovir and famciclovir for HSV and VZV is well recognized as a standard-of-care in the clinical guidelines of various transplant societies. However, questions remain about the potential effect of these antivirals on other HHV, such as EBV and CMV. The pediatric literature on this issue is especially limited. The main goal of this study was, therefore, to measure the association between antiviral prophylaxis with acyclovir and famciclovir and post-transplant EBV and CMV DNAemia among pediatric recipients of allogeneic HSCT.
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
We used data from TREASuRE study, a multicenter prospective cohort study of allogeneic HSCT recipients from four Canadian pediatric tertiary care centers. Study design and methods have been published previously [24]. Briefly, the study enrolled 156 patients under the age of 21 who had undergone allogeneic HSCT (bone marrow, cord blood, or peripheral blood). Recruitment was conducted at different sites: CHU Sainte-Justine in Montreal (n = 86), British Columbia Children’s Hospital of Vancouver (n = 31), Winnipeg Children’s Hospital and CancerCare Manitoba (n = 28) and Alberta Children’s Hospital (n = 11). Patients were recruited approximately one month before transplant and followed up to one-year post-transplant for a maximum follow-up time of 13 months. Recruitment and follow-up began in July 2013 and ended in March 2017. At entry, a case report form (CRF) documented demographic data and pre-transplant clinical indicators such as age, sex, primary diagnosis, previous chemotherapy, conditioning regimen, graft source, donor type (matched or mismatched), EBV serology, and antiviral prophylaxis. During follow-up, data were collected prospectively through CRFs for variables related to diagnosed infections and treatment received. HHV DNAemia was diagnosed following confirmed positive testing by polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Table S1 provides details on the EBV and CMV qPCR tests used in each study site. Completed CRFs were sent prospectively to the coordination center at Sainte-Justine Hospital and data were included in the ACCESS database. This study protocol was approved by the research ethics boards of all four participating institutions, with patient consent waived as all data used in this analysis were collected through medical charts.
2.2. Statistical Analysis
Cumulative incidence (and 95% confidence interval (CI)) of EBV and CMV DNAemia were estimated using the Kaplan–Meier method and compared according to the antivirals (acyclovir and famciclovir) using log-rank testing. The curve for EBV DNAemia was stratified according to the pre-transplant EBV serological status of recipients. Follow-up time was considered from date of transplant up to the date of the EBV or CMV DNAemia event or, for censored information, up to 100 days post-transplant. A proportional hazard Cox regression model was used to measure the association between EBV and CMV DNAemia and antiviral use (famciclovir or acyclovir). Adjusted hazard ratio (HR) and 95% CI were estimated. Confounding was empirically controlled using the 5% change in estimate method for the following potential variables: age (continuous), primary diagnosis (malignant or non-malignant), graft source (stem cell peripheral blood/bone marrow or cord blood), conditioning regimen (myeloablative conditioning or other conditioning), sex (female or male), donor match (alternative or matched related donor), recipient pre-transplant EBV serology (negative, positive or unknown), graft donor EBV serostatus (negative, positive or unknown), Graft-versus-host disease (GvHD) (yes or no), and for the use (yes or no) of antithymocyte globulin (ATG), alemtuzumab, tacrolimus (FK506) or cyclosporine A (CsA), methotrexate (MTX), and mycophenolate mofetil (MMF). Multivariate models included the above-mentioned variables that changed the HR by ±5%. All analyses were done using STATA statistical software, version 14.2 (StataCorp, College Station, TX, USA).
3. Results
Table 1 reports the characteristics of the 156 patients included in the TREASuRE study according to the occurrence of post-transplant HHV DNAemia diagnosed during follow-up. Of these, 79 (50.6%) had at least one active HHV episode throughout the follow-up period (up to day 100 post-transplant) including 53 (34%) EBV episodes and 31 (19.9%) CMV episodes. Only a few cases of HSV (n = 3), VZV (n = 1) and HHV-6 (n = 4) were diagnosed. The post-transplant cumulative incidences of HSV, VZV, EBV, CMV, and HHV-6 DNAemia after 100 days of follow-up were, respectively, 2.5% (95% CI 0.8–7.6), 0.9% (95% CI: 0.1–6.1), 34.5% (95% CI: 27.6–42.6), 19.9% (95% CI: 14.5–27.1), and 3.4% (95% CI: 1.2–9.1). The mean age at transplant for all patients included in the analysis was 7.3 years (standard deviation (SD) ± 5.3). There were 117 patients (75%) treated with intravenous acyclovir and 43 patients (27.6%) with famciclovir. No other antiviral was given to recipients except for four patients who received ganciclovir (two who also received acyclovir and two who received famciclovir). Table S2 provides the characteristics of subjects according to antiviral use.

Table 1.
Characteristics of HSCT recipients according to post-transplant HHV DNAemia.
