The Impact of ABO Blood Type on Developing Venous Thromboembolism in Cancer Patients: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Selection Criteria
2.3. Data Extraction
2.4. Quality Assessment
3. Statistical Analysis
4. Results
4.1. Study Selection
4.2. Characteristics of the Included Studies
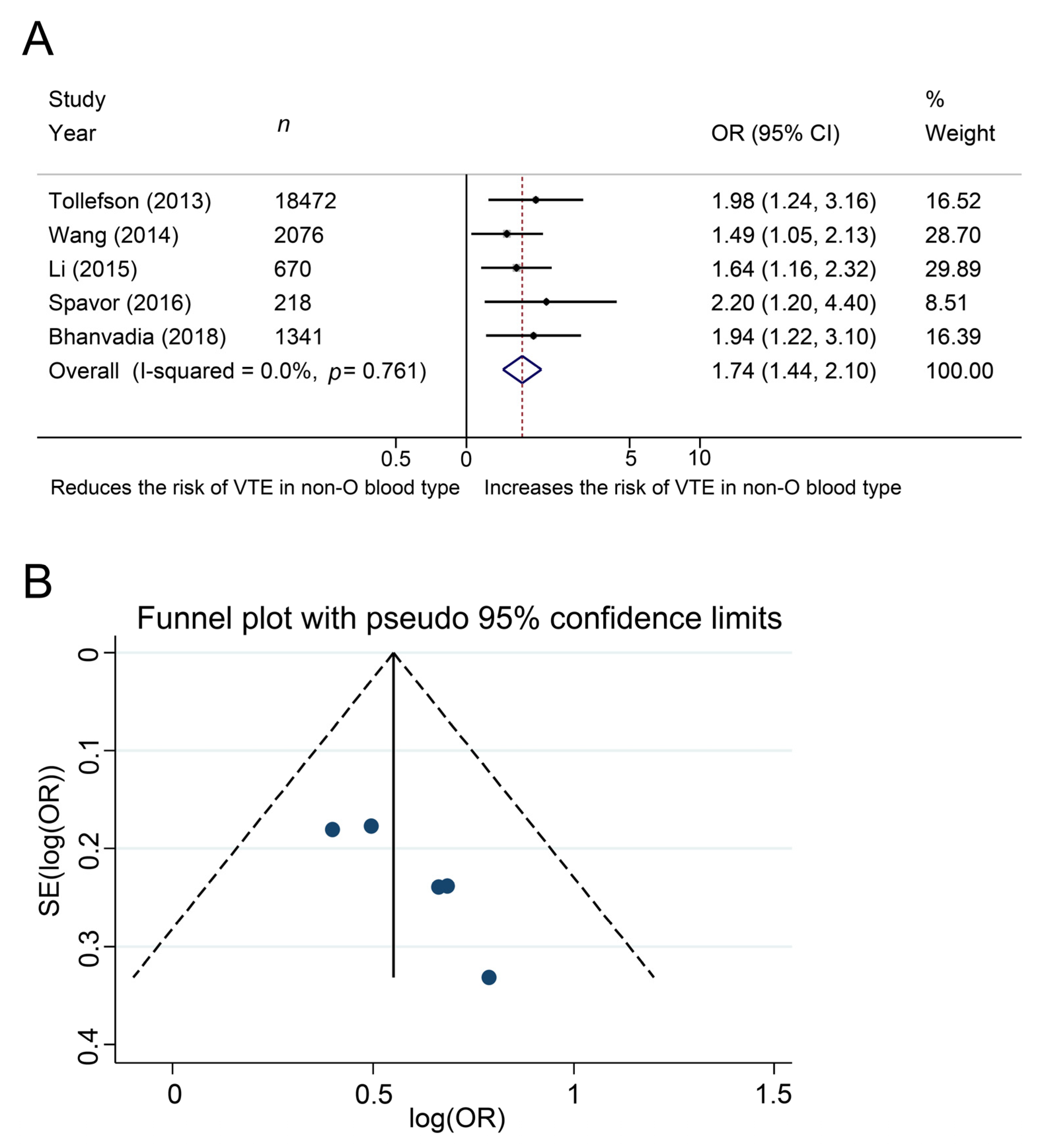
4.3. Meta-Analysis
4.4. Additional Analysis
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Park, B.; Messina, L.; Dargon, P.; Huang, W.; Ciocca, R.; Anderson, F.A. Recent trends in clinical outcomes and resource utilization for pulmonary embolism in the United States: Findings from the nationwide inpatient sample. Chest 2009, 136, 983–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakchbandi, I.A.; Löhr, J.-M. Coagulation, anticoagulation and pancreatic carcinoma. Nat. Clin. Pract. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008, 5, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agnelli, G.; Bolis, G.; Capussotti, L.; Scarpa, R.M.; Tonelli, F.; Bonizzoni, E.; Moia, M.; Rossi, R.; Sonaglia, F.; Valarani, B.; et al. A clinical outcome-based prospective study on venous thromboembolism in cancer surgery: The @RISTOS project. Ann. Surg. 2006, 243, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hemelrijck, M.; Garmo, H.; Holmberg, L.; Bill-Axelson, A.; Carlsson, S. Thromboembolic events following surgery for prostate cancer. Eur. Urol. 2013, 63, 354–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heit, J.A.; Cunningham, J.M.; Petterson, T.M.; Armasu, S.M.; Rider, D.N.; De Andrade, M. Genetic variation within the anticoagulant, procoagulant, fibrinolytic and innate immunity pathways as risk factors for venous thromboembolism. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2011, 9, 1133–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dentali, F.; Sironi, A.P.; Ageno, W.; Turato, S.; Bonfanti, C.; Frattini, F.; Crestani, S.; Franchini, M. Non-O blood type is the commonest genetic risk factor for VTE: Results from a meta-analysis of the literature. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2012, 38, 535–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabrhel, C.; Varraso, R.; Kraft, P.; Rimm, E.B.; Goldhaber, S.Z.; Camargo, C.; Fuchs, C.S.; Wolpin, B.M. Prospective study of ABO blood type and the risk of pulmonary embolism in two large cohort studies. Thromb. Haemost. 2010, 104, 962–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stang, A. Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2010, 25, 603–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Deeks, J.; Dinnes, J.; D’Amico, R.; Sowden, A.J.; Sakarovitch, C.; Song, F.; Petticrew, M.; Altman, D.G. Evaluating non-randomised intervention studies. Health Technol. Assess. 2003, 7, 1–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DerSimonian, R.; Kacker, R. Random-effects model for meta-analysis of clinical trials: An update. Contemp. Clin. Trials 2007, 28, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DerSimonian, R.; Laird, N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control. Clin. Trials 1986, 7, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thompson, S.G.; Deeks, J.J.; Altman, D.G. