Interventional and Surgical Treatments for Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Right-to-Left Shunting
2.1. Atrial Septostomy
2.2. Atrial Flow Regulator
2.3. The Potts Shunt and Its Modifications
3. Pulmonary Artery Denervation
4. Surgical Modalities
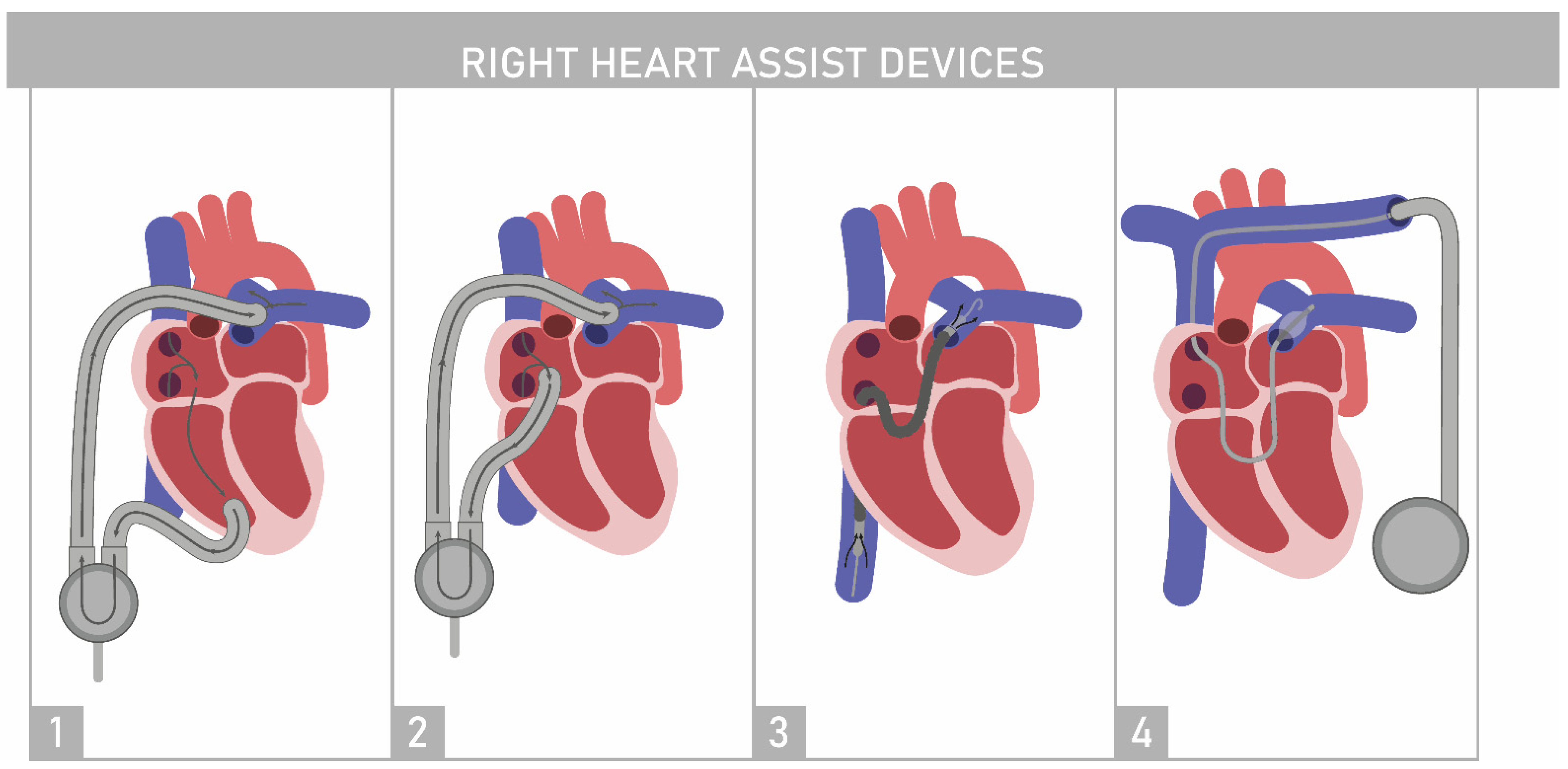
4.1. Right Ventricle Assist Device
4.2. Aria CV PH System
4.3. Right Ventricular Pacing
4.4. Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation
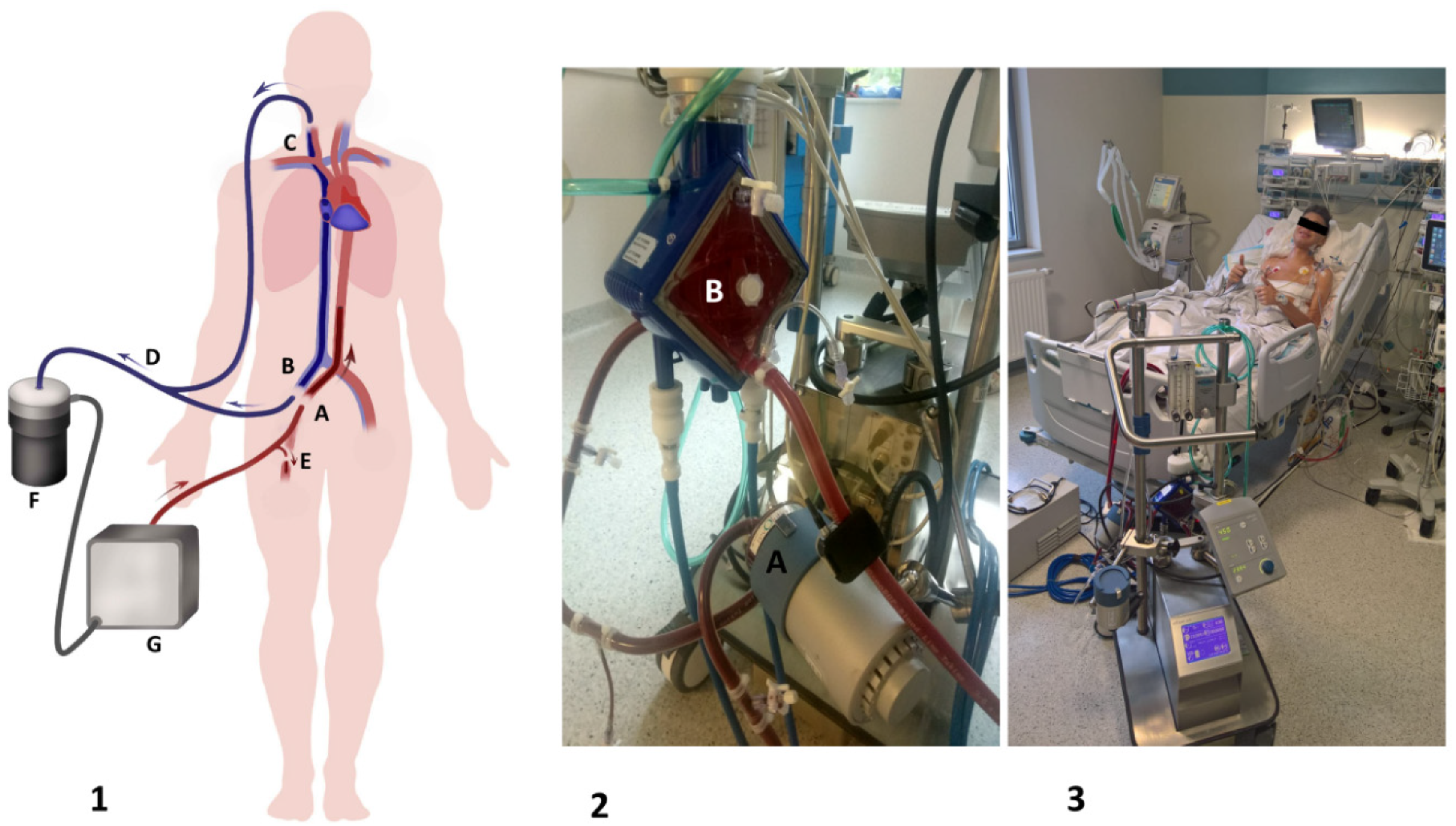
4.4.1. Methods of Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation Implantation
- (a)
- Surgical: This method is the most common method of ECMO implementation, which is based on the preparation and visualization of the targeted vessels followed by cannulation. Usually, the working part of the venous cannula (drainage site) should be positioned within the right atrium and superior vena cava under ultrasound supervision (preferably transesophageal echocardiography). One must not forget about peripheral perfusion of the leg (PLP) (Figure 3(1-E)), which is obtained as a connection between the arterial cannula and the distal part of the femoral artery. Rarely, when Willis circulation is sufficient, there is a possibility of placing an arterial cannula through the right common carotid artery surgically and placing a venous cannula in the right internal jugular vein (IJV) so the patient can be treated not only awake but also mobilized [48]. This type of implantation can be used for intermediate- and long-term ECMO support.
