Clinical Epidemiology of Systolic and Diastolic Orthostatic Hypotension in Patients on Peritoneal Dialysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
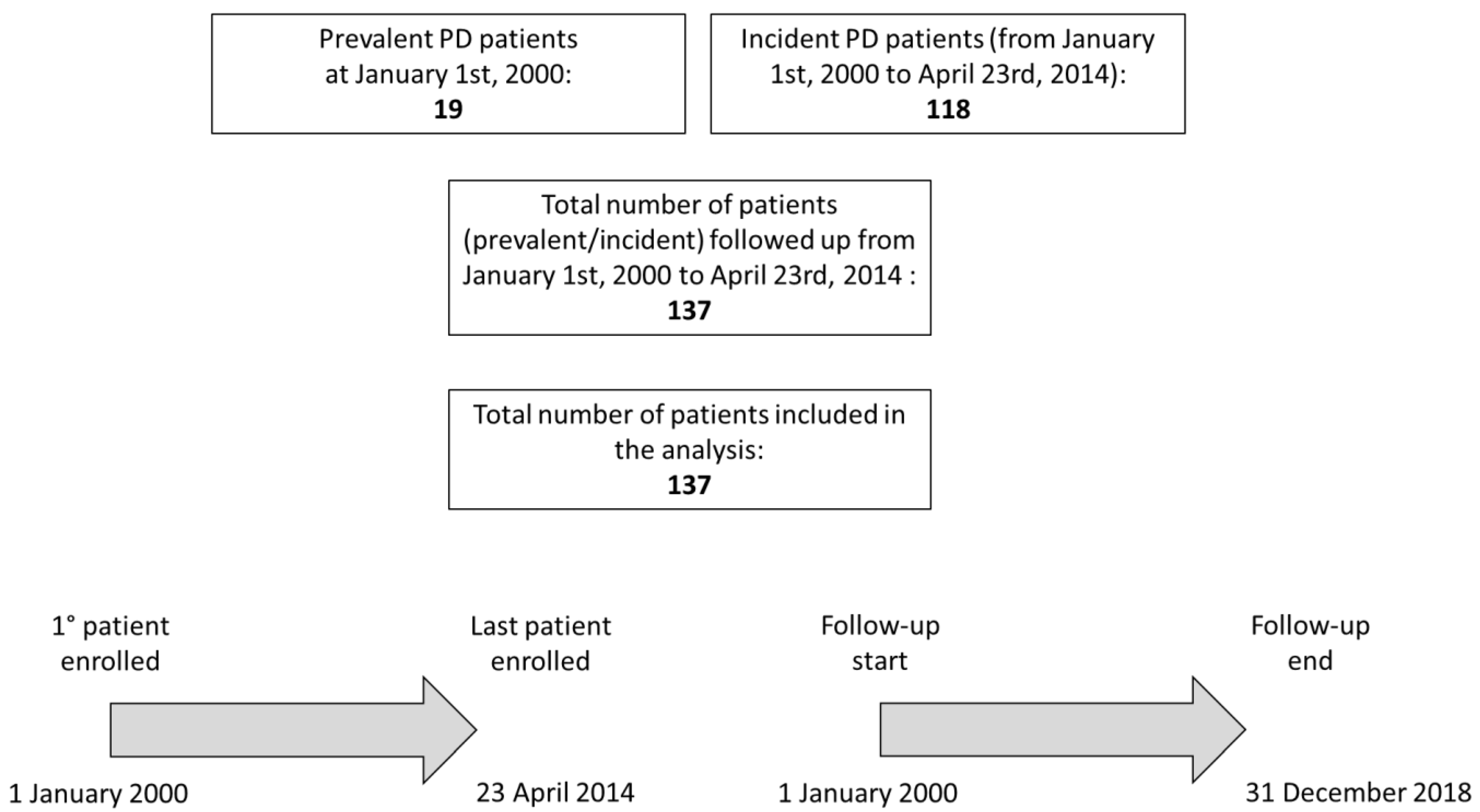
2.1. Study Population
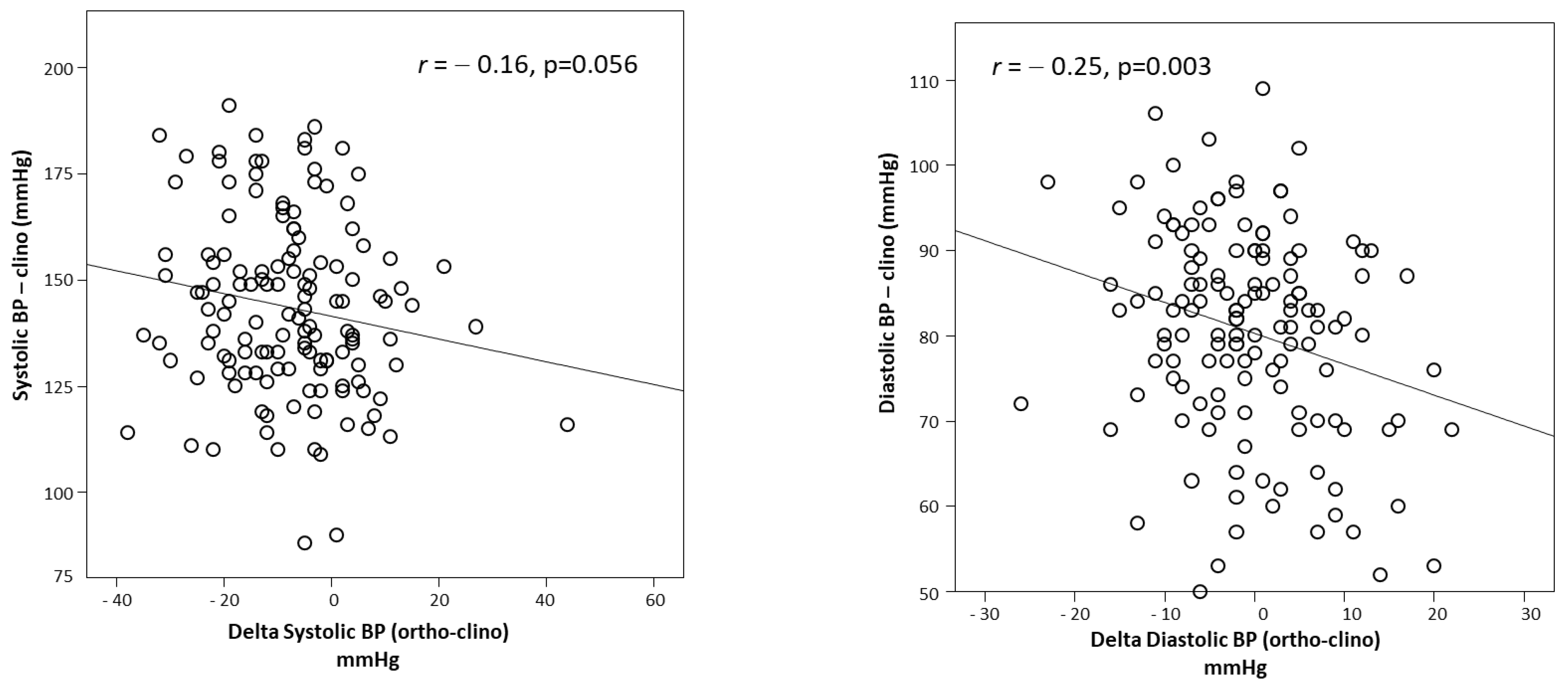
2.2. Measurement of the Response to Orthostasis
2.3. Laboratory Measurements
2.4. Study End-Points
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
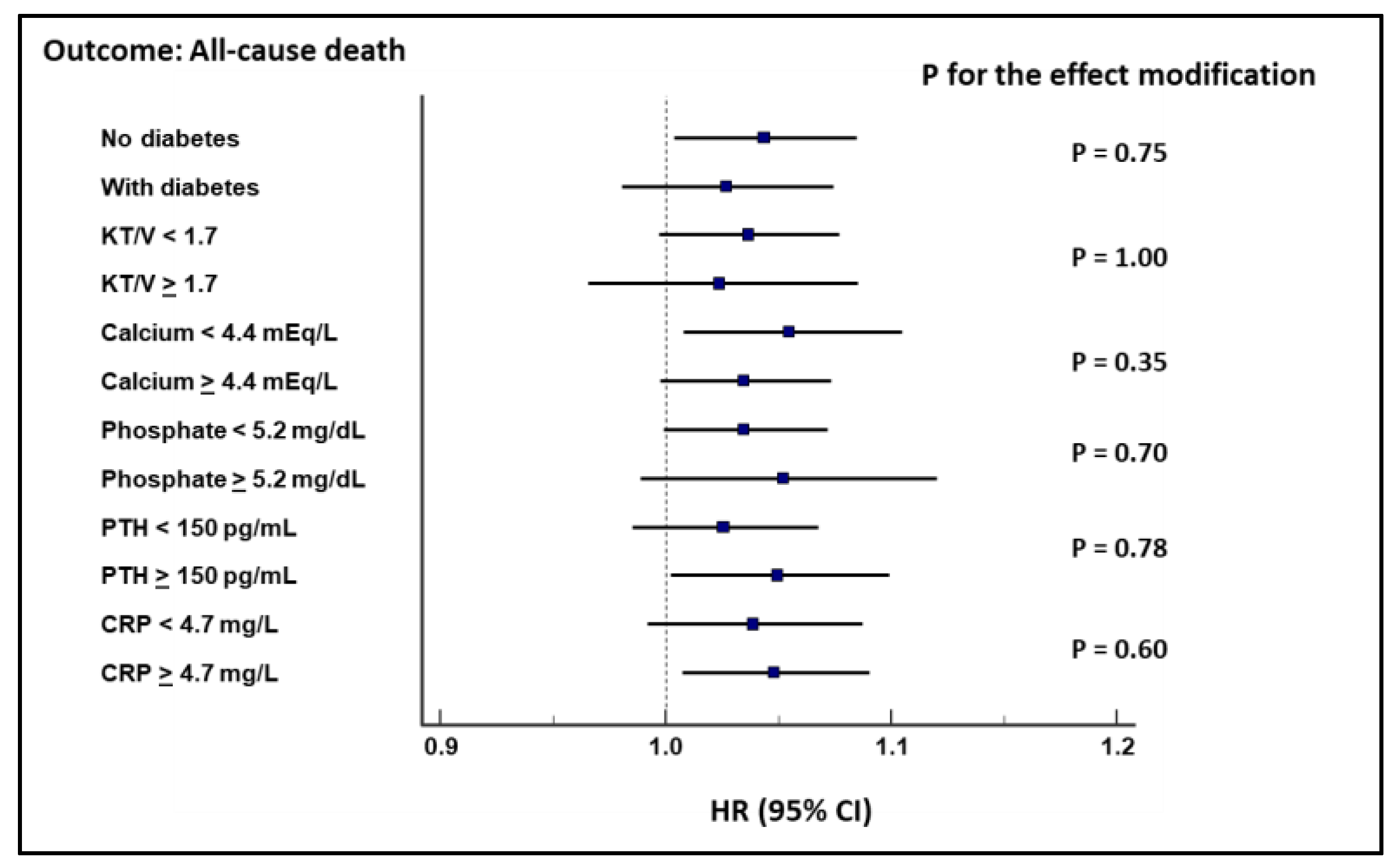
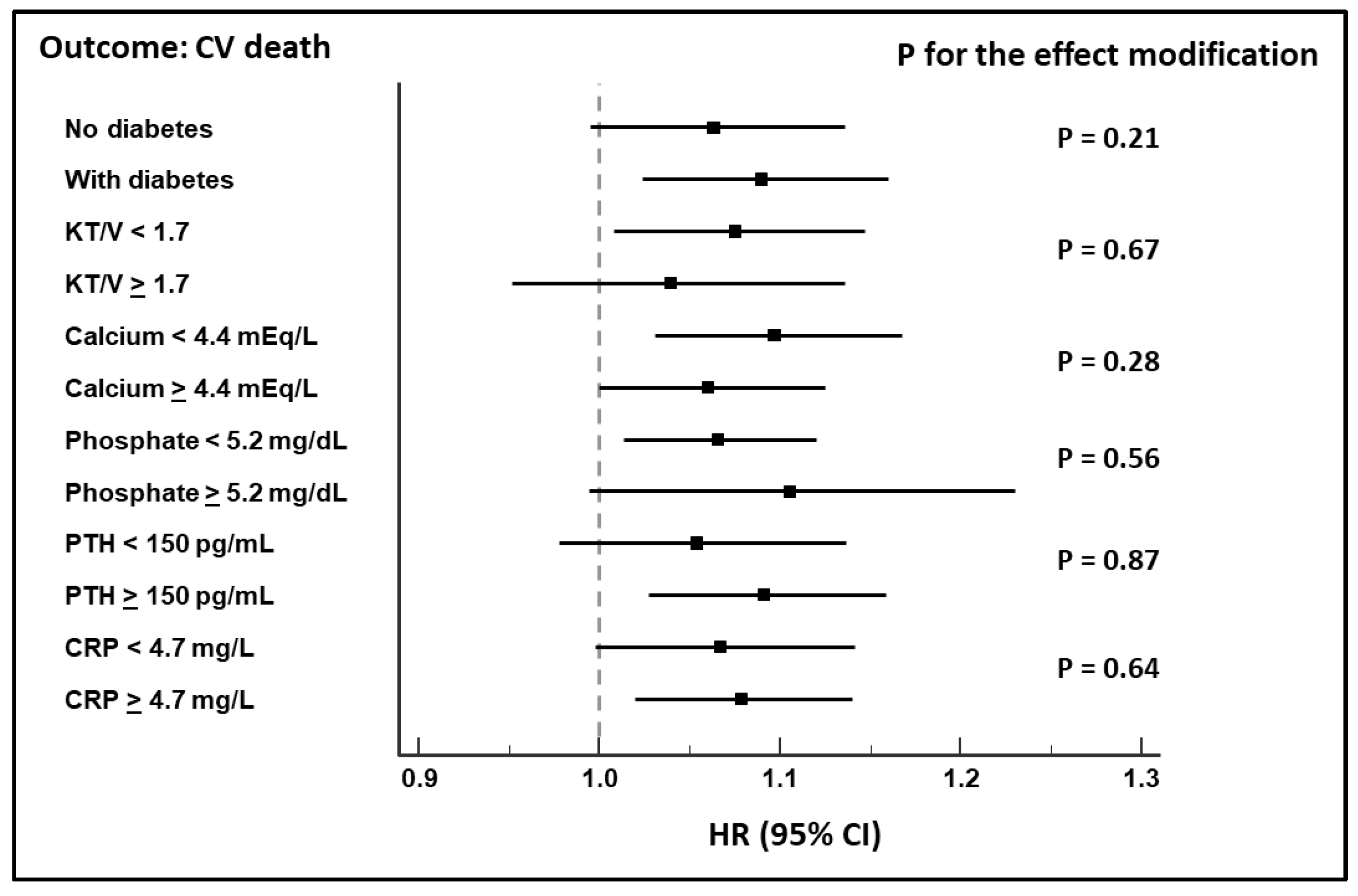
Survival Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sandeep, C.; Baby, C.; Jacob, J.J. Neuro-endocrine regulation of blood pressure. Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 15, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanutto, B.S.; Valentinuzzi, M.E.; Segura, E.T. Neural set point for the control of arterial pressure: Role of the nucleus tractus solitarius. Biomed. Eng. Online 2010, 9, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dampney, R.A.L.; Coleman, M.J.; Fontes, M.A.P.; Hirooka, Y.; Horiuchi, J.; Li, Y.W.; Polson, J.W.; Potts, P.D.; Tagawa, T. Central mechanisms underlying short- and long-term regulation of the cardiovascular system. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2002, 29, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jänig, W.; McLachlan, E.M. Specialized functional pathways are the building blocks of the autonomic nervous system. J. Auton. Nerv. Syst. 1992, 41, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, H. Basic Medical Endocrinology, 3rd ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, K.P.; Zhang, R. Neurohumoral activation in heart failure: Role of paraventricular nucleus. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 1996, 23, 722–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, J.M.; Plowey, E.D.; Beatty, J.A.; Little, H.R.; Waldrop, T.G. Hypothalamus, hypertension, and exercise. Brain Res. Bull. 2000, 53, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadei, H.M.; Textor, S.C. The role of the kidney in regulating arterial blood pressure. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2012, 8, 602–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhaleb, N.E.; Yang, X.P.; Carretero, O.A. The Kallikrein-Kinin system as a regulator of cardiovascular and renal function. Compr. Physiol. 2011, 1, 971–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, W.O.; Thompson, P.K.; Dailey, M.E. The Effect of Posture upon the Composition and Volume of the Blood in Man. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1928, 14, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, S.; Bagordo, D.; Perrotta, A.M.; Gigante, A.; Gasperini, M.L.; Muscaritoli, M.; Mazzaferro, S.; Cianci, R. Autonomic dysfunction in kidney diseases. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 8458–8468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, S.; Winney, R.J.; Ewing, D.J. Chronic renal failure and cardiovascular autonomic function. Nephron 1986, 43, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daugirdas, J.T. Dialysis hypotension: A hemodynamic analysis. Kidney Int. 1991, 39, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoccali, C. Traditional and emerging cardiovascular and renal risk factors: An epidemiologic perspective. Kidney Int. 2006, 70, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wabel, P.; Moissl, U.; Chamney, P.; Jirka, T.; Machek, P.; Ponce, P.; Taborsky, P.; Tetta, C.; Velasco, N.; Vlasak, J.; et al. Towards improved cardiovascular management: The necessity of combining blood pressure and fluid overload. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2008, 23, 2965–2971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecking, M.; Moissl, U.; Genser, B.; Rayner, H.; Dasgupta, I.; Stuard, S.; Stopper, A.; Chazot, C.; Maddux, F.W.; Canaud, B.; et al. Greater fluid overload and lower interdialytic weight gain are independently associated with mortality in a large international hemodialysis population. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2018, 33, 1832–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, M.; Lake, C.; Kopin, I. The defect in primary orthostatic hypotension. N. Engl. J. Med. 1977, 296, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ensrud, K.; Nevitt, M.; Yunis, C.; Hulley, S.; Grimm, R.; Cumming, S. Postural Hypotension and Postural Dizziness in Elderly Women. The Study of Osteoporotic Fractures. The Study of Osteoporotic Fractures Research Group—PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1580709/ (accessed on 13 April 2021).