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 2003, 327, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Streiff, M.B.; Segal, J.; Grossman, S.A.; Kickler, T.S.; Weir, E.G. ABO blood group is a potent risk factor for venous thromboembolism in patients with malignant gliomas. Cancer 2004, 100, 1717–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tollefson, M.K.; Karnes, R.J.; Rangel, L.; Carlson, R.; Boorjian, S.A. Blood type, lymphadenectomy and blood transfusion predict venous thromboembolic events following radical prostatectomy with pelvic lymphadenectomy. J. Urol. 2014, 191, 646–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.K.; Boorjian, S.A.; Frank, I.; Tarrell, R.F.; Thapa, P.; Jacob, E.K.; Tauscher, C.D.; Tollefson, M.K. Non-O blood type is associated with an increased risk of venous thromboembolism after radical cystectomy. Urology 2014, 83, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizrahi, T.; Leclerc, J.-M.; David, M.; Ducruet, T.; Robitaille, N. ABO group as a thrombotic risk factor in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: A retrospective study of 523 pediatric patients. Blood 2013, 122, 2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Pise, M.N.; Overman, M.J.; Liu, C.; Tang, H.; Vadhan-Raj, S.; Abbruzzese, J.L. ABO non-O type as a risk factor for thrombosis in patients with pancreatic cancer. Cancer Med. 2015, 4, 1651–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spavor, M.; Halton, J.; Dietrich, K.; Israels, S.; Shereck, E.; Yong, J.; Yasui, Y.; Mitchell, L.G. Age at cancer diagnosis, non-O blood group and asparaginase therapy are independently associated with deep venous thrombosis in pediatric oncology patients: A risk model. Thromb. Res. 2016, 144, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhanvadia, S.; Kazerouni, K.; Bazargani, S.T.; Miranda, G.; Cai, J.; Daneshmand, S.; Djaladat, H. Validating the role of ABO blood type in risk of perioperative venous thromboembolism after radical cystectomy. World J. Urol. 2018, 37, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heenkenda, M.K.; Malmström, A.; Lysiak, M.; Mudaisi, M.; Bratthäll, C.; Milos, P. Assessment of genetic and non-genetic risk factors for venous thromboembolism in glioblastoma—The predictive significance of B blood group. Thromb. Res. 2019, 183, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Wang, H.; Shen, Y.; Dong, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Zheng, Y.; Guo, S. Association between ABO blood group and venous thrombosis related to the peripherally inserted central catheters in cancer patients. J. Vasc. Access 2020, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeller, A.; Weippert-Kretschmer, M.; Prinz, H.; Kretschmer, V. Influence of ABO blood groups on primary hemostasis. Transfusion 2001, 41, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gastineau, D.A.; Moore, S.B. How