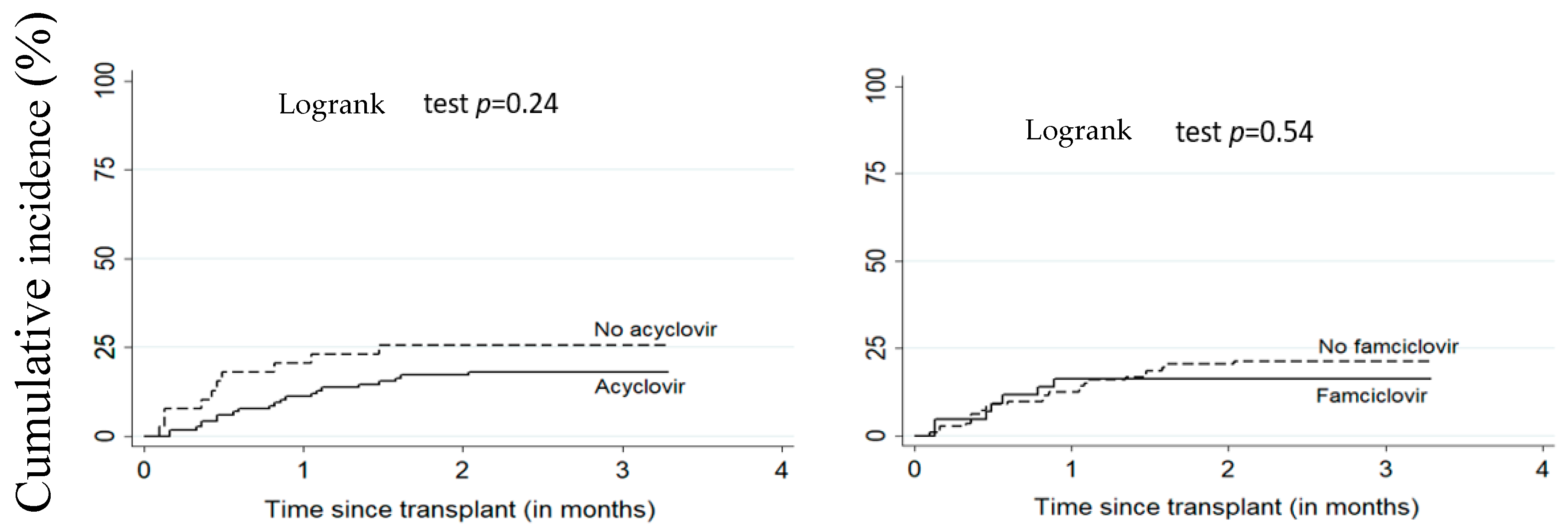
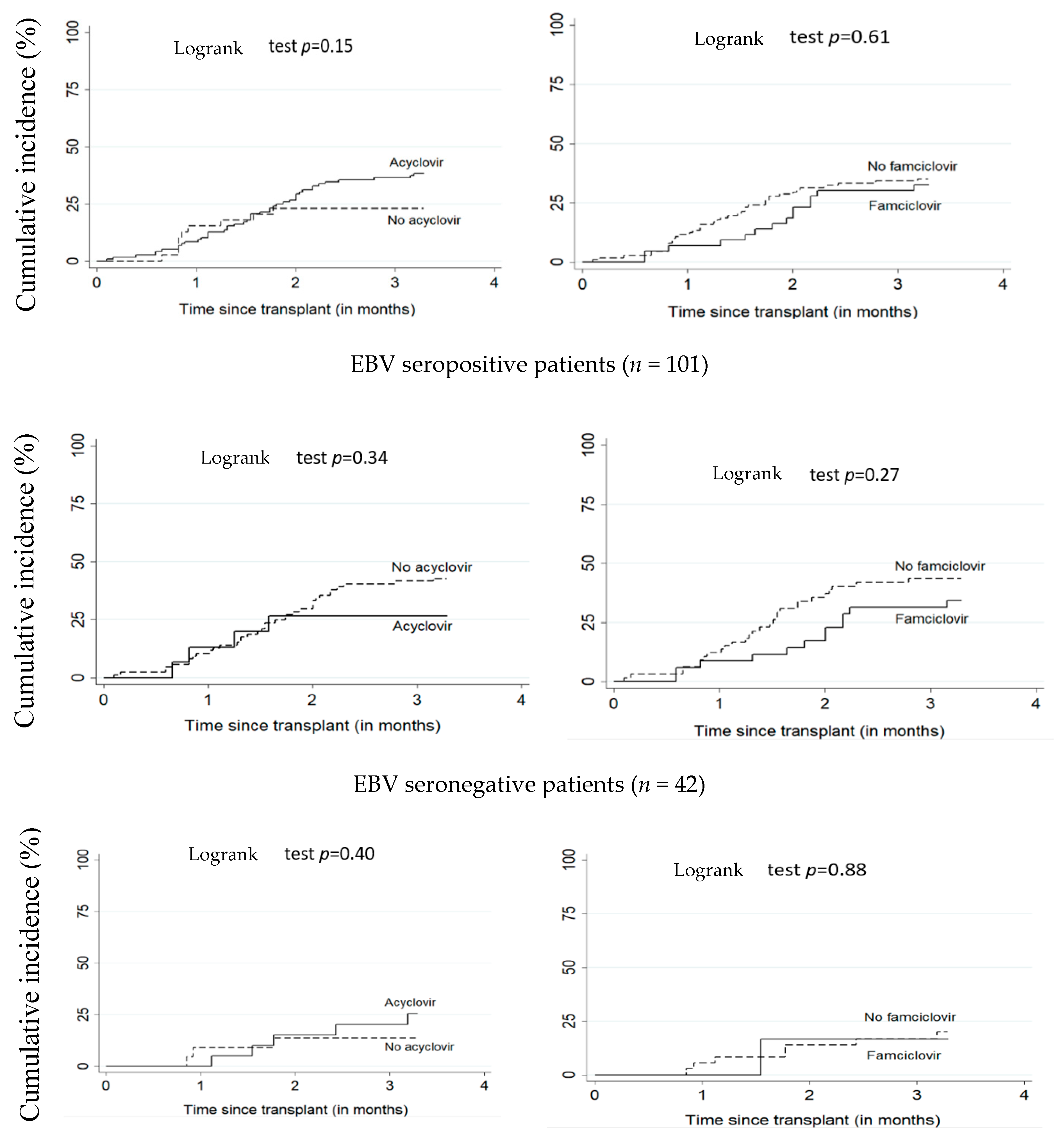
Figure 1 and Figure 2 illustrate the cumulative incidence of CMV and EBV DNAemia in transplant recipients according to antiviral treatment. Table 2 shows the estimates for associations between antivirals (acyclovir or famciclovir) and post-transplant EBV and CMV DNAemia. There was no significant difference between patients on antiviral treatment versus untreated. The adjusted HR for the relationship between acyclovir and EBV and CMV DNAemia were respectively 1.41 (95% CI: 0.63–3.14) and 0.55 (95% CI: 0.24–1.26). For famciclovir, the adjusted HR for EBV and CMV DNAemia were, respectively, 0.80 (95% CI: 0.42–1.51) and 0.82 (95% CI: 0.30–2.29).
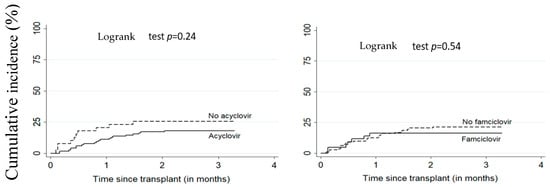
Figure 1.
Cumulative incidence of CMV DNAemia according to acyclovir or famciclovir use. All patients (n = 156), CMV: cytomegalovirus.
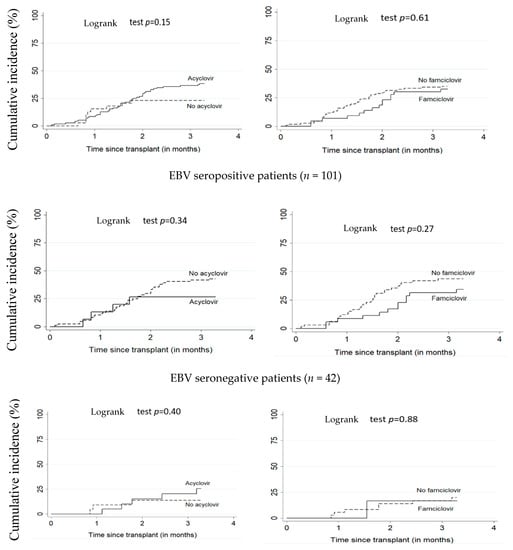
Figure 2.
Cumulative incidence of EBV DNAemia according to acyclovir and famciclovir use. All patients (n = 156). EBV: Epstein–Barr virus.

Table 2.
Hazard ratios for the associations between antiviral prophylaxis (acyclovir or famciclovir) and post-transplant EBV and CMV DNAemia.
4. Discussion
In this study, we found no statistically significant protective effect of acyclovir or famciclovir prophylaxis on EBV and CMV DNAemia incidence in our HSCT pediatric population. Other herpesvirus infections were infrequent with less than 5% cumulative incidence. Only three patients had HSV infection within 100 days post-transplant. The efficacy of acyclovir in the prophylaxis of HSV among seropositive patients has been demonstrated previously [20,25,26].
There was only one case of VZV infection in our cohort of 156 HSCT patients. The efficacy of acyclovir in the prevention of VZV reactivation has also been shown in numerous prior studies [20,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33]. Moreover, universal vaccination against VZV with an attenuated wild strain, recommended since 1999 in all Canadian provinces [34], has also likely reduced wild-type VZV exposure in our cohort.