- Rose, K.M.; Tyroler, H.A.; Nardo, C.J.; Arnett, D.K.; Light, K.C.; Rosamond, W.; Sharrett, A.R.; Szklo, M. Orthostatic hypotension and the incidence of coronary heart disease: The atherosclerosis risk in communities study. Am. J. Hypertens. 2000, 13, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedorowski, A.; Stavenow, L.; Hedblad, B.; Berglund, G.; Nilsson, P.M.; Melander, O. Orthostatic hypotension predicts all-cause mortality and coronary events in middle-aged individuals (The Malmö Preventive Project). Eur. Heart J. 2010, 31, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedorowski, A.; Hedblad, B.; Engström, G.; Gustav Smith, J.; Melander, O. Orthostatic hypotension and long-term incidence of atrial fibrillation: The malmö preventive project: Original Article. J. Intern. Med. 2010, 268, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, S.K.; Alonso, A.; Whelton, S.P.; Soliman, E.Z.; Rose, K.M.; Chamberlain, A.M.; Simpson, R.J.; Coresh, J.; Heiss, G. Orthostatic change in blood pressure and incidence of atrial fibrillation: Results from a bi-ethnic population based study. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, W.; Lin, Z.; Li, X. Orthostatic Hypotension and the Risk of Congestive Heart Failure: A Meta-Analysis of Prospective Cohort Studies. PLoS ONE 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedorowski, A.; Engström, G.; Hedblad, B.; Melander, O. Orthostatic hypotension predicts incidence of heart failure: The malmö preventive project. Am. J. Hypertens. 2010, 23, 1209–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eigenbrodt, M.L.; Rose, K.M.; Couper, D.J.; Arnett, D.K.; Smith, R.; Jones, D. Orthostatic hypotension as a risk factor for stroke: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study, 1987–1996. Stroke 2000, 31, 2307–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelousi, A.; Girerd, N.; Benetos, A.; Frimat, L.; Gautier, S.; Weryha, G.; Boivin, J.M. Association between orthostatic hypotension and cardiovascular risk, cerebrovascular risk, cognitive decline and falls as well as overall mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Hypertens. 2014, 32, 1562–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, W.; Lin, Z.; Mi, S. Orthostatic hypotension and mortality risk: A meta-analysis of cohort studies. Heart 2014, 100, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoji, T.; Tsubakihara, Y.; Fujii, M.; Imai, E. Hemodialysis-associated hypotension as an independent risk factor for two-year mortality in hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int. 2004, 66, 1212–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, B.; Mancia, G.; Spiering, W.; Rosei, E.A.; Azizi, M.; Burnier, M.; Clement, D.L.; Coca, A.; De Simone, G.; Dominiczak, A.; et al. 2018 ESC/ESH Guidelines for themanagement of arterial hypertension. Eur. Heart J. 2018, 39, 3021–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrell, F.; Lee, K.; Mark, D. Tutorial in Biostatistics: Multivariable prognostic models: Issues in developing models, evaluating assumptions and adequacy, and measuring and reducing errors. Stat. Med. 1996, 15, 361–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingall, T.J.; McLeod, J.G.; O’Brien, P.C. The effect of ageing on autonomic nervous system function. Aust. N. Z. J. Med. 1990, 20, 570–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jassal, S.V.; Douglas, J.F.; Stout, R.W. Prevalence of central autonomic neuropathy in elderly dialysis patients. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 1998, 13, 1702–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinik, A.I.; Maser, R.E.; Mitchell, B.D.; Freeman, R. Diabetic autonomic neuropathy. Diabetes Care 2003, 26, 1553–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, P.A. Prevalence of orthostatic hypotension. Clin. Auton. Res. 2008, 18, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, R.; Wieling, W.; Axelrod, F.B.; Benditt, D.G.; Benarroch, E.; Biaggioni, I.; Cheshire, W.P.; Chelimsky, T.; Cortelli, P.; Gibbons, C.H.; et al. Consensus statement on the definition of orthostatic hypotension, neurally mediated syncope and the postural tachycardia syndrome. Clin. Auton. Res. 2011, 21, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valbusa, F.; Labat, C.; Salvi, P.; Vivian, M.E.; Hanon, O.; Benetos, A. Orthostatic hypotension in very old individuals living in nursing homes: The PARTAGE study. J. Hypertens. 