important are ABO-related variations in coagulation factor levels? Transfusion 2001, 41, 4–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, J.; Laffan, M.A. The relationship between ABO histo-blood group, factor VIII and von Willebrand factor. Transfus. Med. 2001, 11, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Galaly, T.C.; Kristensen, S.R.; Overvad, K.; Steffensen, R.; Tjønneland, A.; Severinsen, M.T. Interaction between blood type, smoking and factor V Leiden mutation and risk of venous thromboembolism: A Danish case-cohort study. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2012, 10, 2191–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nauffal, V.; Achanta, A.; Goldhaber, S.Z.; Piazza, G. Association of ABO blood group type with cardiovascular events in COVID-19. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2021, 51, 584–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Martino, R.R.; Goodney, P.P.; Spangler, E.L.; Wallaert, J.B.; Corriere, M.A.; Rzucidlo, E.M. Variation in thromboembolic complications among patients undergoing commonly performed cancer operations. J. Vasc. Surg. 2012, 55, 1035–1040.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sterious, S.; Simhan, J.; Uzzo, R.G.; Gershman, B.; Li, T.; Devarajan, K.; Canter, D.; Walton, J.; Fogg, R.; Ginzburg, S.; et al. Familiarity and self-reported compliance with american urological association best practice recommendations for use of thromboembolic prophylaxis among American urological association members. J. Urol. 2013, 190, 992–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, M.O.; Smith, J.A. Low molecular weight heparin and radical prostatectomy: A prospective analysis of safety and side effects. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 1997, 1, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bigg, S.W.; Catalona, W.J. Prophylactic mini-dose heparin in patients undergoing radical retropubic prostatectomy a prospective trial. Urology 1992, 39, 309–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| VTE | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First Author of Study and [Ref.] | Country | Recruitment Period | Study Design | Total | Yes | No | NOS |
| Streiff et al. [13] | USA | 1991–2001 | Cohort, retrospective | 130 | 28 | 102 | 6 |
| Tollefson et al. [14] | USA | 1987–2010 | Cohort, retrospective | 18472 | 271 | 18201 | 7 |
| Wang J et al. [15] | USA | 1980–2005 | Cohort, retrospective | 2076 | 216 | 2060 | 7 |
| Mizrahi et al. [16] | Canada | 1995–2013 | Cohort, retrospective | 523 | 56 | 467 | 6 |
| Li et al. [17] | USA | NR | Cohort, retrospective | 670 | 236 | 434 | 6 |
| Spavor et al. [18] | Canada | NR | Cohort, retrospective | 218 | 63 | 155 | 6 |
| Bhanvadia et al. [19] | USA | 2003–2015 | Cohort, retrospective | 1341 | 90 | 1251 | 7 |
| Heenkenda et al. [20] | Sweden | NR | Cohort, retrospective | 139 | 47 | 92 | 6 |
| Wang G et al. [21] | China | 2018–2019 | Cohort, retrospective | 2315 | 131 | 2174 | 7 |