CMV reactivation is common after allogeneic HSCT [32]. In our cohort, the cumulative incidence of CMV DNAemia at 100 days post-transplant was 19.9% (95% CI: 14.5–27.1), while it ranged from 21.8% to 24% within four months in similar pediatric HSCT studies [6,35,36]. Importantly, in our study, the incidence of CMV DNAemia remained unchanged with the use of acyclovir or famciclovir. This is similar to findings reported by Selby et al. [37], Lundgren et al. [38], Ljungman et al. [39], and Prentice et al. [40] who suggested that acyclovir was ineffective for the prevention of CMV infection. However, some studies have shown that a high dose of acyclovir might have a protective effect against CMV among HSCT recipients. Prentice et al. [41] undertook a randomized study to compare the long-term (one-year) efficacy of acyclovir in three groups: group A (intravenous acyclovir 500 mg/m2 given three times/day from day 3 to day 30, then oral acyclovir 800 mg four times/day from day 31 to 210); group B (intravenous acyclovir 500 mg/m2, three times/day from day 3 to day 30, then placebo from day 31 to day 210); and group C (oral acyclovir 400 mg, four times/day from day 3 to day 30, then placebo from day 31 to day 210). Their survival analysis showed a 360-day post-transplant cumulative incidence of CMV viremia of 54% in group A, 50% in group B and 60% in group C. The difference between group B and group C was statistically significant (p = 0.03). Meyers et al. [42] studied the efficacy of acyclovir in a cohort of CMV seropositive HSCT recipients and showed that acyclovir significantly reduced the probability of CMV infection (0.70% vs. 0.87% p = 0.0001) and CMV disease (22% vs. 38% p = 0.008) after 100 days of follow-up among the group of patients who received intravenous acyclovir 500 mg/m2 every 8 h from day 5 to day 30 post-transplant, in comparison to the group which did not receive acyclovir. Another randomized study by Gluckman et al. [43] on the prophylaxis of herpesviruses with oral acyclovir 200 mg every 6 h from day 8 to day 35 post-transplant reported that oral acyclovir was effective against CMV compared to placebo on day 35 (0% vs. 7% p ˂ 0.007). It appears from these studies that the use of high-dose acyclovir may have a certain effect on CMV. However, despite a possible protective effect noted in some studies, the number of incident cases of CMV remains high in the exposed groups. Indeed, at the dose commonly prescribed as prophylaxis for HSV or VZV seropositive recipients, acyclovir does not appear to influence the incidence of CMV. Our study also showed no potential impact of famciclovir on CMV. The effect of famciclovir on CMV has been examined in only one study among adults [44], which showed that CMV reactivation was higher in seropositive patients who received oral acyclovir or famciclovir (p = 0.0001) compared to those who received oral valacyclovir and ganciclovir.
In our cohort, the 100-day post-transplant cumulative incidence of EBV DNAemia was 34.5% (95% CI: 27.6–42.6). This is similar to the cumulative incidence reported in several studies ranging from 22.6% to 32% in a follow-up period of one to two years among pediatric HSCT recipients [45,46,47]. Our study showed no effect of acyclovir or famciclovir on the incidence of EBV. Hann et al. [48] also found no reduction in the risk of EBV with the use of acyclovir in a randomized study. Similarly, Paula et al. [49], Krzysztof et al. [50], and Zutter et al. [51] showed no effect of acyclovir on EBV incidence. To our knowledge, no study on famciclovir and EBV has been conducted among pediatric HSCT recipients. However, among children with solid organ transplants, a meta-analysis [52] showed no significant effect of famciclovir on EBV (adjusted HR = 0.80 (95% CI: 0.42–1.51)).
These results are consistent with the mechanism of action of acyclovir-based anti-herpesvirus drugs. In their active form, acyclovir and famciclovir are deoxyguanosine analogs that competitively inhibit herpesvirus DNA polymerase causing arrest of lytic-cycle viral DNA replication [53]. These drugs have no effect on latent EBV DNA replication which is dependant on the cellular polymerase, thereby explaining their inefficacy in our study and in other studies referenced above. In the case of CMV, its lack of a specific thymidine kinase [53], which converts these drugs to their active form, would explain the observed lack of effect in clinical trials.
Our study has several strengths and limitations. It is a multicenter study with a good sample size and external validity. Although we cannot rule out a lack of power in our results, our cohort is one of the largest prospective studies on EBV outcomes in pediatric HSCT. However, as with any observational study, residual confounding cannot be excluded, although we attempted to compensate with rigorous and meticulous adjustment. Unmeasured variables such as pre-transplant CMV serostatus may also have led to residual confounding. Furthermore, our study focused on HHV measured by qPCR and did not distinguish between DNAemia and disease. This must be interpreted accordingly. It is also difficult to study the effect of different antiviral doses in an observational cohort study. Exposure to antivirals was analyzed by considering standard doses administered according to clinical guidelines and monitoring in pediatric HSCT programs. While beneficial effects of higher acyclovir and famciclovir doses on EBV and CMV may be possible, future clinical studies should target the effect of other more novel antivirals (such as maribavir) in pediatric populations. Maribavir is still pending approval (with its last phase III study completed in August 2020), but may provide some antiviral effect on EBV and CMV [54]. Letermovir is a new CMV inhibitor that targets the viral terminase complex to disrupt CMV DNA packaging (it was approved by the FDA in November 2017 and by Health Canada in June 2018 for prevention of clinically significant CMV infection in adult recipients of an allogeneic stem cell transplant in cases of contraindication or resistance to other antivirals for prophylaxis against CMV) [55]. Neither of these antivirals are known to impact HSV or VZV, but there are reports of inhibitory activity against EBV and/or CMV [54,55]. However, neither maribavir (still pending approval) nor letermovir (approved for CMV prophylaxis in adults only) was given to patients included in our study. In addition, there are several other potentially more promising avenues (such as cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) therapy) that require further study.