2012, 30, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhat, S.; Hegde, S.; Szpunar, S. Orthostatic Blood Pressure (BP) Variance in a Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Clinic. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2013, 15, 72. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.S.; Wu, N.H.; Lu, F.H.; Chang, C.J. Factors associated with orthostatic hypotension in the Chinese population in Taiwan. Am. J. Hypertens. 1996, 9, 999–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fleg, J.L.; Evans, G.W.; Margolis, K.L.; Barzilay, J.; Basile, J.N.; Bigger, J.T.; Cutler, J.A.; Grimm, R.; Pedley, C.; Peterson, K.; et al. Orthostatic Hypotension in the ACCORD (Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes) Blood Pressure Trial: Prevalence, Incidence, and Prognostic Significance. Hypertension 2016, 68, 888–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dey, A.; Kenny, R. Orthostatic hypotension in the elderly: Aetiology, manifestations andmanagement. J. Ir. Coll. Physicians Surg. 1998, 27, 182–187. [Google Scholar]
- Franceschini, N.; Rose, K.M.; Astor, B.C.; Couper, D.; Vupputuri, S. Orthostatic hypotension and incident chronic kidney disease: The atherosclerosis risk in communities study. Hypertension 2010, 56, 1054–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, O.; Nakahama, H.; Nakamura, S.; Yoshihara, F.; Inenaga, T.; Yoshii, M.; Kohno, S.; Kawano, Y. Orthostatic hypotension at the introductory phase of haemodialysis predicts all-cause mortality. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2005, 20, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Musso, G.; Gambino, R.; Tabibian, J.H.; Ekstedt, M.; Kechagias, S.; Hamaguchi, M.; Hultcrantz, R.; Hagström, H.; Yoon, S.K.; Charatcharoenwitthaya, P.; et al. Association of Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. PLoS Med. 2014, 11, e1001680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juraschek, S.P.; Daya, N.; Appel, L.J.; Miller, E.R.; McEvoy, J.W.; Matsushita, K.; Ballantyne, C.M.; Selvin, E. Orthostatic hypotension and risk of clinical and subclinical cardiovascular disease in middle-aged adults. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2018, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Wang, S.; Wan, S.; Zhou, Y.; Pan, P.; Wen, B.; Zhang, X.; Liao, H.; Shi, D.; Shi, R.; et al. Arterial Stiffness, Central Pulsatile Hemodynamic Load, and Orthostatic Hypotension. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2016, 18, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirkham, F.A.; Rankin, P.; Parekh, N.; Holt, S.G.; Rajkumar, C. Aortic stiffness and central systolic pressure are associated with ambulatory orthostatic BP fall in chronic kidney disease. J. Nephrol. 2020, 33, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enia, G.; Mallamaci, F.; Benedetto, F.A.; Panuccio, V.; Parlongo, S.; Cutrupi, S.; Giacone, G.; Cottini, E.; Tripepi, G.; Malatino, L.S.; et al. Long-term CAPD patients are volume expanded and display more severe left ventricular hypertrophy than haemodialysis patients. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2001, 16, 1459–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schurig, R.; Gahl, G.M.; Becker, H.; Schiller, R.; Kesel, M.; Paeprer, H. Hemodynamic Studies in Long-Term Peritoneal Dialysis Patients. Artif. Organs 1979, 3, 215–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutan, G.H.; Hermanson, B.; Bild, D.E.; Kittner, S.J.; LaBaw, F.; Tell, G.S. Orthostatic hypotension in older adults. The Cardiovascular Health Study. CHS Collaborative Research Group. Hypertension 1992, 19, 508–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, A.K.; Chang, T.I.; Cushman, W.C.; Furth, S.L.; Hou, F.F.; Ix, J.H.; Knoll, G.A.; Muntner, P.; Pecoits-Filho, R.; Sarnak, M.J.; et al. KDIGO 2021 Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Blood Pressure in Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Int. 2021, 99, S1–S87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fagard, R.H.; De Cort, P. Orthostatic hypotension is a more robust predictor of cardiovascular events than nighttime reverse dipping in elderly. Hypertension 2010, 56, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieling, W.; van Dijk, N.; Thijs, R.D.; de Lange, F.J.; Krediet, C.T.P.; Halliwill, J.R. Physical countermeasures to increase orthostatic tolerance. J. Intern. Med. 2015, 277, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| With OH (n = 34) | Without OH (n = 103) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 66 ± 12 | 65 ± 14 | 0.57 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 27 ± 4 | 27 ± 4 | 0.48 |
| Male sex N (%) | 25 (74) | 62 (60) | 0.16 |
| Diabetics N (%) | 15 (44) | 39 (38) | 0.29 |
| With cardiovascular comorbidities | 17 (50) | 44 (43) | 0.46 |
| KT/V | 1.7 ± 0.3 | 1.8 ± 0.4 | 0.06 |
| On antihypertensive treatment N (%) | 32 (94) | 93 (90) | 0.49 |
| Systolic BP clino (mmHg) | 147 ± 20 | 143 ± 21 | 0.27 |
| Diastolic BP clino (mmHg) | 82 ± 12 | 80 ± 12 | 0.45 |
| Systolic BP ortho (mmHg) | 126 ± 23 | 139 ± 21 | 0.004 |
| Diastolic BP ortho (mmHg) | 74 ± 13 | 82 ± 12 | 0.002 |
| Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 176 ± 46 | 182 ± 45 | 0.49 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 11.4 ± 2.0 | 11.5 ± 1.4 | 0.65 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 3.6 ± 0.6 | 3.6 ± 0.4 | 0.99 |
| CRP (mg/L) | 4.3 (3.1–16.3) | 5.0 (3.3–12.1) | 0.60 |
| Calcium (mEq/L) | 4.4 ± 0.6 | 4.4 ± 0.5 | 0.96 |
| Phosphate (mmol/L) | 5.3 ± 1.3 | 5.4 ± 1.8 | 0.79 |
| PTHi (pg/mL) | 210 (47–321) | 146 (57–247) | 0.85 |
| All-Cause Death | CV Death | CV Death (after Shrinkage) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Changes in SBP (1 mmHg) * | 1.01 (0.99–1.03), p = 0.35 | 1.01 (0.99–1.03), p = 0.22 | --- |
| Changes in SBP (1 mmHg) ** | 1.01 (0.99–1.02), p = 0.59 | 1.02 (0.99–1.04), p = 0.26 | 1.01 (0.99–1.04), p = 0.37 |
| Changes in DBP (1 mmHg) * | 1.04 (1.01–1.07), p = 0.006 | 1.08 (1.03–1.12), p = 0.001 | --- |
| Changes in DBP (1 mmHg) ** | 1.03 (1.00–1.07), p = 0.05 | 1.09 (1.03–1.14), p = 0.002 | 1.07 (1.02–1.13), p = 0.01 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Torino, C.; Tripepi, R.; Versace, M.C.; Vilasi, A.; Tripepi, G.; Panuccio, V. Clinical Epidemiology of Systolic and Diastolic Orthostatic Hypotension in Patients on Peritoneal Dialysis. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3075. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10143075
Torino C, Tripepi R, Versace MC, Vilasi A, Tripepi G, Panuccio V. Clinical Epidemiology of Systolic and Diastolic Orthostatic Hypotension in Patients on Peritoneal Dialysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(14):3075. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10143075
Chicago/Turabian StyleTorino, Claudia, Rocco Tripepi, Maria Carmela Versace, Antonio Vilasi, Giovanni Tripepi, and Vincenzo Panuccio. 2021. "Clinical Epidemiology of Systolic and Diastolic Orthostatic Hypotension in Patients on Peritoneal Dialysis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 14: 3075. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10143075
APA StyleTorino, C., Tripepi, R., Versace, M. C., Vilasi, A., Tripepi, G., & Panuccio, V. (2021). Clinical Epidemiology of Systolic and Diastolic Orthostatic Hypotension in Patients on Peritoneal Dialysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(14), 3075. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10143075