| Age (y) | Gender (Male) | Blood Type | BMI | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First Author of Study and [Ref.] | No. of pts | Total | No VTE | VTE | Total | No VTE | VTE | Total | No VTE | VTE | Total | No VTE | VTE |
| Streiff et al. [13] | 130 | median 55 (47–66) | median 56 (44–66) | median 54 (51–62) | 83 | 64 (63%) | 19 (68%) | NR | NR | NR | median 25.8 (24–28.3) | median 26 (24–28) | median 26 (25–29) |
| Tollefson et al. [14] | 18,472 | median 63 (58–68) | median 63 (58–68) | median 65 (59–68) | 18,472 | 18,201 (100%) | 271 (100%) | NR | NR | NR | median 27.7 (25.4–30.3) | median 27.7 (25.4–30.3) | median 27.8 (25.7–30.5) |
| Wang J.K. et al. [15] | 2076 | NR | median 68 (62–74) | median 69 (61–76) | 1670 | 1498 (80.5%) | 172 (79.6%) | O: 865 (41.7%) Non-O: 1143 (55.1%) Missing: 61 (3.3%) | O: 794 (44.1%) Non-O: 1007 (55.9%) Missing: 59 (3.2%) | O: 71 (34.3%) Non-O: 136 (65.7%) Missing: 9 (4.2%) | NR | ≥30: 437 (23.6%) <30: 1515 (76.4%) Missing: 8 (0.4%) | ≥30: 71 (32.8%) <30: 145 (67.1%) Missing: 0 (0.0%) |
| Mizrahi et al. [16] | 523 | mean 6.5 SD 4.4 | ≥10 y: 101 (20.4%) <10 y: 395 (79.6%) | ≥10 y: 20 (35.7%) <10 y: 36 (64.3%) | 302 | 270 (57.8%) | 32 (57.1%) | O: 221 (42.3%) A: 230 (44.0%) AB: 11 (2.61%) B: 60 (11.5%) | O: 207 (44.7%) Non-O: 259 (55.3%) | O: 14 (25%) Non-O: 42 (75%) | NR | NR | NR |
| Li et al. [17] | 670 | median 62 (31-87) | ≤60 y: 193 (44.5%) >60 y: 241 (55.5%) | ≤60 y: 98 (41.5%) >60 y: 138 (58.5%) | 388 | 249 (57.4%) | 139 (58.9%) | O: 251 (37.5%) A: 328 (49.0%) AB: 19 (2.8%) B: 72 (10.7%) | O: 178 (41.0%) A: 200 (46.1%) AB: 9 (2.1%) B: 47 (10.8%) | O: 73 (30.9%) A: 128 (54.2%) AB: 10 (4.2%) B: 25 (10.6%) | NR | >30: 130 (30.2%) | >30: 88 (37.6%) |
| Spavor et al. [18] | 218 | NR | mean SD 8.5 ± 5.4 | mean SD 7.1 ± 4.6 | 121 | 82 (53%) | 39 (62.3%) | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR |
| Bhanvadia et al. [19] | 1341 | median 70 | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | O: 595 (44.4%) A: 520 (38.8%) AB: 63 (4.7%) B: 163 (12.2%) | NR | NR | 27 | NR | NR |
| Heenkenda et al. [20] | 139 | NR | median 60 (25–76) | median 58 (39–69) | NR | 58 (63%) | 29 (62%) | O: 49 (35.3%) A: 67 (48.2%) AB: 5 (3.6%) B: 18 (12.9%) | O: 38 (41%) A: 45 (49%) AB: 3 (3%) B: 6 (7%) | O: 11 (23%) A: 22 (47%) AB: 2 (4%) B: 12 (26%) | NR | NR | NR |
| Wang G et al. [21] | 2315 | mean 52 (18–89) | <65 y: 1781 (81.5%) ≥65 y: 403 (18.5%) | <65 y: 111 (84.7%) ≥65 y: 20 (15.3%) | 1084 | 1025 (46.9%) | 59 (45%) | O: 677 (29.2%) A: 619 (26.7%) AB: 245 (10.6%) B: 774 (33.4%) | O: 656 (30.0%) A: 577 (26.4%) AB: 225 (10.3%) B: 726 (33.2%) | O: 21 (16.0%) A: 42 (32.1%) AB: 20 (15.3%) B: 48 (36.6%) | NR | ≥30: 814 (37.3%) | ≥30: 58 (44.3%) |
| First Author of Study and [Ref.] | Cancer Type | Treatment Content | Pharmacoprophylaxis | VTE Criteria |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Streiff et al. [13] | Glioma | Surgery ± local or systemic chemotherapy | Some patients (21%) received subcutaneous heparin | DVT: Duplex ultrasonography or venography. PE: High-probability ventilation perfusion scan, a positive spiral CT, or pulmonary angiography |