5. Conclusions
Our study suggests a lack of efficacy of antiviral prophylaxis with acyclovir and famciclovir on EBV and CMV DNAemia in a large cohort of pediatric HSCT recipients. Prevention of active herpesvirus infections that can cause severe morbidity in HSCT recipients continues to be crucial to the success of the transplant. Further studies are needed to better delineate the potential impact of several other novel therapies that could have a more significant effect on these viruses.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/vaccines9060610/s1, Table S1: Details of EBV and CMV qPCR tests according to study site, Table S2: Characteristics of hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT) recipients according to acyclovir and famciclovir use.
Author Contributions
All authors have directly contributed to the conception and design (H.T., C.A., C.B., J.L., M.T., M.D., N.R., P.C.S.), or acquisition of data (N.S.D., P.R.E.B., L.L., G.C., S.M.V., V.L.), or analysis and interpretation (N.S.D., P.R.E.B., H.T., C.A., M.D., C.B.) of the study. Finally, N.S.D., H.T., C.A. wrote the first draft of the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
TREASuRE study was supported by a grant from Canadian Blood Services (CBS). HT holds a salary award (Research Scholar) from the Fonds de la recherche du Québec en santé (FRQ-S) and a new Investigator Salary Award from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR). PREB received a doctoral end-of-studies grant from the Faculty of Graduate Studies, Université de Montréal.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the research ethics boards of all four participating institutions with the Ethics committee of CHU Sainte-Justine as having the main responsibility for project oversight (protocol number 2014-534, date of approval: 10 May 2013).
Informed Consent Statement
Patient consent was waived because all data used in this analysis were collected through medical charts.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to privacy/ethical restrictions.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Nicole Poitras, Lucy Clayton, Ferima Sanogo, Caroline Proulx-Clerc, Isabelle Grisoni, Ilona Shemyakina, and Sylvie Lacasse for coordinating the TREASuRE study; to Mary-Ellen French, Djouher Nait Ladjemil, Mariana Dumitrascu, Emilie Roy-Robertson, Gaëlle Cyr, Maria Trinidad Madrid Guillen, Kim Shore, Michelle Dittrick, and Debra Rich for their help in data collection. All authors are also grateful to the transplant team: Marie-France Vachon, Marie St-Jacques, Samira Mezziani, Marion Cortier and all nurses for their help in data collection. The authors are grateful to Héma-Québec and Canadian Blood Services for their help in collecting data on transfusion.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Gratwohl, A.; Brand, R.; Frassoni, F.; Rocha, V.; Niederwieser, D.; Reusser, P.; Einsele, H.; Cordonnier, C. Cause of death after allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) in early leukaemias: An EBMT analysis of lethal infectious complications and changes over calendar time. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2005, 36, 757–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dominietto, A.; Lamparelli, T.; Raiola, A.M.; Van Lint, M.T.; Gualandi, F.; Berisso, G.; Bregante, S.; Di Grazia, C.; Soracco, M.; Pitto, A.; et al. Transplant-related mortality and long-term graft function are significantly influenced by cell dose in patients undergoing allogeneic marrow transplantation. Blood 2002, 100, 3930–3934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frassoni, F.; Labopin, M.; Gluckman, E.; Prentice, H.G.; Vernant, J.P.; Zwaan, F.; Granena, A.; Gahrton, G.; De Witte, T.; Gratwohl, A.; et al. Results of allogeneic bone marrow transplantation for acute leukemia have improved in Europe with time—A report of the acute leukemia working party of the European group for blood and marrow transplantation (EBMT). Bone Marrow Transplant. 1996, 17, 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Eapen, M.; Rubinstein, P.; Zhang, M.J.; Camitta, B.M.; Stevens, C.; Cairo, M.S.; Davies, S.M.; Doyle, J.J.; Kurtzberg, J.; Pulsipher, M.A.; et al. Comparable long-term survival after unrelated and HLA-matched sibling donor hematopoietic stem cell transplantations for acute leukemia in children younger than 18 months. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasserman, R.; August, C.; Plotkin, S. Viral-Infections in Pediatric Bone-Marrow Transplant Patients. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 1988, 7, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olkinuora, H.A.; Taskinen, M.H.; Saarinen-Pihkala, U.M.; Vettenranta, K.K. Multiple viral infections post-hematopoietic stem cell transplantation are linked to the appearance of chronic GVHD among pediatric recipients of allogeneic grafts. Pediatr. Transplant. 