- (b)
- Percutaneous: The Seldinger method used for cannulation of the right IJV and/or inferior vena cava as well as the femoral artery. If intended for short-term support, a PLP shunt may be omitted in exceptional circumstances, and strict supervision of the lower extremity is applied.
- (c)
- Mixed: This method includes the cannula to right IJV with the Seldinger method and surgical insertion of the arterial cannula (through the femoral artery into the distal part of the abdominal aorta) and the PLP cannula. This type of implantation can be used in patients requiring intermediate- and long-term ECMO support.
4.4.2. Purpose of Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation Implantation
Ultimate Bridge to Lung or Heart-Lung Transplantation
Perioperative Support and Left Ventricular Conditioning
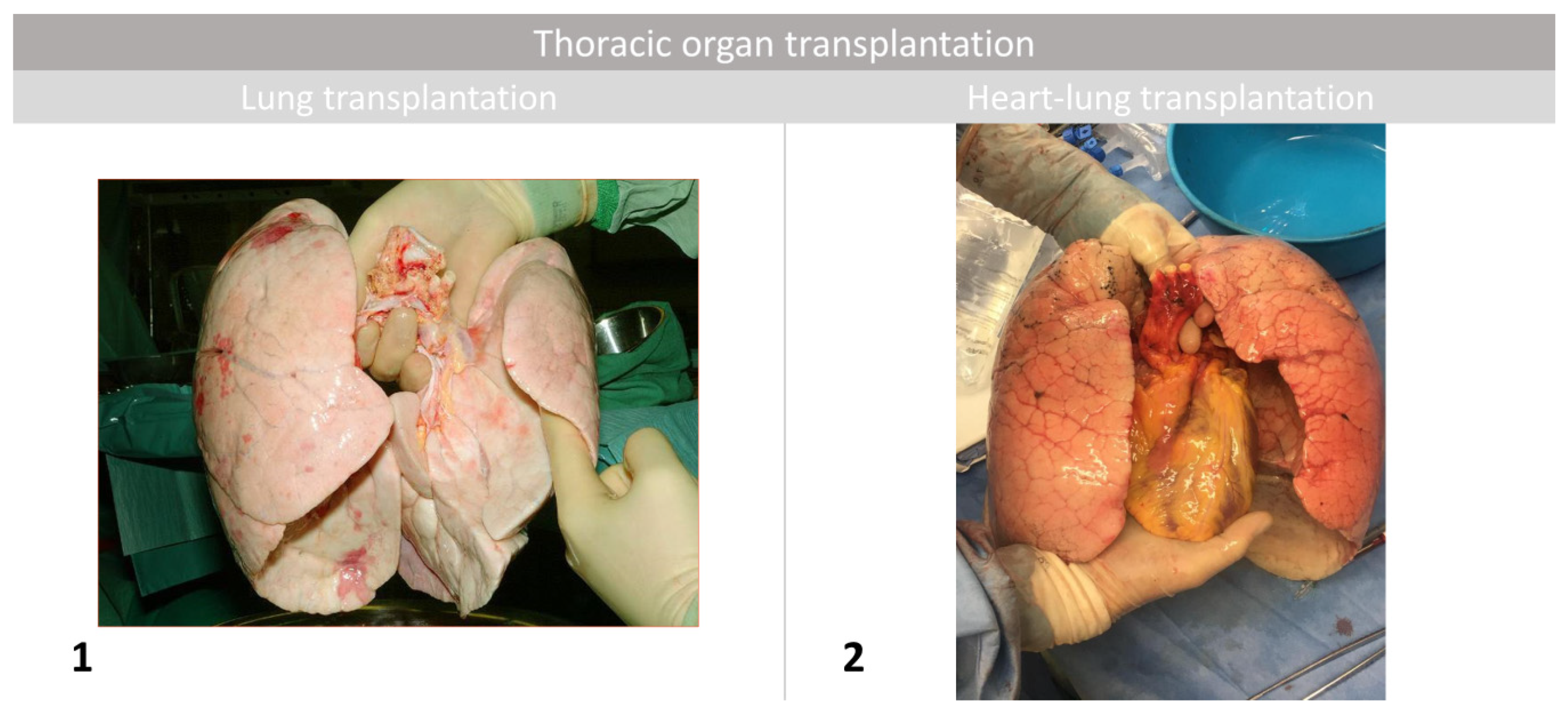
5. Thoracic Organ Transplantation
5.1. Lung Transplantation
5.2. Heart-Lung Transplantation
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Westerhof, B.E.; Saouti, N.; Van Der Laarse, W.J.; Westerhof, N.; Noordegraaf, A.V. Treatment strategies for the right heart in pulmonary hypertension. Cardiovasc. Res. 2017, 113, 1465–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kopeć, G.; Kurzyna, M.; Mroczek, E.; Chrzanowski, Ł.; Mularek-Kubzdela, T.; Skoczylas, I.; Kuśmierczyk, B.; Pruszczyk, P.; Błaszczak, P.; Lewicka, E.; et al. Characterization of Patients with Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: Data from the Polish Registry of Pulmonary Hypertension (BNP-PL). J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Galiè, N.; Corris, P.A.; Frost, A.; Girgis, R.E.; Granton, J.; Jing, Z.C.; Klepetko, W.; McGoon, M.D.; McLaughlin, V.V.; Preston, I.R.; et al. Updated Treatment Algorithm of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013, 62, D60–D72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildenbrand, F.F.; Bloch, K.E.; Speich, R.; Ulrich, S. Daytime Measurements Underestimate Nocturnal Oxygen Desaturations in Pulmonary Arterial and Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension. Respiration 2012, 84, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Medarov, B.I.; Judson, M.A. The role of calcium channel blockers for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension: How much do we actually know and how could they be positioned today? Respir. Med. 2015, 109, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Taichman, D.B.; Ornelas, J.; Chung, L.; Klinger, J.R.; Lewis, S.; Mandel, J.; Palevsky, H.I.; Rich, S.; Sood, N.; Rosenzweig, E.B.; et al. Pharmacologic Therapy for Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension in Adults. Chest 2014, 146, 449–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sobański, P.Z.; Rajszys, G.B.; Grodzicki, T.; Jakubów, P.; Jankowski, P.; Kurzyna, M.; Nessler, J.; Przybylski, A.; Ratajska, A.; Pająk, L.T.; et al. Palliative care for people living with cardiac disease. Kardiol. Pol. 2020, 78, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Amsallem, M.; Mercier, O.; Kobayashi, Y.; Moneghetti, K.; Haddad, F. Forgotten No More. JACC Heart Fail. 2018, 6, 891–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kula, S.; Atasayan, V. Surgical and transcatheter management alternatives in refractory pulmonary hypertension: Potts shunt. Anatol. J. Cardiol. 2015, 15, 843–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keogh, A.M.; Mayer, E.; Benza, R.L.; Corris, P.; Dartevelle, P.G.; Frost, A.E.; Kim, N.H.; Lang, I.M.; Pepke-Zaba, J.; Sandoval, J. Interventional and Surgical Modalities of Treatment in Pulmonary Hypertension. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2009, 54, S67–S77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baruteau, A.-E.; Serraf, A.; Lévy, M.; Petit, J.; Bonnet, D.; Jais, X.; Vouhé, P.; Simonneau, G.; Belli, E.; Humbert, M. Potts Shunt in Children with Idiopathic Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: Long-Term Results. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2012, 94, 817–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delhaas, T.; Koeken, Y.; Latus, H.; Apitz, C.; Schranz, D. Potts Shunt to Be Preferred Above Atrial Septostomy in Pediatric Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Patients: A Modeling Study. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badesch, D.B.; Abman, S.H.; Ahearn, G.S. Hypertension * ACCP Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines. Chest 2004, 126, 35S–62S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sivakumar, K. Atrial septal stenting—How I do it? Ann. Pediatr. Cardiol. 2015, 8, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeper, M.; Ghofrani, H.; Grimminger, F.; Rosenkranz, S. Dana Point: Was ist neu in der Therapie der pulmonalen Hypertonie? DMW Dtsch. Med. Wochenschr. 2008, 133 (Suppl. 6), S191–S195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval, J.; Gaspar, J.; Pulido, T.; Bautista, E.; Martínez-Guerra, M.L.; Zeballos, M.; Palomar, A.; Gómez, A. Graded balloon dilation atrial septostomy in severe primary pulmonary hypertension: A therapeutic alternative for patients nonresponsive to vasodilator treatment. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1998, 32, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurzyna, M.; Dąbrowski, M.; Bielecki, D.; Fijalkowska, A.; Pruszczyk, P.; Opolski, G.; Burakowski, J.; Florczyk, M.; Tomkowski, W.Z.; Wawrzyńska, L.; et al. Atrial Septostomy in Treatment of End-Stage Right Heart Failure in Patients with Pulmonary Hypertension. Chest 2007, 131, 977–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paitazoglou, C.; Özdemir, R.; Pfister, R.; Bergmann, M.W.; Bartunek, J.; Kilic, T.; Lauten, A.; Schmeisser, A.; Zoghi, M.; Anker, S.; et al. The AFR-PRELIEVE trial: A prospective, non-randomised, pilot study to assess the Atrial Flow Regulator (AFR) in heart failure patients with either preserved or reduced ejection fraction. EuroIntervention 2019, 15, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- RajeshKumar, R.; Pavithran, S.; Sivakumar, K.; Vettukattil, J.J. Atrial septostomy with a predefined diameter using a novel occlutech atrial flow regulator improves symptoms and cardiac index in patients with severe pulmonary arterial hypertension. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2017, 90, 1145–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janus, A.M.; Sławek, S.; Araszkiewicz, A. Atrial flow regulator as a bridge to lung transplantation in a young patient with drug-resistant idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension. Kardiologia Polska 2020, 78, 461–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stącel, T.; Antończyk, R.; Latos, M.; Nęcki, M.; Przybyłowski, P.; Zembala, M.; Ochman, M.; Urlik, M. Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation as a Postoperative Left Ventricle Conditioning Tool After Lung Transplantation in Patients with Primary Pulmonary Artery Hypertension: First Polish Experience. Transplant. Proc. 2020, 52, 2113–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.K.; Gaine, S.P.; Walsh, K.P. Percutaneous Atrial Septostomy with Modified Butterfly Stent and Intracardiac Echocardiographic Guidance in a Patient with Syncope and Refractory Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Heart Lung Circ. 2013, 22, 668–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prieto, L.R.; Latson, L.A.; Jennings, C. Atrial septostomy using a butterfly stent in a patient with severe pulmonary arterial hypertension. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2006, 68, 642–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorbachevsky, S.V.; Shmalts, A.A.; Dadabaev, G.M.; Nishonov, N.A.; Pursanov, M.G.; Shvartz, V.A.; Zaets, S.B. Outcomes of Atrioseptostomy with Stenting in Patients with Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension from a Large Single-Institution Cohort. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval, J. The Long and Winding Road of Atrial Septostomy. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, M.; Grady, R.M.; Choudhry, S.; Anwar, S.; Eghtesady, P.; Singh, G.K. Potts Shunt Improves Right Ventricular Function and Coupling with Pulmonary Circulation in Children with Suprasystemic Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2018, 11, e007964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rosenzweig, E.B.; Ankola, A.; Krishnan, U.; Middlesworth, W.; Bacha, E.; Bacchetta, M. A novel unidirectional-valved shunt approach for end-stage pulmonary arterial hypertension: Early experience in adolescents and adults. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2021, 161, 1438–1446.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanjani, K.S. Radiofrequency perforation may increase the safety of transcatheter Potts shunt creation. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2013, 32, 938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-L.; Zhang, F.-F.; Xu, J.; Xie, D.-J.; Zhou, L.; Nguyen, T.; Stone, G.W. Pulmonary Artery Denervation to Treat Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: The Single-Center, Prospective, First-in-Man PADN-1 Study (First-in-Man Pulmonary Artery Denervation for Treatment of Pulmonary Artery Hypertension). J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013, 62, 1092–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Le, T.; Makar, C.; Morway, P.; Hoftman, N.; Umar, S. Pulmonary artery denervation: A novel treatment modality for pulmonary hypertension. J. Thorac. Dis. 2019, 11, 1094–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esler, M.D.; Krum, H.; Schlaich, M.; Schmieder, R.E.; Böhm, M.; Sobotka, P.A. Renal Sympathetic Denervation for Treatment of Drug-Resistant Hypertension. Circulation 2012, 126, 2976–2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, S.-L.; Zhang, Y.-J.; Zhou, L.; Xie, D.-J.; Zhang, F.-F.; Du-Jiang, X.; Wong, S.S.; Kwan, T.W. Percutaneous pulmonary artery denervation completely abolishes experimental pulmonary arterial hypertension in vivo. EuroIntervention 2013, 9, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Pan, H.-Z.; Zhang, X.-L.; Li, J.; Xiang, L.; Meng, J.; Wang, P.-H.; Yang, J.; Jing, Z.-C.; et al. Transthoracic Pulmonary Artery Denervation for Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2019, 39, 704–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.-L.; Zhang, H.; Xie, D.-J.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, L.; Rothman, A.; Stone, G.W. Hemodynamic, Functional, and Clinical Responses to Pulmonary Artery Denervation in Patients with Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension of Different Causes. Circ. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2015, 8, e002837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoeper, M.M.; Galie, N. Letter by Hoeper and Galiè Regarding Article, “Hemodynamic, Functional, and Clinical Responses to Pulmonary Artery Denervation in Patients with Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension of Different Causes: Phase II Results From the Pulmonary Artery Denervation-1 S. Circ. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2016, 9, e003422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, S.-L. Pulmonary Artery Denervation: Update on Clinical Studies. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2019, 21, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.W.; Aronow, W.S.; Dutta, T.; Spevack, D.M.; Frishman, W.H. Pulmonary Artery Denervation as an Innovative Treatment for Pulmonary Hypertension with and without Heart Failure. Cardiol. Rev. 2021, 29, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punnoose, L.; Burkhoff, D.; Rich, S.; Horn, E.M. Right ventricular assist device in end-stage pulmonary arterial hypertension: Insights from a computational model of the cardiovascular system. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2012, 55, 234–243.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenzweig, E.B.; Chicotka, S.; Bacchetta, M. Right ventricular assist device use in ventricular failure due to pulmonary arterial hypertension: Lessons learned. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2016, 35, 1272–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, L.N.; Berg, H.; Veien, K.T.; Jensen, M.K.; Junker, A.; Møller, J.E.; Schmidt, H. Percutaneous right ventricular assist device in sepsis due to right ventricular failure and pulmonary hypertension. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2016, 60, 1470–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, D.K.; Shim, T.S.; Jo, K.-W.J.; Park, S.-I.; Kim, D.K.; Choi, S.; Lee, G.D.; Jung, S.-H.; Kang, P.-J.; Hong, S.-B. Right ventricular assist device with an oxygenator using extracorporeal membrane oxygenation as a bridge to lung transplantation in a patient with severe respiratory failure and right heart decompensation. Acute Crit. Care 2020, 35, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Treatment of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Using the Aria CV Pulmonary Hypertension System (ASPIRE PH). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04555161 (accessed on 20 July 2021).
- Aria CV PH System. Available online: https://ariacv.com/technology/ (accessed on 20 July 2021).
- Handoko, M.L.; Lamberts, R.R.; Redout, E.M.; De Man, F.S.; Boer, C.; Simonides, W.S.; Paulus, W.J.; Westerhof, N.; Allaart, C.P.; Vonk-Noordegraaf, A. Right ventricular pacing improves right heart function in experimental pulmonary arterial hypertension: A study in the isolated heart. Am. J. Physiol. Circ. Physiol. 2009, 297, H1752–H1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lumens, J.; Arts, T.; Broers, B.; Boomars, K.A.; Van Paassen, P.; Prinzen, F.W.; Delhaas, T. Right ventricular free wall pacing improves cardiac pump function in severe pulmonary arterial hypertension: A computer simulation analysis. Am. J. Physiol. Circ. Physiol. 2009, 297, H2196–H2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardziyenka, M.; Surie, S.; De Groot, J.R.; De Bruin-Bon, H.R.; Knops, R.E.; Remmelink, M.; Yong, Z.-Y.; Baan, J.; Bouma, B.; Bresser, P.; et al. Right ventricular pacing improves haemodynamics in right ventricular failure from pressure overload: An open observational proof-of-principle study in patients with chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Europace 2011, 13, 1753–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Right Ventricular Pacing in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04194632 (accessed on 20 July 2021).