| Tollefson et al. [14] | Prostate cancer | Radical prostatectomy | Not standardized | NR |
| Wang J.K. et al. [15] | Bladder cancer | Radical cystectomy | Not standardized | DVT: Duplex ultrasonography or venography. PE: Arteriography, ventilation/perfusion scan, or enhanced CT. With at least one sign of VTE |
| Mizrahi et al. [16] | Acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Intrathecal chemotherapy | None | Doppler ultrasound, CT scan, MRI, cardiac ultrasound, or ventilation/perfusion lung scan |
| Li et al. [17] | Pancreatic cancer | NR | None | Radiological imaging |
| Spavor et al. [18] | Acute lymphoblastic leukemia: 92 (42.2%) Lymphoma: 45 (20.6%) Sarcoma: 26 (11.9%) Others: 55 (25.2%) | NR | NR | Ultrasonography, CT scan, MRI, venography, ventilation perfusion scan or echocardiography with at least one sign of VTE |
| Bhanvadia et al. [19] | Bladder cancer | Radical cystectomy | Immediate postoperative Coumadin Or Postoperative subcutaneous heparin | Ultrasonography, ventilation/perfusion scan or pulmonary angiography with at least one sign of VTE |
| Heenkenda et al. [20] | Glioblastoma | Surgery/biopsy + RT + temzolomide | Pre- and post- postoperative tinzaparin | Ultrasound sonography or pulmonary angiography with at least one sign of VTE |
| Wang G et al. [21] | Lymphoma: 1000 (43.2%) Lung tumor: 46 (2.0%) Tumor of digestive system: 532 (23.0%) Urologic tumor: 72 (3.1%) Breast tumor: 531 (22.9%) Gynecological tumor: 42 (0.043%) Others: 91 (3.9%) | Peripherally inserted central catheter | None | Doppler ultrasound with at least one sign of VTE |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Urabe, F.; Kimura, S.; Iwatani, K.; Yasue, K.; Koike, Y.; Tashiro, K.; Tsuzuki, S.; Sasaki, H.; Kimura, T.; Egawa, S. The Impact of ABO Blood Type on Developing Venous Thromboembolism in Cancer Patients: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3692. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10163692
Urabe F, Kimura S, Iwatani K, Yasue K, Koike Y, Tashiro K, Tsuzuki S, Sasaki H, Kimura T, Egawa S. The Impact of ABO Blood Type on Developing Venous Thromboembolism in Cancer Patients: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(16):3692. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10163692
Chicago/Turabian StyleUrabe, Fumihiko, Shoji Kimura, Kosuke Iwatani, Keiji Yasue, Yuhei Koike, Kojiro Tashiro, Shunsuke Tsuzuki, Hiroshi Sasaki, Takahiro Kimura, and Shin Egawa. 2021. "The Impact of ABO Blood Type on Developing Venous Thromboembolism in Cancer Patients: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 16: 3692. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10163692
APA StyleUrabe, F., Kimura, S., Iwatani, K., Yasue, K., Koike, Y., Tashiro, K., Tsuzuki, S., Sasaki, H., Kimura, T., & Egawa, S. (2021). The Impact of ABO Blood Type on Developing Venous Thromboembolism in Cancer Patients: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(16), 3692. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10163692