2010, 14, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyers, J. Infection in Bone-Marrow Transplant Recipients. Am. J. Med. 1986, 81, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, W.; Flynn, P.; Mccullough, J.; Balfour, H.; Goldman, A.; Haake, R.; McGlave, P.; Ramsay, N.; Kersey, J. Cytomegalovirus-Infection After Bone-Marrow Transplantation—An Association with Acute Graft-V-Host Disease. Blood 1986, 67, 1162–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochs, L.; Shu, X.; Miller, J.; Enright, H.; Wagner, J.; Filipovich, A.; Miller, W.; Weisdorf, D. Late Infections After Allogeneic Bone-Marrow Transplantation—Comparison of Incidence in Related and Unrelated Donor Transplant Recipients. Blood 1995, 86, 3979–3986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tutschka, P. Infections and Immunodeficiency in Bone-Marrow Transplantation. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 1988, 7, S22–S29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiley, K.; Blumberg, E. Herpes viruses in transplant recipients: HSV, VZV, human herpes viruses, and EBV. Infect. Dis Clin. N. Am. 2010, 24, 373–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rieger, C.T.; Rieger, H.; Kolb, H.J.; Peterson, L.; Huppmann, S.; Fiegl, M.; Ostermann, H. Infectious complications after allogeneic stem cell transplantation: Incidence in matched-related and matched-unrelated transplant settings. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2009, 11, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Björklund, A.; Aschan, J.; Labopin, M.; Remberger, M.; Ringdén, O.; Winiarski, J.; Ljungman, P. Risk factors for fatal infectious complications developing late after allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2007, 40, 1055–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welniak, L.A.; Blazar, B.R.; Murphy, W.J. Immunobiology of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 25, 139–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenzwajg, M.; Fery, N.; Bons, V.; Damaj, G.; Gluckman, E.; Gluckman, J. Human herpes virus 8 (HHV8) serology in allogeneic bone marrow transplant recipients. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1999, 24, 351–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sala, I.; Faraci, M.; Magnano, G.M.; Sementa, A.; di Marco, E.; Garaventa, A.; Micalizzi, C.; Lanino, E.; Morreale, G.; Moroni, C.; et al. HHV-8-related visceral Kaposi’s sarcoma following allogeneic HSCT: Report of a pediatric case and literature review. Pediatr. Transplant. 2011, 15, E8–E11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verdeguer, A.; de Heredia, C.D.; González, M.; Martínez, A.M.; Fernández-Navarro, J.M.; Pérez-Hurtado, J.M.; Badell, I.; Gómez, P.; González, M.E.; Muñoz, A.; et al. Observational prospective study of viral infections in children undergoing allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation: A 3-year GETMON experience. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2011, 46, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Styczynski, J.; Reusser, P.; Einsele, H.; de la Camara, R.; Cordonnier, C.; Ward, K.N.; Ljungman, P.; Engelhard, D. Management of HSV, VZV and EBV infections in patients with hematological malignancies and after SCT: Guidelines from the Second European Conference on Infections in Leukemia. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2009, 43, 757–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; Infectious Disease Society of America; American Society of Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Guidelines for preventing opportunistic infections among hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients. MMWR Recomm. Rep. 2000, 49, 1–125. [Google Scholar]
- Lewalle, P.; Pochon, C.; Michallet, M.; Turlure, P.; Brissot, E.; Paillard, C.; Puyade, M.; Roth-Guepin, G.; Yakoub-Agha, I.; Chantepie, S. Prophylaxis of infections post-allogeneic transplantation: Guidelines from the Francophone Society of Bone Marrow Transplantation and Cellular Therapy (SFGM-TC). Bull. Cancer 2019, 106 (Suppl. 1), S23–S34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, K.; Wada, H.; Yamasaki, R.; Ishihara, Y.; Sakamoto, K.; Ashizawa, M.; Sato, M.; Machishima, T.; Terasako, K.; Kimura, S.I.; et al. Low-dose acyclovir prophylaxis for the prevention of herpes simplex virus disease after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2013, 15, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, K.M.; Dykewicz, C.A.; Longworth, D.; Boeckh, M.; Baden, L.R.; Rubin, R.H.; Sepkowitz, K.A. Preventing Opportunistic Infections After Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Infectious Diseases Society of America, and American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation Practice Guidelines and Beyond. Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program. 2001, 2001, 392–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullmann, A.J.; Schmidt-Hieber, M.; Bertz, H.; Heinz, W.J.; Kiehl, M.; Krüger, W.; Mousset, S.; Neuburger, S.; Neumann, S.; Penack, O.; et al. Infectious diseases in allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplantation: Prevention and prophylaxis strategy guidelines 2016. Ann. Hematol. 