- Abrams, D.C.; Brodie, D.; Rosenzweig, E.B.; Burkart, K.M.; Agerstrand, C.L.; Bacchetta, M.D. Upper-Body Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation as a Strategy in Decompensated Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Pulm. Circ. 2013, 3, 432–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Urlik, M.; Latos, M.; Antończyk, R.; Nęcki, M.; Kaczur, E.; Miernik, M.; Zawadzki, F.; Król, B.; Pasek, P.; Przybyłowski, P.; et al. Suboptimal Donors Do Not Mean Worse Results: A Single-Center Study of Extending Donor Criteria for Lung Transplant. Transplant. Proc. 2020, 52, 2123–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bera, K.D.; Shah, A.; English, M.R.; Harvey, D.; Ploeg, R.J. Optimisation of the organ donor and effects on transplanted organs: A narrative review on current practice and future directions. Anaesthesia 2020, 75, 1191–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregoric, I.D.; Chandra, D.; Myers, T.J.; Scheinin, S.A.; Loyalka, P.; Kar, B. Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation as a Bridge to Emergency Heart-Lung Transplantation in a Patient with Idiopathic Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2008, 27, 466–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stącel, T.; Urlik, M.; Antończyk, R.; Latos, M.; Wiklińska, A.; Przybyłowski, P.; Zembala, M.; Ochman, M.; Nęcki, M. Extra-corporeal membrane oxygenation as a bridge to lung transplantation. Transplant. Proc. 2020, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ochman, M.; Urlik, M.; Latos, M.; Stącel, T.; Nęcki, M.; Zembala, M. ECMO i transplantacja płuc u pacjentów ze schyłkową niewydolnością oddechową [ECMO and lung transplantation among patients with end-stage lung disease. In Transplantologia Praktyczna Tom 10 [Practical Transplantology Part 10]; Wydawnictwo Naukowe PWN: Warszawa, Poland, 2018; pp. 89–96. [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin, V.V.; Shah, S.J.; Souza, R.; Humbert, M. Management of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2015, 65, 1976–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Posluszny, J.; Rycus, P.T.; Bartlett, R.H.; Engoren, M.; Haft, J.W.; Lynch, W.R.; Park, P.K.; Raghavendran, K.; Napolitano, L.M. Outcome of Adult Respiratory Failure Patients Receiving Prolonged (≥14 Days) ECMO. Ann. Surg. 2016, 263, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tipograf, Y.; Salna, M.; Minko, E.; Grogan, E.L.; Agerstrand, C.; Sonett, J.; Brodie, D.; Bacchetta, M. Outcomes of Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation as a Bridge to Lung Transplantation. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2019, 107, 1456–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chambers, D.C.; Cherikh, W.S.; Harhay, M.O.; Hayes, D.; Hsich, E.; Khush, K.K.; Meiser, B.; Potena, L.; Rossano, J.W.; Toll, A.E.; et al. The International Thoracic Organ Transplant Registry of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation: Thirty-sixth adult lung and heart–lung transplantation Report—2019; Focus theme: Donor and recipient size match. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2019, 38, 1042–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoetzenecker, K.; Schwarz, S.; Muckenhuber, M.; Benazzo, A.; Frommlet, F.; Schweiger, T.; Bata, O.; Jaksch, P.; Ahmadi, N.; Muraközy, G.; et al. Intraoperative extracorporeal membrane oxygenation and the possibility of postoperative prolongation improve survival in bilateral lung transplantation. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2018, 155, 2193–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machuca, T.N.; Collaud, S.; Mercier, O.; Cheung, M.; Cunningham, V.; Kim, S.J.; Azad, S.; Singer, L.; Yasufuku, K.; de Perrot, M.; et al. Outcomes of intraoperative extracorporeal membrane oxygenation versus cardiopulmonary bypass for lung transplantation. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2015, 149, 1152–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moser, B.; Jaksch, P.; Taghavi, S.; Muraközy, G.; Lang, G.; Hager, H.; Krenn, C.; Roth, G.; Faybik, P.; Bacher, A.; et al. Lung transplantation for idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension on intraoperative and postoperatively prolonged extracorporeal membrane oxygenation provides optimally controlled reperfusion and excellent outcome. Eur. J. Cardio-Thorac. Surg. 2018, 53, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, J.; Ius, F.; Sommer, W.; Siemeni, T.; Kuehn, C.; Avsar, M.; Boethig, D.; Molitoris, U.; Bara, C.; Gottlieb, J. Mid-term results of bilateral lung transplant with postoperatively extended intraoperative extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for severe pulmonary hypertension†. Eur. J. Cardio-Thorac. Surg. 2017, 52, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tudorache, I.; Sommer, W.; Kühn, C.; Wiesner, O.; Hadem, J.; Fühner, T.; Ius, F.; Avsar, M.; Schwerk, N.; Böthig, D.; et al. Lung Transplantation for Severe Pulmonary Hypertension—Awake Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation for Postoperative Left Ventricular Remodelling. Transplantation 2015, 99, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereszlenyi, A.; Lang, G.; Steltzer, H.; Hetz, H.; Kocher, A.; Neuhauser, P.; Wisser, W.; Klepetko, W. Bilateral lung transplantation with intra- and postoperatively prolonged ECMO support in patients with pulmonary hypertension q. Eur. J. Cardio-Thorac. Surg. 2002, 21, 858–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradela, M.; Mercier, O.; Baruteau, A.-E.; Fadel, E. Endovascular closure of Potts shunt before double lung transplantation for idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2013, 146, e5–e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klinger, J.R.; Elliott, C.G.; Levine, D.J.; Bossone, E.; Duvall, L.; Fagan, K.; Frantsve-Hawley, J.; Kawut, S.M.; Ryan, J.J.; Rosenzweig, E.B.; et al. Therapy for Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension in Adults. Chest 2019, 155, 565–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, B.S.; Mulvihill, M.S.; Barac, Y.D.; Bishawi, M.; Cox, M.L.; Megna, D.J.; Haney, J.C.; Klapper, J.A.; Daneshmand, M.A.; Hartwig, M.G. Single lung transplantation in patients with severe secondary pulmonary hypertension. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2019, 38, 939–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weill, D.; Benden, C.; Corris, P.A.; Dark, J.H.; Davis, R.D.; Keshavjee, S.; Lederer, D.; Mulligan, M.J.; Patterson, G.A.; Singer, L.; et al. A consensus document for the selection of lung transplant candidates: 2014—An update from the Pulmonary Transplantation Council of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2015, 34, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivulich, S.; Westall, G.; Dooley, M.; Snell, G. The Evolution of Lung Transplant Immunosuppression. Drugs 2018, 78, 965–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoeper, M.M.; Benza, R.L.; Corris, P.; De Perrot, M.; Fadel, E.; Keogh, A.M.; Kühn, C.; Savale, L.; Klepetko, W. Intensive care, right ventricular support and lung transplantation in patients with pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 53, 1801906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reitz, B.A. The first successful combined heart–lung transplantation. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2011, 141, 867–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zembala, M.; Religa, Z.; Large, S.; Perdeus, J.; Wojarski, J.; Nowalany-Kozielska, E.; Małyszek-Tumidajewicz, J.; Zawadzki, F.; Wajda-Pokrontka, M.; Ochman, M. An 18-year follow-up after the first successful heart-lung transplant in Poland. Authors’ tribute to the pioneers of heart and lung transplantation. Kardiologia Polska 2020, 78, 773–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouckaert, J.; Verleden, S.; Verbelen, T.; Coosemans, W.; Decaluwe, H.; De Leyn, P.; Depypere, L.; Nafteux, P.; Van Veer, H.; Meyns, B.; et al. Double-lung versus heart-lung transplantation for precapillary pulmonary arterial hypertension: A 24-year single-center retrospective study. Transpl. Int. 2019, 32, 717–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, C.; Maxwell, B.; Boulate, D.; Haddad, F.; Ha, R.; Afshar, K.; Weill, D.; Dhillon, G.S. Heart-lung vs. double-lung transplantation for idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension. Clin. Transplant. 2015, 29, 1067–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stącel, T.; Latos, M.; Urlik, M.; Nęcki, M.; Antończyk, R.; Hrapkowicz, T.; Kurzyna, M.; Ochman, M. Interventional and Surgical Treatments for Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3326. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10153326
Stącel T, Latos M, Urlik M, Nęcki M, Antończyk R, Hrapkowicz T, Kurzyna M, Ochman M. Interventional and Surgical Treatments for Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(15):3326. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10153326
Chicago/Turabian StyleStącel, Tomasz, Magdalena Latos, Maciej Urlik, Mirosław Nęcki, Remigiusz Antończyk, Tomasz Hrapkowicz, Marcin Kurzyna, and Marek Ochman. 2021. "Interventional and Surgical Treatments for Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 15: 3326. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10153326
APA StyleStącel, T., Latos, M., Urlik, M., Nęcki, M., Antończyk, R., Hrapkowicz, T., Kurzyna, M., & Ochman, M. (2021). Interventional and Surgical Treatments for Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(15), 3326. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10153326