2016, 95, 1435–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enok Bonong, P.R.; Buteau, C.; Delage, G.; Tanner, J.E.; Lacroix, J.; Duval, M.; Laporte, L.; Tucci, M.; Robitaille, N.; Spinella, P.C.; et al. Transfusion-related Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection: A multicenter prospective cohort study among pediatric recipients of hematopoietic stem cell transplants (TREASuRE study). Transfusion 2021, 61, 144–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanda, Y.; Mineishi, S.; Saito, T.; Saito, A.; Yamada, S.; Ohnishi, M.; Chizuka, A.; Niiya, H.; Suenaga, K.; Nakai, K.; et al. Long-term low-dose acyclovir against varicella-zoster virus reactivation after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2001, 28, 689–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boeckh, M.; Kim, H.W.; Flowers, M.E.D.; Meyers, J.D.; Bowden, R.A. Long-term acyclovir for prevention of varicella zoster virus disease after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation—a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled study. Blood 2006, 107, 1800–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steer, C.B.; Szer, J.; Sasadeusz, J.; Matthews, J.P.; Beresford, J.A.; Grigg, A. Varicella-zoster infection after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation: Incidence, risk factors and prevention with low-dose aciclovir and ganciclovir. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2000, 25, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erard, V.; Wald, A.; Corey, L.; Leisenring, W.M.; Boeckh, M. Use of long-term suppressive acyclovir after hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation: Impact on herpes simplex virus (HSV) disease and drug-resistant HSV disease. J. Infect. Dis. 2007, 196, 266–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asano-Mori, Y.; Kanda, Y.; Oshima, K.; Kako, S.; Shinohara, A.; Nakasone, H.; Sato, H.; Watanabe, T.; Hosoya, N.; Izutsu, K.; et al. Long-term ultra-low-dose acyclovir against varicella-zoster virus reactivation after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Am. J. Hematol. 2008, 83, 472–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, A.; Miller, K.B.; Sprague, K.; DesJardin, J.A.; Snydman, D.R. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of valacyclovir prophylaxis to prevent zoster recurrence from months 4 to 24 after BMT. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2011, 46, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pai, V.B.; Davis, D.I.; Clayton, J.; Pietryga, D.W. Efficacy of Low-Dose Acyclovir Prophylaxis Against Varicella Zoster Virus in Pediatric Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation Patients. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2013, 19 (Suppl. 2), S378–S380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jamani, K.; MacDonald, J.; Lavoie, M.; Williamson, T.S.; Brown, C.B.; Chaudhry, A.; Jimenez-Zepeda, V.H.; Duggan, P.; Tay, J.; Stewart, D.; et al. Zoster prophylaxis after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation using acyclovir/valacyclovir followed by vaccination. Blood Adv. 2016, 1, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.H.; Kumar, D.; Messner, H.A.; Minden, M.; Gupta, V.; Kuruvilla, J.; Chae, Y.S.; Sohn, S.K.; Lipton, J.H. Clinical efficacy of prophylactic strategy of long-term low-dose acyclovir for Varicella-Zoster virus infection after allogeneic peripheral blood stem cell transplantation. Clin. Transplant. 2008, 22, 770–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, B.; Bettinger, J.; McConnell, A.; Scheifele, D.; Halperin, S.; Vaudry, W.; Law, B. The Effect of Funded Varicella Immunization Programs on Varicella-related Hospitalizations in IMPACT Centers, Canada, 2000–2008. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2012, 31, 956–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haastrup, E.; Müller, K.; Baekgaard, H.; Heilmann, C. Cytomegalovirus infection after allogeneic stem cell transplant in children. Pediatr. Transplant. 2005, 9, 734–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, H.S.; Lee, J.H.; Choi, E.S.; Seo, J.J.; Moon, H.N.; Kim, M.-N.; Im, H.J. Cytomegalovirus infection in children who underwent hematopoietic stem cell transplantation at a single center: A retrospective study of the risk factors. Pediatr. Transplant. 2009, 13, 898–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selby, P.J.; Powles, R.L.; Easton, D.; Perren, T.J.; Stolle, K.; Jameson, B.; Fiddian, A.P.; Tryhorn, Y.; Stern, H. The prophylactic role of intravenous and long-term oral acyclovir after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Br. J. Cancer 1989, 59, 434–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundgren, G.; Wilczek, H.; Lönnqvist, B.; Lindholm, A.; Wahren, B.; Ringdén, O. Acyclovir prophylaxis in bone marrow transplant recipients. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. Suppl. 1985, 47, 137–144. [Google Scholar]
- Ljungman, P.; Wilczek, H.; Gahrton, G.; Gustavsson, A.; Lundgren, G.; Lonnqvist, B.; Ringdén, O.; Wahren, B. Long-term acyclovir prophylaxis in bone marrow transplant recipients and lymphocyte proliferation responses to herpes virus antigens in vitro. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1986, 1, 185–192. [Google Scholar]
- Prentice, H.G. Use of acyclovir for prophylaxis of herpes infections in severely immunocompromised patients. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 1983, 12 (Suppl. B), 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prentice, H.G.; Gluckman, E.; Powles, R.; Ljungman, P.; Milpied, N.J.; Fernandez-Rañada, J.M.; Mandelli, F.; Kho, P. Impact of long-term acyclovir on cytomegalovirus infection and survival after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Lancet 1994, 343, 749–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyers, J.D.; Reed, E.C.; Shepp, D.H.; Thornquist, M.; Dandliker, P.S.; Vicary, C.A.; Flournoy, N.; Kirk, L.E.; Kersey, J.H.; Thomas, E.D.; et al. Acyclovir for Prevention of Cytomegalovirus Infection and Disease after Allogeneic Marrow Transplantation. N. Engl. J. Med. 1988, 318, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gluckman, E.; Lotsberg, J.; Devergie, A.; Zhao, X.M.; Melo, R.; Gomez-Morales, M.; Nebout, T.; Mazeron, M.C.; Perol, Y. Prophylaxis of herpes infections after bone-marrow transplantation by oral acyclovir. Lancet 1983, 2, 706–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graef, T.; Bobrikova, T.; Adams, O.; Fenk, R.; Ruf, L.; Zohren, F.; Gattermann, N.; Haas, R.; Kobbe, G. Prognostic Factors for CMV Reactivation/Infection after Stem Cell Transplantation and Value of Oral Valganciclovir for Preemptive Therapy. Blood 2005, 106, 5369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordon, V.; Padalko, E.; Benoit, Y.; Dhooge, C.; Laureys, G. Incidence, kinetics, and risk factors of Epstein–Barr virus viremia in pediatric patients after allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Pediatr. Transplant. 2012, 16, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Düver, F.; Weißbrich, B.; Eyrich, M.; Wölfl, M.; Schlegel, P.G.; Wiegering, V. Viral reactivations following hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in pediatric patients—A single center 11-year analysis. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0228451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoumakas, K.; Giamaiou, K.; Goussetis, E.; Graphakos, S.; Kossyvakis, A.; Horefti, E.; Mentis, A.; Elefsiniotis, I.; Pavlopoulou, I.D. Epidemiology of viral infections among children undergoing hematopoietic stem cell transplant: A prospective single-center study. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2019, 21, e13095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hann, I.M.; Prentice, H.G.; Blacklock, H.A.; Ross, M.G.; Brigden, D.; Rosling, A.E.; Burke, C.; Crawford, D.H.; Brumfitt, W.; Hoffbrand, A.V. Acyclovir prophylaxis against herpes virus infections in severely immunocompromised patients: Randomised double blind trial. Br. Med. J. Clin. Res. Ed. 1983, 287, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalán, P.; Alba, A. Prophylaxis against Epstein Barr disease in pediatric and adult patients undergoing solid organ and hematopoietic stem cells transplantation. Rev. Chil. Infectol. 2012, 29 (Suppl. 1), S29–S31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czyzewski, K.; Dziedzic, M.; Salamonowicz, M.; Fraczkiewicz, J.; Zajac-Spychala, O.; Zaucha-Prazmo, A.; Gozdzik, J.; Galazka, P.; Bartoszewicz, N.; Demidowicz, E.; et al. Epidemiology, Outcome and Risk Factors Analysis of Viral Infections in Children and Adolescents Undergoing Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation: Antiviral Drugs Do Not Prevent Epstein–Barr Virus Reactivation. Infect. Drug Resist. 2019, 12, 3893–3902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zutter, M.M.; Martin, P.J.; Sale, G.E.; Shulman, H.M.; Fisher, L.; Thomas, E.D.; Durnam, D.M. Epstein-Barr virus lymphoproliferation after bone marrow transplantation. Blood 1988, 72, 520–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AlDabbagh, M.A.; Gitman, M.R.; Kumar, D.; Humar, A.; Rotstein, C.; Husain, S. The Role of Antiviral Prophylaxis for the Prevention of Epstein–Barr Virus–Associated Posttransplant Lymphoproliferative Disease in Solid Organ Transplant Recipients: A Systematic Review. Am. J. Transplant. 2017, 17, 770–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paintsil, E.; Cheng, Y.C. Antiviral Agents, Encyclopedia of Microbiology, 4th ed.; Schmidt, T.M., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 176–225. [Google Scholar]
- Pagano, J.S.; Whitehurst, C.B.; Andrei, G. Antiviral Drugs for EBV. Cancers 2018, 10, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marty, F.M.; Ljungman, P.; Chemaly, R.F.; Maertens, J.; Dadwal, S.S.; Duarte, R.F.; Haider, S.; Ullmann, A.J.; Katayama, Y.; Brown, J.; et al. Letermovir Prophylaxis for Cytomegalovirus in Hematopoietic-Cell Transplantation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 2433–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).